Sketch-Guided Topology Optimization with Enhanced Diversity for Innovative Structural Design
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Novel sketch-based constraints, including a stroke-based undirected structural boundary constraint and a closed-shape-based regional constraint, are proposed to enable sketch-based TO control.
- Sketch-based constraints and length-scale control of geometric features are integrated, providing multifaceted control strategies to enable fine-grained and flexible control.
- A diversifying method based on random sampling of Fourier mapping frequencies in a neural implicit TO process is proposed, and quantitative studies on different diversifying methods as well as the effects of human control strategies on design quality and diversity are conducted.
- An adaptive parallel computing scale adjustment method is incorporated to improve the efficiency of multiple TO processes.
2. Related Works
2.1. Human Control in Topology Optimization
2.2. Deep Learning-Enhanced Topology Optimization
3. Method
3.1. TO Process with Neural-Encoded Density Function
3.2. Length-Scale Control
3.3. Sketch-Based Constraints
3.4. Parallel Computing for Multi-Solution TO Framework
| Algorithm 1: Pseudo-code of multi-solution TO framework with human controllability and adaptive parallel scale. |
|
4. Experiments
4.1. Experiment Settings
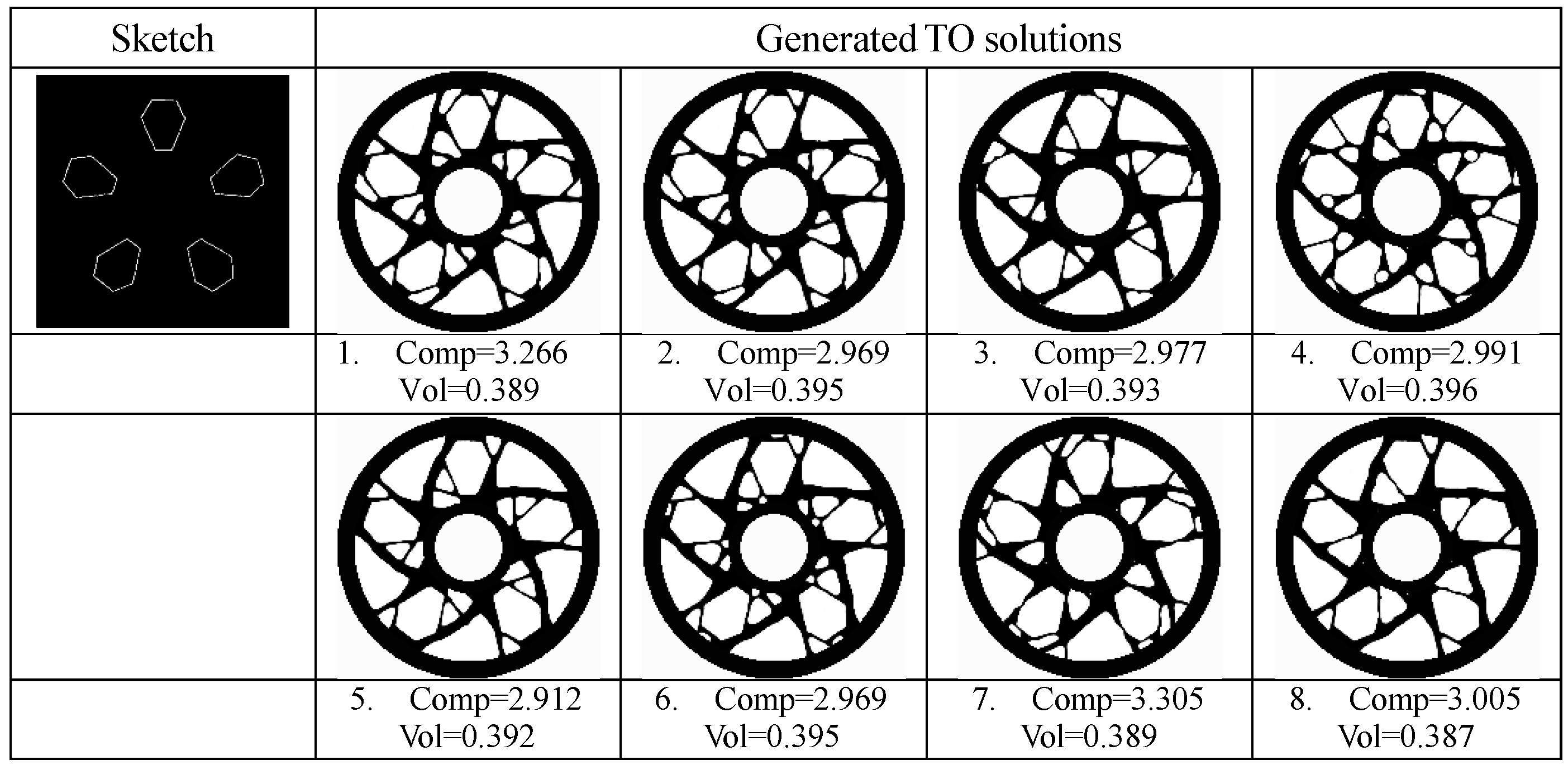
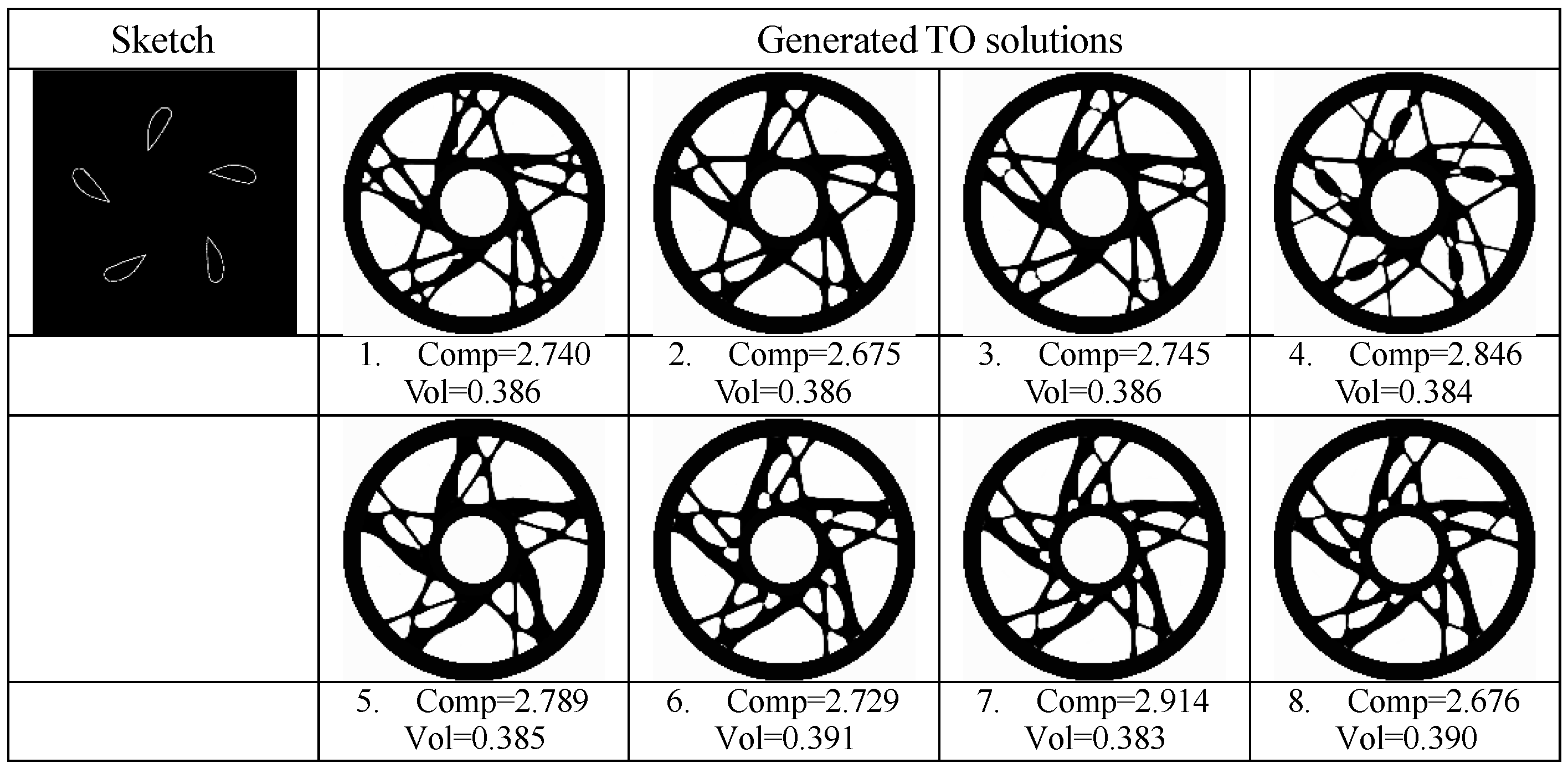
4.2. Experiment for Generating Innovative Structural Designs
4.3. Experiment of Human Controllability
4.4. Impacts of Human Control on Design Quality and Diversity
4.5. Comparative Analysis with Existing Methods
4.6. Analysis of Adaptive-Scale Parallel Computing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amir, O.; Sigmund, O. Reinforcement layout design for concrete structures based on continuum damage and truss topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2013, 47, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, O.; Maute, K. Topology optimization approaches: A comparative review. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2013, 48, 1031–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Jung, Y.; Lee, I.; Kang, N. Design automation by integrating generative adversarial networks and topology optimization. In Proceedings of the ASME International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 26–29 August 2018; Volume 2A, p. V02AT03A008. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Clausen, A.; Sigmund, O. Minimum compliance topology optimization of shell-infill composites for additive manufacturing. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 326, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-H.; Zhang, W.-H.; Xia, L. Topology Optimization in Aircraft and Aerospace Structures Design. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2016, 23, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandersen, J.; Sigmund, O.; Aage, N. Large scale three-dimensional topology optimisation of heat sinks cooled by natural convection. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 100, 876–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilgen, S.B.; Dilgen, C.B.; Fuhrman, D.R.; Sigmund, O.; Lazarov, B.S. Density based topology optimization of turbulent flow heat transfer systems. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2018, 57, 1905–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilgen, C.B.; Dilgen, S.B.; Fuhrman, D.R.; Sigmund, O.; Lazarov, B.S. Topology optimization of turbulent flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 331, 363–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrechtsen, M.; Lahijani, B.V.; Christiansen, R.E.; Nguyen, V.T.H.; Casses, L.N.; Hansen, S.E.; Stenger, N.; Sigmund, O.; Jansen, H.; Mørk, J.; et al. Nanometer-scale photon confinement in topology-optimized dielectric cavities. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, R.E.; Sigmund, O. Inverse design in photonics by topology optimization: Tutorial. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B-Opt. Phys. 2021, 38, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulos, S.; Kazakis, G.; Lagaros, N.D. Conceptual design of structural systems based on topology optimization and prefabricated components. Comput. Struct. 2020, 226, 106136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lee, T.-U.; Xie, Y.M. Interactive Structural Topology Optimization with Subjective Scoring and Drawing Systems. Comput.-Aided Des. 2023, 160, 103532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Yoo, S.; Kang, N. Generative Design by Reinforcement Learning: Enhancing the Diversity of Topology Optimization Designs. Comput.-Aided Des. 2022, 146, 103225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, A.; Suresh, K. Approximate Length Scale Filter in Topology Optimization using Fourier Enhanced Neural Networks. Comput.-Aided Des. 2022, 150, 103277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.Q.; Carstensen, J.V. Human-Informed Topology Optimization: Interactive application of feature size controls. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2023, 66, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, G.; Ha, D.Q.; Carstensen, J.V. HiTop 2.0: Combining topology optimisation with multiple feature size controls and human preferences. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2023, 18, e2268603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Lazarov, B.S.; Wang, F.; Sigmund, O. Minimum length scale in topology optimization by geometric constraints. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 293, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellens, J.; Lombaert, G.; Lazarov, B.; Schevenels, M. Combined length scale and overhang angle control in minimum compliance topology optimization for additive manufacturing. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2019, 59, 2005–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Yarlagadda, T.; Zheng, Y.; Usmani, A. A novel multi-pattern control for topology optimization to balance form and performance needs. Eng. Struct. 2024, 303, 117581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Zhao, Z.-L.; Xie, Y.M. A direct approach to achieving efficient free-form shells with embedded geometrical patterns. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 185, 110559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, J.; Peng, W.; Zhou, W.; Yao, W. Concurrent topology optimization of shells with pattern-guided infills for intuitive design and additive manufacturing. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 418, 116485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Peng, J.; Zhang, D.; Yin, S. Topology optimization of periodic mechanical structures with orthotropic materials based on the element-free Galerkin method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2022, 143, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Du, Z.; Liu, C.; Youn, S.-K.; Guo, X. Machine-learning assisted topology optimization for architectural design with artistic flavor. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2023, 413, 116041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulimiri, P.S.; Deng, H.; Dugast, F.; Zhang, X.; To, A.C. Integrating Geometric Data into Topology Optimization via Neural Style Transfer. Materials 2021, 14, 4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Youn, S.-K.; Guo, X. Machine learning powered sketch aided design via topology optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 419, 116651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Jung, Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, I.; Kang, N. Deep Generative Design: Integration of Topology Optimization and Generative Models. J. Mech. Des. 2019, 141, 111405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Hwang, K.H.; Park, J.H.; Kang, N. Integrating deep learning into CAD/CAE system: Generative design and evaluation of 3D conceptual wheel. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2021, 64, 2725–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C. Intelligent design of key joints in aerial building machine using topology optimization and generative adversarial network. Autom. Constr. 2024, 168, 105747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Guo, D.M. A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2003, 192, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsoe, M.P.; Sigmund, O. Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Arch. Appl. Mech. 1999, 69, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, T.E.; Tortorelli, D.A. Topology optimization of non-linear elastic structures and compliant mechanisms. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2001, 190, 3443–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegard, T.; Paulino, G.H. Bridging topology optimization and additive manufacturing. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2016, 53, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantyghem, G.; De Corte, W.; Shakour, E.; Amir, O. 3D printing of a post-tensioned concrete girder designed by topology optimization. Autom. Constr. 2020, 112, 103084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liang, G.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, S. An explicit formulation for minimum length scale control in density-based topology optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2023, 404, 115761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, Z.-L.; Lin, X.; Xie, Y.M. A hole-filling based approach to controlling structural complexity in topology optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2023, 416, 116391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarov, B.S.; Wang, F.; Sigmund, O. Length scale and manufacturability in density-based topology optimization. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2016, 86, 189–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Punpongsanon, P.; Iwai, D.; Sato, K. Topology optimization with text-guided stylization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2023, 66, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Pouyanfar, S.; Sadiq, S.; Yan, Y.; Tian, H.; Tao, Y.; Reyes, M.P.; Shyu, M.-L.; Chen, S.-C.; Iyengar, S.S. A Survey on Deep Learning: Algorithms, Techniques, and Applications. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 51, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Lin, T.; Jiang, H.; Kara, L.B. TopologyGAN: Topology Optimization Using Generative Adversarial Networks Based on Physical Fields Over the Initial Domain. J. Mech. Des. 2021, 143, 031715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maze, F.; Ahmed, F. Diffusion Models Beat GANs on Topology Optimization. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 9108–9116. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Hur, T.; Jung, J.; Jang, I.G. Deep learning for determining a near-optimal topological design without any iteration. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2019, 59, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; He, Z.; Liu, H. Generating three-dimensional structural topologies via a U-Net convolutional neural network. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021, 159, 107263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, A.; Suresh, K. TOuNN: Topology Optimization using Neural Networks. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2021, 63, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Joglekar, A.; Kara, L.B. Topology Optimization Using Neural Networks With Conditioning Field Initialization for Improved Efficiency. J. Mech. Des. 2024, 146, 061702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Melkote, S.; Rosen, D.W. Generative Design by Embedding Topology Optimization into Conditional Generative Adversarial Network. J. Mech. Des. 2023, 145, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Ye, W.; Gao, Y. A 3D Structure Mapping-Based Efficient Topology Optimization Framework. J. Mech. Des. 2023, 145, 081703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Ye, W. Accelerating gradient-based topology optimization design with dual-model artificial neural networks. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2021, 63, 1687–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wen, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Dynamically configured physics-informed neural network in topology optimization applications. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 426, 117004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Nichol, A.; Dhariwal, P. Improved Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. 2021, 139, 116041. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Med. Image Comput. Comput.-Assist. Interv. 2015, 9351, 234–241. [Google Scholar]

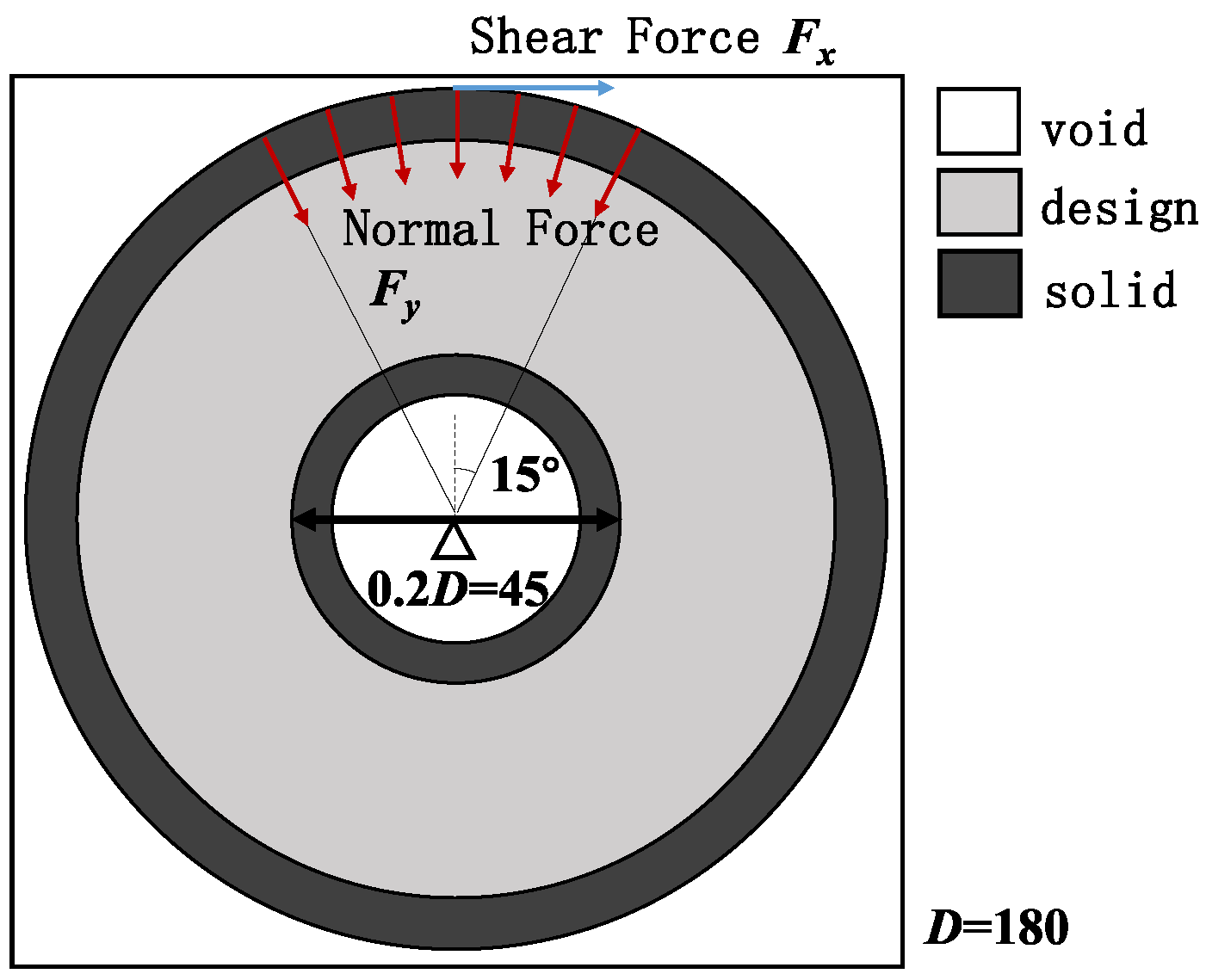



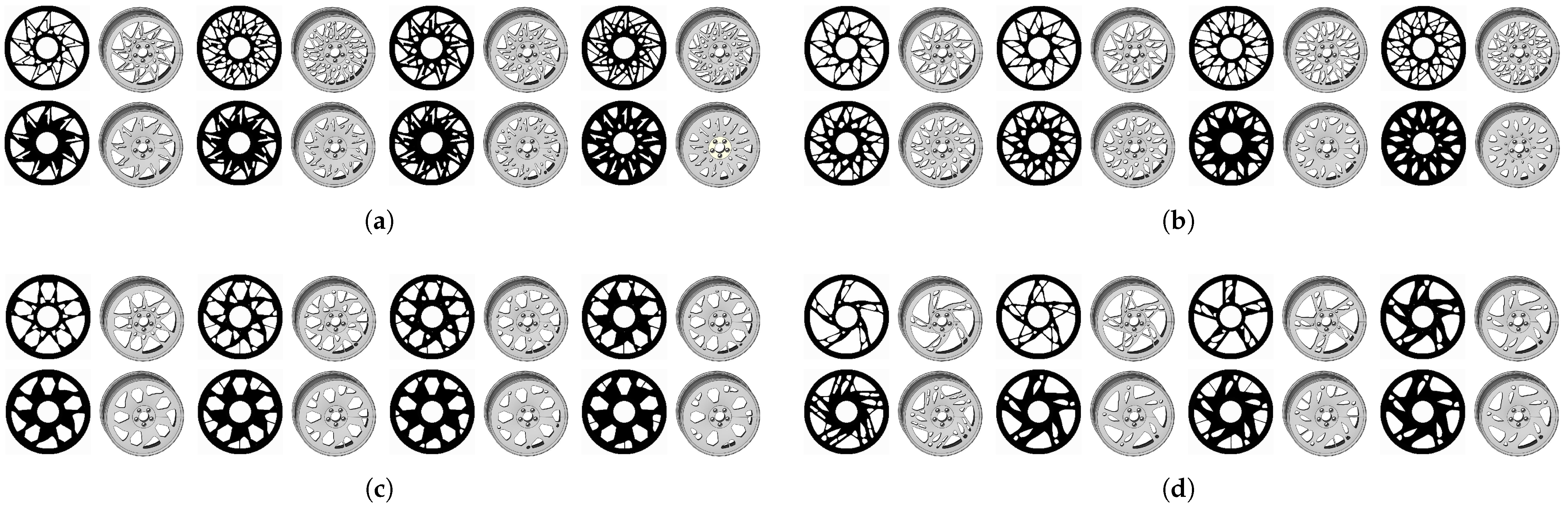
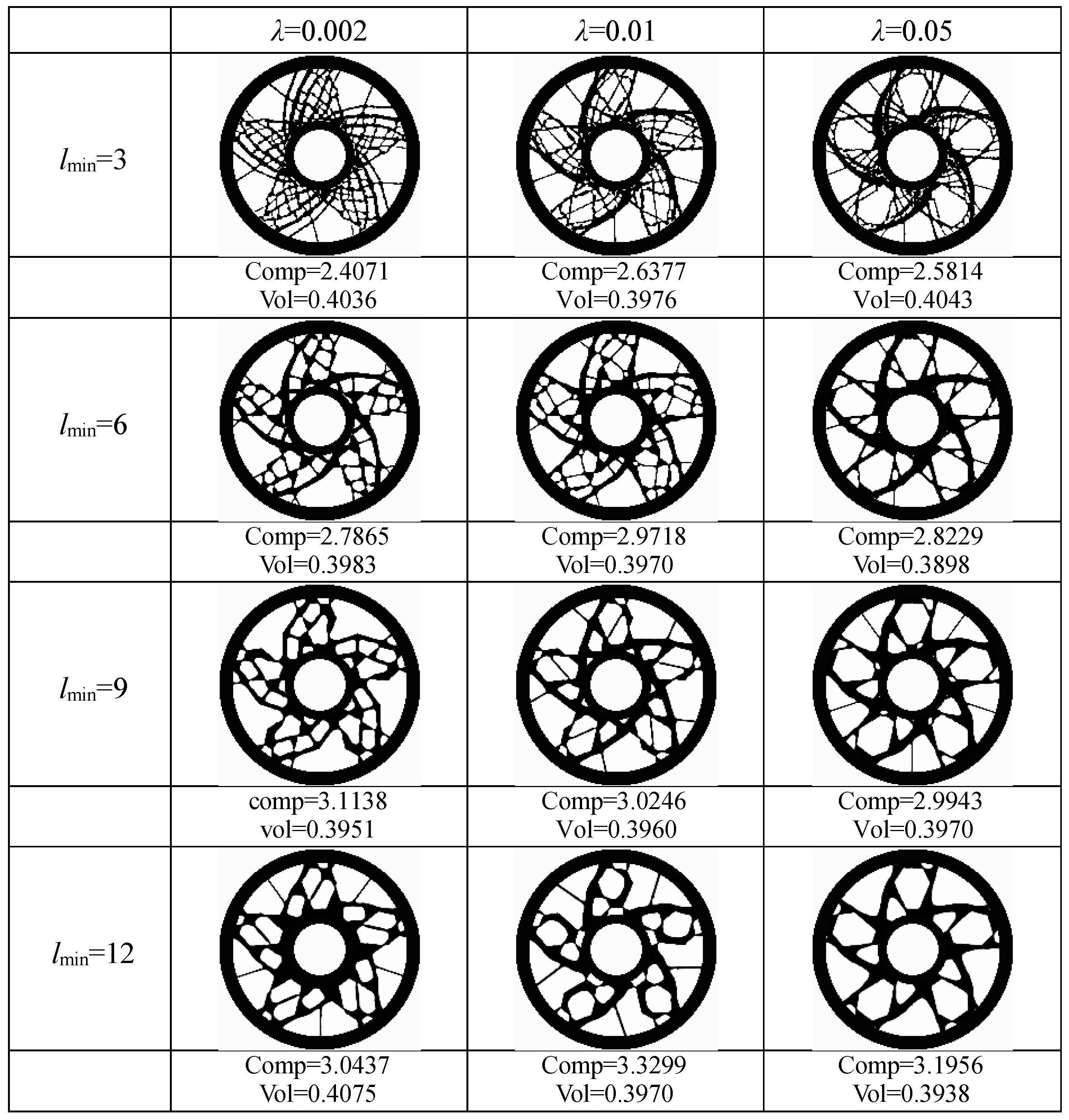



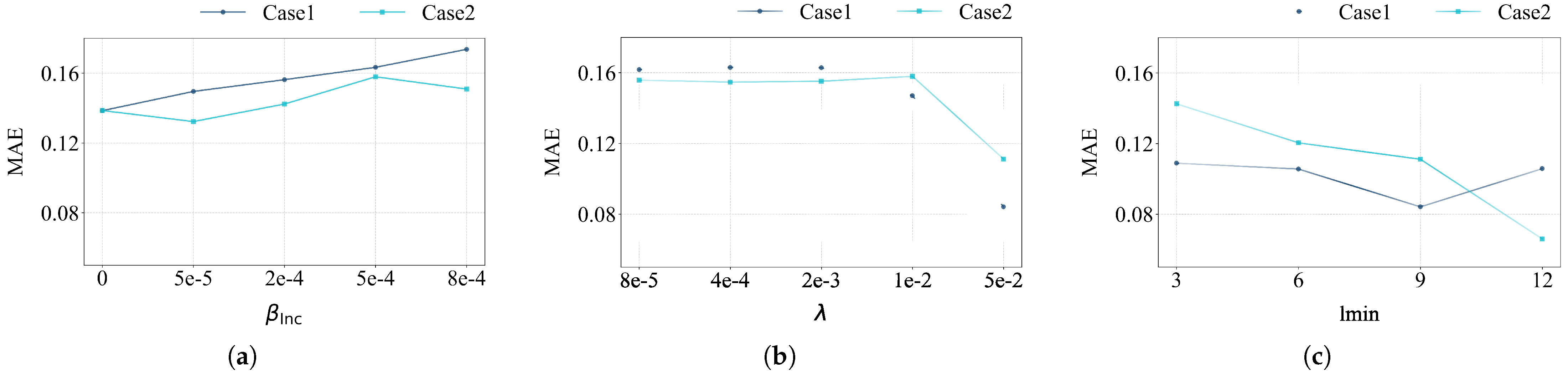

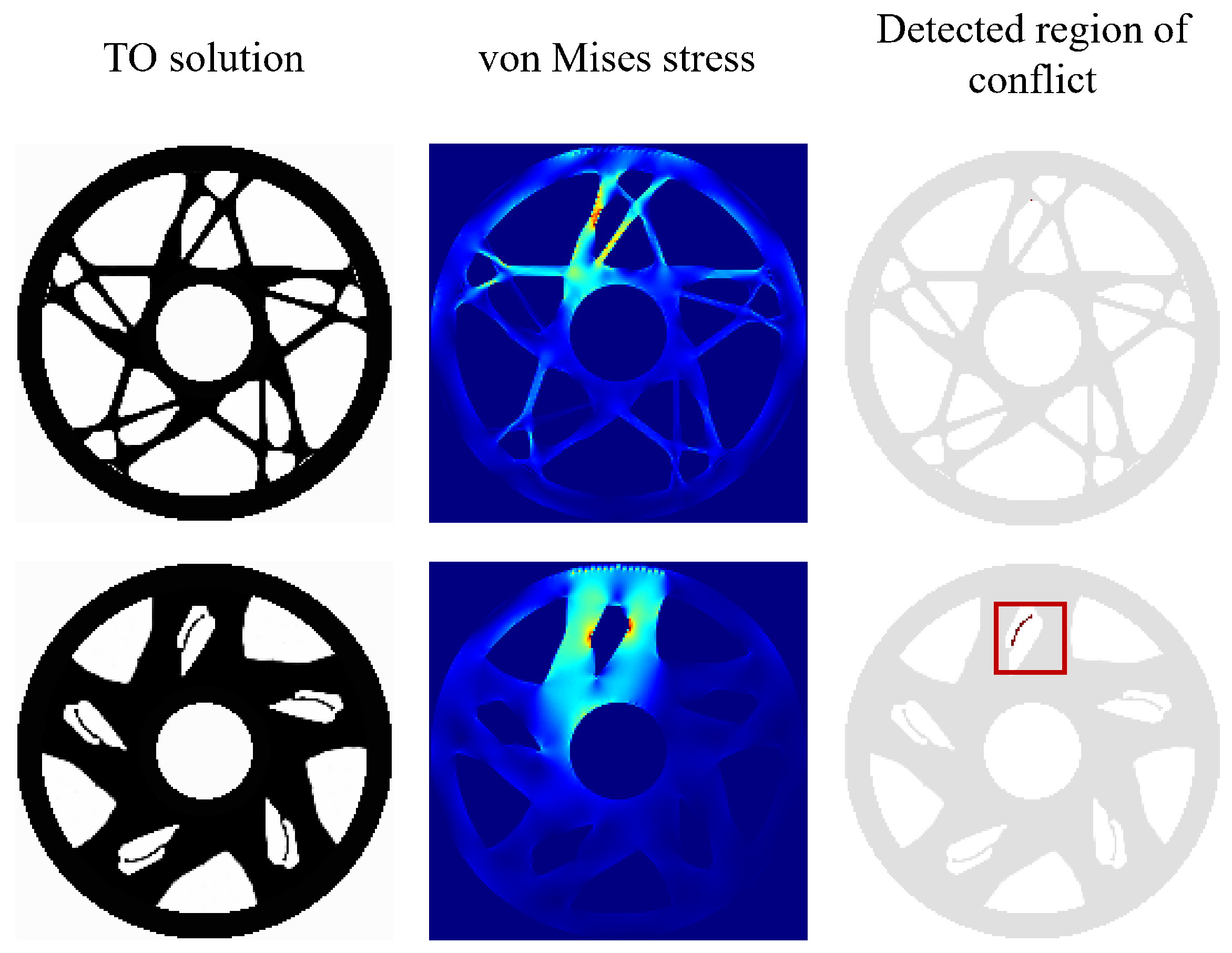
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Desired volume | 0.35 | 30 | 100 | ||
| NN layers | 1 × (100,) | n | 5 | 1 | |
| 180 | M | 20 | 0.1 | ||
| 9 | 0.3 | 6 | |||
| 80 | 5 × | E | 1 | ||
| 1000 | 5 × | Nu | 0.3 | ||
| 30 | 0.04 |
| Case 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Setting | ||||||
| = 0 | 2.5831 | 0.3892 | 0.0204 | 0.0074 | 0.6461 | 0.1385 |
| 3.1602 | 0.3970 | 0.0687 | 0.0111 | 0.6069 | 0.1634 | |
| , = 0.05 | 3.1263 | 0.3948 | 0.0523 | 0.0073 | 0.7585 | 0.0841 |
| , = 0.05, = 12 | 3.4158 | 0.3952 | 0.0798 | 0.0068 | 0.7170 | 0.1058 |
| Case 2 | ||||||
| Setting | ||||||
| = 0 | 2.5979 | 0.3884 | 0.0230 | 0.0079 | 0.6457 | 0.1386 |
| 2.9896 | 0.3919 | 0.0939 | 0.0094 | 0.6199 | 0.1579 | |
| , = 0.1 | 2.8207 | 0.3894 | 0.0558 | 0.0070 | 0.7235 | 0.1111 |
| , = 0.1, = 12 | 2.9787 | 0.3928 | 0.0565 | 0.0138 | 0.8138 | 0.0659 |
| Setting | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density perturb (amp = 0) | 3.1164 | 0.3960 | 0.0151 | 0.0033 | 0.9731 | 0.0097 |
| Density perturb (amp = 0.1) | 3.3117 | 0.4019 | 0.0204 | 0.0047 | 0.9084 | 0.0207 |
| Density perturb (amp = 0.4) | 3.8991 | 0.4382 | 0.0192 | 0.0049 | 0.7358 | 0.0663 |
| Load cond perturb | 3.0322 | 0.3955 | 0.0243 | 0.0067 | 0.8700 | 0.0399 |
| Fourier freq perturb | 3.0322 | 0.3955 | 0.0298 | 0.0067 | 0.8641 | 0.0411 |
| Proposed | 3.0322 | 0.3955 | 0.0317 | 0.0075 | 0.8339 | 0.0516 |
| Setting | Time (s) | Num | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/Ad M = 50 | 3060.7 | 50 | 2.7101 | 0.3887 | 0.0264 | 0.0058 | 0.8428 | 0.0488 |
| filtered | / | 23 | 2.7320 | 0.3895 | 0.0320 | 0.0063 | 0.8110 | 0.0601 |
| N/A M = 40 | 2448.6 | 40 | 2.7164 | 0.3888 | 0.0253 | 0.0060 | 0.8453 | 0.0477 |
| filtered | / | 19 | 2.7391 | 0.3897 | 0.0313 | 0.0065 | 0.8170 | 0.0578 |
| N/Ad M = 30 | 1836.4 | 30 | 2.7190 | 0.3888 | 0.0273 | 0.0058 | 0.8473 | 0.0472 |
| filtered | / | 16 | 2.7415 | 0.3894 | 0.0330 | 0.0065 | 0.8241 | 0.0555 |
| Ad N = 50 | 1810.4 | 16 | 2.7267 | 0.3891 | 0.0278 | 0.0054 | 0.8041 | 0.0617 |
| filtered | / | 16 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, S.; Hu, J.; Qi, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Ma, J.; Zhu, G. Sketch-Guided Topology Optimization with Enhanced Diversity for Innovative Structural Design. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052753
Zhu S, Hu J, Qi J, Wang L, Guo J, Ma J, Zhu G. Sketch-Guided Topology Optimization with Enhanced Diversity for Innovative Structural Design. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(5):2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052753
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Siyu, Jie Hu, Jin Qi, Lingyu Wang, Jing Guo, Jin Ma, and Guoniu Zhu. 2025. "Sketch-Guided Topology Optimization with Enhanced Diversity for Innovative Structural Design" Applied Sciences 15, no. 5: 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052753
APA StyleZhu, S., Hu, J., Qi, J., Wang, L., Guo, J., Ma, J., & Zhu, G. (2025). Sketch-Guided Topology Optimization with Enhanced Diversity for Innovative Structural Design. Applied Sciences, 15(5), 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15052753






