Multi-Head Structural Attention-Based Vision Transformer with Sequential Views for 3D Object Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a lightweight multi-view classification model.We present CNN-ViT, a lightweight hybrid architecture integrating Structural Self-Attention mechanisms to jointly model spatial and temporal structural patterns in sequential view convolutional features. The modular design enables efficient feature extraction and fusion.
- We improve Sparse Structured Self-Attention for computational efficiency.To address the computational limitations of self-attention mechanisms, we introduce an improved Sparse Structured Self-Attention module. By employing a learnable sparse mask to restrict Query–Key connections, the proposed module dramatically reduces computational complexity while maintaining high expressiveness. This design not only alleviates the computational burden but also prevents overfitting caused by redundant feature modeling, ensuring a balance between efficiency and accuracy.
- We realize Multiscale Structural Feature Representation.In our work, the SSSA and TSSA modules progressively reduce the resolution of feature maps. This architectural design significantly reduces computational costs and parameter counts while aggregating multiscale feature representations. The resolution-reducing Structural Self-Attention mechanism enhances both the efficiency and representational capacity of the model, providing a compact yet expressive feature representation for multi-view classification tasks.
2. Related Works
3. Methodology
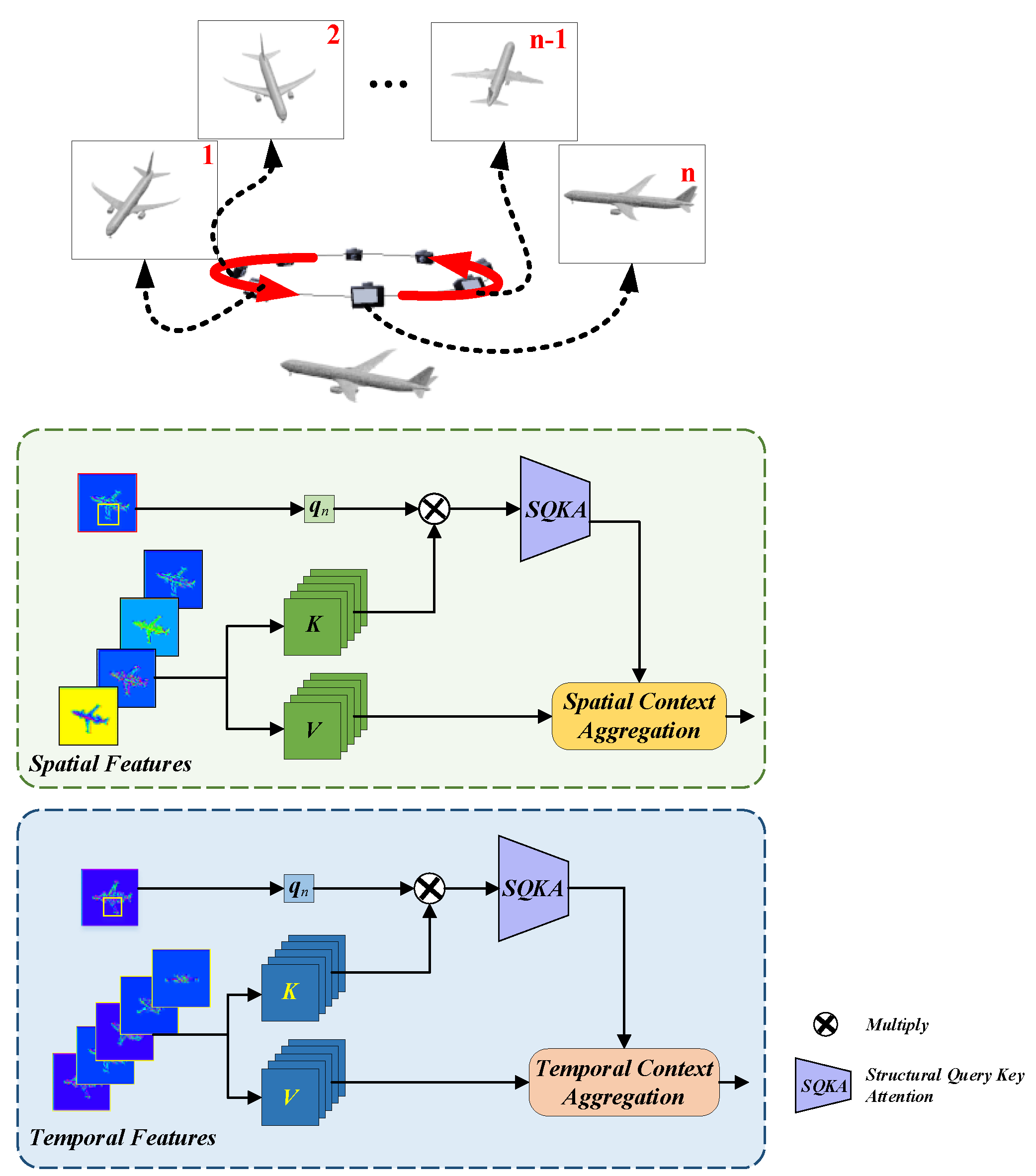
3.1. Sequential-View Capturing Schemes
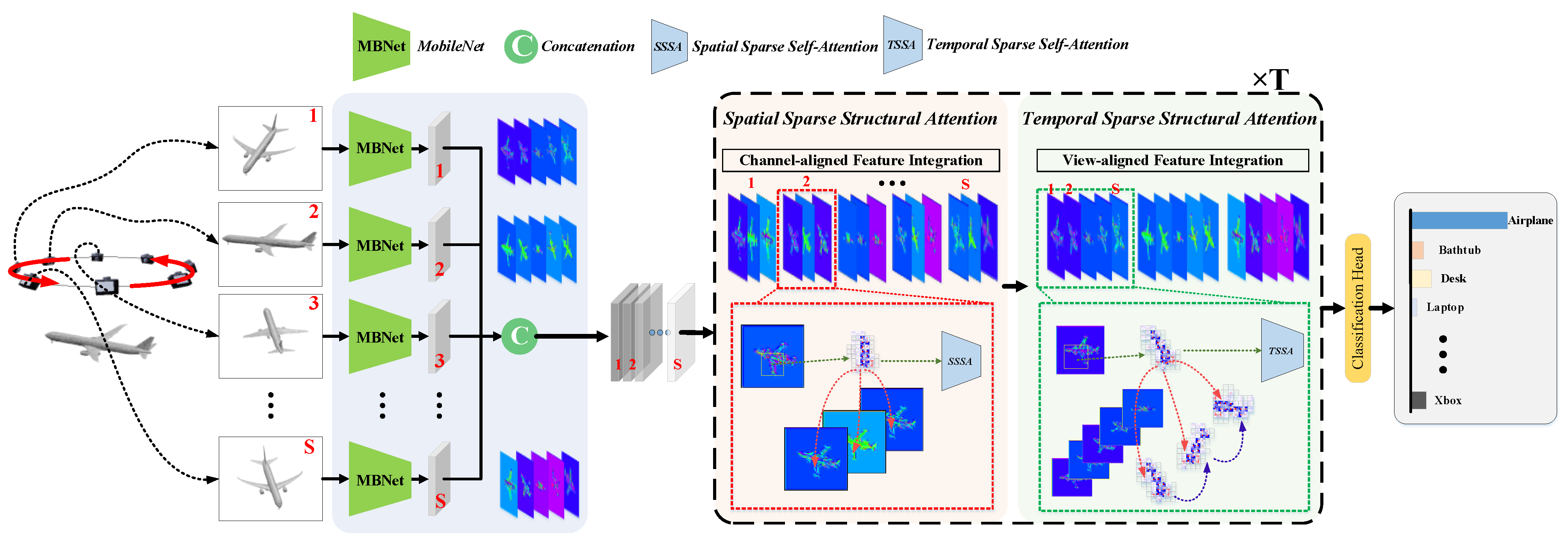
3.2. Network Architectures
3.2.1. Architecture of Proposed MSSAViT Model
3.2.2. Feature Extraction Module
3.2.3. Sparse Attention Mechanism
3.2.4. Temporal/Spatial Sparse Structural Attention Network
3.2.5. Model Structure Overview
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Dataset and Experimental Configure
4.2. Definition of Loss with Dynamic Weight Adjustment
4.3. Experimental Configuration
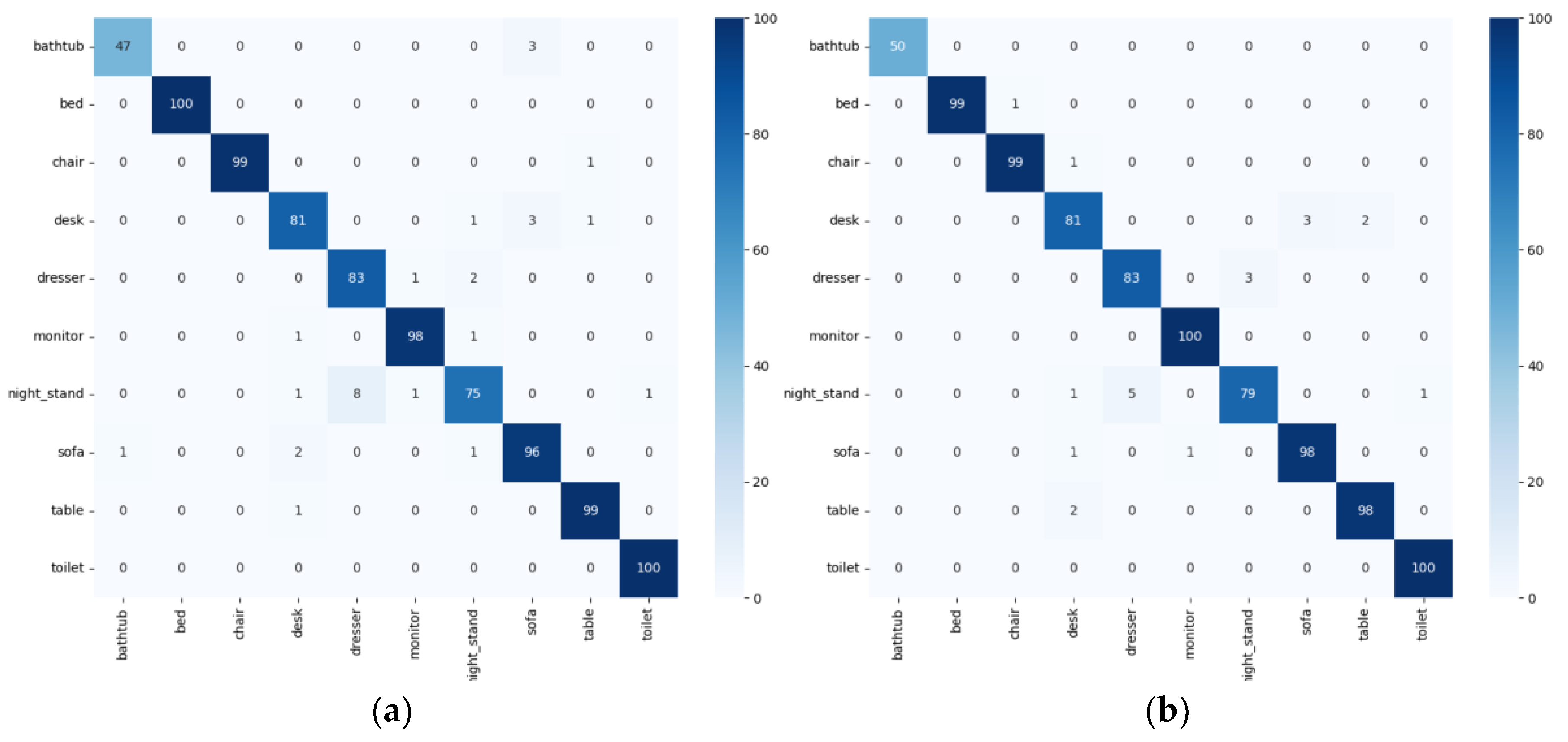
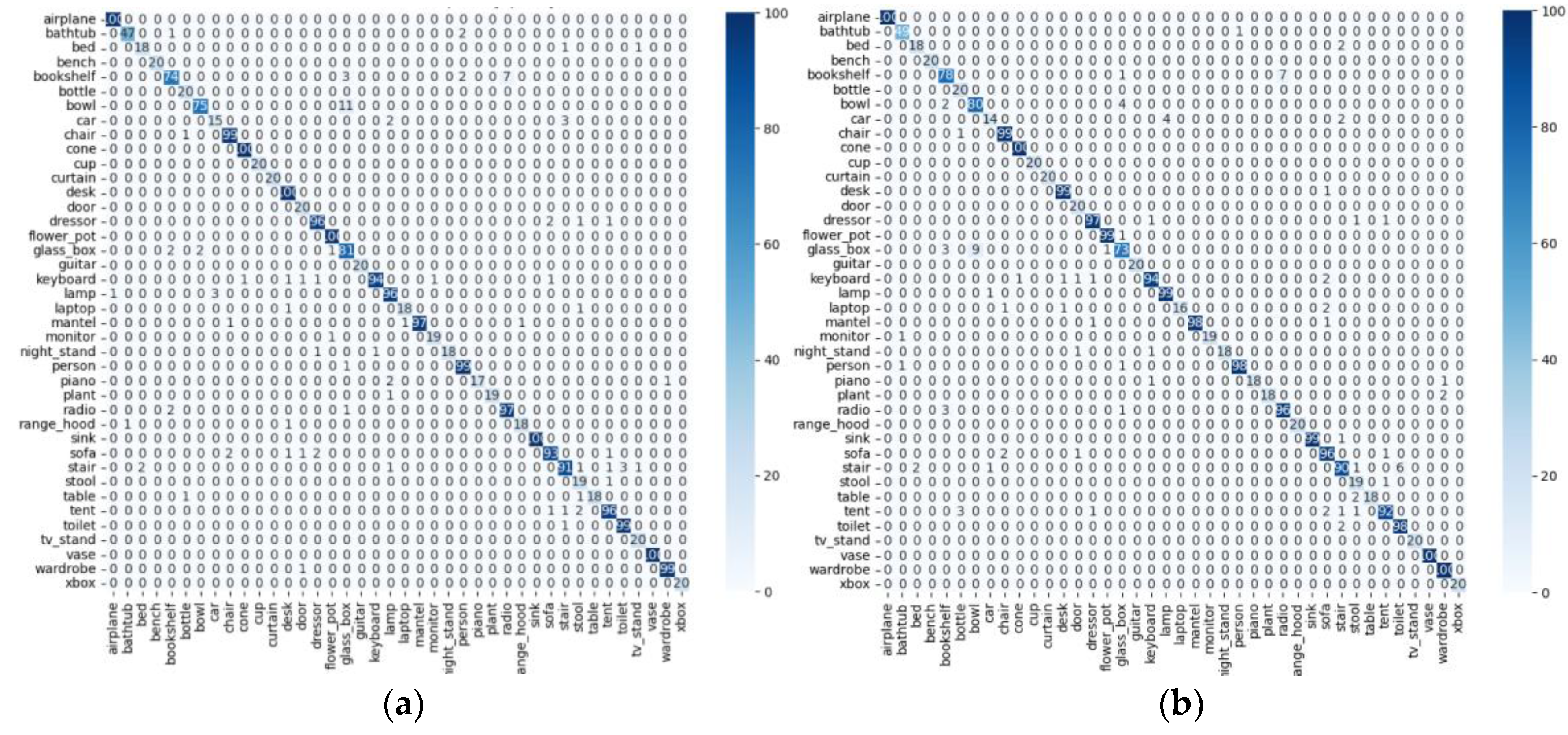
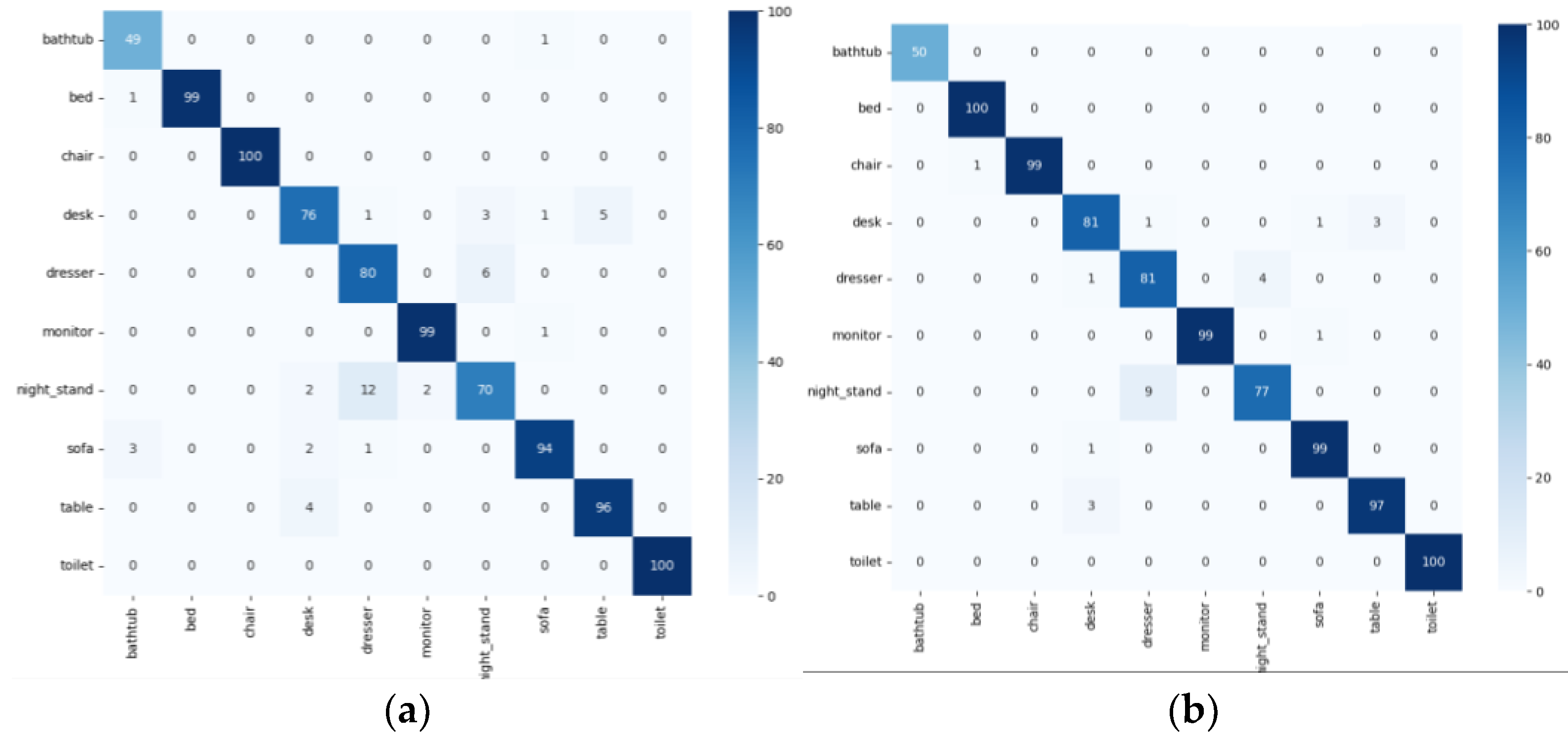
4.4. Main Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Model Parameter Comparison
5.2. The Output Selection of FEM for Lightweight Model Design
5.3. Ablation Study on Structural Attention Modules
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UWB | Ultra-Wideband; |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network; |
| ViTs | Vision Transformers; |
| MSSAViT | Multi-head Sparse Structural Attention-based Vision Transformer; |
| FEM | Feature Extraction Module; |
| SSSA | Spatial Sparse Self-Attention; |
| TSSA | Temporal Sparse Self-Attention; |
| StructSA | structural self-attention; |
| SQKA | Sparse Query–Key Attention. |
References
- Wang, Q.; Song, J.; Du, C.; Wang, C. Online Scene Semantic Understanding Based on Sparsely Correlated Network for AR. Sensors 2024, 24, 4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J. Large-Scale 3D Reconstruction from Multi-View Imagery: A Comprehensive Review. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tan, J.; Fu, J.; Shao, G. Fast 3D Transmission Tower Detection Based on Virtual Views. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Okby, M.F.R.; Junginger, S.; Roddelkopf, T.; Thurow, K. UWB-Based Real-Time Indoor Positioning Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, X.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, X.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, D. ViewFormer: Exploring Spatiotemporal Modeling for Multi-View 3D Occupancy Perception via View-Guided Transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 90–106. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Seo, P.H.; Schmid, C.; Cho, M. Learning Correlation Structures for Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 18941–18951. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.X.; Wang, W.J.; Zhu, Y.K.; Pang, R.M.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.C.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5105–5114. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Maji, S.; Kalogerakis, E.; Learned-Miller, E. Multi-view Convolutional Neural Networks for 3D Shape Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 17–18 December 2015; pp. 945–953. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.Z.; Liu, Z.B.; Vong, C.M.; Bu, S.H.; Li, X.L. Unsupervised 3D local feature learning by circle convolutional restricted Boltzmann machine. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 11, 5331–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.Z.; Liu, Z.B.; Han, J.W.; Vong, C.M.; Bu, S.H.; Chen, C.L.P. Mesh convolutional restricted Boltzmann machines for unsupervised learning of features with structure preservation on 3-D meshes. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 28, 2268–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.T.; Feng, Y.F.; You, H.X.; Zhao, X.B.; Gao, Y. MeshNet: Mesh neural network for 3D shape representation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; pp. 8279–8286. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Fan, R.; Song, Y. MEAN: An attention-based approach for 3D mesh shape classification. Visual Comput. 2024, 40, 2987–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Chen, B.M.; Lee, G.H. So-net: Self-organizing network for point cloud analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 9397–9406. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.H.; Han, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.S.; Zwicker, M. Point2Sequence: Learning the shape representation of 3d point clouds with an attention-based sequence to sequence network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; pp. 8778–8785. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.F.; Rao, Y.M.; Lu, J.W.; Yan, H.B. X-3D: Explicit 3D Structure Modeling for Point Cloud Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 5074–5083. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.R.; Song, S.R.; Khosla, A.; Yu, F.; Zhang, L.G.; Tang, X.O.; Xiao, J.X. 3d shapenets: A deep representation for volumetric shapes. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 11–12 June 2015; pp. 1912–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdi, A.; Giancola, S.; Ghanem, B. Mvtn: Multi-view transformation network for 3d shape recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Virtual, 10 March 2021; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, S.; Ning, X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, L.; Long, P.; Cai, W.; Li, W. Review of multi-view 3D object recognition methods based on deep learning. Displays 2021, 69, 102053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yu, R.; Sun, J. View-gcn: View-based graph convolutional network for 3d shape analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1850–1859. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.Z.; Shang, M.Y.; Liu, Z.B.; Vong, C.M.; Liu, Y.S.; Zwicker, M.; Han, J.W.; Chen, C.L.P. SeqViews2SeqLabels: Learning 3D global features via aggregating sequential views by RNN with attention. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.Z.; Lu, H.L.; Liu, Z.B.; Vong, C.M.; Liu, Y.S.; Zwicker, M.; Han, J.W.; Chen, C.L.P. 3D2SeqViews: Aggregating sequential views for 3D global feature learning by CNN with hierarchical attention aggregation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 3986–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Nie, W.; Li, Q. MVCLN: Multi-View convolutional LSTM network for cross-media 3D shape recognition. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 139792–139802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexey, D.; Philipp, F.; Eddy, I.; Philip, H.; Caner, H.; Vladimir, G.; Patrick, V.D.S.; Daniel, C.; Thomas, B. Flownet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 13–16 December 2015; pp. 2758–2766. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.S.; Ramanan, D. Volumetric Correspondence Networks for Optical Flow. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Y.; Yun, F. Human action recognition and prediction: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2022, 130, 1366–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ke, Q.; Rahmani, H.; Bennamoun, M.; Wang, G.; Liu, J. Human action recognition from various data modalities: A review. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 3200–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anirudh, T.; Sanath, N.; Salman, K.; Rao, M.A.; Fahad, S.K.; Bernard, G. Spatio-temporal relation modeling for few-shot action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 19958–19967. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Kwon, H.; Wang, C.Y.; Kwak, S.; Cho, M. Relational self-attention: What’s missing in attention for video understanding. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Virtual, 6–14 December 2021; pp. 8046–8059. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo Vadis, Action Recognition? A New Model and the Kinetics Dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–27 July 2017; pp. 6299–6308. [Google Scholar]
- Feichtenhofer, C.; Fan, H.; Malik, J.; He, K. SlowFast Networks for Video Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6202–6211. [Google Scholar]
- Bertasius, G.; Wang, H.; Torresani, L. Is Space-Time Attention All You Need for Video Understanding? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 813–824. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Virtual, 10 March 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Feng, C.; Shen, Y.R.; Tian, D. Foldingnet: Point cloud auto-encoder via deep grid deformation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 19–21 June 2018; pp. 206–215. [Google Scholar]
- Maurana, D.; Scherer, S. Voxnet: A 3d convolutional neural network for real-time object recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 922–928. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, S.F.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.L. LightNet: A lightweight 3d convolutional neural network for real-time 3d object recognition. In Proceedings of the 10th Eurographics Workshop on 3D Object Retrieval (3DOR), Lyon, France, 23–24 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, A.; Bai, J.; Ramani, K. Deep learning 3D shape surfaces using geometry images. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 223–240. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Zhou, H. Multi-view SoftPool attention convolutional networks for 3D model classification. Front. Neurorobotics 2022, 16, 1029968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Mi, Q.; Ma, W.; Zha, H. View-relation constrained global representation learning for multi-view-based 3D object recognition. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 7741–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, V.; Zadeh, R. Fusionnet: 3d object classification using multiple data representations. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.05695. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, M.; Sohel, F.; Bennamoun, M.; Li, J. NormalNet: A voxel-based CNN for 3D object classification and retrieval. Neurocomputing 2018, 323, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.H. MVPointNet: Multi-view network for 3D object based on point cloud. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 12145–12152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cai, Y.; Wang, T. Multi-view dual attention network for 3D object recognition. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 3201–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Kang, W. MVContrast: Unsupervised Pretraining for Multi-view 3D Object Recognition. Mach. Intell. Res. 2023, 20, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Lin, J.; Yao, J.; Tu, J. Multi-view convolutional vision transformer for 3D object recognition. J. Vis. Commun. Image. Represent. 2023, 95, 103906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Yu, Z.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Tiwari, P. DILF: Differentiable rendering-based multi-view Image–Language Fusion for zero-shot 3D shape understanding. Inf. Fusion 2024, 102, 102033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, M.; Usman, M.; Anwar, S.; Helmy, T. Selective Multi-View Deep Model for 3D Object Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 728–736. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Velipasalar, S. PointOfView: A Multi-modal Network for Few-shot 3D Point Cloud Classification Fusing Point and Multi-view Image Features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 784–793. [Google Scholar]



| No. | Layer/Module Name | Input Shape | Output Shape |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FEM | S × 3 × H × W | S × C × N × N |
| 2 | SSSA | S × C × N × N | S × C × N × N |
| 3 | Dimensional Resetting Layer | S × C × N × N | C × S × N × N |
| 4 | TSSA | C × S × N × N | C × S × N × N |
| 5 | Dimensional Resetting Layer | C × S × N × N | S × C × N × N |
| 6 | SSSA | S × C × N × N | S × C × N/2 × N/2 |
| 7 | Dimensional Resetting Layer | S × C × N/2 × N/2 | C × S × N/2 × N/2 |
| 8 | TSSA | C × S × N/2 × N/2 | C × S × N/2 × N/2 |
| 9 | Dimensional Resetting Layer | C × S × N/2 × N/2 | S × C × N/2 × N/2 |
| 10 | SSSA | S × C × N/2 × N/2 | S × C × N/4 × N/4 |
| 11 | Dimensional Resetting Layer | S × C × N/4 × N/4 | C × S × N/4 × N/4 |
| 12 | TSSA | C × S × N/4 × N/4 | C × S × N/4 × N/4 |
| 13 | Classification Head | C × S × H × W | Number of Classes |
| Methods | Representation Type | Points/View Number | Average Class Accuracy (%) | Average Instance Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point2Sequence [16] | Points | 1024 × 3 | 95.10 | 95.30 |
| FoldingNet [35] | Points | - | - | 94.40 |
| VoxNet [36] | Voxel | - | 92.00 | - |
| LightNet [37] | Voxel | - | 93.39 | - |
| Geometry image [38] | View | 1 | 88.40 | - |
| MVMSAN [39] | View | 20 | 98.42 | 98.57 |
| VCGR-Net [40] | View | 12 | 97.24 | 97.79 |
| SV2SL [22] | SeqView | 12 | 94.56 | 94.71 |
| 3D2SV [23] | SeqView | 12 | 94.68 | 94.71 |
| FusionNet [41] | Voxel + View | -/20 | - | 93.11 |
| NormalNet [42] | Voxel + Normal | - | 93.10 | - |
| SO-Net [15] | Points | 2048 × 3 | 93.90 | 94.10 |
| MVPointNet [43] | Points + View | -/5 | 95.10 | 95.20 |
| MSSAViT-TV (ours) | View | 12 | 97.41 | 97.58 |
| MSSAViT-SV (ours) | View | 12 | 98.40 | 98.46 |
| Methods | Representation Type | Points/View Number | Average Class Accuracy | Average Instance Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MeshNet [13] | Mesh | - | 91.90 | - |
| Point2Sequence [16] | Point | 1024 × 3 | 90.40 | 92.60 |
| FoldingNet [35] | Point | - | - | 88.40 |
| PointNet [8] | Point | - | 86.20 | 89.20 |
| PointNet++ [9] | Point | - | - | 91.90 |
| VoxNet [36] | Voxel | - | 83.00 | - |
| LightNet [37] | Voxel | - | 86.90 | - |
| MVCNN [9] | View | 80 | 90.10 | - |
| Geometry image [38] | View | 1 | 83.90 | - |
| MVDAN [44] | View | 12 | 95.50 | 96.60 |
| MVMSAN [39] | View | 6 | - | 96.84 |
| MVMSAN [39] | View | 12 | - | 96.80 |
| MVMSAN [39] | View | 20 | 95.68 | 96.96 |
| VCGR-Net [40] | View | 12 | 93.33 | 95.62 |
| MVContrast [45] | View | 12 | 90.24 | 92.54 |
| MVCVT [46] | View | 12 | - | 95.40 |
| DILF [47] | View | 6 | - | 94.80 |
| SelectiveMV [48] | View | 1 | - | 88.13 |
| PointOfView [49] | Point + View | -/6 | 92.17 | - |
| SV2SL [22] | SeqView | 12 | 91.12 | 93.31 |
| 3D2SV [23] | SeqView | 12 | 91.51 | 93.40 |
| FusionNet [41] | Voxel + View | 20 | - | 90.80 |
| MSSAViT-TV (ours) | View | 12 | 94.91 | 96.07 |
| MSSAViT-SV (ours) | View | 12 | 95.31 | 96.11 |
| Methods | Representation Type | Backbone Network | Total Parameters | ModelNet10 | ModelNet40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SV2SL [1] | SeqView | VGG | >130 M | 94.60 | 93.31 |
| 3D2SV [2] | SeqView | Restnet101 | >45 M | - | 93.40 |
| MVCNN [4] | View | VGG | >130 M | - | 90.10 |
| MVPointNet [38] | Points + View | VGG | >130 M | 95.20 | - |
| PVRNet [40] | Point + View | AlexNet | >60 M | - | 93.60 |
| FusionNet [31] | Voxel + View | - | 118 M | 93.11 | 90.80 |
| 3DGAN [20] | Voxel | - | 11 M | 91.00 | 83.30 |
| MVDAN [44] | View | VGG | >130 M | - | 96.60 |
| MVMSAN [39] | View | ResNest14d | >8.8 M | 98.57 | 96.96 |
| MVContrast [45] | View | ResNet18 | >11.7 M | - | 92.54 |
| SelectiveMV [48] | View | Restnet152 | >60 M | - | 88.13 |
| MSSAViT-TV (ours) | SeqView | MobileNet | 6.1 M | 98.45 | 96.07 |
| MSSAViT-SV (ours) | SeqView | MobileNet | 6.1 M | 98.57 | 96.11 |
| Output Size of the FEM | Total Parameters | Trainable Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| 7 × 7 × 160 | 6.1 M | 1.5 M |
| 14 × 14 × 112 | 7.7 M | 3.1 M |
| 28 × 28 × 40 | 19.3 M | 14.7 M |
| 56 × 56 × 24 | 152.4 M | 147.9 M |
| Method | ModelNet10 | ModelNet40 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Class Accuracy | Average Instance Accuracy | Average Class Accuracy | Average Instance Accuracy | |
| MSSAViT-SV (SSSA-only) | 94.88 | 95.04 | 92.05 | 94.17 |
| MSSAViT-SV (TSSA-only) | 96.79 | 97.25 | 93.45 | 94.69 |
| MSSAViT (SSSA + TSSA) | 98.40 | 98.46 | 95.31 | 96.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, J.; Luo, K.; Kou, Q.; He, L.; Zhao, G. Multi-Head Structural Attention-Based Vision Transformer with Sequential Views for 3D Object Recognition. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063230
Bao J, Luo K, Kou Q, He L, Zhao G. Multi-Head Structural Attention-Based Vision Transformer with Sequential Views for 3D Object Recognition. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063230
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Jianjun, Ke Luo, Qiqi Kou, Liang He, and Guo Zhao. 2025. "Multi-Head Structural Attention-Based Vision Transformer with Sequential Views for 3D Object Recognition" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063230
APA StyleBao, J., Luo, K., Kou, Q., He, L., & Zhao, G. (2025). Multi-Head Structural Attention-Based Vision Transformer with Sequential Views for 3D Object Recognition. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3230. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063230






