Abstract
In this work, mesoporous silicas with two types of mesoporous structures were synthesized and functionalized with sulfonic acid groups: MCM-41-SO3H (honeycomb-like hexagonal structure) and MSU-2-SO3H (three-dimensional porous structure with wormhole pores). The synthesized materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, nitrogen adsorption–desorption, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, 29Si solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and elemental analysis. The obtained functionalized materials were evaluated as sorbents for strong cation-exchange solid-phase extraction (SPE) to determine their efficiency in the adsorption and desorption of tropane alkaloids (atropine and scopolamine). The loading solvents, loading volume, analyte concentration, and elution volume were studied, using 50 mg of both materials. Analyses were carried out by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. The synthesized MCM-41-SO3H material presented the highest recovery efficiency and has proven to be a promising sorbent for strong cation-exchange SPE of atropine and scopolamine in aqueous media. The high degree of functionalization of MCM-41-SO3H and the high accessibility of the sulfonic groups for the target analytes, due to the regularity and uniformity of their pores, maximize the contact between the alkaloids and the sorbent, favoring efficient adsorption.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the application of mesoporous silicas in sorbent-based extraction techniques for sample preparation has gained research interest [1]. This is due to the unique properties and remarkable advantages of these materials such as (i) large surface area and high pore volume, with uniform mesopores of 2–10 nm; (ii) well-defined pore network arrangement (e.g., 2D hexagonal, 3D cubic, wormhole, etc.); (iii) tunability of the morphology and size of the particles; and (iv) good thermal and chemical stability. Furthermore, mesoporous silicas can be easily functionalized with organic ligands that allow for tuning the chemical properties of the surface and expanding the range of their application for the extraction and purification of various analytes by solid-phase extraction (SPE) [2]. The choice of the type of sorbent packed in cartridges for SPE is crucial, as it regulates aspects such as capacity and selectivity, depending on the interaction of the sorbent with the functional groups of the analyte (e.g., hydrophilic, hydrophobic, ion-exchange, or mixed-mode) [3]. In this sense, the selection of the appropriate mesoporous silica sorbent is important to optimize the extraction performance of the SPE process since it determines the specific surface area, the accessibility of the active sites, and the interaction with the target molecules, allowing better recovery and purification of the analytes in a complex matrix [4].
Although SBA-15 (Santa Barbara Amorphous type material-15) has been one of the most studied mesoporous silicas as sorbent for SPE [5,6,7], other mesoporous silicas also show great potential. For example, MCM-41 (Mobil Composition of Matter) and MSU-X (Michigan State University material) are widely recognized for their adsorptive properties. MCM-41, with its small-pore hexagonal structure, exhibits a remarkable order that facilitates the adsorption of a variety of analytes, including metals [8,9,10], pesticides [11,12], and pharmaceuticals [13,14,15] in different samples. On the other hand, MSU-X lacks a regular packing order but exhibits a three-dimensional porous structure with wormhole-like pores and uniform diameters, which gives it versatility in the adsorption of substances in complex matrices, including applications in the analysis of pesticides [16,17] or metals [18], among others. Nevertheless, there is still a requirement to investigate the potential of new sorbents for SPE with diverse core structures and functionalities, depending on the specific use for which they are intended, to promote the retention of different analytes and achieve high enrichment and good recovery. These factors are mandatory to reduce detection limits to a level compatible with the detection technique [19]. Furthermore, thanks to these new sorbents, miniaturized sample preparation procedures can be developed, using smaller quantities of sorbents, solvents, and reagents, to comply with the precepts of Green Analytical Chemistry (GAC) [20,21]. This is of particular importance in food safety, where sample preparation is a critical and indispensable step to determine the presence of contaminants at low concentrations in complex food matrices [2,22].
Nowadays, there is great interest in the development of analytical methodologies that facilitate the monitoring of natural toxins in food products, to comply with current regulations and thus contribute to food safety [23]. For example, the recently published Commission Regulation (EU) 2023/915 establishes the need to control tropane alkaloids (TAs), setting limits for atropine and scopolamine in processed cereal-based infant foods, unprocessed sorghum, millet, maize, buckwheat as well as for herbal infusions, ranging from 1 to 50 µg/kg as the sum of atropine and scopolamine [24]. TAs are secondary metabolites naturally produced by different plants, mainly of the Solanaceae family. These alkaloids are known for their toxicity, which is due to their ability to bind to muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the central and autonomic nervous system, causing symptoms such as dry mucous membranes, ataxia, and hallucinations, and in high doses can even be lethal [25]. Food contamination with TAs has become an issue of concern due to the increase in cases of food poisoning. The main contamination pathways are often related to the occurrence of TAs-producing plants in fields for crop production that can lead to contamination of the harvested foods, being seeds of Datura stramonium as the common source of contamination. Given the wide range of products affected, it is crucial to implement stringent control and regulatory measures [26]. However, the detection of these alkaloids in food presents significant challenges, since they are often found in very low concentrations. In addition, the identification and quantification of these substances can be complicated by interferences arising from the complexity of food samples. In this context, proper sample preparation becomes an essential step for the accurate determination of alkaloids in food matrices [27].
To date, different commercial sorbents have been widely used for SPE of TAs in food analysis. In general, mixed-mode polymeric sorbents with anionic functional groups have been used to extract TAs in acidic solutions, as is the case of the commercial Oasis MCX® and Strata-XC® cartridges containing a chemically modified polymeric sorbent with polar and strong cation-exchange (SCX) groups [28,29,30]. Nevertheless, the development of new materials for their application as sorbents in SPE has become essential to obtain materials with greater adsorption capacity, which allows the development of miniaturized protocols that minimize the generation of waste in this sample preparation stage. In this context, mesoporous silicas have gained increasing interest as a viable alternative to commercial sorbents [27]. For example, González-Gómez et al. have evaluated sulfonic acid-functionalized SBA-15 mesoporous silicas (150 mg) as SPE sorbents for the analysis of TAs in gluten-free grains and flours and demonstrated excellent extraction performance compared to an analogous commercial material (MFE-PAK® SCX) [30]. In addition, other mesoporous silicas such as HMS (hexagonal mesoporous silica) have been studied for atropine and scopolamine determination in thyme, basil, and coriander samples, using 75 mg of material in SPE showing recoveries close to 100% [31]. However, it is interesting to evaluate other mesoporous silicas not explored to date, presenting different pore structures and other textural characteristics in the evolution to green miniaturized sorbent-based sample preparation protocols.
In this sense, this work has aimed to evaluate the adsorption of atropine and scopolamine in two mesoporous materials with different pore structures. Through this evaluation, we seek to understand the potential of these materials as sorbents in SPE and how the specific characteristics of the pore structure affect the adsorption capacity. Additionally, we aim to develop more efficient sorbents that improve the accuracy and sensitivity in detecting these compounds in various matrices, thus contributing to significant advances in the control of natural toxins in foods.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Reagents, and Standard Solutions
The atropine reference standard (≥99%) and scopolamine hydrobromide (≥98%) were acquired from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). To prepare the individual standard solutions (1000 mg/L), the precise amount of solid substance was weighed and dissolved in methanol (MeOH) of HPLC−MS quality purchased from Scharlab (Barcelona, Spain). The solution was then stored in the dark at −20 °C. Working solutions at the desired concentrations were prepared in MeOH and stored in the dark at −20 °C. Ultra-pure water (resistance 18.2 MΩ.cm) was purified using the Millipore Milli-Q-System (Billerica, MA, USA), ethanol (EtOH) absolute HPLC grade, and 32% (v/v) ammonia solution was acquired from Scharlab (Barcelona, Spain). Formic acid (FA) and acetonitrile (ACN) LC/MS grade were purchased from Fisher Chemical (Loughborough, UK). For the SPE process, empty 3 mL cartridges, polyethylene frits with a pore size of 0.20 µm, and nylon membrane filters with a pore size of 0.45 µm provided by Scharlab (Barcelona, Spain) were used.
Tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) 98% (MW = 208.33, d = 0.934 g/mL), Tergitol® NP-9 (MW = 616.82), sodium silicate SiO2·NaOH (MW = 242.23, d = 1.390 kg/m3), and cetyltrimethyammonium bromide (CTAB) (MW = 364.46) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Schnelldorf, Germany), while sodium fluoride 99% (MW = 41.99) was purchased from Fluka (Buchs, Switzerland). Sulfuric acid 96% (MW = 98.08, d = 1.840 kg/m3) was acquired from Panreac (Barcelona, Spain). Hydrochloric acid 37% (MW = 36.46, d = 1.2 g/mL) and hydrogen peroxide 30% (MW = 34.01, d = 1.110 g/cm3) were obtained from Scharlab (Barcelona, Spain). (3-Mercaptopropyl) triethoxysilane 94% (MPTES) (MW = 196.34, d = 1.057 g/mL) was purchased from Alfa Aesar (Karlsruhe, Germany).
2.2. Synthesis and Functionalization of the Mesoporous Silicas
The synthesis of the MSU-2 was carried out following the previous work of Pérez-Quintanilla et al. [32]. A milky suspension was prepared by adding TEOS to a 0.08 M solution of Tergitol® NP-9 in Milli-Q water. This suspension was then aged without stirring for 20 h, and then a 0.24 M sodium fluoride solution was added dropwise with stirring, aiming to obtain a NaF/TEOS molar ratio of 0.025/1. The resulting solution was placed in a shaking bath at 55 °C for 48 h. Finally, the product obtained was filtered, washed with Milli-Q water, dried, and calcined in air at 600 °C for 12 h.
The synthesis of the MCM-41 was carried out following the previous work of Pérez-Quintanilla et al. [33]. First, sodium silicate was prepared, with a composition of 14% NaOH, 27% SiO2, and 59% water. Then, 4.20 g of 98% H2SO4 and 140 mL of water were added dropwise to 65.45 g of the sodium silicate solution. The solution was kept stirred at room temperature for 30 min. A total of 58.66 g of CTAB was dissolved in 176 mL of water and added to the mixture. After this, the resulting gel was mixed with 70 mL of water, keeping the process stirred for a period of 30 min at room temperature. The formed gel was transferred to a Teflon-coated autoclave and heated at 121 °C for 144 h. Subsequently, the resulting solid was separated by vacuum filtration and subjected to a drying process at 100 °C for 8 h. Finally, the surfactant was removed by a calcination process in air at 530 °C for 6 h.
MSU-2 and MCM-41 were subjected to further functionalization. For this, 2.5 g of bare mesoporous silica was suspended in 250 mL of 0.1 M HCl, and 1.0 g of MPTES was added. The mixture was stirred for 7 h at room temperature and transferred to a reactor for 24 h at 100 °C. The solid obtained was filtered, washed with Milli-Q water, and allowed to dry at 50 °C overnight. The recovered materials (MSU-2-SH or MCM-41-SH) were mixed with 300 mL of 2M HCl and then 11.6 g H2O2 (30%) was added to oxidize the thiols to sulfonic acid. After 5 min of stirring at room temperature, the mixture was heated in a reactor for 6 h at 100 °C. The resulting materials designated as MSU-2-SO3H and MCM-41-SO3H, were filtered and washed with Milli-Q water.
2.3. Characterization of Mesoporous Silicas
The synthesized materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) to evaluate the structure of the materials. Low-angle powder XRD patterns of the silicas were performed to determine if the materials showed the typical long mesoscopic ordered structure. XRD patterns were obtained on a Philips Diffractometer model PW3040/00 X’Pert MPD/MRD (Philips, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) at 45 kV and 40 mA, using Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å). The samples were treated in power and placed in a sample holder. The sample and detector were rotated and the XRD patterns were collected from 0 to 10°. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images were performed on JEOL JEM 1010 (Tokyo, Japan) with an accelerating voltage of 80 kV. The samples were dispersed in acetone and deposited on carbon-supported grids. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images were scanned by a Nova Nano SEM230 (FEG-SEM) (Denton, TX, USA) with an energy-dispersive spectrometry system (EDS). The metallizer used was Leica ACE600 (Wetzlar, Germany), using a gold target and depositing a layer of less than 5 nm. Nitrogen gas adsorption–desorption isotherms were performed with a Micromeritics ASAP 2020 (Norcross, GA, USA) analyzer. The isotherms were measured at −196 °C with an interval of relative pressures (P/P0) from 1 × 10−4 to 0.99. Previously, samples were degassed at 90 °C under vacuum for 10 h. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method was utilized to obtain the specific surface area (SBET), and the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) model was used to calculate the pore volume and pore size distribution by the desorption branches of isotherms. The total pore volume (Vt) was estimated from the desorbed amount at a relative pressure P/P0 of 0.97. Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra were recorded with a Spotlight 200i, Perkin Elmer (Waltham, MA, USA) spectrometer in the region 4000–400 cm−1 using KBr pellets with 16 scans and a resolution of 4 cm−1. 29Si solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (29Si-PDA-MAS-NMR) spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance III-WB Spectrometer 400 MHz, operating at 79.4 MHz to 29Si nucleus, Half-pi pulse: 6 μs, number of accumulations: 1000, rotation speed: 12,000 Hz, time between pulses: 60 s. Finally, elemental analysis (% S) was performed using a microanalyzer Flash 2000 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (Hampton, NY, USA).
2.4. Evaluation of Mesoporous Silica as Sorbents in Solid-Phase Extraction
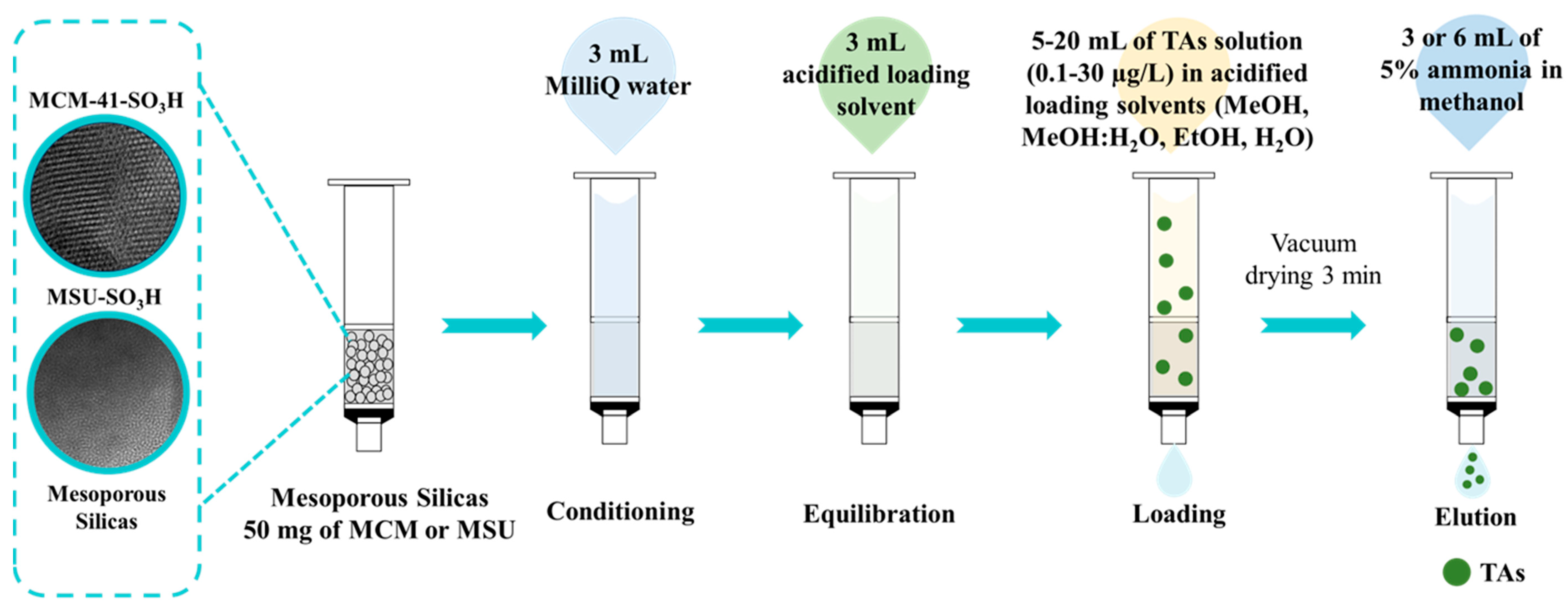
The functionalized mesoporous silicas prepared and characterized were tested as sorbents in SPE for TAs extraction before ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-TQ-MS/MS) analysis. The SPE procedure was carried out by packing polypropylene cartridges with 50 mg of the prepared sorbents. Both ends were sealed with polyethylene frits. In addition, a nylon filter membrane (0.45 µm) was incorporated at the bottom of the bed to prevent material loss during the process. First, the cartridges were conditioned with 3 mL of Milli-Q water, followed by equilibration with 3 mL of the same solvent used for the loading step. They were then loaded with the standard solution at 0.8 mL/min. The cartridges were then vacuum dried using a Supelco Visiprep SPE 12-port vacuum manifold (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) connected to a vacuum pump at 7.6 psi for 3 min. Elution of the analytes retained on the cartridge was performed with 5% ammonia solution in MeOH, followed by another vacuum drying process for 3 min. Finally, the eluate was evaporated to dryness using a vacuum/nitrogen manifold system (Schlenk line) at ambient temperature and reconstituted in 0.3 mL of MeOH for subsequent injection into the UHPLC-TQ-MS/MS. Several loading solvents, including EtOH, MeOH, H2O, and a mixture of MeOH:H2O (50:50, v/v), all acidified with 1% HCl (pH 1) and analyte concentrations, in the range of 0.1 to 30 µg/L, were studied. In addition, sample loading volumes from 5 to 20 mL and analyte elution volumes from 3 to 6 mL, were studied (Figure 1). Studies were performed in triplicate, and the results were expressed as percentage recovery of atropine and scopolamine. The recovery was calculated by comparing the results obtained by UHPLC-MS/MS for a loading solvent spiked with the target analytes under the study conditions prior to the SPE with the result obtained by a loading solvent spiked with the analytes after the SPE (blank control).
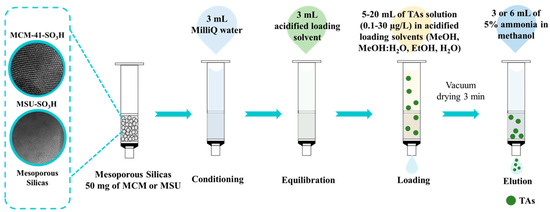
Figure 1.
Schematic of the evaluation of mesoporous silicas as sorbents in the solid-phase extraction of tropane alkaloids (TAs).
2.5. UHPLC-TQ-MS/MS Analysis
Liquid chromatographic separations were carried out using an Elute UHPLC system (Bruker Daltonics Inc., Billerica, MA, USA), consisting of an Elute UHPLC HPG 1300 pump with two pairs of individually controlled linear drive pump heads coupled in series, an Elute autosampler maintained at 10 °C, and an Elute CSV column oven preheater equipped with an Intensity Solo 2 C18 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm, 2.0 μm, Bruker Daltonics Inc., Billerica, MA, USA) maintained at room temperature. Optimum separation conditions were achieved using a solvent mixture as a mobile phase consisting of 0.1% FA in water (solvent A) and 0.1% FA in ACN (solvent B) in a gradient elution mode as follows: 0.00 min 95% solvent A; 0.00–3.00 min 70% solvent A; 3.00–4.00 min 95% solvent A; 4.00–5.00 min 95% solvent A at a flow rate of 0.450 mL/min, and an injection volume of 2 µL (partial injection), resulting in an analysis time of 5 min, including equilibration time.
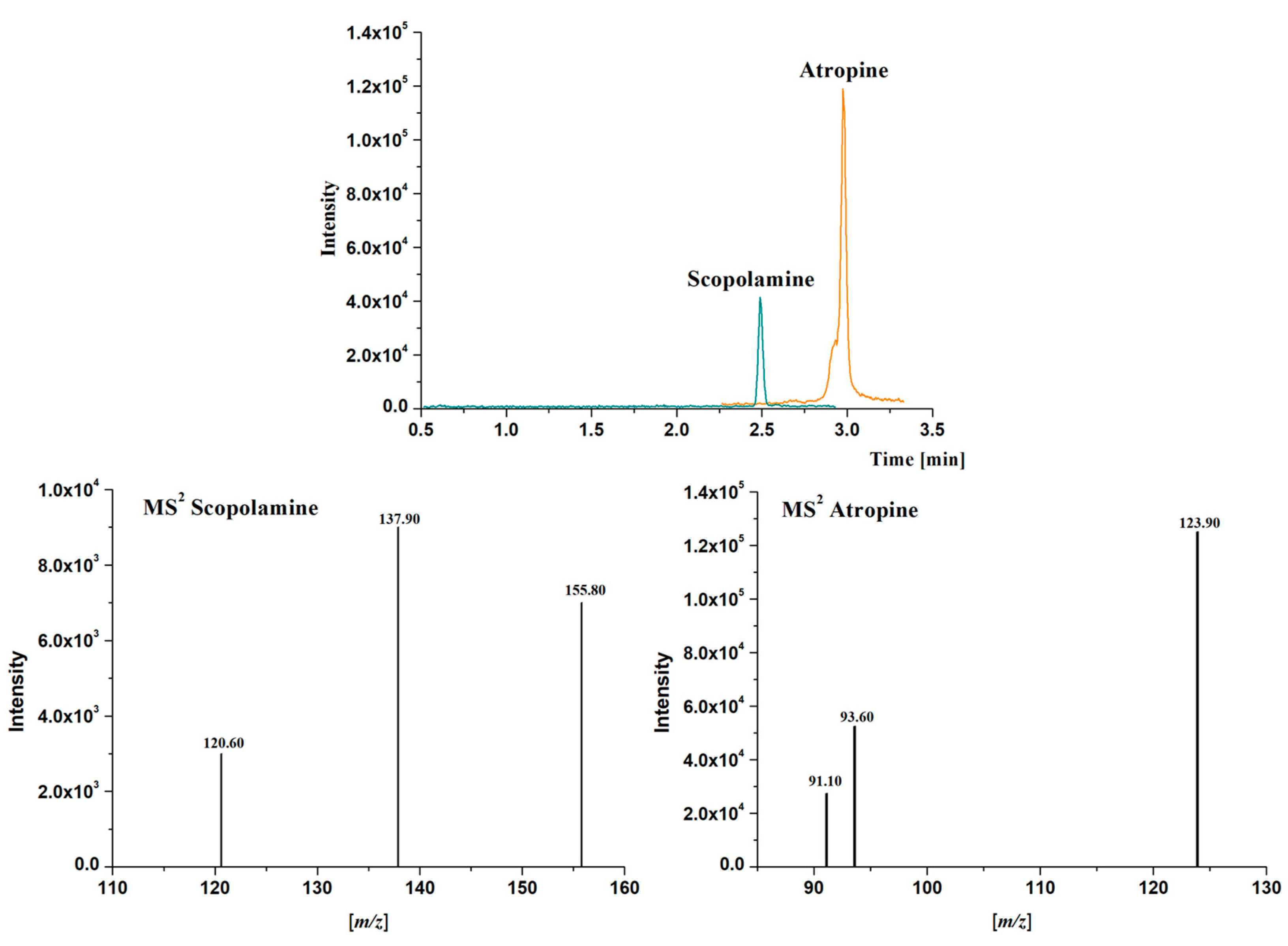
Detection was carried out using a Bruker EvoQ LC-TQ Elite triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonics Inc., Billerica, MA, USA) equipped with a heated electrospray ionization interface (HESI). The instrument was operated in positive ionization mode. The mass spectrum is registered with multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) of three transitions per compound (Q1 resolution 2.5; Q3 resolution 2.5; scan time 93.80 ms). Optimization of MRM collision-induced dissociation (CID) energies was performed by direct infusion of individual standard solutions (1 μg/mL) at a flow rate of 5 μL/min. HESI source parameters were optimized with multiple runs of UHPLC-MS/MS using gradient and flow rate-optimized conditions. The optimum HESI source parameters were: N2 as drying and nebulizer gas, argon as collision gas, collision pressure at 2.0 mTorr, spray voltage positive at 1535 V, spray amp positive 100.0 µA, cone pressure 20.0 psi, probe pressure 25.0 PSI, nebulizer pressure 60 psi, cone temperature 280 °C, and probe temperature 225 °C. The MS parameters for each analyte are listed in Table 1. Therefore, the most intense production of each analyte in its MS2 spectrum was used for quantification, while other less intense product ions (at least one of them was mandatory) were controlled for confirmation purposes (Table 1, Figure 2). The software tqControl 2.2.0.1 (Bruker Daltonics, Billerica MA, USA) was used for data processing. Linear ranges were established, from 0.007 to 100 µg/L for atropine and from 0.14 to 100 µg/L for scopolamine. LODs and LOQs values ranged from 0.002 to 0.007 µg/L for atropine and from 0.04 to 0.14 µg/L for scopolamine.

Table 1.
Retention time and optimal parameters to mass spectrometry detection by MRM mode for the analysis of atropine and scopolamine using the UHPLC-TQ-MS/MS method developed in this work.
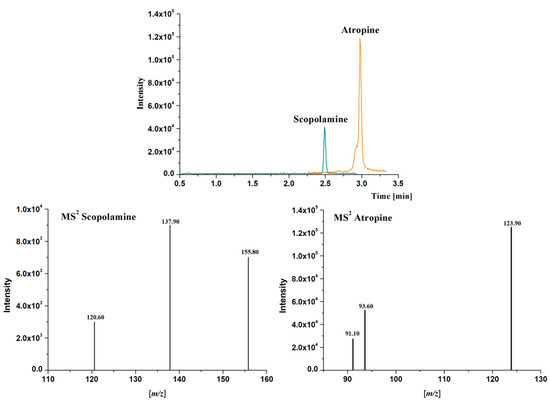
Figure 2.
Extracted Ion Chromatograms (EIC) of the most intense production and Mass Spectra (MS2) obtained for atropine (m/z 290.5 > 123.9) and scopolamine (m/z 303.5 > 137.9) in a standard solution containing 1 μg/L of each analyte in methanol using the chromatographic method described in Section 2.5.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis of the optimization process was performed with IBM SPSS Statistics version 29.0.2.0 (20) software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA), using Student’s t-test for comparison of two means or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s post hoc multiple range test (significant differences at p ≤ 0.05) for comparison of more than two means, and different letters were used to denote them. All experiments were performed in triplicate, and the results are presented as the means of the values ± standard deviation (SD) obtained in this investigation.
3. Results
Two mesoporous silicas with different structural characteristics such as MCM-41 and MSU-2 were evaluated for adsorption studies due to their well-defined properties and their ability to accommodate a variety of analytes. While MCM-41 presents an ordered, cylindrical pore structure, MSU-2 features a highly interconnected three-dimensional (3D) wormhole-like framework. These structural differences allow us to evaluate how the configuration of the material influences the adsorption process of the target analytes.
3.1. Characterization of Mesoporous Silica
3.1.1. X-Ray Diffraction
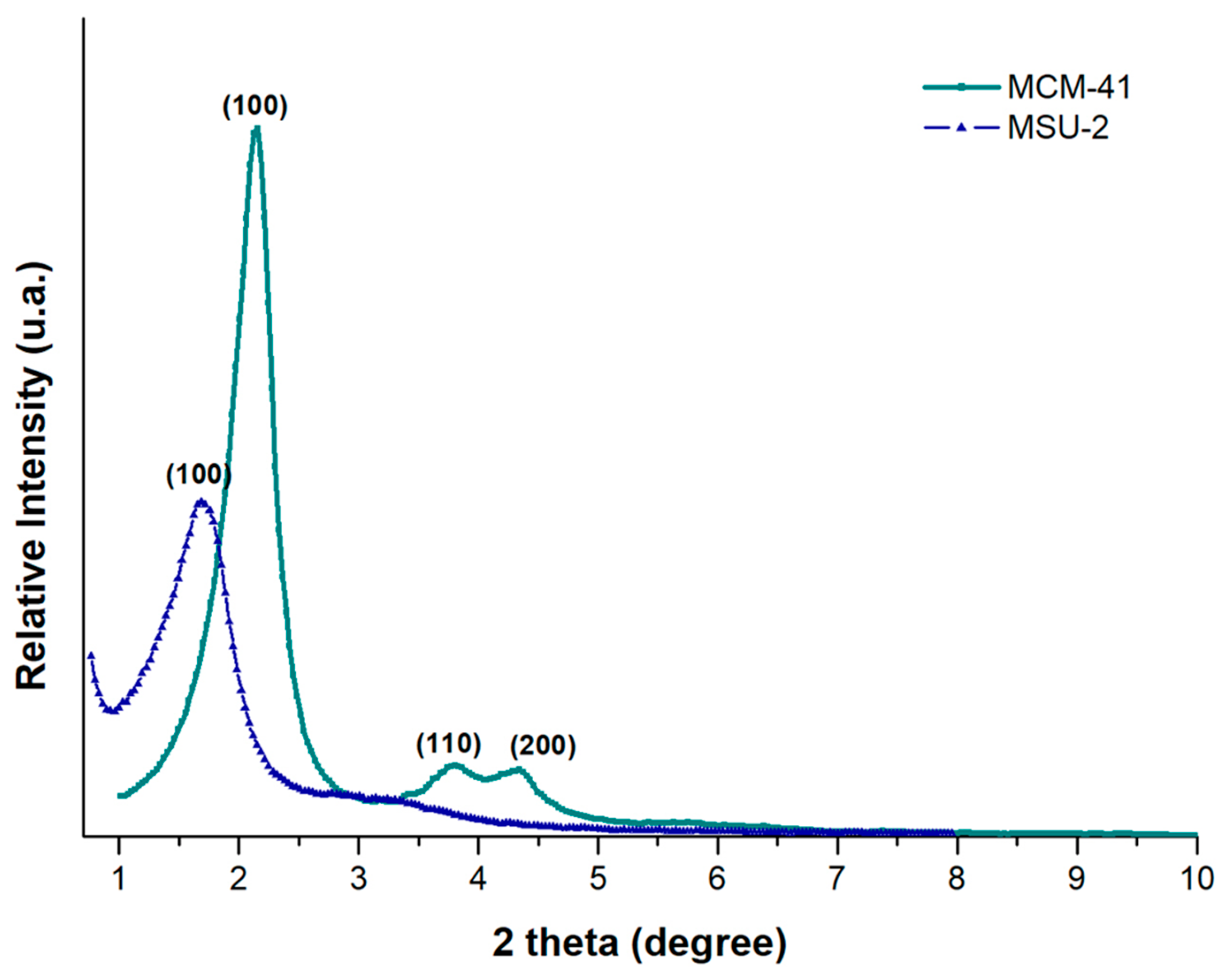
Figure 3 shows the XRD patterns for MCM-41 and MSU-2. The XRD pattern of MCM-41 shows a very sharp diffraction peak at 2.17° (100), accompanied by two additional peaks of lower intensity (110 and 200) at 3.76° and 4.36°, corresponding to d-spacing values of 40.63, 23.46, and 20.26 Å, respectively. A unit cell parameter, a0, of 46.92 Å was obtained. The X-ray diffractogram of MSU-2 (Figure 3) shows a single, much broader peak, indicating that this material exhibits a lower mesoscopic order compared to MCM-41, with a d-spacing value of 60.25 Å, and a unit cell parameter, a0, of 69.57 Å.
where k is a constant (k = 0.9), λ is the wavelength of X-rays (1.5418 Å), β is the full width at half-maxima of the diffraction peak line (in radians), and θ is the diffraction angle yielding values of 380 and 219 Å for MCM-41 and MSU-2, respectively. The obtained values of the crystal sizes of these materials are related to the sharpness and position of the diffractogram peaks. Consequently, the larger the crystals of a particular component, the sharper the peaks on the XRD pattern for each crystal plane. Additionally, the narrower X-ray diffraction peak of MCM-41 compared to the diffraction peak of MSU-2 is related not only to the crystal size but also to a more ordered pore distribution in MCM-41 than in MSU-2, as evidenced by the TEM images indicated in Section 3.1.2 [34,35].
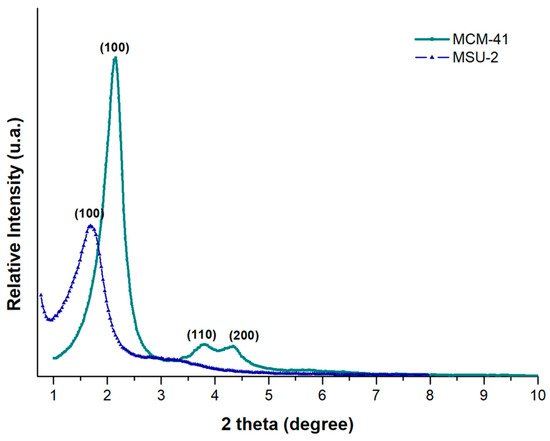
Figure 3.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of MCM-41 (green color) and MSU-2 (blue color).
3.1.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy Measurements
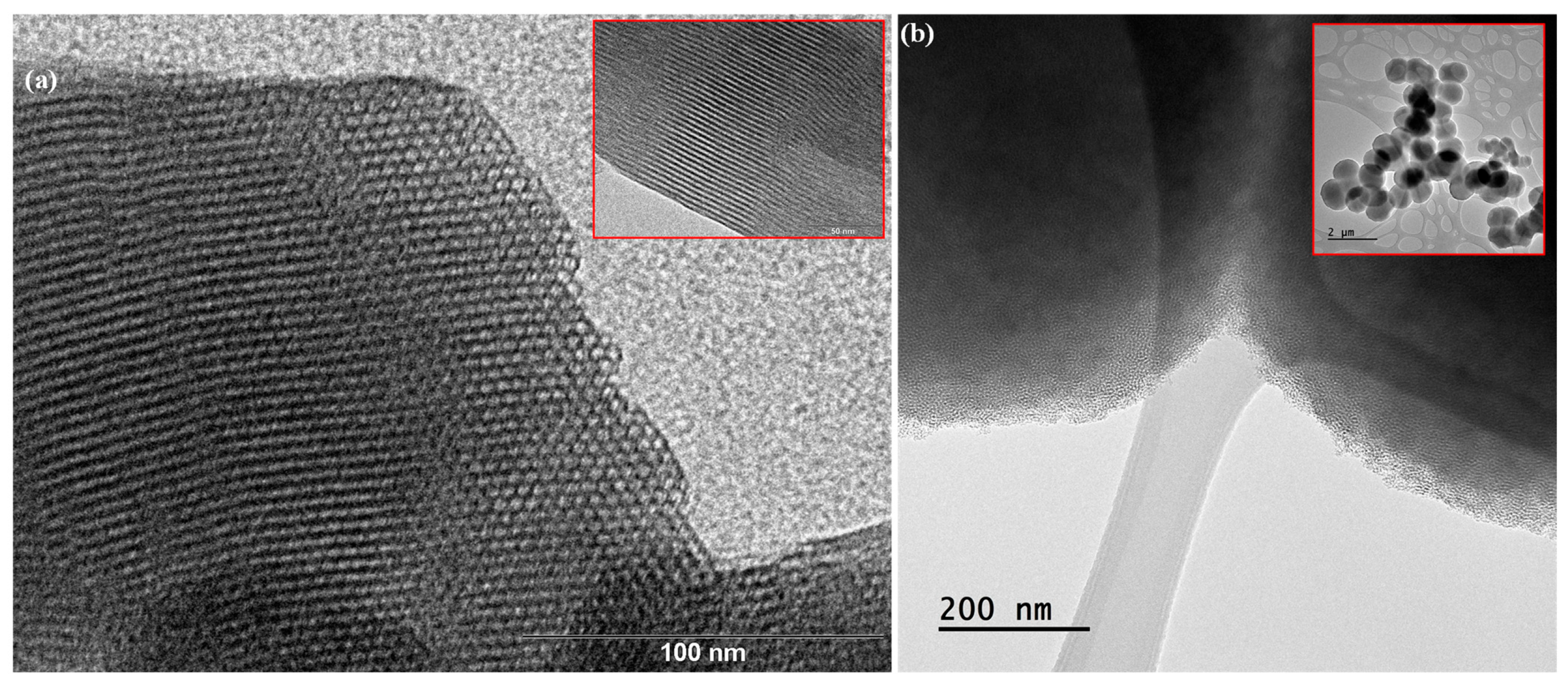
The type and pore distribution of the materials were evaluated by TEM, as illustrated in Figure 4. TEM micrographs of the MCM-41 sample exhibit a well-defined and ordered porous structure, showing a parallel arrangement of cylindrical pore channels in the [100] direction (Figure 4a) and a hexagonal honeycomb-like arrangement along the [001] axis (Figure 4a inset) [34]. On the other hand, the less ordered structure of the MSU-2 silica, with a wormhole-like pattern, is illustrated by the TEM micrographs in Figure 4b. These micrographs show that the silica particle contains a large number of channels that are regular in diameter, although they lack long-range packing order. Furthermore, TEM confirms that the entire material is composed of this porous structure, with no non-porous components present, and reveals the spherical shape of the particles [35].
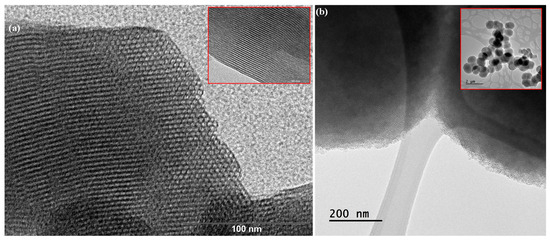
Figure 4.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of (a) MCM-41 and (b) MSU-2 material. In the case of MCM-41, TEM images show a distribution of parallel pores along the [100] axis (see inset image) and a hexagonal pore distribution in a honeycomb pattern along the [001]. The scale bars correspond to 100 nm and 50 nm, in the case of MSU-2, the scale bars correspond to 200 nm and 2 µm.
3.1.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy Measurements
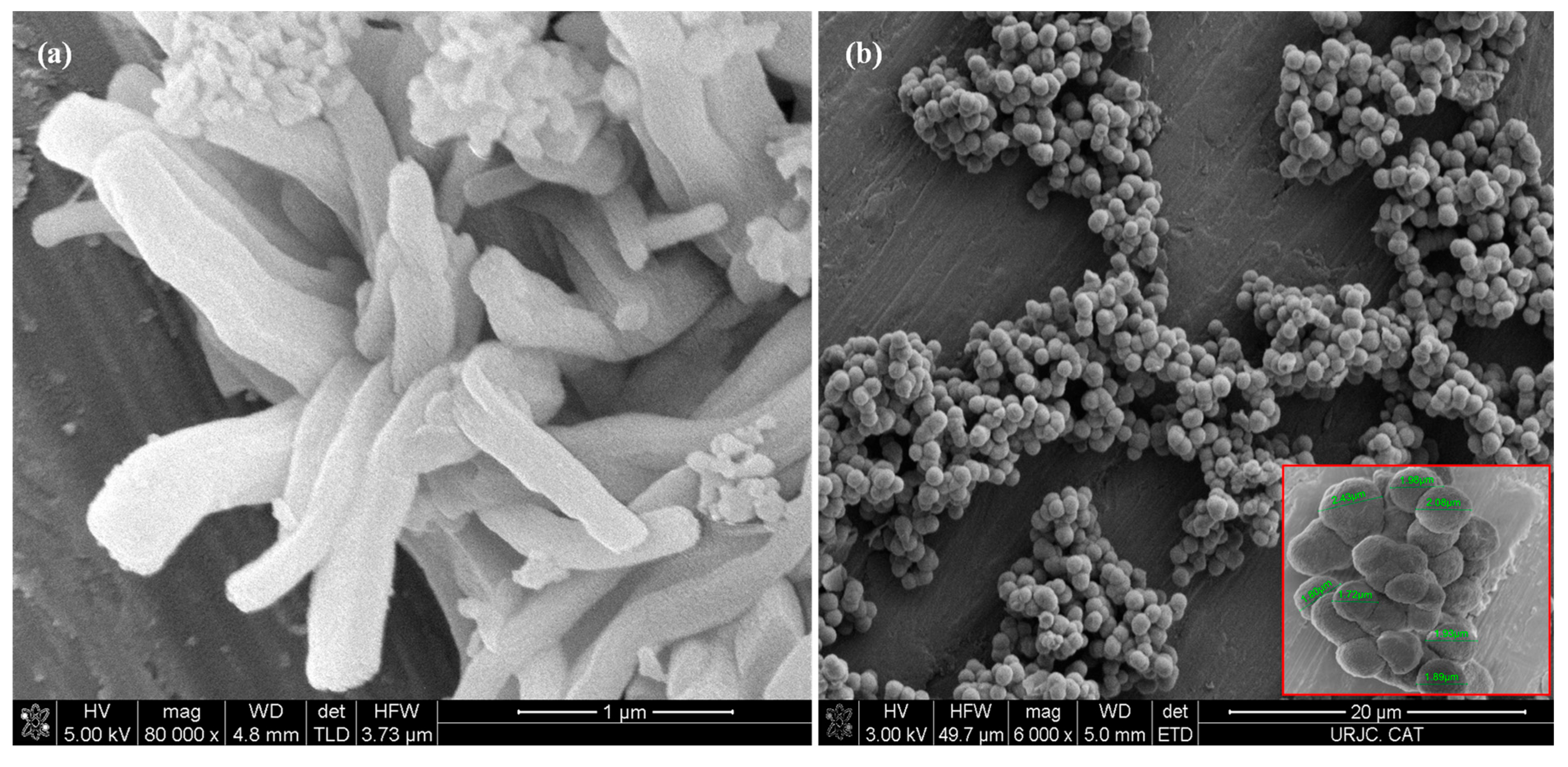
SEM micrographs of the mesoporous silica MCM-41 (Figure 5a) reveal agglomerates of curved prismatic rods (with particle sizes of approximately 2 µm in length and 0.5 µm in width), which form large particles of disordered shapes due to their interlocking [36]. The SEM images of MSU-2 show spherical particles with a very homogeneous size distribution around 2 µm with a sponge-like appearance (Figure 5b) [35].
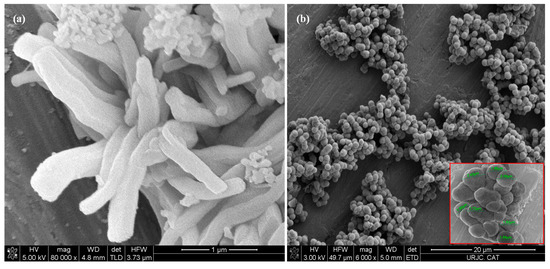
Figure 5.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) micrographs of (a) MCM-41 and (b) MSU-2 material. In the case of the MSU-2 two different magnifications are shown, the scale bars correspond to 20 µm and 4 µm.
3.1.4. Nitrogen Adsorption–Desorption Isotherms
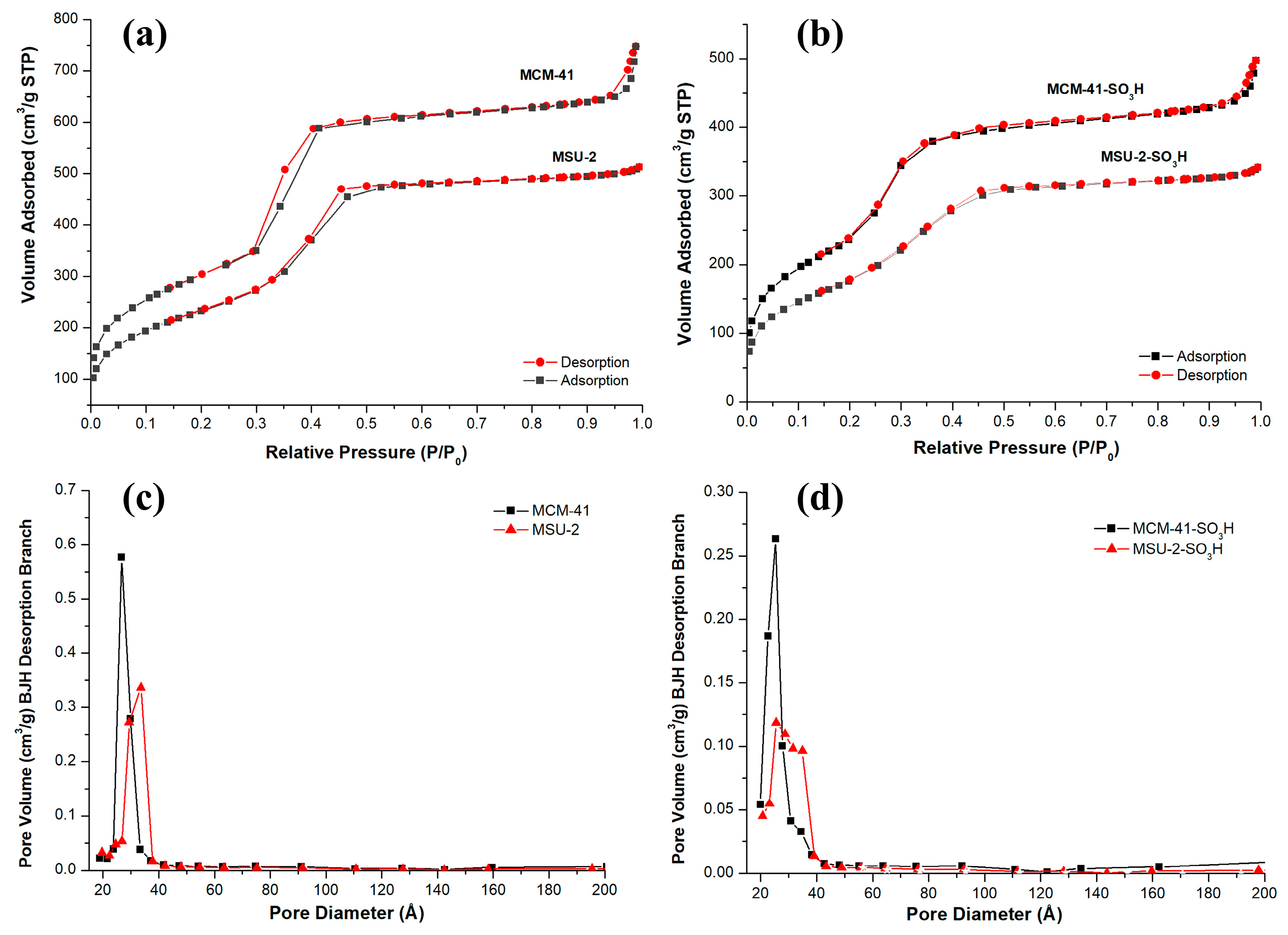
The adsorption isotherms for both materials are type IV according to the IUPAC, in the isotherms, an abrupt increase in adsorbed volume occurs at a relative pressure (P/P0) of approximately 0.4, indicative of nitrogen capillary condensation within the mesopore structure. The isotherms also show that the adsorption volume is higher in the case of MCM-41 due to its larger pore volume. The hysteresis loop presented by MCM-41 and MSU-2 is of type H1 according to the IUPAC classification, which is associated with porous materials consisting of regular-shaped aggregates or compacts and a narrow pore size distribution [35,36]. This is consistent with what has been observed in the SEM and TEM images for these materials. The average BJH pore diameter for MCM-41 is 26.6 Å, and the wall thickness is 26.32 Å. On the other hand, for MSU-2, pore diameter of 33.6 Å and wall thickness of 18.58 Å was found. In the case of the functionalized materials, it can be seen that the attachment of organic ligands to the pore walls has increased the effective thickness of the walls. This does not significantly alter the pore diameter but has reduced the internal volume of the pores and surface area as can be seen in the data on their textural properties. These data on wall thickness, volume, and pore diameter demonstrate why MCM-41 has a higher number of pores per gram of material. All these physical parameters obtained from nitrogen isotherms, such as the BET surface area, average BJH pore diameter, pore volume, and wall thickness of the materials are presented in Table 2, where it is observed that the MCM-41 has a larger surface area (1101 m2/g) than the MSU-2 (852 m2/g).

Table 2.
Textural properties and functionalization degree of the prepared functionalized mesoporous silicas.
Figure 6 shows the pore size distribution using the BJH method in the desorption branch of the functionalized and unfunctionalized materials. It can be observed that MCM-41 presents a narrower pore distribution than MSU-2 (Figure 6a), indicative of a higher uniform mesoporosity in the structure. After functionalization (Figure 6b), a decrease in SBET, BJH pore diameter, and pore volume took place (see Table 2) in both materials. The adsorbed volume in the adsorption isotherms of the two materials decreased, and the hysteresis loops were reduced (Figure 6c,d). These changes can be attributed to the presence of sulfonic groups on the surface and pores of the materials, which partially block nitrogen molecule adsorption. Additionally, it is observed that the inflection point of the isotherm in the adsorption branch is shifted slightly toward lower relative pressures because of the earlier filling of the monolayer due to the reduction in the pore volume of the material [37].
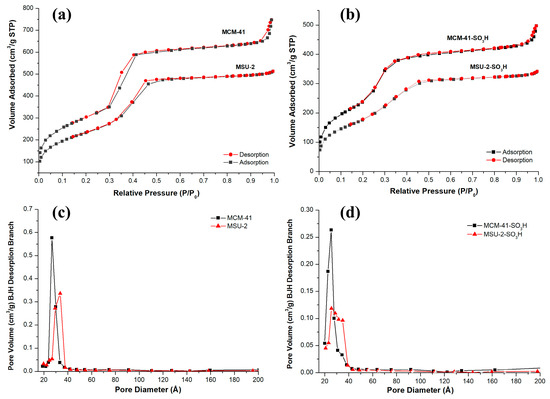
Figure 6.
Nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms of (a) bare MCM-41 and MSU-2 and (b) functionalized MCM-41-SO3H and MSU-2-SO3H. Pore size distribution curves of (c) bare MCM-41 and MSU-2, (d) functionalized MCM-41-SO3H and MSU-2-SO3H.
3.1.5. FT-IR Spectra
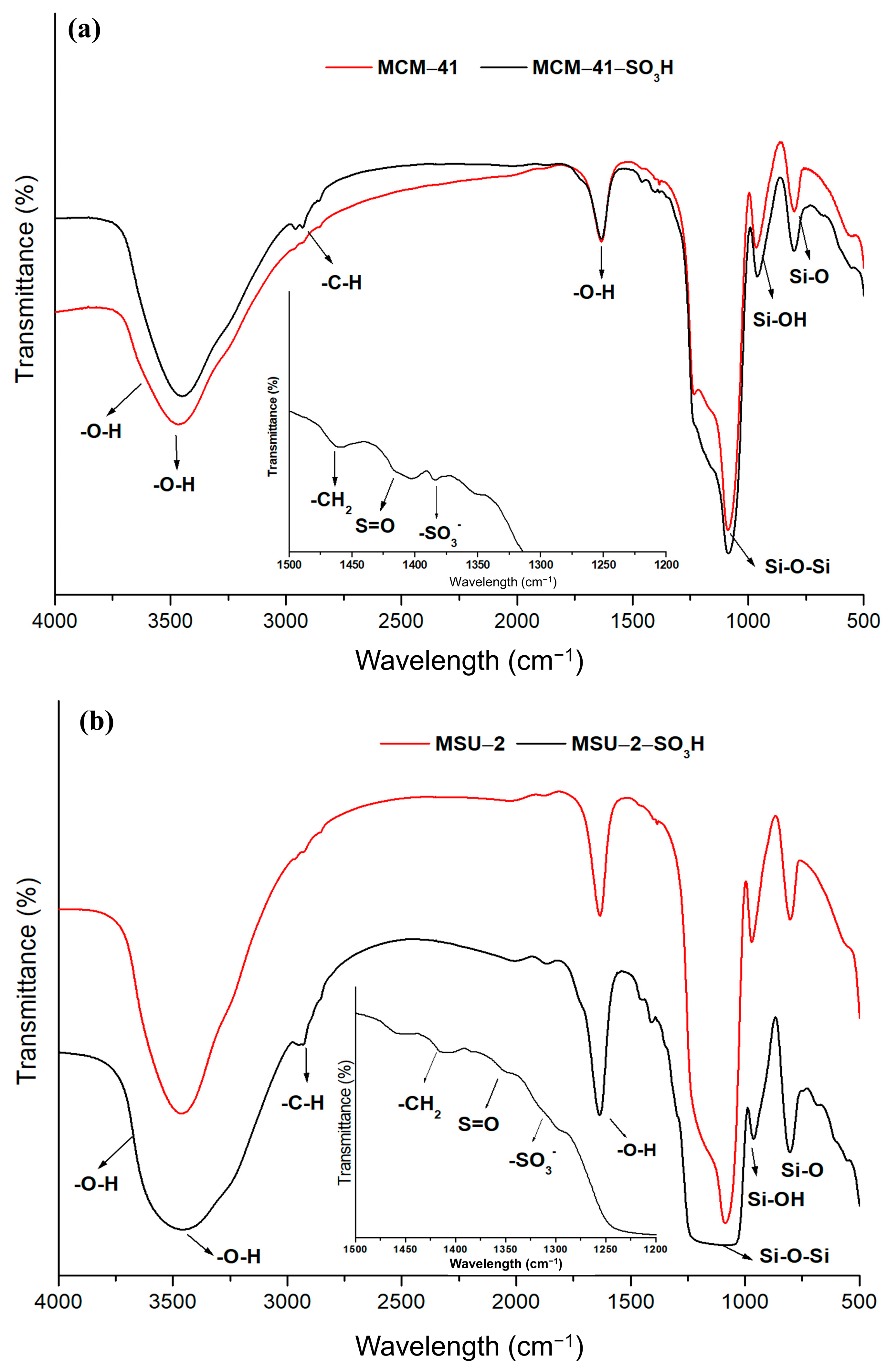
Figure 7 shows the FT-IR patterns for the functionalized and non-functionalized materials covering a range from 4000 to 400 cm−1. The functionalized materials show the characteristic bands of the organic ligands attached to the material. The peaks observed in the spectra at 1620 cm−1 and 3400 cm−1 have been attributed to OH vibration and stretching vibrations of physisorbed water. Also, a weak peak is observed at 3640 cm−1 associated with the surface hydroxyl groups involved in forming hydrogen bonds with other neighboring silanol groups. The intensity of these signals is reduced in the functionalized materials because of the decrease in the number of free silanol groups. The presence of sulfonic groups in functionalized mesoporous silica is confirmed by the identification of bands characteristic of the ligands, like deformation vibration bands of -CH2 detected at 1447 cm−1 due to the alkyl chains of the ligand. The peaks located around 1410 cm−1 correspond to S=O stretching vibrations present in undissociated acidic sulfonic groups, while the peak at 1344 cm−1 is attributed to stretching vibrations of -SO3− species. The spectra also can be identified as characteristic bands for aliphatic stretching vibrations (C-H) of pendant alkyl chains located around 3000–2800 cm−1. In addition, bands corresponding to the Si-O vibration at 790 cm−1, the symmetric Si-OH vibration at 950 cm−1, and a large band between 1000 and 1240 cm−1 attributed to the asymmetric Si-O-Si vibrations are distinguished [38]. The greater intensity of these bands in the functionalized MCM-41 is a consequence of the higher degree of functionalization that this material presents compared to MSU-2.
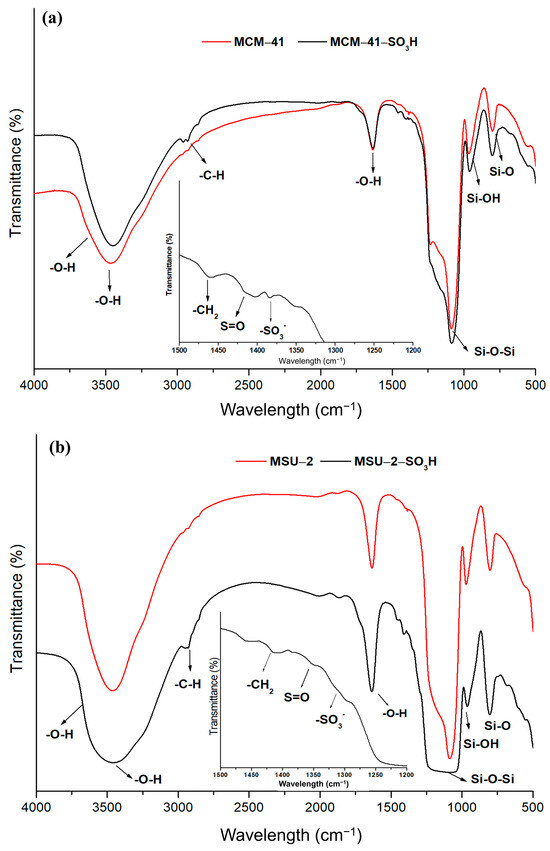
Figure 7.
Fourier-transform infrared spectra (FT-IR) of (a) bare MCM-41 and functionalized MCM-41-SO3H and (b) bare MSU-2 and functionalized MSU-2-SO3H.
3.1.6. NMR Spectra
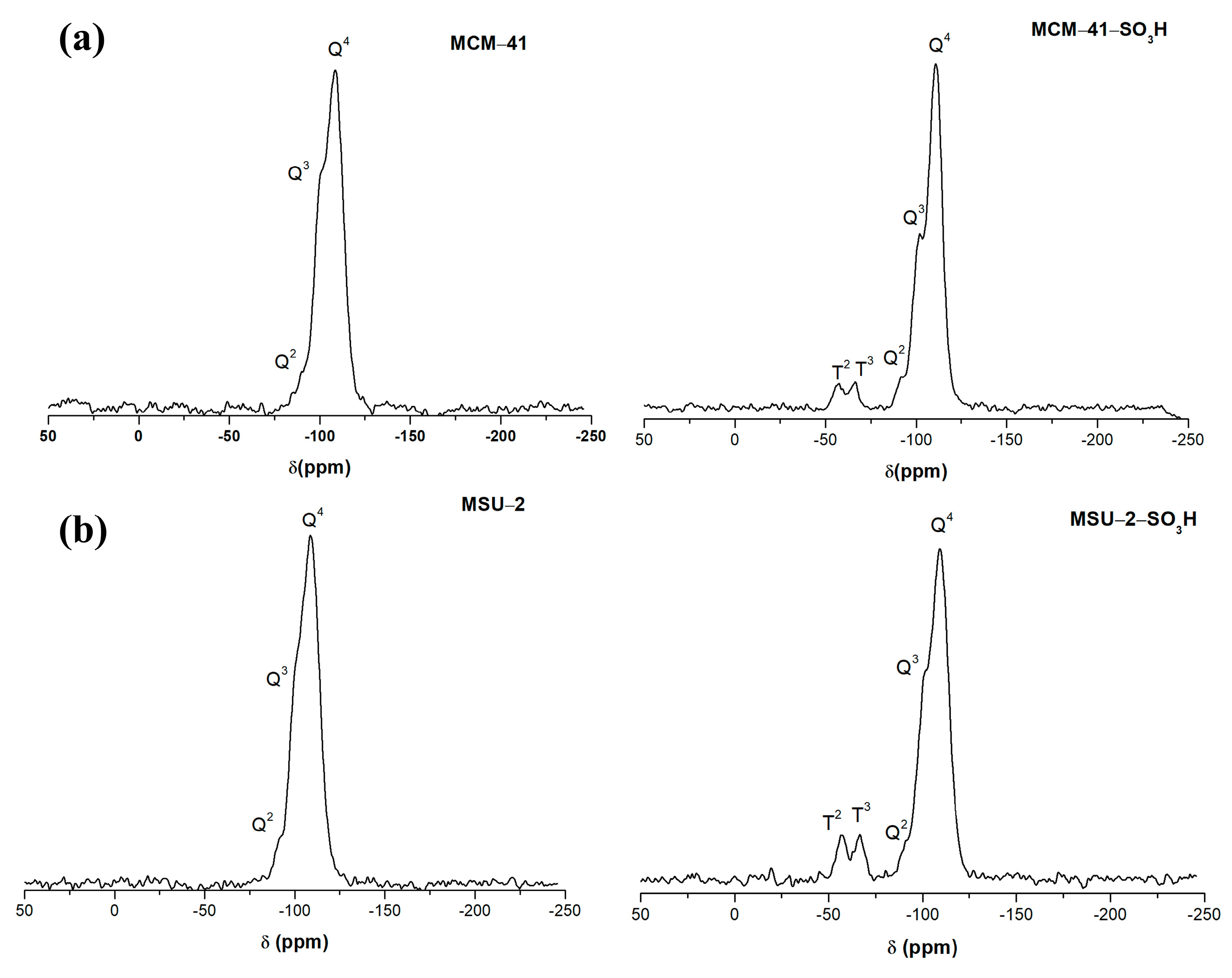
Figure 8 shows the 29Si-PDA-MAS-NMR spectra of the functionalized and non-functionalized materials.
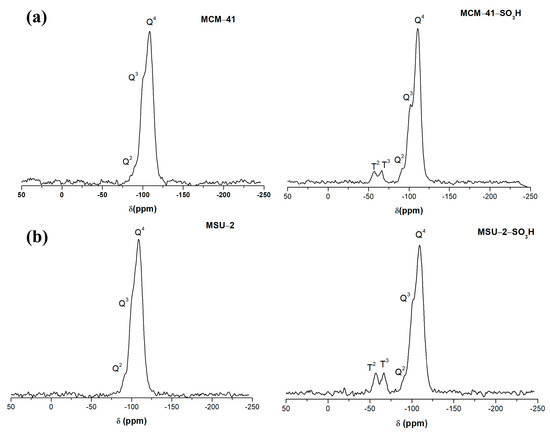
Figure 8.
29Si solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectra (29Si-PDA-MAS-NMR) of (a) bare MCM-41 and functionalized MCM-41-SO3H and (b) bare MSU-2 and functionalized MSU-2-SO3H.
In these spectra, it can be observed that the two materials present three signals due to the structural silica sites Q4 ((SiO)4Si) at −110 ppm (MCM-41 and MCM-41-SO3H), at −109 ppm (MSU-2 and MSU-2-SO3H), and the silanol sites Q3 ((SiO)3SiOH), and Q2 sites ((SiO)2Si(OH)2), (−102 ppm and −91 ppm for MCM-41 and MCM-41-SO3H), (−101 ppm and −90 ppm for MSU-2 and MSU-2-SO3H). In the two materials, the signal from the Q4 sites is the most intense, which indicates a high degree of condensation. In the case of MCM-41-SO3H, it is observed that the Q3 and Q2 sites are more intense than in MSU-2-SO3H, which indicates a greater presence of surface silanol groups [39]. Additionally, after the functionalization, two signals can be observed at a lower chemical shift (δ) due to the Si atoms bonded to the carbons of the sulfonic ligands (-R), T sites, corresponding to the T3 ((SiO)3Si-R) (−67 and −66 ppm for MCM-41-SO3H and MSU-2-SO3H, respectively), and T2 ((SiO)2Si(OH)-R) (−57 ppm in both materials) sites. The high intensity of T sites in the functionalized materials indicates a high degree of functionalization as is confirmed by the elemental analysis.
3.1.7. Elemental Analysis
Finally, the degree of functionalization (L0, mmol of the sulfonic groups attached to mesoporous silica) of MCM-41-SO3H and MSU-2-SO3H were estimated based on sulfur content calculated through elemental analysis and found to be 1.12 mmol/g and 1.08 mmol/g, respectively. The higher degree of functionalization of MCM-41 is attributed to the larger surface area and higher number of free silanol groups, along with a more ordered structure and accessible pore distribution, as evidenced by gas physisorption and XRD. Compared to MSU-2, MCM-41 has a more ordered pore distribution that facilitates better ligand diffusion, leading to higher functionalization and improved analyte diffusion toward the active sites in MCM-41 functionalized with sulfonic groups.
3.2. Evaluation of Mesoporous Silicas as Sorbents in SPE
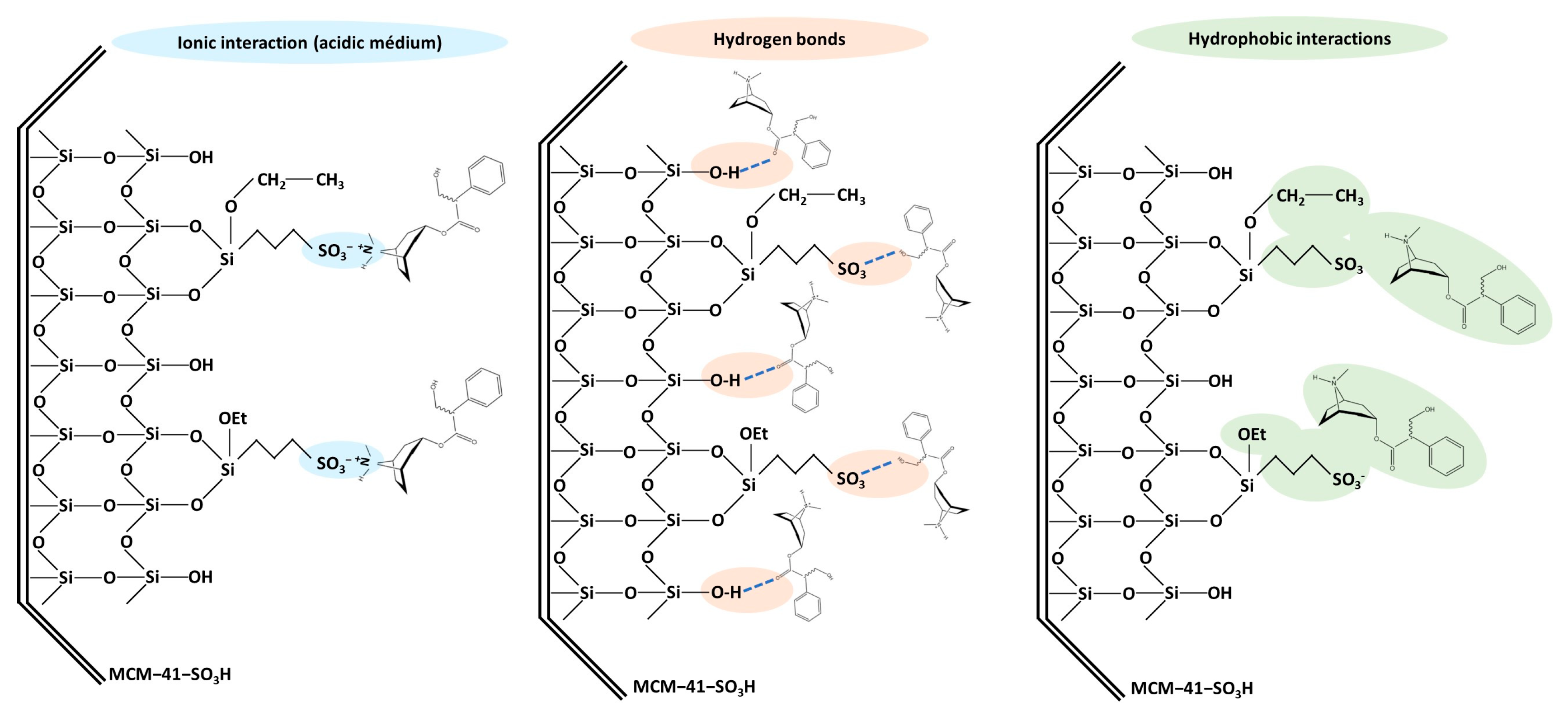
In the purification step by SPE, the selection of a suitable sorbent is crucial, as it directly influences the experimental results. The affinity of the sorbent toward the target analytes is a determining factor to be considered. The target TAs have basic characteristics (pKa values of 9.43 and 7.75 for atropine and scopolamine, respectively), with a ternary amine protonated at low pH [40,41]. Since the pH of media determines whether the analytes are in their ionic or molecular form, this variable plays a crucial role in strong cation-exchange SPE. In the functionalized silicas, their negatively charged sulfonic acid group has a strong cation-exchange capacity, so this sorbent interacts with the positively charged TAs via electrostatic (ionic) interactions that can be achieved by adding to the loading solvent HCl. However, other types of interactions can also occur, such as hydrophobic interactions between non-polar alkyl chains and the non-polar parts of the analytes, or hydrogen bonds between the free silanol groups of the silica or the sulfonic groups and suitable functional groups present in the analytes, such as hydroxyl or carbonyl groups. These multiple interactions enhance the efficiency of the sorbent material in capturing the target TAs. Figure 9 shows the types of interactions described that can occur between functionalized mesoporous silicas and target TAs.
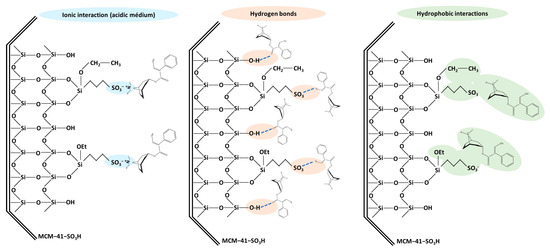
Figure 9.
Different types of interactions that can occur between TAs with the MCM-41-SO3H sorbent used for solid phase extraction.
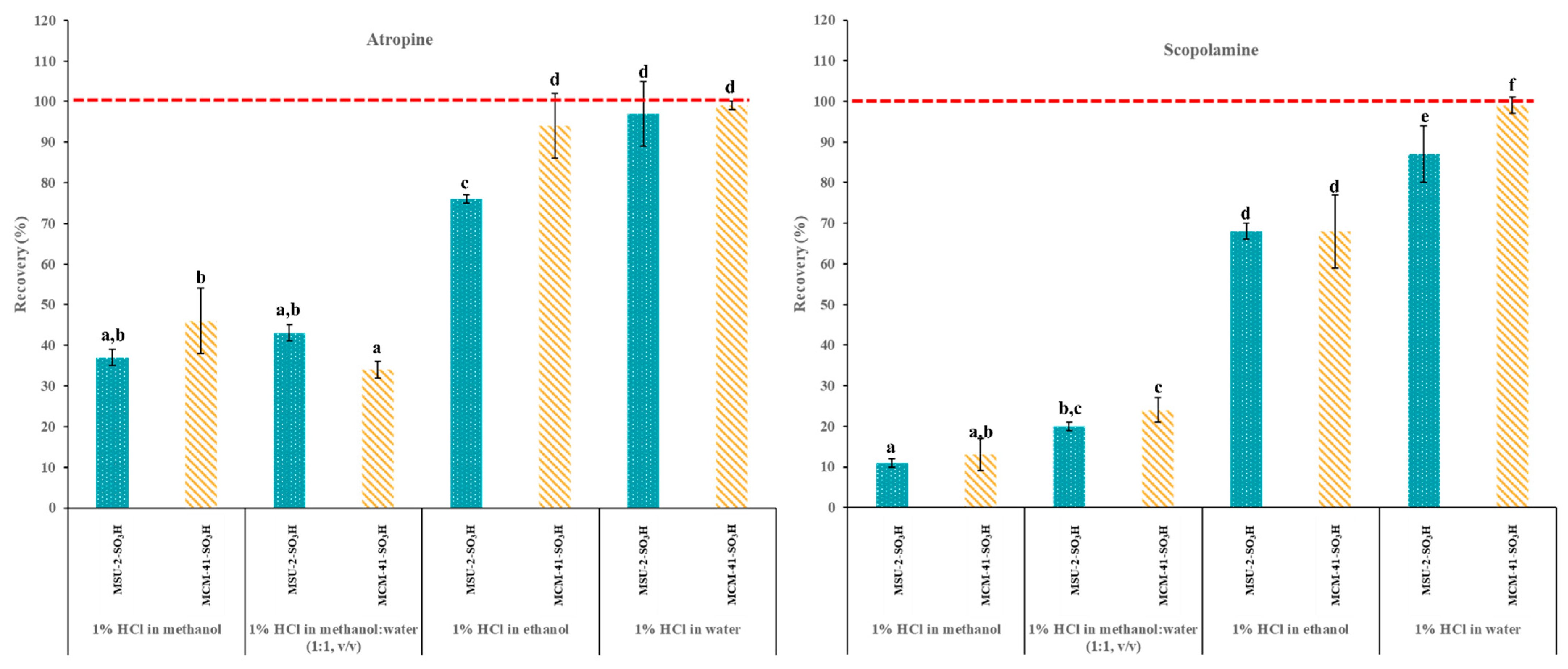
Therefore, to evaluate the recovery efficiencies (%) of the functionalized mesoporous silicas, cartridges were packed with 50 mg of MCM-41-SO3H or MSU-2-SO3H and the following protocol was followed: (1) conditioning the cartridge with 3 mL of H2O; (2) equilibration with 3 mL of the acidified loading solvent; (3) loading with 10 mL of a 0.1 µg/L acidified solution (pH 1) of the target analytes in EtOH, MeOH, H2O or MeOH:H2O (50:50, v/v); and (4) elution with 3 mL of 5% ammonia solution in MeOH. Figure 10 shows the atropine and scopolamine recoveries obtained for the two different sorbent materials and four loading solvents. As can be seen, in general, the best recoveries were obtained with acidified H2O as loading solvent, with recoveries >85% for both analytes and both materials, followed by EtOH, (recoveries >70%), while with MeOH and the MeOH:H2O (50:50, v/v) the recoveries were generally below 50%. The affinity of analytes such as scopolamine and atropine for mesoporous materials (MCM-41 and MSU-2) functionalized with sulfonic groups in different media can be explained by several reasons related to the properties of the solvent and the interaction of the analytes with the functional groups of the material (sulfonic groups). Water is a highly polar solvent that can form an extensive network of hydrogen bonds. This ability to form hydrogen bonds facilitates the interaction between the sulfonic groups of the mesoporous material and the analytes, thus increasing the affinity in an aqueous medium at pH 1 [42]. In contrast, although MeOH and EtOH are also polar solvents, their ability to form hydrogen bonds is lower and their structure is less extensive. This can reduce the interaction with the sulfonic groups of the mesoporous material, resulting in a lower affinity compared to water. Additionally, at pH 1, both in water and in alcohols, analytes such as scopolamine and atropine will be predominantly in their protonated form. However, the ionization of these analytes may be more favored in an aqueous medium due to the higher dielectric constant of water (79.99), significantly higher than that of MeOH (33.30) and EtOH (24.55), which allows for better stabilization of charged species [43,44].
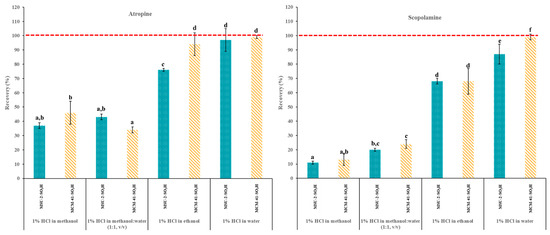
Figure 10.
Atropine and scopolamine recoveries (% ± SD) obtained in SPE assays using 50 mg of MSU-2-SO3H or MCM-41-SO3H as sorbents when the target analytes were loaded in 10 mL of acidified (pH 1) methanol, methanol:water (50:50, v/v), ethanol or water (0.1 µg/L of each analyte) and eluted with 3 mL of 5% methanolic ammonia solution. For the remaining conditions, see Figure 2. Error bars represent the standard deviation of replicate samples (n = 3). In each graphic, a different letter indicates a statistically significant difference (p ≤ 0.05).
This greater stabilization in water can result in a higher affinity of the analytes for the sulfonic groups of the mesoporous material. On the other hand, although both EtOH and MeOH are polar solvents, EtOH has a larger molecular structure and can form stronger and more extensive hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals interactions than MeOH [45]. This can facilitate better solvation of the sulfonic groups and the analytes, improving the affinity of the analytes for the material in EtOH compared to MeOH. On the other hand, the differences in performance for these two materials can be explained by considering different factors like the surface characteristics of the sorbents and the number of functional groups present in them. On one hand, MCM-41-SO3H presents a higher degree of functionalization (1.12 mmol ligand/g) than MSU-2-SO3H (1.08 mmol ligand/g), which allows for greater interaction with the analytes. However, this higher degree of functionalization is not particularly significant, suggesting that its better performance as sorbent for these analytes is due to its textural properties. These include a larger pore volume (0.69 cm3/g vs. 0.52 cm3/g) after functionalization, which implies less pore blockage and greater accessibility to bulky analytes like atropine and scopolamine. Additionally, MCM-41-SO3H has a more ordered pore structure with greater long-range order, as observed in XRD data, and a more ordered pore distribution, as seen in TEM images. This allows for better and faster diffusion of the analytes throughout the entire volume of the particle, enabling them to reach the active sites of the material where analyte–ligand interactions occur more effectively.
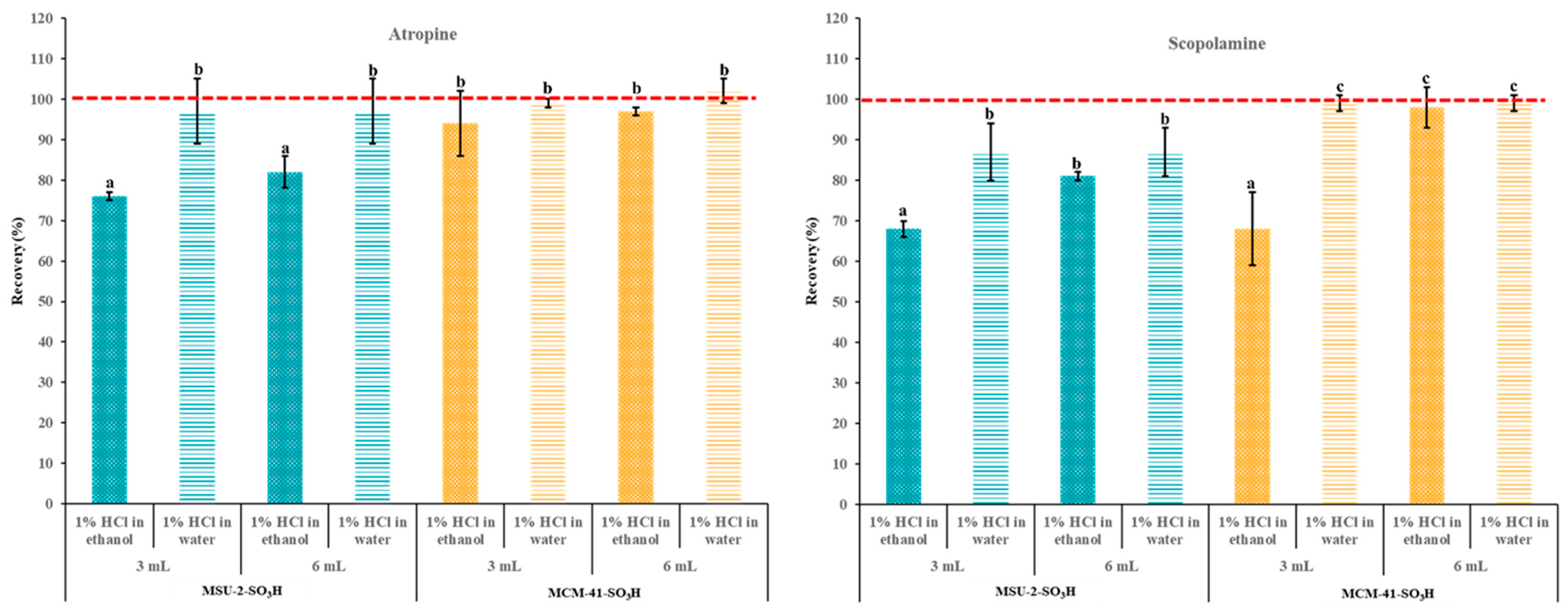
To elute the maximum amount of the target alkaloids, it is important to use a desorption solvent that is powerful enough to break the analyte–sorbent ionic interactions while also minimizing the volume of solvent required. Based on our previous works [29] a 5% methanolic ammonia solution was used for this task and the effect of elution solvent volume was evaluated (Figure 11). As can be seen, the increase in the elution volume from 3 to 6 mL of the 5% methanolic ammonia solution did not improve the recovery percentage for atropine. On the other hand, in the case of scopolamine, the increase in the elution volume resulted in a significant improvement with both sorbents when the loading solvent was EtOH (reaching over 95% and 80% for MCM-41-SO3H and MSU-2-SO3H, respectively), and there were no significant differences when the loading solvent was H2O. These results highlight that, in general, the poorer recoveries observed when using MSU-2-SO3H as a sorbent compared with MCM-41-SO3H are due to lower retention of the analytes in this material and not to a lack of elution, especially when the loading was performed in EtOH.
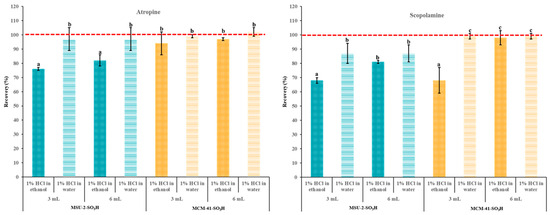
Figure 11.
Atropine and scopolamine recoveries (% ± SD) obtained in SPE assays using 50 mg of MSU-2-SO3H or MCM-41-SO3H as sorbents when the target analytes were loaded in 10 mL of acidified (pH 1) ethanol or water (0.1 µg/L of each analyte) and eluted with 3 or 6 mL of 5% methanolic ammonia solution. For the remaining conditions, see Figure 2. Error bars represent the standard deviation of replicate samples (n = 3). In each graphic, a different letter indicates a statistically significant difference (p ≤ 0.05).
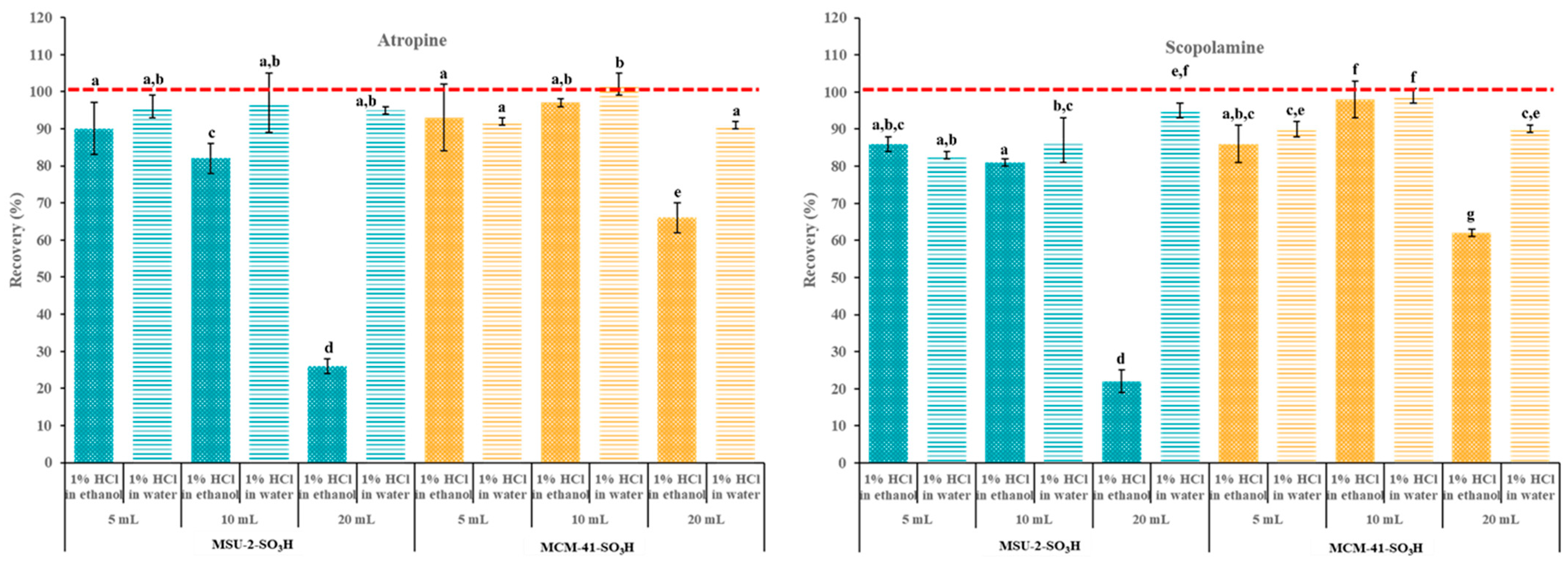
Next, the breakthrough volume was determined. The breakthrough volume in SPE refers to the volume of solvent that can pass through the sorbent before the target analytes start to elute. So, when the breakthrough volume is reached, the analyte begins to appear in the eluate, indicating that the sorbent can no longer retain it effectively. To investigate this, increasing volumes (5, 10, and 20 mL) of 0.1 µg/L atropine and scopolamine solutions in acidified (pH 1) EtOH and H2O were passed through the SPE cartridges containing 50 mg of MCM-41-SO3H or MSU-2-SO3H as sorbents. As seen in Figure 12, when the loading solvent was H2O, no significant differences were observed in the recoveries of both analytes with both materials. However, when the loading solvent was EtOH, there was a significant reduction in retention capacity when increasing the loading volume from 10 to 20 mL. This effect was more pronounced when the sorbent was MSU-2-SO3H (recoveries around 25%) compared to MCM-41-SO3H (recoveries around 60%). These results can be explained by polar interactions, especially hydrogen-bond interactions of EtOH tend to reduce retention by the sorbents and result in smaller breakthrough volumes. Therefore, if the solvent most suitable for the prior solid–liquid extraction of analytes is EtOH, the low breakthrough volume observed with this loading solvent should be considered to achieve adequate recoveries, which is especially necessary for very diluted extracts.
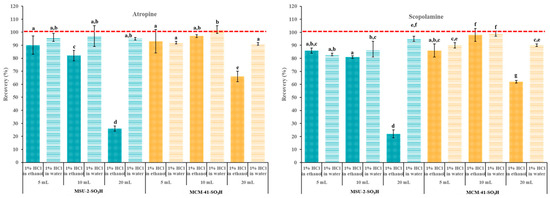
Figure 12.
Atropine and scopolamine recoveries (% ± SD) obtained in SPE assays using 50 mg of MSU-2-SO3H or MCM-41-SO3H as sorbents when the target analytes were loaded in 5, 10, or 20 mL of acidified (pH 1) ethanol or water (0.1 µg/L of each analyte) and eluted with 6 mL of 5% methanolic ammonia solution. For the remaining conditions, see Figure 2. Error bars represent the standard deviation of replicate samples (n = 3). In each graphic, a different letter indicates a statistically significant difference (p ≤ 0.05).
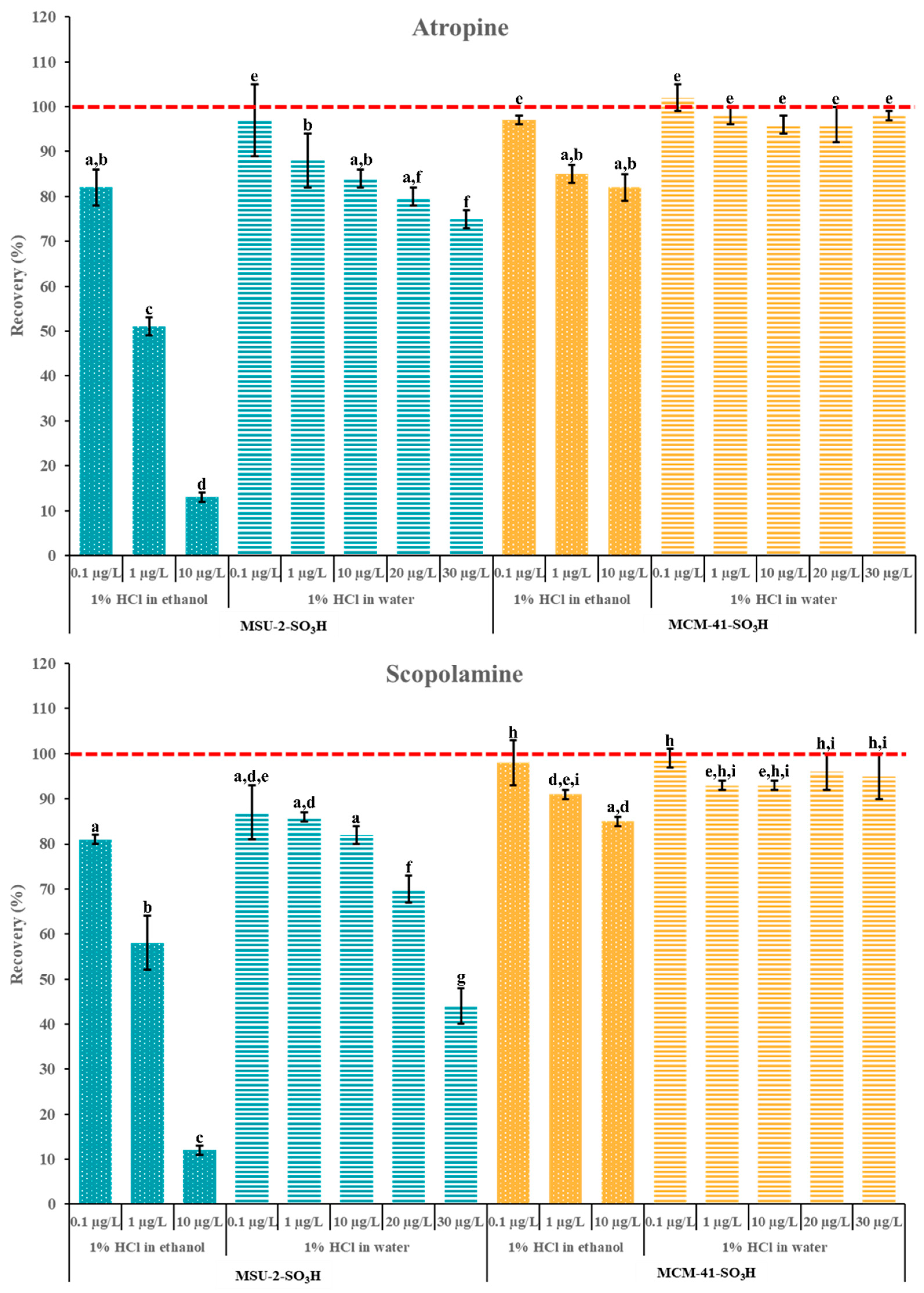
Finally, additional experiments were carried out to evaluate the adsorption capacity of these materials, maintaining the optimal loading volume of 10 mL. These studies were carried out in a concentration range of 0.1–30 µg/L and 50 mg of MCM-41-SO3H and MSU-2-SO3H as a sorbent (Figure 13). As can be observed, the adsorption capacity of MCM-41-SO3H was superior to that of MSU-2-SO3H in both solvents. For MSU-2-SO3H, the increase in analyte concentration resulted in a significant reduction in retention for both analytes when the solvent was EtOH, with recoveries as low as 10% for a concentration of 10 µg/L. Similarly, for MSU-2-SO3H, the increase in analyte concentration from 0.1 to 10 µg/L led to a significant reduction in recovery, with recoveries of approximately 80% for 10 µg/L. However, when the loading was performed in H2O, the increase in concentration up to 30 µg/L resulted in a significant reduction in recovery when the sorbent was MSU-2-SO3H, which was more evident for scopolamine (recoveries around 45%). In contrast, for MSU-2-SO3H, as shown in Figure 13, this same concentration allowed for recoveries close to 100% for both analytes. These results demonstrated the effectiveness of MCM-41-SO3H as a sorbent material for SPE of tropane alkaloids in aqueous samples or extracts.
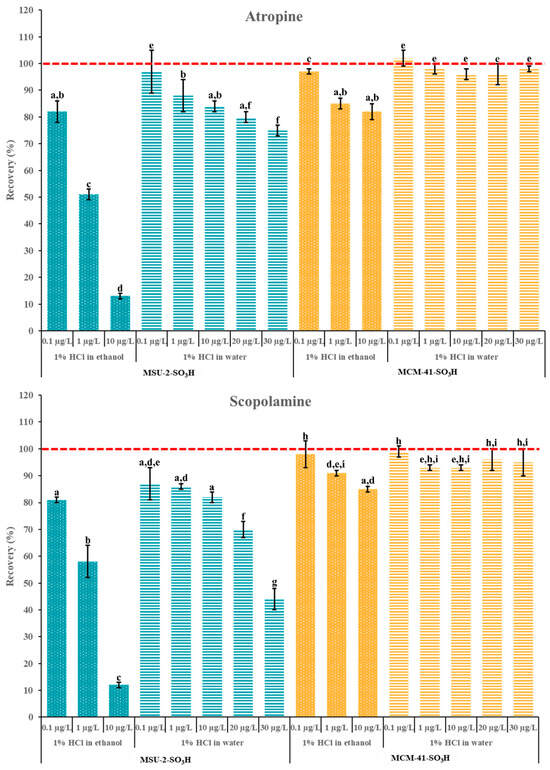
Figure 13.
Atropine and scopolamine recoveries (% ± SD) obtained in SPE assays using 50 mg of MSU-2-SO3H or MCM-41-SO3H as sorbents when the target analytes were loaded in 10 mL of acidified (pH 1) ethanol or water (0.1 to 30 µg/L of each analyte) and eluted with 6 mL of 5% methanolic ammonia solution. For the remaining conditions, see Figure 2. Error bars represent the standard deviation of replicate samples (n = 3). In each graphic, a different letter indicates a statistically significant difference (p ≤ 0.05).
4. Conclusions
In this study, two types of mesoporous silicas with sulfonic acid groups were synthesized and functionalized: MCM-41-SO3H, with hexagonal honeycomb structure, and MSU-2-SO3H, with a three-dimensional interconnected pore structure. These silicas were characterized and their performance as strong cation-exchange sorbents was evaluated in the solid phase extraction of atropine and scopolamine, using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. The results indicated that the MCM-41-SO3H material presented the highest recovery efficiency, around 100% for both analytes when acidified water was used as the loading solvent. This was attributed mainly to the accessibility of the sulfonic groups, favored by the regularity and uniformity of their pores. These findings highlight MCM-41-SO3H as a promising sorbent for solid-phase extraction of tropane alkaloids in aqueous solutions, with potential applications in the control of natural toxins in food. Furthermore, this work underlines the importance of the pore structure of the mesoporous silicas in the optimization of extraction processes, opening new perspectives for the development of more efficient and sustainable miniaturized sample preparation protocols, in line with the principles of Green Analytical Chemistry.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.L.V.-B., S.M.-Z., D.P.-Q. and I.S.; methodology, F.L.V.-B., S.M.-Z. and D.P.-Q.; software, F.L.V.-B. and D.P.-Q.; validation, F.L.V.-B.; formal analysis, F.L.V.-B., S.M.-Z., D.P.-Q. and I.S.; investigation, F.L.V.-B., S.M.-Z., D.P.-Q. and I.S.; resources, F.L.V.-B., S.M.-Z., D.P.-Q. and I.S.; data curation, F.L.V.-B. and D.P.-Q.; writing—original draft preparation, F.L.V.-B., S.M.-Z., D.P.-Q. and I.S.; writing—review and editing, F.L.V.-B., S.M.-Z., D.P.-Q. and I.S.; visualization, F.L.V.-B., S.M.-Z., D.P.-Q. and I.S.; supervision, S.M.-Z. and I.S.; project administration, I.S.; funding acquisition, I.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033/FEDER, UE, grant number PID2022-137278OB-I00, EVALKALIM II.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Feng, J.; Sun, M. Recent advances of ordered mesoporous silica materials for solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1675, 463157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, I.; Morante-Zarcero, S. Chapter 5—New Advances in Food Sample Preparation With Nanomaterials for Organic Contaminants Analysis by Liquid Chromatography. In Nanomaterials in Chromatography: Current Trends in Chromatographic Research Technology and Techniques, 1st ed.; Hussain, C.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 118–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.E.I.; El-Nouby, M.A.M.; Kimani, P.K.; Lim, L.W.; Rabea, E.I. A review of the modern principles and applications of solid-phase extraction techniques in chromatographic analysis. Anal. Sci. 2022, 38, 1457–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado, N.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Sierra, I. Evaluation of Mesostructured Silicas with Wormhole-Like Framework Functionalized with Hydrophobic Groups as Alternative Sorbents for Extraction of Drug Residues from Food Samples. Mater. Lett. 2018, 220, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larki, A.; Saghanezhad, S.J.; Ghomi, M. Recent advances of functionalized SBA-15 in the separation/preconcentration of various analytes: A review. Microchem. J. 2021, 169, 106601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezian, S.M.; Azizi, S.N.; Biparva, P.; Bekhradnia, A. High-Efficiency Purification of Sulforaphane from the Broccoli Extract by Nanostructured SBA-15 Silica using Solid-Phase Extraction Method. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1108, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Peng, L.; Chu, J.; Shi, J.; Cui, Q.; Shi, Q. D-Limonene as an Alternative for the Extraction and Purification of Nuciferine from Lotus Leaf Via Multi-Stage Vortex Assisted Two-Phase Solvent Extraction Integrated with Solid Phase Extraction using Mesoporous Material SBA-15 as Adsorbent. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 32, 100997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leśniewska, B.; Arciszewska, Ż.; Wawrzyńczak, A.; Jarmolińska, S.; Nowak, I.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B. Method development for determination of trace amounts of palladium in environmental water samples by ICP-MS/MS after pre-concentration on thiol-functionalized MCM-41 materials. Talanta 2020, 217, 121004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zhong, R.; Yang, M.; Hou, X. Novel Pb(II) ion-imprinted materials based on bis-pyrazolyl functionalized mesoporous silica for the selective removal of Pb(II) in water samples. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 241, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortada, W.I.; Nabieh, K.A.; Helmy, T.E.; Abou El-Reash, Y.G. Microwave-assisted synthesis of MCM-41 composite with rice husk and its functionalization by dithizone for preconcentration of some metal ions from water and food samples. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 106, 104352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil García, M.D.; Dahane, S.; Arrabal-Campos, F.M.; SocíasViciana, M.M.; García, M.A.; Fernández, I.; Martínez Galera, M. MCM-41 as novel solid phase sorbent for the pre-concentration of pesticides in environmental waters and determination by microflow liquid chromatography-quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2017, 134, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.F.S.; de Jesus, R.A.; Costa, J.A.S.; Gouveia, L.G.T.; de Mesquita, M.E.; Navickiene, S. Evaluation of MCM-41 and MCM-48 mesoporous materials as sorbents in matrix solid phase dispersion method for the determination of pesticides in soursop fruit (Annona muricata). Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 101, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Yi, L.; Ye, L.; Chen, Y.; Cao, J.; Peng, L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y. Miniaturized solid-phase extraction of macrolide antibiotics in honey and bovine milk using mesoporous MCM-41 silica as sorbent. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1537, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahane, S.; Martínez Galera, M.; Marchionni, M.E.; Socías Viciana, M.M.; Derdour, A.; Gil García, M.D. Mesoporous silica based MCM-41 as solid-phase extraction sorbent combined with micro-liquid chromatography–quadrupole-mass spectrometry for the analysis of pharmaceuticals in waters. Talanta 2016, 152, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trzeciak, K.; Kaźmierski, S.; Wielgus, E.; Potrzebowski, M.J. DiSupLo—New extremely easy and efficient method for loading of active pharmaceutical ingredients into the pores of MCM-41 mesoporous silica particles. Microporous Mesoporous. Mater. 2020, 308, 110506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharbouche, L.; Gil García, M.D.; Lozano, A.; Hamaizi, H.; Galera, M.M. Solid phase extraction of pesticides from environmental waters using an MSU-1 mesoporous material and determination by UPLC-MS/MS. Talanta 2019, 199, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharbouche, L.; Martínez Galera, M.; Díaz Galiano, F.J.; Gil García, M.D. Pre-concentration of 218 multiclass pesticide in groundwater samples using MSU-1 mesoporous sorbent. Microchem. J. 2023, 184, 108168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Sánchez, A.; del Hierro, I.; Fajardo, M.; Sierra, I. Solid phase extraction of Pb(II) in water samples using a new hybrid inorganic-organic mesoporous silica prior to its determination by FAAS. Microchim. Acta 2009, 165, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, F.N.; Prince, D.L.; Peirano, S.R.; Giovannoni, S.; Echevarría, R.N.; Keunchkarian, S.; Reta, M. New sorbents for sample pretreatment: Development and applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 180, 117924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas Medina, D.A.; Cardoso, A.T.; Maciel, E.V.S.; Lanças, F.M. Current materials for miniaturized sample preparation: Recent advances and future trends. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 165, 117120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Shi, Y.; Cao, J. Recent advances and applications of novel advanced materials in solid-phase microextraction for natural products. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 178, 117858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, J.; Frankowski, R.; Grześkowiak, T.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A. Green Sorbents in Sample Preparation Techniques—Naturally Occurring Materials and Biowastes. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 176, 117772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frugier, C.; Bégin, P. Food Toxins. In Encyclopedia of Food Allergy, 1st ed.; Sicherer, S.H., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2024; pp. 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2023/915 of 25 April 2023 on Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Food and Repealing Regulation (EC) No. 1881/2006 (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32023R0915 (accessed on 4 October 2024).
- González-Gómez, L.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Sierra, I. Occurrence and Chemistry of Tropane Alkaloids in Foods, with a Focus on Sample Analysis Methods: A Review on Recent Trends and Technological Advances. Foods 2022, 11, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Nijs, M.; Crews, C.; Dorgelo, F.; MacDonald, S.; Mulder, P.P.J. Emerging Issues on Tropane Alkaloid Contamination of Food in Europe. Toxins 2023, 15, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morante-Zarcero, S.; Gañán, J.; Casado, N.; Sierra, I. Analytical Strategies for the Control of Plant Alkaloids in Food: New Advances in Sample Preparation and Analysis. In Encyclopedia of Food Safety, 2nd ed.; Smithers, G.W., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Sáez, J.; Romero-González, R.; Garrido Frenich, A. Reliable determination of tropane alkaloids in cereal based baby foods coupling online spe to mass spectrometry avoiding chromatographic step. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Baquero, F.L.; Casado, N.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Sierra, I. Improving the food safety of bakery products by simultaneously monitoring the occurrence of pyrrolizidine, tropane and opium alkaloids. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Gómez, L.; Gañán, J.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Sierra, I. Sulfonic Acid-Functionalized SBA-15 as Strong Cation-Exchange Sorbent for Solid-Phase Extraction of Atropine and Scopolamine in Gluten-Free Grains and Flours. Foods 2020, 9, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Gómez, L.; Gañán, J.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Sierra, I. Mesostructured Silicas as Cation-Exchange Sorbents in Packed or Dispersive Solid Phase Extraction for the Determination of Tropane Alkaloids in Culinary Aromatics Herbs by HPLC-MS/MS. Toxins 2022, 14, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Sánchez, A.; del Hierro, I.; Fajardo, M.; Sierra, I. Synthesis and characterization of novel mesoporous silicas of the MSU-X family for environmental applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 4901–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Hierro, I.; Fajardo, M.; Sierra, I. Preparation of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole-derivatized mesoporous silica and removal of Hg (II) from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Monit. 2006, 8, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, M.V.; Dafa, E.; Kaliya, M.L.; Sen, T.; Herskowitz, M. Mesoporous alumina catalytic material prepared by grafting wide-pore MCM-41 with an alumina multilayer. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2001, 49, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prouzet, E.; Cot, F.; Boissière, C.; Kooyman, P.J.; Larbot, A. Nanometric hollow spheres made of MSU-X-type mesoporous silica. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 1553–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, M.; Unger, K.K.; Matsumoto, A.; Tsutsumi, K. Novel pathways for the preparation of mesoporous MCM-41 materials: Control of porosity and morphology. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 27, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz-Ekloff, G.; Rathouský, J.; Zukal, A. Controlling of morphology and characterization of pore structure of ordered mesoporous silicas. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 27, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, L.; Hohn, K.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, D. Synthesis of Propyl-Sulfonic Acid-Functionalized Nanoparticles as Catalysts for Cellobiose Hydrolysis. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 5, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, M.V.; Varkey, S.P.; Herskowitz, M.; Regev, O.; Pevzner, S.; Sen, T.; Luz, Z. Wetting stability of Si-MCM-41 mesoporous material in neutral, acidic and basic aqueous solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 33, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Library of Medicine. PubChem Reference Collection SID 481107725, Atropine. 2024. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Atropine (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- National Library of Medicine. PubChem Reference Collection CID 11968014, Scopolamine. 2024. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/11968014 (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Thuéry, P.; Atoini, Y.; Harrowfield, J. The Sulfonate Group as a Ligand: A Fine Balance between Hydrogen Bonding and Metal Ion Coordination in Uranyl Ion Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 8756–8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, D.; Cassettari, M.; Salvetti, G. The Dielectric Properties of Alcohols–water Solutions. I. the Alcohol Rich Re-gion. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 78, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunner, M.R.; Alexov, E.; Torres, E.; Lipovaca, S. The importance of the protein in controlling the electrochemistry of heme metalloproteins: Methods of calculation and analysis. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 2, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Physical Properties of Alcohols; Hydrogen Bonding. 2022. Available online: https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Winona_State_University/Klein_and_Straumanis_Guided/13%3A_Alcohols_and_Phenols/13.09%3A_Physical_Properties_of_Alcohols_Hydrogen_Bonding (accessed on 27 December 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).