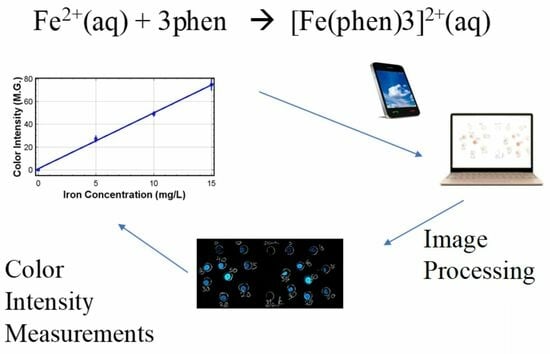
Method Development and Validation of a Rapid Silica Plate-Based Smartphone-Assisted Device in the Detection of Iron in Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Standards Preparations
2.3. Fabrication on Silica Plate
2.4. Fe Detection
2.5. Image Processing
2.6. Box Enclosure
3. Results and Discussion
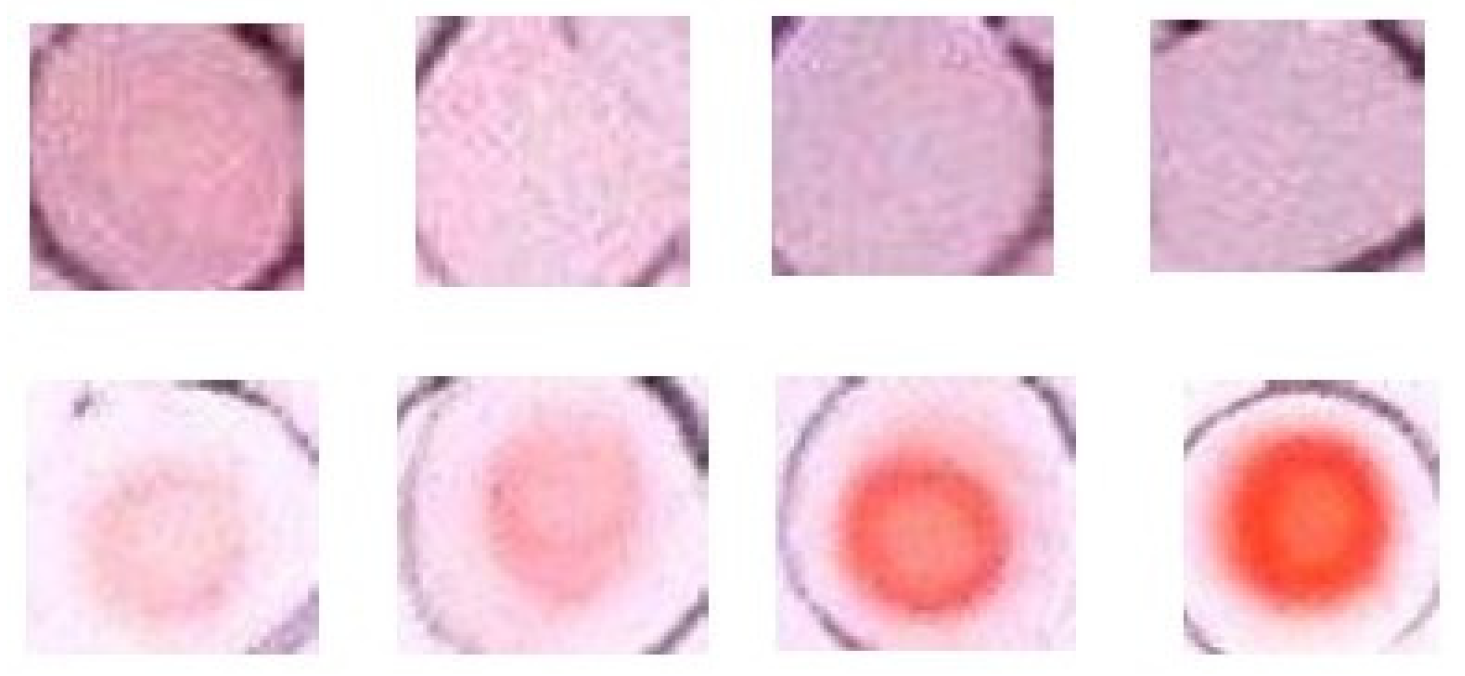
3.1. Color Development on Silica Plate
3.2. Results of Image Processing
3.3. Box Enclosure
3.4. Color Intensity Measurements
3.5. Effect of Amount Deposited
3.6. Method Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katole, S.B.; Kumar, P.; Patil, R.D. Environmental pollutants and livestock health: A review. Vet. Res. Int. 2013, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Raikwar, M.K.; Kumar, P.; Singh, M.; Singh, A. Toxic effect of heavy metals in livestock health. Vet. World 2008, 1, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.R.; Bandhyopadhyay, S.; Sultana, F.; Swarup, D. Heavy metal poisoning and its impact on livestock health and production system. Indian J. Anim. Health 2021, 60, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaria, J.M.; Munenge, R.W.; Njuguna, A.N.; Orre, J.L.; Dabasso, D. Occurrence of a Severe Acute Livestock Poisoning by Borehole Water in Marsabit District, Kenya A Case Study. Kenya Vet. 2005, 28, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fifield, F.; Kealey, D. Principles and Practice of Analytical Chemistry, 5th ed.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2000; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Skoog, D.A.; West, D.M.; Holler, F.J.; Crouch, S.R. Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dincer, C.; Bruch, R.; Costa-Rama, E.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T.; Merkoçi, A.; Manz, A.; Urban, G.A.; Güder, F. Disposable sensors in diagnostics, food, and environmental monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1806739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.K. From highly sophisticated analytical techniques to life-saving diagnostics: Technical developments in breath analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2006, 25, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, N.A.; Quinn, C.; Cate, D.M.; Reilly, T.H., III; Volckens, J.; Henry, C.S. Paper-based analytical devices for environmental analysis. Analyst 2016, 141, 1874–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, G.; Jobin, Y.S. ICP-OES, ICP-MS and AAS Techniques Compared; ICP Optical Emission Spectroscopy Technical Note; Jobin Yvon Inc.: Edison, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Mestek, O.; Loula, M.; Kaňa, A.; Vosmanská, M. Can ultrafast single-particle analysis using ICP-MS affect the detection limit? Case study: Silver nanoparticles. Talanta 2020, 210, 120665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cate, D.M. Development of Paper-Based Analytical Devices for Particulate Metals in Welding Fume. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur, S. A Comparison of the Relative Cost and Productivity of Traditional Metals Analysis Techniques versus ICP-MS in High Throughput Commercial Laboratories; Agilent Technologies Application Note; Agilent Technologies, Inc.: Bellevue, WA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, A.; Zou, Z.; Lee, K.K.; Ahn, C.H.; Bishop, P.L. State-of-the-art lab chip sensors for environmental water monitoring. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 032001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.R.; Koglin, E.N. Biosensors for environmental monitoring: An EPA perspective. In Biosensors for Direct Monitoring of Environmental Pollutants in Field; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, O.A.; Wanekaya, A.K.; Andreescu, S. Advances in analytical technologies for environmental protection and public safety. J. Environ. Monit. 2004, 6, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.P.; Kurkuri, M.; Losic, D.; Kigga, M.; Altalhi, T. New optofluidic based lab-on-a-chip device for the real-time fluoride analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1159, 338439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyrzynska, K.; Kubiak, A.; Wysocka, I. Application of solid phase extraction procedures for rare earth elements determination in environmental samples. Talanta 2016, 154, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Udayabhanu, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Muthamilselvi, P.; Eswari, C.; Vasantavada, A.; Kanetkar, S.; Kapoor, A. Digital colorimetric analysis for estimation of iron in water with smartphone-assisted microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 103, 2480–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenstein, G.; Larsen, U.D. Modular concept of a laboratory on a chip for chemical and biochemical analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1998, 13, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentele, M.M.; Cunningham, J.; Koehler, K.; Volckens, J.; Henry, C.S. Microfluidic paper-based analytical device for particulate metals. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4474–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cate, D.M.; Adkins, J.A.; Mettakoonpitak, J.; Henry, C.S. Recent developments in paper-based microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Whitesides, G.M.; Carrilho, E. Diagnostics for the developing world: Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, K.M.; Lepore, A.L.; Kurian, J.A.; Martinez, A.W. Fully enclosed microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 1340–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, J.; Boehle, K.; Henry, C. Electrochemical paper-based microfluidic devices. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 1811–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sanchez, M.M.; Yin, Y.; Herzer, R.; Ma, L.; Schmidt, O.G. Silicon-based integrated label-free optofluidic biosensors: Latest advances and roadmap. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1901138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaysuy, O.; Alorabi, A.Q.; Aljohani, M.M.; Alluhaybi, A.A.; Snari, R.M.; Bedowr, N.S.; Shah, R.; El-Metwaly, N.M. Aluminum MOF-based sensor for simultaneous colorimetric and fluorometric detection of Co+2 in electroplating wastewater samples and recovery of Pd+2 ions from electronic wastes. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 59, 104993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Cui, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, L. Applications of smartphone-based colorimetric biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2022, 11, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; Sabio, L.; Gálvez, N.; Capdevila, M.; Dominguez-Vera, J.M. Iron chemistry at the service of life. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Dong, H.; Zeng, G.; Tang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Deng, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. The interactions between nanoscale zero-valent iron and microbes in the subsurface environment: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 390–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srole, D.N.; Ganz, T. Erythroferrone structure, function, and physiology: Iron homeostasis and beyond. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 236, 4888–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. A review of human carcinogens. Part F: Chemical agents and related occupations. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC Press, International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Baan, R.; Grosse, Y.; Straif, K.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; Galichet, L.; et al. A review of human carcinogens—Part F: Chemical agents and related occupations. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 1143–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camaschella, C. Iron deficiency. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2019, 133, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanshahi, R.; Zare, M. Assessment of heavy metals pollution in groundwater of Golgohar iron ore mine area, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, T.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Sengupta, S. Nature of arsenic pollutants in groundwater of Bengal basin-a case study from Baruipur area, West Bengal, India. Curr. Sci. 2002, 82, 554–561. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cate, D.M.; Nanthasurasak, P.; Riwkulkajorn, P.; L’Orange, C.; Henry, C.S.; Volckens, J. Rapid detection of transition metals in welding fumes using paper-based analytical devices. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2014, 58, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.-T.; Wang, H.-B.; Zhang, T.; Li, C.-Q.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.-D. Quantitative analysis of various targets based on aptamer and functionalized Fe3O4@graphene oxide in dairy products using pregnancy test strip and smartphone. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarujamrus, P.; Meelapsom, R.; Pencharee, S.; Obma, A.; Amatatongchai, M.; Ditcharoen, N.; Chairam, S.; Tamuang, S. Use of a smartphone as a colorimetric analyzer in paper-based devices for sensitive and selective determination of mercury in water samples. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, B. Laboratory Methods in Microfluidics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, F.; Pan, F.; Yang, J.; Yan, Y.; Huang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Nie, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Quantitative colorimetric sensing of heavy metal ions via analyte-promoted growth of Au nanoparticles with timer or smartphone readout. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 2705–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ki, J.; Kwon, I.H.; Lee, J.; Lim, J.; Jang, S.; Son, S.U.; Seo, S.B.; Oh, S.Y.; Kang, T.; Jung, J.; et al. A portable smartphone-based colorimetric sensor that utilizes dual amplification for the on-site detection of airborne bacteria. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Ha, H.-T.; Kim, S. Smartphone-based image analysis coupled to paper-based colorimetric devices. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2020, 20, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Hagen, J.A.; Papautsky, I. Point-of-care colorimetric detection with a smartphone. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 4240–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbach, S.; Jiang, N.; Moreddu, R.; Dong, X.; Kurz, W.; Wang, C.; Dong, J.; Yin, Y.; Butt, H.; Brischwein, M.; et al. Smartphone-based colorimetric detection system for portable health tracking. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 4361–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanarat, P.; Dungchai, W.; Cate, D.; Volckens, J.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. Multilayer paper-based device for colorimetric and electrochemical quantification of metals. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 3555–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-L.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, H.-L.; Qiu, X.-B.; Yu, D.-L. Smartphone-based microfluidic colorimetric sensor for gaseous formaldehyde determination with high sensitivity and selectivity. Sensors 2018, 18, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.-H.; Chen, W.-Y.; Yen, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-W.; Chang, H.-T.; Chen, C.-F. Detection of mercury (II) ions using colorimetric gold nanoparticles on paper-based analytical devices. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6843–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motalebizadeh, A.; Bagheri, H.; Asiaei, S.; Fekrat, N.; Afkhami, A. New portable smartphone-based PDMS microfluidic kit for the simultaneous colorimetric detection of arsenic and mercury. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 27091–27100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellerbee, A.K.; Phillips, S.T.; Siegel, A.C.; Mirica, K.A.; Martinez, A.W.; Striehl, P.; Jain, N.; Prentiss, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Quantifying colorimetric assays in paper-based microfluidic devices by measuring the transmission of light through paper. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 8447–8452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Yu, X.; He, H.; Cao, G.; Lu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, S.-Y. Smartphone-based point-of-care microfluidic platform fabricated with a ZnO nanorod template for colorimetric virus detection. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 3298–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariati, S.; Khayatian, G. The colorimetric and microfluidic paper-based detection of cysteine and homocysteine using 1,5-diphenylcarbazide-capped silver nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 3295–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abràmoff, M.D.; Magalhães, P.J.; Ram, S.J. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, Analytical Validation (Q2R2 Guideline). Available online: https://www.ich.org/page/quality-guidelines (accessed on 22 April 2024).
- Bruce, P.; Minkkinen, P.; Riekkola, M.-L. Practical method validation: Validation sufficient for an analysis method. Microchim. Acta 1998, 128, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walfish, S. Analytical methods: A statistical perspective on the ICH Q2A and Q2B guidelines for validation of analytical methods. Biopharm. Int. 2006, 19, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Renger, B.; Végh, Z.; Ferenczi-Fodor, K. Validation of thin layer and high performance thin layer chromatographic methods. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 2712–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dołowy, M.; Kulpińska-Kucia, K.; Pyka, A. Validation of a thin-layer chromatography for the determination of hydrocortisone acetate and lidocaine in a pharmaceutical preparation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 107879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovato, P.F.F.; Chaves, E.S.; Vidal, L.N.; Santos, P.M. Feasibility of digital image colorimetric methods for iron determination in river sediment. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2024, in press. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1001627924000180 (accessed on 22 April 2024).


| Box Enclosed | Tabletop Scan | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Gray | Integrated Density | Mean Gray | Integrated Density |
| 0.772 | 0.733 | 0.967 | 0.981 |
| 0.822 | 0.731 | 0.963 | 0.992 |
| 0.777 | 0.772 | 0.947 | 0.982 |
| 0.864 | 0.815 | 0.982 | 0.987 |
| 0.864 | 0.815 | 0.982 | 0.987 |
| 0.787 | 0.744 | 0.957 | 0.976 |
| 0.862 | 0.756 | 0.997 | 0.995 |
| 0.823 | 0.727 | 0.997 | 0.995 |
| 0.795 | 0.709 | 0.990 | 0.994 |
| 0.881 | 0.859 | 0.970 | 0.978 |
| 0.8247 | 0.7661 | 0.9752 | 0.9867 |
| No. of Deposits | R2 | Calibration Equation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.9984 | y = 4.91x + 0.91 |
| 2 | 0.9576 | y = 7.43x + 9.45 |
| 3 | 0.8829 | y = 8.41x + 18.0 |
| Fe Amount (ng) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|
| 1.5 | 18.6 |
| 3.0 | 7.36 |
| 4.5 | 12.7 |
| Certified | FAAS Analysis | Silica Device Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| 20.00 | 20.03 ± 0.17 | 20.73 ± 1.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senna, B.S.; Masamba, W.; Obuseng, V. Method Development and Validation of a Rapid Silica Plate-Based Smartphone-Assisted Device in the Detection of Iron in Water. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3651. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093651
Senna BS, Masamba W, Obuseng V. Method Development and Validation of a Rapid Silica Plate-Based Smartphone-Assisted Device in the Detection of Iron in Water. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(9):3651. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093651
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenna, Bame Sanah, Wellington Masamba, and Veronica Obuseng. 2024. "Method Development and Validation of a Rapid Silica Plate-Based Smartphone-Assisted Device in the Detection of Iron in Water" Applied Sciences 14, no. 9: 3651. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093651
APA StyleSenna, B. S., Masamba, W., & Obuseng, V. (2024). Method Development and Validation of a Rapid Silica Plate-Based Smartphone-Assisted Device in the Detection of Iron in Water. Applied Sciences, 14(9), 3651. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093651