Abstract
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) has been widely used to realize daily human–machine interactions. Face masks have become everyday wear in our post-pandemic life, and speech through masks may have impaired the ASR. This study explored the effects of different kinds of face masks (e.g., surgical mask, KN95 mask, and cloth mask) on the Mandarin word accuracy of two ASR systems with or without noises. A mouth simulator was used to play speech audio with or without wearing a mask. Acoustic signals were recorded at distances of 0.2 m and 0.6 m. Recordings were mixed with two noises at a signal-to-noise ratio of +3 dB: restaurant noise and speech-shaped noise. Results showed that masks did not affect ASR accuracy without noise. Under noises, masks did not significantly influence ASR accuracy at 0.2 m but had significant effects at 0.6 m. The activated-carbon mask had the most significant impact on ASR accuracy at 0.6 m, reducing the accuracy by 18.5 percentage points compared to that without a mask, whereas the cloth mask had the least effect on ASR accuracy at 0.6 m, reducing the accuracy by 0.9 percentage points. The acoustic attenuation of masks on the high-frequency band at around 3.15 kHz of the speech signal attributed to the effects of masks on ASR accuracy. When training ASR models, it may be important to consider mask robustness.
1. Introduction
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, masks are widely used to prevent the spread of the virus. Although the pandemic is fading, masks are still an integral part of our daily lives because of the constant mutation of virus strains [1]. However, wearing masks can impair automatic speech recognition (ASR), which is an important means of realizing human–machine interaction [2,3,4] in many fields, such as home automation [5], vehicle systems [6], and reception [7] and healthcare services [8].
Recent acoustic studies showed that masks work like a low-pass filter, attenuating frequencies above 1–2 kHz [9,10,11]. The transmission loss of the masks affects relevant frequency components of speech transmission and impairs speech intelligibility [11]. In addition, the visual cues obscured by masks also negatively affect human speech recognition [12]. The results of Wittum et al. showed that, compared to those made under unmasked conditions, listeners have a lower percentage of correct responses when listening to audio-only recordings made with masks, and authors suggested using a lower signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in future studies to avoid the ceiling effect [13]. Palmiero et al. found that the masks reduced Speech Transmission Index scores by 3%–45% [14]. Bottalico et al. conducted speech recognition tests using audio-only recordings made with or without masks and found that masks negatively affected speech intelligibility (p < 0.001) [9]. Barrett et al. studied the effects of facial masks on face-to-face speech recognition in real-world noisy environments. They found that speech recognition was poorer (p < 0.001) when the talker wore a non-medical disposable mask [15].
However, other studies have given different results. Atcherson et al. showed no impact of the paper or transparent face masks on the speech recognition performance of normal-hearing listeners in a four-talker babble background at +10 dB of SNR, with or without visual cues [16]. Mendel et al. found that the surgical mask did not influence speech understanding in a normal-hearing group [17]. These two studies were conducted before the COVID-19 pandemic and only tested the traditional medical mask (surgical mask) [16,17]. The ceiling effect in the test of Mendel et al. with intelligibility higher than 96.9% in all conditions should also be considered, as Bottalico et al. indicated [9]. It might be concluded that masks significantly affect English speech recognition at a low SNR, and until now, there has been no relevant research on ASR.
Most prior research on the factors that affect ASR has focused on noise, speaker accent, speaker age, and multiple speakers. Noise persists as a significant hurdle to developing ASR, and many approaches have been proposed to enhance the robustness of ASR systems [18,19]. Our previous study suggested a method to associate the Articulation Index to estimate the influence of stationary noise on the ASR word accuracy (ACC) [20]. Feng et al. quantified the bias of a SOTA ASR system and found that the speech of native speakers is recognized much better than that of non-native speakers of Dutch [21]. Shao et al. proposed a novel decoupling and interacting multi-task network to improve joint speech and accent recognition [22]. Accurate recognition of child and elderly speech remains challenging because of the inherent differences between such and adult voices [23,24]. Multi-talker speech recognition, expected to identify “who spoke what”, is also a complex problem [25]. GB/T 41813.1-2022 [26] provides general test items and a general testing method for speech recognition in intelligent speech-interaction applications. The effects of noise, speaker accent, speaker age, multiple speakers, etc., on ASR are considered in the GB/T 41813.1-2022 [26]. To date, the impact of masks as a factor that impairs ASR due to acoustic attenuation and alteration of the speech time–frequency characteristics, has not been considered.
This study evaluated the effects of masks on ASR accuracy with or without noise. We used a mouth simulator to play speech audio with or without a mask and recorded at a distance of 0.2 m and 0.6 m. Restaurant noise and speech-shaped noise were added to the recordings at +3 dB of SNR. The speech was recognized by two ASR systems, i.e., Baidu Cloud (labelled ASRD) and Tencent Cloud (labelled ASRT). Three medical masks, two laboratory or industry masks, and one cloth mask were used.
2. Methods
2.1. Apparatus
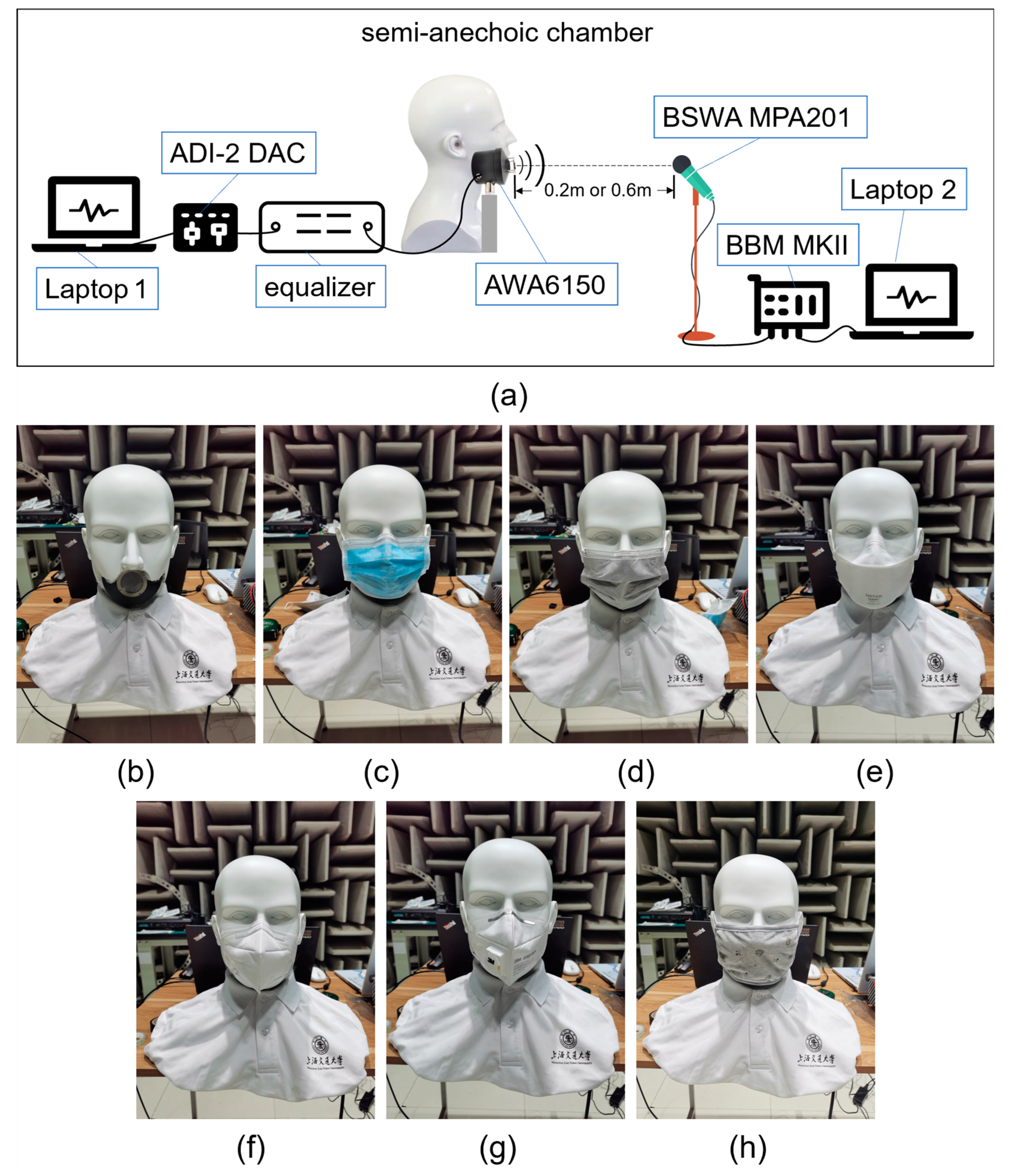
We used a mouth simulator (AWA6150, Hangzhou Aihong Instrument Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China) to play the audios in a specified mask condition and the data acquisition system (BBM MKII, Müller-BBM VibroAkustik Systeme GmbH, Munich, Germany) to save the sound recorded by the microphone (BSWA MPA201, BSWA Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) in the semi-anechoic chamber. The mouth simulator simulated the sound field near the human mouth. The mouth simulator was placed inside a customized dummy head and driven by a USB sound adapter (ADI-2 DAC, RME Audio, Haimhausen, Germany). The microphone was placed on a tripod directly opposite the mouth simulator at the same height as the lip ring of the mouth simulator. The distance between the microphone and the mouth simulator was set as 0.2 m and 0.6 m. The recordings were conducted in 7 mask conditions: without a mask (M0), with a surgical mask [27] (M1), an activated-carbon mask [28] (M2), with a hanging-ear medical protective mask [29] (M3), with a headwear medical protective mask [29] (M4), with an anti-particulate mask (with a breather valve) [30] (M5), and with a cloth mask (M6). M1, M3, and M4 are medical masks that can prevent virus. M2 and M5 are often used in laboratories and factories, and M5 is also known as the KN95 mask. M6 is used for warmth. Figure 1 shows the connection set-up of the apparatus and 7 mask conditions.
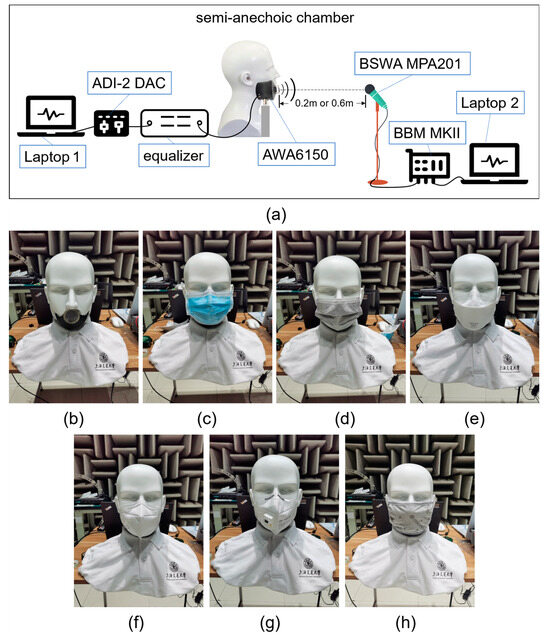
Figure 1.
Connection set-up of apparatus and 7 mask conditions. (a) Connection set-up of apparatus; (b) No mask (M0); (c) Surgical mask (M1); (d) Activated-carbon mask (M2); (e) Hanging-ear medical protective mask (M3); (f) Headwear medical protective mask (M4); (g) Anti-particulate mask (M5); and (h) Cloth mask (M6).
2.2. Stimuli
The speech stimuli came from the AISHELL-ASR0009-OS1, an open Mandarin speech database released by Beijing AISHELL Company [31]. AISHELL-ASR0009-OS1 involves 400 speakers from different accent areas in China. Each speech item is a short sentence selected from finance, technology, sports, entertainment, and news. All recordings are stored in 16 kHz, 16-bit mono WAV file format. We selected 50 male speakers and 50 female speakers randomly. For each mask condition, one speech item was chosen randomly from the database of each selected speaker.
We employed two kinds of interference background noise, i.e., restaurant noise and random noise, with power spectra that are equivalent to the average power spectrum of Mandarin (hereafter called speech-shaped noise). The restaurant noise was from AISHELL-ASR0015, a scene-noise database released by Beijing AISHELL Company (Beijing, China). The power spectrum of speech-shaped noise is equivalent to the average power spectrum of Mandarin proposed by Wei Yang et al. in 2012 [32], which was more accurate than the earlier national standard GB/T 7347-1987 [33]. The speech-shaped noise was obtained by filtering the white noise through a 30-band graphic equalizer, which was set according to the data proposed by Wei Yang et al. [32] Restaurant noise and speech-shaped noise were added to each recording with an SNR of +3 dB.
2.3. Method of Speech Recognition
We carried out speech recognition using two commercial ASR systems, i.e., ASRD and ASRT. The version of ASRD is API-Short speech recognition (standard edition), and that of ASRT is API 3.0-Sentence Recognition. The audios to be recognized were uploaded to the cloud platforms through the Application Programming Interface, and then recognized message texts were returned. By introducing the minimum edit distance, also known as the Levenshtein Distance, the ACC of the ASR is given as
where ‘str0’ is the correct message strings of the speech, ‘strR’ is the recognized message strings of the audio by ASR, the function ‘len(str)’ gives the length of the string ‘str’, and ‘MED (str0, strR)’ is the minimum edit distance between the strings ‘str0’ and ‘strR’. The punctuation in ‘str0’ and ‘strR’ is removed to calculate the ACC.
2.4. Procedure
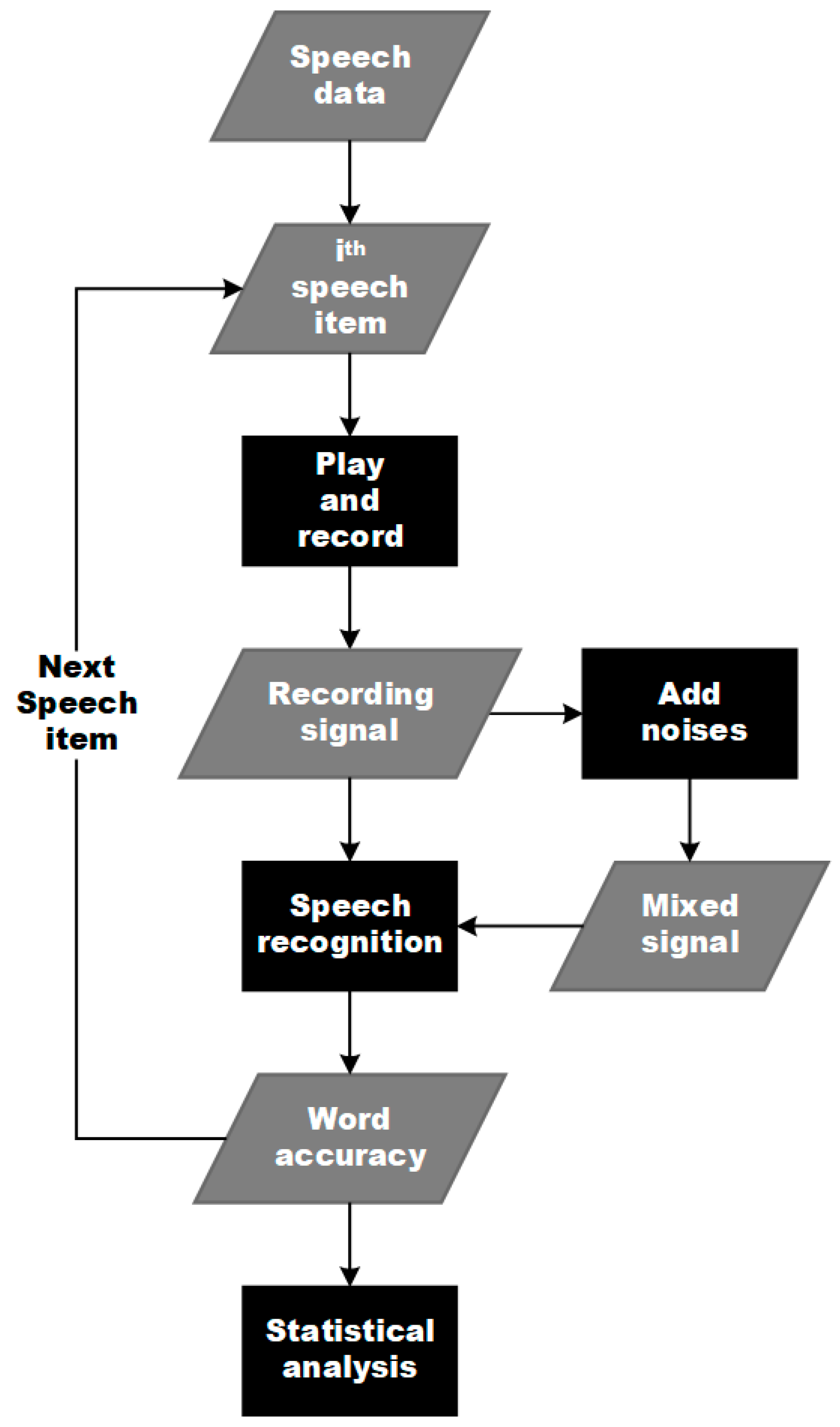
We conducted the research through a procedure demonstrated in Figure 2. A test pattern was executed for one mask condition. In each test pattern, 100 speech items were selected from the database. The speech-shaped noise at the microphone, 0.6 m from the mouth simulator, was calibrated at 70 dB SPL. Then, we played the speech items in a specified mask condition in succession and obtained the recordings at the distance of 0.2 m and 0.6 m. The speech-shaped noise at the microphone 0.2 m from the mouth simulator was around 80 dB SPL. There was 1 s of dwell time between two consecutive plays. The recordings were stored in 16 kHz, 16-bit mono WAV file format. Restaurant noise and speech-shaped noise were added, respectively, to each recording at an SNR of +3 dB in the digital domain, forming the mixed signals. We carried out the speech recognition and obtained the ACC of recordings and mixed signals.
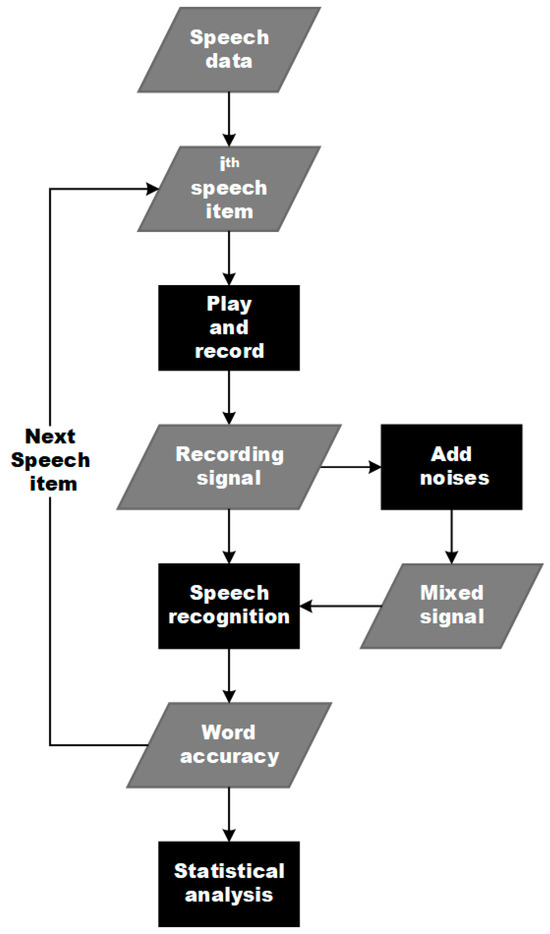
Figure 2.
The research procedure.
2.5. Data Analysis
As the ACCs are non-normally distributed (Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, p < 0.001), we used the median of ACC for each group to describe the accuracy of the ASR system. The Kruskal–Wallis test was used to examine the effect across the 7 mask conditions on ASR accuracy. A significance level of 0.05 was used. We also separated the data by male and female speakers for post-hoc analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Recording Distance: 0.2 m
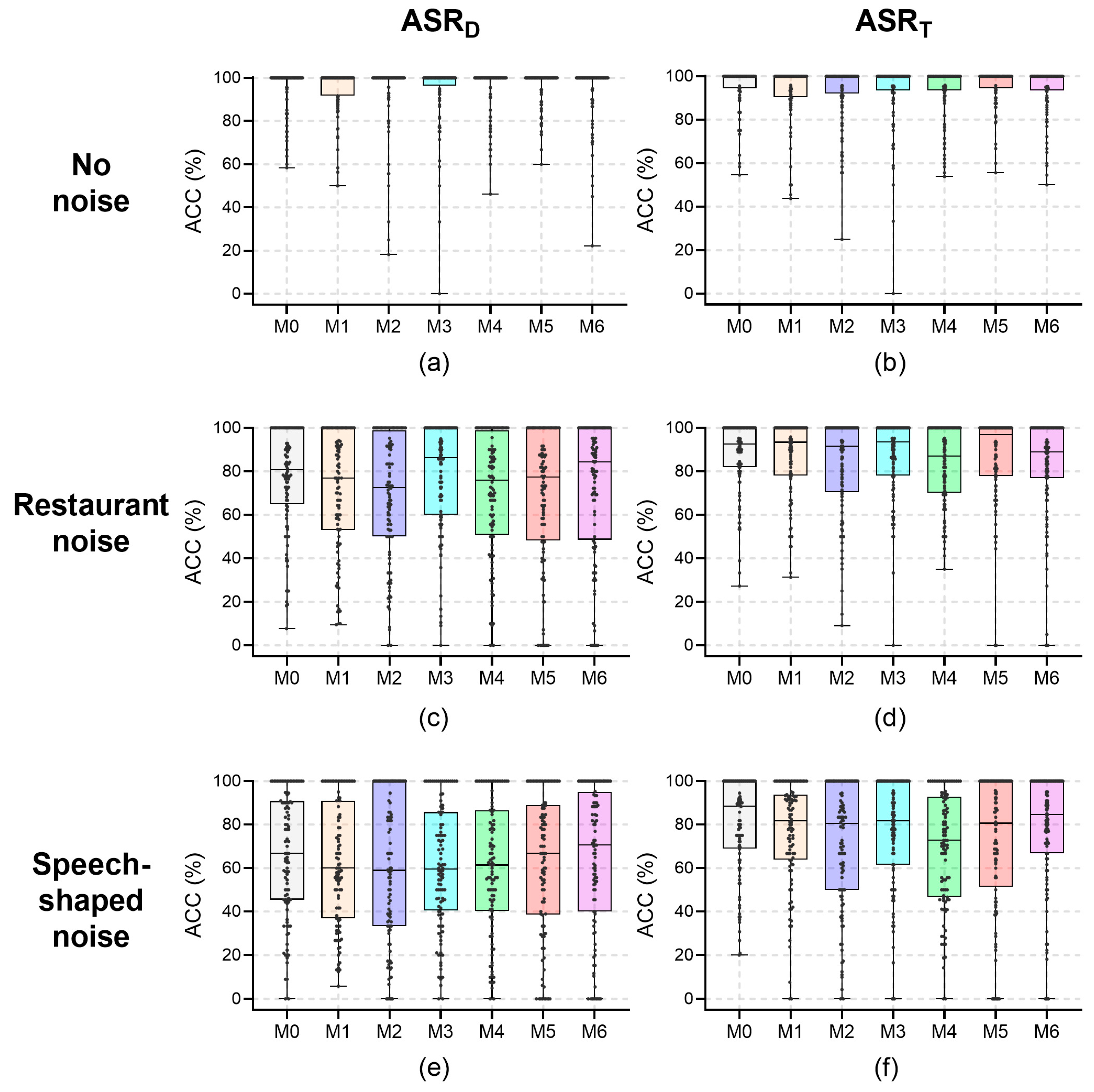
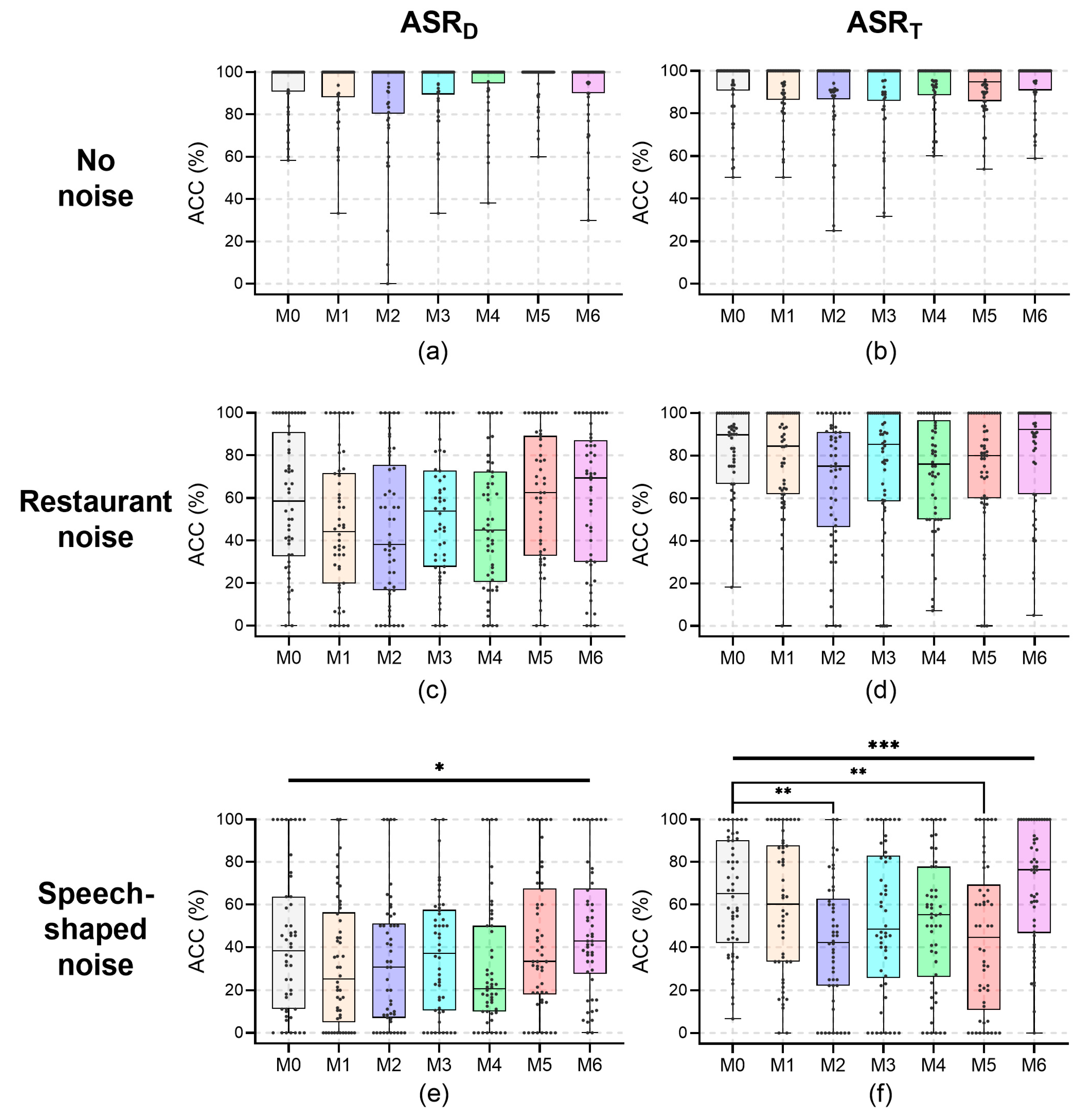
The results of the ACC for all speakers at a recording distance of 0.2 m are shown in Figure 3; their median values under the noises are reported in Table 1. For the recording distance of 0.2 m, no significant effects of wearing a mask on ASR for all speakers were found for any conditions (p > 0.054). The medians of ACC with no noise were 100% for all mask conditions. Despite the lack of significance, the ACC of ASRD under restaurant noise in the M2 condition was 8.2 percentage points (pp) less than that in the M0 condition. In addition, the ACC of ASRT under speech-shaped noise in the M4 condition was 15.8 pp less than that in the M0 condition, and in the M2 condition was 8.1 pp less than that in the M0 condition. In all other cases, the differences between the ACC with and without a mask were less than 8.0 pp.
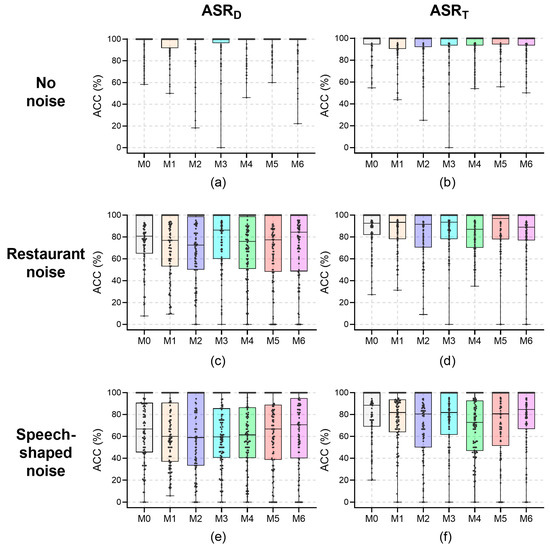
Figure 3.
The word accuracy (ACC) values for all speakers at a recording distance of 0.2 m. (a) ASRD, no noise; (b) ASRT, no noise; (c) ASRD, restaurant noise; (d) ASRT, restaurant noise; (e) ASRD, speech-shaped noise; and (f) ASRT, speech-shaped noise.

Table 1.
Median ACC (%) for all speakers under noises at a recording distance of 0.2 m.
3.2. Recording Distance: 0.6 m
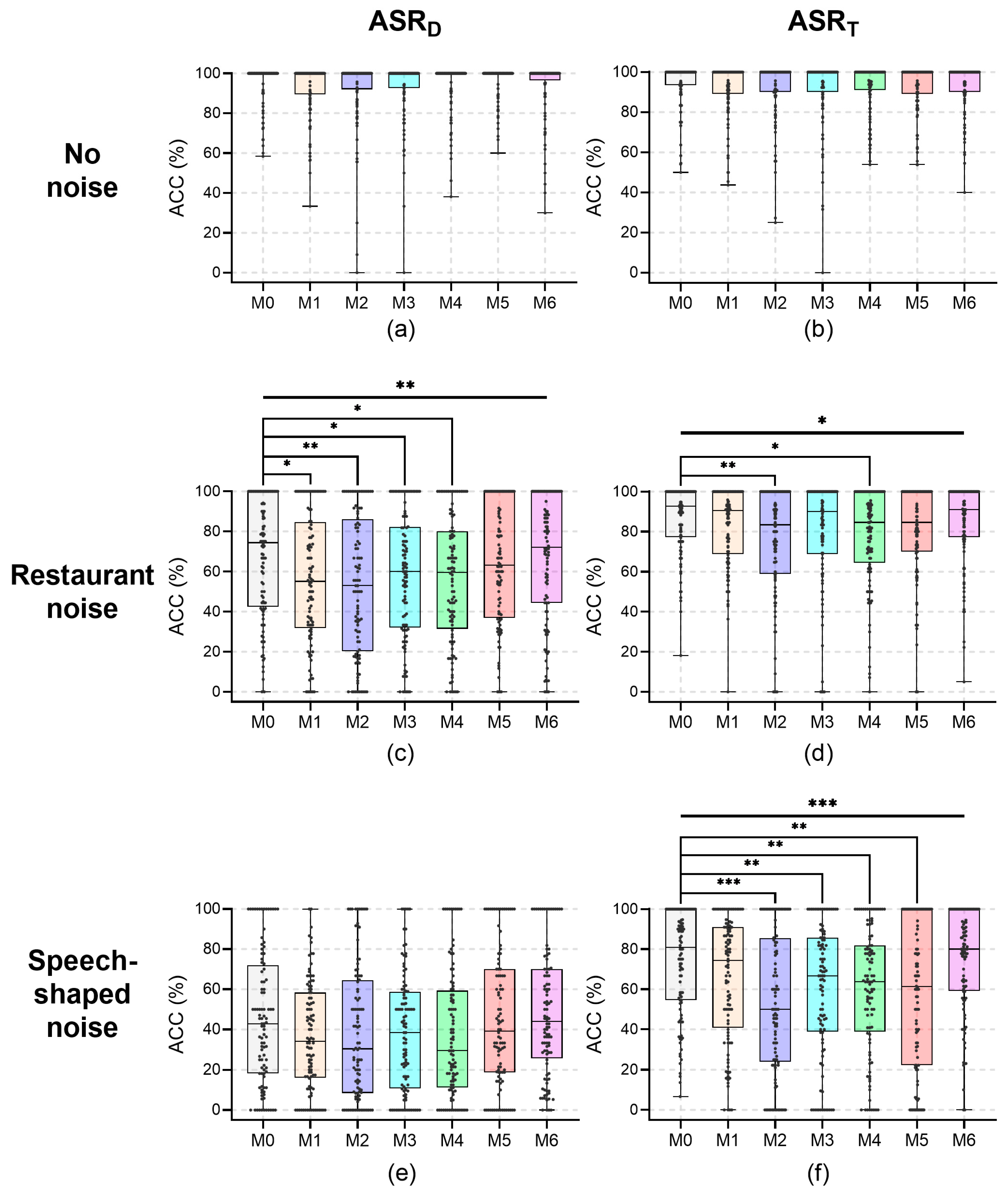
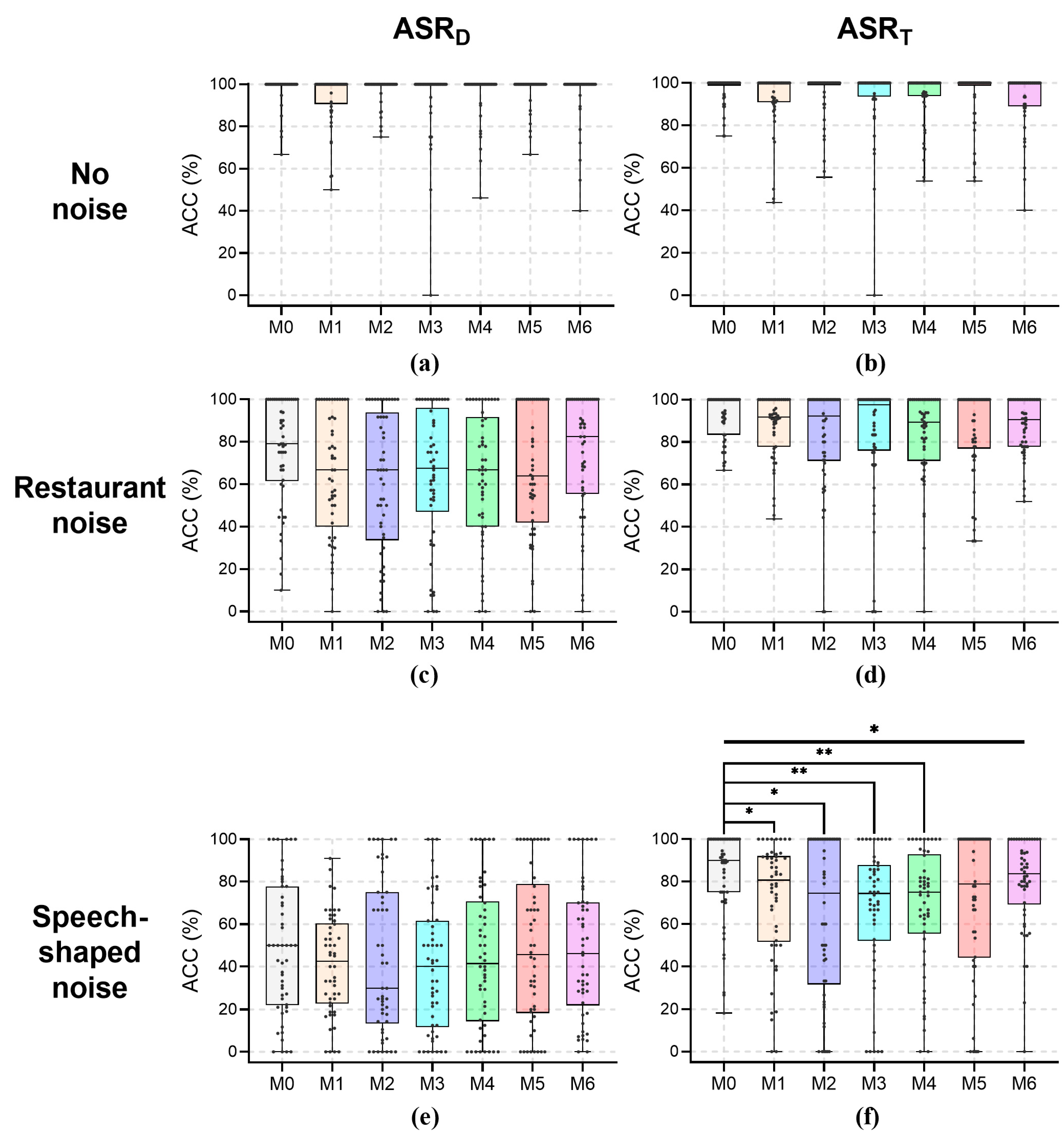
The results of the ACC for all speakers at a recording distance of 0.6 m are shown in Figure 4; their median values under noises are reported in Table 2. For the recording distance of 0.6 m, no significant effects of wearing a mask with no noise on ASR were found for any speakers (p > 0.276). The medians of ACC with no noise were 100% for all mask conditions. Under restaurant noise, mask-wearing significantly affected ASRD (H = 18.599, p = 0.005) and ASRT (H = 12.694, p = 0.048). For ASRD, the ACCs under restaurant noise for mask conditions compared to than that in the M0 condition were as follows: for the M1 condition it was 19.3 pp less (H = 70.910, p = 0.013), for the M2 condition it was 21.4 pp less (H = 87.910, p = 0.002), for the M3 condition it was 14.3 pp less (H = 59.400, p = 0.037), and for the M4 condition it was 14.8 pp less (H = 73.290, p = 0.010). Despite the lack of significance, the ACC of ASRD under restaurant noise in the M5 condition was 11.3 pp less than that in the M0 condition (H = 26.135, p = 0.358). For ASRT, the ACC under restaurant noise in the M2 condition was 9.3 pp less than that in the M0 condition (H = 78.270, p = 0.005), and for the M4 condition it was 8.0 pp less than that for M0 (H = 71.790, p = 0.010). Despite the lack of significance, the ACC of ASRT under restaurant noise in the M5 condition was 8.0 pp less than that in the M0 condition (H = 43.015, p = 0.123). Under speech-shaped noise, mask-wearing had significant main effects on ASRT (H = 32.092, p < 0.001), whereas no significant main effects of wearing a mask on ASRD were found (H = 12.483, p = 0.052). Despite the lack of significance, the ACC of ASRD under speech-shaped noise in the M1 condition was 8.7 pp less than that in the M0 condition, in the M2 condition it was 12.5 pp less than that for M0, and in the M4 condition it was 13.5 pp less than that for M0. For ASRT, the ACC under speech-shaped noise in the M2 condition was 30.9 pp less than that in the M0 condition (H = 118.290, p < 0.001), in the M3 condition it was 14.2 pp less than that for M0 (H = 81.760, p = 0.004), in the M4 condition it was 17.3 pp less than that for M0 (H = 86.655, p = 0.002), and in the M5 condition it was 19.6 pp less than that for M0 (H = 83.565, p = 0.003).
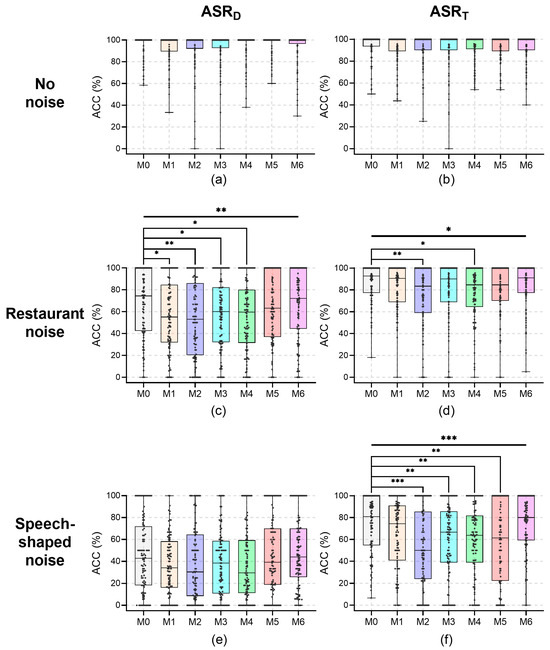
Figure 4.
The ACC for all speakers at a recording distance of 0.6 m. (a) ASRD, no noise; (b) ASRT, no noise; (c) ASRD, restaurant noise; (d) ASRT, restaurant noise; (e) ASRD, speech-shaped noise; and (f) ASRT, speech-shaped noise. Kruskal–Wallis tests and post-pairwise comparisons: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; and ***, p < 0.001.

Table 2.
Median ACC (%) for all speakers under noises at a recording distance of 0.6 m.
The results of post-hoc tests on the effects of masks on the ACC for the male speakers at a recording distance of 0.6 m are shown in Figure 5; their median values under noises are reported in Table 3. For the recording distance of 0.6 m, no significant effects of wearing a mask with no noise and restaurant noise on ASR for male speakers were found (p > 0.058). The medians of ACC with no noise for male speakers were all 100%, except for the condition of M5 for ASRT, where the median was 94.70%. Despite the lack of significance, the ACC of ASRD under restaurant noise in the M1 condition for male speakers was 14.4 pp less than that in the M0 condition, in the M2 condition it was 20.3 pp less than that for M0, and in the M4 condition it was 13.6 pp less than that for M0. In addition, the ACC of ASRT under restaurant noise in the M2 condition for male speakers was 14.7 pp less than that in the M0 condition, in the M4 condition it was 13.8 pp less than that for M0, and in the M5 condition it was 9.7 pp less than that for M0. Under speech-shaped noise, there were significant main effects of mask-wearing for male speakers on ASRD (H = 12.987, p = 0.043) and ASRT (H = 27.560, p < 0.001). However, there was no significant difference between the ACC of ASRD for male speakers under speech-shaped noise with or without a mask in the pairwise comparison tests. Despite the lack of statistical significance, the ACC of ASRD under speech-shaped noise for male speakers in the M1 condition was 12.9 pp less than that in the M0 condition (H = 28.610, p = 0.156), and in the M4 condition it was 17.5 pp less than that for M0 (H = 35.620, p = 0.078). For ASRT, the ACC under speech-shaped noise for male speakers in the M2 condition was 22.9 pp less than that in the M0 condition (H = 67.360, p = 0.001), and in the M5 condition it was 20.6 pp less than that for M0 (H = 57.290, p = 0.005). Strangely, the ACC values under noises for male speakers in the M6 condition were all higher than that in the M0 condition. Specifically, compared to that in the M0 condition, for male speakers in the M6 condition the ASRD ACC was 10.9 pp higher under restaurant noise and 4.7 pp higher under speech-shaped noise, and the ASRT ACC was 2.6 pp higher under restaurant noise and 11.2 pp higher under speech-shaped noise.
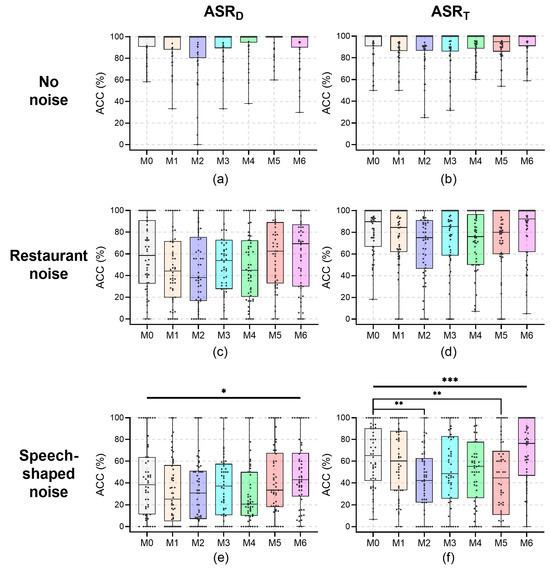
Figure 5.
The ACC for male speakers at a recording distance of 0.6 m. (a) ASRD, no noise; (b) ASRT, no noise; (c) ASRD, restaurant noise; (d) ASRT, restaurant noise; (e) ASRD, speech-shaped noise; and (f) ASRT, speech-shaped noise. Kruskal–Wallis tests and post-pairwise comparisons: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, and p < 0.001.

Table 3.
Median ACC (%) for male speakers under noises at a recording distance of 0.6 m.
The results of post-hoc tests on the effects of masks on the ACC for the female speakers at a recording distance of 0.6 m are shown in Figure 6; their median values under noises are reported in Table 4. For the recording distance of 0.6 m, no significant effects of wearing a mask with no noise or restaurant noise on ASR were found for female speakers (p > 0.157). The median values of ACC with no noise for female speakers were 100% for all mask conditions. Despite the lack of significance, the ACC of ASRD under restaurant noise in the M1 condition for female speakers was 12.3 pp less than that in the M0 condition, in the M2 condition it was 12.3 pp less than that for M0, in the M3 condition it was 11.4 pp less than that for M0, in the M4 condition it was 12.3 pp less than that for M0, and in the M5 condition it was 15.0 pp less than that for M0. In addition, the ACC of ASRT under restaurant noise for female speakers in the M1 condition was 8.3 pp less than that in the M0 condition, in the M4 condition it was 10.8 pp less than that for M0, and in the M6 condition it was 9.6 pp less than that for M0. Under speech-shaped noise, there were significant main effects of mask-wearing for female speakers on ASRT (H = 14.671, p = 0.023), whereas no significant effects of wearing a mask on ASRD were found (H = 3.401, p = 0.757). Despite the lack of significance, the ACC of ASRD under speech-shaped noise for female speakers in the M2 condition was 20.0 pp less than that in the M0 condition, in the M3 condition it was 9.9 pp less than that for M0, and in the M4 condition it was 8.6 pp less than that for M0. For ASRT, the ACC under speech-shaped noise for female speakers in the M1 condition was 9.4 pp less than that in the M0 condition (H = 45.470, p < 0.023), in the M2 condition it was 15.5 pp less than that for M0(H = 48.890, p = 0.015), in the M3 condition it was 15.7 pp less than that for M0 (H = 60.230, p = 0.003), and in the M4 condition it was 15.0 pp less than that for M0 (H = 58.600, p = 0.003). Despite the lack of significance, the ACC of ASRT under speech-shaped noise for female speakers in the M5 condition was 11.1 pp less than that in the M0 condition (H = 29.580, p = 0.139).
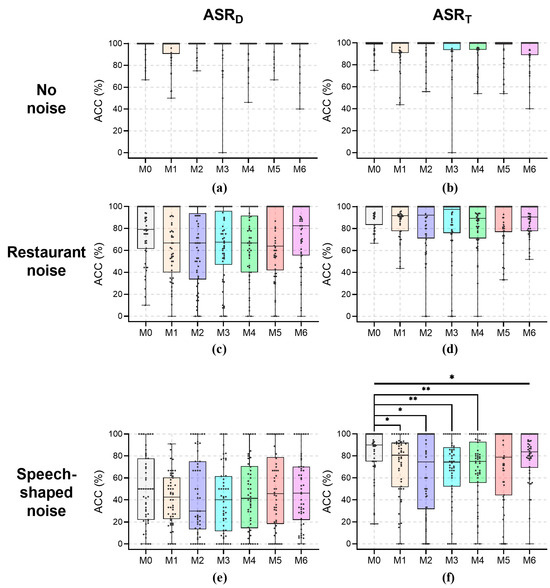
Figure 6.
The ACC for female speakers at a recording distance of 0.6 m. (a) ASRD, no noise; (b) ASRT, no noise; (c) ASRD, restaurant noise; (d) ASRT, restaurant noise; (e) ASRD, speech-shaped noise; (f) ASRT, speech-shaped noise. Kruskal–Wallis tests and post-pairwise comparisons: *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.

Table 4.
Median ACC (%) for female speakers under noises at a recording distance of 0.6 m.
3.3. Summary
In general, masks decreased the ACC by 10.2 pp under noises at the recording distance of 0.6 m. The order of the effects of masks on the ACC from greatest to smallest is as follows: M2 (activated-carbon mask, 18.5 pp) > M4 (headwear medical protective mask, 13.4 pp) > M5 (KN95, 10.6 pp) > M1 (surgical mask, 9.1 pp) > M3 (hanging-ear medical protective mask, 8.9 pp) > M6 (cloth mask, 0.9 pp). Both ASR systems performed worse under speech-shaped noise than under restaurant noise at the recording distance of 0.6 m. The ACC of ASRD (i.e., Baidu ASR) under speech-shaped noise was 25.5 pp less than that under restaurant noise, and the ASRT (i.e., Tencent ASR) was 19.9 pp less than that under restaurant noise. It is worth noting that the above results only apply to the specific versions of two ASR systems. In the current version, Tencent ASR is doing better overall.
4. Discussion
Overall, masks decreased the Baidu Cloud ASR accuracy by 10.4 pp and Tencent Cloud ASR accuracy by 10.1 pp under noises at a recording distance of 0.6 m, which is roughly the distance between a car driver or machine operator and the ASR system. When people cannot get closer to the ASR system or raise their volume, masks could hinder ASR. Given the wide use of masks in daily life in the post-pandemic era, considering the influence of masks on speech is strongly recommended when training ASR models.
There is no effect of masks on ASR accuracy in a quiet situation, with the ACC median values showing the ceiling effect for most situations as being 100%. These results are consistent with those from human subject studies of Atcherson et al. and Mendel et al., who reported that the difference between the speech recognition scores with the surgical mask present and without the mask was less than 1 pp for normal-hearing listeners [16,17]. Noting that the speech recognition scores were high in all conditions (i.e., higher than 99% for Atcherson et al., and 96.9% for Mendel et al.), the ceiling effect [9] might be a possible reason for the non-significant differences in the speech recognition scores in the two studies [16,17].
Under the restaurant noise and speech-shaped noise, significant main effects of masks on ASR accuracy at a recording distance of 0.6 m were found (restaurant noise gave ASRD, p = 0.005, ASRT, p = 0.048, and speech-shaped noise gave ASRT, p < 0.001). At the recording distance of 0.6 m and under noises, the activated-carbon mask (M2) impacted ASR accuracy most, followed by the headwear medical protective mask (M4) and KN95 mask (M5). The activated-carbon mask decreased the ASR accuracy by 18.5 pp, the headwear medical protective mask decreased it by 13.4 pp, and the KN95 mask decreased it by 10.6 pp at the recording distance of 0.6 m. The cloth mask (M6) has the least effect on ASR, reducing ASR accuracy by 0.9 pp. The surgical mask (M1) and hanging-ear medical protective mask (M3) performed similarly, decreasing the ASR accuracy by 9.1 pp and 8.9 pp. These results are consistent with those from human subject studies of Bottalico et al., [9] and Palmiero et al. [14]. Bottalico et al., reported that the speech was 12 pp less intelligible with the surgical mask and 13 pp less intelligible with the N95 mask than for the unmasked condition [9]. The results of Palmiero et al. showed that the surgical masks reduced the STI by 3% and 4%, and the N95 masks reduced the STI by 13% and 17% [14].
In this study, we established two recording distances, 0.2 m for mobile phone users and 0.6 m for machine operators (such as in vehicles and for robots), to evaluate the impacts of masks on ASR performance in standard human–machine interactions. For the 0.2 m distance, masks decreased the ASR accuracy by 3.6 pp on average under noises but without statistical significance (p > 0.054), whereas for the 0.6 m distance, masks significantly decreased the ASR accuracy by 10.2 pp on average under noises (restaurant noise gave ASRD, p = 0.005, ASRT, p = 0.048, and speech-shaped noise gave ASRT, p < 0.001). There might be debate about whether the signals recorded at 0.6 m with lower voice amplitudes could be amplified easily by the speech enhancement algorithms of the ASR systems. However, results indicate that the ASR accuracy was affected by the absolute SPL of the speech signals given equal SNR (at least in an anechoic environment).
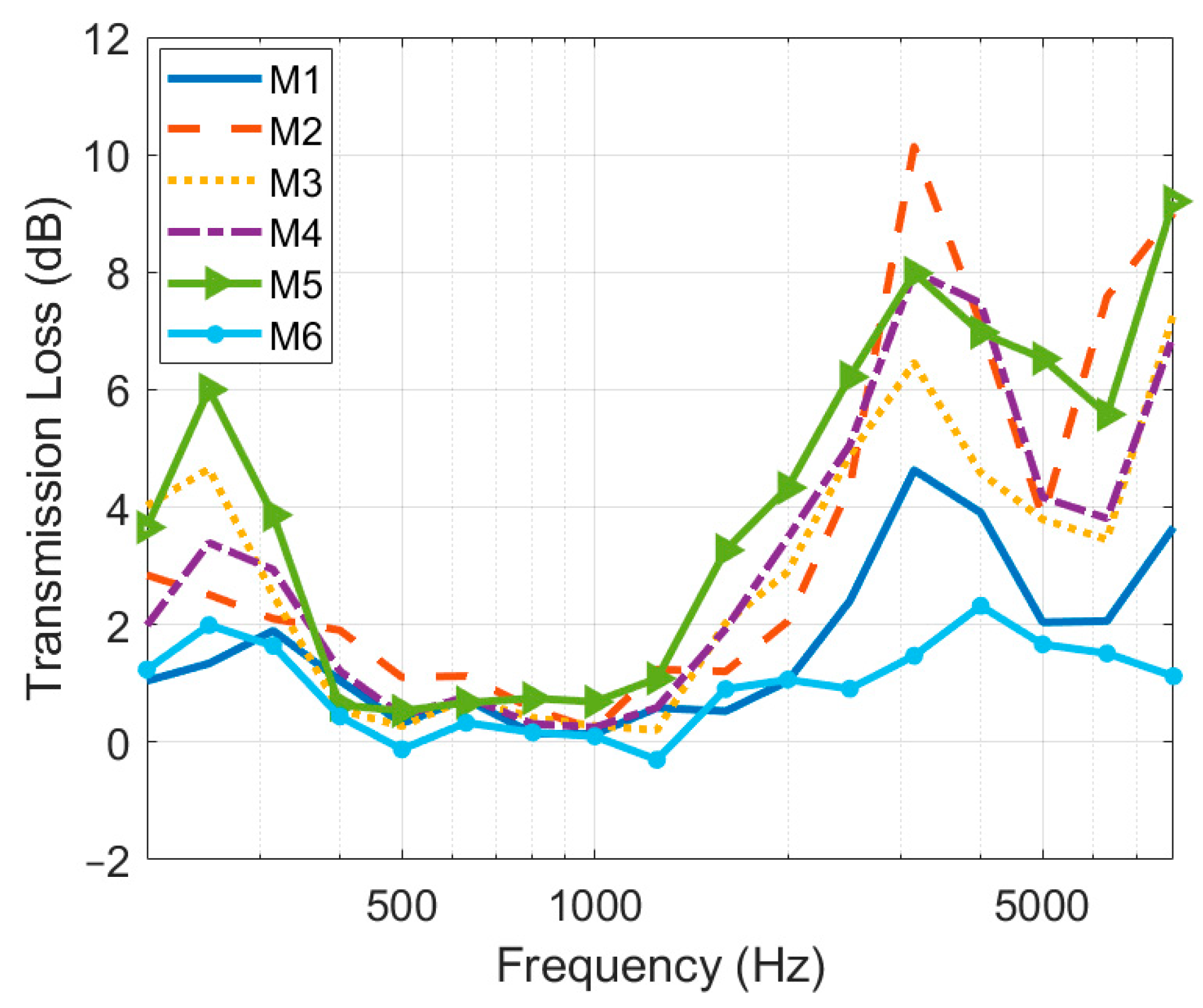
For the medical protective masks, the headwear medical protective mask (M4) decreased the ASR accuracy under noises much more than the hanging-ear medical protective mask (M3), by an average of 5.2 pp. this can be explained by the fact that that the headwear medical protective masks had better airtightness and higher sound-transmission loss than hanging-ear medical protective masks [34,35]. In our test, cloth masks had little effect on the ASR accuracy, only reducing the ACC by 0.9 pp at the recording distance of 0.6 m under noises, which is inconsistent with the results of Toscano et al. [36] The results of Toscano et al., showed that the fitted cloth mask impaired human speech recognition most [36]. The tightness of the cloth mask weave may account for the difference in results. To delve deeper into the mechanisms by which masks affect ASR accuracy, we measured the sound-transmission losses of these six masks. We used the mouth simulator to play the sweep signal with or without a mask and recorded it at a distance of 0.6 m. The sound-transmission loss was calculated using Equation (2), and the results are shown in Figure 7.
where ‘’ is the input sound pressure and ‘’ is the transmitted sound pressure.
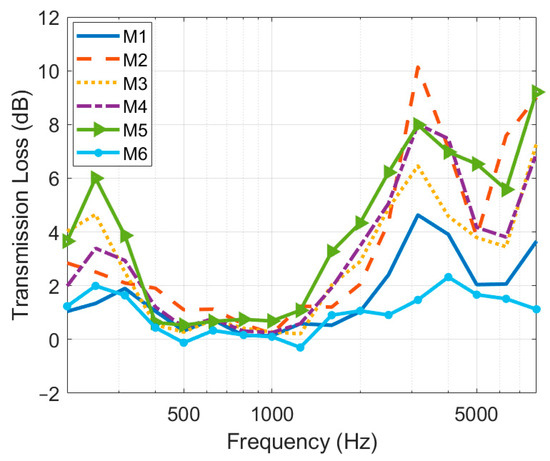
Figure 7.
The sound-transmission loss of masks.
All masks gave a large attenuation in the frequency band centered at about 3.15 kHz and a smaller attenuation at around 250 Hz, consistent with the results of Corey et al. [10] In general, the sound-transmission loss of masks was consistent with their influence on ASR accuracy: the cloth mask (M6), which produced the least acoustic attenuation, yielded the least effect on ASR accuracy; the activated-carbon mask (M2), which attenuated sounds most at around 3.15 kHz, impaired ASR accuracy the most. Furthermore, we analyzed the correlation between the sound-transmission loss of masks and their effect on ASR accuracy at the recording distance of 0.6 m. The results showed that there was a significant positive correlation between the declined values in the ACC with wearing masks and the sound-transmission loss of masks at 3.15 kHz (ρ = 0.943, p = 0.005), but no correlation between those at 250 Hz (ρ = 0.200, p = 0.704). The results indicated that the effects of masks on ASR accuracy can be attributed to the acoustic attenuation of masks on the high-frequency band of the speech signal. The low-pass-filtering characteristic of masks seems to greatly attenuate the energy of clear consonants and impair the ASR accuracy. Although masks attenuate the sound power at 250 Hz, which is around the fundamental monophthong frequency of Mandarin, the attenuation of low-frequency sound contributed little to the decline in ASR accuracy.
Post-hoc test results showed that masks similarly affected ASR accuracy for male and female speakers. On average, masks decreased the ASR accuracy for male speakers by 7.8 pp and for female speakers by 9.4 pp under noises at a recording distance of 0.6 m. However, it is worth noting that the cloth mask (M6) increased the ASR accuracy of male speakers for all noise conditions and ASR systems at a recording distance of 0.6 m by an average of 7.3 pp. There is no such anomaly for female speakers. Possibly, the cloth mask could enhance the feature extraction of ASR systems for male voices. It seems that the effects of masks on ASR are mediated through a complex mechanism related to the physical properties of masks (mainly affecting the sound-transmission loss), the voice characteristics, and the ASR algorithm. Future studies could further explore this issue by analyzing the effects of masks on the spectrum of speech signals and speech feature extraction of ASR systems for male speakers.
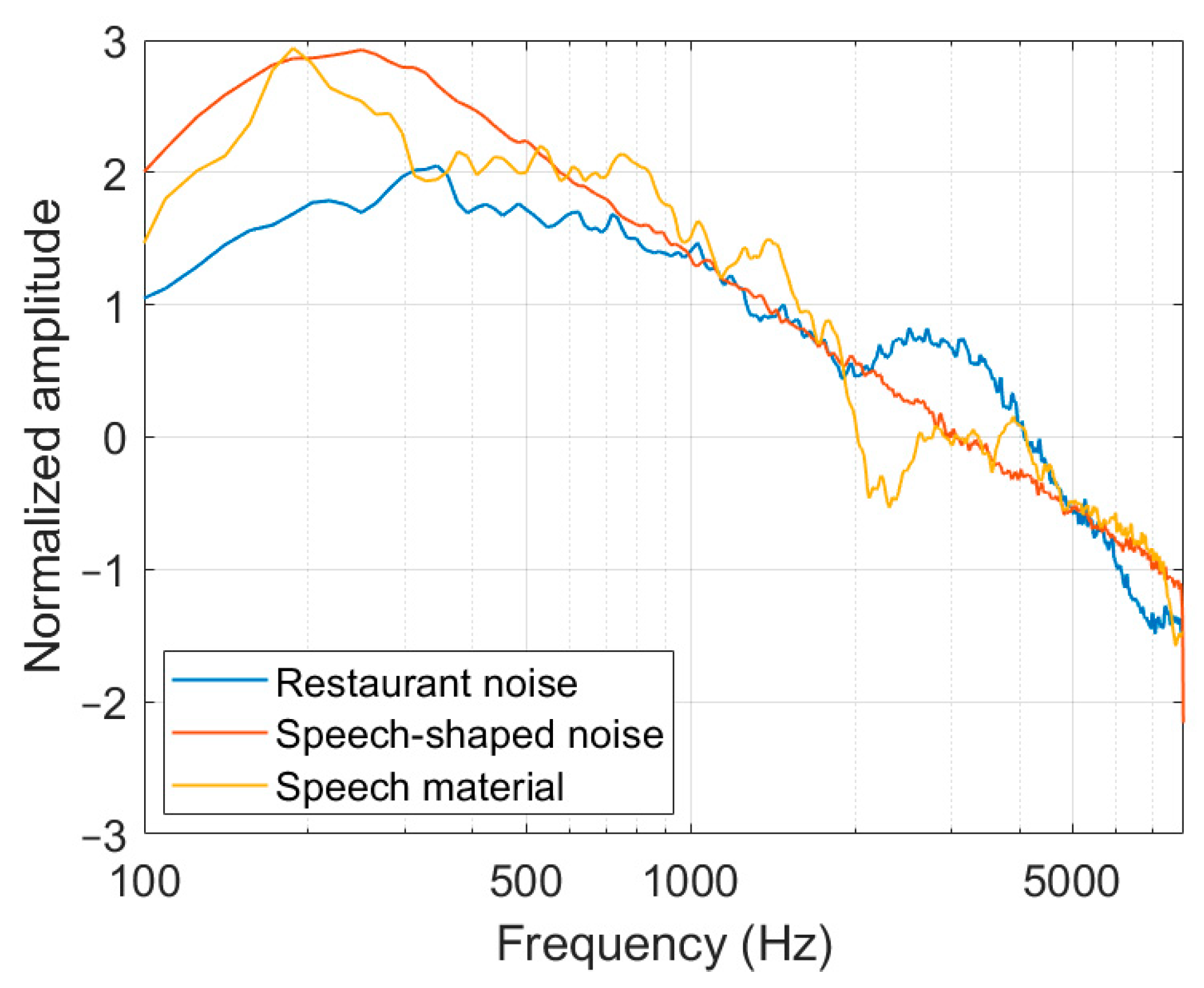
The results showed that speech-shaped noise had a larger effect on ASR accuracy than the restaurant noise at the same SNR. The ASR accuracy under speech-shaped noise was 22.7 pp less than that under restaurant noise at the recording distance of 0.6 m. The average spectra of the two noises and the speech material are shown in Figure 8. Compared to restaurant noise, the spectrum of speech-shaped noise is more similar to that of the speech material, possibly resulting in a more substantial energetic masking effect [37] and informational masking [38].
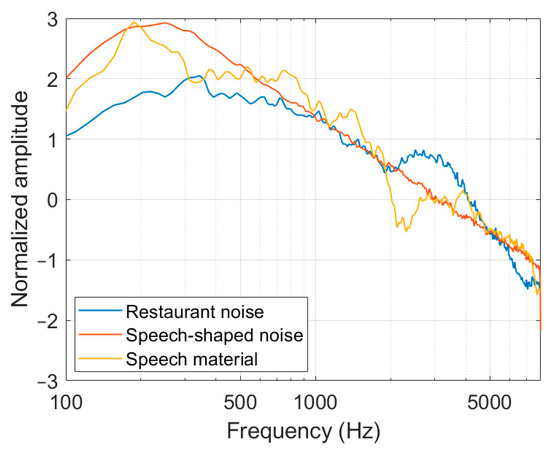
Figure 8.
The average spectra of the restaurant noise, the speech-shaped noise, and the speech material. The amplitude of the spectra was normalized.
Although the mouth simulator approximates human voice radiation well, it cannot simulate the actual situation of human speaking. Humans may adjust their voices while wearing a mask, but the mouth simulator does not. Magee et al., reported that humans’ speech rates were lower when wearing N95 and surgical masks, possibly as speakers compensate when wearing masks to improve intelligibility [39]. Speakers wearing masks might increase their speech level to compensate for any communication difficulties, or conversely, they might inadvertently lower their speech levels because they are having difficulty adjusting their voice level to one that can be heard but will not disturb others in the environment [15]. However, uncontrollability and inconsistency are generated by humans when they unconsciously adjust their way of speaking. We use the mouth simulator to play standard audio, which aligns with Bottalico et al. [9] and Porschmann et al. [11] and provided an efficient and human-independent way, with high repeatability, to test the ASR systems.
The metric of ASR performance in our test is word accuracy, which considers literal correctness instead of semantic correctness [40]. More speech understanding metrics, such as Semantic Distance [40] and Aligned Semantic Distance [41], can be used. In future studies, the stimuli should be more abundant, generated by humans in natural conditions, and appropriate for specific application scenarios.
5. Conclusions
When the speaker is not close to the ASR system, masks impair the ASR accuracy under restaurant noise and speech-shaped noise. Different types of masks have different effects on ASR accuracy. The activated-carbon mask reduced the accuracy by 18.5 pp compared to that without a mask, whereas the cloth mask reduced the accuracy by 0.9 pp. The acoustic attenuation of masks on the high-frequency band of the speech signal is attributed to the decline in ASR accuracy. Under the premise of meeting the requirements for protection and warmth, masks with lower acoustic attenuation should be used when conducting ASR. We recommend considering the impacts of masks when training ASR models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.H.; methodology, Y.H.; investigation, X.L. and K.N.; formal analysis, X.L.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grand No. 52072242) and the Participation in Research Program of Shanghai Jiao Tong University: T020PRP40062.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Name |
| ASR | Automatic speech recognition |
| pp | Percentage points |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| ASRD | Baidu Cloud automatic speech recognition |
| ASRT | Tencent Cloud automatic speech recognition |
| M0 | Without a mask |
| M1 | Surgical mask |
| M2 | Activated-carbon mask |
| M3 | Hanging-ear medical protective mask |
| M4 | Headwear medical protective mask |
| M5 | Anti-particulate mask (with a breather valve) |
| M6 | Cloth mask |
| ACC | Word accuracy |
References
- Bai, J. Wear masks scientifically to protect public health. People’s Daily, 14 April 2023; p. 004. [Google Scholar]
- Korayem, M.H.; Azargoshasb, S.; Korayem, A.H.; Tabibian, S. Design and Implementation of the Voice Command Recognition and the Sound Source Localization System for Human–Robot Interaction. Robotica 2021, 39, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Martín, F.; Salichs, M.A. Integration of a voice recognition system in a social robot. Cybern. Syst. 2011, 42, 215–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingol, M.C.; Aydogmus, O. Performing predefined tasks using the human–robot interaction on speech recognition for an industrial robot. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 95, 103903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irugalbandara, I.B.C.; Naseem, A.S.M.; Perera, M.S.H.; Logeeshan, V. HomeIO: Offline Smart Home Automation System with Automatic Speech Recognition and Household Power Usage Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE World AI IoT Congress (AIIoT), Seattle, WA, USA, 6–9 June 2022; pp. 571–577. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Intelligent automobile auxiliary propagation system based on speech recognition and AI driven feature extraction techniques. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2022, 25, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.J.; Ahn, B.K.; Lim, J.Y.; Macdonald, B.A.; Ahn, H.S. Robot Dialog System in the Context of Hospital Receptionist and its Demonstration. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2023, 15, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranto, S.I.; Nabid, R.A.; Samin, A.M.; Mohammed, N.; Sarker, F.; Huda, M.N.; Mamun, K.A. Human-Robot Interaction in Bengali language for Healthcare Automation integrated with Speaker Recognition and Artificial Conversational Entity. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd International Conference on Electrical & Electronic Engineering (ICEEE), Rajshahi, Bangladesh, 22–24 December 2021; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bottalico, P.; Murgia, S.; Puglisi, G.E.; Astolfi, A.; Kirk, K.I. Effect of masks on speech intelligibility in auralized classrooms. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 2878–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, R.M.; Jones, U.; Singer, A.C. Acoustic effects of medical, cloth, and transparent face masks on speech signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 2371–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porschmann, C.; Lubeck, T.; Arend, J.M. Impact of face masks on voice radiation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 3663–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumby, W.H.; Pollack, I. Visual Contribution to Speech Intelligibility in Noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1954, 26, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittum, K.J.; Feth, L.; Hoglund, E. The effects of surgical masks on speech perception in noise. Proc. Mtgs. Acoust. 2013, 19, 060125. [Google Scholar]
- Palmiero, A.J.; Symons, D.; Morgan, J.W., 3rd; Shaffer, R.E. Speech intelligibility assessment of protective facemasks and air-purifying respirators. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2016, 13, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, M.E.; Gordon-Salant, S.; Brungart, D.S. The cafeteria study: Effects of facial masks, hearing protection, and real-world noise on speech recognition. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 150, 4244–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atcherson, S.R.; Mendel, L.L.; Baltimore, W.J.; Patro, C.; Lee, S.; Pousson, M.; Spann, M.J. The Effect of Conventional and Transparent Surgical Masks on Speech Understanding in Individuals with and without Hearing Loss. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2017, 28, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendel, L.L.; Gardino, J.A.; Atcherson, S.R. Speech Understanding Using Surgical Masks: A Problem in Health Care? J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2008, 19, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandela, S.R.; Sadhu, S.S.; Rathore, V.S.; Jagini, S.K. Development of Noise Robust Automatic Speech Recognition System. In Proceedings of the 2023 14th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Delhi, India, 6–8 July 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jaroslavceva, J.; Wake, N.; Sasabuchi, K.; Ikeuchi, K. Robot Ego-Noise Suppression with Labanotation-Template Subtraction. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2022, 17, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Jiang, W. Estimate the noise effect on automatic speech recognition accuracy for mandarin by an approach associating articulation index. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 203, 109217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Kudina, O.; Halpern, B.M.; Scharenborg, O. Quantifying Bias in Automatic Speech Recognition; Cornell University Library: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Q.; Guo, P.; Yan, J.; Hu, P.; Xie, L. Decoupling and Interacting Multi-Task Learning Network for Joint Speech and Accent Recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2024, 32, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcovschi, A.; Jain, R.; Corcoran, P. A comparative analysis between Conformer-Transducer, Whisper, and wav2vec2 for improving the child speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Speech Technology and Human-Computer Dialogue (SpeD), Bucharest, Romania, 25–27 October 2023; pp. 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Geng, M.; Deng, J.; Wang, T.; Hu, S.; Li, G.; Liu, X. Personalized Adversarial Data Augmentation for Dysarthric and Elderly Speech Recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2024, 32, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, J.; Du, Z.; Yu, F.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, S.; Dai, L.R. A Comparative Study on Multichannel Speaker-Attributed Automatic Speech Recognition in Multi-party Meetings. In Proceedings of the 2023 Asia Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Taipei, Taiwan, 31 October–3 November 2023; pp. 1943–1948. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 41813.1-2022; Information Technology-Intelligent Speech Interaction Testing Method-Part 1: Speech Recognition. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- YY 0469-2011; Surgical Mask. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Q/JY001-2021; Disposable Protective Face Mask (Non-Medical). Dongguan Junyi Labor Insurance Products Ltd.: Dongguan, China, 2021.
- GB 19083-2010; Technical Requirements for Protective Face Mask for Medical Use. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- GB 2626-2019; Respiratory Protection—Non-Powered Air-Purifying Particle Respirator. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Bu, H.; Du, J.; Na, X.; Wu, B.; Zheng, H. AISHELL-1: An open-source Mandarin speech corpus and a speech recognition baseline. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th Conference of the Oriental Chapter of the International Coordinating Committee on Speech Databases and Speech I/O Systems and Assessment (O-COCOSDA), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1–3 November 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Z. The average spectrum of Chinese speech. J. Nanjing Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2012, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 7347-1987; The Standard Spectrum of Chinese Speech. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1987.
- Chu, C. Mask, who works best? When should we wear it? How to maintain? CNKI, 8 December 2016; p. 016. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Harb, C.; Leng, W.; Marr, L.C. Inward and outward effectiveness of cloth masks, a surgical mask, and a face shield. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, J.C.; Toscano, C.M. Effects of face masks on speech recognition in multi-talker babble noise. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, B. An Introduction to the Psychology of Hearing, 5th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, M.; Garcia Lecumberri, M.L.; Barker, J. The foreign language cocktail party problem: Energetic and informational masking effects in non-native speech perception. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magee, M.; Lewis, C.; Noffs, G.; Reece, H.; Chan, J.C.S.; Zaga, C.J.; Paynter, C.; Birchall, O.; Rojas Azocar, S.; Ediriweera, A.; et al. Effects of face masks on acoustic analysis and speech perception: Implications for peri-pandemic protocols. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 3562–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Arora, A.; Le, D.; Yeh, C.-F.; Fuegen, C.; Kalinli, O.; Seltzer, M.L. Semantic Distance: A New Metric for ASR Performance Analysis Towards Spoken Language Understanding; Cornell University Library: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rugayan, J.; Svendsen, T.; Salvi, G. Semantically Meaningful Metrics for Norwegian ASR Systems. Interspeech 2022, 2283–2287. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).