Generative Architectural Design from Textual Prompts: Enhancing High-Rise Building Concepts for Assisting Architects
Abstract
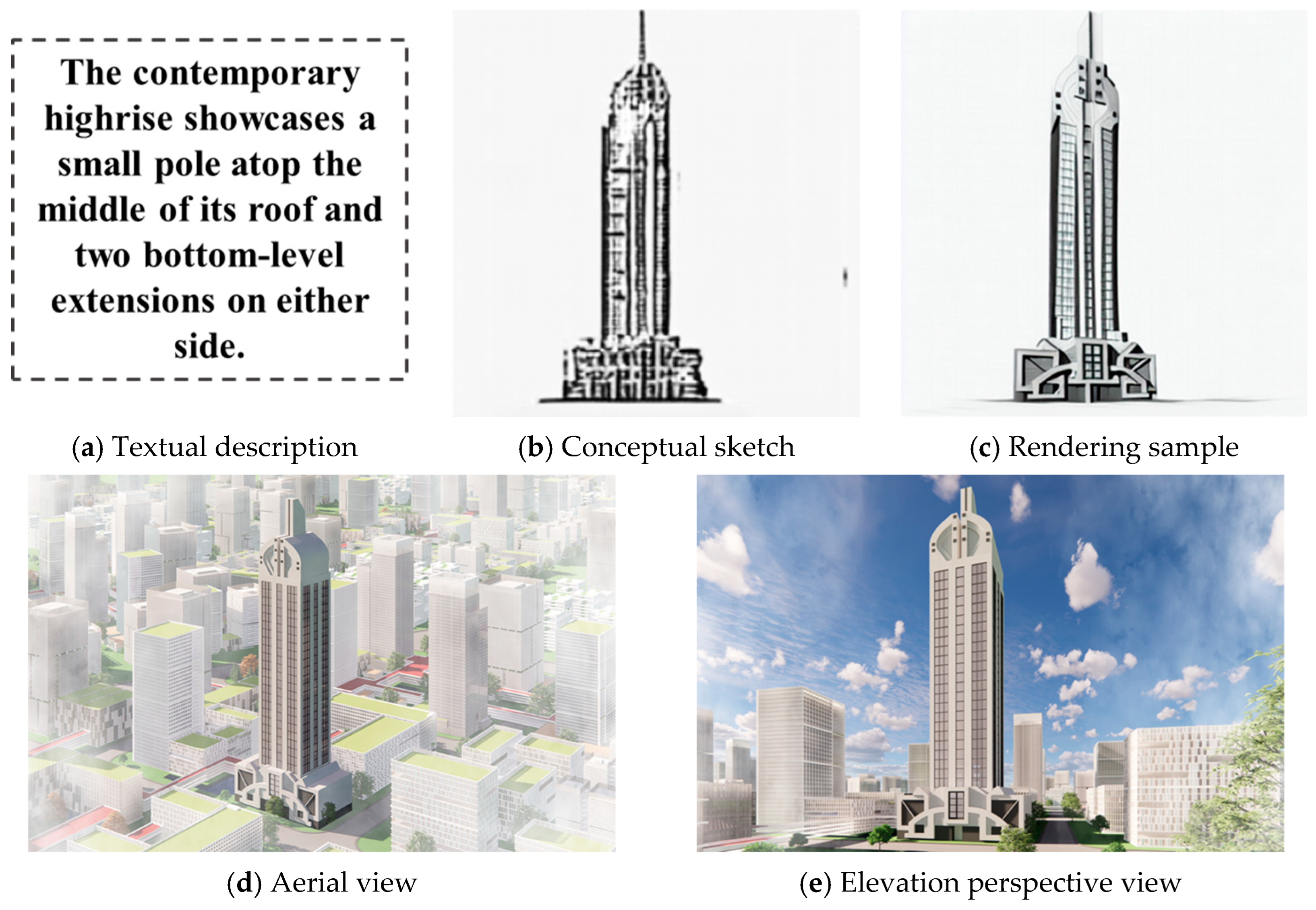
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
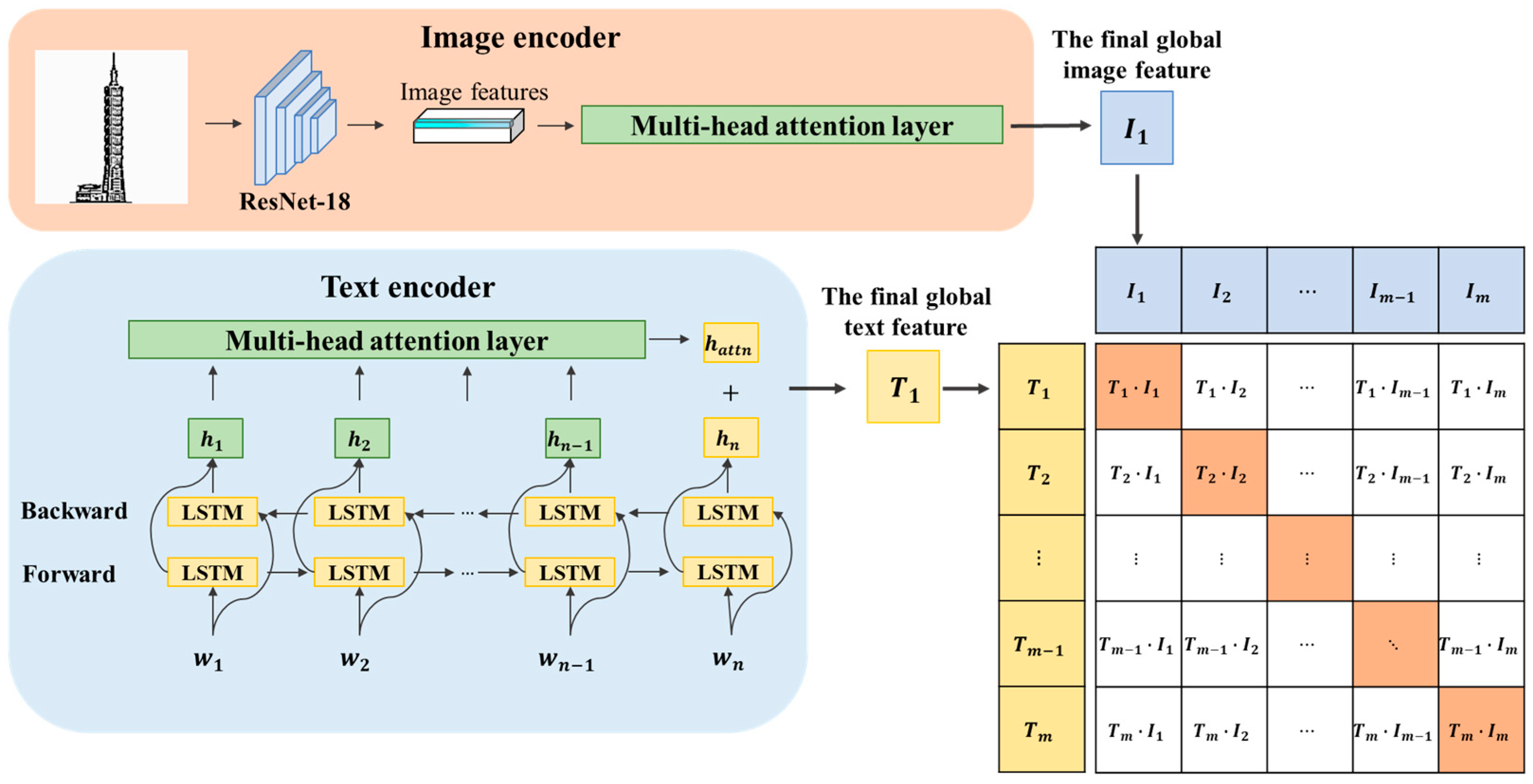
2.1. Design Concept Extraction Module
| Algorithm 1. Pseudocode for the training of the CTIMM. |
| Contrastive text–image matching model: AdamW optimizer with , , ; CosineAnnealingWarmRestarts lr_scheduler with . |
| 1: Extract the features of sketch and textual description |
| 2: Normalization with L2 norm |
| 3: Calculate the cosine similarities |
| 4: Calculate the loss |
| # is a learnable parameter |
| # CosineAnnealingWarmRestarts refers to Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts. |
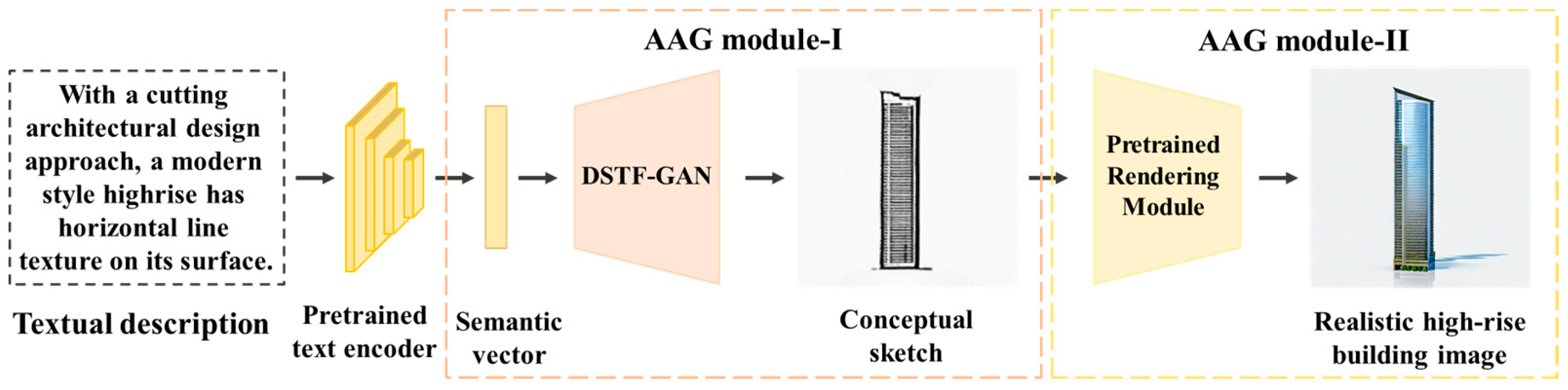
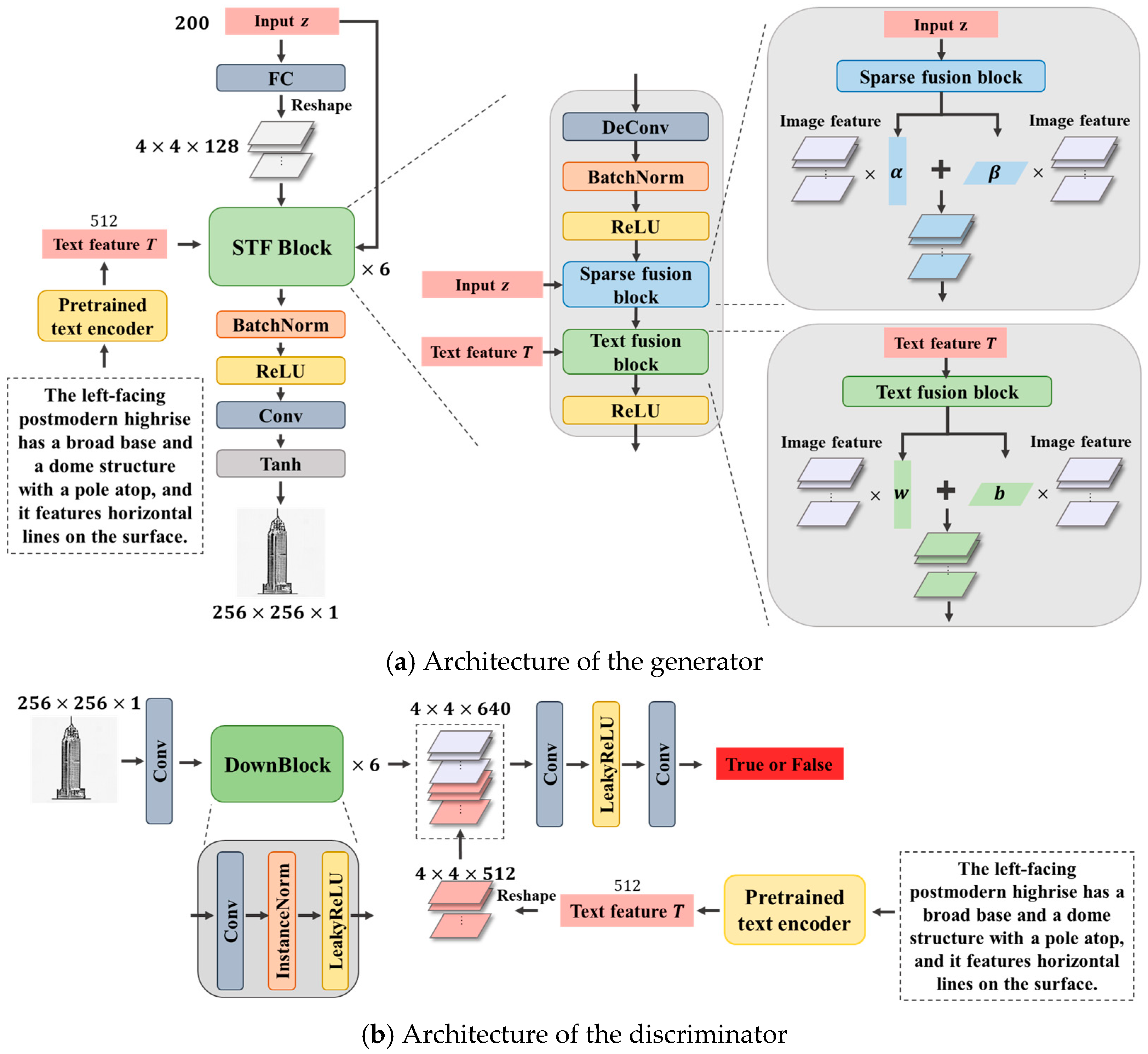
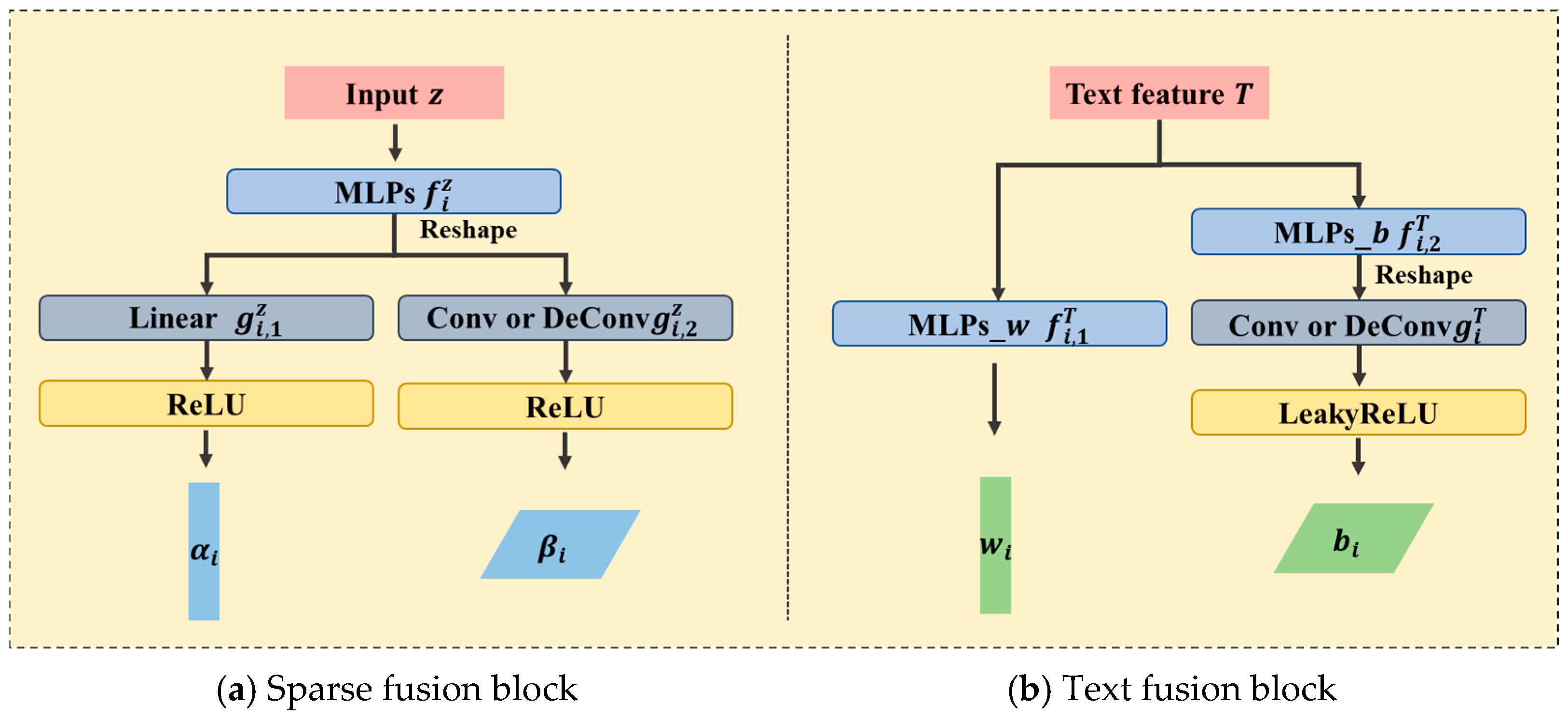
2.2. Architectural Appearance Generation Module
| Algorithm 2. Pseudocode for the training of DSTF-GAN. |
| Deep sparse and text fusion generative adversarial network: Adam optimizer with |
| 1: Initialize discriminator parameters and generator parameters |
| 2: for number of training epoch do |
| 3: sampling real data pairs , latent variables |
| 4: extract semantics: |
| 5: calculate loss function: |
| 6: update the discriminator parameters: |
| 7: sampling latent variables |
| 8: calculate loss function: |
| 9: update the discriminator: |
| 10: end for |
| # is pre-trained from the Contrastive text–image matching model |
3. Experiments and Results
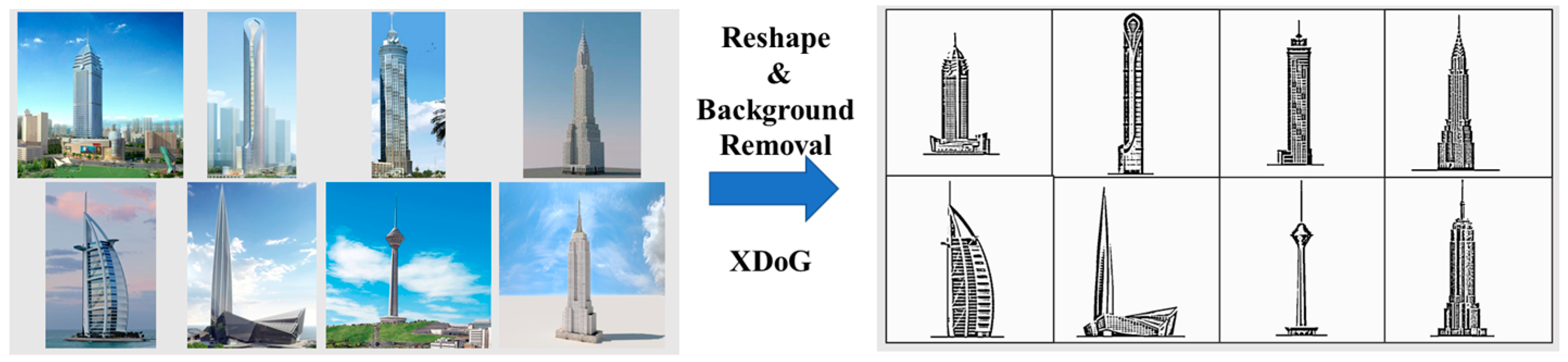
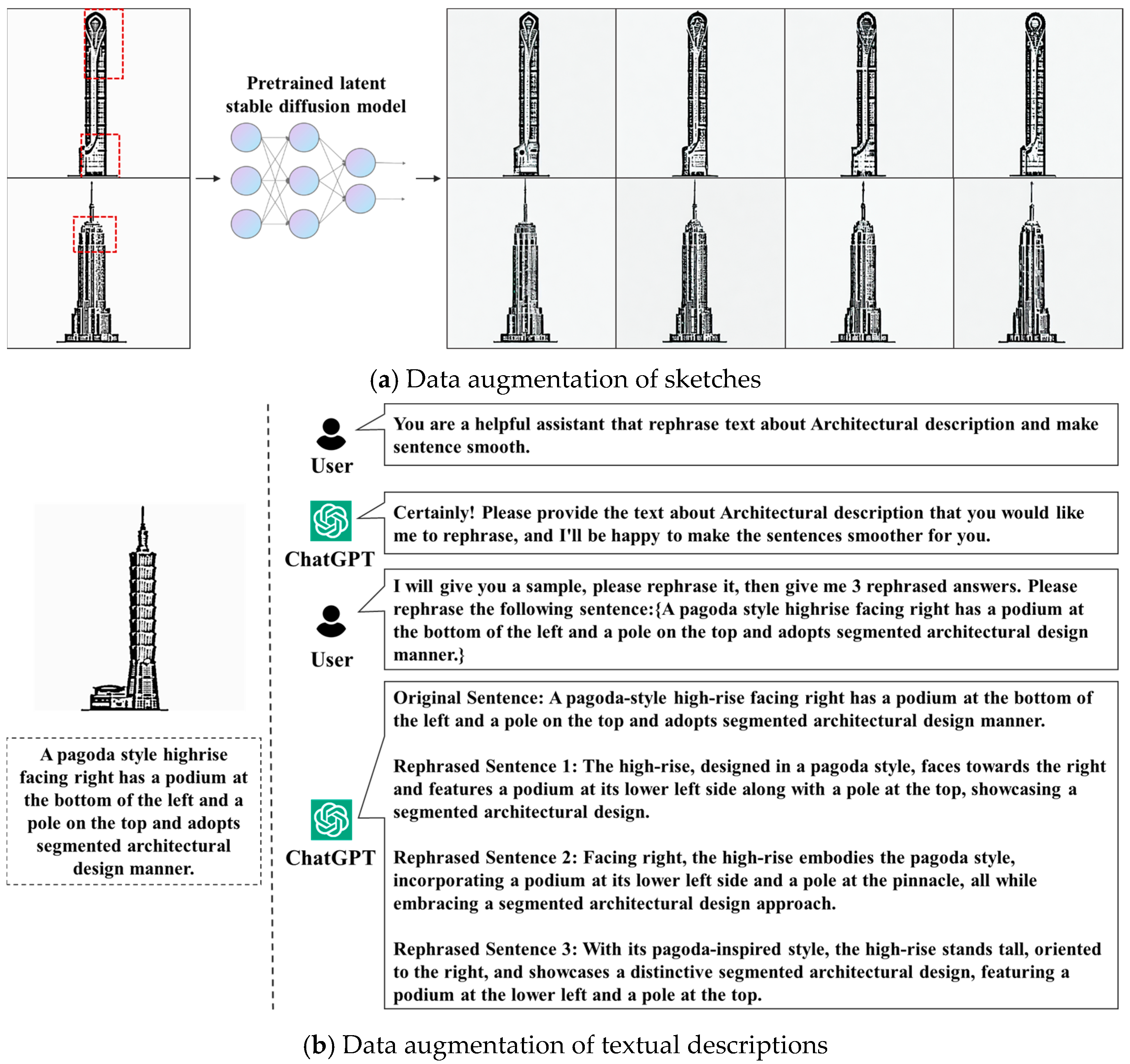
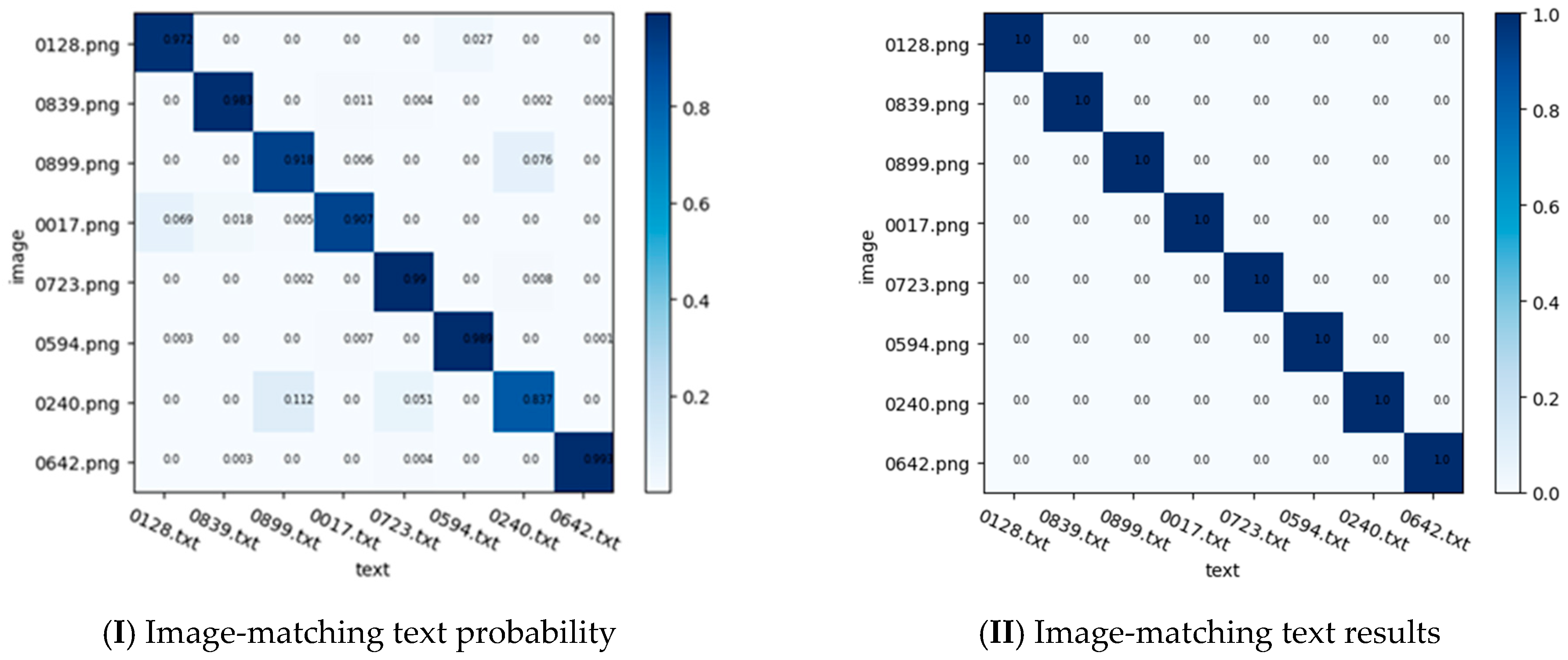
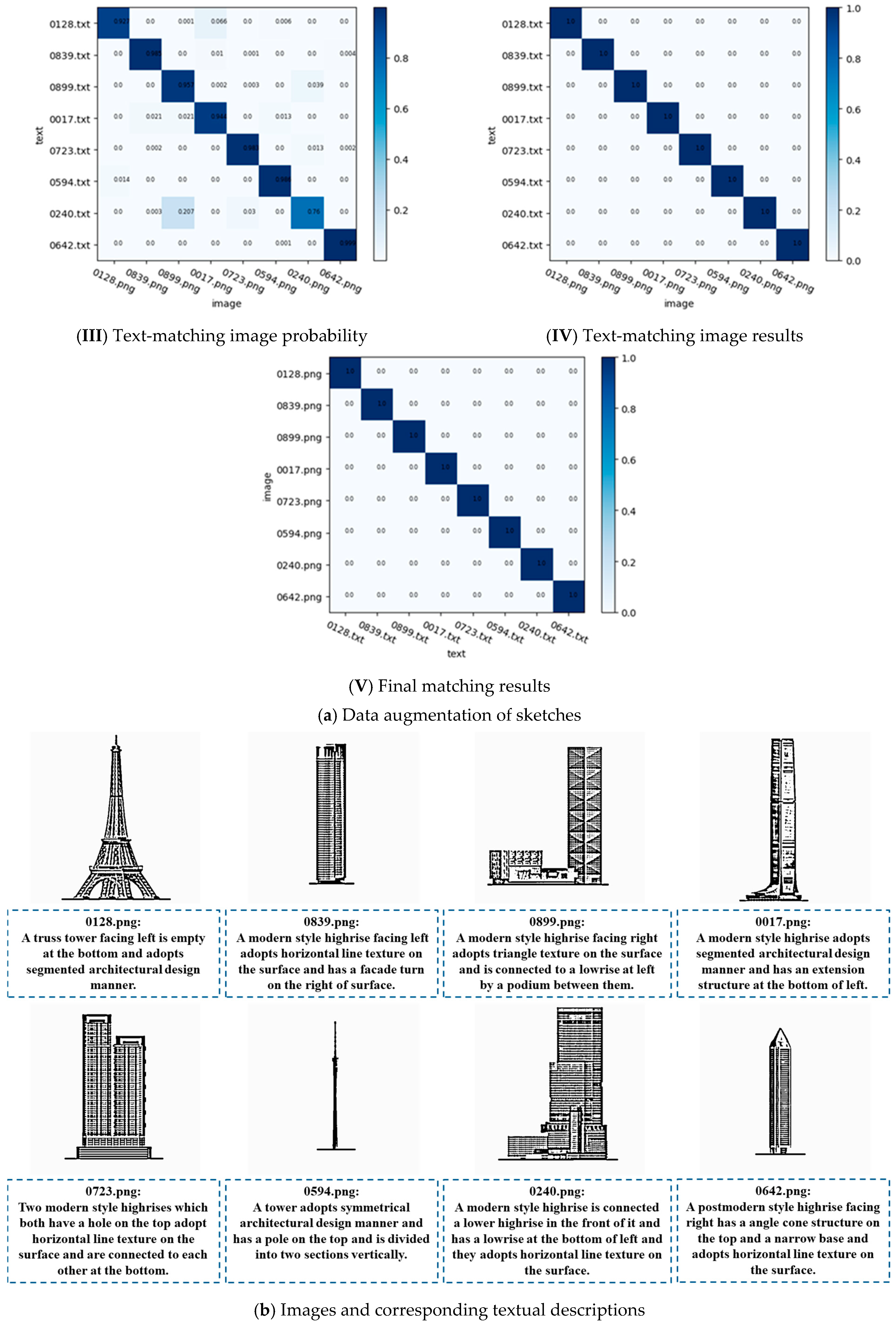
3.1. Sketch–Text Dataset
3.2. Training Details
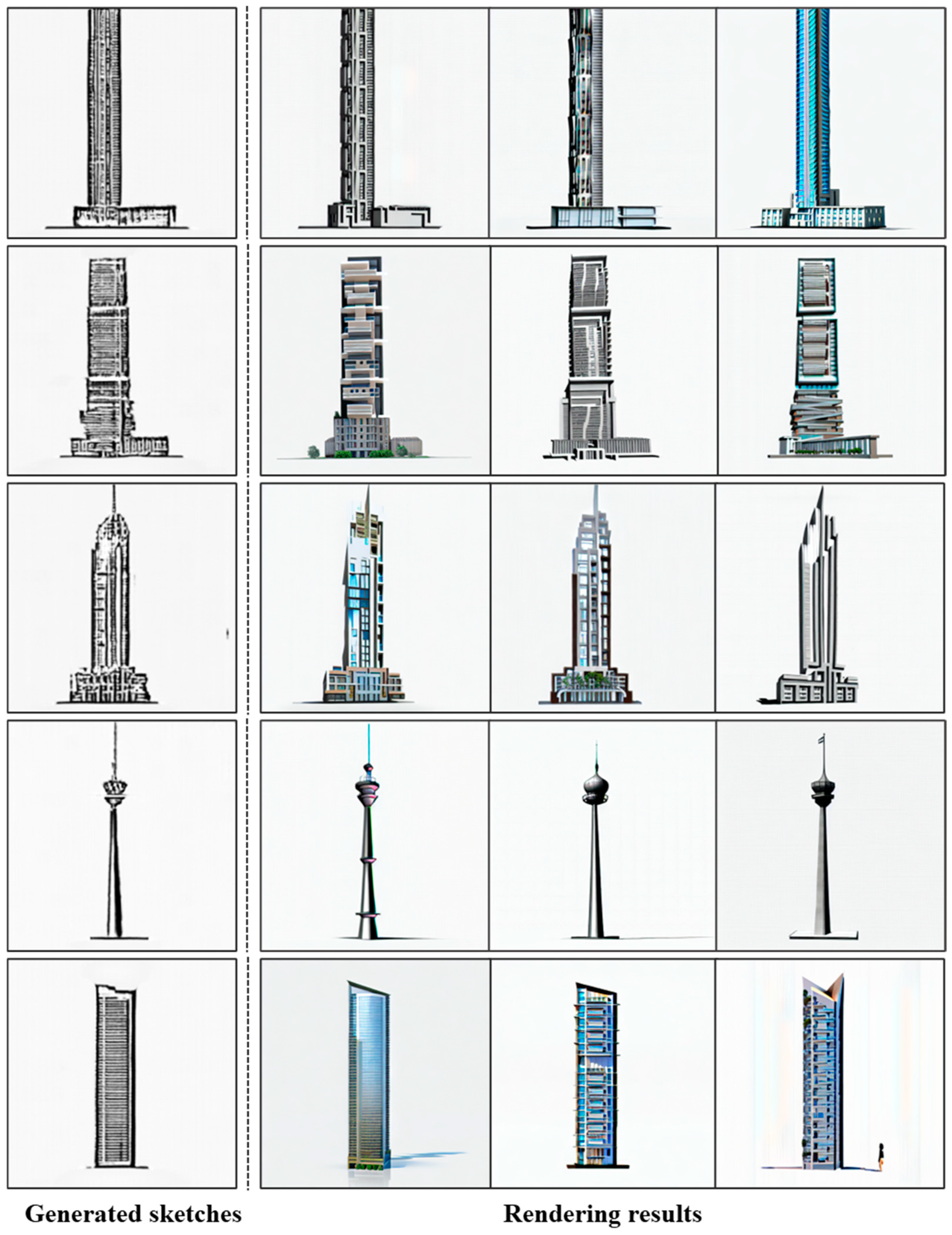
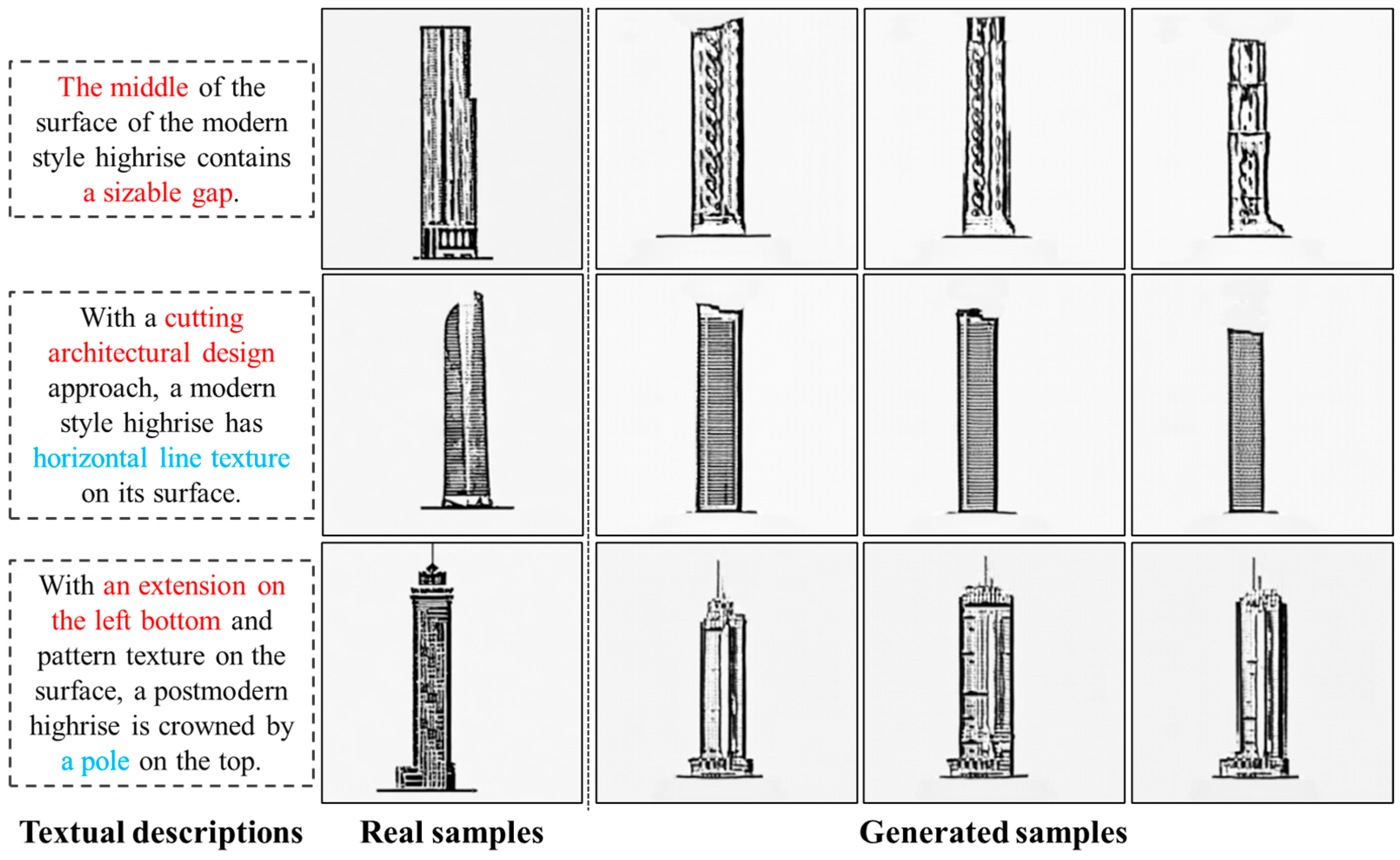
3.3. Experimental Results
4. Discussion
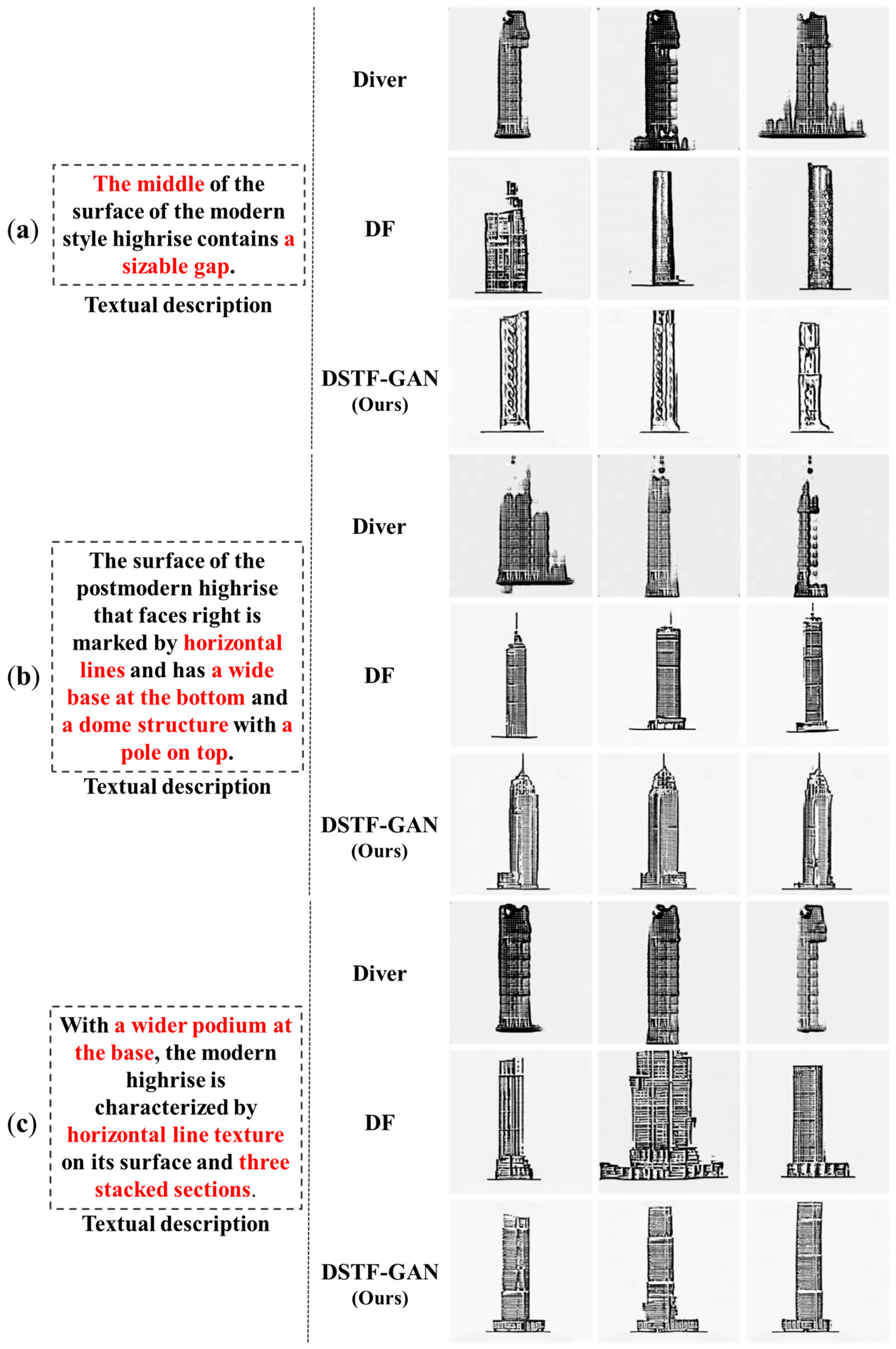
4.1. Comparison of Different Text Fusion Methods
4.2. Component Analysis
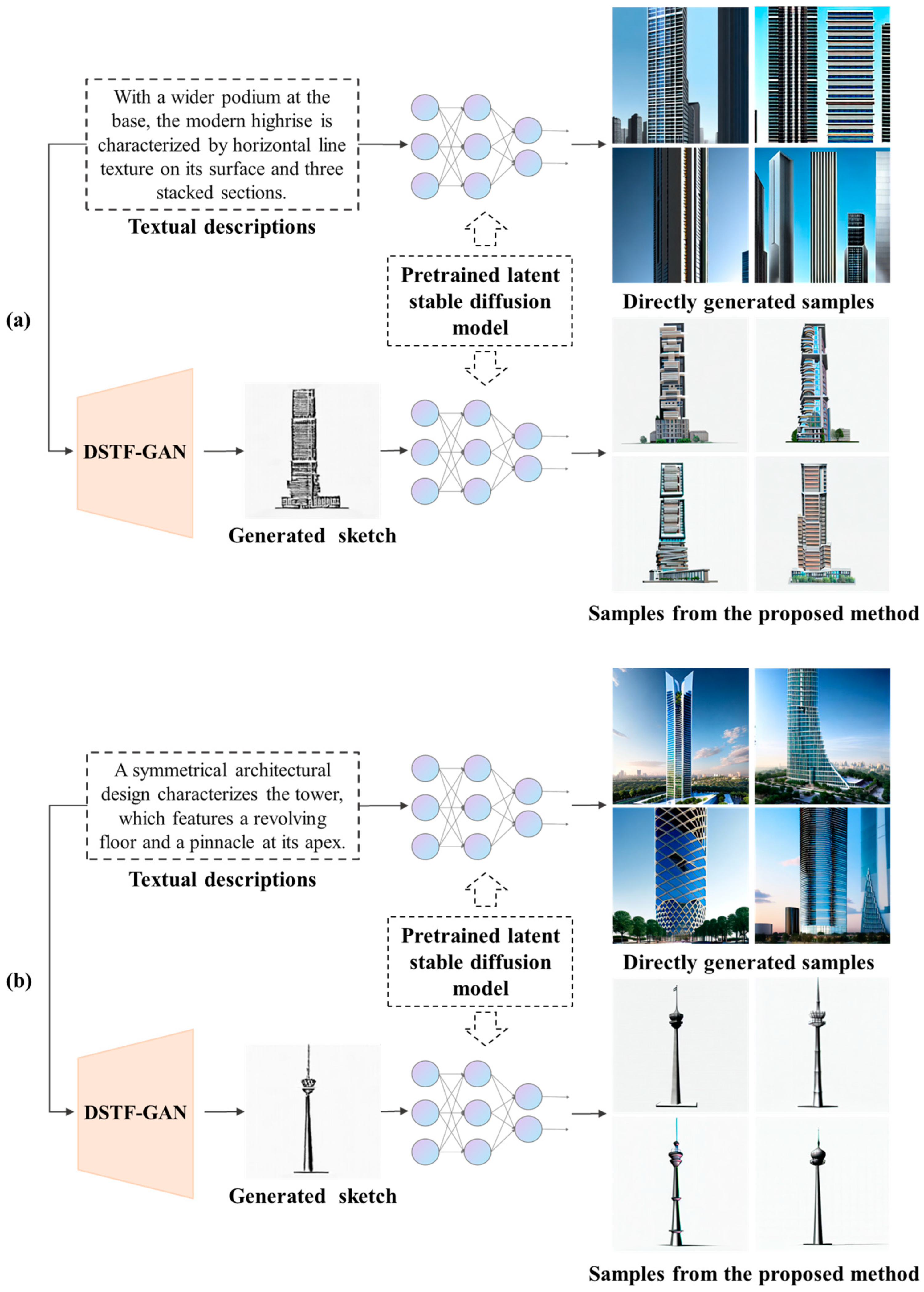
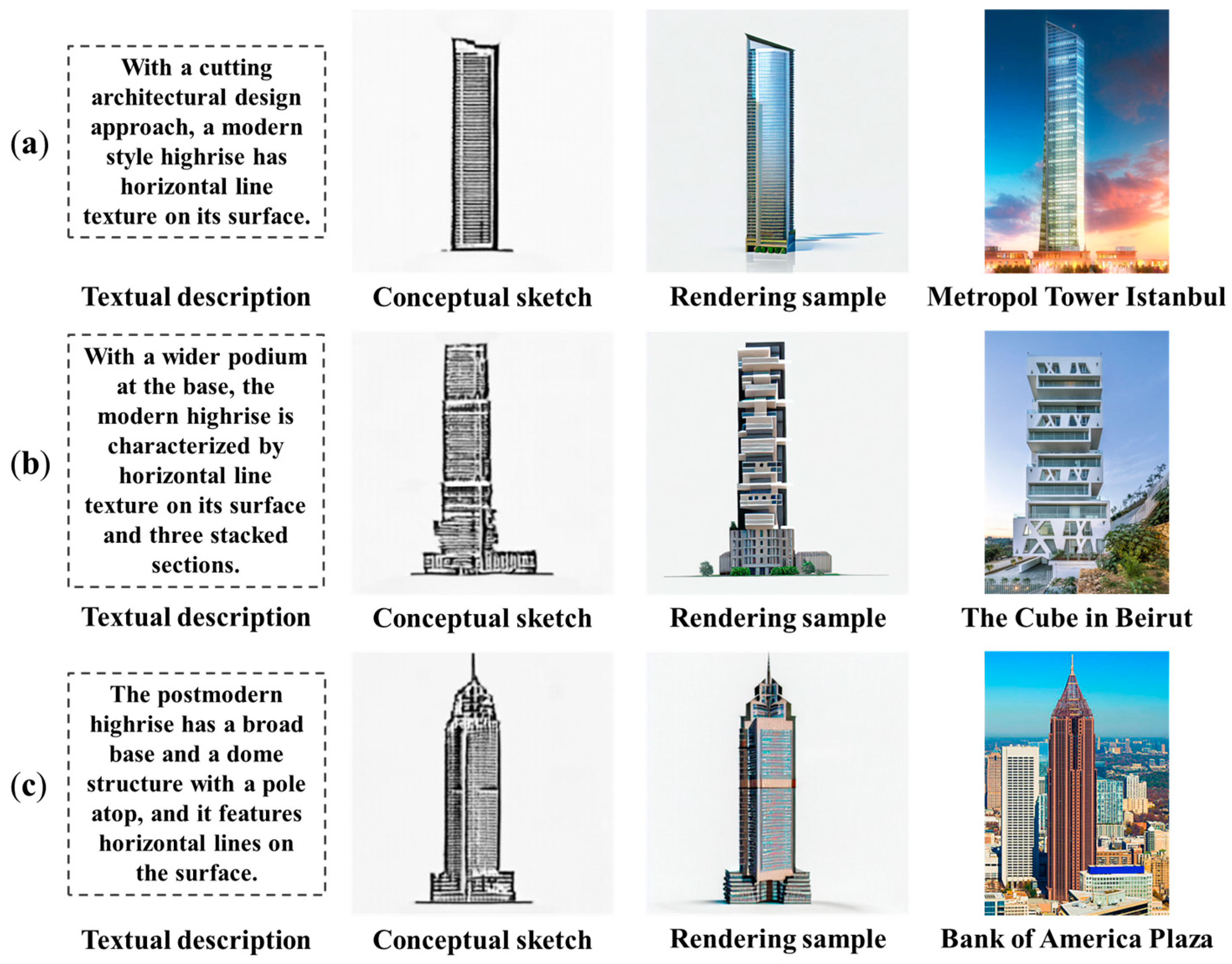
5. Application
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Linear: | Conv. , stride = 1, padding = 1 |
| DeConv. , stride = 2, padding = 1, BN-128, ReLU, Sparse Fusion Block, Text Fusion Block, ReLU | Conv. , stride = 2, padding = 1, BN-128, LeakyReLU |
| DeConv. , stride = 2, padding = 1, BN-128, ReLU, Sparse Fusion Block, Text Fusion Block, ReLU | Conv. , stride = 2, padding = 1, BN-128, LeakyReLU |
| DeConv. , stride = 2, padding = 1, BN-128, ReLU, Sparse Fusion Block, Text Fusion Block, ReLU | Conv. , stride = 2, padding = 1, BN-128, LeakyReLU |
| DeConv. , stride = 2, padding = 1, BN-128, ReLU, Sparse Fusion Block, Text Fusion Block, ReLU | Conv. , stride = 2, padding = 1, BN-128, LeakyReLU |
| DeConv. , stride = 2, padding = 1, BN-128, ReLU, Sparse Fusion Block, Text Fusion Block, ReLU | Conv. , stride = 2, padding = 1, BN-128, LeakyReLU |
| DeConv. , stride = 2, padding = 1, BN-128, ReLU, Sparse Fusion Block, Text Fusion Block, ReLU | Conv. , stride = 2, padding = 1, BN-128, LeakyReLU |
| BN-128, ReLU, Conv. , stride = 1, padding = 1, Tanh | Conv. , stride = 1, padding = 1, LeakyReLU, Conv. , stride = 1, padding = 0 |
| ReLU ReLU ReLU | LeakyReLU LeakyReLU | Linear: LeakyReLU | |
| Linear: 512 | Conv or DeConv: | Conv or DeConv: | |
| ReLU | ReLU | LeakyReLU | |

References
- Menezes, A.; Lawson, B. How designers perceive sketches. Des. Stud. 2006, 27, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y. The methodology for evaluating the fire resistance performance of concrete-filled steel tube columns by integrating conditional tabular generative adversarial networks and random oversampling. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 97, 110824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Zong, S.; Zhu, S. A fast-response-generation method for single-layer reticulated shells based on implicit parameter model of generative adversarial networks. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 72, 106563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wang, W.; Gao, Y. Physical rule-guided generative adversarial network for automated structural layout design of steel frame-brace structures. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 86, 108943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Yuan, C.; Li, P.; Kong, Q. Damage analysis and quantification of RC beams assisted by Damage-T Generative Adversarial Network. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 117, 105536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauata, N.; Chang, K.-H.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Mori, G.; Furukawa, Y. House-Gan: Relational Generative Adversarial Networks for Graph-Constrained House layout Generation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part I 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 162–177. [Google Scholar]
- Nauata, N.; Hosseini, S.; Chang, K.-H.; Chu, H.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Furukawa, Y. House-gan++: Generative adversarial layout refinement network towards intelligent computational agent for professional architects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 13632–13641. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.-H.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Luo, J.; Murata, S.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Tsuji, Y. Building-GAN: Graph-conditioned architectural volumetric design generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 11956–11965. [Google Scholar]
- Ghannad, P.; Lee, Y.-C. Automated modular housing design using a module configuration algorithm and a coupled generative adversarial network (CoGAN). Autom. Constr. 2022, 139, 104234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-Y.; Tuzel, O. Coupled Generative Adversarial Networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Lee, D., Sugiyama, M., Luxburg, U., Guyon, I., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, W.; Lu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, Y. Automated structural design of shear wall residential buildings using generative adversarial networks. Autom. Constr. 2021, 132, 103931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Gao, Y.; Wang, W. Dual generative adversarial networks for automated component layout design of steel frame-brace structures. Autom. Constr. 2023, 146, 104661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhou, Y.; Han, Y. Automatic generation of architecture facade for historical urban renovation using generative adversarial network. Build. Environ. 2022, 212, 108781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.; Xu, Y.; Zuo, W.; Li, H. Self sparse generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.10556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, H. A self-sparse generative adversarial network for autonomous early-stage design of architectural sketches. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2022, 37, 612–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Yang, F.; Mei, H.; Li, H. Artificial intelligence-designer for high-rise building sketches with user preferences. Eng. Struct. 2023, 275, 115171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, S.; Akata, Z.; Yan, X.; Logeswaran, L.; Schiele, B.; Lee, H. Generative adversarial text to image synthesis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 1060–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Metaxas, D. Stackgan: Text to photo-realistic image synthesis with stacked generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5907–5915. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, X. Stackgan++: Realistic image synthesis with stacked generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 1947–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, T.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D.; Tao, D. Mirrorgan: Learning text-to-image generation by redescription. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 1505–1514. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, M.; Tang, H.; Wu, F.; Jing, X.-Y.; Bao, B.-K.; Xu, C. DF-GAN: A Simple and Effective Baseline for Text-to-Image Synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 16515–16525. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, W.; Hu, K.; Yang, M.Y.; Rosenhahn, B. Text to Image Generation with Semantic-Spatial Aware GAN. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 18166–18175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Schomaker, L. DiverGAN: An Efficient and Effective Single-Stage Framework for Diverse Text-to-Image Generation. Neurocomputing 2022, 473, 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2021, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; Volume 139, pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, M.; Paliwal, K.K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 17 June–2 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.H.; Ye, J.C. Geometric gan’. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.02894. [Google Scholar]
- Winnemöller, H.; Kyprianidis, J.E.; Olsen, S.C. XDoG: An eXtended difference-of-Gaussians compendium including advanced image stylization. Comput. Graph. 2012, 36, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled weight decay regularization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Sgdr: Stochastic gradient descent with warm restarts. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.03983. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar]
- Fusaro, G.; Kang, J. Participatory approach to draw ergonomic criteria for window design. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2021, 82, 103098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Text Fusion Method | FID ↓ | CM Precision (%) ↑ |
|---|---|---|
| Diver | 116.99 | 6.81 |
| DF | 25.88 | 27.64 |
| DSTF (the proposed method) | 25.73 | 36.08 |
| Architecture | FID ↓ | CM Precision (%) ↑ | LPIPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| DSTF (the proposed method) | 25.73 | 36.08 | 0.2200 |
| DSTF w/o SF block | 26.51 | 30.83 | 0.0588 |
| DSTF w/o TF block | 32.43 | 4.31 | 0.3095 |
| DTSF | 29.43 | 32.01 | 0.2235 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, F.; Qian, W. Generative Architectural Design from Textual Prompts: Enhancing High-Rise Building Concepts for Assisting Architects. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063000
Yang F, Qian W. Generative Architectural Design from Textual Prompts: Enhancing High-Rise Building Concepts for Assisting Architects. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063000
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Feng, and Wenliang Qian. 2025. "Generative Architectural Design from Textual Prompts: Enhancing High-Rise Building Concepts for Assisting Architects" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063000
APA StyleYang, F., & Qian, W. (2025). Generative Architectural Design from Textual Prompts: Enhancing High-Rise Building Concepts for Assisting Architects. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063000






