Multifactorial Analysis of Wood Deterioration in Ancient Egypt: A Case Study of Khufu’s Second Solar Boat
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
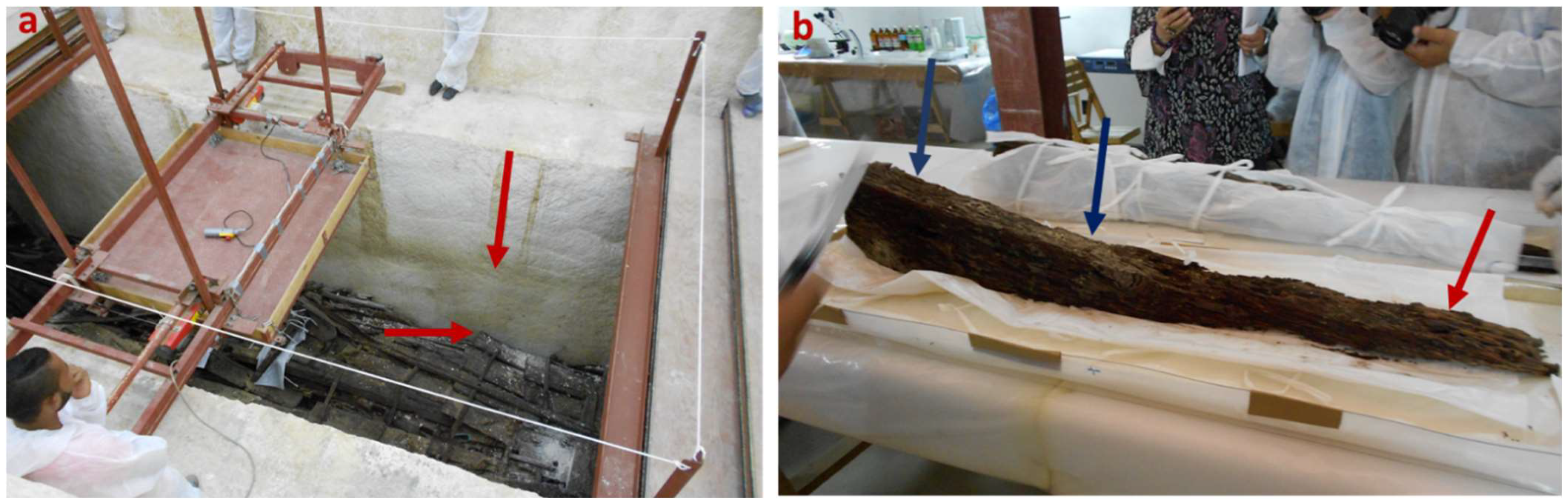
2.1. Historical Background and Samples’ Description
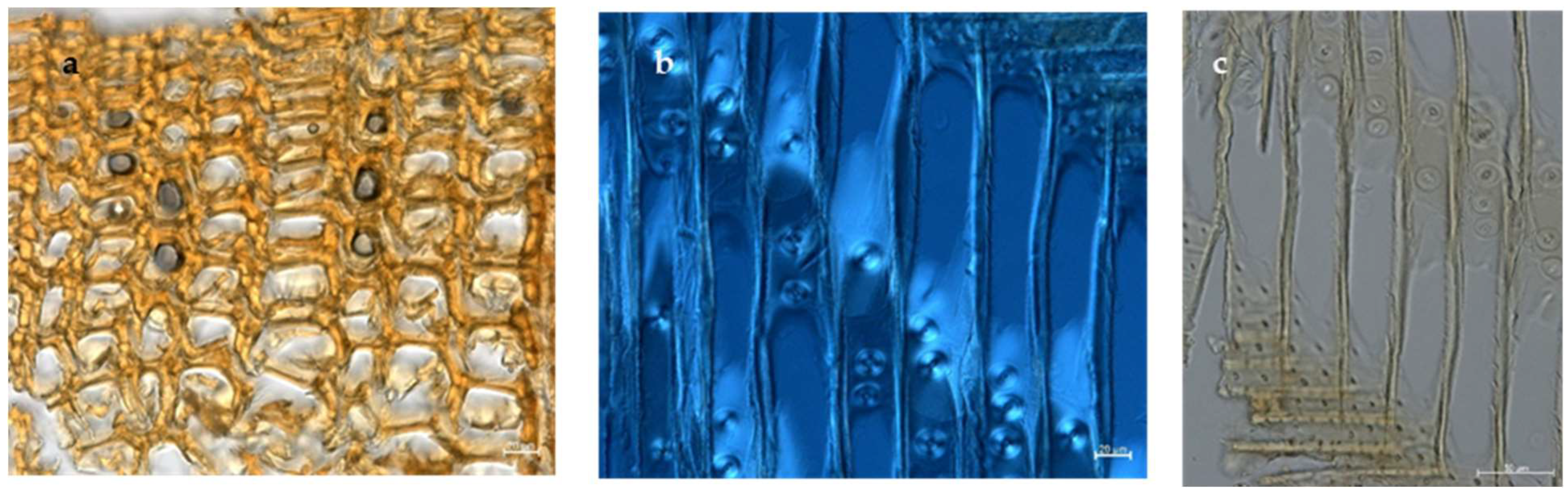
2.2. Wood Identification
2.3. Physical and Chemical Wood Degradation
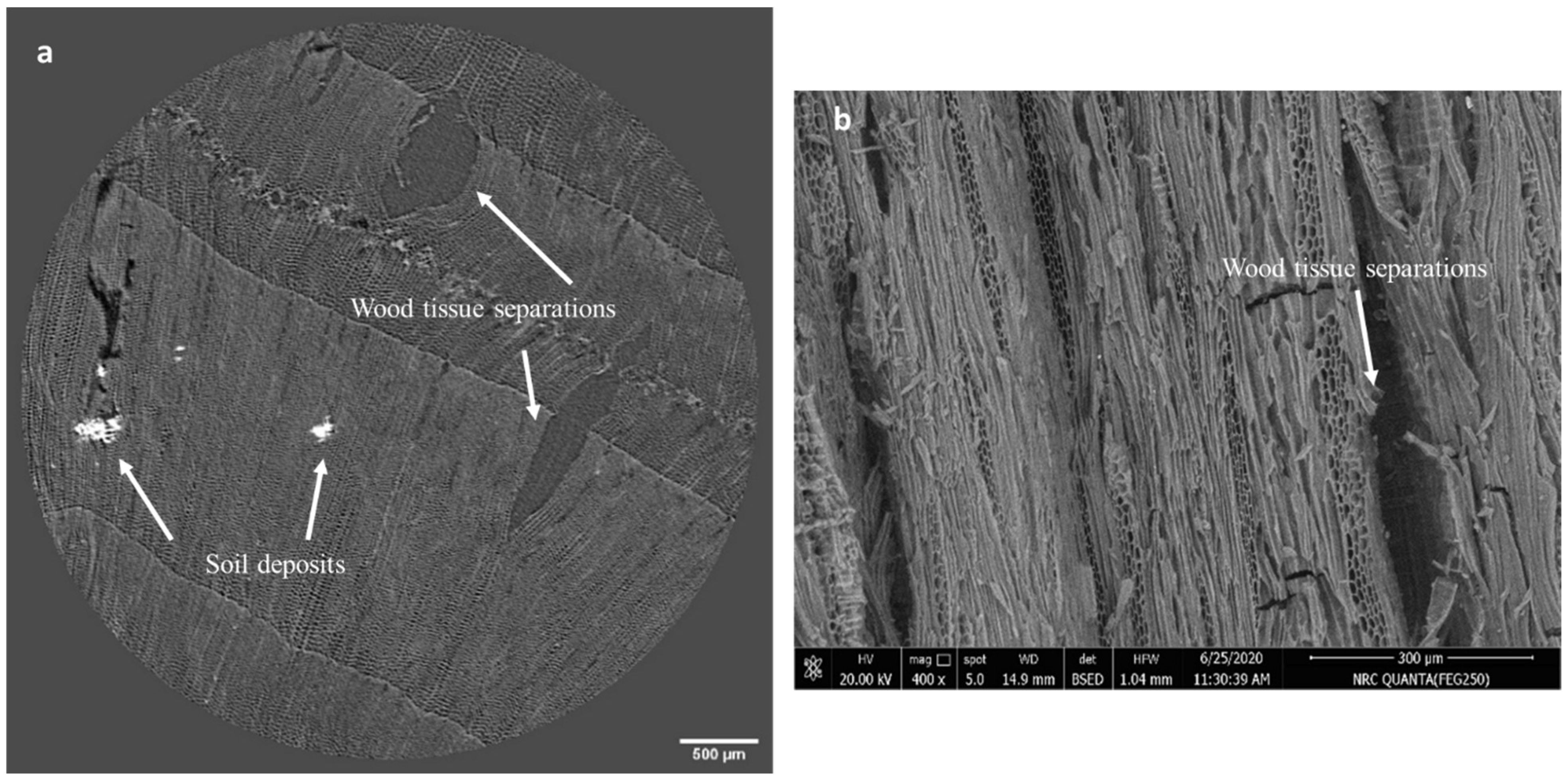
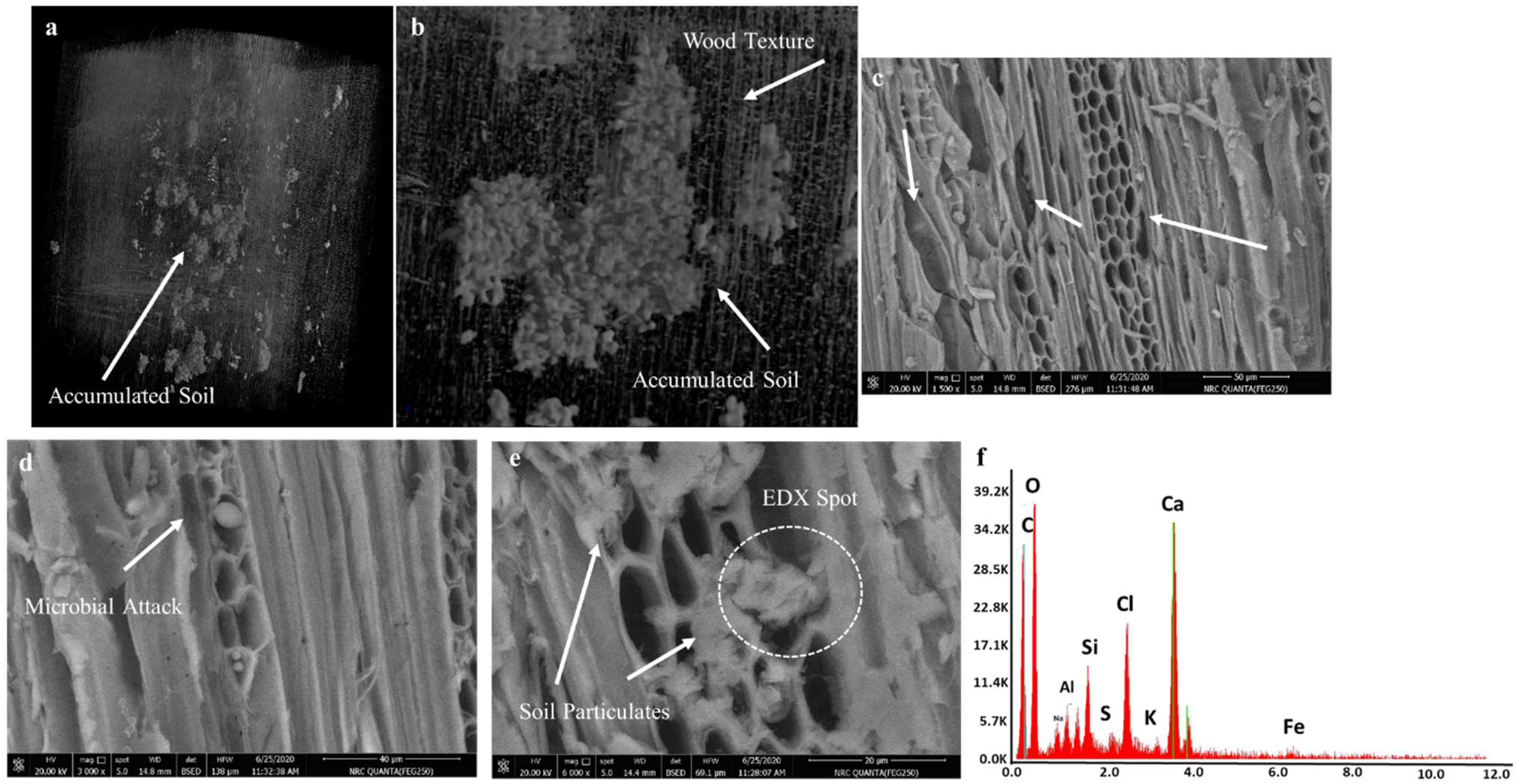
2.3.1. SEM Analyses
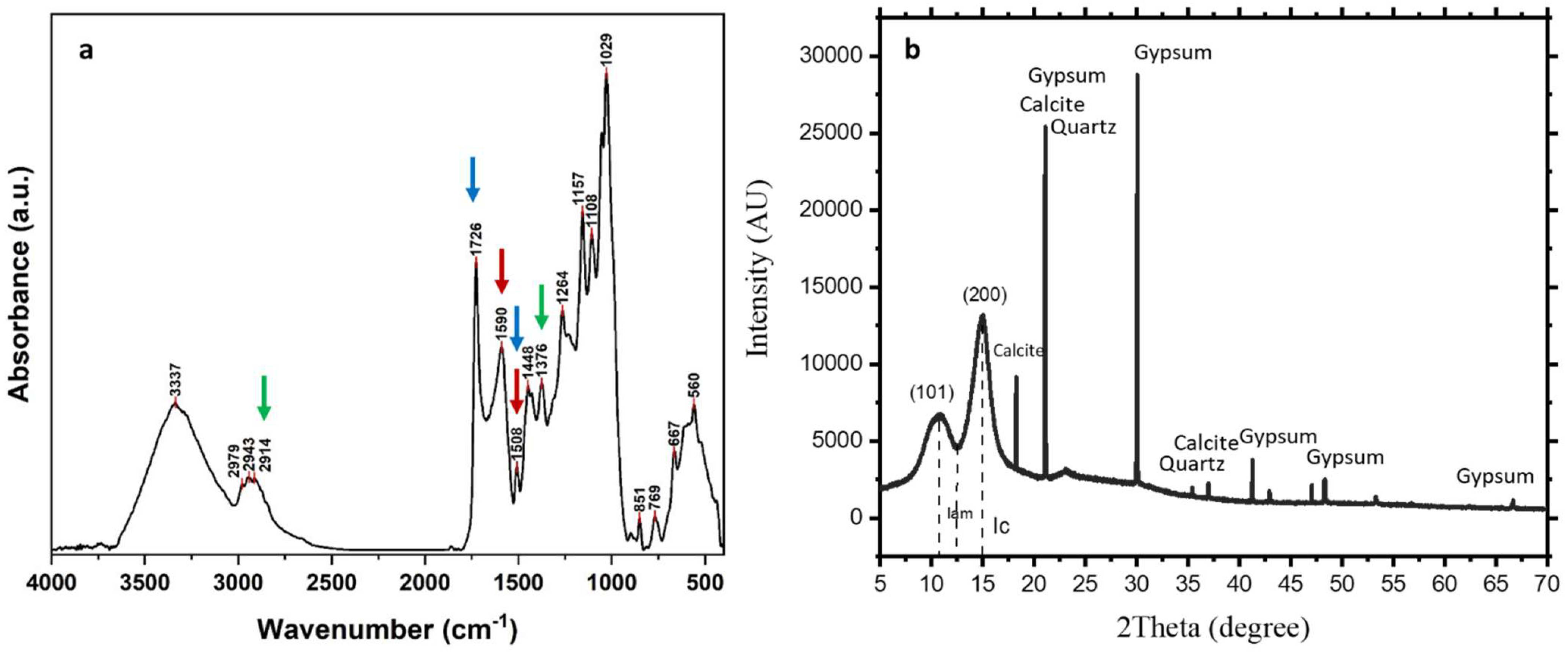
2.3.2. XRD Analyses
2.3.3. FTIR Analyses
2.4. Evaluation of Biodeteriogens
2.4.1. Isolation of Deteriorating Fungi
2.4.2. Morphological Identification of Deteriorating Fungal Isolates
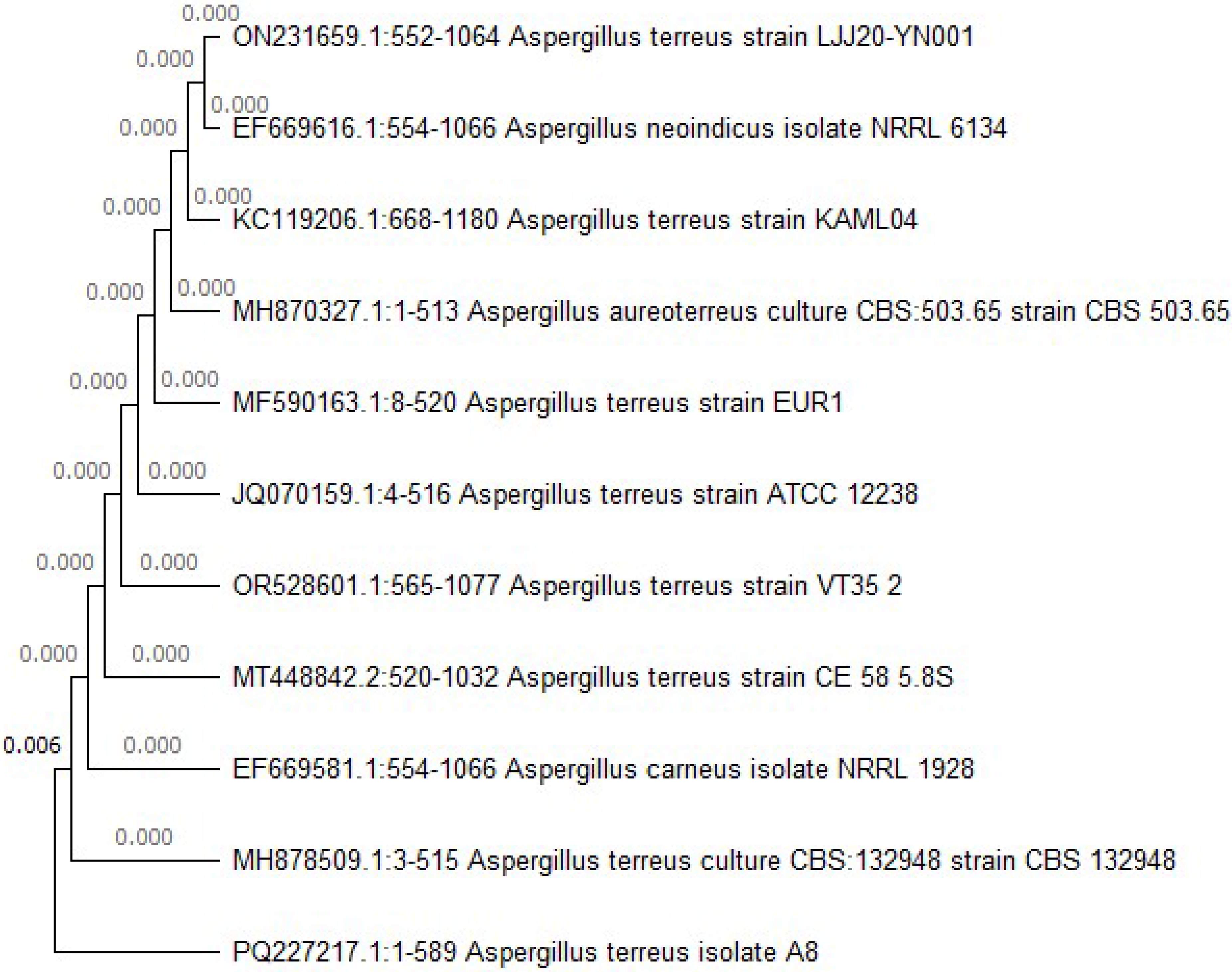
2.4.3. Identification of the Highly Frequent Fungal Species by Molecular Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Wood Species Identification
3.2. Physical and Chemical Degradation
3.2.1. Results of SEM Analysis
3.2.2. FTIR Spectral Characterization and FTIR Indices
3.2.3. XRD Results
3.3. Deteriorating Fungi
Identification of the Selected Deteriorating Fungal Isolates by Metagenomic Analyses
4. Implications for Egyptian Woodworking and Conservation Practices
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gale, R.; Gasson, P.; Hepper, N.; Killen, G. Wood. In Ancient Egyptian Materials and Technology; Nicholson, P.T., Shaw, I., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. 334–371. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Singh, A.P. Wood as Cultural Heritage Material and its Deterioration by Biotic and Abiotic Agents. In Secondary Xylem Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 233–257. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, N. The Boat Beneath The Pyramid. King Cheops’ Royal Ship; Holt Rinehart & Winston: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Mark, S. The Abydos BG 10 Boat and Implications for Standardisation, Innovation, and Timber Conservation in Early Dynastic Boat-Building. J. Egypt. Archaeol. 2012, 98, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, A.Y.; Osman, M.S.; Nour, M.Z.; Iskander, Z. The Cheops Boats; General Organization for Government Printing Offices: Cairo, Egypt, 1960.
- Morabito, M.G.; Brier, B.; Greene, S. Preliminary Stability and Resistance Analysis of the Cheops Boat. J. Sh. Prod. Des. 2020, 36, 14–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landström, B. Ships of the Pharaohs; 4000 Years of Egyptian Shipbuilding; Doubleday: Garden City, NY, USA, 1970; ISBN 978-0385078306. [Google Scholar]
- Vinson, S. Transportation. In UCLA Encyclopedia of Egyptology; Wendrich, W., Dieleman, J., Frood, E., Baines, J., Eds.; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Moortel, A. Sacred and Secular: Ancient Egyptian Ships and Boats; Archaeological Institute of America Monographs: Philadelphia, PA, USA; University of Pennsylvania Museum: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000; ISBN 0-7872-7182-9. [Google Scholar]
- Creasman, P.P. Ship Timber and the Reuse of Wood in Ancient Egypt. J. Egypt Hist. 2013, 6, 152–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H. Density Images by Microgravity. In Imaging the Cheops Pyramid. Solid Mechanics and Its Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K. A Comparative Study Between Khufu’s First and Second Boats in Respect of Their Materials, Archaeological Conditions, and Conservation. Master’s Thesis, American University in Cairo, AUC Knowledge Fountain, Cairo, Egypt, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Arranz-Otaegui, A. Evaluating the impact of water flotation and the state of the wood in archaeological wood charcoal remains: Implications for the reconstruction of past vegetation and identification of firewood gathering strategies at Tell Qarassa North (south Syria). Quat. Int. 2017, 457, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.; Abdel-Fatah, M.A.; Mohamed, W.S.; Omar, A.M.; Waly, N.; Hamdy, R. Conservation of A Painted Wooden Coffin at Dahshur Archaeological Area. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2024, 15, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łucejko, J.J.; Modugno, F.; Ribechini, E.; Tamburini, D.; Colombini, M.P. Analytical Instrumental Techniques to Study Archaeological Wood Degradation. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2015, 50, 584–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwa, D.M.; Ibrahim, S.; Stani, C.; Birarda, G.; Ali, N.; Abdullah, E.; Vaccari, L.; Grenni, P.; Visca, A.; Badr, Y.; et al. Biodeterioration Assessment of a Unique Old Pharaonic Kingdom Wooden Statue Using Advanced Diagnostic Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D. Physicochemical structure and micromechanical properties of archaeological wood under alternating dry and wet conditions. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 19, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwajca, A.; Lucejko, J.J.; Berdychowska, N.; Zborowska, M. Understanding changes in holocellulose and lignin compounds in wooden structure of veneers: Molecular insights post hydrothermal treatment and aging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 130920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Xi, G.; Dai, W.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, S.; Han, X.; Guo, H. Influence of Natural Aging on the Moisture Sorption Behaviour of Wooden Structural Components. Molecules 2023, 28, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qi, M.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, B.; Hu, Y. Microbiome Diversity and Cellulose Decomposition Processes by Microorganisms on the Ancient Wooden Seawall of Qiantang River of Hangzhou, China. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 2109–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Feyereisen, G.W.; Zhang, J.; Ishii, S. Fungal degradation of complex organic carbon supports denitrification in saturated woodchip bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 417, 131826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzner, I.; Stelzner, J.; Gwerder, D.; Martinez-Garcia, J.; Schuetz, P. Imaging and Assessment of the Microstructure of Conserved Archaeological Pine. Forests 2023, 14, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouramdane, Y.; Haddad, M.; Mazar, A.; Aît Lyazidi, S.; Oudghiri Hassani, H.; Boukir, A. Aged Lignocellulose Fibers of Cedar Wood (9th and 12th Century): Structural Investigation Using FTIR-Deconvolution Spectroscopy, X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Crystallinity Indices, and Morphological SEM Analyses. Polymers 2024, 16, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Azeem, A.M.; Held, B.W.; Richards, J.E.; Davis, S.L.; Blanchette, R.A. Assessment of biodegradation in ancient archaeological wood from the Middle Cemetery at Abydos, Egypt. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchette, R.A.; Haight, J.E.; Koestler, R.J.; Hatchfield, P.B.; Arnold, D. Assessment of Deterioration in Archaeological Wood from Ancient Egypt. J. Am. Inst. Conserv. 1994, 33, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, D.; Colston, B. Investigating the effects of humidity and salt crystallisation on medieval masonry. Build. Environ. 2000, 35, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, C.; Albano, A.; Di Blasi, C. Critical evaluation of global mechanisms of wood devolatilization. Thermochim. Acta 2005, 429, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geweely, N.; Abu Taleb, A.; Ibrahim, S.; Grenni, P.; Caneva, G.; Galotta, G.; Abdallah, M.; Atwa, D.; Plaisier, J.; Antonelli, F. New data on relevant ancient Egyptian wooden artifacts: Identification of wooden species and study of the state of conservation with multidisciplinary analyses. Archaeometry 2023, 65, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ma, W.; Liu, X. Evaluation of Deterioration Degree of Archaeological Wood from Luoyang Canal No. 1 Ancient Ship. Forests 2024, 15, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrabou, A.; Hussein, A.; Sultan, G.M.; Kamal, H.M. New insights into a polychrome Middle Kingdom palette applied to a wooden coffin: A multidisciplinary analytical approach. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 54, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigorelli, L.; Re, A.; Giudorzi, L.; Cavaleri, T.; Buscaglia, P.; Nervo, M.; Del Vesco, P.; Borla, M.; Grassini, S.; Lo Giudice, A. Multi-analytical approach for the study of an ancient Egyptian wooden statuette from the collection of Museo Egizio of Torino. Acta Imeko 2022, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, H.A.M.; Basta, S.A.; Mostafa, A.M. Examination and analysis of a stored stucco window in the conservation lab of Bab Al-azab area, citadel of Salah Al-din Al-Ayyubi, Cairo Egypt. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2024, 218, 111627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzano, A.; Merela, M.; Čufar, K. Scanning Electron Microscopy Protocol for Studying Anatomy of Highly Degraded Waterlogged Archaeological Wood. Forests 2022, 13, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, D.; Łucejko, J.J.; Pizzo, B.; Mohammed, M.Y.; Sloggett, R.; Colombini, M.P. A critical evaluation of the degradation state of dry archaeological wood from Egypt by SEM, ATR-FTIR, wet chemical analysis and Py(HMDS)-GC-MS. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 146, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traoré, M.; Kaal, J.; Martínez Cortizas, A. Application of FTIR spectroscopy to the characterization of archeological wood. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 153, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, H.A.M.; Mansour, M.M.A.; Hassan, A.G.A.I.; Salem, M.Z.M. Biodeterioration effects of three Aspergillus species on stucco supported on a wooden panel modeled from Sultan al-Ashraf Qaytbay Mausoleum, Egypt. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geweely, N.S.; Abu Taleb, A.M.; Grenni, P.; Caneva, G.; Atwa, D.M.; Plaisier, J.R.; Ibrahim, S. Eco-Friendly Preservation of Pharaonic Wooden Artifacts using Natural Green Products. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andonova, M. Ancient basketry on the inside: X-ray computed microtomography for the non-destructive assessment of small archaeological monocotyledonous fragments: Examples from Southeast Europe. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzner, J.; Million, S. X-ray Computed Tomography for the anatomical and dendrochronological analysis of archaeological wood. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2015, 55, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodini, N.; Dreossi, D.; Giordano, A.; Kaiser, J.; Zanini, F.; Zikmund, T. Comparison of different experimental approaches in the tomographic analysis of ancient violins. J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 27, S88–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreossi, D.; Sodini, N.; Zanini, F. Synchrotron Radiation Microtomography: A Tool for the Non-Invasive Structural Analysis of Historical Musical Instruments. Synchrotron Radiat. News 2019, 32, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentivoglio-Ravasio, B.; Marconi, E.; Trotta, L.; Dreossi, D.; Sodini, N.; Mancini, L.; Zanini, F.; Tonini, C. Synchrotron radiation microtomography of musical instruments: A non-destructive monitoring technique for insect infestations. J. Entomol. Acarol. Res. 2011, 43, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitau, R.; Dilkes-Hall, I.E.; Dotte-Sarout, E.; Langley, M.C.; Balme, J.; O’Connor, S. X-ray computed microtomography and the identification of wood taxa selected for archaeological artefact manufacture: Rare examples from Australian contexts. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skóra, J.; Gutarowska, B.; Pielech-Przybylska, K.; Stępień, Ł.; Pietrzak, K.; Piotrowska, M.; Pietrowski, P. Assessment of microbiological contamination in the work environments of museums, archives and libraries. Aerobiologia 2015, 31, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Park, J.E.; Suh, D.Y.; Hong, S.B.; Ko, S.J.; Kim, S.H. Comparison of Dyes for Easy Detection of Extracellular Cellulases in Fungi. Mycobiology 2007, 35, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jiao, L.; Sun, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Guo, J.; Jiang, X.; et al. Preservation status and microbial community of waterlogged archaeological woods over 7800 years old at the Jingtoushan Site, China. Wood Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrabou, A.; Zidan, E.; Nishisaka, A.; Kurokochi, H.; Yoshimura, S. King Khufu’s Second Boat: Scientific Identification of Wood Species for Deckhouse, Canopy, and Forecastle. Forests 2022, 13, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrab, A. Scientific Species Identification for the Deckhouse, Canopy and Forecastle of King Khufu’s Second Boat. Arts Soc. Sci. J. 2022, 13, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giachi, G.; Guidotti, M.C.; Lazzeri, S.; Macchioni, N.; Sozzi, L. Wood identification of some coffins from the Necropolis of Thebes held in the collection of the Egyptian Museum in Florence. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 47, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, E.; Contillo, A.; D’Amico, L.; Prašek, M.; Saccomano, G.; Sodini, N.; Dullin, C.; Dreossi, D.; Tromba, G. SYRMEP beamline: State of the art, upgrades and future prospects. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2024, 139, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloetens, P.; Pateyron-Salomé, M.; Buffière, J.Y.; Peix, G.; Baruchel, J.; Peyrin, F.; Schlenker, M. Observation of microstructure and damage in materials by phase sensitive radiography and tomography. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 5878–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganin, D.; Mayo, S.C.; Gureyev, T.E.; Miller, P.R.; Wilkins, S.W. Simultaneous phase and amplitude extraction from a single defocused image of a homogeneous object. J. Microsc. 2002, 206, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, F.; Pacilè, S.; Accardo, A.; Kourousias, G.; Dreossi, D.; Mancini, L.; Tromba, G.; Pugliese, R. Enhanced and Flexible Software Tools for X-ray Computed Tomography at the Italian Synchrotron Radiation Facility Elettra. Fundam. Informaticae 2015, 141, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, K.; Chen, K.; Lin, L.; Fu, F.; Zhong, Y. Deterioration of Microstructures and Properties in Ancient Architectural Wood from Yingxian Wooden Pagoda (1056 AD) during Natural Aging. Forests 2023, 14, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebuffi, L.; Plaisier, J.R.; Abdellatief, M.; Lausi, A.; Scardi, P. MCX: A Synchrotron Radiation Beamline for X-ray Diffraction Line Profile Analysis. Zeitschrift für Anorg. und Allg. Chemie 2014, 640, 3100–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaisier, J.R.; Nodari, L.; Gigli, L.; Rebollo San Miguel, E.P.; Bertoncello, R.; Lausi, A. The X-ray diffraction beamline MCX at Elettra: A case study of non-destructive analysis on stained glass. Acta Imeko 2017, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.; Martin, A.; Conrad, C. An Empirical Method for Estimating the Degree of Crystallinity of Native Cellulose Using the X-Ray Diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faix, O. Classification of Lignins from Different Botanical Origins by FT-IR Spectroscopy. Holzforschung 1991, 45, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.; Pitman, A. FTIR studies of the changes in wood chemistry following decay by brown-rot and white-rot fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2003, 52, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, S.; El Hadidi, N.M.N.; Mansour, M. The Effect of Fungal Decay on Ficus Sycomorus Wood. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2013, 4, 271–282. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallaro, G.; Agliolo Gallitto, A.; Lisuzzo, L.; Lazzara, G. Comparative study of historical woods from XIX century by thermogravimetry coupled with FTIR spectroscopy. Cellulose 2019, 26, 8853–8865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, S.; Serimaa, R.; Paakkari, T.; SaranpÄÄ, P.; Pesonen, E. Crystallinity of wood and the size of cellulose crystallites in Norway spruce (Picea abies). J. Wood Sci. 2003, 49, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xiao, L.; Han, L.; Wu, H.; Yang, T.; Wu, S.; Yin, Y. Deterioration of the cell wall in waterlogged wooden archeological artifacts, 2400 years old. IAWA J. 2019, 40, 820–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozhidaev, V.M.; Retivov, V.M.; Panarina, E.I.; Sergeeva, Y.E.; Zhdanovich, O.A.; Yatsishina, E.B. Development of a Method for Identifying Wood Species in Archaeological Materials by IR Spectroscopy. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 74, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucejko, J.J.; Tamburini, D.; Zborowska, M.; Babiński, L.; Modugno, F.; Colombini, M.P. Oak wood degradation processes induced by the burial environment in the archaeological site of Biskupin (Poland). Herit. Sci. 2020, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruer-Zerhusen, N.; Cantero-Tubilla, B.; Wilson, D.B. Characterization of cellulose crystallinity after enzymatic treatment using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Cellulose 2018, 25, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raper, K.B.; Thom, C.; Fennell, D.I. A Manual of the Penicillia; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Raper, K.; Fennell, D. The Genus Aspergillus; Krieger Publishing Company, Huntington: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raper, K.; Fennell, D. The Genus Aspergillus; Williams and Wilkins Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Gilman, J.C. A Manual of Soil Fungi; Biotech Books: New Delhi, India, 1977; ISBN 8176220116. [Google Scholar]
- Samson, R.A.; Pitt, J.I. The Genus Penicillium and Its Teleomorphic States Eupenicillium and Talaromyces. Mycologia 1981, 73, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafie, A.K. Soil fungi in Qatar and other Arab countries. Econ. Bot. 1996, 50, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, M.E.; Blevins, K.S. Laboratory procedures for fungal culture and isolation. In Medical Mycology: A Self-Instructional Text; FA Davis Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997; pp. 27–72. [Google Scholar]
- Domsch, K.H.; Gams, W.; Anderson, T.H. Compendium of Soil Fungi, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Klich, M.A. Identification of Common Aspergillus Species; Centraal Bureau Voor Schim: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowska, M.; Ważny, R.; Turnau, K.; Wójcik, A. Fungi as deterioration agents of historic glass plate negatives of Brandys family collection. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 115, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Yaman, B. Anatomy of Lebanon cedar (Cedrus libani A. Rich.) wood with indented growth rings. Acta Biol. Cracoviensia 2007, 49, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Arbuckle MacLeod, C. Lebanese Cedar, Skeuomorphs, Coffins, and Status in Ancient Egypt. Arts 2024, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, T. The Thames & Hudson Dictionary of Ancient Egypt; Thames & Hudson: London, UK, 2005; ISBN 9780500051375. [Google Scholar]
- Broda, M.; Popescu, C.-M.; Curling, S.F.; Timpu, D.I.; Ormondroyd, G.A. Effects of Biological and Chemical Degradation on the Properties of Scots Pine Wood—Part I: Chemical Composition and Microstructure of the Cell Wall. Materials 2022, 15, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Magaña, B.; Ruelas, R.; Quintanilla-Domínguez, J.; Robledo-Hernández, J.G.; Sturrock, C.J.; Mooney, S.J.; Tarquis, A.M. Detection and quantification of pore, solid and gravel spaces in CT images of a 3D soil sample. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 85, 360–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouramdane, Y.; Fellak, S.; El Mansouri, F.; Boukir, A. Impact of Natural Degradation on the Aged Lignocellulose Fibers of Moroccan Cedar Softwood: Structural Elucidation by Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) and X-ray Diffraction (XRD). Fermentation 2022, 8, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, C.; Wang, B.; Zhang, B.; Hu, Y. Analysis of the biocorrosion community from ancient wooden constructions at Tianluoshan (7000–6300 cal BP), Zhejiang Province, China. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinelli, L.; Drula, E.; Gaillard, J.-C.; Navarro, D.; Armengaud, J.; Berrin, J.-G.; Tron, T.; Tarrago, L. Methionine oxidation of carbohydrate-active enzymes during white-rot wood decay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e01931-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalamea, M.; González, G.; Lodge, D. Physical, Chemical, and Biological Properties of Soil under Decaying Wood in a Tropical Wet Forest in Puerto Rico. Forests 2016, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliša, M.; Belančić, A.; Kepčija, R.M.; Sertić-Perić, M.; Ostojić, A.; Habdija, I. Calcite deposition in karst waters is promoted by leaf litter breakdown and vice versa. Ann. Limnol.—Int. J. Limnol. 2010, 46, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, R.; van ’t Oor, M.; Kloppenburg, A.; Huisman, H. Rate of occurrence of wood degradation in foundations and archaeological sites when groundwater levels are too low. J. Cult. Herit. 2023, 63, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Moneim, A.A. Overview of the geomorphological and hydrogeological characteristics of the Eastern Desert of Egypt. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, S.; de La Boisse, H.; Makroum, F.M.; Bertho, J. Geological and topographical study of the original hills at the base of Fourth Dynasty Egyptian monuments of the Memphite plateau. Bull. la Société Géologique Fr. 2010, 181, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, C.M.; Vasile, C.; Popescu, C.; Singurel, G. Degradation of Lime Wood Painting Supports II. Spectral Characterisation. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2006, 40, 649–658. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Matsui, T.; Liu, C.; Wang, F. Degradation Phenomena of Wooden Pillars in the Main Hall of the Fengguo Monastery, Yixian, Liaoning, China—Scientific Investigation with XRD, IC, and FTIR Analysis. J. Conserv. Sci. 2020, 36, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavinejad, S.M.; Madhoushi, M.; Vakili, M.; Rasouli, D. Evaluation of degradation in chemical compounds of wood in historical buildings using FT-IR and FT-Raman vibrational spectroscopy. Maderas. Cienc. y Tecnol. 2019, 21, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, V.; Odile, B.; Céline, R. FTIR spectroscopy of woods: A new approach to study the weathering of the carving face of a sculpture. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 136, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, P.; Gierlinger, N. Infrared and Raman spectra of lignin substructures: Coniferyl alcohol, abietin, and coniferyl aldehyde. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2019, 50, 778–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-N.; Zhang, F.-D.; Huang, A.-M.; Zhou, Q. Distinction of four Dalbergia species by FTIR, 2 nd derivative IR, and 2D-IR spectroscopy of their ethanol-benzene extractives. Holzforschung 2016, 70, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geminiani, L.; Campione, F.; Corti, C.; Luraschi, M.; Motella, S.; Recchia, S.; Rampazzi, L. Differentiating between Natural and Modified Cellulosic Fibres Using ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy. Heritage 2022, 5, 4114–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Taylor, G.; Polle, A. FTIR-ATR-based prediction and modelling of lignin and energy contents reveals independent intra-specific variation of these traits in bioenergy poplars. Plant Methods 2011, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukir, A.; Fellak, S.; Doumenq, P. Structural characterization of Argania spinosa Moroccan wooden artifacts during natural degradation progress using infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) and X-Ray diffraction (XRD). Heliyon 2019, 5, e02477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Chen, J.; Meng, Q.; Ploszczanski, L.; Liu, J.; Luo, R.; Jin, T.; Siedlaczek, P.; Lichtenegger, H.C.; Yin, Y.; et al. Molecular and crystal structures of cellulose in severely deteriorated archaeological wood. Cellulose 2022, 29, 9549–9568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A.I.; Çiftçi, A.; İlkuçar, M. Use of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Artificial Neural Networks to predict the wood density of Cedrus libani A. Rich. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2021, 30, 3141–3148. [Google Scholar]
- Strudwick, N. The Old Kingdom and First Intermediate Period. In The Oxford Handbook of Egyptology; Shaw, I., Bloxam, E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 618–637. [Google Scholar]
- Opdenbosch, D. Van Influences on the accuracy of crystallinities determined by the method of Ruland and Vonk. Cellulose 2023, 30, 4197–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, A.; Santra, R. Theory of high-energy correlated multiphoton x-ray diffraction for synchrotron-radiation sources. Phys. Rev. Res. 2023, 5, 023158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y. High-Energy Synchrotron X-Ray Diffraction and Its Application to In Situ Structural Phase-Transition Studies in Complex Sample Environments. JOM 2012, 64, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Elserogy, A.; Al-Muheisen, Z.; Villeneuve, F.; El-Oqlah, A. The conservation of a wooden nabataean coffin box from Jordan-application of non-destructive ultrasonic technique. Wood Res. 2018, 63, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, M.E.S.; El-Shaphy, A.A.E.N.; Meligy, D.A.; Ayid, M.M. Survey for fungal decaying archaeological wood and their enzymatic activity. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2015, 5, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Helmi, F.M.; Ali, S.M.; Ismael, N.M. Nanomaterials for the inhibition of microbial growth on ancient Egyptian funeral masks. Mediterr. Archaeol. Archaeom. 2015, 15, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Santana, B.; Lindner, D.L.; Miettinen, O.; Justo, A.; Hibbett, D.S. A phylogenetic overview of the antrodia clade (Basidiomycota, Polyporales). Mycologia 2013, 105, 1391–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.B.; Matthiesen, H.; Blanchette, R.A.; Alfredsen, G.; Held, B.W.; Westergaard-Nielsen, A.; Hollesen, J. Fungal attack on archaeological wooden artefacts in the Arctic—Implications in a changing climate. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchette, R.A. A review of microbial deterioration found in archaeological wood from different environments. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 2000, 46, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| FTIR Band (cm−1) | Band Assignment |
|---|---|
| 3337 | O-H stretching of intermolecular hydrogen bonds |
| 2979 | Asymmetric CH stretch of the methoxy group of lignin |
| 2943 | Asymmetric CH stretching of CH2 groups of lignin, cellulose, hemicellulose |
| 2914 | Symmetric CH stretching of CH3 groups of lignin, cellulose, hemicellulose |
| 1726 | C=O stretching of acetyl and carbonyl groups in hemicelluloses |
| 1590 | Skeletal vibrations of the aromatic ring, together with C=O stretch in lignin |
| 1508 | C=C skeletal vibrations of the aromatic ring in lignin |
| 1448 | Aromatic C-H deformation in lignin and carbohydrates |
| 1429 | C-H in-plane deformation in lignin and carbohydrates |
| 1376 | CH bending in cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin |
| 1264 | Aromatic C-O stretching vibrations of methoxyl and phenyl propane guaiacol ring units of lignin |
| 1233 | Stretching vibrations of C-O in Xylene and syringyl ring |
| 1157 | Asymmetric bridge C-O-C stretch mode in carbohydrates |
| 1108 | Asymmetric in-plane aromatic skeletal stretching, C-C and C-O stretching |
| 1054 | C-O stretching |
| 1029 | Aromatic C-H in-plane deformation, and C-O deformation in primary alcohols |
| 898 | Aromatic C-H out-of-plane ring deformations of cellulose |
| 851 | Ring vibrations |
| Index | Index | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Lignin Index | I1590/I1508 | 4.040 |
| Carbohydrates/Lignin Index | I1726/I1508 | 7.656 |
| Crystallinity Index of Cellulose Bands | I1376/I2914 | 1.019 |
| Fungal Species | Total Count | Relative Density % |
|---|---|---|
| Aspergillus clavatus | 6 | 3.84 |
| Aspergillus flavus | 34 | 21.79 |
| Aspergillus fumigatus | 12 | 7.69 |
| Aspergillus niger | 15 | 9.61 |
| Aspergillus ochraceus | 4 | 2.56 |
| Aspergillus parasiticus | 8 | 5.12 |
| Aspergillus terreus | 24 | 15.38 |
| Aspergillus versicolor | 3 | 1.92 |
| Total Aspergillus spp. | 106 | 67.95 |
| Penicillium citrinum | 13 | 8.33 |
| Penicillium chrysogenum | 10 | 6.41 |
| Penicillium glabrum | 5 | 3.20 |
| Penicillium multicolor | 6 | 3.84 |
| Penicillium capsulatum | 7 | 4.48 |
| Penicillium oxalicum | 9 | 5.76 |
| Total Penicillium spp. | 50 | 32.05 |
| Total count | 156 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, S.; Grenni, P.; Mancini, L.; Voltolini, M.; Abdel-Fatah, H.M.K.; Refaat, A.; Atwa, D.M. Multifactorial Analysis of Wood Deterioration in Ancient Egypt: A Case Study of Khufu’s Second Solar Boat. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3952. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073952
Ibrahim S, Grenni P, Mancini L, Voltolini M, Abdel-Fatah HMK, Refaat A, Atwa DM. Multifactorial Analysis of Wood Deterioration in Ancient Egypt: A Case Study of Khufu’s Second Solar Boat. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3952. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073952
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Shimaa, Paola Grenni, Lucia Mancini, Marco Voltolini, Hanan Mohamed Kamal Abdel-Fatah, Ahmed Refaat, and Dina M. Atwa. 2025. "Multifactorial Analysis of Wood Deterioration in Ancient Egypt: A Case Study of Khufu’s Second Solar Boat" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3952. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073952
APA StyleIbrahim, S., Grenni, P., Mancini, L., Voltolini, M., Abdel-Fatah, H. M. K., Refaat, A., & Atwa, D. M. (2025). Multifactorial Analysis of Wood Deterioration in Ancient Egypt: A Case Study of Khufu’s Second Solar Boat. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3952. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073952









