The Impact of Total Replacement of Sodium Chloride with Potassium and Magnesium Chloride on Pickling of Granny Smith Apples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
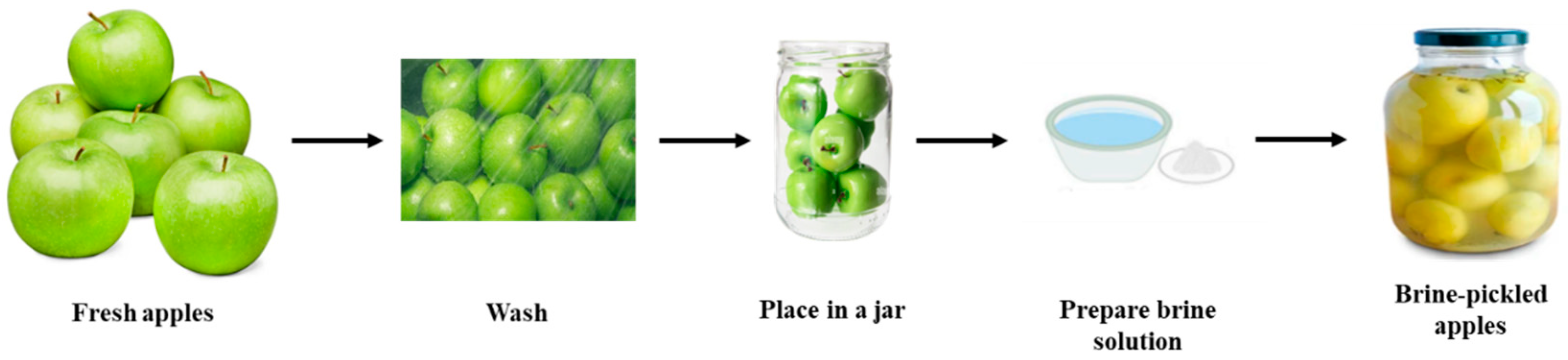
2.2. Preparation of Pickled Apples and Sampling
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis
2.3.1. Determination of pH and Lactic Acid, Reducing Sugar, and Uronic Acid Contents in Pickled Apples
2.3.2. Determination of Sodium, Potassium, and Magnesium Contents
2.3.3. Antioxidant Activity Detection by DPPH Assay
2.3.4. Texture Profile Analysis
2.3.5. Color Assessment
2.4. Microbiological Analysis
Enumeration of Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB), Mesophilic Aerobic Bacteria (MAB), and Yeast and Mold (YM) Values
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in pH, as Well as Lactic Acid, Reducing Sugar, and Uronic Acid Contents, During Pickling
3.1.1. Changes in pH Values During Pickling
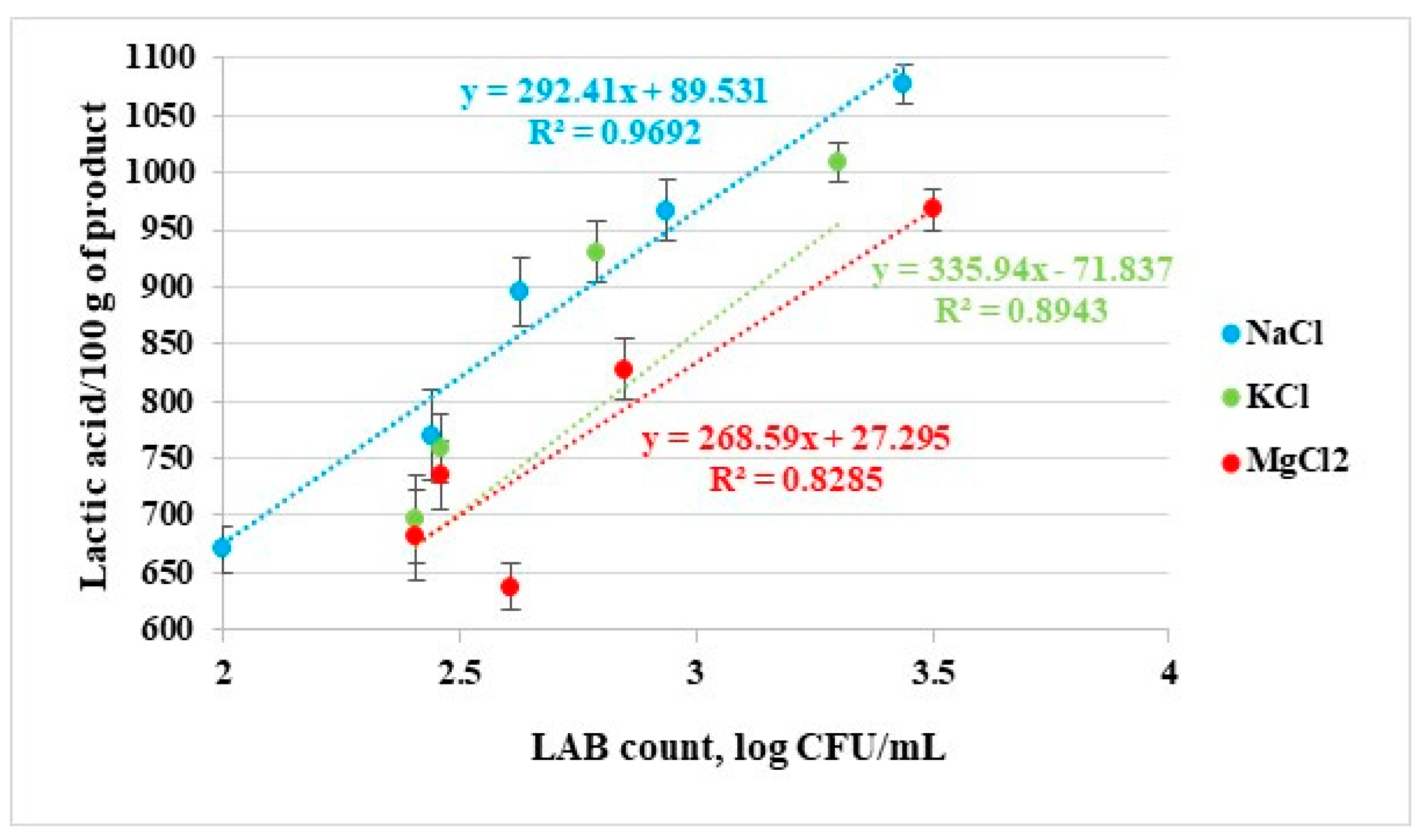
3.1.2. The Results of Lactic Acid Changes
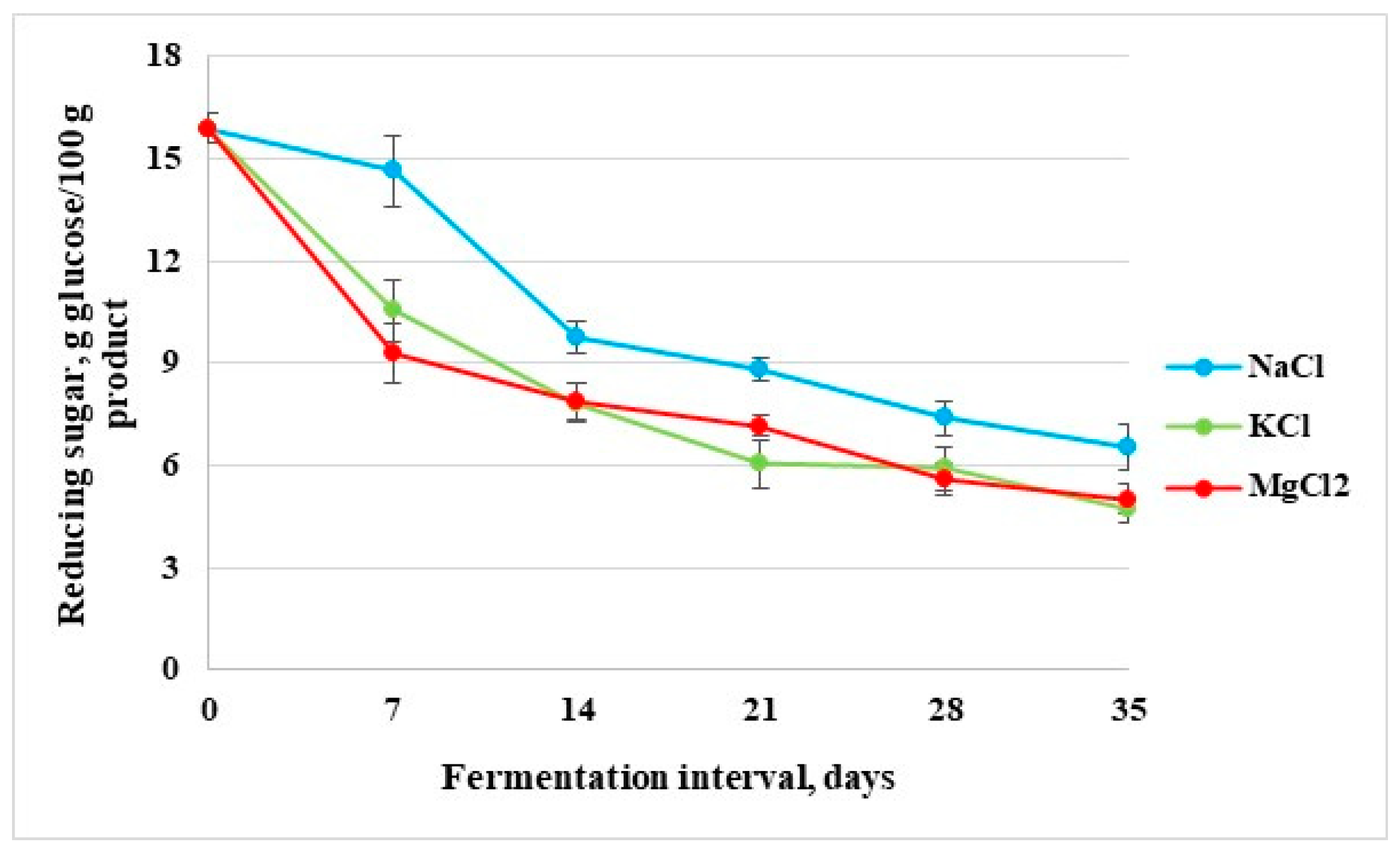
3.1.3. Reducing Sugar Content
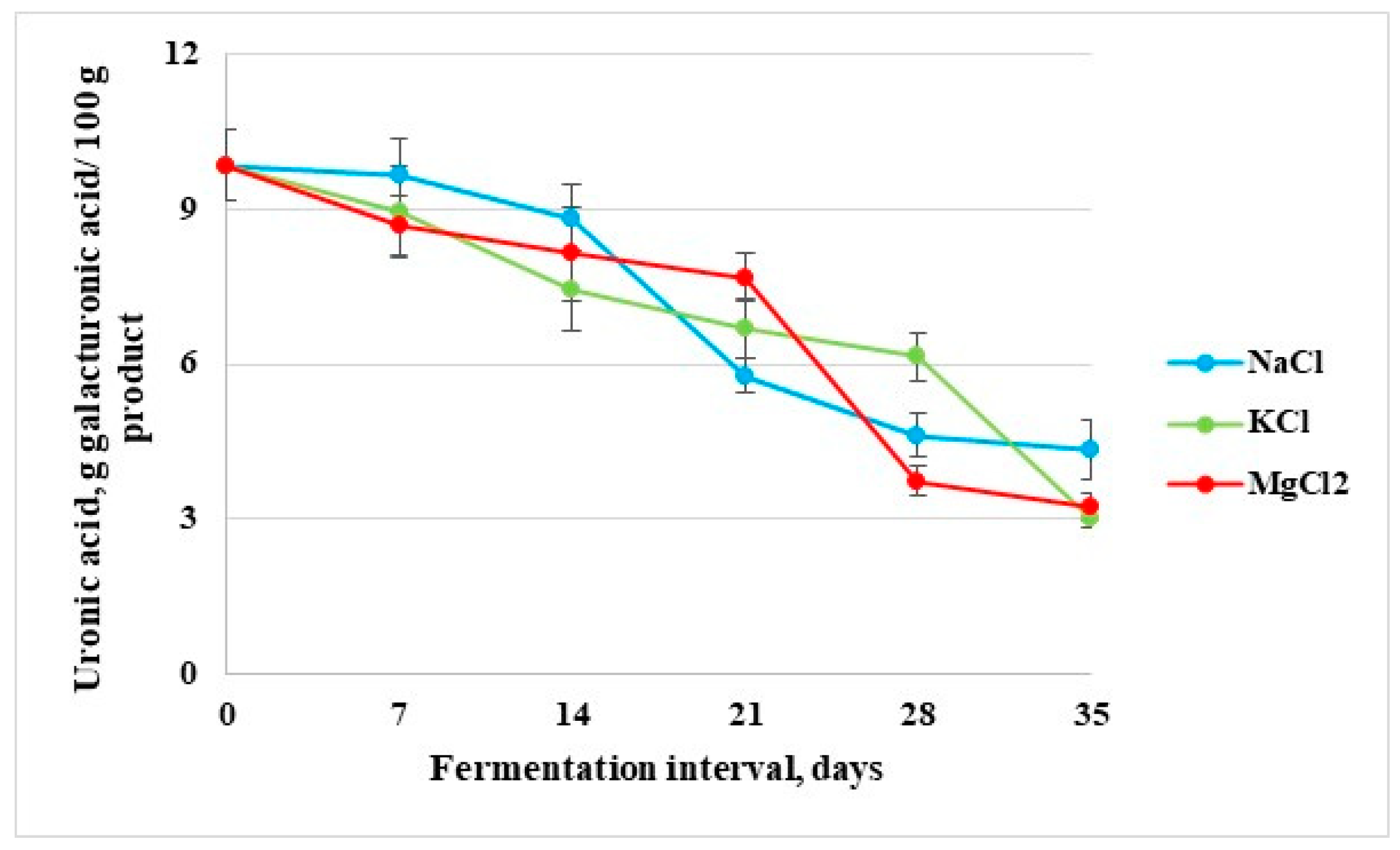
3.1.4. Uronic Acid Content
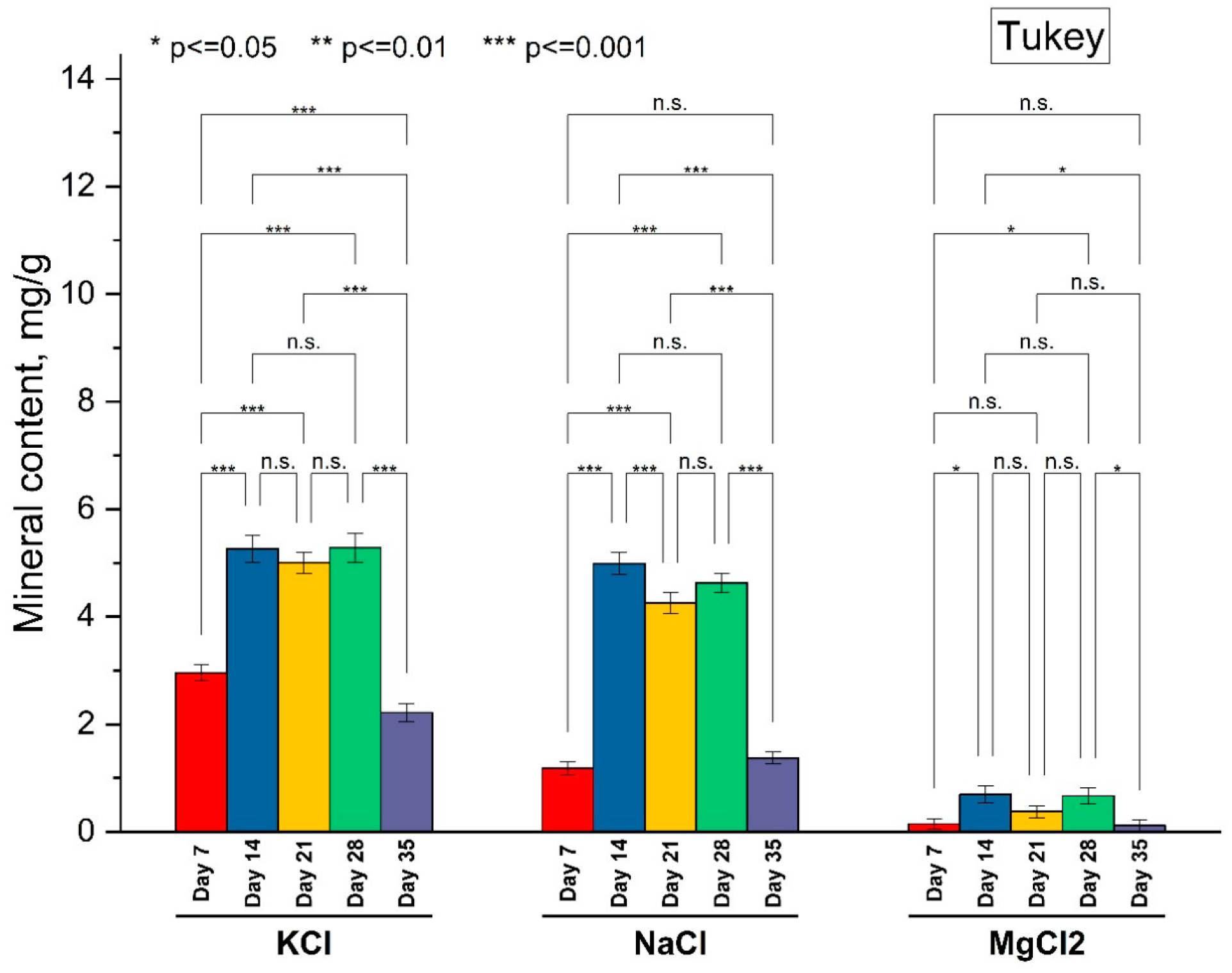
3.2. Mineral Content
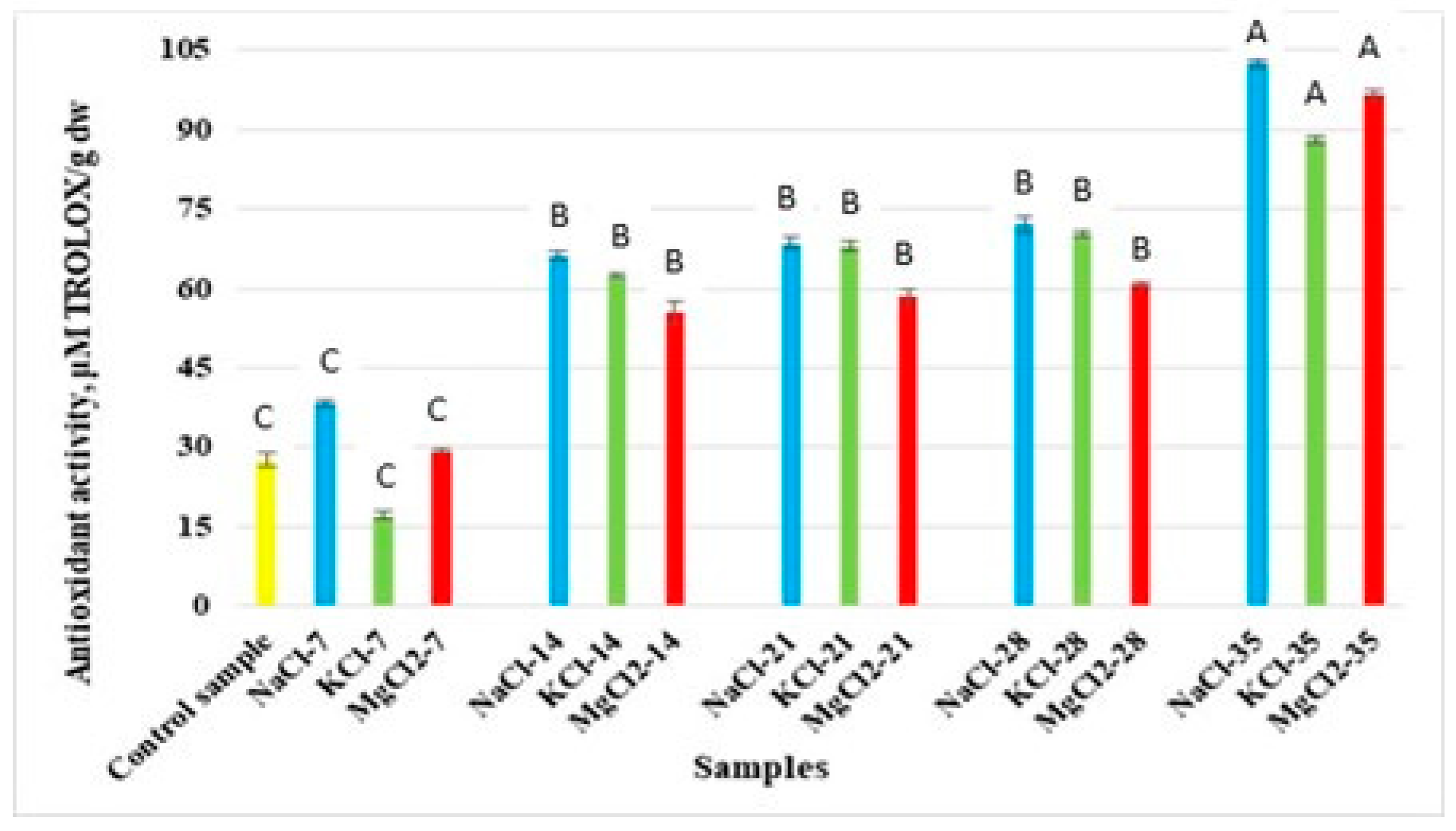
3.3. Antioxidant Activity Analysis
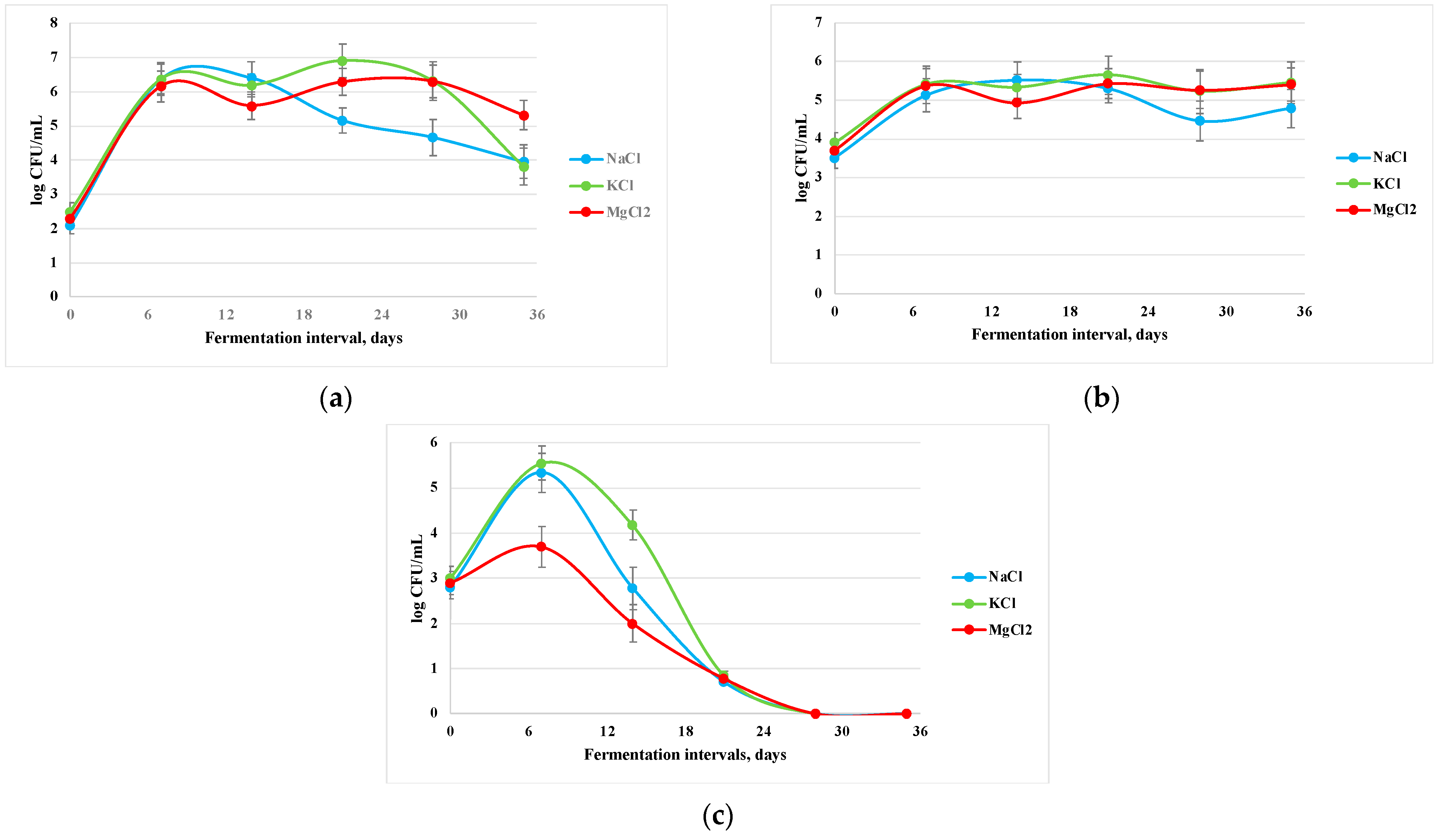
3.4. Microbiological Changes in Apple Pickle Fermentation
3.5. Textural Properties of Pickled Apples
3.6. Color Analysis of Pickled Apples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NaCl | Sodium chloride |
| KCl | Potassium chloride |
| MgCl2 | Magnesium chloride |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| MAB | Mesophilic aerobic bacteria |
| YM | Yeast and molds |
| CFU | Colony-forming unit |
| MRS | de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe |
| AA | Antioxidant activity |
References
- Yuan, X.; Wang, T.; Sun, L.; Qiao, Z.; Pan, H.; Zhong, Y.; Zhuang, Y. Recent Advances of Fermented Fruits: A Review on Strains, Fermentation Strategies, and Functional Activities. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Tan, M. Hollow Salt for Sodium Reduction in Foods: Mechanisms, Influence Factors, Applications and Challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 147, 104451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.W.; Roobab, U.; Wang, Z.; Raza, M.M.; Nawazish, H.; Islam, F.; Aadil, R.M. Salt Reduction in Food Products: A Systematic Review of Clean-Label Ingredients and Non-Thermal Technologies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 153, 104695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt Intake—PAHO/WHO|Pan American Health Organization. Available online: https://www.paho.org/en/enlace/salt-intake (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Ponzo, V.; Pellegrini, M.; Costelli, P.; Vázquez-Araújo, L.; Gayoso, L.; D’eusebio, C.; Ghigo, E.; Bo, S. Strategies for Reducing Salt and Sugar Intakes in Individuals at Increased Cardiometabolic Risk. Nutrients 2021, 13, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragomir, C.M.; Ilie, S.-M.; Poiana, M.-A.; Misca, C.D.; Cocan, I.; Dumbravă, D.-G.; Moldovan, C.; Popa, V.-M.; Petcu, C.D.; Roman, C.; et al. Traditional Romanian culinary practices and their historical and cultural significance—A review. Sci. Papers. Ser. E. Land. Reclam. Earth Obs. Surv. Environ. Eng. 2024, XIII, 882–889. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, M.E.; E Bhnsawy, R.M.; Gabal, S. Production of Low-Sodium Pickles for Hypertensive Patients. Middle East J. Agric. Res. 2017, 6, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Fouladkhah, A.; Berlin, D.; Bruntz, D. High-Sodium Processed Foods: Public Health Burden and Sodium Reduction Strategies for Industry Practitioners. Food Rev. Int. 2015, 31, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.M.; Hwang, I.K.; Eog, G.; Moon, B. Effects of Salts and Preheating Temperature of Brine on the Texture of Pickled Cucumbers. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, C97–C101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, A.; Moreno-Baquero, J.M.; Garrido-Fernández, A. Relationships between Na, K, and Ca Mineral Nutrients in Brine and Table Olive Flesh. Nutritional Labelling Implications. LWT 2023, 189, 115546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Gallego, J.; Arroyo-López, F.N.; López-López, A.; Garrido-Fernández, A. Effect of Chloride Salt Mixtures on Selected Attributes and Mineral Content of Fermented Cracked Aloreña Olives. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effect of Increased Potassium Intake on Blood Pressure, Renal Function, Blood Lipids and Other Potential Adverse Effects. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241504881?ua=1&ua=1 (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Razzaque, M.S. Magnesium: Are We Consuming Enough? Nutrients 2018, 10, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chu, Y.F.; Wu, X.; Liu, R.H. Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Activities of Common Fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7449–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovač, A.; Babojelić, M.S.; Pavičić, N.; Voća, S.; Voća, N.; Dobričević, N.; Jagatić, A.M.; Šindrak, Z. Influence of Harvest Time and Storage Duration on “Cripps Pink” Apple Cultivar (Malus × Domestica Borkh) Quality Parameters Del Tiempo de Cosecha y Duración En Almacenamiento En Los Parámetros de Calidad de La Variedad de Manzana Cripps Pink (Malus × Domestica Borkh). CyTA—J. Food 2010, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorn, D.; Nguyen, T.K.C.; Ho, P.H.; Tan, R.; Licandro, H.; Waché, Y. Screening of Lactic Acid Bacteria for Their Potential Use as Aromatic Starters in Fermented Vegetables. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 350, 109242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Cui, C.; Ruan, Z. Fermentation-Enabled Wellness Foods: A Fresh Perspective. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 203–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardeau, M.; Guguen, M.; Vernoux, J.P. Beneficial Lactobacilli in Food and Feed: Long-Term Use, Biodiversity and Proposals for Specific and Realistic Safety Assessments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 487–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alan, Y.; Savcı, A.; Koçpınar, E.F.; Ertaş, M. Postbiotic Metabolites, Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities of Probiotic Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides Strains in Natural Pickles. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocanu, G.D.; Nistor, O.V.; Constantin, O.E.; Andronoiu, D.G.; Barbu, V.V.; Botez, E. The Effect of Sodium Total Substitution on the Quality Characteristics of Green Pickled Tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Molecules 2022, 27, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, D.; Chhetri, S.B.B. Reducing Sugar, Total Phenolic Content, and Antioxidant Potential of Nepalese Plants. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 7296859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, M.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Different Extraction Methods on Structural and Physicochemical Properties of Pectins from Finger Citron Pomace. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 258, 117662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, S.; Mahnot, N.K.; Mahanta, C.L. Effect of Spray Drying of Four Fruit Juices on Physicochemical, Phytochemical and Antioxidant Properties. J. Food Process Preserv. 2015, 39, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksay, S.; Arslan, R.; Tokbaş, H.; Eroğlu, E.Ç. Changes in Some Biochemical Properties of Brassica Vegetables (Cabbage, Cauliflower and Broccoli) Pickles and Brines. J. Raw Mater. Process. Foods 2022, 3, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Barbu, V. Phenotypical Characterization of Several Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains Isolated from Wheat’s Epiphyte Microbiota. Roum. Biotechnol. Lett. 2008, 13, 4074–4085. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 4833-2:2013(en); Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms—Part 2: Colony Count at 30 Degrees C by the Surface Plating Technique. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:4833:-2:ed-1:v1:en (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- ISO 21527-2:2008(en); Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Yeasts And Moulds—Part 2: Colony Count Technique in Products with Water Activity Less Than or Equal to 0.95. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:21527:-2:ed-1:v1:en (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Rao, M.S.; Pintado, J.; Stevens, W.F.; Guyot, J.P. Kinetic Growth Parameters of Different Amylolytic and Non-Amylolytic Lactobacillus Strains Under Various Salt and PH Conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 94, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dastager, S.G. Isolation, Improvement, and Preservation of Microbial Cultures. In Fermentation Processes Engineering in the Food Industry; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 46–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.F.; DuVivier, R.; Johanningsmeier, S.D. Changes in the Free Amino Acid Profile of Pickling Cucumber during Lactic Acid Fermentation. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennox, J.A.; Efiuvwevwere, B.J.O. Microbial Dynamics of Fermenting Garden Egg (Solanum melongena). Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2014, 3, 950–957. [Google Scholar]
- Rollán, G.C.; Gerez, C.L.; Leblanc, J.G. Lactic Fermentation as a Strategy to Improve the Nutritional and Functional Values of Pseudocereals. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 447741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satora, P.; Skotniczny, M.; Strnad, S.; Piechowicz, W. Chemical Composition and Sensory Quality of Sauerkraut Produced from Different Cabbage Varieties. LWT 2021, 136, 110325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Qian, Y.; Tao, Y.; She, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Guo, S.; Xiang, W.; Liu, L.; Du, H.; et al. Characterization of the Microbial Communities and Their Correlations with Chemical Profiles in Assorted Vegetable Sichuan Pickles. Food Control. 2020, 113, 107174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, B.M.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, G.J.; Song, S.H.; Lee, J.I.; Lee, S.B.; Shim, J.M.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Effects of Different Salt Treatments on the Fermentation Metabolites and Bacterial Profiles of Kimchi. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palani, K.; Harbaum-Piayda, B.; Meske, D.; Keppler, J.K.; Bockelmann, W.; Heller, K.J.; Schwarz, K. Influence of Fermentation on Glucosinolates and Glucobrassicin Degradation Products in Sauerkraut. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Bakyrbay, S.; Liu, L.; Tang, X.; Liu, Y. Microbiota Succession and Chemical Composition Involved in Lactic Acid Bacteria-Fermented Pickles. Fermentation 2023, 9, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, D.; Grosu-Tudor, S.; Zamfir, M.; De Vuyst, L. Bacterial Community Dynamics, Lactic Acid Bacteria Species Diversity and Metabolite Kinetics of Traditional Romanian Vegetable Fermentations. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurtrie, E.K.; Johanningsmeier, S.D.; Breidt, F.; Price, R.E. Effect of Brine Acidification on Fermentation Microbiota, Chemistry, and Texture Quality of Cucumbers Fermented in Calcium or Sodium Chloride Brines. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, D.; Hu, R.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ming, J.; Chi, Y. Effects of Dry-Salting and Brine-Pickling Processes on the Physicochemical Properties, Nonvolatile Flavour Profiles and Bacterial Community during the Fermentation of Chinese Salted Radishes. LWT 2022, 157, 113084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthpala, T.G.G.; Marapana, R.A.U.J.; Jayawardana, S.A.S. Sensory Quality and Physicochemical Evaluation of Two Brine Pickled Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Varieties. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2018, 5, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Lv, M.; Shao, Z.; Hungwe, M.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, W. Metabolism Characteristics of Lactic Acid Bacteria and the Expanding Applications in Food Industry. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 612285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Filho, N.; Linforth, R.; Bora, N.; Powell, C.D.; Fisk, I.D. The Role of Inorganic-Phosphate, Potassium and Magnesium in Yeast-Flavour Formation. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Lv, X.; Liu, S.; Dong, Q.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Su, B. A Selective Separation Mechanism for Mono/Divalent Cations and Properties of a Hollow-Fiber Composite Nanofiltration Membrane Having a Positively Charged Surface. Membranes 2024, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagou, E.Z.; Hondrodimou, O.; Mallouchos, A.; Nychas, G.J.E. A Study on the Implications of NaCl Reduction in the Fermentation Profile of Conservolea Natural Black Olives. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiczorowski, P.; Kiczorowska, B.; Samolińska, W.; Szmigielski, M.; Winiarska-Mieczan, A. Effect of Fermentation of Chosen Vegetables on the Nutrient, Mineral, and Biocomponent Profile in Human and Animal Nutrition. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knez, E.; Kadac-Czapska, K.; Grembecka, M. Effect of Fermentation on the Nutritional Quality of the Selected Vegetables and Legumes and Their Health Effects. Life 2023, 13, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahidsanan, T.; Sittisart, P.; Phonanake, S. Characterization of Pickled Madan Made by Lactobacillus Plantarum NR-MD6-18 (K2) Fermentation. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol 2022, 44, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinowska, M.; Gołebiewska, E.; Zawadzka, M.; Choińska, R.; Koronkiewicz, K.; Piasecka-Jóźwiak, K.; Bujak, M. Sustainable Extraction of Bioactive Compound from Apple Pomace through Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) Fermentation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenderov, B.A. Metabiotics: Novel Idea or Natural Development of Probiotic Conception. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2013, 24, 20399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Díaz, I.M.; Breidt, F.; Buescher, R.W.; Arroyo-López, F.N.; Jiménez-Díaz, R.; Garrido-Fernández, A.; Bautista-Gallego, J.; Yoon, S.-S.; Johanningsmeier, S.D. Fermented and Acidified Vegetables. In Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, D.; Bernaert, N.; Conjaerts, W.; Van Droogenbroeck, B.; De Loose, M.; De Vuyst, L. Species Diversity, Community Dynamics, and Metabolite Kinetics of Spontaneous Leek Fermentations. Food Microbiol. 2013, 33, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, R.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Karami, M. Incorporation of Lactobacillus Casei in Iranian Ultrafiltered Feta Cheese Made by Partial Replacement of NaCl with KCl. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 4209–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hystead, E.; Diez-Gonzalez, F.; Schoenfuss, T.C. The Effect of Sodium Reduction with and Without Potassium Chloride on the Survival of Listeria Monocytogenes in Cheddar Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 6172–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Emara, A.M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; He, Z. Study on the Mechanism of KCl Replacement of NaCl on the Water Retention of Salted Pork. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, A.; Fliss, I.; Filteau, M. High-Throughput Characterization of the Effect of Sodium Chloride and Potassium Chloride on 31 Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Co-Cultures. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1328416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Díaz, I.M.; Hayes, J.S.; Medina, E.; Webber, A.M.; Butz, N.; Dickey, A.N.; Lu, Z.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A. Assessment of the Non-Lactic Acid Bacteria Microbiota in Fresh Cucumbers and Commercially Fermented Cucumber Pickles Brined with 6% NaCl. Food Microbiol. 2019, 77, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljahani, A.H. Microbiological and Physicochemical Quality of Vegetable Pickles. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2020, 19, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.S.; Howard, L.R.; Wagner, A.B. Physicochemical factors affecting firmness of pasteurized jalapeno pepper rings. J. Food Qual. 1999, 22, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Baik, M.-Y.; Kim, B.-Y. Permeation Rate of Salt and Sugar into Cabbage Pickles and Sensory Changes During Storage. Food Eng. Progress. 2018, 22, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorca, E.; Puig, A.; Hernando, I.; Salvador, A.; Fiszman, S.M.; Lluch, M.A. Effect of Fermentation Time on Texture and Microstructure of Pickled Carrots. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, A.; El-Mageed, M.A.; Shaaban, H. Influence of Appropriate Starter Cultures on the Sensory Qualities and Volatiles of Fermented Broccoli and Onion Pickles. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Li, M.; Ren, H.; Cai, S.; Hu, X.; Yi, J. Dynamics of Microbial Communities, Flavor, and Physicochemical Properties of Pickled Chayote during an Industrial-Scale Natural Fermentation: Correlation between Microorganisms and Metabolites. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 132004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangija, F.; Martin, H.; Matemu, A. Effect of Lactic Acid Fermentation on the Nutritional Quality and Consumer Acceptability of African Nightshade. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 3128–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, E.; Gandul-Rojas, B.; Romero, C.; Brenes, M.; Gallardo-Guerrero, L. Composition of Pigments and Colour Changes in Green Table Olives Related to Processing Type. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Salt Solution | Variable | pH | Lactic Acid | Reducing Sugars | Uronic Acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl | pH | 1 | |||
| KCl | 1 | ||||
| MgCl2 | 1 | ||||
| NaCl | Lactic acid | −0.8779 | 1 | ||
| KCl | −0.8540 | 1 | |||
| MgCl2 | −0.8831 | 1 | |||
| NaCl | Reducing sugar | 0.8245 | −0.6873 | 1 | |
| KCl | 0.9549 | −0.7695 | 1 | ||
| MgCl2 | 0.9868 | −0.8975 | 1 | ||
| NaCl | Uronic acid | 0.7043 | −0.5335 | 0.9104 | 1 |
| KCl | 0.7296 | −0.3486 | 0.8604 | 1 | |
| MgCl2 | 0.7361 | −0.5618 | 0.8023 | 1 |
| Parameter | Fermentation Interval | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Days | 7 Days | 14 Days | 21 Days | 28 Days | 35 Days | |
| NaCl | ||||||
| Firmness, N | 4.69 ± 0.11 a | 4.33 ± 0.21 b | 5.74 ± 0.19 c | 1.75 ± 0.22 d | 1.70 ± 0.15 d | 1.74 ± 0.17 d |
| Cohesiveness | 0.69 ± 0.02 a | 0.48 ± 0.03 b | 0.53 ± 0.01 c | 0.49 ± 0.02 d | 0.46 ± 0.02 d | 0.44 ± 0.01 d |
| Springiness, mm | 4.64 ± 0.16 a | 2.95 ± 0.22 b | 3.27 ± 0.19 b | 2.66 ± 0.32 c | 2.92 ± 0.43 c | 3.15 ± 0.35 c |
| Chewiness, mJ | 5.55 ± 0.15 a | 1.43 ± 0.15 b | 1.19 ± 0.11 c | 0.96 ± 0.19 c | 0.66 ± 0.25 c | 0.71 ± 0.17 c |
| KCl | ||||||
| Firmness, N | 4.69 ± 0.11 a | 3.45 ± 0.18 b | 4.13 ± 0.23 c | 3.02 ± 0.22 d | 3.14 ± 0.19 d | 3.02 ± 0.15 d |
| Cohesiveness | 0.69 ± 0.02 a | 0.47 ± 0.01 b | 0.51 ± 0.01 c | 0.41 ± 0.03 d | 0.40 ± 0.02 d | 0.41 ± 0.01 d |
| Springiness, mm | 4.64 ± 0.16 a | 3.70 ± 0.19 b | 2.65 ± 0.21 c | 2.56 ± 0.17 c | 2.53 ± 0.23 c | 2.88 ± 0.16 c |
| Chewiness, mJ | 5.55 ± 0.15 a | 1.92 ± 0.14 b | 1.42 ± 0.15 c | 0.76 ± 0.12 d | 0.64 ± 0.21 d | 0.65 ± 0.14 d |
| MgCl2 | ||||||
| Firmness, N | 4.69 ± 0.11 a | 4.29 ± 0.18 b | 5.35 ± 0.21 c | 4.42 ± 0.13 d | 4.98 ± 0.25 d | 4.76 ± 0.12 d |
| Cohesiveness | 0.69 ± 0.02 a | 0.51 ± 0.03 b | 0.46 ± 0.01 c | 0.48 ± 0.02 c | 0.46 ± 0.01 c | 0.46 ± 0.02 c |
| Springiness, mm | 4.64 ± 0.16 a | 3.47 ± 0.22 b | 2.61 ± 0.18 c | 2.84 ± 0.17 c | 2.95 ± 0.23 c | 3.04 ± 0.19 d |
| Chewiness, mJ | 5.55 ± 0.15 a | 1.69 ± 0.24 b | 1.61 ± 0.27 b | 1.29 ± 0.19 c | 1.34 ± 0.09 c | 1.31 ± 0.28 c |
| Parameter | Fermentation Interval | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Days | 7 Days | 14 Days | 21 Days | 28 Days | 35 Days | |
| NaCl | ||||||
| L* | 70.18 ± 0.65 a | 57.17 ± 1.28 b | 68.81 ± 0.30 c | 70.31 ± 1.47 d | 73.91 ± 0.86 d | 75.94 ± 0.63 e |
| a* | 1.14 ± 0.16 a | −3.78 ± 0.76 b | −0.49 ± 0.04 c | −0.29 ± 0.04 d | −0.27 ±0.05 d | 0.25 ± 0.03 e |
| b* | 15.34 ± 0.54 a | 16.47 ± 0.89 b | 15.57 ± 0.27 c | 14.46 ± 0.86 d | 13.67 ± 0.27 d | 13.25 ± 0.31 e |
| ΔE | - | 13.96 ± 1.05 b | 2.14 ± 0.45 c | 1.68 ± 0.37 d | 4.32 ± 0.14 d | 6.19 ± 0.72 e |
| C* | 14.41 ± 0.79 a | 16.91 ± 0.99 b | 15.57 ± 0.27 c | 14.57 ± 0.83 d | 13.87 ± 0.28 d | 12.65 ± 0.93 e |
| h* | 84.38 ± 2.47 a | −77.14 ± 2.17 b | −88.20 ± 1.16 c | −88.83 ± 1.22 d | −88.85 ± 1.38 d | 88.93 ± 1.33 e |
| KCl | ||||||
| L* | 70.18 ± 0.65 a | 55.94 ± 0.53 b | 61.68 ± 0.86 c | 63.15 ± 1.45 d | 74.34 ± 1.48 d | 75.00 ± 1.65 e |
| a* | 1.14 ± 0.16 a | −4.43 ± 0.53 b | −1.50 ± 0.08 c | −1.37 ± 0.09 d | −1.11 ± 0.09 d | 0.69 ± 0.07 e |
| b* | 15.34 ± 0.54 a | 23.31 ± 1.21 b | 16.14 ± 0.23 c | 15.11 ± 0.87 d | 14.48 ± 0.82 d | 14.43 ± 0.24 e |
| ΔE | - | 17.24 ± 1.17 b | 8.94 ± 0.63 c | 7.47 ± 0.83 d | 4.25 ± 0.86 d | 4.93 ± 0.34 e |
| C* | 14.41 ± 0.79 a | 23.73 ± 1.29 b | 16.21 ± 0.24 c | 15.18 ± 0.88 d | 14.52 ± 0.82 d | 14.46 ± 0.27 e |
| h* | 84.38 ± 2.47 a | −79.26 ± 0.71 b | −84.68 ± 1.28 c | −84.84 ± 0.62 d | −85.60 ± 0.79 d | 86.09 ± 1.21 e |
| MgCl2 | ||||||
| L* | 70.18 ± 0.65 a | 53.42 ± 1.14 b | 71.39 ± 0.77 c | 72.56 ± 1.08 d | 73.10 ± 0.61 d | 74.79 ± 1.32 e |
| a* | 1.14 ± 0.16 a | −5.56 ± 0.98 b | −1.48 ± 0.16 c | −0.78 ± 0.12 d | −0.49 ± 0.03 d | 0.33 ± 0.02 e |
| b* | 15.34 ± 0.54 a | 17.46 ± 1.05 b | 15.55 ± 0.97 c | 14.65 ± 0.33 d | 13.57 ± 0.37 d | 13.41 ± 0.21 e |
| ΔE | - | 18.17 ± 0.78 b | 2.89 ± 0.52 c | 3.13 ± 0.72 d | 3.78 ± 0.53 d | 5.06 ± 0.47 e |
| C* | 14.41 ± 0.79 a | 18.33 ± 1.33 b | 15.62 ± 0.98 c | 14.67 ± 0.33 d | 13.58 ± 0.36 d | 13.41 ± 0.23 e |
| h* | 84.38 ± 2.47 a | −72.43 ± 2.01 b | −84.59 ± 1.28 c | −86.94 ± 0.67 d | −87.92 ± 0.88 d | 88.59 ± 0.95 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Constandache, D.; Andronoiu, D.-G.; Nistor, O.V.; Constantin, O.E.; Moraru, D.I.; Simionov, I.-A.; Botez, E.; Mocanu, G.-D. The Impact of Total Replacement of Sodium Chloride with Potassium and Magnesium Chloride on Pickling of Granny Smith Apples. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073924
Constandache D, Andronoiu D-G, Nistor OV, Constantin OE, Moraru DI, Simionov I-A, Botez E, Mocanu G-D. The Impact of Total Replacement of Sodium Chloride with Potassium and Magnesium Chloride on Pickling of Granny Smith Apples. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073924
Chicago/Turabian StyleConstandache (Lungeanu), Daniela, Doina-Georgeta Andronoiu, Oana Viorela Nistor, Oana Emilia Constantin, Dana Iulia Moraru, Ira-Adeline Simionov, Elisabeta Botez, and Gabriel-Dănuț Mocanu. 2025. "The Impact of Total Replacement of Sodium Chloride with Potassium and Magnesium Chloride on Pickling of Granny Smith Apples" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073924
APA StyleConstandache, D., Andronoiu, D.-G., Nistor, O. V., Constantin, O. E., Moraru, D. I., Simionov, I.-A., Botez, E., & Mocanu, G.-D. (2025). The Impact of Total Replacement of Sodium Chloride with Potassium and Magnesium Chloride on Pickling of Granny Smith Apples. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3924. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073924






