The Parameter of Soil Structural Properties and Their Relationship to Grain Size, Density, and Moisture Content
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. New Definition of Structural Parameter
2.2. Test Materials and Test Program
2.2.1. Basic Physical Property Indicators of Sampled Loess
2.2.2. Experiment Scheme
3. Results
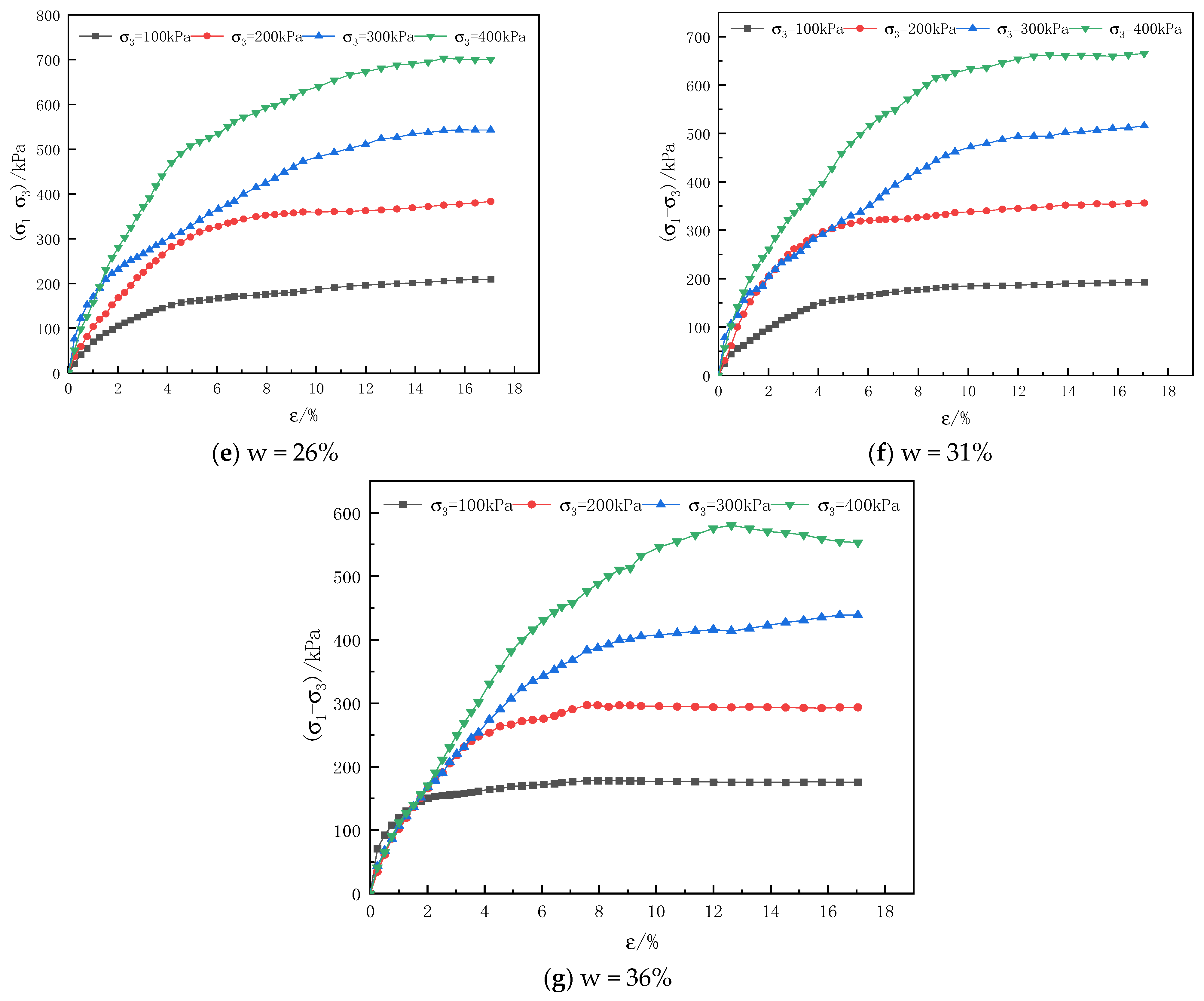
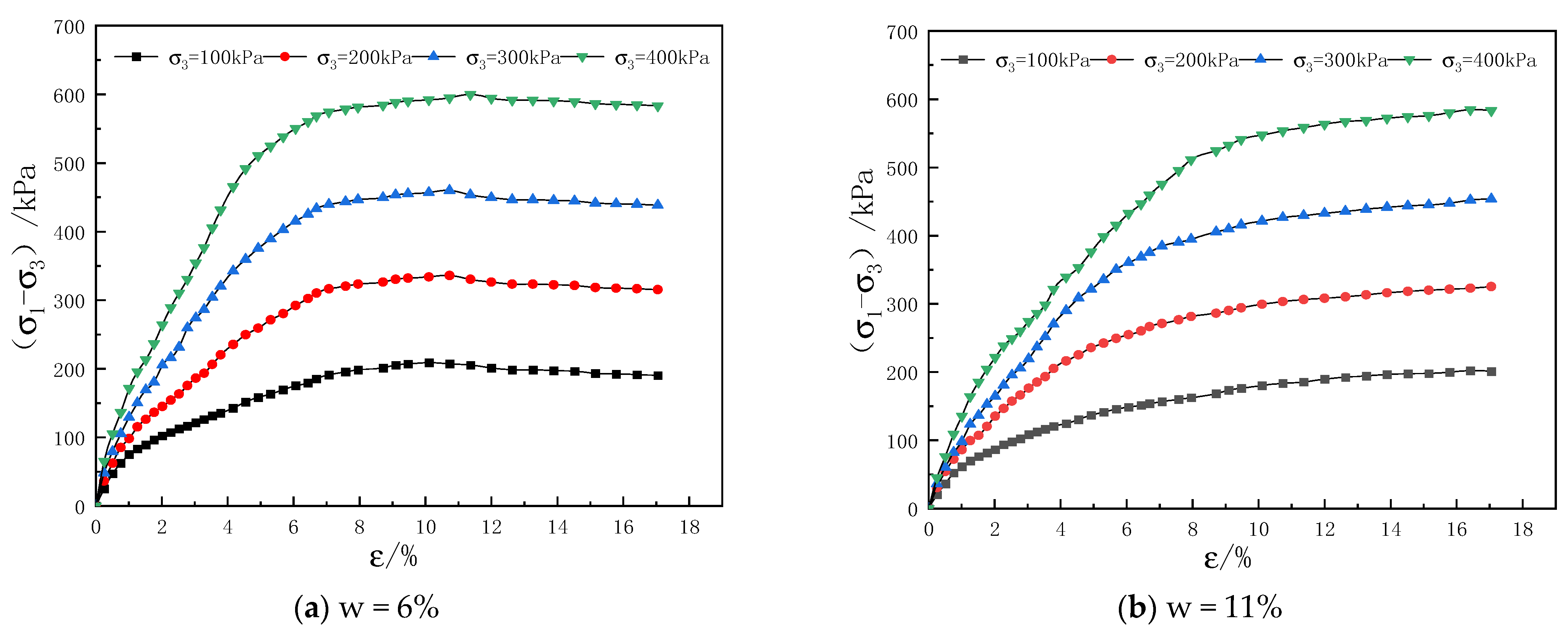
3.1. Analysis of Stress-Strain Characteristics of Loess Soil Samples
3.1.1. Analysis of Stress-Strain Characteristics of Undisturbed Soil
3.1.2. Analysis of Stress-Strain Characteristics of Remolded Soil
3.2. Analysis of Structural Changes in Loess Soil Samples
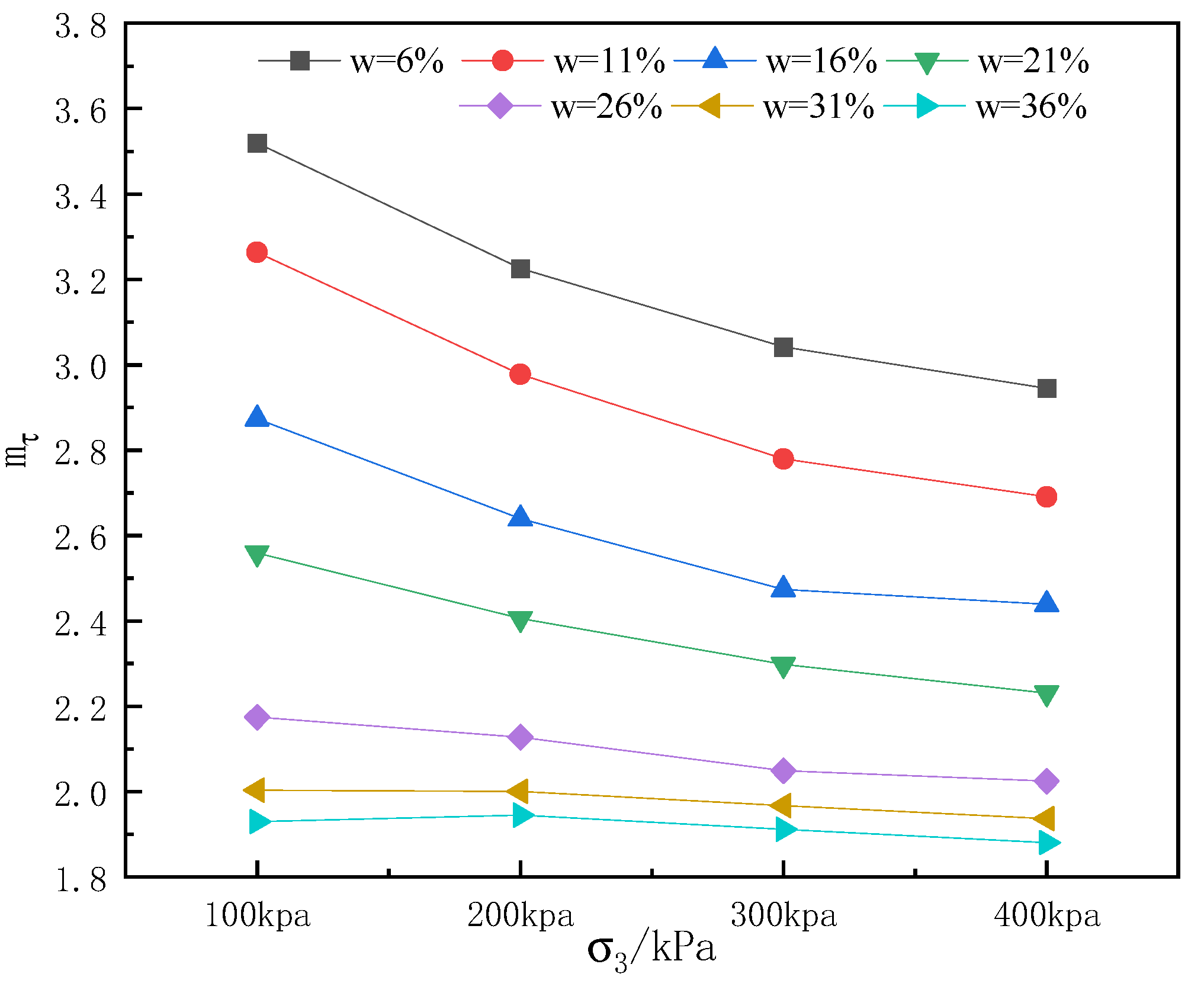
3.2.1. Relationship Between Confining Pressure and Structural Parameter
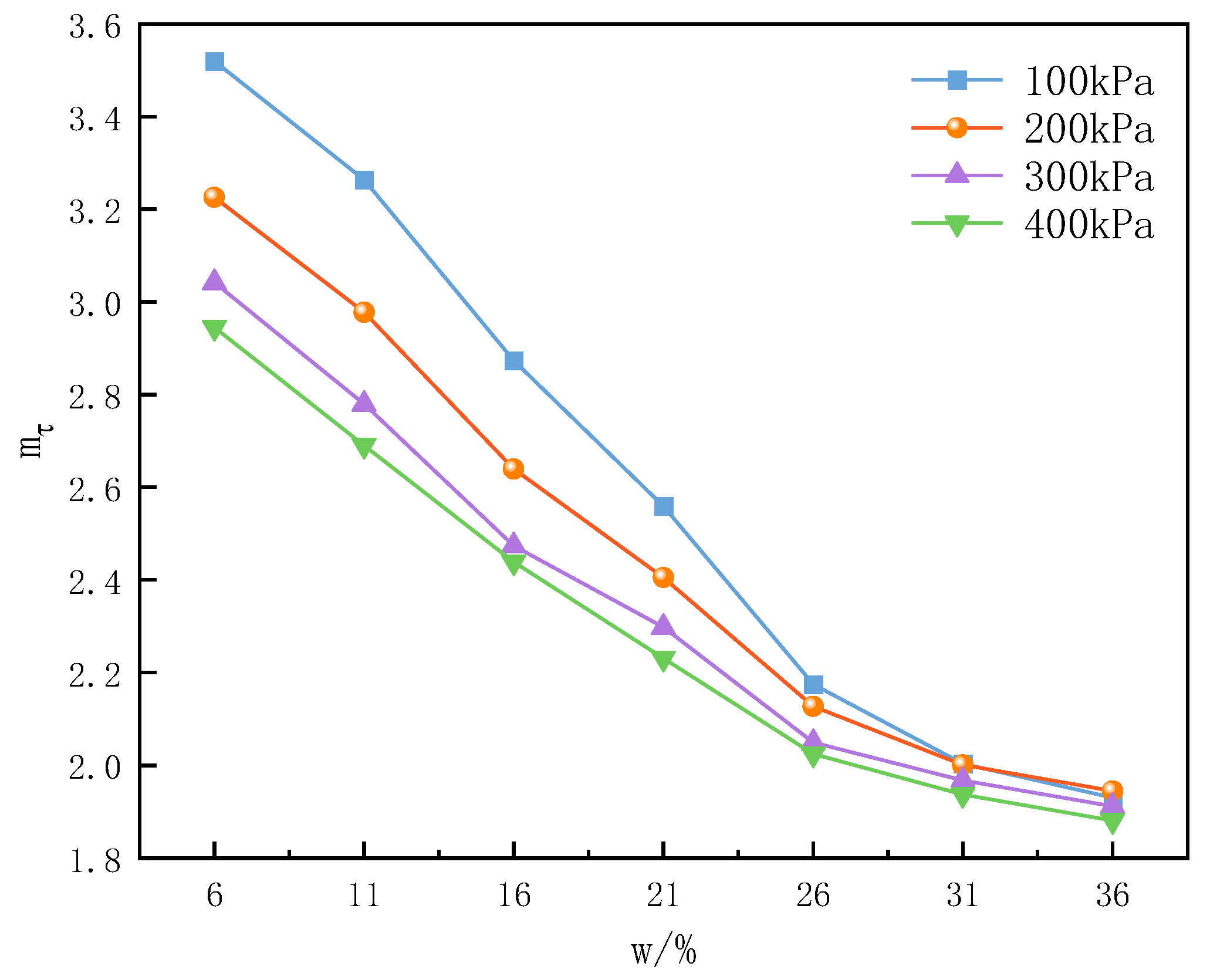
3.2.2. Relationship Between Moisture Content and Structural Parameter
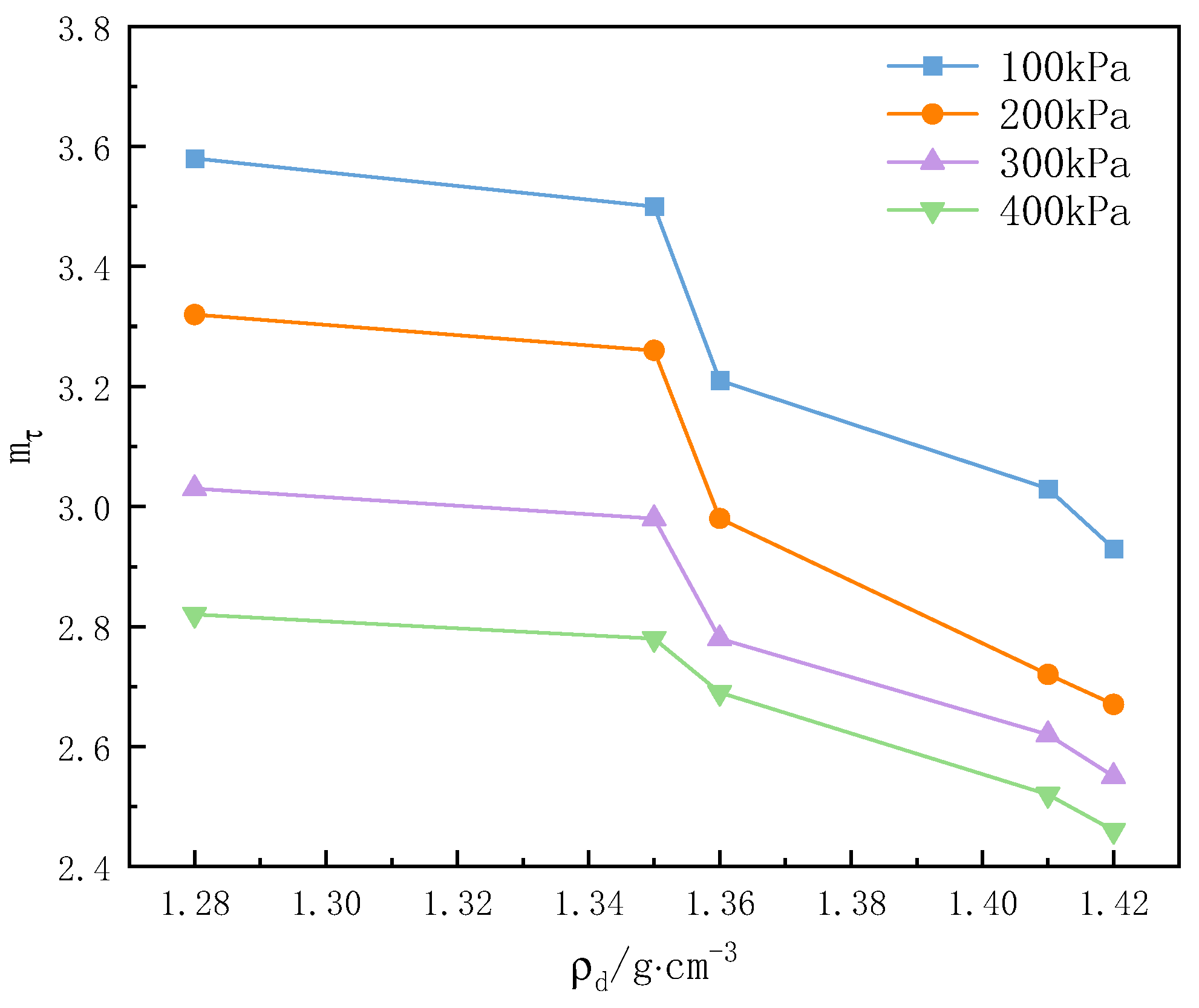
3.2.3. Relationship Between Dry Density and Structural Parameter
3.3. Quantitative Evaluation of Structural Influencing Factors
3.3.1. Concept of Coefficient of Variation Method
3.3.2. Calculate the Weight of Structural Factors
- Moisture content
- Dry density
- Confining pressure
3.3.3. The Weight Values of Each Influencing Factor
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationship Between Structural Parameter and Density
4.2. Relationship Between Structural Parameter and Particle Size
4.3. Relationship Between Structural Parameter and Consistency State
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, T.; Xu, C.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J.; Ding, X.; Jin, X. Study on structure evolution characteristics of undisturbed Q3 loess under plane-strain condition. China Civ. Eng. J. 2022, 55, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Yao, M.; Sun, X.; Xia, W.; Shu, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z. Dynamic characteristics and concept expression of soil structure. J. Eng. Geol. 2022, 30, 1914–1928. [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi, K. Theoretical Soil Mechanics; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1973; pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Liang, H. Study on the difference of mechanical properties of artificial structured loess with different binders. Rock Soil Mech. 2023, 44, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, H.; Song, L.; Xu, J. Three-dimensional modified Cam-clay model for structured soils. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2022, 44, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z. Soil structural mathematical model—21st century, The core issue of soil mechanics. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 1996, 1, 95–97. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, H.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J. Hydromechanics based prediction of suffusion development in spatially random soil structures. Eng. Geol. 2024, 341, 107725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W. Analysis of Quantitative Structural Parameters and Elastoplastic Constitutive Model of Saline Soil Under Freeze-Thaw Cycle. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Yang, G.; Liu, W.; Sun, X. Study of constitutive model for soils based on structural parameter. J. Dalian Univ. Technol. 2021, 61, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Zhang, F.; Hu, H.; Cui, Y.; Peng, J. Structural characterization of natural loess and remolded loess under triaxial tests. Eng. Geol. 2014, 181, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Shao, S.; Zhu, D.; Li, P. Evolution of micro-structure and macro-structural property of loess. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 43, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, F.; Ma, F.; Wang, M.; Bai, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhang, G. Collapsibility, composition, and microstructure of loess in China. Can. Geotech. J. 2015, 53, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, J. Structural properties of unsaturated compacted loess for various sample moisture contents. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. Study on the Relationship Between Structural Properties and Unsaturated Characteristics of Loess. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Study on the Structural Parameter and Structural Constitutive Model of Loess. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.; Ji, J. Soil structure characteristics and new approach in research on its quantitative parameter. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 1999, 21, 651–656. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D. Exploration of some new tendencies in research of loess mechanics. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2001, 23, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Xie, D.; Shi, Y. Research methods and current status of soil structure. Northwestern Seismol. J. 2001, 23, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, S.; Wang, L.; Tao, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S. Structural index of loess and its relation with granularity, density and humidity. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2014, 36, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar]
- Edirisinghe, T.L.; Talbot, J.P. The significance of soil–structure interaction in the response of buildings to ground-borne vibration from underground railways. J. Sound Vib. 2024, 597, 118812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, M.; Du, X. Influence of structure-soil-structure interaction on seismic response and seismic migration performance of building structures. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.K.; Shenoy, S. Soil structure interaction studies on earth retaining wall. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1387, 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish, K.; Shrivastava, H.; Ramana, G.V.; Nagpal, A.K. Effects of Randomness in Fault Rupture and in Soil and Structural Parameters on R. C. Portal Frame Response in Delhi Region. Procedia Eng. 2013, 51, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydemir, M.E. Soil structure interaction effects on structural parameters for stiffness degrading systems built on soft soil sites. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2013, 45, 655–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagan, P.; Visuvasam, J.A. Assessment of the influence of nonlinear soil effects on seismic response of RC structures with floating columns considering soil–structure interaction. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2024, 15, 2401997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia Fouda, M.; Salem, O.; Attia, R.; Ibrahim, A. Influence of concrete cracking in isolated RC footings on cohesive soil–structure interaction. HBRC J. 2024, 20, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Cruz, M.C. Free vibration analysis of tall buildings using a generalized continuous model: Simplified approach to soil-structure interaction. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2024, 52, 9878–9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Far, H. Beneficial and detrimental impacts of soil-structure interaction on seismic response of high-rise buildings. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2024, 27, 1862–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, F. Reliability analysis of foundation bearing capacity based on combined coefficients of variation. Rock Soil Mech. 2014, 35, 1950–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Y.; Zhu, T.; Yin, J. Influences of Soil Structure on Vibration Drainage Volume of Soft Soils. J. Univ. Jinan (Sci. Technol.) 2024, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Jin, Y.; Shen, S.; Sun, P.; Zhou, C. An efficient parameter identification procedure for soft sensitive clays. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A (Appl. Phys. Eng.) 2016, 1, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.S.; Xie, D.Y.; Shao, S.J.; Zhang, A.J. Variation characteristics of soil structure of unsaturated loess. J. Northwest Sci-Tech Univ. Agric. For. (Nat. Sci.) 2004, 8, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 50123-2019; Standard for Geotechnical Test Methods. Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China; China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Yin, Z. Effects of Micropores on the Vapor Sorption Isotherm and Structural Parameters Characterization of Kaolinite. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 172, 106453–106462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; Kong, Y.; Yang, B.S.; Zhen, P.F. Study of Soil Structural Parameters Based on the Gunary Model. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 580, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Leal, O.d.A.; Miguel, P.; Rodrigues, M.F.; Guimarães, R.M.L.; Pinto, L.F.S.; Silva, T.P.; Pinto, M.A.B.; Nachtigall, S.D.; Stumpf, L. First validation of the method Visual Evaluation of Soil Structure in coal mining area using a long-term field revegetation experiment as testbed. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 246, 106347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yang, L.; Peng, B.; Huang, Z.; Hua, D.; Sun, Z.; He, L. Stability of Loess Slopes Under Different Plant Root Densities and Soil Moisture Contents. Water 2024, 16, 3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.S.; Pitanga, H.N.; Ferraz, R.L.; Rodrigues, R.A.; de Paula Rodrigues, K.H.; Nalon, G.H. Ultrasonic Analysis of the Influence of Structure on Tropical Soil Behavior. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2024, 43, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, R.; Fleige, H.; Dörner, J.; Zimmermann, I.; Wendroth, O. Pore rigidity as an undervalued process in soil structure development. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 245, 106280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Uchimura, T. The Effect of Moisture Content at Compaction and Grain Size Distribution on the Shear Strength of Unsaturated Soils. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



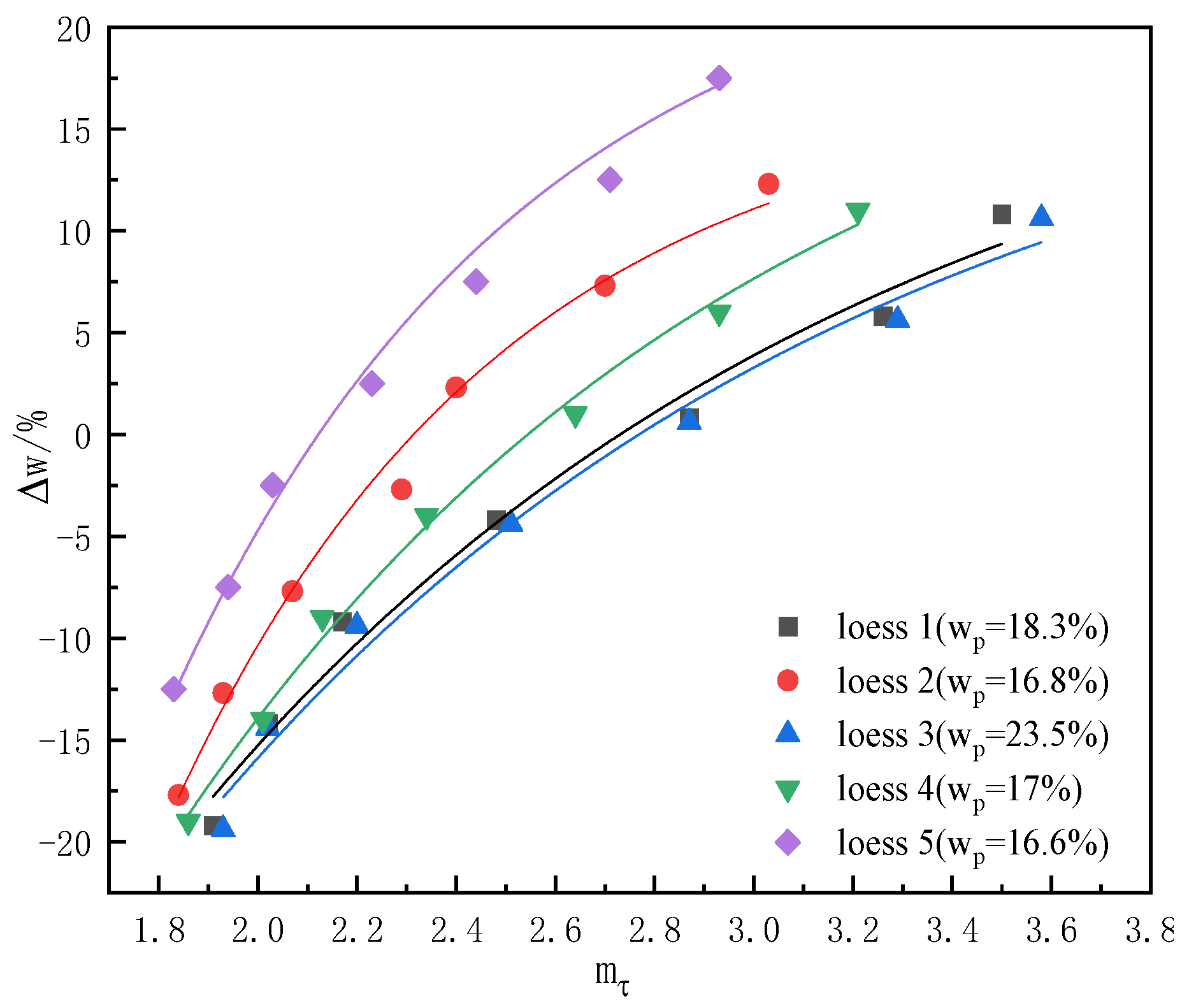
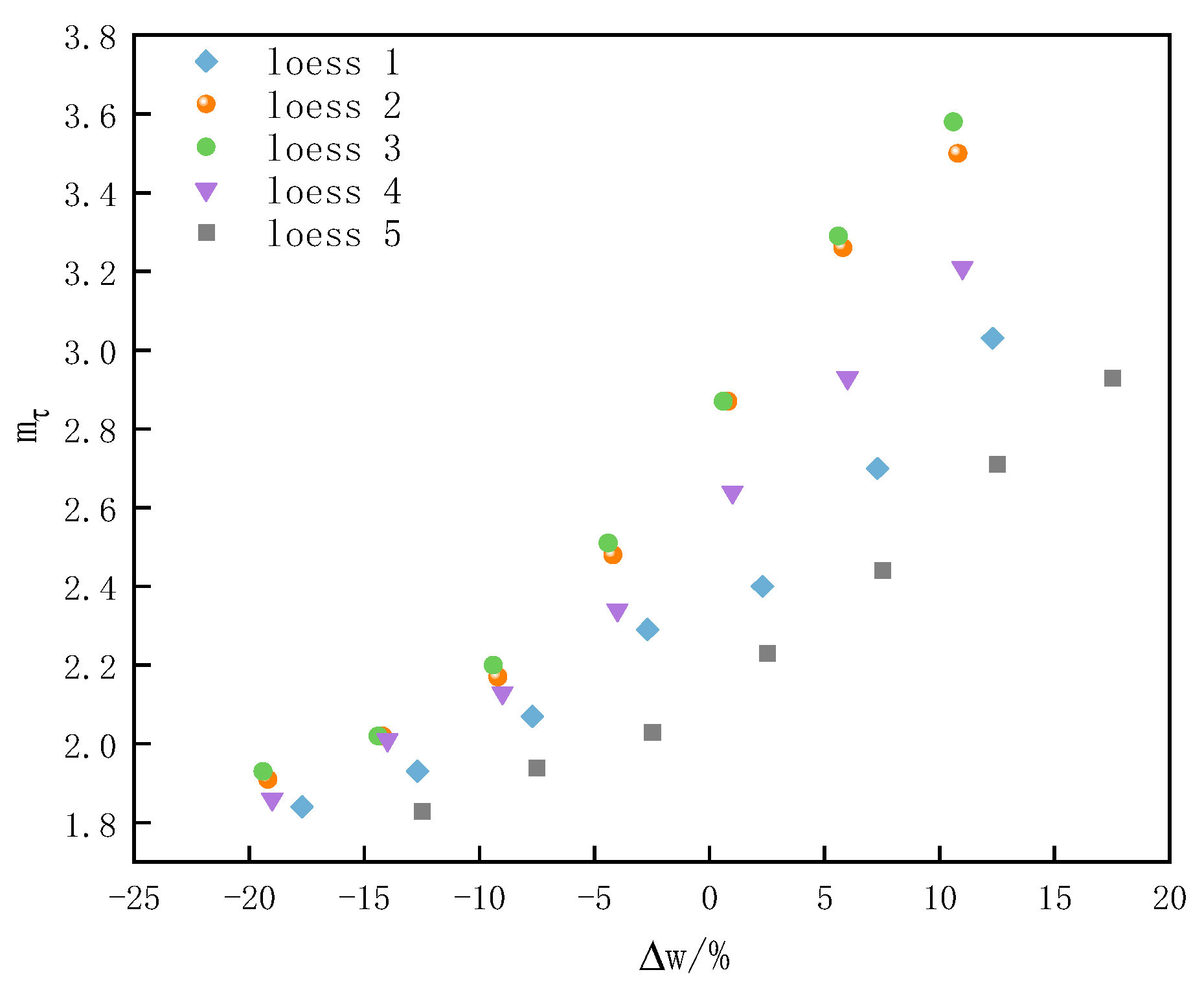


| Extraction Depth (m) | ds ( ) | (%) | (%) | (%) | () | () | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.0 | 2.70 | 9.2 | 30.6 | 18.3 | 12.3 | 1.48 | 1.35 | 1.00 |
| 4.0 | 2.70 | 11 | 27.6 | 16.8 | 10.8 | 1.57 | 1.41 | 0.92 |
| 5.0 | 2.70 | 17 | 34.6 | 16.6 | 18 | 1.66 | 1.42 | 0.91 |
| 6.0 | 2.70 | 16.6 | 28 | 17 | 11 | 1.59 | 1.36 | 0.92 |
| 7.0 | 2.70 | 16.7 | 34.8 | 23.5 | 11.3 | 1.49 | 1.28 | 1.12 |
| Content of Different Particles (%) | Types of Soil | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extraction Depth (m) | Clay Particle (mm) <0.005 | Silt Particle (mm) 0.005~0.075 | Sand Particle (mm) 0.075–2 | |
| 3 m | 18.97 | 80.28 | 0.75 | silty clay |
| 5 m | 17.68 | 80.82 | 1.5 | silty clay |
| 7 m | 19.8 | 77.35 | 2.85 | silty clay |
| Sample Type | () | (%) | Confining Pressure (kPa) | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| undisturbed sample | 1.35, 1.41, 1.42, 1.36, 1.28 | 36, 31, 26, 21, 16, 11, 6 | 100, 200, 300, 400 | 5 × 4 + 7 × 4 |
| remolded sample | 5 × 4 + 7 × 4 |
| (%) | 6% | 11% | 16% | 21% | 26% | 31% | 36% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 153.38 | 142.22 | 110.91 | 111.52 | 94.78 | 87.32 | 84.12 | |
| 43.58 | ||||||||
| 3.52 | 3.26 | 2.87 | 2.56 | 2.17 | 2.00 | 1.93 | ||
| 200 | 255.82 | 236.16 | 180.7 | 190.79 | 168.75 | 158.7 | 154.25 | |
| 79.31 | ||||||||
| 3.22 | 2.98 | 2.64 | 2.41 | 2.13 | 2.00 | 1.94 | ||
| 300 | 354.89 | 324.27 | 245.68 | 268.12 | 239.04 | 229.55 | 223.08 | |
| 116.67 | ||||||||
| 3.04 | 2.78 | 2.48 | 2.30 | 2.05 | 1.97 | 1.91 | ||
| 400 | 444.61 | 415.37 | 319.22 | 344.5 | 312.57 | 299.03 | 290.36 | |
| 154.38 | ||||||||
| 2.88 | 2.69 | 2.44 | 2.23 | 2.02 | 1.94 | 1.88 | ||
| () | 1.28 | 1.35 | 1.36 | 1.41 | 1.42 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 135.61 | 141.33 | 142.22 | 147.02 | 148.99 | |
| 37.88 | 40.15 | 43.58 | 48.52 | 50.85 | ||
| 3.52 | 3.52 | 3.26 | 3.03 | 2.93 | ||
| 200 | 220.15 | 233.58 | 236.16 | 256.39 | 254.02 | |
| 66.31 | 72.54 | 79.31 | 94.26 | 95.14 | ||
| 3.32 | 3.22 | 2.98 | 2.72 | 2.67 | ||
| 300 | 292.91 | 320.36 | 324.27 | 341.73 | 339.86 | |
| 96.67 | 105.38 | 116.67 | 130.43 | 133.28 | ||
| 3.03 | 3.04 | 2.78 | 2.62 | 2.55 | ||
| 400 | 414.12 | 420.05 | 415.37 | 430.37 | 430.97 | |
| 140.38 | 145.85 | 154.38 | 170.78 | 175.19 | ||
| 2.95 | 2.88 | 2.69 | 2.52 | 2.46 | ||
| Confining Pressure | Structural Parameters of Soil Samples with Different Moisture Contents | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6% | 11% | 16% | 20% | 26% | 31% | 36% | |
| 100 | 3.5 | 3.26 | 2.87 | 2.48 | 2.17 | 2.02 | 1.91 |
| 200 | 3.21 | 2.98 | 2.64 | 2.38 | 2.13 | 2.01 | 1.86 |
| 300 | 3.03 | 2.78 | 2.47 | 2.29 | 2.07 | 1.98 | 1.84 |
| 400 | 2.93 | 2.71 | 2.44 | 2.23 | 2.03 | 1.94 | 1.83 |
| Moisture Content | 6% | 11% | 16% | 20% | 26% | 31% | 36% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| coefficient of variation | 0.019 | 0.018 | 0.03 | 0.047 | 0.076 | 0.079 | 0.084 |
| weight value | 0.054 | 0.051 | 0.084 | 0.132 | 0.215 | 0.224 | 0.239 |
| Confining Pressure | Structural Parameters of Soil Samples with Different Dry Densities | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 3.58 | 3.5 | 3.21 | 3.03 | 2.93 |
| 200 | 3.32 | 3.26 | 2.98 | 2.72 | 2.67 |
| 300 | 3.03 | 2.98 | 2.78 | 2.62 | 2.55 |
| 400 | 2.82 | 2.78 | 2.69 | 2.52 | 2.46 |
| Dry Density | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| coefficient of variation | 0.104 | 0.101 | 0.079 | 0.081 | 0.077 |
| weight value | 0.236 | 0.228 | 0.179 | 0.183 | 0.174 |
| Confining Pressure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| coefficient of variation | 0.24 | 0.206 | 0.185 | 0.179 |
| weight value | 0.299 | 0.255 | 0.229 | 0.22 |
| Confining Pressure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| coefficient of variation | 0.088 | 0.1 | 0.076 | 0.06 |
| weight value | 0.271 | 0.309 | 0.235 | 0.185 |
| Interfering Factor | Confining Pressure | Moisture Content | Dry Density |
|---|---|---|---|
| coefficient of variation | 0.288 | 0.579 | 0.268 |
| weight value | 0.254 | 0.51 | 0.236 |
| ranking of evaluation indicators | 2 | 1 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.-J.; Dang, F.-N.; Li, J.-Y. The Parameter of Soil Structural Properties and Their Relationship to Grain Size, Density, and Moisture Content. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041872
Wu X-J, Dang F-N, Li J-Y. The Parameter of Soil Structural Properties and Their Relationship to Grain Size, Density, and Moisture Content. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(4):1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041872
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xiao-Juan, Fa-Ning Dang, and Jia-Yang Li. 2025. "The Parameter of Soil Structural Properties and Their Relationship to Grain Size, Density, and Moisture Content" Applied Sciences 15, no. 4: 1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041872
APA StyleWu, X.-J., Dang, F.-N., & Li, J.-Y. (2025). The Parameter of Soil Structural Properties and Their Relationship to Grain Size, Density, and Moisture Content. Applied Sciences, 15(4), 1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041872





