Experimental Investigation of the Effect of Fault Reactivation Induced by Water Injection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Description and Preparation
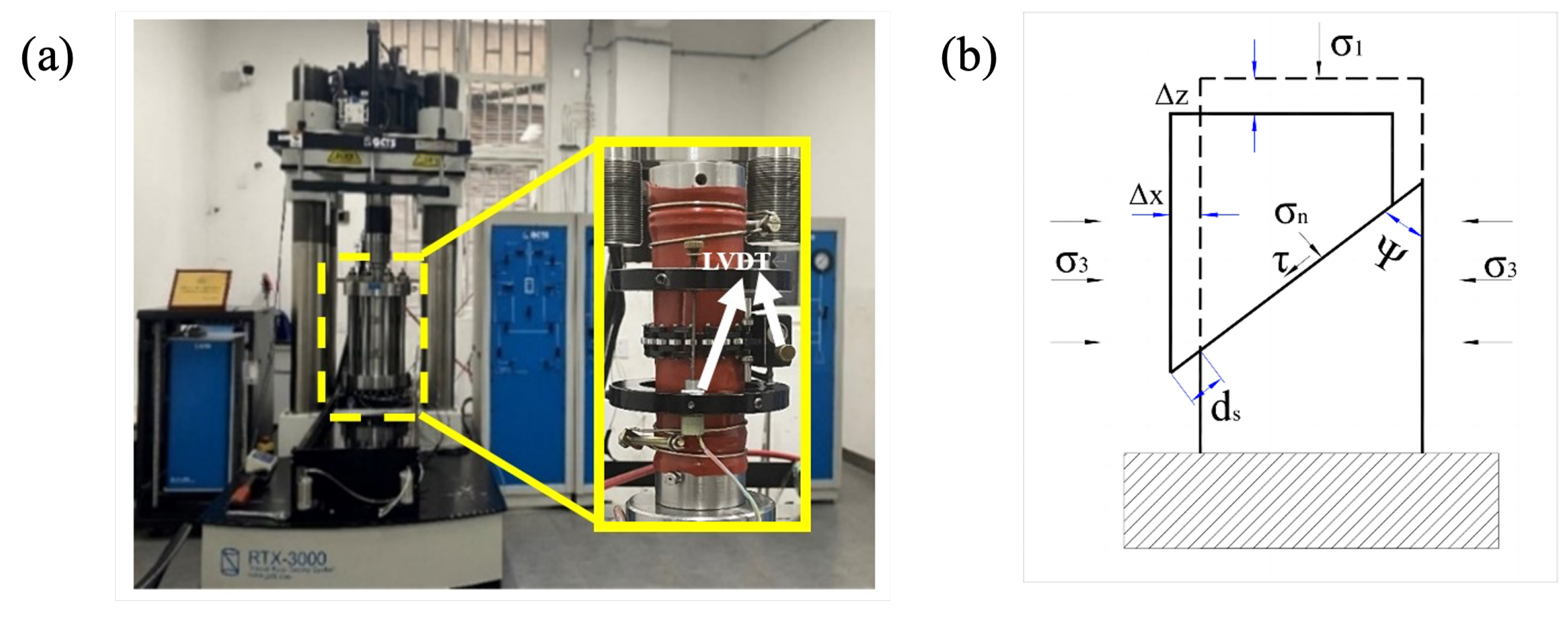
2.2. Experimental Configuration
2.3. Experimental Procedure
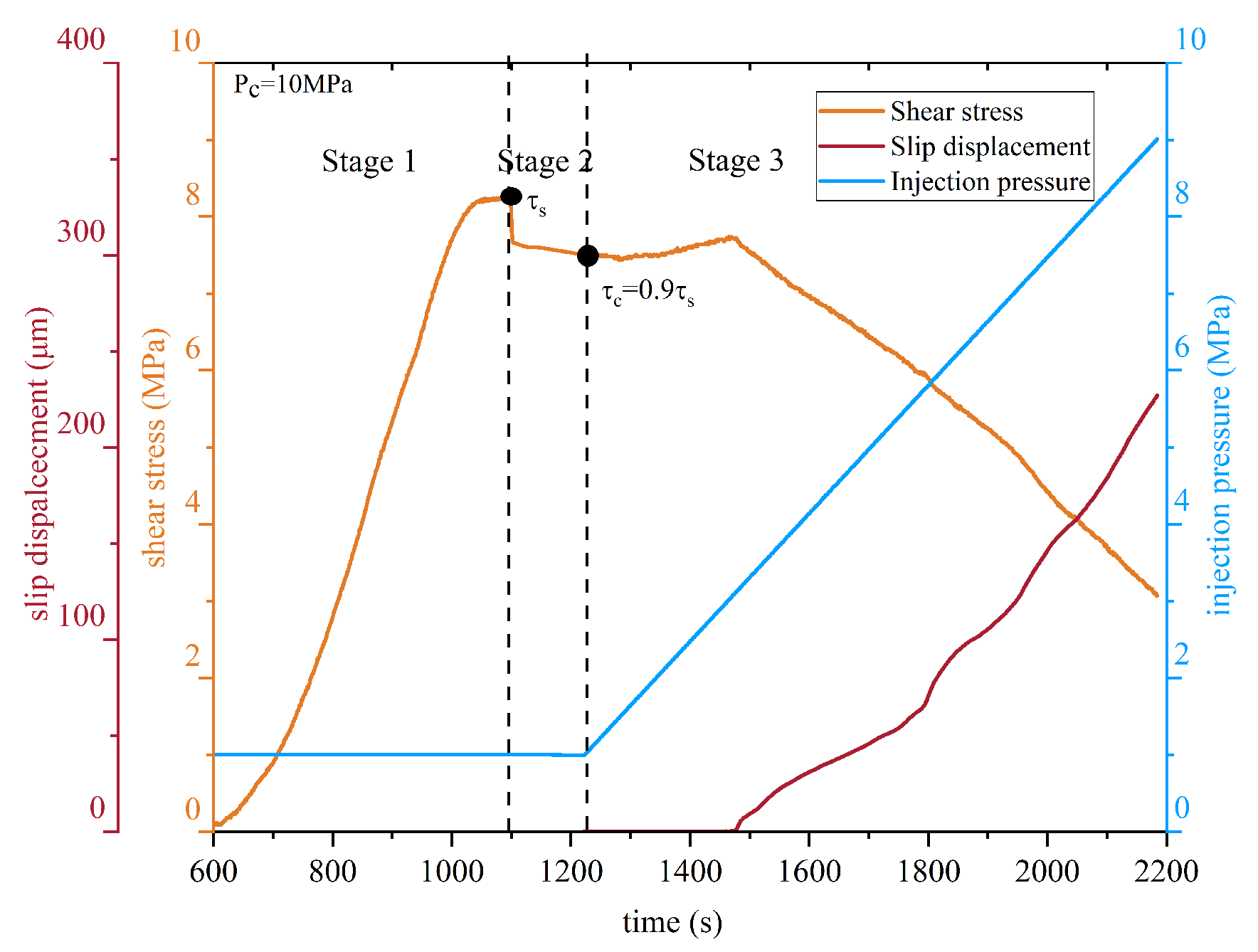
3. Results
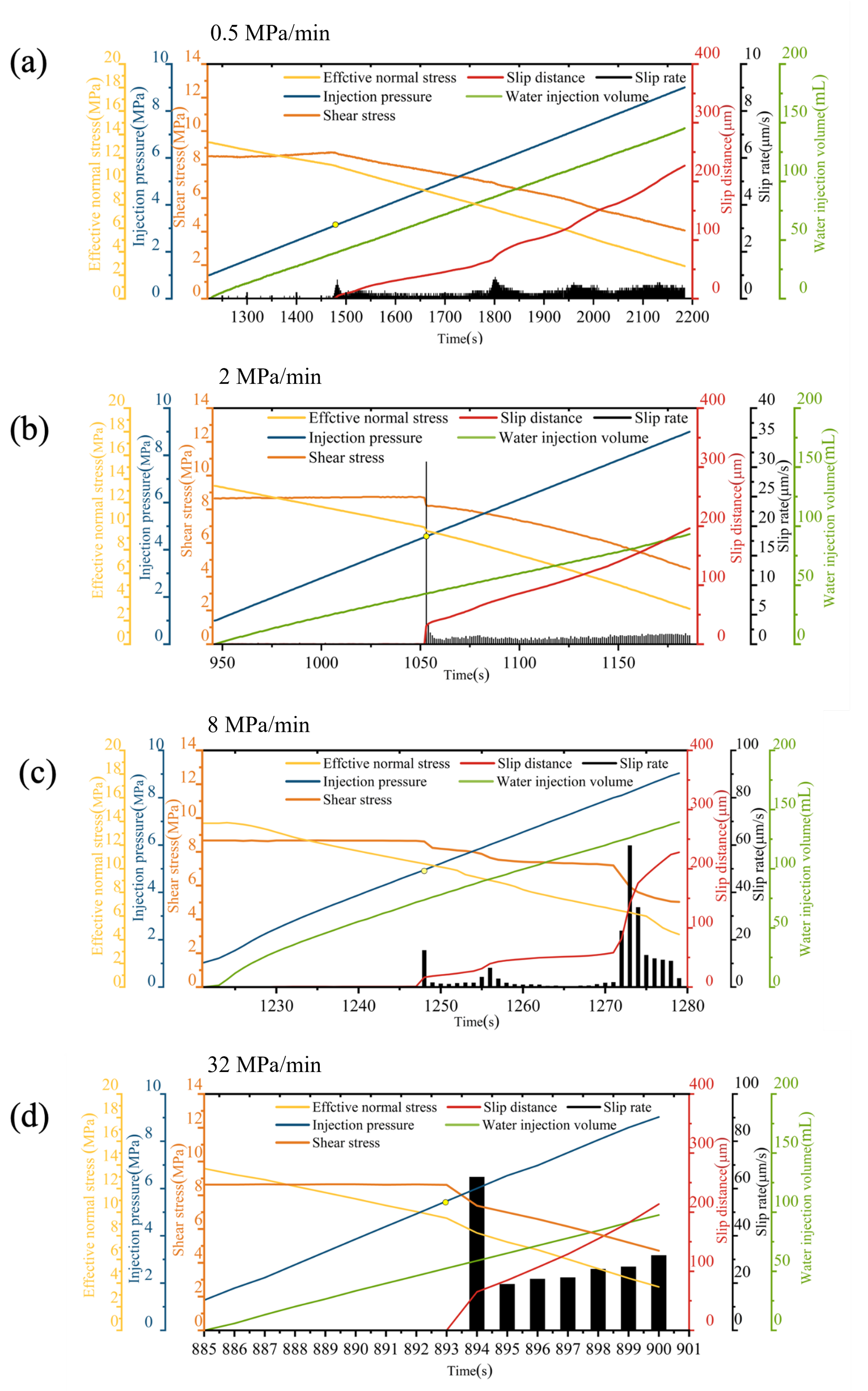
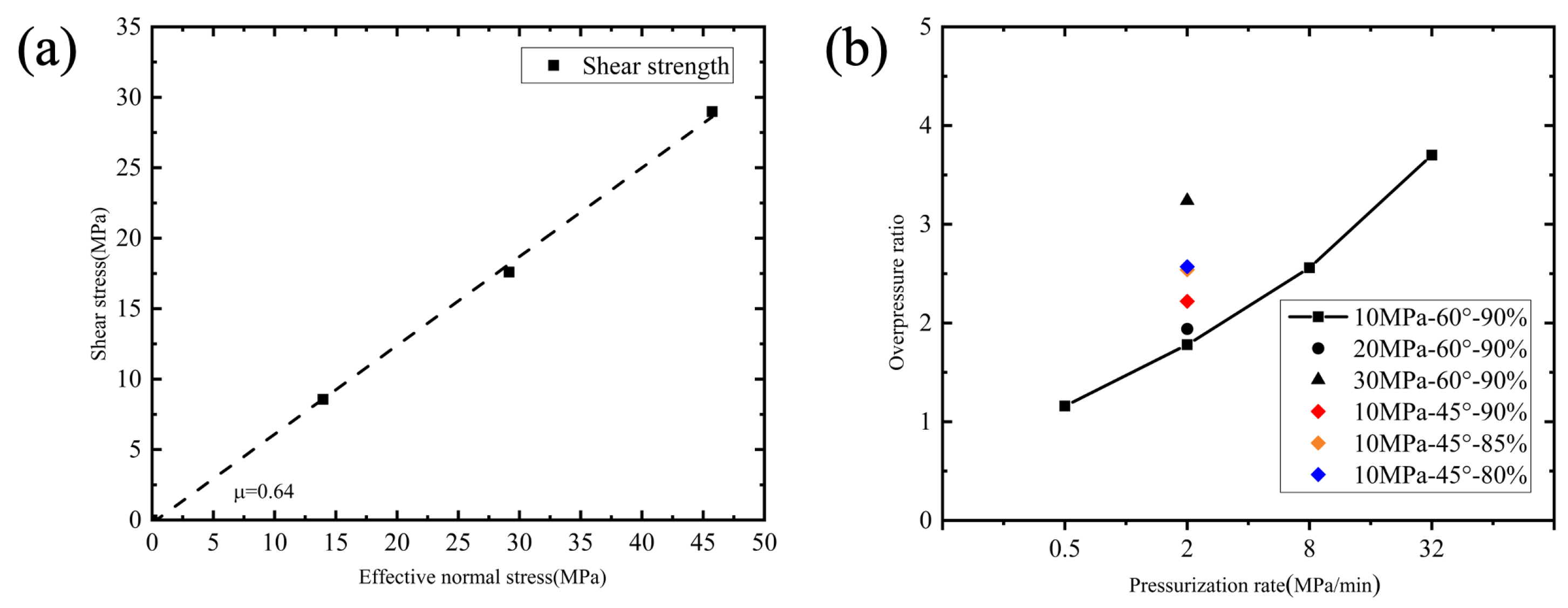
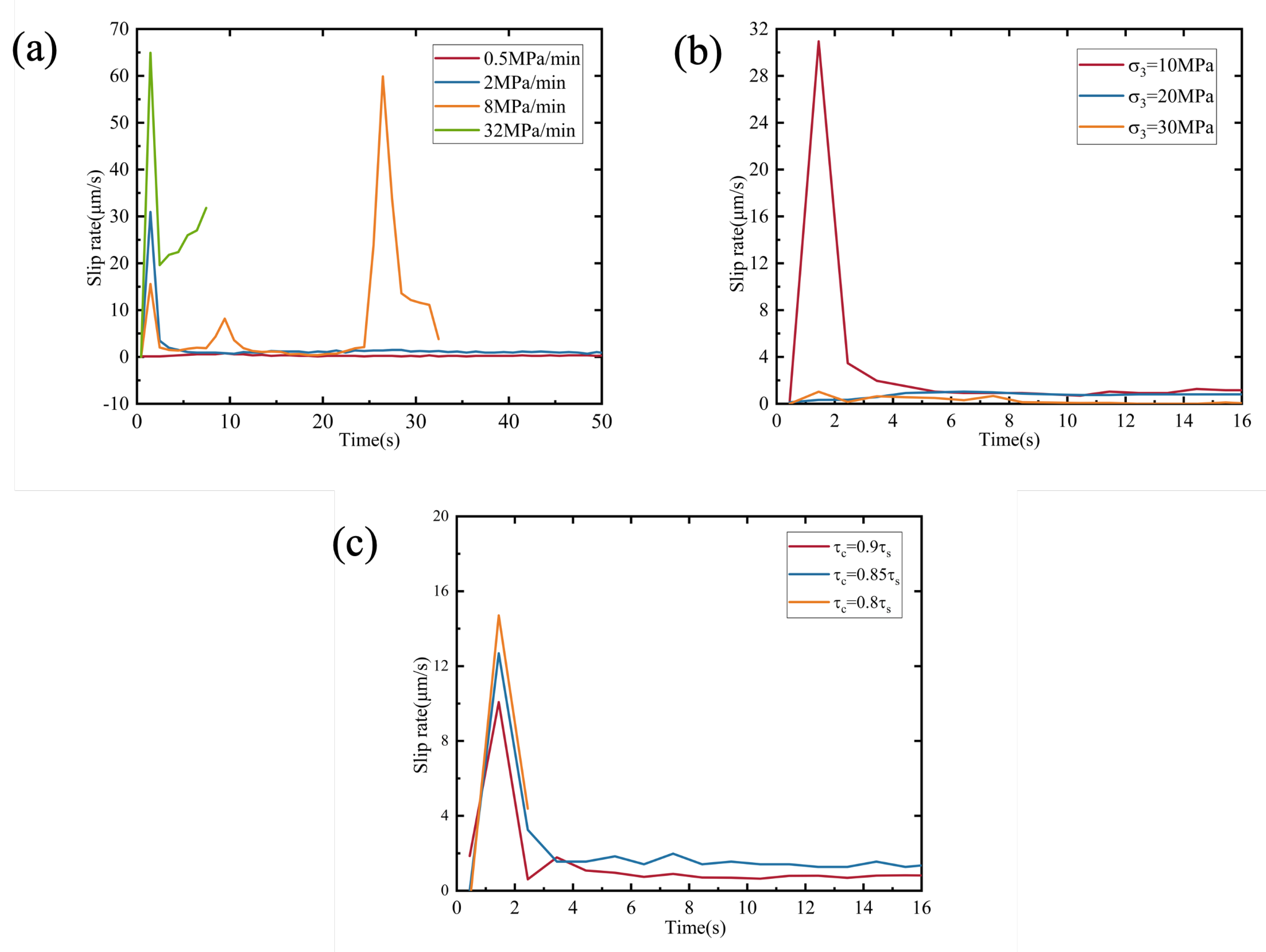
3.1. Cases of Different Pressurization Rates
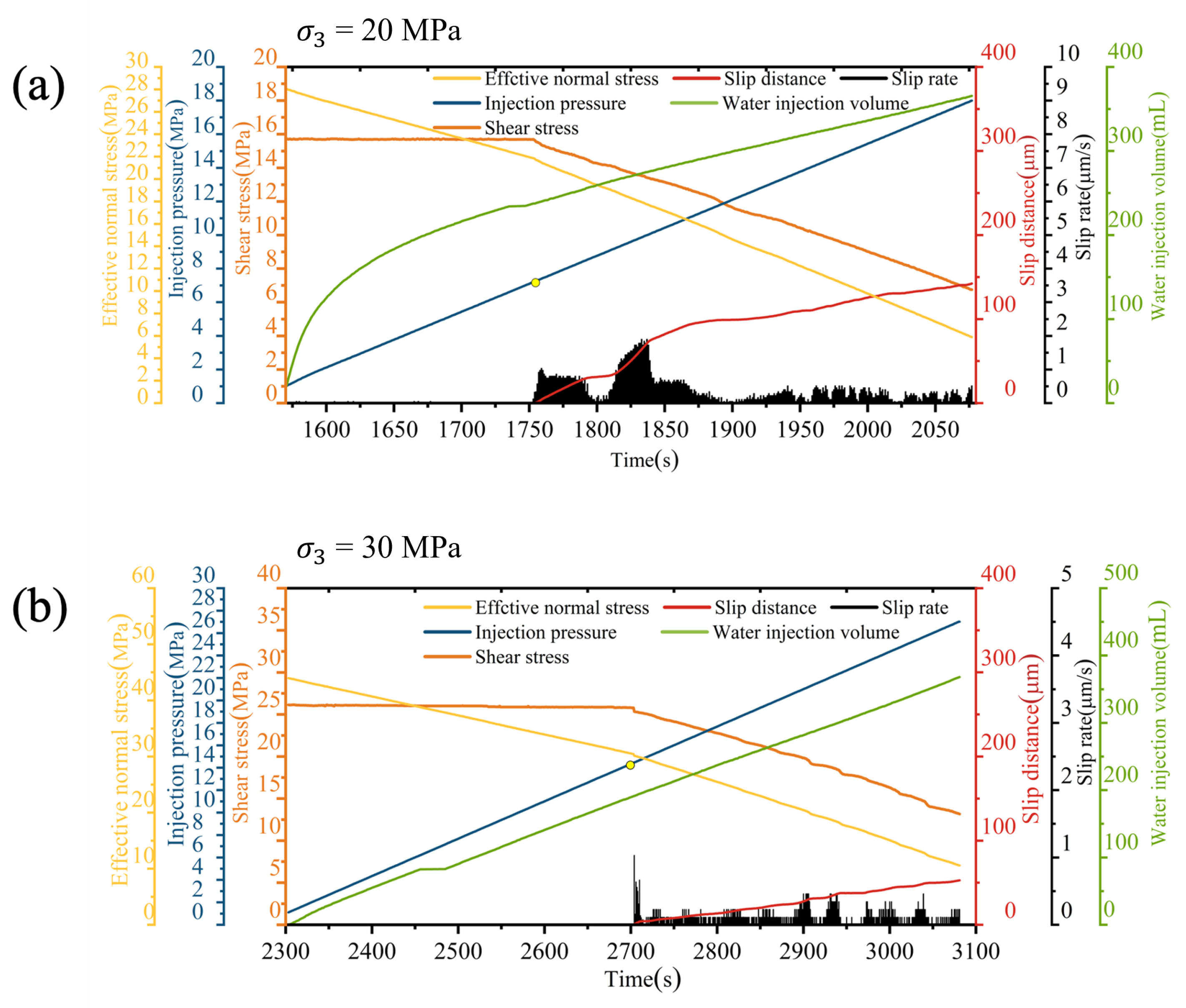
3.2. Cases of Different Confining Pressures
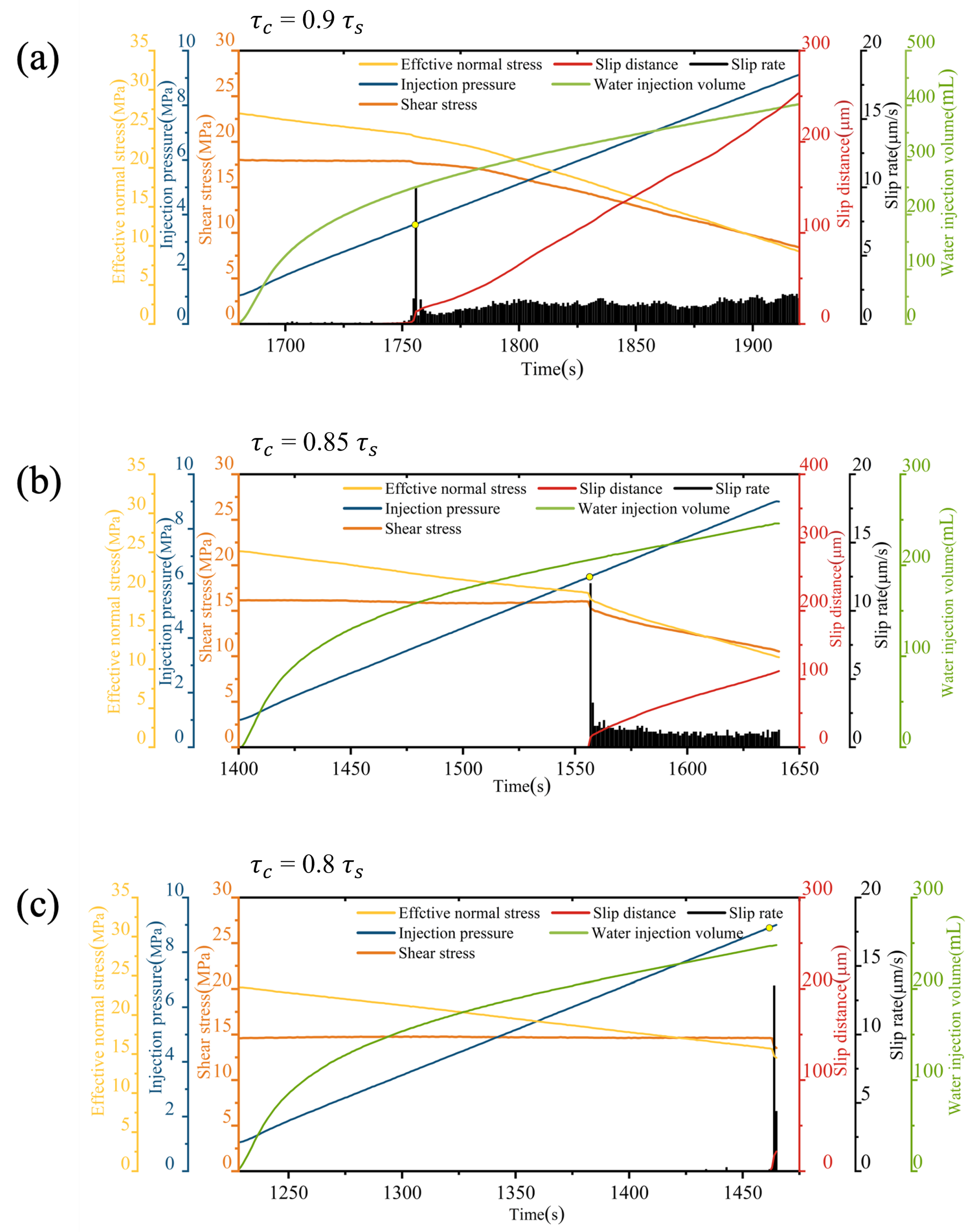
3.3. Cases of Different Initial Stress State
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Pressurization Rate on Fault Slip Initiation
4.2. Slip Modes in Fluid Injection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, Y.; Liu, F. Consumption of energy from conventional sources a challenge to the green environment: Evaluating the role of energy imports, and energy intensity in Australia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 22712–22727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.; Kong, Y.; Jiang, S.; Shao, H.; Zhu, H.; Yang, M. Progress in exploration, development and utilization of geothermal energy. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 911376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balat, M.; Balat, H.; Faiz, U. Utilization of Geothermal Energy for Sustainable Global Development. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2009, 4, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, S.G.; Anderson, A.; Blankenship, D. Geothermal Energy R & D: An Overview of the U.S. Department of Energy’s Geothermal Technologies Office. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2021, 143, 100801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baria, R.; Baumgärtner, J.; Rummel, F.; Pine, R.J.; Sato, Y. HDR/HWR reservoirs: Concepts, understanding and creation. Geothermics 1999, 28, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, J.W.; Anderson, B.J.; Batchelor, A.S. Impact of enhanced geothermal systems on US energy supply in the twenty-first century. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2007, 365, 1057–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Gao, G.; Zhang, S. Fault slip potential induced by fluid injection in the Matouying enhanced geothermal system (EGS) field, Tangshan seismic region, North China. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 2257–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarr, A. Maximum magnitude earthquakes induced by fluid injection. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenbruch, C.; Zoback, M. How will induced seismicity in Oklahoma respond to decreased saltwater injection rates? Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignan, A.; Landtwing, D.; Kästli, P. Induced seismicity risk analysis of the 2006 Basel, Switzerland, Enhanced Geothermal System project: Influence of uncertainties on risk mitigation. Geothermics 2015, 53, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Ree, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Kang, S.Y.; Seo, W. Assessing whether the 2017 Mw 5.4 Pohang earthquake in South Korea was an induced event. Science 2018, 360, 1007–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibson, R.H. A note on fault reactivation. J. Struct. Geol. 1985, 7, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Gao, T.; Zhao, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Shang, D. The role of water lubrication in critical state fault slip. Eng. Geol. 2020, 271, 105606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Dou, Z.; Yang, Q. Shear behaviors of granite fractures immersed in chemical solutions. Eng. Geol. 2020, 279, 105869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth, W.L. Injection-Induced Earthquakes. Science 2013, 341, 1225942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, J.L.; Ellsworth, W.L.; Dougherty, S.L. Erratum to The 2013–2016 Induced Earthquakes in Harper and Sumner Counties, Southern Kansas. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2018, 108, 3699–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; McGarr, A.; Zhou, L.; Zang, Y. An Investigation of Seismicity Induced by Hydraulic Fracturing in the Sichuan Basin of China Based on Data from a Temporary Seismic Network. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2019, 109, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, P.; Fitzgerald, S.D. A note on induced stress changes in hydrocarbon and geothermal reservoirs. Tectonophysics 1998, 289, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, A.J.; Norbeck, J.H.; Rubinstein, J.L. The effects of varying injection rates in Osage County, Oklahoma, on the 2016 M w 5.8 Pawnee earthquake. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2017, 88, 1040–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohlich, C. Two-year survey comparing earthquake activity and injection-well locations in the Barnett Shale, Texas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13934–13938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keranen, K.M.; Weingarten, M. Induced Seismicity. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2018, 46, 149–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keranen, K.M.; Weingarten, M.; Abers, G.A.; Bekins, B.A.; Ge, S. Sharp increase in central Oklahoma seismicity since 2008 induced by massive wastewater injection. Science 2014, 345, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, I.W.; Brown, M.R.M.; Ge, S.; Lee, K.K. Causal mechanism of injection-induced earthquakes through the Mw 5.5 Pohang earthquake case study. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebel, T.H.W.; Rosson, Z.; Brodsky, E.E.; Walter, J.I. Aftershock deficiency of induced earthquake sequences during rapid mitigation efforts in Oklahoma. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2019, 522, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, R.; Gupta, H.K. Characterization of injection-induced seismicity at north central Oklahoma, USA. J. Seismol. 2021, 25, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto-Felgueroso, L.; Santillán, D.; Mosquera, J.C. Stick-slip dynamics of flow-induced seismicity on rate and state faults. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 4098–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, S.; Santillán, D.; Mosquera, J.C.; Cueto-Felgueroso, L. Delayed Weakening and Reactivation of Rate-and-State Faults Driven by Pressure Changes Due to Fluid Injection. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 11917–11937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Allison, K.L.; Dunham, E.M.; Yang, Y. Fault valving and pore pressure evolution in simulations of earthquake sequences and aseismic slip. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Luo, Q. Investigations and new insights on earthquake mechanics from fault slip experiments. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 228, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passelègue, F.X.; Brantut, N.; Mitchell, T.M. Fault Reactivation by Fluid Injection: Controls From Stress State and Injection Rate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 12-837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Ghassemi, A. Heterogeneous fracture slip and aseismic-seismic transition in a triaxial injection test. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, E.; Hackston, A. On the effective stress law for rock-on-rock frictional sliding, and fault slip triggered by means of fluid injection. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2017, 375, 20160001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noël, C.; Passelègue, F.X.; Giorgetti, C.; Violay, M. Fault Reactivation During Fluid Pressure Oscillations: Transition From Stable to Unstable Slip. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 10940–10953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, K.; Moriya, H.; Niitsuma, H.; Tsuchiya, N. Mechanical and hydraulic coupling of injection-induced slip along pre-existing fractures. Geothermics 2008, 37, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, M.E.; Zhu, W.; Banker, J. Fault slip controlled by stress path and fluid pressurization rate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 4330–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brace, W.F.; Byerlee, J.D. Stick-Slip as a Mechanism for Earthquakes. Science 1966, 153, 990–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Wanniarachchi, W.A.M.; Wu, W. Effect of fluid pressure heterogeneity on injection-induced fracture activation. Comput. Geotech. 2020, 123, 103589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, F.; Guglielmi, Y.; Nussbaum, C.; Birkholzer, J. On the Relationship Between Fault Permeability Increases, Induced Stress Perturbation, and the Growth of Aseismic Slip During Fluid Injection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 11-012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Density (g/cm3) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | UCS (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.80 | 92.85 | 0.26 | 152.84 |
| Test No. | Pressurization Rate (MPa/min) | Confining Pressure (MPa) | Inclination Angle (°) | Shear Strength (MPa) | Critical Shear Stress (MPa) | Slip Distance (m) | Peak Slip Rate (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | 0.5 | 10 | 60 | 9.26 | 0.9 | 226.89 | 0.84 |
| Z2 | 2 | 10 | 60 | 9.57 | 0.9 | 198.14 | 30.95 |
| Z3 | 8 | 10 | 60 | 9.59 | 0.9 | 227.9 | 59.89 |
| Z4 | 32 | 10 | 60 | 9.35 | 0.9 | 213.8 | 64.6 |
| W2 | 2 | 20 | 60 | 17.59 | 0.9 | 142 | 1.91 |
| W3 | 2 | 30 | 60 | 28.99 | 0.9 | 52.88 | 1.03 |
| J1 | 2 | 10 | 45 | 19.87 | 0.9 | 253 | 10.08 |
| J2 | 2 | 10 | 45 | 19.01 | 0.85 | 109 | 12.68 |
| J3 | 2 | 10 | 45 | 18.23 | 0.80 | 21.53 | 14.70 |
| Overpressure Ratio px | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample No. | 0.5 MPa/min | 2 MPa/min | 8 MPa/min | 32 MPa/min |
| Test no.1 | 1.18 | 1.85 | 2.68 | 3.77 |
| Test no.2 | 1.14 | 1.69 | 2.47 | 3.71 |
| Test no.3 | 1.29 | 1.82 | 2.52 | 3.63 |
| Average | 1.19 | 1.78 | 2.56 | 3.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Si, H. Experimental Investigation of the Effect of Fault Reactivation Induced by Water Injection. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083322
Liu W, Si H. Experimental Investigation of the Effect of Fault Reactivation Induced by Water Injection. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(8):3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083322
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wenjing, and Hu Si. 2024. "Experimental Investigation of the Effect of Fault Reactivation Induced by Water Injection" Applied Sciences 14, no. 8: 3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083322
APA StyleLiu, W., & Si, H. (2024). Experimental Investigation of the Effect of Fault Reactivation Induced by Water Injection. Applied Sciences, 14(8), 3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083322





