Advanced Brain Tumor Segmentation Using SAM2-UNet
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose SAM2-UNet, a novel hybrid deep learning model that integrates Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) and U-Net to improve the precise segmentation of tumors.
- The model effectively leverages the zero-shot segmentation capabilities of SAM2 along with U-Net’s fine-grained spatial localization to enhance segmentation performance.
- We implement a parameter-efficient fine-tuning approach using Hiera pre-trained models, which helps in capturing multi-scale features with minimal computations.
- The proposed model is evaluated on the BraTS 2020 dataset, demonstrating superior segmentation performance across multiple evaluation metrics, achieving an mDice of 0.771 and an mIoU of 0.569 with minimal hardware resources.
2. Related Work
2.1. U-Net++
2.2. DeepLabV3
2.3. Mask R-CNN
2.4. SAM2-UNet
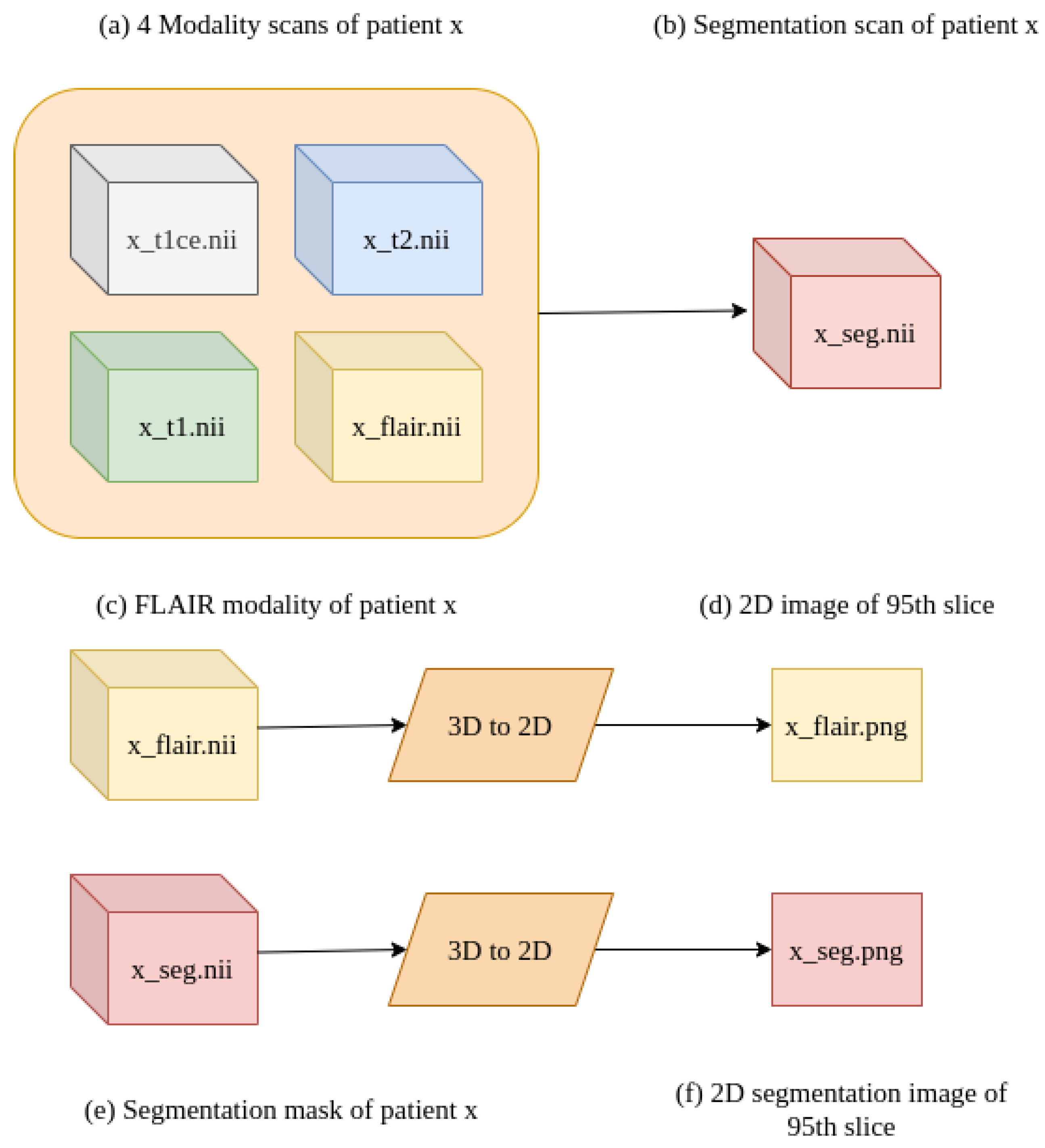
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. BraTS 2020 Dataset
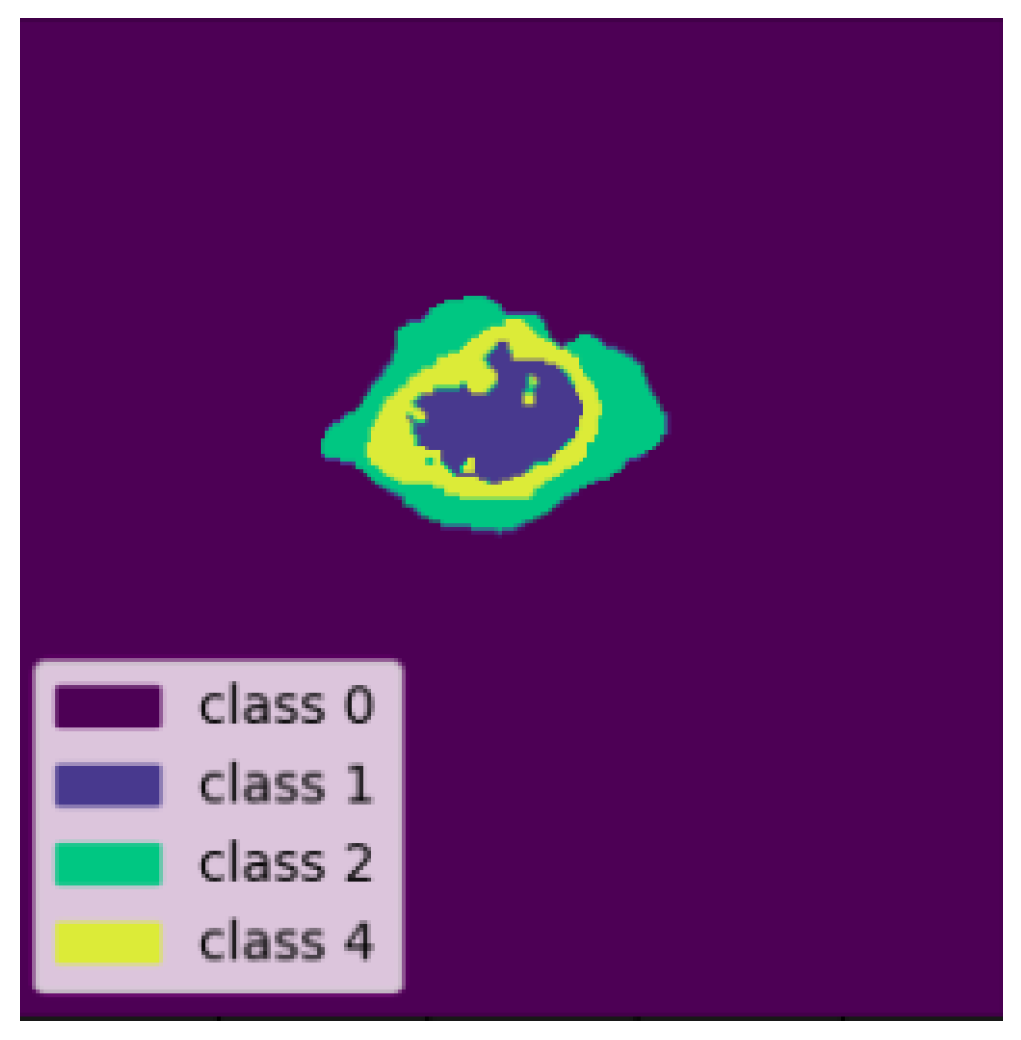
3.2. Data Pre-Processing
3.3. Brain Tumor Segmentation Model
4. Proposed Approach
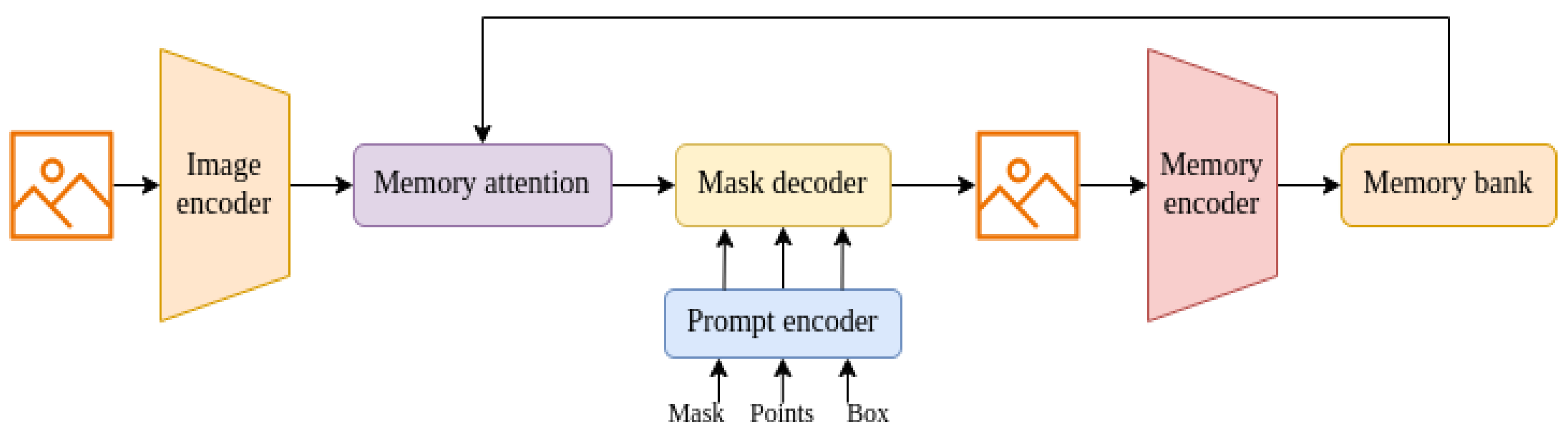
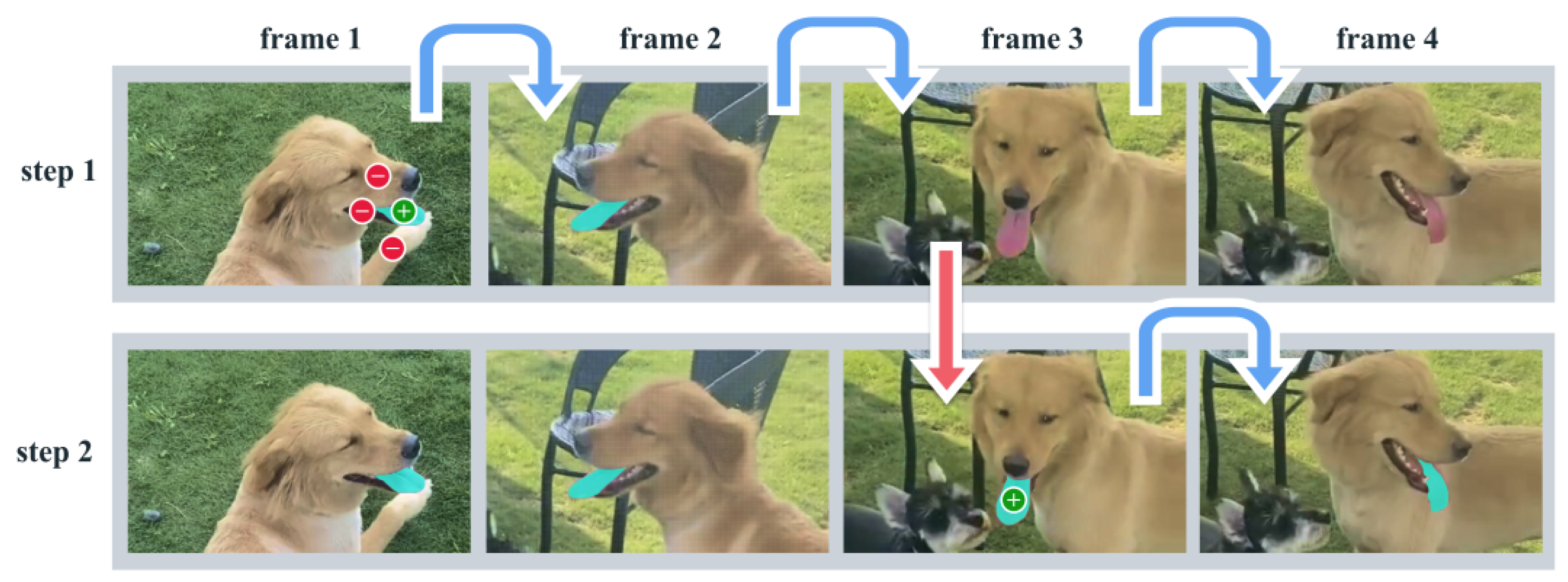
4.1. Segment Anything Model (SAM)-2
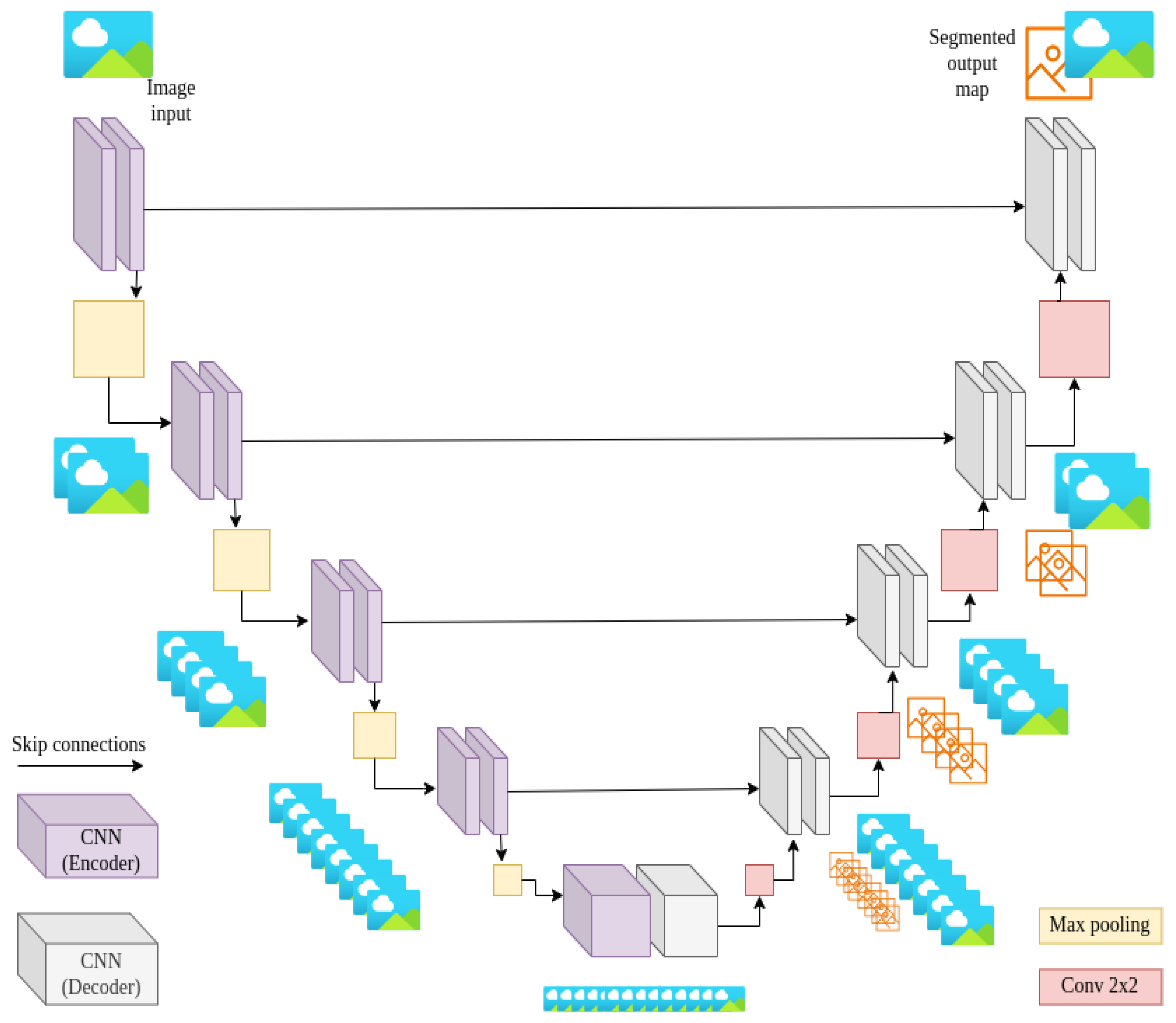
4.2. U-Net Architecture
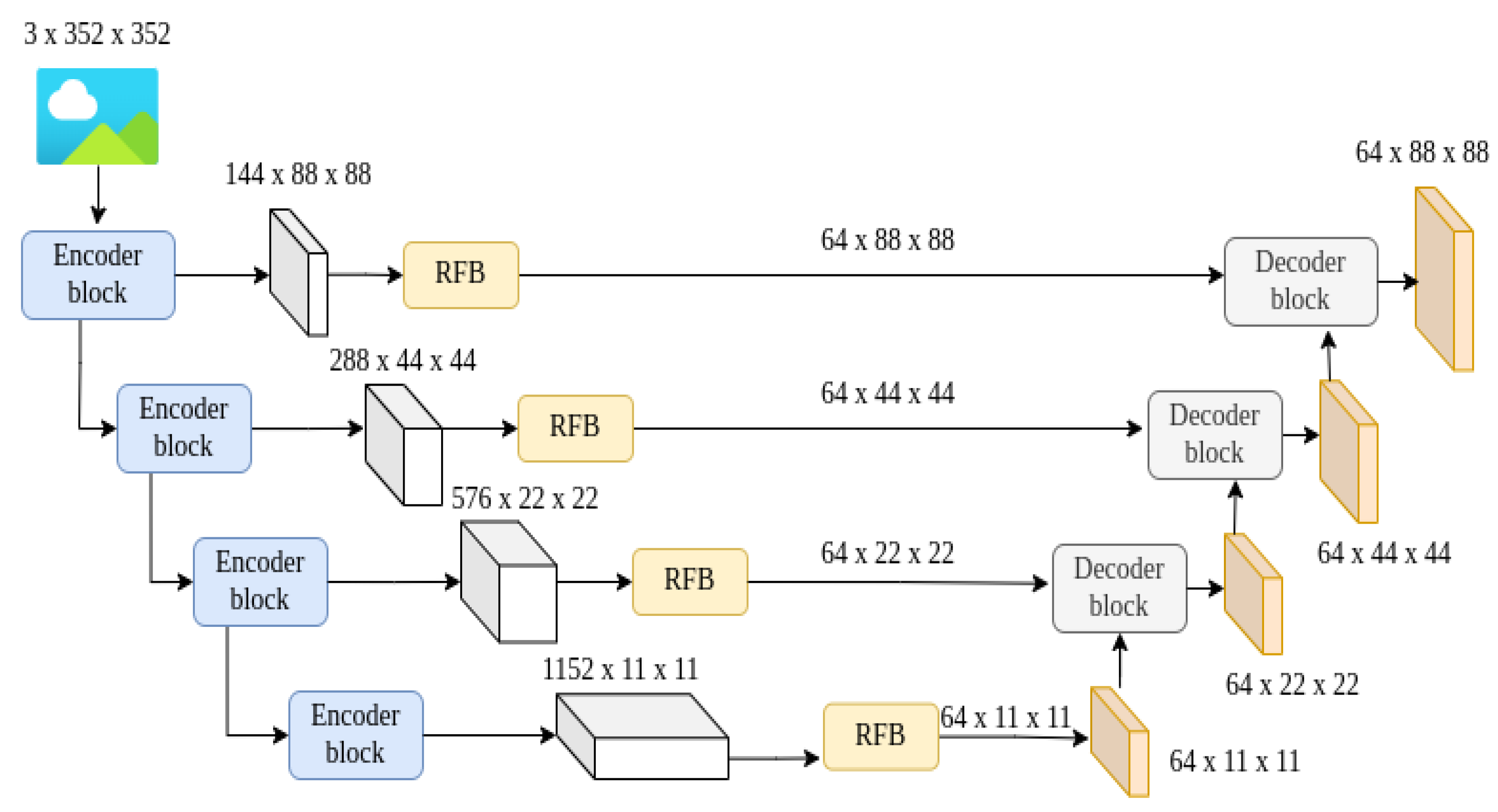
4.3. Integrated SAM2-UNet Model
5. Experiments and Results
5.1. Discerning the Inner Workings of the Proposed SAM2-UNet Architecture
5.1.1. Mean Intersection over Union (mIoU)
5.1.2. Dice Coefficient (DICE)
5.1.3. F1-Measure
5.1.4. Mean Absolute Error
6. Discussion
6.1. Strengths and Contributions
6.2. Limitations and Challenges
7. Error Analysis
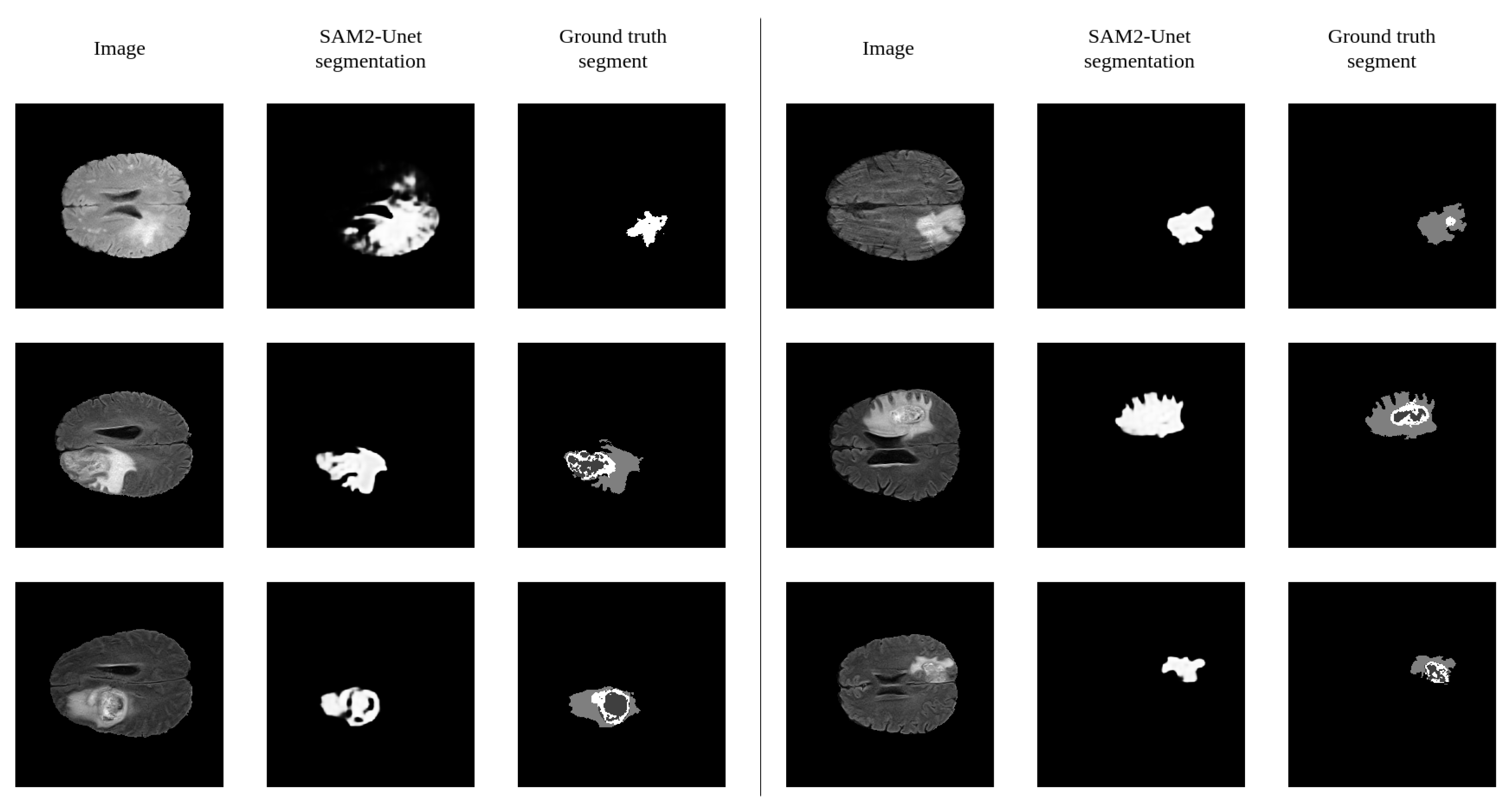
7.1. Visual Error Analysis
7.2. Error Causes
8. Conclusions and Future Work
Future Enhancements
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, R.; Ning, L.; Zhou, C.; Wei, P.; Ding, Y.; Tan, D.; Zheng, C. CFANet: Context Feature Fusion and Attention Mechanism Based Network for Small Target Segmentation in Medical Images. Sensors 2023, 23, 8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, M. Recent deep learning-based brain tumor segmentation models using multi-modality magnetic resonance imaging: A prospective survey. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 1206. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, E.C. Glioma: Biology and diagnosis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 341–353. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.E.; Peterson, D. Glioblastoma: The paradigm of the malignant glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2171–2181. [Google Scholar]
- Ceballos-Ceballos, J.; Loza-Gallardo, D.A.; Barajas-Romero, M.A.; Cantú-Brito, C.; Valdés-Ferrer, S.I. Recognition of Brain Meta’s (Menlo Park, CA, USA)stases Using Gadolinium-Enhanced SWI MRI: Proof-of-Concept Study. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakas, S.; Reyes, M.; Jakab, A.; Smith, J.; Johnson, R.; Lee, C.; Chen, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. BraTS 2020: Prediction of Survival and Pseudoprogression. In Proceedings of the MICCAI 2020, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chougule, A.G.; Srinivasan, S.; Mathivanan, P.; Mathivanan, S.K.; Shah, M.A. Robust brain tumor classification by fusion of deep learning and channel-wise attention mode approach. BMC Med. Imaging 2023, 24, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Qiu, J.; Abaxi, S.M.D.; Wei, H.; Lo, F.P.W.; Yuan, W. Generalist Vision Foundation Models for Medical Imaging: A Case Study of Segment Anything Model on Zero-Shot Medical Segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.12637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Wu, Z.; Tan, S.; Li, W.; Tang, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Ma, J.; Li, G. SAM2-UNet: Segment Anything 2 Makes Strong Encoder for Natural and Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.08870. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, D.; Aizenberg, M. Trialing U-Net Training Modifications for Segmenting Gliomas Using Open Source Deep Learning Framework. In Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Mitra, S.; Shankar, B.U. Multi-planar Spatial-ConvNet for Segmentation and Survival Prediction in Brain Cancer. In Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries; Crimi, A., Smith, J., Johnson, R., Lee, C., Zhao, X., Wang, Y., Li, Z., Brown, T., Green, P., White, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 94–104. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Tustison, N.J.; Patel, S.H.; Meyer, C.H. Brain Tumor Segmentation Using an Ensemble of 3D U-Nets and Overall Survival Prediction Using Radiomic Features. In Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries; Crimi, A., Smith, J., Johnson, R., Lee, C., Zhao, X., Wang, Y., Li, Z., Brown, T., Green, P., White, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Weninger, L.; Rippel, O.; Koppers, S.; Merhof, D. Segmentation of Brain Tumors and Patient Survival Prediction: Methods for the BraTS 2018 Challenge. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jahangard, S.; Zangooei, M.H.; Shahedi, M. U-Net Based Architecture for an Improved Multiresolution Segmentation in Medical Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.08238. [Google Scholar]
- Isensee, F.; Jaeger, P.F.; Kohl, S.A.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K.H. nnU-Net: A self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, N.; Gabeur, V.; Hu, Y.T.; Hu, R.; Ryali, C.; Ma, T.; Khedr, H.; Rädle, R.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; et al. SAM 2: Segment Anything in Images and Videos. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.00714. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Receptive Field Block Net for Accurate and Fast Object Detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 385–400. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: Redesigning Skip Connections to Exploit Multiscale Features in Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Zhou, T.; Chen, G.; Fu, H.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. PraNet: Parallel Reverse Attention Network for Polyp Segmentation. In Proceedings of the MICCAI, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, J. Learnable ophthalmology SAM. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.13425. [Google Scholar]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the Amount of Ecologic Association Between Species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman. Evaluating supervised machine learning classification models in healthcare. Milliman Res. Rep. 2022, 12, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Willmott, C.J.; Matsuura, K. Some Comments on the Evaluation of Model Performance. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
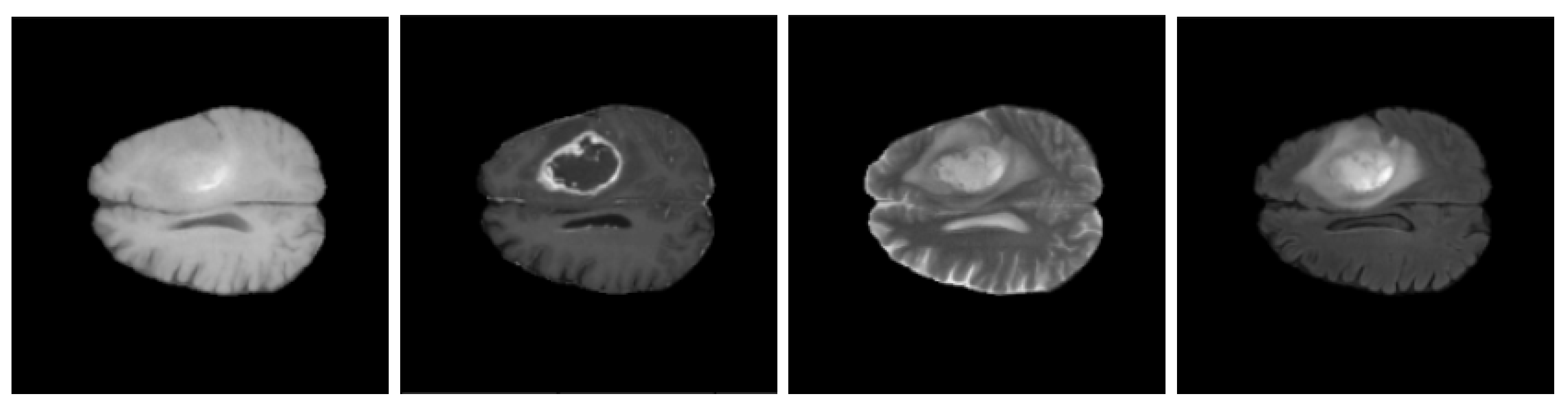






| Dataset | Size | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Training | 295 | 80% |
| Validation | 29 | 10% [Train] |
| Testing | 74 | 20% |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Pre-trained model | Hiera |
| Epochs | 30 |
| Learning rate | |
| Weight decay | |
| Optimizer | AdamW |
| Batch size | 1 |
| Model | mDice | mIoU | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAM2-Unet | 0.771 | 0.569 | 0.046 |
| U-Net | 0.563 | 0.392 | 0.178 |
| U-Net++ | 0.610 | 0.439 | 0.167 |
| Mask R-CNN | 0.746 | 0.571 | 0.094 |
| DeepLabV3 | 0.709 | 0.549 | 0.062 |
| ResUNet | 0.591 | 0.419 | 0.183 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pidishetti, R.V.; Amjad, M.; Sheng, V.S. Advanced Brain Tumor Segmentation Using SAM2-UNet. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063267
Pidishetti RV, Amjad M, Sheng VS. Advanced Brain Tumor Segmentation Using SAM2-UNet. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(6):3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063267
Chicago/Turabian StylePidishetti, Rohit Viswakarma, Maaz Amjad, and Victor S. Sheng. 2025. "Advanced Brain Tumor Segmentation Using SAM2-UNet" Applied Sciences 15, no. 6: 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063267
APA StylePidishetti, R. V., Amjad, M., & Sheng, V. S. (2025). Advanced Brain Tumor Segmentation Using SAM2-UNet. Applied Sciences, 15(6), 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15063267








