Abstract
The growing demand for cement in construction contributes significantly to environmental degradation due to its high energy consumption and carbon emissions. As a result, there is a pressing need for sustainable alternatives to reduce the environmental footprint of cement production. This study explores the use of marble and glass waste powders as supplementary cementitious materials in mortar production to reduce the environmental impact of cement. By partially replacing cement with varying percentages (0–30%) of marble and glass waste powders, the research evaluates their effects on workability, mechanical properties (compressive strength, density, ultrasonic pulse velocity), and durability (sulfate attack, water absorption, porosity). The results show that a 10% replacement of cement with marble and glass waste powder (MGWP) enhances compressive strength by 25.6% at 28 days and 17.26% at 56 days while improving microstructure and durability through compacted morphology and secondary C-S-H formation. The findings suggest that using MGWP up to 10% is optimal for enhancing the performance of mortar, providing a sustainable alternative to traditional cement with practical implications for greener construction practices.
1. Introduction
Concrete stands as one of the most extensively consumed building materials worldwide, with global production exceeding 10 billion tons annually [1]. Mortar, a crucial binding agent in masonry construction, plays a fundamental role in ensuring structural integrity. Typically composed of cement, fine aggregates, and water, mortar benefits significantly from the superior performance of Portland cement. However, the environmental footprint of Portland cement production is a growing concern. The cement industry accounts for approximately 8% of global CO2 emissions, with an estimated 4.1 billion metric tons of cement produced annually, consuming vast amounts of energy and non-renewable resources [2]. As infrastructure development accelerates, particularly in emerging economies, the demand for cement is expected to rise, exacerbating environmental challenges associated with its production [3,4,5].
The extraction and processing of raw materials for cement manufacturing contribute to resource depletion, while the carbon-intensive clinkerization process further amplifies greenhouse gas emissions. Given the urgent need for sustainable solutions, researchers are actively exploring alternative materials to partially replace cement without compromising performance. Industrial by-products and solid wastes have gained prominence as viable supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs), offering the dual benefits of waste valorization and environmental impact mitigation [6,7].
Among these waste materials, marble and glass waste have emerged as promising candidates for sustainable construction practices [8,9]. Utilizing waste as a substitute for clinker offers significant benefits, as it not only conserves energy and reduces CO2 emissions but also enhances concrete properties by increasing its compactness and altering its microstructure [10]. The global marble industry produces millions of tons of waste annually, with an estimated 30–40% of extracted marble ending up as unusable scrap [11]. Improper disposal of marble waste leads to soil degradation, water contamination, and dust-related health hazards [10]. Similarly, glass waste constitutes a major fraction of municipal solid waste, with over 130 million tons generated worldwide each year. Despite existing recycling efforts, only about 20% of glass waste is effectively reused, leaving vast quantities to accumulate in landfills [12]. Recycling glass can reduce energy consumption by up to 27% and lower CO2 emissions by 37%, underscoring its significance in sustainable construction [13].
Marble waste, rich in calcium carbonate, serves as an effective filler in cementitious systems, improving packing density and reducing porosity [14]. Conversely, glass waste, primarily composed of silica, actively contributes to pozzolanic reactions, promoting calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) formation—a key factor in cement matrix strengthening. The complementary properties of these materials create a synergistic effect, enhancing both mechanical performance and durability in mortar applications [15].
Given these advantages, the utilization of marble and glass waste as SCMs aligns with global sustainability goals, addressing resource scarcity, waste management challenges, and environmental concerns. This study aims to make a significant scientific contribution by systematically investigating the feasibility of partially replacing cement with marble and glass waste powder (MGWP) in mortar. Through a comprehensive analysis of its effects on fresh, mechanical, durability, and microstructural properties, this research seeks to establish a robust understanding of MGWP’s role in sustainable construction. By bridging the gap between material science and practical application, this study contributes to the advancement of eco-friendly cementitious materials and paves the way for more resilient and environmentally responsible infrastructure development.
2. Materials and Methods
In this section, the details of the experimental methodology, mortar mix design, material preparation, and the production process of marble waste powder (MWP) and glass waste powder (GWP) are given. The investigation focuses on the fresh, hardened, and microstructural properties of mortar containing MGWP as a partial replacement for cement, as outlined in Section 2.3.
2.1. Materials
The materials used in this study for the production of mortar include cement, fine aggregate (natural river sand), water, MWP, and GWP.
2.1.1. Cement
The binding material employed in this study was locally sourced Messebo ordinary Portland cement (OPC 42.5R), which conforms to the requirements of the American Society Testing and Materials (ASTM) C150 [16] and the Ethiopian Standard ES 1177 [17].
2.1.2. MWP
Marble waste powder was sourced from the Kokeb Painting and Marble Factory in Bahir Dar, Ethiopia. The collected waste was initially wet and was sun-dried to remove moisture. The dried marble waste was then sieved to a particle size of 75 μm to ensure uniformity and suitability for BET-specific surface area measurements, chemical composition analysis, and specific gravity tests. The prepared MWP was subsequently utilized in all mortar mix designs.
2.1.3. GWP
Glass waste was collected from the waste disposal site at Bahir Dar Institute of Technology (BiT), Bahir Dar University, Ethiopia. The collected glass waste was thoroughly washed and cleaned with water to remove impurities and dirt. After drying, the cleaned glass waste was crushed using a jaw crusher and further ground using a disk milling machine. The resultant GWP was sieved to a particle size of 75 μm, ensuring consistency for its use in mortar mix designs and subsequent investigations.
2.1.4. Fine Aggregate
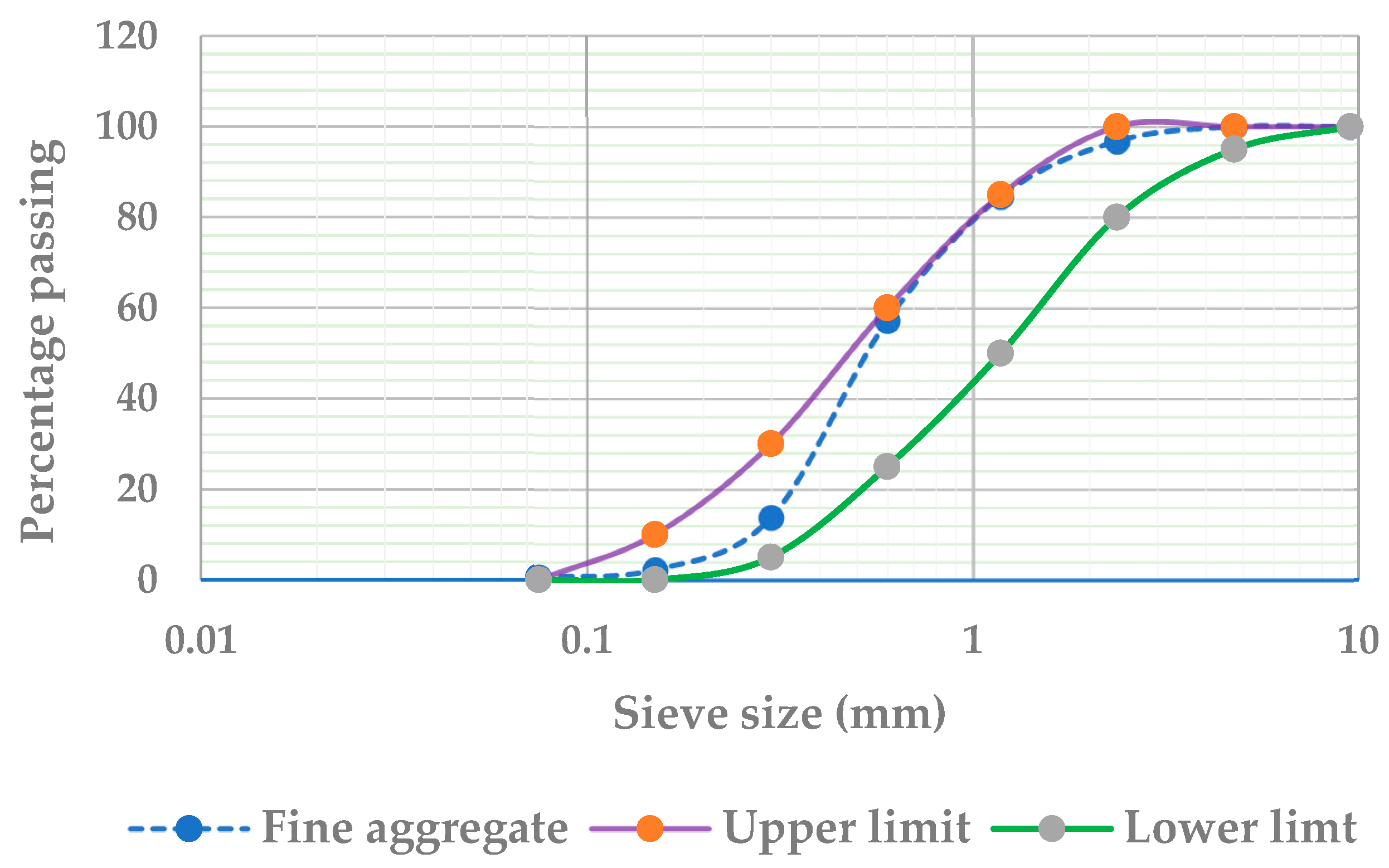
For this study, Arbaya natural river sand, sourced from Ethiopia, was utilized for mortar production. A comprehensive series of tests were conducted to evaluate the fine aggregate’s properties in strict adherence to ASTM standards, ensuring its suitability for construction applications. The results, summarized in Table 1, confirm that the sand’s fineness modulus, determined to be 2.5, falls within the optimal range of 2.3 to 3.1 specified by ASTM C33 [18]. Additionally, the gradation was analyzed in compliance with ASTM C136 [19] and ASTM C33 standards, with the gradation curve illustrated in Figure 1. As per ASTM C33 [18], aggregates with particle sizes below 4.75 mm are classified as sand. The Arbaya River sand exhibits the required physical characteristics and meets all quality benchmarks, making it an appropriate choice for mortar production.

Table 1.
Physical properties of fine aggregate.
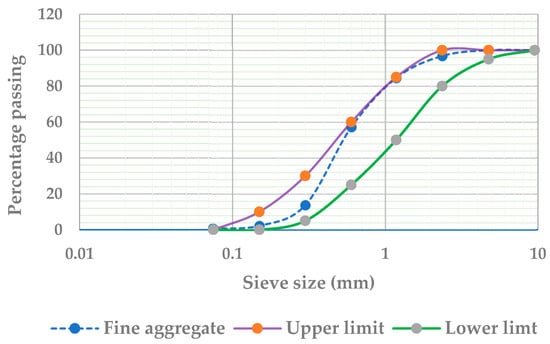
Figure 1.
Gradation curve for fine aggregate according to ASTM C33.
2.2. Physical and Chemical Properties of OPC, GWP, and MWP
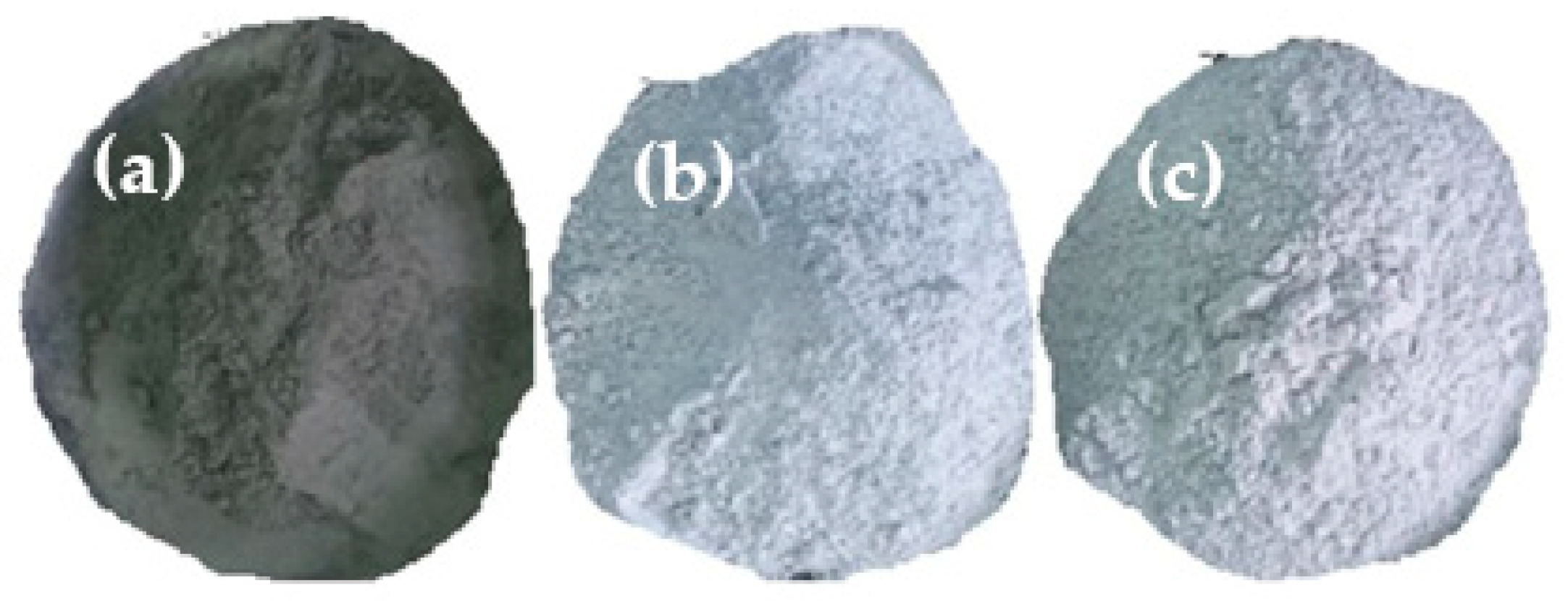
Distinct differences in the color of OPC, GWP, and MWP were observed during the production process, as shown in Figure 2. OPC exhibits a dark gray color, whereas both MWP and GWP are white. The white coloration of MWP and GWP is attributed to the lower amount of Tetra Calcium Alumino-ferrite (C4AF) present in these powders [24].

Figure 2.
Visual appearance of (a) OPC, (b) GWP, and (c) MWP.
The physical properties of OPC, GWP, and MWP are summarized in Table 2. Notably, the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area test analysis revealed that GWP (485.15 m2/g) and MWP (439.47 m2/g) exhibit significantly larger surface areas compared to OPC (339.56 m2/g). This increased surface area contributes to enhanced strength development of mortar as hydration reactions progress. The fineness of cement, a critical parameter representing the specific surface area, is closely linked to the physical and mechanical properties of the hydrated cement, including strength, setting time, and rheology [25].

Table 2.
Physical and chemical properties of OPC, GWP, and MWP.
The results of X-ray fluorescence (XRF) showed that the main component of GWP is silicon oxide (SiO2), with minor quantities of aluminum oxide (Al2O3) and iron oxide (Fe2O3), as presented in Table 2. According to ASTM C618 [26], GWP qualifies as a Class N natural pozzolans because the sum of SiO2, Al2O3, and Fe2O3 exceeds 70% (73.04%), and the LOI is below 10% (0.58). In contrast, MWP does not meet the pozzolanic material requirements specified in ASTM C618 [26]. It is classified as a calcareous material due to its high calcium oxide (CaO) content (52.82%) and a LOI of 41.8%.
2.3. Mix Design
The mortar mix design for this study was tailored to meet the requirements of ASTM C109 [27] with the mix proportions determined based on the number of cubes to be produced. Mortar batches, sufficient to create six cubes each, were prepared in accordance with ASTM C305, incorporating GWP and MWP as partial replacements for cement. The mixes were prepared using a mechanical mixer. Table 3 presents the detailed mix proportions utilized in the experimental study.

Table 3.
Material proportion for mortar production.
To optimize the replacement levels, three proportions of waste powders (1:1, 1:2, and 2:1 MWP: GWP) were tested for the selected percentage replacements of cement. A pilot study was conducted using a trial with a constant water-to-binder ratio (w/b) of 0.53 and a cement-to-sand ratio of 1:2.75 for the production of 2-inch (50 mm) mortar cubes. The compressive strength results from the trial mixes indicated that the 1:2 (MWP: GWP) ratio consistently delivered the highest strength for the selected replacement percentages. As a result, the 1:2 ratio was adopted for all subsequent experimental studies at various cement replacement levels (0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, and 30%).
For the comprehensive experimental investigation, 420 mortar cubes were produced in compliance with ASTM C109 [27], each measuring 2 inches (50 mm). The study encompassed testing for compressive strength, ultrasonic pulse velocity, sulfate attack resistance, water absorption, porosity, and microstructural properties. A minimum number of three cube specimens were tested for each percentage replacement at various curing ages (3, 7, 28, 56, and 91 days).
2.4. Test Methods
Before evaluating the mortar properties, the physical properties of OPC and OPC blended with MGWP at varying proportions were thoroughly tested. These properties, including setting time and soundness, were examined in strict compliance with ASTM C187 [28], ASTM C191 [29], and ES 1177 [17] standards, respectively. Consistency is a vital parameter that determines the precise amount of water required to initiate chemical reactions between the binder and water, ensuring a smooth and uniform flow of the paste. This critical property was measured using the Vicat apparatus. Furthermore, the soundness of the cementitious materials, an indicator of volume stability, was assessed using the Le-Chatelier apparatus to guarantee the structural integrity of the mix. These tests provided essential insights into the behavior of the cementitious materials, forming the foundation for subsequent mortar property evaluations.
The workability of mortar was determined using a flow table according to ASTM C1437 [30]. This method measures the flowability of the mortar by recording the percentage increase in the base diameter of a truncated cone after it is mechanically raised and dropped 25 times within 15 s.
To assess the hardened properties of mortar, specimens were prepared and cast in molds measuring 50 mm × 50 mm × 50 mm. The specimens were covered with plastic bags for 24 h, then demolded and submerged in a curing tank at room temperature for periods of 3, 7, 28, 56, and 91 days. For all tests, the average value of three mortar cube samples was used. Compressive strength was measured following the procedures outlined in ASTM C109 [27]. The bulk density of hardened mortar was calculated by measuring the weight of the cubes in a saturated surface-dry (SSD) condition and determining their actual dimensions.
Water absorption and porosity tests were conducted for all curing ages as per ASTM C642 [31]. Mortar cubes were immersed in water under SSD conditions, and their mass gain was measured as a percentage of the dry mass. This is critical for understanding the porosity and permeability of the mortar. Additionally, the resistance of the mortar to sulfate attack was evaluated by curing the samples in a 5% sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) solution as per ASTM C1012 [32]. The strength loss was then measured to determine the impact of sulfate exposure.
The ultrasonic pulse velocity (UPV) test, carried out according to ASTM C597-09 [33], was used to access the uniformity, relative quality, and potential defects in the hardened mortar. The analysis was performed using the Controls Model 58-E4900, ensuring precise and reliable measurements. The test involved passing electronic waves through the mortar and measuring the time required for the waves to travel between transducers. This process was repeated for all curing ages, and the average results from three mortar cubes were recorded for each partial cement replacement with MGWP.
Microstructural analysis included scanning electron microscope (SEM), conducted in accordance with ASTM C1723-16 [34]. A JCM 6000 PLUS SEM machine was employed for imaging and analysis. Following compressive strength testing, broken mortar samples were stored in ethanol to halt hydration. These samples were then sectioned into smaller pieces for SEM image analysis after the 28th day of curing. Measurements were performed at 15 kV under a high vacuum with suitable magnification to study the morphology of the mortar.
Thermal analysis, comprising thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential thermal analysis (DTA), was carried out following ASTM E1131 [35]. A Thermogravimetric Analyzer, Model HCP-1, was utilized for precise measurements. Samples were heated to 900 °C at a rate of 20 °C per minute to examine the thermal stability and mass loss among control mixes and those containing MGWP. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), as per ASTM E1252 [36], was utilized to identify functional groups in the mortar. FT-IR analyses were conducted with a wave range of 4000–400 cm−1 for various mortar mixes. The test methods and standards applied are summarized in Table 4.

Table 4.
Summary of tests performed on fresh, hardened, and microstructural properties of the mortar.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fresh Properties
3.1.1. Normal Consistency of Paste
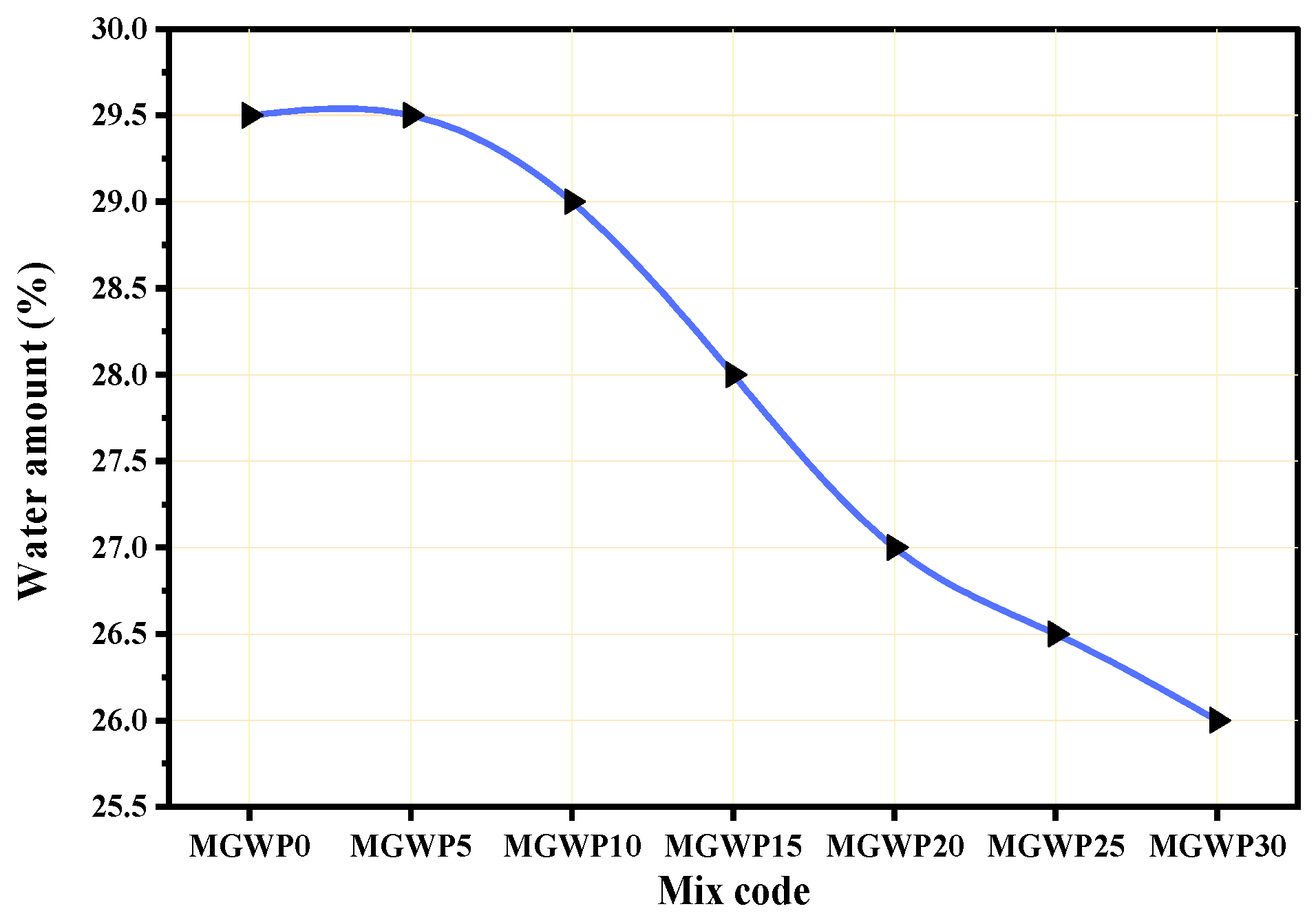
The consistency of OPC and OPC blended with varying MGWP is depicted in Figure 3. As illustrated, the water demand of mortar mixes decreased as the amount of MGWP increased. While all mortar mixes required slightly more water than the control mix, the water content across all mixes remained within the acceptable range of 26–33%, as specified by ASTM standards [28], ensuring normal consistency. This reduction in water demand can be attributed to the non-absorbent and smooth behavior of MGWP, which aids in reducing water demand. This behavior is consistent with observations from previous studies [37,38]. Moreover, the soundness (expansion) of cement increased as the percentage of MGWP in the mix grew. This may be due to the free lime content, which causes expansion, similar to findings from other studies [10,37]. However, the results were within acceptable limits, with an expansion of less than 10 mm, as per ES 1177 [17].
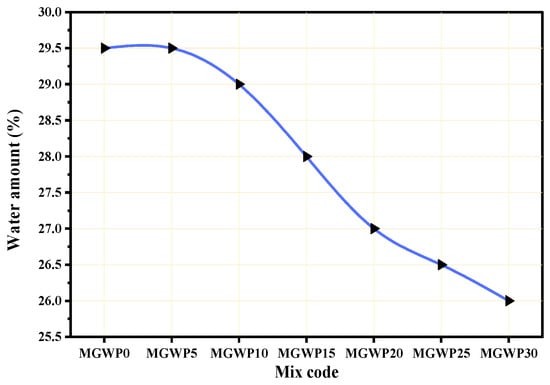
Figure 3.
Consistency of binder with various replacement levels of MGWP.
3.1.2. Initial and Final Setting Time
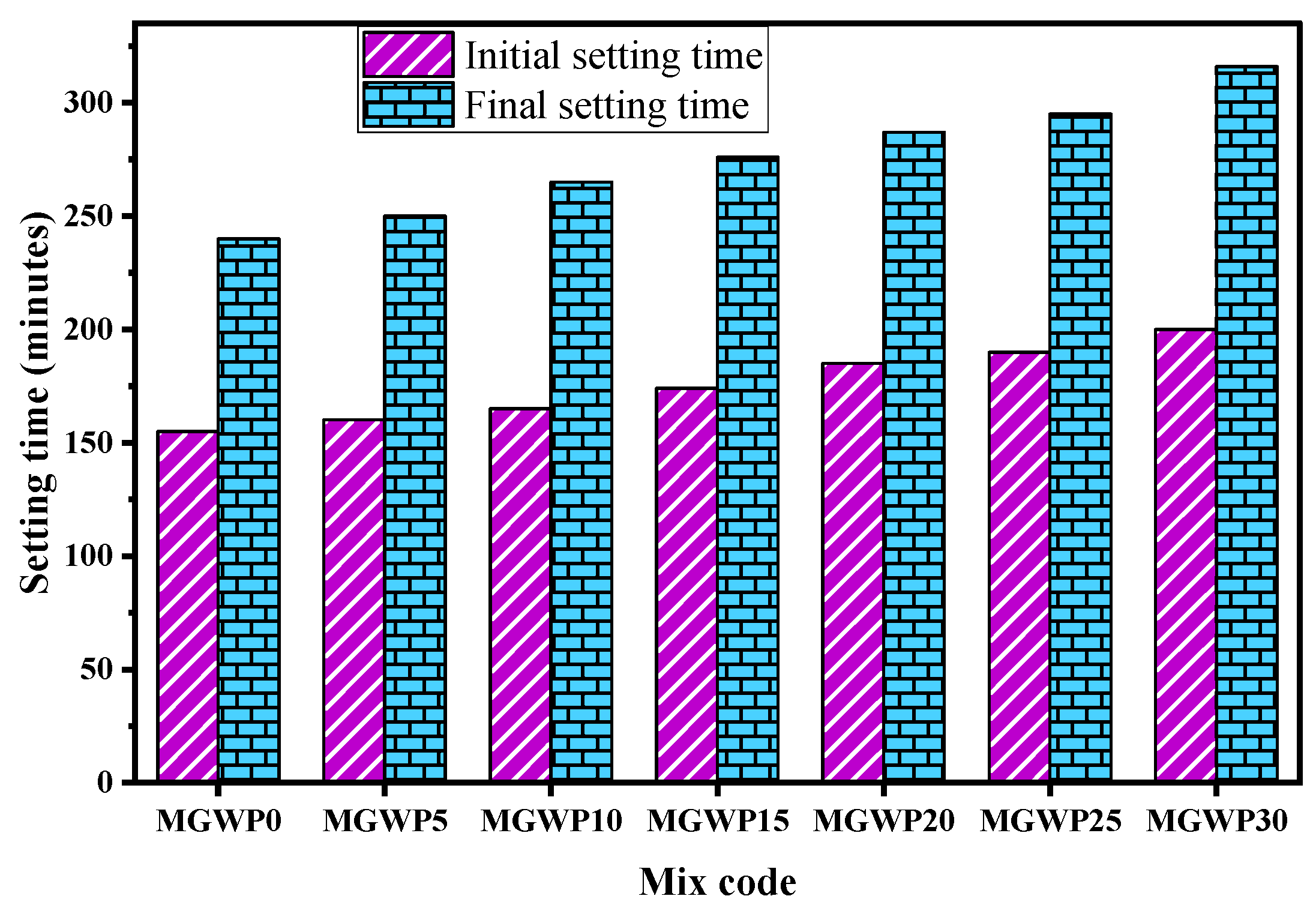
Both the initial and final setting times increased as the replacement level of MGWP rose, as shown in Figure 4. For the MGWP30 mix, the initial setting time was 200 min, and the final setting time was 316 min, representing a 29.0% and 31.7% increase, respectively, compared to the control mix. The increased setting time is attributed to the presence of silicon oxide in MGWP, which has a retarding effect on the cement paste. Silicon oxide contributes to delaying the setting time by initiating a pozzolanic reaction that affects the hydration of the cement, particularly by lowering the C3S content in the mix [39]. Similar findings have been reported in other studies [40,41], while contrasting results were observed in research involving marble as a cement replacement [42]. Both ES 1177 [17] and ASTM C150 [16] recommend a minimum initial setting time of 45 min and a maximum final setting time of 600 and 375 min, respectively, which were comfortably met by all the mixes.
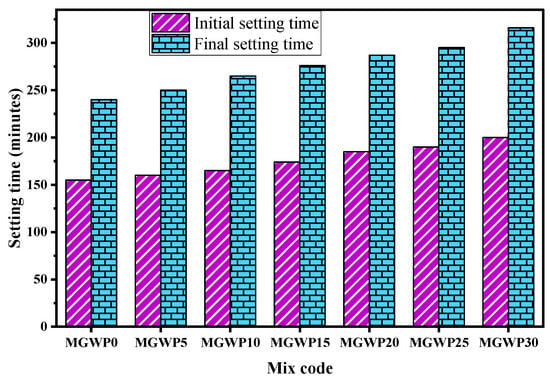
Figure 4.
Setting time of binder with various replacement levels of MGWP.
3.1.3. Slump Flow
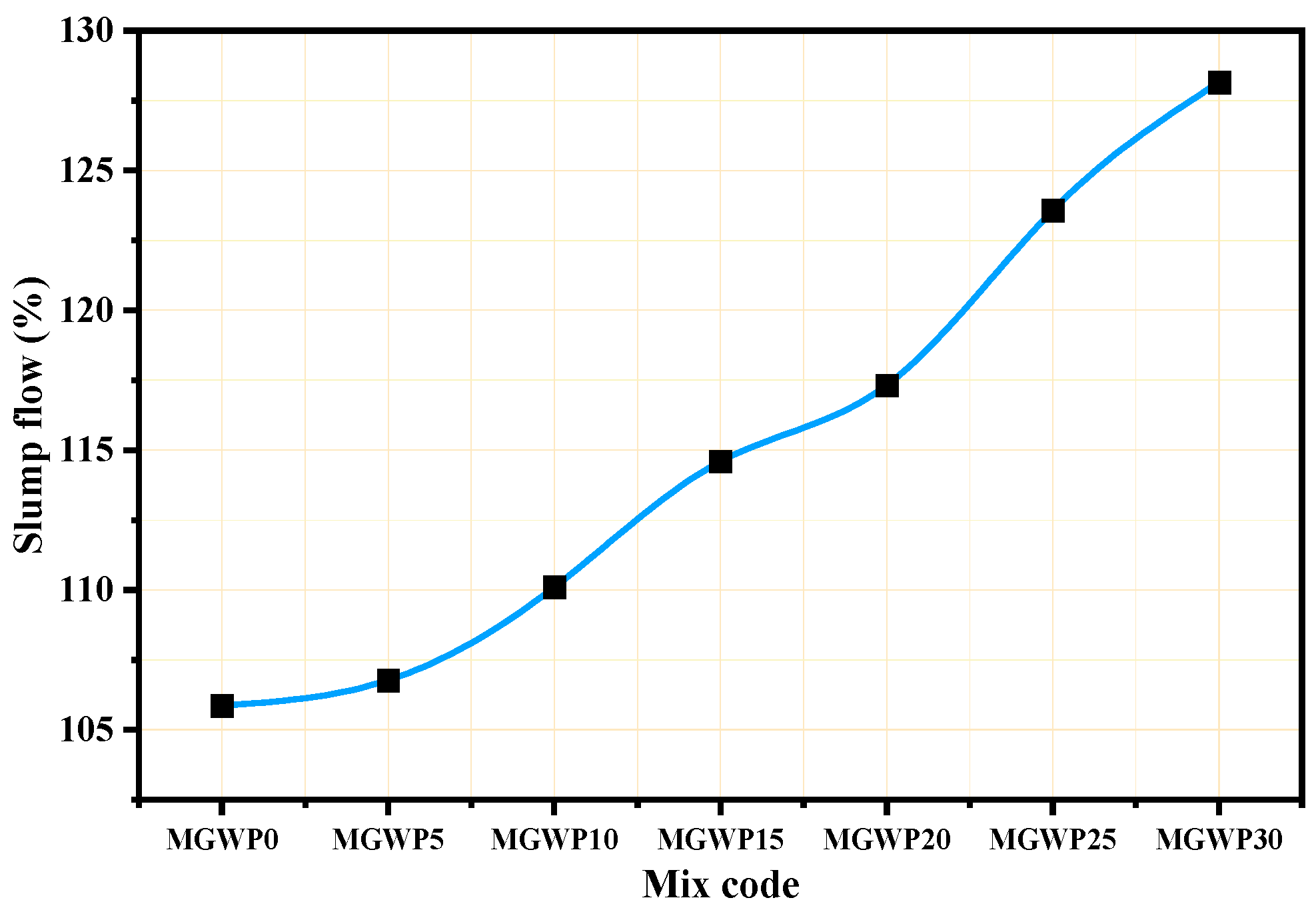
The workability of fresh mortar was assessed using the flow table test in accordance with ASTM C1437 [30]. As specified by ASTM C270 [43], laboratory-prepared mortar should have a flow rate of 110 ± 5%. Figure 5 illustrates that the workability of the mortar mix is increased with the partial replacement of cement by MGWP when compared to the control mix. This trend is consistent with previous studies on the impact of marble and glass waste powders on mortar workability [41,44,45]. The addition of up to 15% MGWP resulted in good workability, in line with ASTM C270. The increased workability can be attributed to the non-absorptive and smooth surface behavior of the GWP, which enhances the mortar’s flow. Despite the finer particle size of both marble and glass waste powders compared to cement, their smooth surfaces help improve their workability. Furthermore, the micro-filling effect due to the fine nature of the glass powder contributes to better packing of the mortar, filling voids and thus improving its overall flow [46,47].
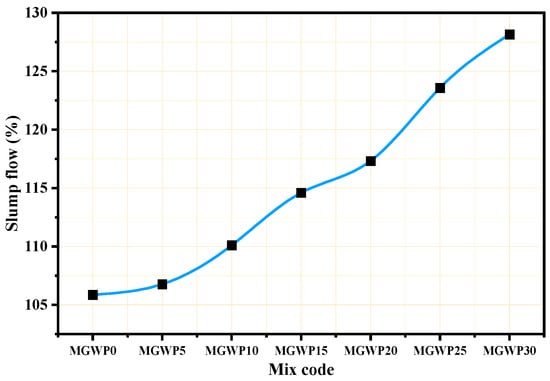
Figure 5.
Slump flow of mortar with various replacement levels of MGWP.
3.2. Mechanical Properties of Mortar
3.2.1. Compressive Strength
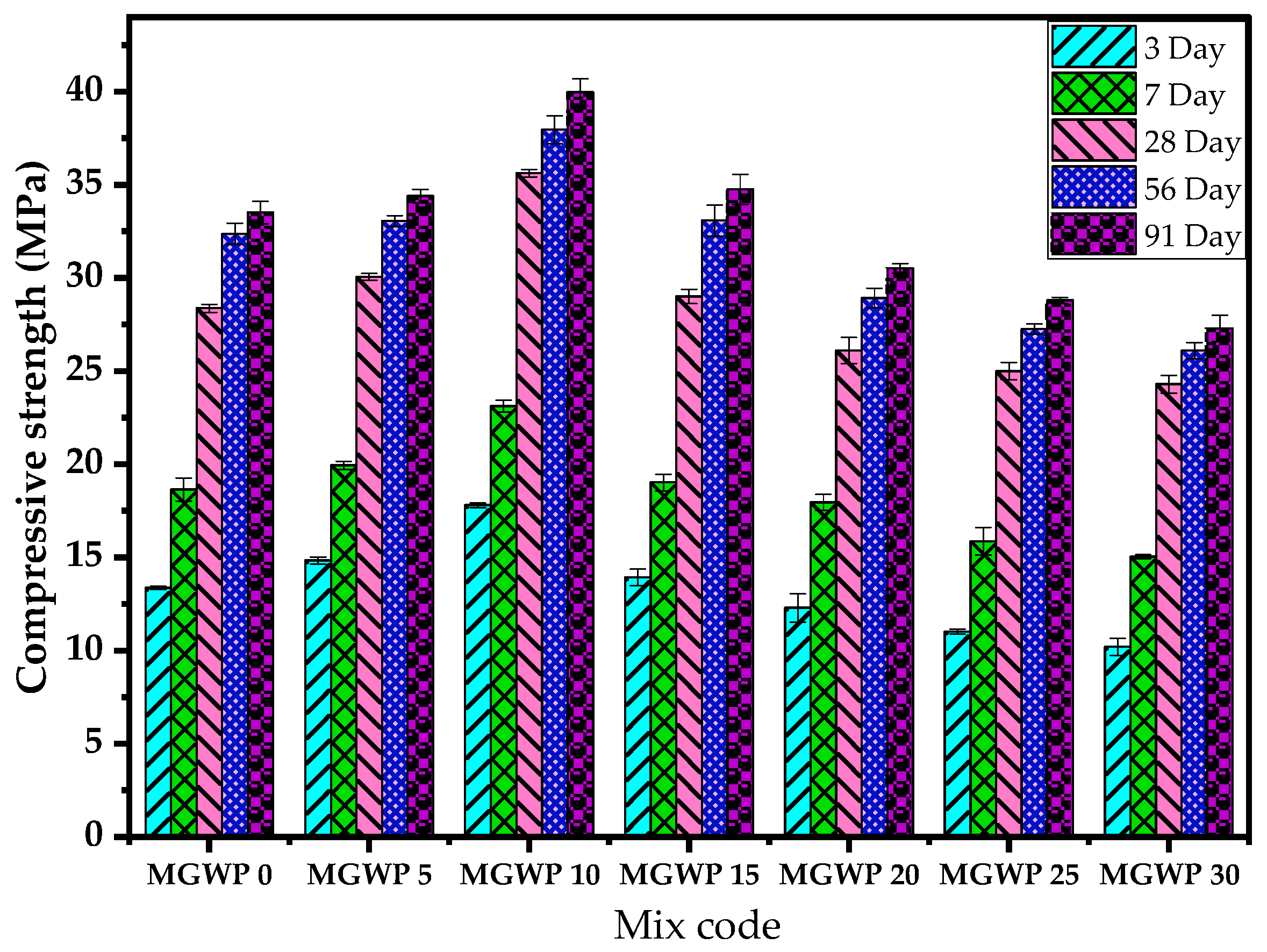
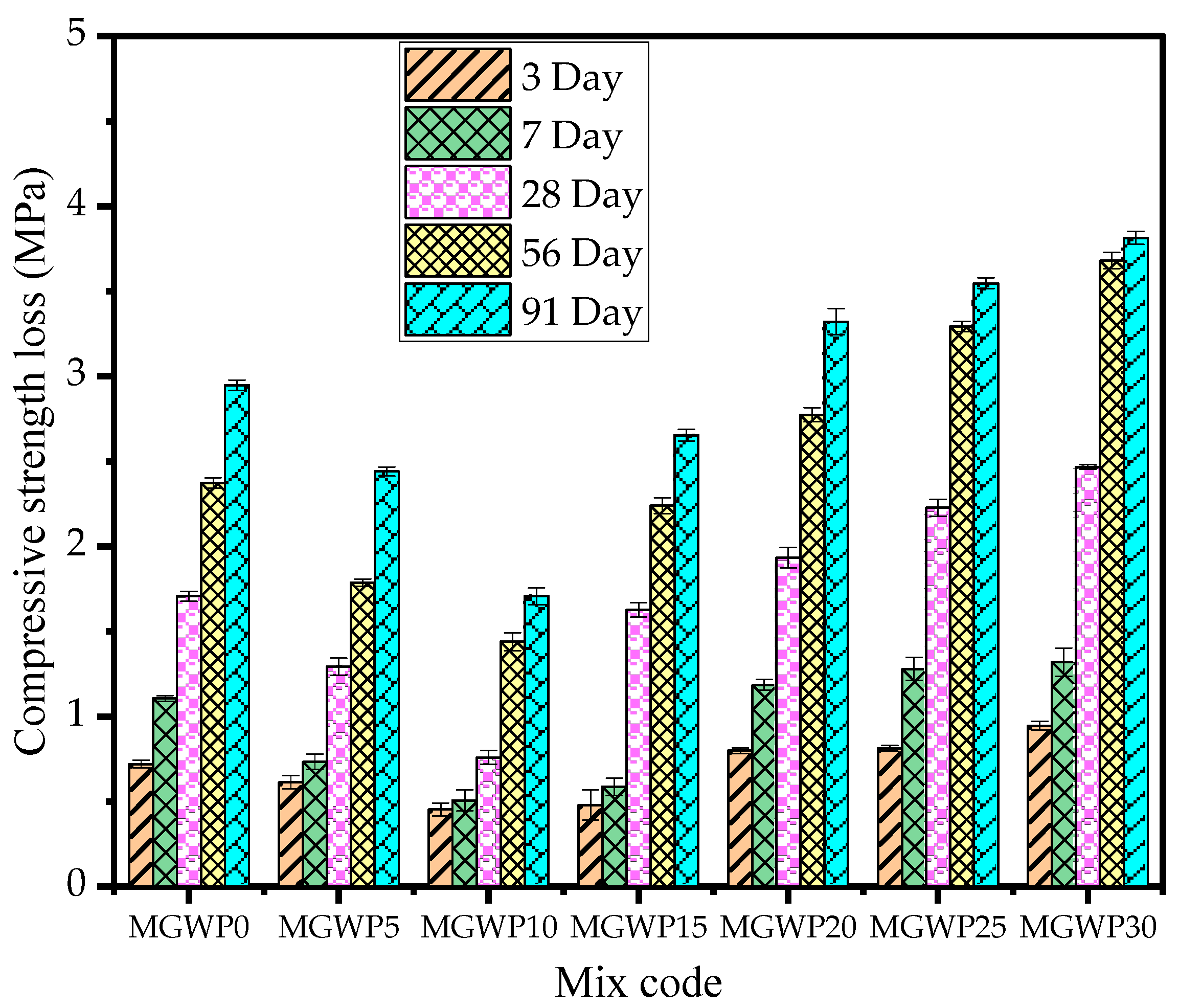
The effects of MGWP on the compressive strength of mortar are presented in Figure 6. The compressive strength tests were conducted at curing intervals of 3, 7, 28, 56, and 91 days, utilizing an average of three mortar cubes. Results revealed a significant improvement in compressive strength as the percentage of MGWP increased, peaking at a 10% replacement level. Specifically, the compressive strength at 28 days increased by 25.6% and 17.26% at 10% MGWP replacement compared to the control mix. A slight reduction in strength was observed at 15% replacement, although the values still surpassed the control mix, showing an increase of 2.3% and 2.2% at 28 and 56 days, respectively.
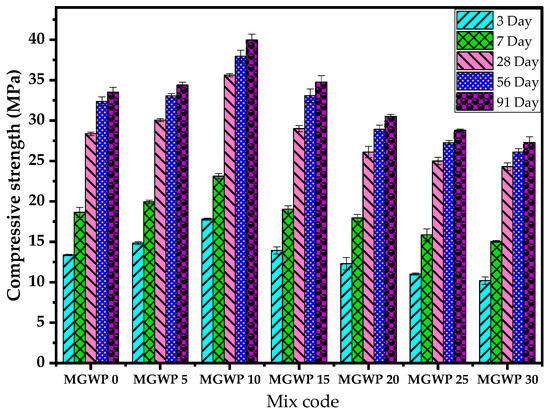
Figure 6.
Effects of MGWP on the compressive strength of mortar.
The increment of compressive strength with MGWP can be attributed to enhanced C-S-H gel formation by the pozzolanic activity of MGWP. The finer glass powder particles fill the capillary pores, reducing porosity and densifying the mortar matrix, which contributes to the strength improvement [46,48,49]. As curing age advanced to 91 days, the hydration reactions progressed further, leading to continued strength gains. However, at 30% MGWP replacement, compressive strength declined significantly due to the reduction in the cementitious material since MGWP replaced a larger proportion of cement [50,51].
Furthermore, the BET surface area analysis demonstrated that MGWP has a higher fineness compared to OPC, enhancing its reactivity. The pozzolanic reaction of the amorphous silica in GWP with calcium hydroxide results in secondary C-S-H, thereby improving the microstructure and long-term strength of the mortar. This reaction also minimizes the calcium hydroxide content, a known weak phase in concrete, further strengthening the composite [52,53].
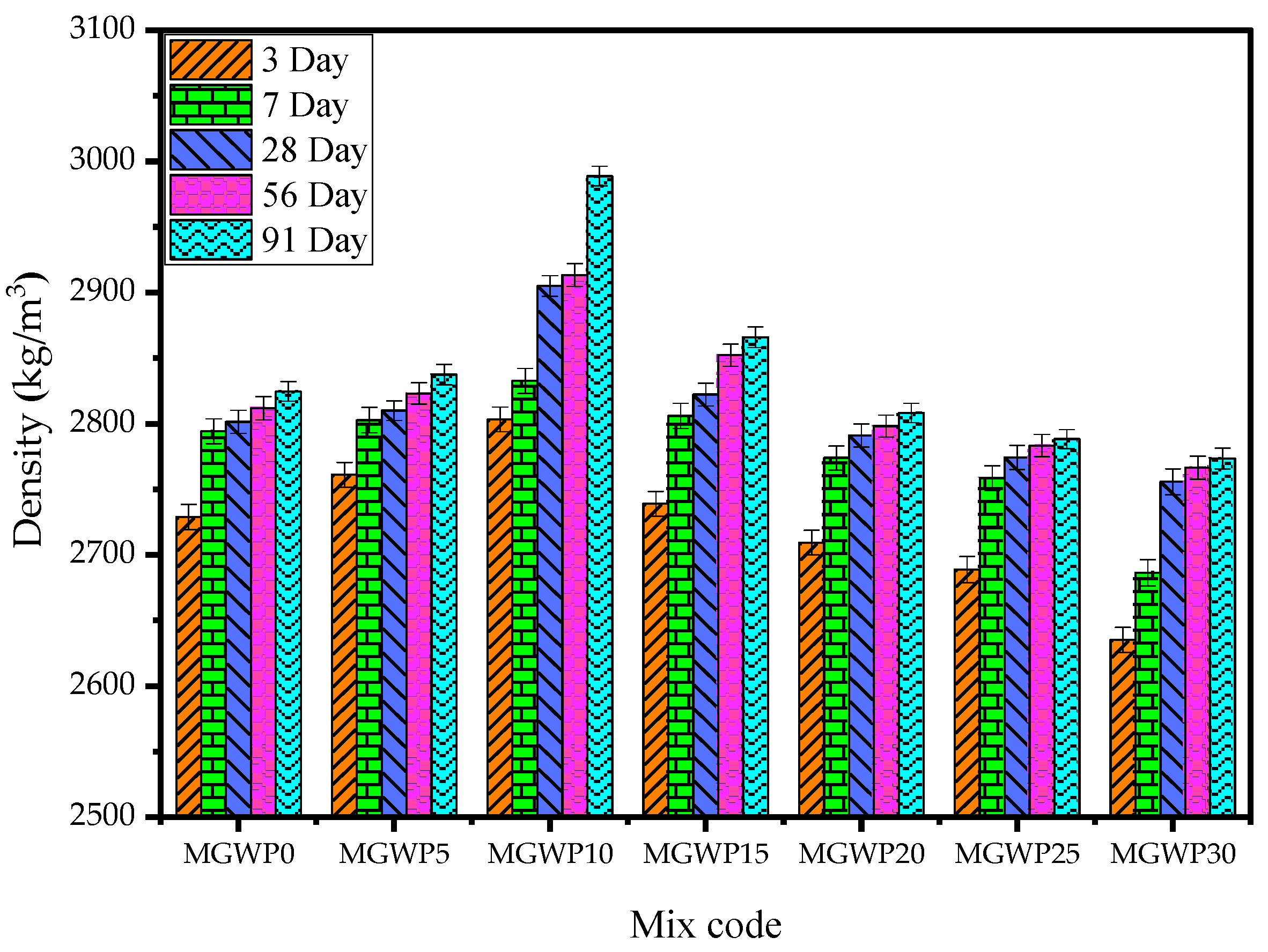
3.2.2. Bulk Density
The bulk density of mortar, measured using SSD weights for various curing ages, is illustrated in Figure 7. For each mix composition, the average values of three mortar cubes were recorded at curing intervals of 3, 7, 28, 56, and 91 days. As shown in Figure 7, the bulk density increased with MGWP content up to 15% replacement level. The highest bulk density was observed at 10% MGWP replacement, followed by a gradual decline with further increases in MGWP content.
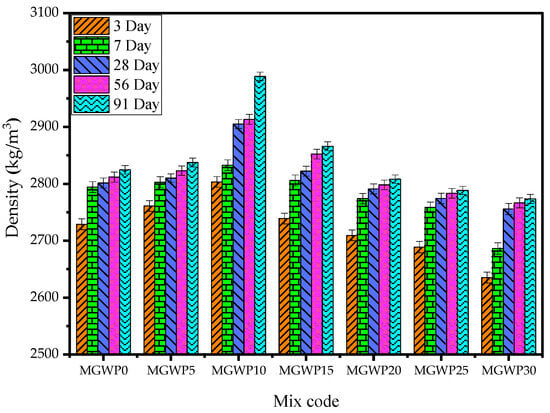
Figure 7.
Bulk density of mortar with various replacement levels of MGWP.
The enhanced bulk density at lower replacement levels is linked to the micro-filler effect of MGWP, where fine particles infiltrate and plug capillary pores, reducing permeability and densifying the mortar structure [54,55]. This densification improves the paste-to-aggregate bond, resulting in a more compact and durable matrix compared to conventional mortar [3]. Beyond 15% replacement, however, the reduction in cementitious material leads to a decrease in density, as confirmed by earlier studies [15,44,56].
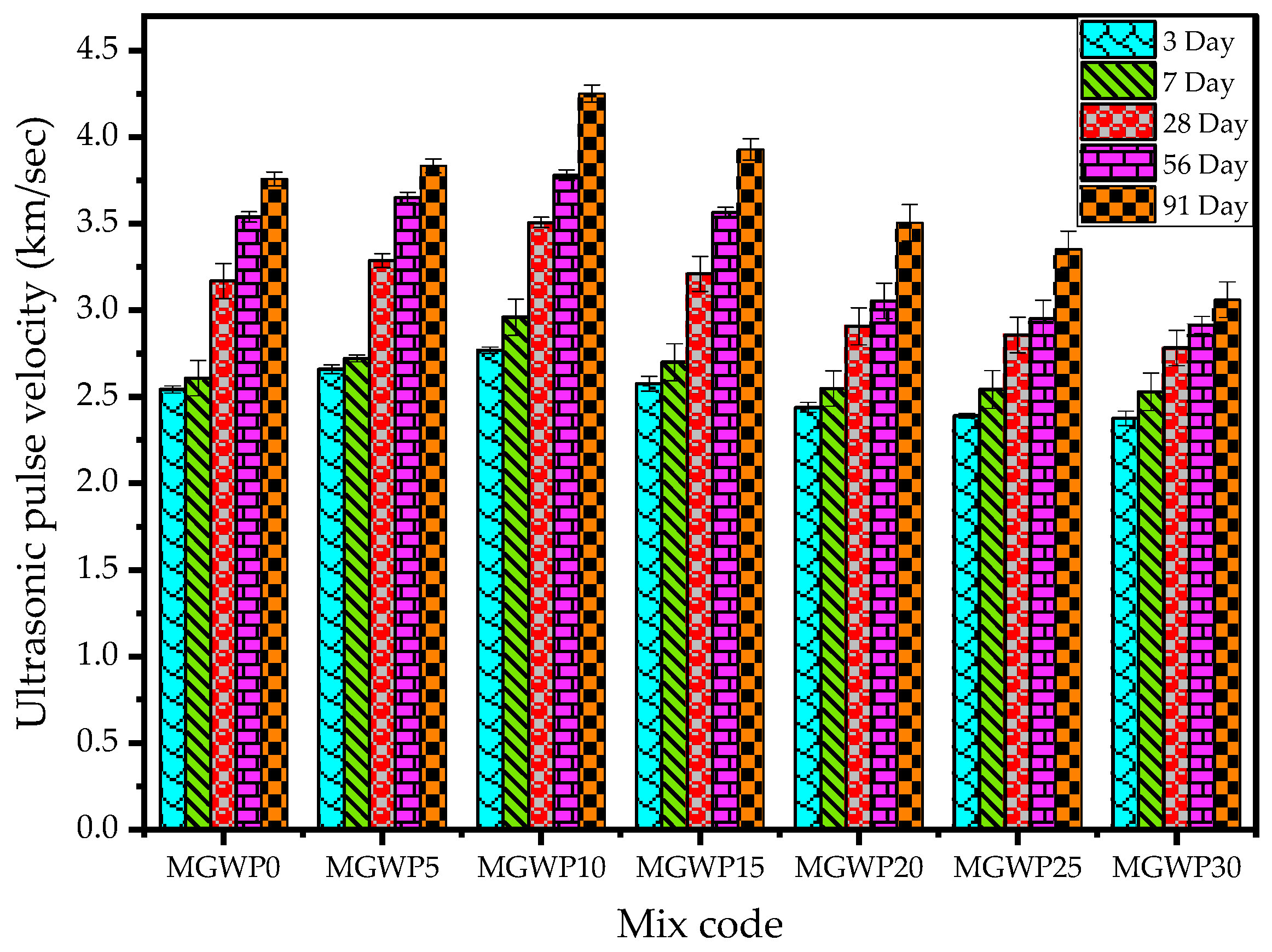
3.2.3. UPV
The UPV test, conducted in accordance with ASTM C597-09 [33], assess the uniformity, relative quality, and durability of mortar. Figure 8 presents the UPV results for mortar samples with partial MGWP replacement, evaluated at curing ages of 3, 7, 28, 56, and 91 days.
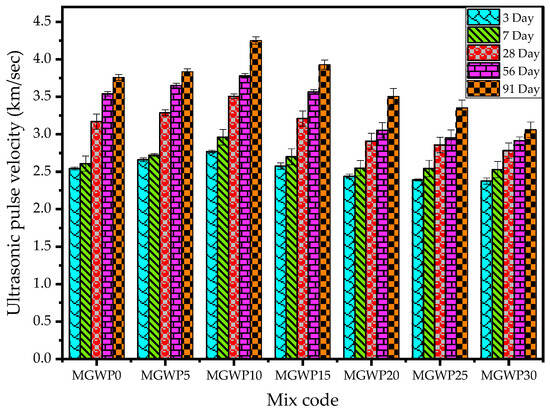
Figure 8.
Effect of MGWP on UPV of mortar.
The UPV values progressively increased with curing age, ranging from 2.53 to 2.96 km/sec at 28 days to 3.06–4.25 km/sec at 91 days. At 10% MGWP replacement, the UPV results were 18.5% higher at 28 days compared to the 7-day results and 7.8% higher at 56 days relative to the 28-day values. The rate of increase in UPV values diminished after 28 days.
According to the IS 13311 (Part 1): 1992 [57], mortar incorporating MGWP was rated as “good” at 10% replacement and “medium” at 15% replacement at 28 days. Significant improvements in quality were observed at 56 and 91 days, with the highest UPV value achieved at 10% MGWP replacement. This result aligns with the highest bulk density and compressive strength values, as well as reduced porosity and water absorption in these mixes. The improved UPV performance is attributed to the additional C-S-H gel formation from the pozzolanic reaction of GWP, combined with the filler effect of MGWP, which reduces air voids and densifies the matrix [58]. These factors enhance the durability and mechanical properties of the mortar, as supported by previous research [55].
3.3. Durability Properties
3.3.1. Sulfate Attack
The combined effects of MGWP on sulfate resistance are illustrated in Figure 9. The mortar cubes were immersed in a sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) solution according to ASTM C1012-09 and tested at 3, 7, 28, 56, and 91 days of curing. The average value of three mortar cubes was recorded to assess the compressive strength loss due to the sulfate attack. The incorporation of MGWP as a partial replacement at 10% and 15% significantly improved the sulfate resistance of mortar compared to the control mix. Using MGWP as an SCM improves sulfate resistance and prevents thaumasite formation by decreasing the Ca(OH)2 content, reducing the calcium to silica (Ca/Si) ratio in C-S-H, and refining the pore structure to limit the penetration of external aggressive ions [59]. This enhancement is attributed to the densification effect (micro-filling) and additional C-S-H gel formation, which restricts sulfate ingress into the mortar matrix [60]. As shown in Figure 9, compressive strength loss decreases with MGWP replacement up to 15%, beyond which it increases at 30% replacement.
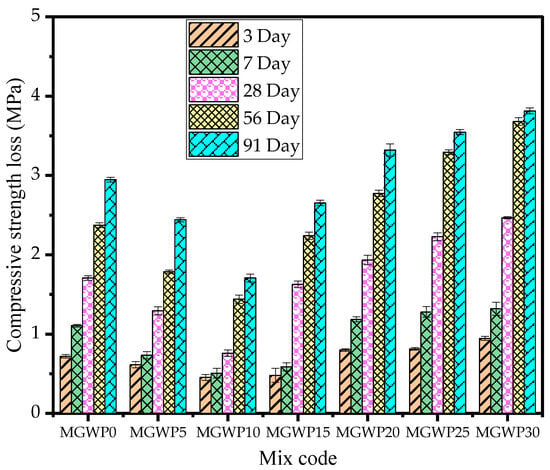
Figure 9.
Effect of MGWP on sulfate resistance of mortar.
3.3.2. Water Absorption
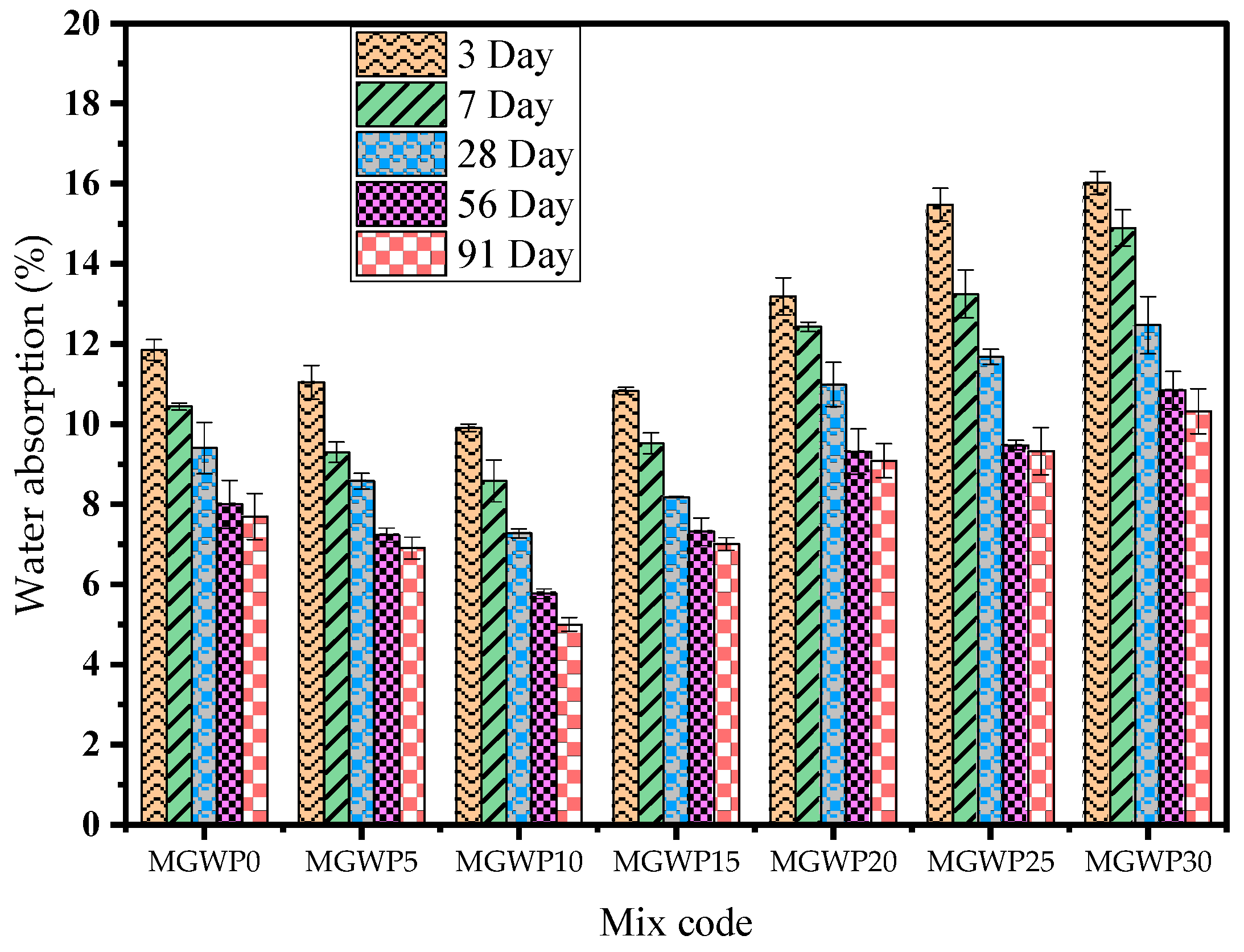
Figure 10 presents the results of the water absorption test conducted on mortar specimens following ASTM C642-06 [31], evaluated at curing durations of 3, 7, 28, 56, and 91 days. The water absorption of mortar cubes initially decreases up to 15% and increases as the replacement level of cement reaches 30% across all curing ages. Notably, the lowest water absorption values were observed at a 10% MGWP replacement of cement. Specifically, at 28 days, water absorption reduced by 22.3% and 12.8% for the 10% and 15% MGWP replacements, respectively, when compared to the control mix. At 56 days, the reductions were 27.8% and 8.8%, and at 91 days, the reductions were 35.1% and 9.1% for the 10% and 15% replacements, respectively. Mortar with 10% MGWP replacement reached a water absorption value of just 5.0%, the lowest observed at 91 days of curing, outperforming all other mixes. This suggests enhanced matrix compaction, strength, and durability in the presence of MGWP, which is known to reduce the water absorption of the mortar. Water absorption, which is generally associated with the structural pores—especially in the aggregate-interface zone—decreases with the MGWP, indicating refinement in this region and a corresponding improvement in overall durability. This finding aligns with the trends observed in the compressive strength and porosity results. Additionally, at a 30% MGWP replacement, water absorption increases by 33.0%, 35%, and 33.8% after 28, 56, and 91 days of curing, respectively, when compared to the control mix, as indicated in Figure 10. These results highlight that the water absorption of mortar decreases as the content of MGWP increases up to 15%, which is consistent with previous studies [41,61,62].
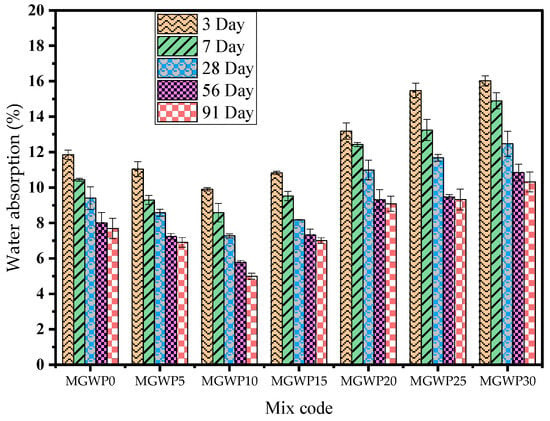
Figure 10.
Effect of MGWP on water absorption of mortar.
3.3.3. Porosity
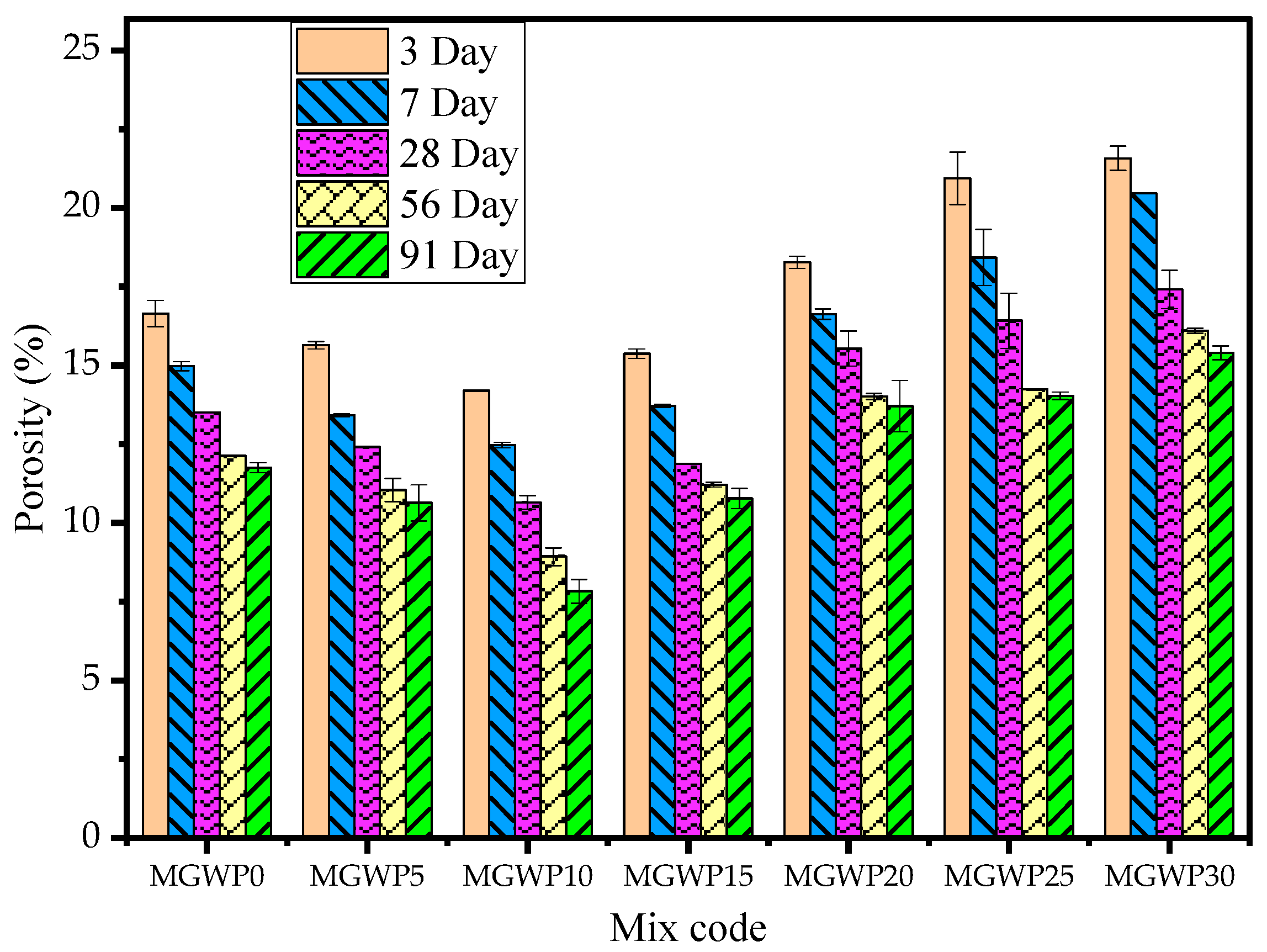
Figure 11 presents the porosity performance of mortar containing MGWP at different curing ages (3, 7, 28, 56, and 91 days). Porosity decreases with increasing MGWP replacement up to 15% relative to the control mix across all curing ages. As expected, porosity declines with age due to continuous hydration, which also explains the parallel trend observed in water absorption results [63].
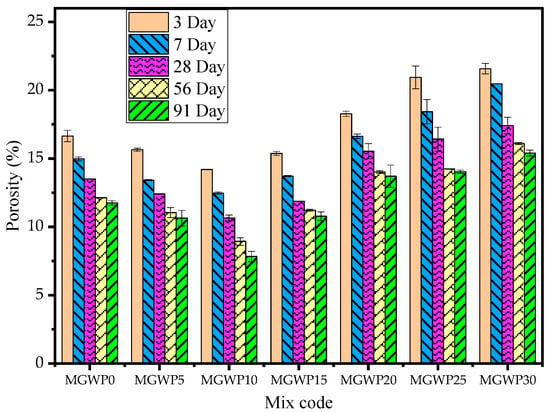
Figure 11.
Effect of MGWP on the porosity of mortar.
The lowest porosity was observed at 10% MGWP replacement, attributed to micro-filling effects of glass and marble waste powder [46,61,62]. Additionally, enhanced hydration promotes C-S-H gel formation, reducing pore volume within the mortar matrix [45,64]. Reduced porosity also correlated with long-term strength development. However, porosity increases beyond 15% MGWP replacement, likely due to reduced cementitious content and decreased hydration reaction efficiency [50]. Specifically, porosity reductions of 21.5% and 11.9% were observed for 10% and 15% MGWP replacement at 28 days, with further improvements at 56 and 91 days. Conversely, porosity increased by 28.9%, 25.0%, and 33.8% at 28, 56, and 91 days of curing, respectively, at 30% replacement, reinforcing the notion that excessive MGWP substitution adversely impacts mortar densification.
3.4. Microstructure Properties of Hardened Mortar
3.4.1. SEM
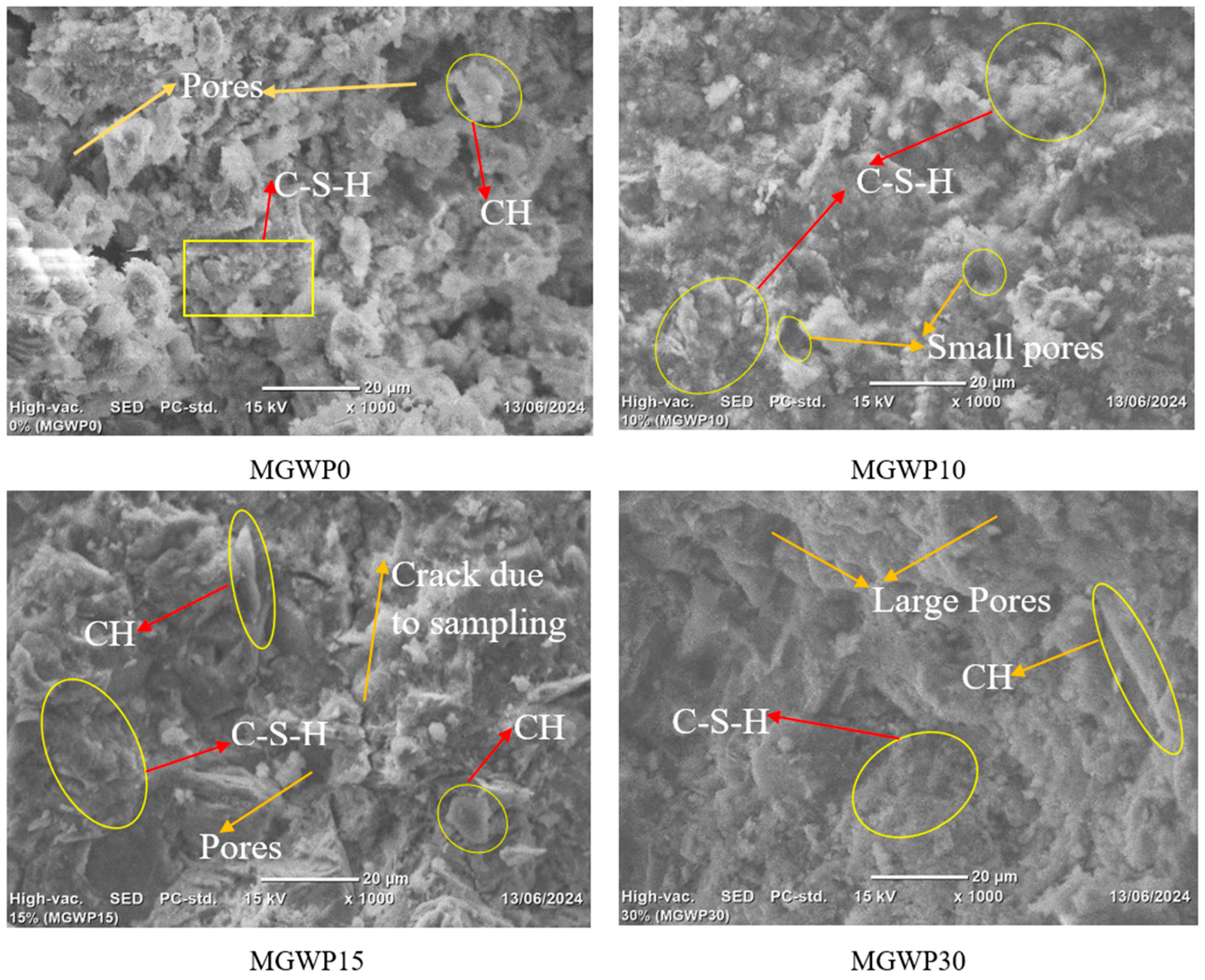
The pozzolanic reaction between pozzolanic materials and calcium hydroxide, as reported by Ahmad and Zhou [60], leads to the formation of additional cementitious compounds such as C-S-H. This reaction densifies the mortar matrix, resulting in a more compact morphology. Nega, Yifru [65] observe that the C-S-H gel exhibits a fiber-like structure, while calcium hydroxide (CH) crystals are visible in variable shapes and sizes such as flat, prism-shaped, and long crystals, or showed as a plate-like and hexagonal structure. Additionally, Ettringite typically manifests as a needle-like structure during cement hydration.
Figure 12 presents an SEM image of mortar samples at 28 days of curing, following compressive strength for samples with 0%, 10%, 15%, and 30% replacement of cement with MGWP. The SEM analysis reveals several key structural features, including the amorphous phase of C-S-H, CH, pores, and cracks due to the sampling process. The mortar containing 10% MGWP demonstrates a notably denser and more compact structure, reflecting the enhanced cementitious properties due to the pozzolanic activity of the glass waste powder. The reduction in CH content is attributed to the chemical reaction between the reactive silica present in GWP and calcium hydroxide. Additionally, the SEM results are consistent with the highest compressive strength observed at 10% MGWP, as this mixture exhibits less porosity compared to the control mix, which is further corroborated by the results of the TGA-DTA analysis reported in the following subsection.
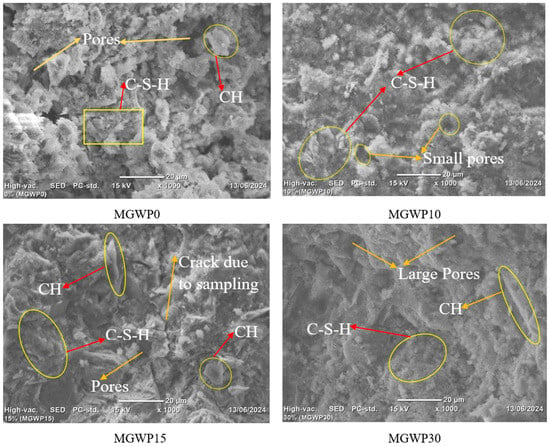

Figure 12.
SEM image for MGWP-containing mortar at curing age of 28 days.
In contrast, the SEM for the 0% MGWP mix shows a greater presence of pores and CH, indicating a less compact structure. The 30% MGWP mix exhibits a high number of pores, suggesting that this higher replacement level may lead to reduced packing efficiency. Meanwhile, mortar with 15% MGWP shows a less porous and more compact morphology, suggesting an improvement in the cement matrix due to the inclusion of MGWP. These SEM observations align with the compressive strength, UPV, water absorption, and porosity tests, which demonstrate that incorporating MGWP into mortar significantly refines the microstructure and enhances the material properties.
3.4.2. TGA and DTA
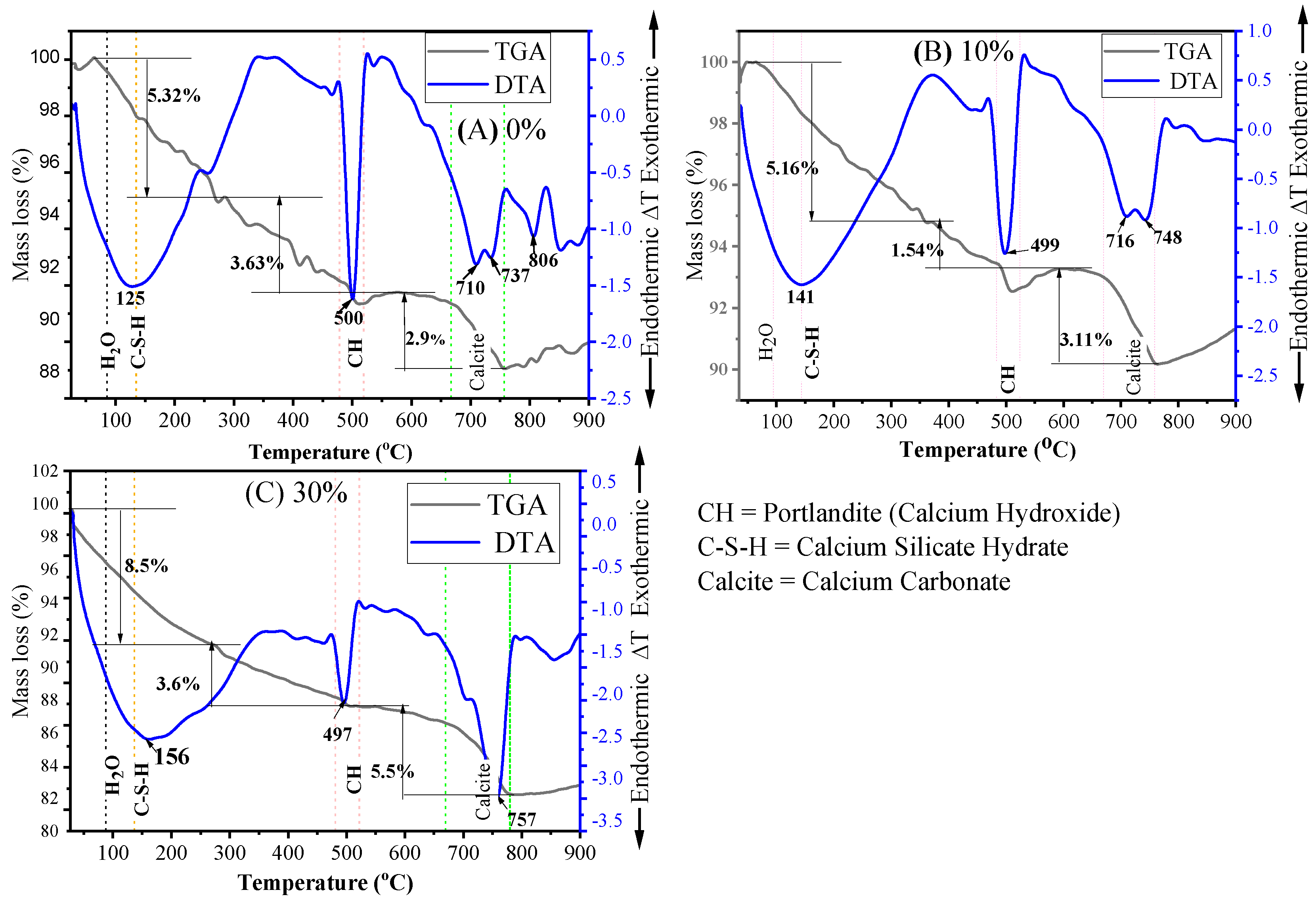
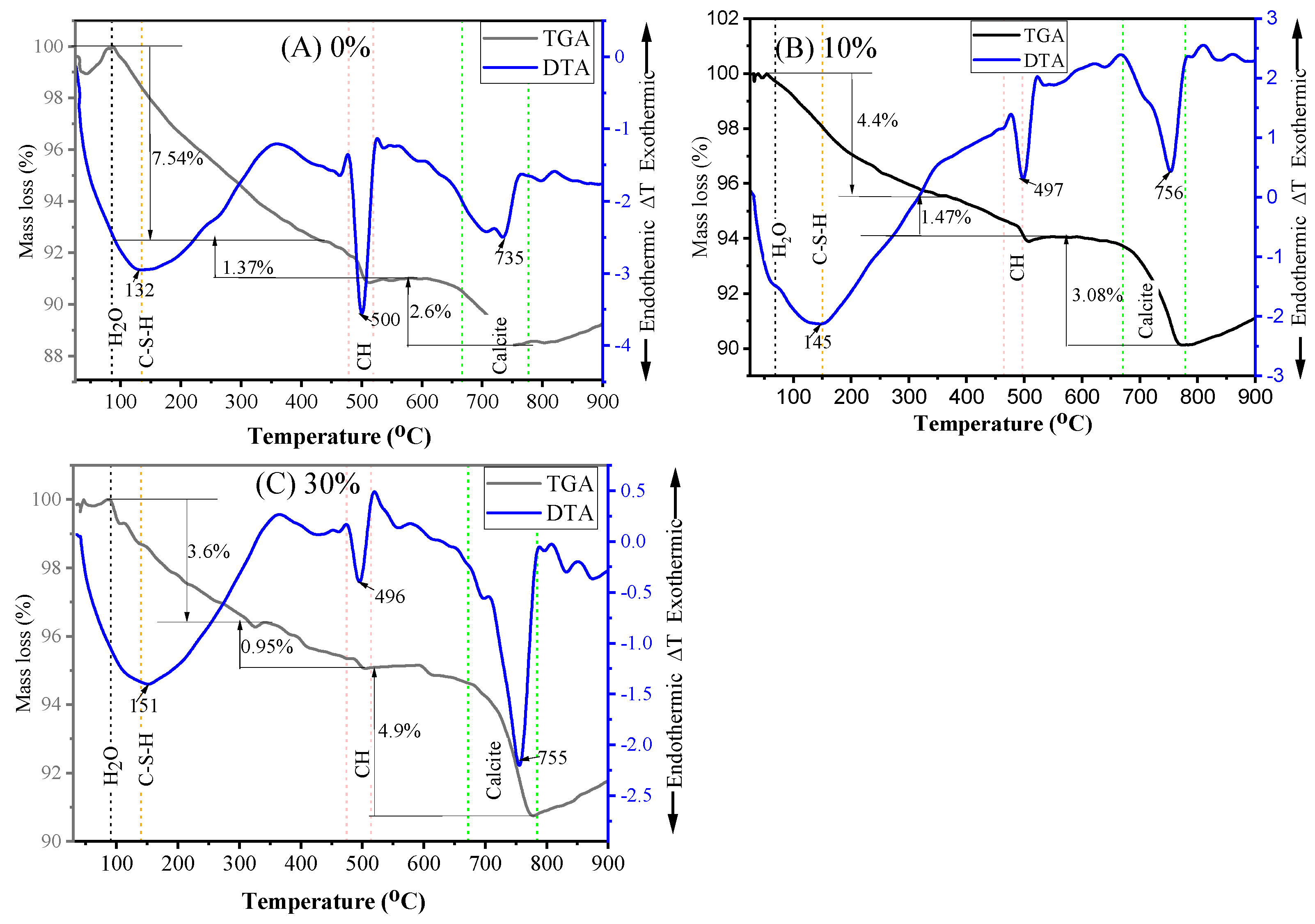
TGA and DTA analyses were carried out on mortar specimens containing 0%, 10%, and 30% MGWP at both 7 and 28 days of curing. The sample materials were heated up to 900 °C at a rate of 20 °C/min to analyze mass loss and thermal transitions. Figure 13 presents the TGA-DTA curves for 7-day cured mortar, while Figure 14 shows the results for 28-day cured mortar. These analyses help to quantify the loss of mass due to the evaporation of free water in C-S-H, the decomposition of CH, and the decarbonation of calcium carbonates.
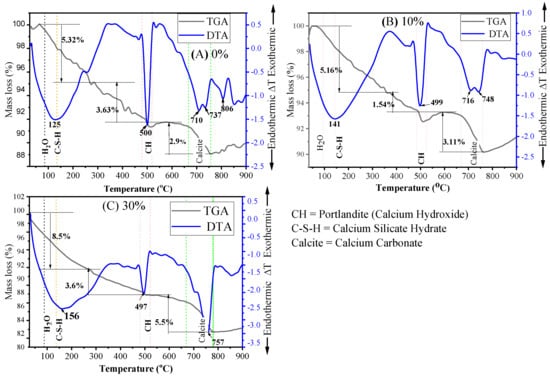
Figure 13.
TGA and DTA analyses of mortar specimens containing MGWP at curing age of 7 days.
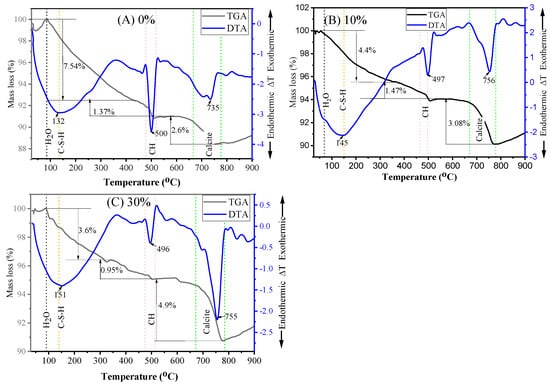
Figure 14.
TGA and DTA analysis of mortar specimens containing MGWP at curing ages of 28 days.
The TGA-DTA curves reveal three major endothermic peaks. The first peak, observed at approximately 125 °C, 141 °C, and 156 °C for 0%, 10%, and 30% MGWP, respectively, corresponds to the evaporation of physically and chemically bound water in C-S-H, as well as Ettringite. Mass losses associated with this peak were recorded on TGA curves. This process is indicative of the ongoing hydration and pozzolanic reactions occurring within the samples [66].
The second peak, occurring between 450 °C and 550 °C, corresponds to the dehydroxylation of Portlandite or calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2. The temperatures for this event were recorded at 500 °C, 499 °C, and 497 °C for the 0%, 10%, and 30% MGWP mixes, respectively. A reduction in the mass loss of CH at 10% MGWP suggests that glass waste powder reacts with Ca(OH)2, thereby consuming Portlandite and forming additional C-S-H gel. This further reduces the chemically bound water content at 10% MGWP, contributing to a denser microstructure.
The third peak, between 500 °C and 900 °C, is associated with the decarbonation of calcite (CaCO3). The temperatures for this reaction were found to be 737 °C, 748 °C, and 755 °C for the 0%, 10%, and 30% MGWP mixes, respectively. This event signifies the breakdown of calcium carbonate in the samples, and the higher temperature decomposition of calcite can be more easily distinguished from other carbonates, such as vaterite and aragonite, which decompose at lower temperatures [67].
The TGA data summarized in Table 5 further support these observations. The lowest total mass loss was recorded for the 10% MGWP mix at 7 days of curing, which aligns with the highest compressive strength and lowest porosity observed for this mix. The results suggest that the presence of MGWP significantly impacts the cement hydration process, promoting the formation of additional C-S-H gel and reducing the porosity of the mortar.
3.4.3. FT-IR
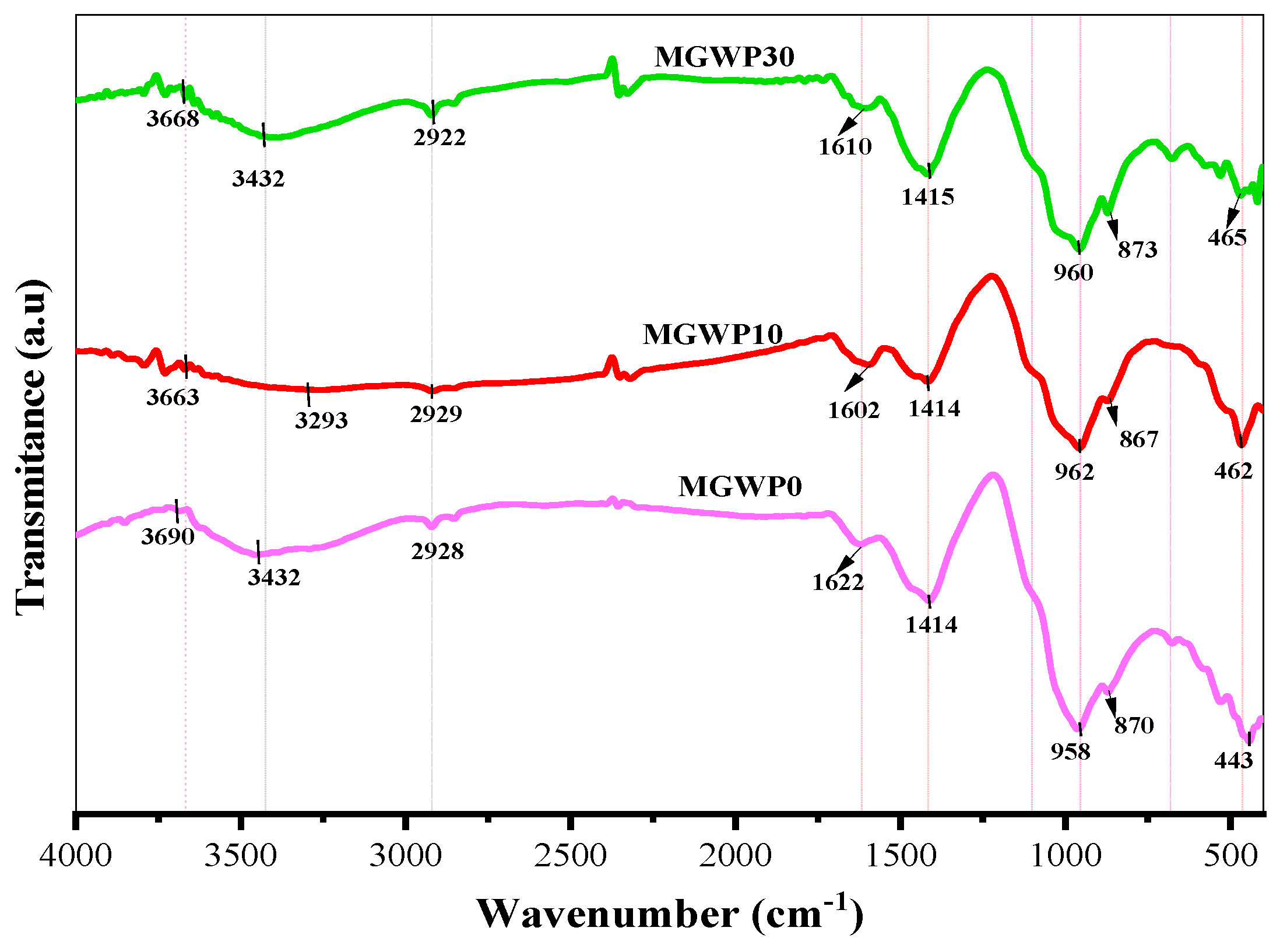
Figure 15 illustrates the IR spectra of mortar pastes containing MGWP as a partial replacement alongside the control mix. The spectra reveal peaks at 443, 462, and 465 cm−1, corresponding to the Si-O-Si bond bending/vibrations typically associated with C2S. Similarly, peaks at 870, 867, and 873 cm−1 are attributed to C3S for 0%, 10%, and 30% MGWP mixes, respectively, at 7 days of curing [68]. The incorporation of 10% MGWP exhibits a broader and more intense absorption band at 958, 962, and 960 cm−1 for the control, MGWP10, and MGWP30 mixes, respectively. This peak is associated with hydrated silica phases (Si-O-T (T: tetrahedral Si or Al) asymmetric stretching vibration). The enhanced intensity at 10% MGWP aligns well with the improvements observed in compressive strength, UPV, and SEM analyses. Notably, the formation of C-S-H gel typically manifests within the wavenumber range of 900–1100 cm−1 [69,70].
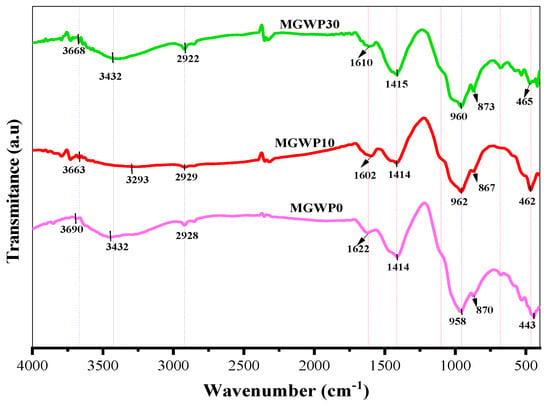
Figure 15.
FT-IR of mortar mixes containing MGWP at curing age of 7 days.
Water absorption is evident at 1622 cm−1, within the characteristic range of 1600–1700 cm−1, due to H-O-H bending vibrations. As shown in Figure 15, the bandwidth at 10% MGWP is narrower compared to both the control and 30% MGWP mixes. This suggests that at 10% MGWP, a greater proportion of water is consumed in hydration reactions, facilitating C-S-H gel formation and enhancing the microstructural properties of the mortar [70]. Similarly, O-H stretching of water appears within the range of 3000–3700 cm−1 at 3432 cm−1 [71,72].
The O-H stretching bond of Ca(OH)2 is observed around 3663 cm−1. The C-O asymmetric stretching bond of CO32−, indicative of atmospheric carbonation, appears at 1414 cm−1, within the range of 1300–1700 cm−1 [72]. The lower intensity of Portlandite in the 10% MGWP mix compared to the control suggests that more Ca(OH)2 is utilized in the formation of C-S-H gel as the hydration reaction progresses [69]. Additionally, the asymmetric stretching vibrations of the sulfate group (SO42−) in gypsum at 1104 cm⁻1 are replaced by a new band at approximately 1116 cm−1, corresponding to SO42− vibrations in Ettringite. Furthermore, the C-H stretching bond of CH2 appears at 2928 cm−1 [70].
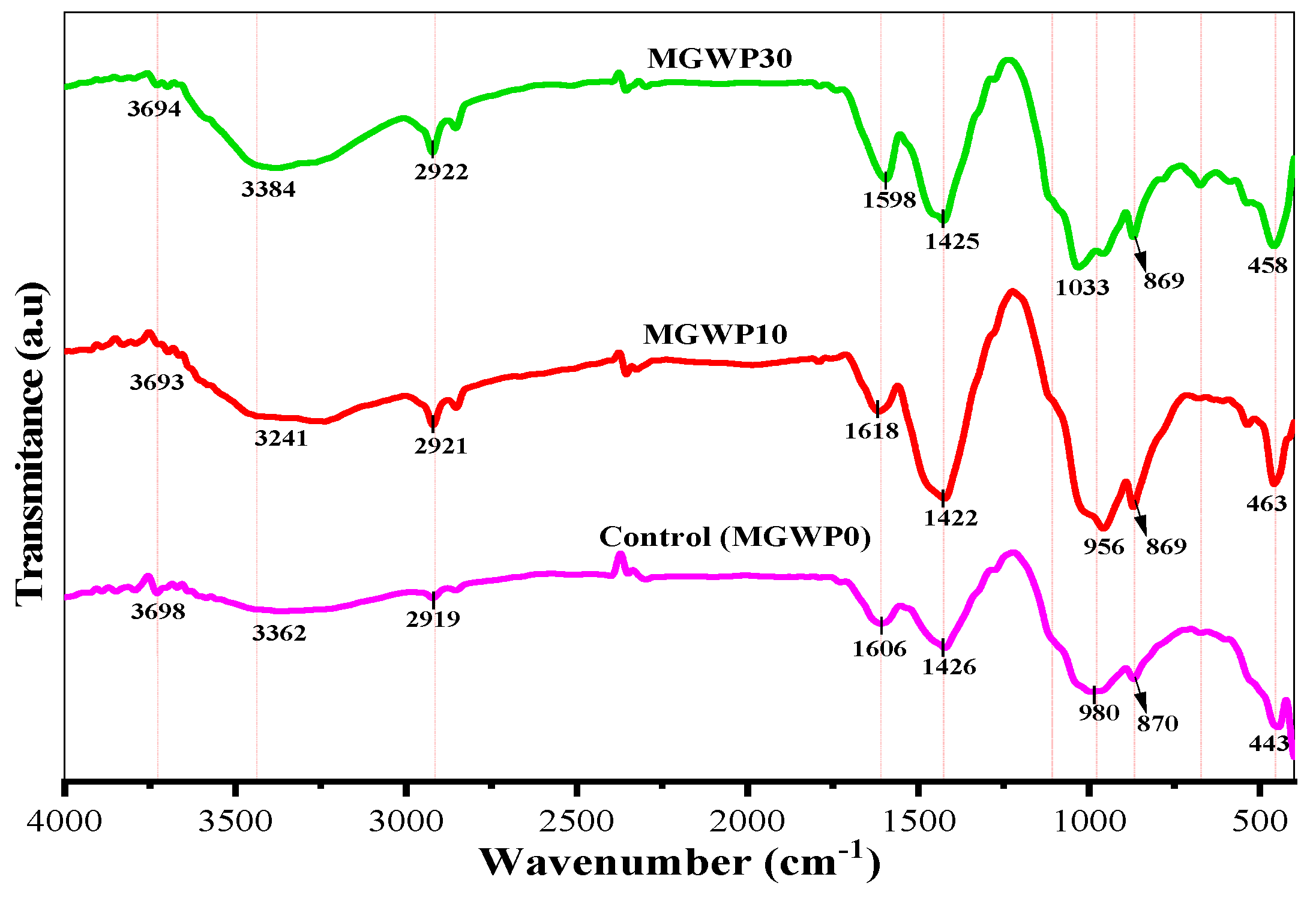
Figure 16 illustrates the FT-IR spectra of MGWP-containing mortar after 28 days of curing. A pronounced improvement in C-S-H gel formation is observed at 10% MGWP replacement compared to 7-day spectra. The primary C-S-H bands appear at 980, 985, and 1033 cm−1 for the control, MGWP10, and MGWP30 mixes, respectively. The broader and more intense C-S-H peaks at 10% MGWP at 28 days suggest enhanced pozzolanic reactivity, resulting in greater gel formation.
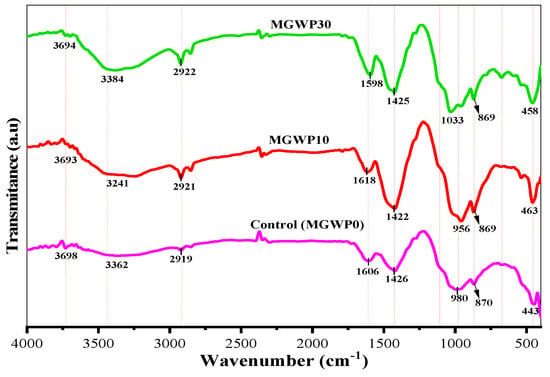
Figure 16.
FT-IR spectra of MGWP mortar cured at the age of 28 days.
The O-H bending and stretching bonds of H2O are detected at approximately 1606 cm−1 and 3362 cm−1, respectively. Portlandite (Ca(OH)2 remains present at around 3698 cm−1, while calcite (CaCO3) appears at approximately 1426 cm−1. Peaks associated with C2S and C3S persist at 443, 463, and 458 cm−1 and at 870, 865, and 869 cm−1, respectively, indicating ongoing hydration. The enhanced C-S-H gel formation at 10% MGWP, compared to the control, is attributed to the higher availability of reactive SiO2 in the MGWP mix, facilitating secondary hydration reactions [46]. Table 6 summarizes the FT-IR absorption peaks, their corresponding molecular bonds, and phase assignments for mortar mixes cured at 28 days.

Table 6.
Summary of FT-IR absorption peaks and phase assignments for mortar mixes cured at 28 days.
3.5. Correlations Between Properties of Mortar
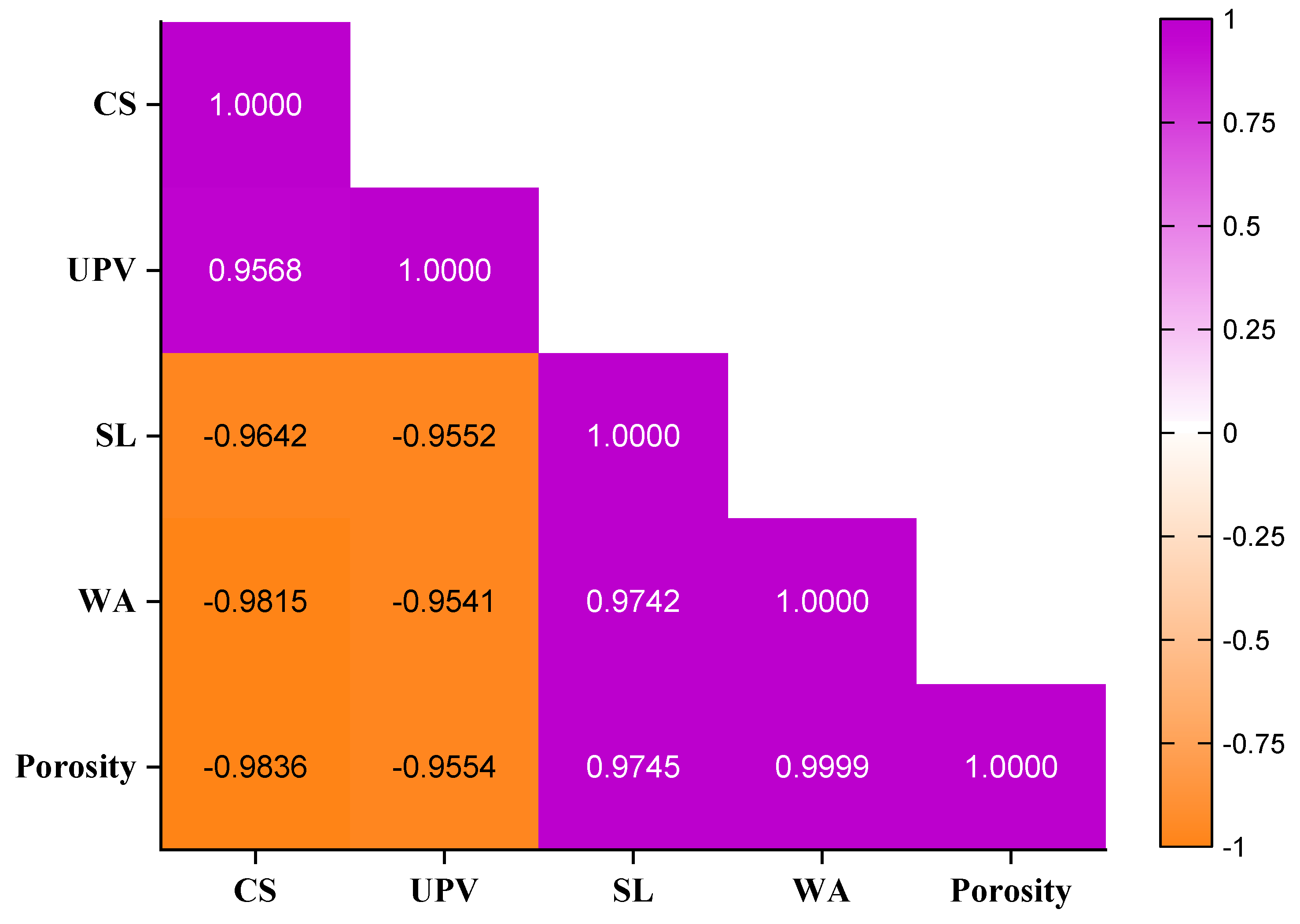
Pearson correlation analysis is a valuable statistical method used to assess the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two numeric variables. The Pearson correlation coefficient, denoted as r, ranges from −1 to 1, where r = 1 indicates a perfect positive correlation, meaning that as one variable increases, the other also increases in direct proportion. Conversely, r = −1 represents a perfect negative correlation, signifying that as one variable increases, the other decreases in a perfectly linear fashion. When r = 0, it implies no linear relationship between the variables [73].
The degree of correlation can be categorized into different ranges: values between 0.9 and 1 indicate a very strong relationship, while those between 0.7 and 0.89 signify a strong correlation. A moderate correlation falls within 0.4 to 0.69, whereas values between 0.1 and 0.39 suggest a weak association. Correlations below 0.19 are considered negligible [24,73].
Figure 17 presents the Pearson correlation matrix for key MGWP mortar properties, including compressive strength (CS), UPV, strength loss due to sulfate attack (SL), and water absorption (WA). The results reveal significant interdependencies between these parameters, with strong positive and negative correlations observed. This analysis provides critical insights into how mortar properties influence each other, which is essential for optimizing material performance and improving the durability of cementitious composites.
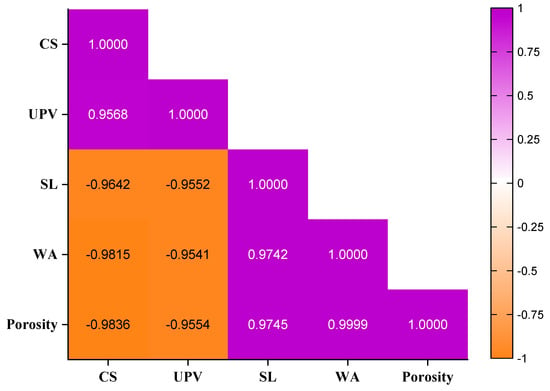
Figure 17.
Correlation of MGWP mortar properties at curing age of 56 days.
4. Conclusions
The main objective of this research was to study the effects of partially replacing cement with MGWP on the fresh, hardened, durability, and microstructure properties of mortar, as well as material characterization. The following conclusions were drawn from this study based on the objectives and results provided using MGWP as a partial replacement for cement:
- Glass waste powder is classified as a Class N pozzolanic material according to ASTM C618. Marble waste powder, on the other hand, does not meet the requirements specified in the ASTM standard.
- The workability of the mortar increased as the percentage of MGWP increased to replace cement because of the non-absorbent and smooth behavior of GWP.
- The compressive strength, density, and ultrasonic pulse velocity improve with up to 15% replacement of cement with marble and glass waste powder compared to control mixes over a period of 91 days. The maximum compressive strength is observed with a 10% replacement compared to control mixes.
- Related to durability, adding MGWP in mortar production reduces the loss of compressive strength by up to 15%, with the minimum loss observed at a 10% replacement. The porosity and water absorption of the mortar were improved with up to a 15% MGWP replacement.
- The SEM results demonstrated that mortar containing 10% MGWP is denser and has a more compact morphology as a result of additional C-S-H gel formation compared to the control mixes. Additionally, the TGA-DTA results showed that the total mass loss at 28 days is less than at 7 days, with the minimum mass loss determined at 10% MGWP.
- The more intense and broader bandwidth polymerization of C-S-H is observed at 28 days than 7 days compared to control mixes, as can be seen in FT-IR results.
- Using MGWP as a partial replacement for cement enhances the performance of mortar—improving its strength and durability—but also contributes to reducing cement costs and supports environmentally sustainable practices by lowering carbon emissions associated with cement production.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Y.A. and M.D.Y.; methodology, M.Y.A., M.D.Y. and W.M.N.; software, M.Y.A. and M.D.N.; validation, M.D.Y., W.M.N. and W.Z.T.; formal analysis, M.Y.A. and W.M.N.; investigation, M.Y.A. and M.D.N.; resources, M.D.Y.; data curation, M.Y.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Y.A. and W.M.N.; writing—review and editing, M.D.Y. and W.Z.T.; visualization, M.D.Y. and W.Z.T.; supervision, W.M.N. and M.D.Y.; funding acquisition, W.Z.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their sincere gratitude to the Faculty of Civil and Water Resources and the Faculty of Chemical and Food Engineering at Bahir Dar University for their valuable support during the laboratory testing. Special thanks are also extended to Adama Science and Technology University and the Ethiopian Geological Survey Institute for their invaluable assistance throughout the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Meyer, C. The greening of the concrete industry. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 601–605. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, V.V.; Parameshwaran, R.; Ram, V.V. PCM-mortar based construction materials for energy efficient buildings: A review on research trends. Energy Build. 2018, 158, 95–122. [Google Scholar]
- Getachew, E.M.; Yifru, B.W.; Taffese, W.Z.; Yehualaw, M.D. Enhancing Mortar Properties through Thermoactivated Recycled Concrete Cement. Buildings 2023, 13, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntzinger, D.N.; Eatmon, T.D. A life-cycle assessment of Portland cement manufacturing: Comparing the traditional process with alternative technologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 668–675. [Google Scholar]
- Yehualaw, M.D.; Alemu, M.; Hailemariam, B.Z.; Vo, D.-H.; Taffese, W.Z. Aquatic Weed for Concrete Sustainability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.; Muthusamy, K.; Embong, R.; Kusbiantoro, A.; Hashim, M.H. Environmental impact of cement production and Solutions: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 48, 741–746. [Google Scholar]
- Sakir, S.; Sudharshan, N.; Safiuddin, A.; Amrul, K.; Azrul, A. Utilization of by-products and wastes as supplementary cementitious materials in structural mortar for sustainable construction. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidou, M.; Kesikidou, F.; Konopisi, S.; Vasiadis, T. Investigating the suitability of waste glass as a supplementary binder and aggregate for cement and concrete. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufian, M.; Ullah, S.; Ostrowski, K.A.; Ahmad, A.; Zia, A.; Śliwa-Wieczorek, K.; Siddiq, M.; Awan, A.A. An experimental and empirical study on the use of waste marble powder in construction material. Materials 2021, 14, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belouadah, M.; Rahmouni, Z.E.A.; Tebbal, N. Influence of the addition of glass powder and marble powder on the physical and mechanical behavior of composite cement. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 158, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.; Lima, N. Incorporating marble sludge in laying mortars and their microstructural, thermal, mechanical, and chemical characteristics. Next Mater. 2025, 8, 100552. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdous, W.; Manalo, A.; Siddique, R.; Mendis, P.; Zhuge, Y.; Wong, H.S.; Lokuge, W.; Aravinthan, T.; Schubel, P. Recycling of landfill wastes (tyres, plastics and glass) in construction—A review on global waste generation, performance, application and future opportunities. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 173, 105745. [Google Scholar]
- Olofinnade, O.M.; Ndambuki, J.M.; Ede, A.N.; Booth, C. Application of waste glass powder as a partial cement substitute towards more sustainable concrete production. Int. J. Eng. Res. Afr. 2017, 31, 77–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Ahmad, S.; Ullah, I. Utilization of waste marble dust as cement and sand replacement in concrete. Discov. Civ. Eng. 2024, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A. The influence of waste glass powder as a pozzolanic material in concrete. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2016, 7, 131–148. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM C150; Standard Specification for Portland Cement. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2007.
- ES 1177; Composition, Specifications and Conformity Criteria for Common Cements. Ethiopian Standard Agency: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2005.
- ASTM C33; Standard Specification for Concrete Aggregates. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- ASTM C136; Standard Test Method for Sieve Analysis of Fine and Coarse Aggregates. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- ASTM C29; Standard Test Method for Bulk Density (“Unit Weight”) and Voids in Aggregate. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- ASTM C117; Standard Test Method for Materials Finer than 75-μm (No. 200) Sieve in Mineral Aggregates by Washing. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- ASTM C128; Standard Test Method for Density, Relative Density (Specific Gravity), and Absorption of Fine Aggregate. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- ASTM C566; Standard Test Method for Total Evaporable Moisture Content of Aggregate by Drying. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- Ephrem, M. Experimental Investigation on the Binary and Ternary Effect of Ground Recycled Cement and Thermo-Activated Recycled Cement for Mortar Product. Masters’s Thesis, Bahir Dar University, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraris, C.; Garboczi, E. Identifying improved standardized tests for measuring cement particle size and surface area. Transp. Res. Rec. 2013, 2342, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM C618; Standard Specification for Coal Fly Ash and Raw or Calcined Natural Pozzolan for Use in oncrete. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- ASTM C109; Standard Test Method forCompressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube Specimens). American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- ASTM C187; Standard Test Method for Amount of Water Required for Normal Consistency of Hydraulic Cement Paste. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- ASTM C191; Standard Test Methods for Time of Setting of Hydraulic Cement by Vicat Needle. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- ASTM C1437; Standard Test Method for Flow of Hydraulic Cement Mortar. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001.
- ASTM C642; Standard Test Method for Density, Absorption, and Voids in Hardened Concrete. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM C1012; Standard Test Method for Length Change of Hydraulic-Cement Mortars Exposed to a Sulfate Solution. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- ASTM C597; Standard Test Method for Pulse Velocity Through Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- ASTM C1723; Standard Guide for Examination of Hardened Concrete Using Scanning Electron Microscopy. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM-E1131; Standard Test Method for Compositional Analysis by Thermogravimetry. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- ASTM-E1252; Standard Practice for General Techniques for Obtaining Infrared Spectra for Qualitative Analysis. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Aruntaş, H.Y.; Gürü, M.; Dayı, M.; Tekin, I. Utilization of waste marble dust as an additive in cement production. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4039–4042. [Google Scholar]
- ul Islam, R.; Kaushal, M. Glass Waste Powder as Partial Replacement of Cement for Sustainable Concrete. Int. J. Innov. Res. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2022, 10, 292–298. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, A.; Gül, R. Influence of volcanic originated natural materials as additives on the setting time and some mechanical properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Kalab, A.M. Investigate the Suitability of Scoria and Glass Waste as a Cement Replacement in Binary and Ternary Blended Cement Mortar. Masters’s Thesis, Bahir Dar University, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Vardhan, K.; Goyal, S.; Siddique, R.; Singh, M. Mechanical properties and microstructural analysis of cement mortar incorporating marble powder as partial replacement of cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyuksagis, I.S.; Uygunoglu, T.; Tatar, E. Investigation on the usage of waste marble powder in cement-based adhesive mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 734–742. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM C270; Standard Specification for Mortar for Unit Masonry. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Kumarappan, N. Partial replacement cement in concrete using waste glass. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2013, 2, 1880–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Yamanel, K.; Durak, U.; İlkentapar, S.; Atabey, İ.İ.; Karahan, O.; Duran, C. Influence of waste marble powder as a replacement of cement on the properties of mortar. Rev. De La Construcción J. Constr. 2019, 18, 290–300. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, J.; Martinez-Garcia, R.; Algarni, S.; de-Prado-Gil, J.; Alqahtani, T.; Irshad, K. Characteristics of sustainable concrete with partial substitutions of glass waste as a binder material. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2022, 16, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Omran, A.; Soliman, N.; Zidol, A.; Tagnit-Hamou, A. Performance of ground-glass pozzolan as a cementitious material—A review. Adv. Civ. Eng. Mater. 2018, 7, 237–270. [Google Scholar]
- Endale, S.A.; Taffese, W.Z.; Vo, D.-H.; Yehualaw, M.D. Rice Husk Ash in Concrete. Sustainability 2023, 15, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, J.; Wu, S.; Li, Q. Strength development and microcosmic mechanism of waste glass powder cement mortar. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2022, 17, 564–584. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C. Study on compressive strength and sulfate corrosion resistance of limestone powder and waste glass powder mixed concrete. Mater. Res. Express 2024, 11, 025502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, M.A.; Taffese, W.Z.; Hailemariam, B.Z.; Yehualaw, M.D. Cow dung ash in mortar: An experimental study. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merida, A.; Kharchi, F. Pozzolan concrete durability on sulphate attack. Procedia Eng. 2015, 114, 832–837. [Google Scholar]
- Soroushian, P.; Sufyan-Ud-Din, M. Long-term field performance of concrete produced with powder waste glass as partial replacement of cement. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00745. [Google Scholar]
- Vandhiyan, R.; Ramkumar, K.; Ramya, R. Experimental study on replacement of cement by glass powder. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol 2013, 2, 234–238. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Srivastava, A.; Bhunia, D. An investigation on effect of partial replacement of cement by waste marble slurry. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 471–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabdo, A.A.; Abd Elmoaty, M.; Aboshama, A.Y. Utilization of waste glass powder in the production of cement and concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IS 13311; Method of Non-Destructive Testing of Concrete, Part 1: Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity. Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 1992.
- Alducin-Ochoa, J.M.; Martín-del-Río, J.J.; Torres-González, M.; Flores-Alés, V.; Hernández-Cruz, D. Performance of mortars based on recycled glass as aggregate by accelerated decay tests (ADT). Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 300, 124057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, X. A review of the influence of aluminum phases from cement, SCMs and external aluminum phases on the thaumasite sulfate attack in cement-based materials. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 94, 109966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Zhou, Z. Waste marble based self compacting concrete reinforced with steel fiber exposed to aggressive environment. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 81, 108142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvila, M.T.; Alexandre, J.; de Azevedo, A.R.; Zanelato, E.B. Evaluation of the use of marble waste in hydrated lime cement mortar based. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 21, 1250–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, K.L.; Sancheti, G.; Gupta, L.K. Durability performance of waste granite and glass powder added concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252, 119075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Rukzon, S. Strength, porosity and corrosion resistance of ternary blend Portland cement, rice husk ash and fly ash mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouleghebar, Y.; Bentchikou, M.; Boukendakdji, O.; El-Hadj, K.; Debieb, F.; Maisarah, A. The effect of brick and glass powder on the mechanical properties and porosity of self-compacting mortar. J. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2023, 13, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nega, D.M.; Yifru, B.W.; Taffese, W.Z.; Ayele, Y.K.; Yehualaw, M.D. Impact of Partial Replacement of Cement with a Blend of Marble and Granite Waste Powder on Mortar. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.A.; de Oliveira e Silva, G.A.; Ribeiro, D.V. Mineralogical analysis of portland cement pastes rehydrated. J. Solid Waste Technol. Manag. 2020, 46, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogler, N.; Drabetzki, P.; Lindemann, M.; Kühne, H.-C. Description of the concrete carbonation process with adjusted depth-resolved thermogravimetric analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 147, 6167–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.D.; Ravande, K. Fourier transformed–infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) studies on the concrete/cement mortar mass made of cent percentage recycled coarse and fine aggregates. Int. J. Adv. Res. Eng. Technol 2021, 12, 387–400. [Google Scholar]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Oktiani, R.; Ragadhita, R. How to read and interpret FTIR spectroscope of organic material. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantawy, M. Effect of high temperatures on the microstructure of cement paste. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.-L.; Yehualaw, M.D.; Vo, D.-H.; Huynh, T.-P.; Largo, A. Performance evaluation of alkali activated mortar containing high volume of waste brick powder blended with ground granulated blast furnace slag cured at ambient temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 223, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylmen, R.; Jäglid, U. Carbonation of Portland cement studied by diffuse reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2013, 7, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation coefficients: Appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).