Effects of Amyloid Beta (Aβ) Oligomers on Blood–Brain Barrier Using a 3D Microfluidic Vasculature-on-a-Chip Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Microfluidic Cell Culture
2.3. Amyloid Beta 1–42 (Aβ1–42) Oligomer Preparation and Treatment
2.4. Barrier Integrity Assay
2.5. Immunocytochemistry
2.6. Cell Viability Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
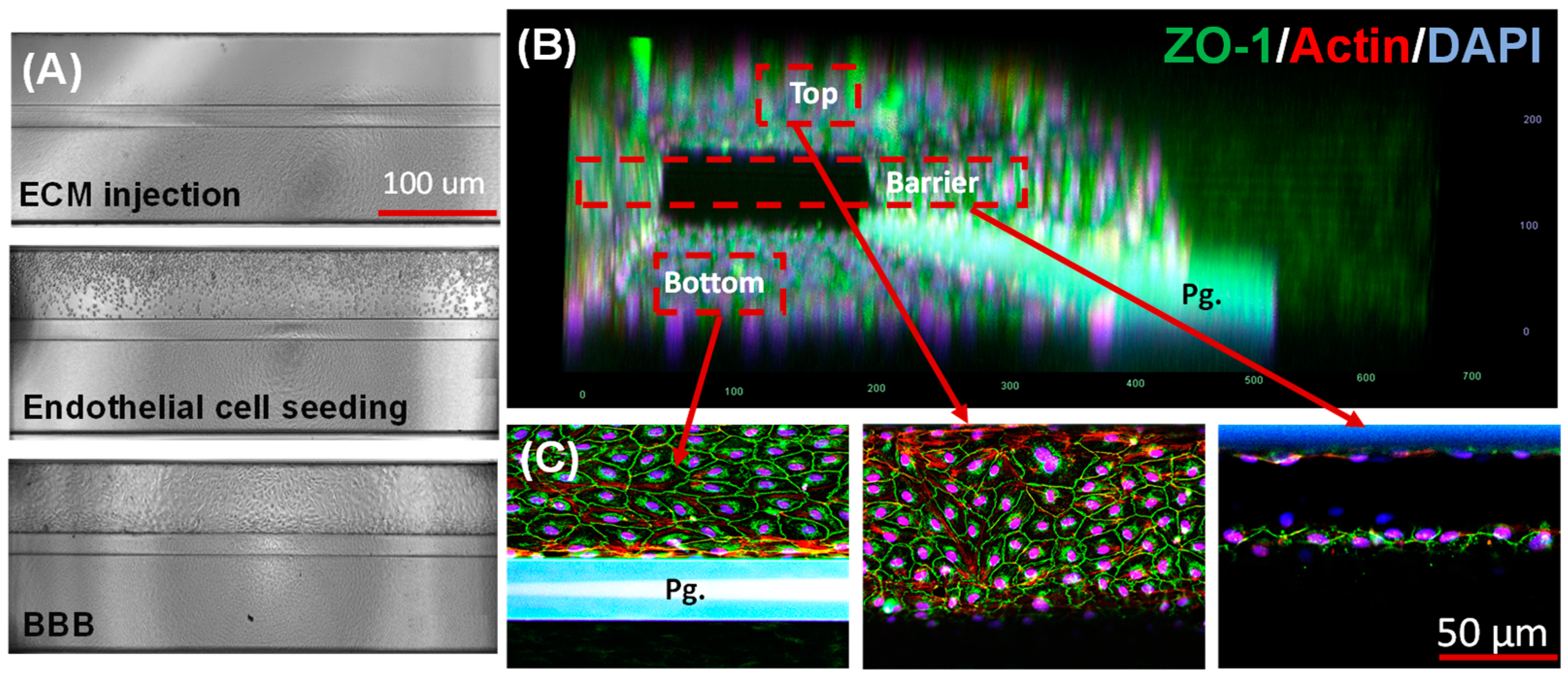
3.1. Microfluidic 3D BBB-on-a-Chip
3.2. Barrier Formation Characterization
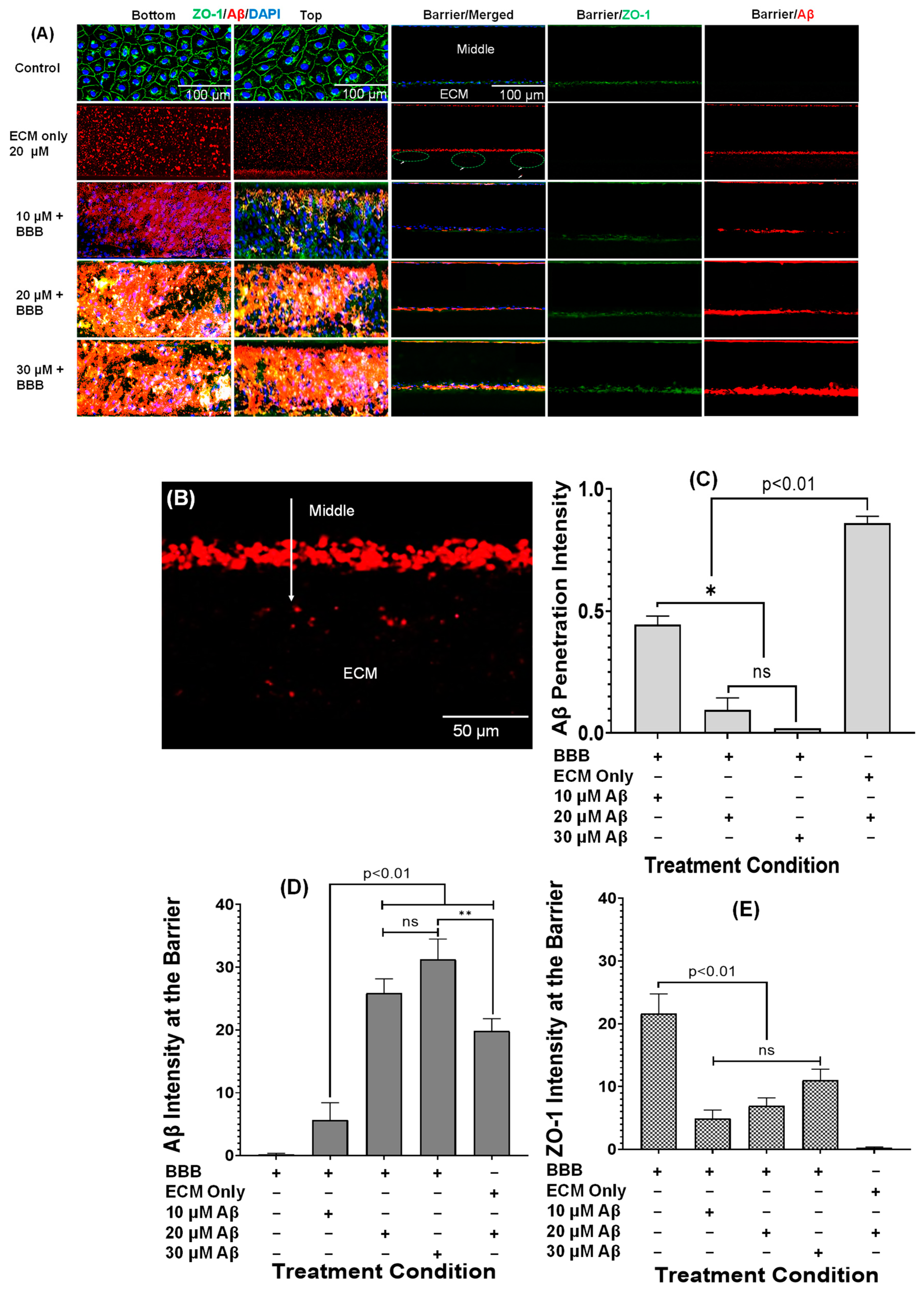
3.3. Aβ1–42 Treatment and Associated Tight Junction Behavior
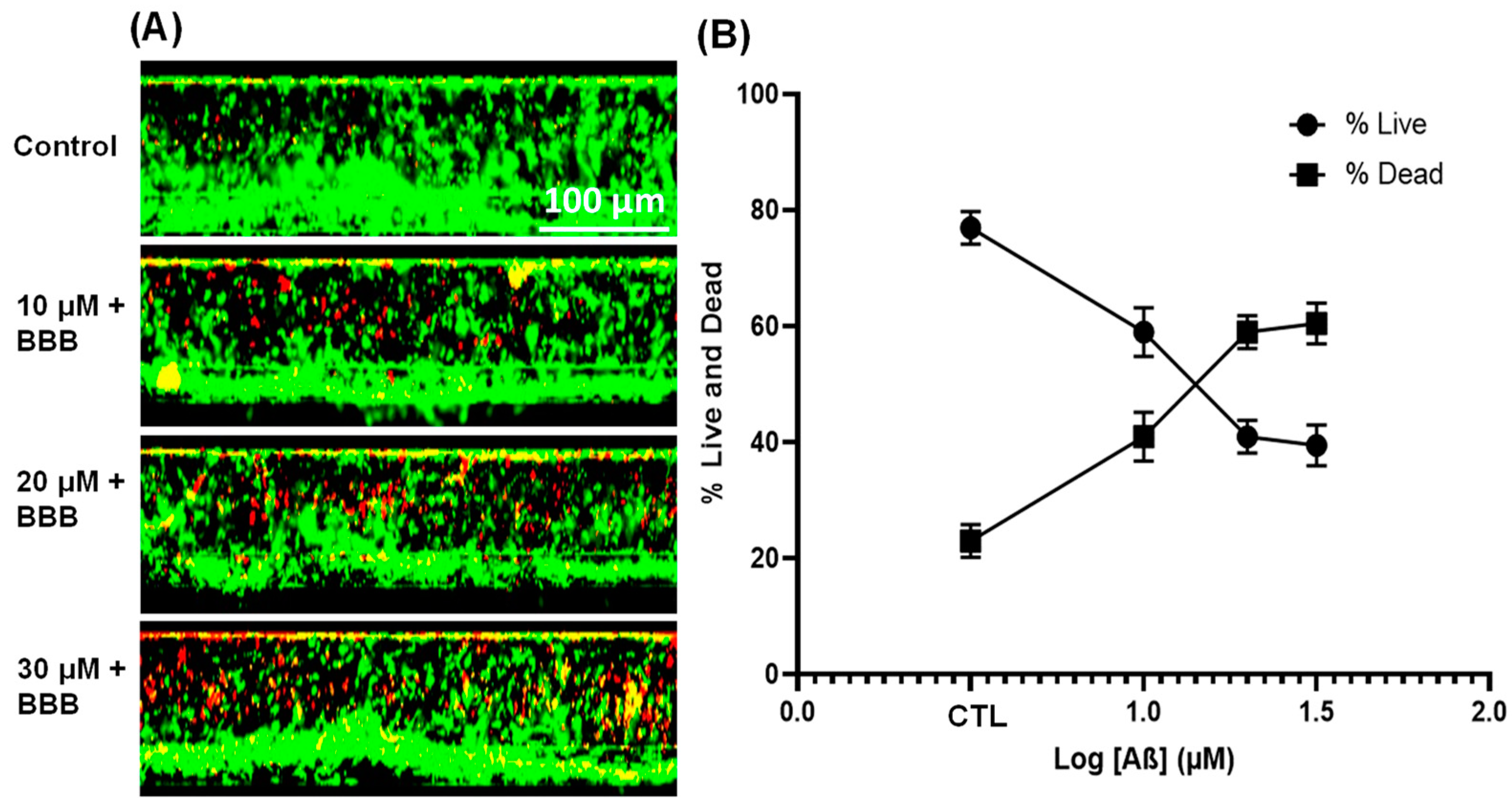
3.4. Effect of Aβ1–42 on Endothelial Cell Viability
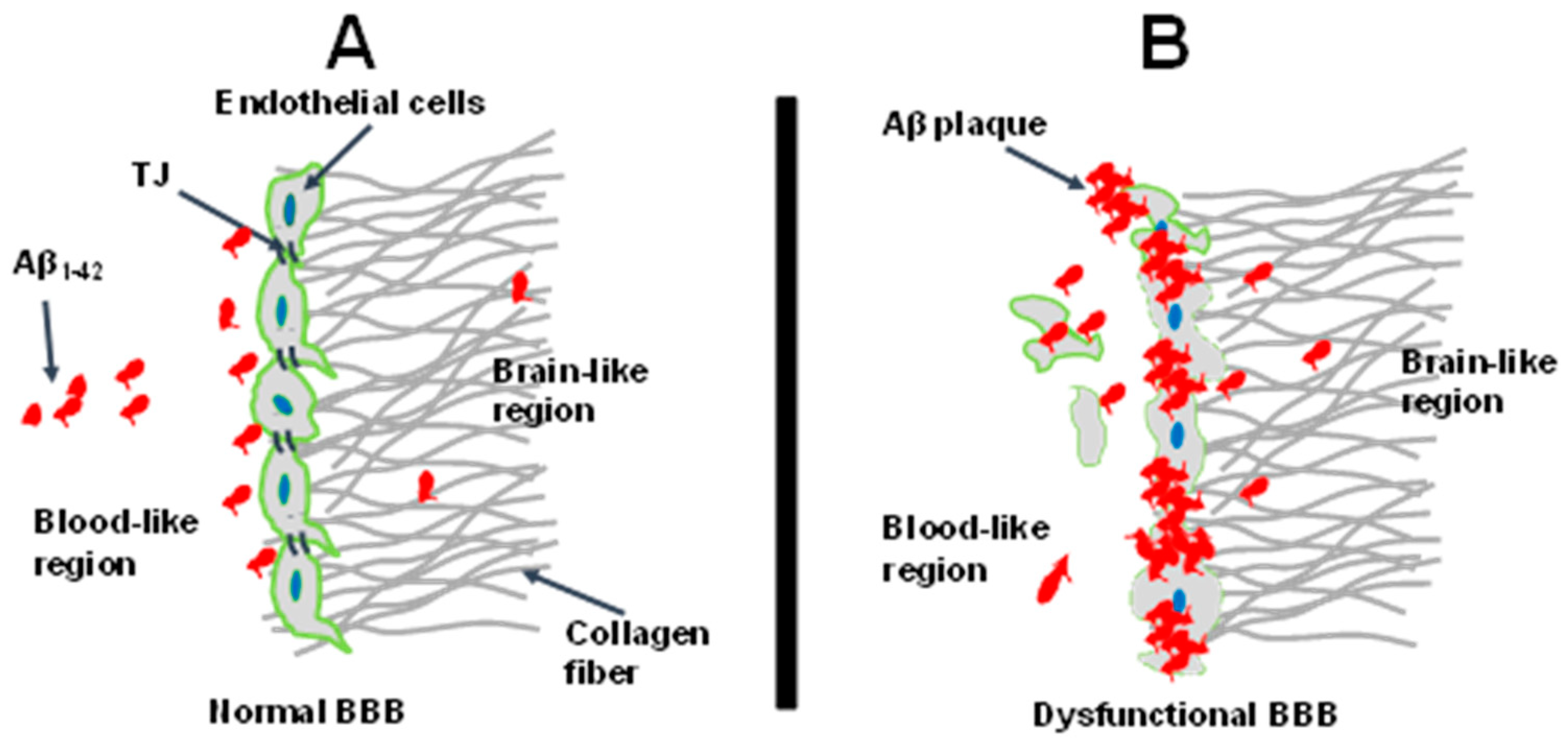
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobbing, J. The Blood-Brain Barrier. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1961, 3, 610–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Koo, Y.; Akwitti, C.; Russell, T.; Gay, E.; Laskowitz, D.T.; Yun, Y. Three-dimensional (3D) brain microphysiological system for organophosphates and neurochemical agent toxicity screening. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J.; Patabendige, A.A.K.; Dolman, D.E.M.; Yusof, S.R.; Begley, D.J. Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wevers, N.R.; de Vries, H.E. Morphogens and blood-brain barrier function in health and disease. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1090524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardridge, W.M. Drug transport across the blood-brain barrier. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1959–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P.; LeVine, H., 3rd. Alzheimer’s disease and the amyloid-β peptide. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2010, 19, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Cao, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Kalionis, B.; Tai, X.; Li, Y.; Xiantao, T. Aβ1–42 oligomer-induced leakage in an in vitro blood-brain barrier model is associated with up-regulation of RAGE and metalloproteinases, and down-regulation of tight junction scaffold proteins. J. Neurochem. 2015, 134, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlokovic, B.V.; Gottesman, R.F.; Bernstein, K.E.; Seshadri, S.; McKee, A.; Snyder, H.; Greenberg, S.M.; Yaffe, K.; Schaffer, C.B.; Yuan, C.; et al. Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia (VCID): A report from the 2018 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Workshop. Alzheimer's Dement. 2020, 16, 1714–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffi, A.; Greenberg, S.M. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: A systematic review. J. Clin. Neurol. 2011, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilodeau, P.A.; Dickson, J.R.; Kozberg, M.G. The Impact of Anti-Amyloid Immunotherapies on Stroke Care. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, W.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. The potential mechanisms of A beta-receptor for advanced glycation end-products interaction disrupting tight junctions of the blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Neurosci. 2014, 124, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, R.; Sterling, K.; Song, W. Amyloid β-based therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: Challenges, successes and future. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. MMP-Mediated Disruption of Claudin-5 in the Blood–Brain Barrier of Rat Brain After Cerebral Ischemia. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 762, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wevers, N.R.; de Vries, H.E. Modeling ischemic stroke in a triculture neurovascular unit on-a-chip. Fluids Barriers CNS 2021, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.J.; Hughes, C.C.W.; Revest, P.A.; Greenwood, J. Development and characterisation of a rat brain capillary endothelial culture: Towards an in vitro blood-brain barrier. J. Cell Sci. 1992, 103, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biegel, D.; Pachter, J.S. Growth of brain microvessel endothelial cells on collagen gels: Applications to the study of blood-brain barrier physiology and CNS inflammation. Vitr. Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1994, 30A, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yao, Y.; Tsirka, S.E.; Cao, Y. Cell-Culture Models of the Blood–Brain Barrier. Stroke 2014, 45, 2514–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, A.; Antfolk, M.; Brodin, B.; Tenje, M. In Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Models-An Overview of Established Models and New Microfluidic Approaches. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 101, 2727–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, P.; Nandakumar, K.; Wang, L.; Song, Y. Microfluidics-based systems in diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and biomimetic modeling. Micromachines 2020, 11, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakarpandian, B.; Shen, M.-C.; Nichols, J.B.; Mills, I.R.; Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz, M.; Aschner, M.; Pant, K. SyM-BBB: A microfluidic blood brain barrier model. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, Y.; Hawkins, B.T.; Yun, Y. Three-dimensional (3D) tetra-culture brain on chip platform for organophosphate toxicity screening. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, T.; Dirar, Q.; Li, Y.; Chiang, C.; Laskowitz, D.T.; Yun, Y. Cortical Spheroid on Perfusable Microvascular Network in a Microfluidic Device. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wevers, N.R.; Kasi, D.G.; Gray, T.; Wilschut, K.J.; Smith, B.; van Vught, R.; Shimizu, F.; Sano, Y.; Kanda, T.; Marsh, G.; et al. A perfused human blood-brain barrier on-a-chip for high-throughput assessment of barrier function and antibody transport. Fluids Barriers CNS 2018, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanini, F.; Kurek, D.; Previdi, S.; Nicolas, A.; Hendriks, D.; de Ruiter, S.; Meyer, M.; Cabrer, M.C.; Dinkelberg, R.; García, S.B.; et al. In vitro grafting of hepatic spheroids and organoids on a microfluidic vascular bed. Angiogenesis 2022, 25, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stine, W.B.; Dahlgren, K.N.; Krafft, G.A.; LaDu, M.J. In vitro characterization of conditions for amyloid-β peptide oligomerization and fibrillogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11612–11622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fa, M.; Orozco, I.J.; Francis, Y.I.; Saeed, F.; Gong, Y.; Arancio, O. Preparation of oligomeric β-amyloid1–42 and induction of synaptic plasticity impairment on hippocampal slices. J. Vis. Exp. 2010, 41, e1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soragni, C.; Vergroesen, T.; Hettema, N.; Rabussier, G.; Lanz, H.L.; Trietsch, S.J.; de Windt, L.J.; Ng, C.P. Quantify permeability using on-a-chip models in high-throughput applications. STAR Protoc. 2023, 4, 102051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, A.; Trietch, S.J. High throughput transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) measurements on perfused membrane-free epithelia. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 1676–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Koo, Y.; Russell, T.; Gay, E.; Li, Y.; Yun, Y. Three-dimensional brain-on-chip model using human iPSC-derived GABAergic neurons and astrocytes: Butyrylcholinesterase posttreatment for acute malathion exposure. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok, J.-S.; Byun, S.-H.; Park, B.-W.; Kang, Y.-H.; Lee, S.-L.; Rho, G.-J.; Hwang, S.-C.; Woo, D.K.; Lee, H.-J.; Byun, J.-H. The role of human umbilical vein endothelial cells in osteogenic differentiation of dental follicle-derived stem cells in in vitro co-cultures. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachetti, T.; Morbidelli, L. Endothelial cells in culture: A model for studying vascular functions. Pharmacol. Res. 2000, 42, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Leyte, D.J.; Domínguez-Pérez, M.; Mercado, I.; Villarreal-Molina, M.T.; Jacobo-Albavera, L. Use of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) as a Model to Study Cardiovascular Disease: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaterra, V.A.G.; Fiusa, M.M.L.; Hounkpe, B.W.; Chenou, F.; Tonasse, W.V.; da Costa, L.N.G.; Garcia-Weber, D.; Domingos, I.d.F.; de Lima, F.; Borba-Junior, I.T.; et al. Endothelial Barrier Integrity Is Disrupted In Vitro by Heme and by Serum From Sickle Cell Disease Patients. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 535147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosova, M.; Ridinger, D.; Marinovic, I.; Heigwer, J.; Zhang, C.; Levai, E.; Westhoff, J.H.; Schaefer, F.; Terjung, S.; Hildenbrand, G.; et al. An experimental workflow for studying barrier integrity, permeability, and tight junction composition and localization in a single endothelial cell monolayer: Proof of concept. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudio, L. Ultrastructural features of the blood-brain barrier in biopsy tissue from Alzheimer’s disease patients. Acta Neuropathol. 1996, 91, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco, S.; Skaper, S.D. Amyloid β-peptide1–42 alters tight junction protein distribution and expression in brain microvessel endothelial cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 401, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ni, N.; Lee, M.; Wei, W.; Andrikopoulos, N.; Kakinen, A.; Davis, T.P.; Song, Y.; Ding, F.; Leong, D.T.; et al. Endothelial leakiness elicited by amyloid protein aggregation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarafdar, A.; Wolska, N.; Krisp, C.; Schlüter, H.; Pula, G. The amyloid peptide β disrupts intercellular junctions and increases endothelial permeability in a NADPH oxidase 1-dependent manner. Redox Biol. 2022, 52, 102287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pober, J.S.; Sessa, W.C. Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Take, Y.; Chikai, Y.; Shimamori, K.; Kuragano, M.; Kurita, H.; Tokuraku, K. Amyloid β aggregation induces human brain microvascular endothelial cell death with abnormal actin organization. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 29, 101189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenaro, E.; Piacentino, G.; Constantin, G.; Brito, M. The blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 107, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.; Vasilevko, V.; Passos, G.F.; Ventura, C.; Quiring, D.; Cribbs, D.H. Therapeutic modulation of cerebral microhemorrhage in a mouse model of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Stroke 2011, 42, 3300–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartz, A.M.; Bauer, B.; Soldner, E.L.; Wolf, A.; Boy, S.; Backhaus, R.; Mihaljevic, I.; Bogdahn, U.; Klünemann, H.H.; Schuierer, G.; et al. Amyloid-β contributes to blood-brain barrier leakage in transgenic human amyloid precursor protein mice and in humans with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Stroke 2012, 43, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoke, F.; Mazzone, V.; Persichini, T.; Maraschi, A.; Harris, M.B.; Venema, R.C.; Colasanti, M.; Gliozzi, M.; Muscoli, C.; Bartoli, M.; et al. Amyloid β peptide-induced inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide production involves oxidative stress-mediated constitutive eNOS/HSP90 interaction and disruption of agonist-mediated Akt activation. J. Neuroinflammation 2015, 12, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulyatnikova, T.; Hayden, M.R. Why Are Perivascular Spaces Important? Medicina 2023, 59, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uzoechi, S.C.; Collins, B.E.; Badeaux, C.J.; Li, Y.; Kwak, S.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Laskowitz, D.T.; Lee, J.-M.; Yun, Y. Effects of Amyloid Beta (Aβ) Oligomers on Blood–Brain Barrier Using a 3D Microfluidic Vasculature-on-a-Chip Model. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093917
Uzoechi SC, Collins BE, Badeaux CJ, Li Y, Kwak SS, Kim DY, Laskowitz DT, Lee J-M, Yun Y. Effects of Amyloid Beta (Aβ) Oligomers on Blood–Brain Barrier Using a 3D Microfluidic Vasculature-on-a-Chip Model. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(9):3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093917
Chicago/Turabian StyleUzoechi, Samuel Chidiebere, Boyce Edwin Collins, Cody Joseph Badeaux, Yan Li, Sang Su Kwak, Doo Yeon Kim, Daniel Todd Laskowitz, Jin-Moo Lee, and Yeoheung Yun. 2024. "Effects of Amyloid Beta (Aβ) Oligomers on Blood–Brain Barrier Using a 3D Microfluidic Vasculature-on-a-Chip Model" Applied Sciences 14, no. 9: 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093917
APA StyleUzoechi, S. C., Collins, B. E., Badeaux, C. J., Li, Y., Kwak, S. S., Kim, D. Y., Laskowitz, D. T., Lee, J.-M., & Yun, Y. (2024). Effects of Amyloid Beta (Aβ) Oligomers on Blood–Brain Barrier Using a 3D Microfluidic Vasculature-on-a-Chip Model. Applied Sciences, 14(9), 3917. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093917






