The 3D Gaussian Splatting SLAM System for Dynamic Scenes Based on LiDAR Point Clouds and Vision Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A 3DGS-SLAM system designed specifically for dynamic environments, incorporating tracking, 3D segmentation, and mapping threads to enable real-time dynamic scene tracking and reconstruction with both vision and LiDAR inputs. This system addresses key challenges in dynamic scene reconstruction and improves the robustness of SLAM in real-world environments.
- A hybrid uncertainty-based 3D segmentation method accurately segments dynamic LiDAR point clouds and effectively removes uncertain dynamic points at the boundaries. This method ensures that moving objects and other uncertainties do not interfere with the static map reconstruction.
- A dynamic rendering loss function and a sensor-fusion-based keyframe selection strategy ensure accurate removal of dynamic artifacts while minimizing computational overhead. This approach allows the system to operate in real time, even in large-scale and highly dynamic environments.
- Evaluation of our approach on multiple public and in-house real-world datasets demonstrates superior performance across multiple metrics, achieving high-fidelity reconstruction and effective dynamic interference removal. Our system consistently outperforms existing methods in both dynamic object handling and overall map quality.
2. Related Work
2.1. NeRF-Based LiDAR–Visual Fusion
2.2. 3DGS-Based LiDAR–Visual Fusion
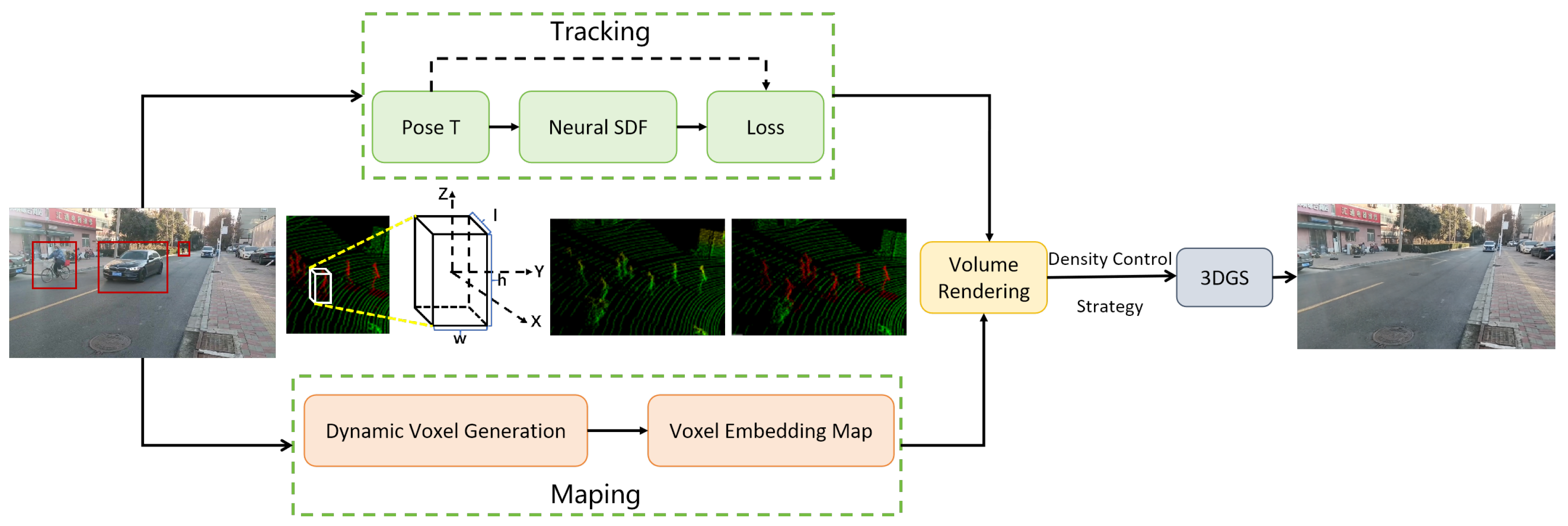
3. Methodology
3.1. Foreground–Background Segmentation
3.2. Sliding Window-Based Reconstruction Strategy
3.3. 3DGS-Based Dense Scene Representation
| Algorithm 1 Sliding Window-Based Dynamic Scene Reconstruction |
Note: , are depth and color thresholds; , are temporal and spatial decay factors |
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets and Metrics
4.2. Implementation Details
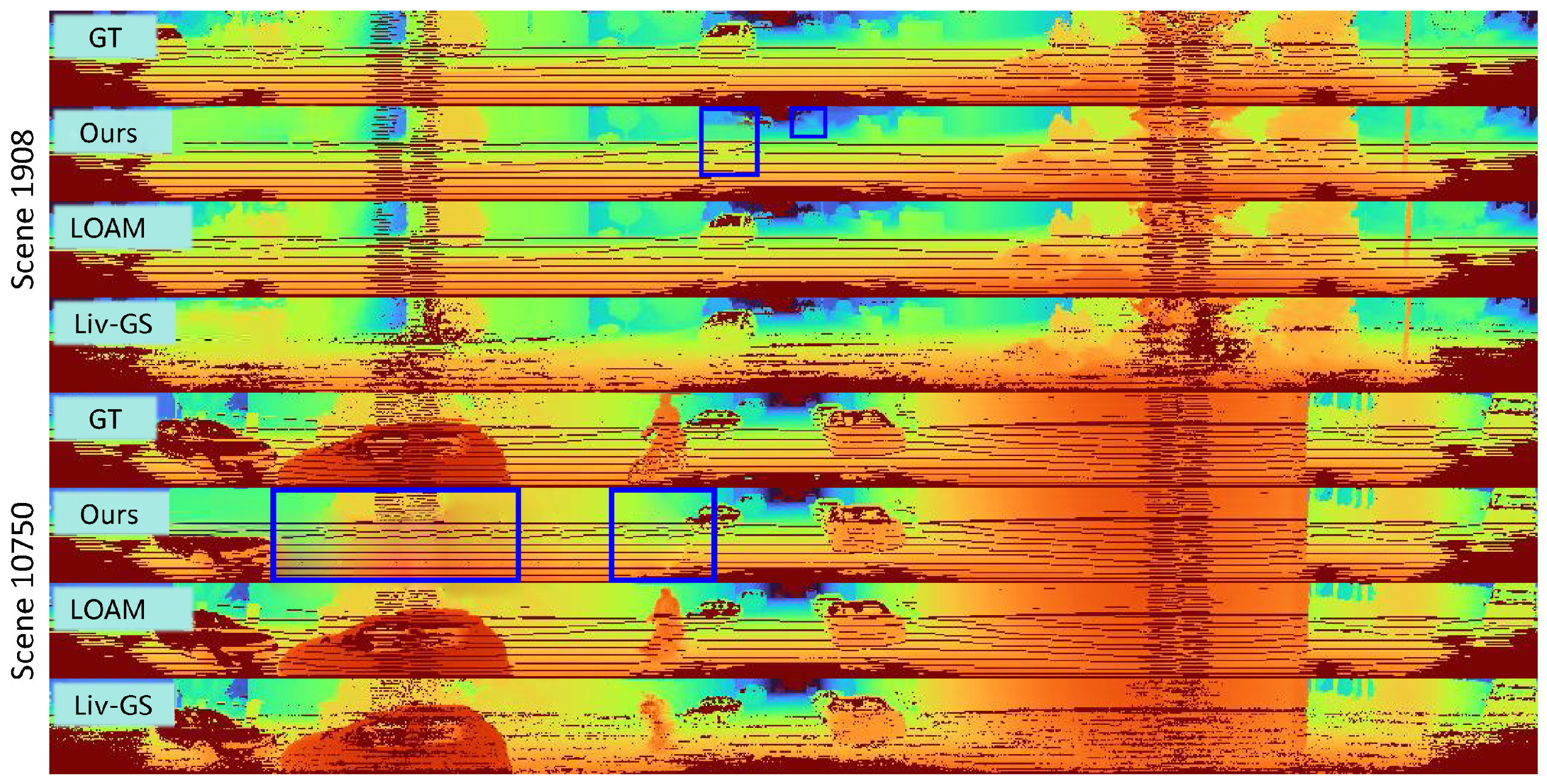
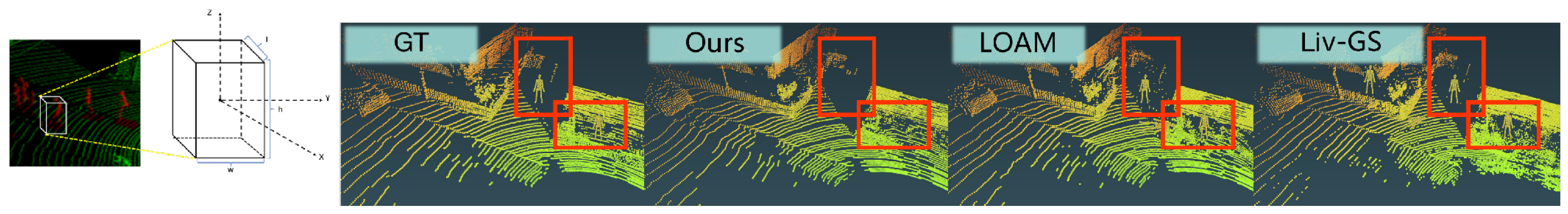
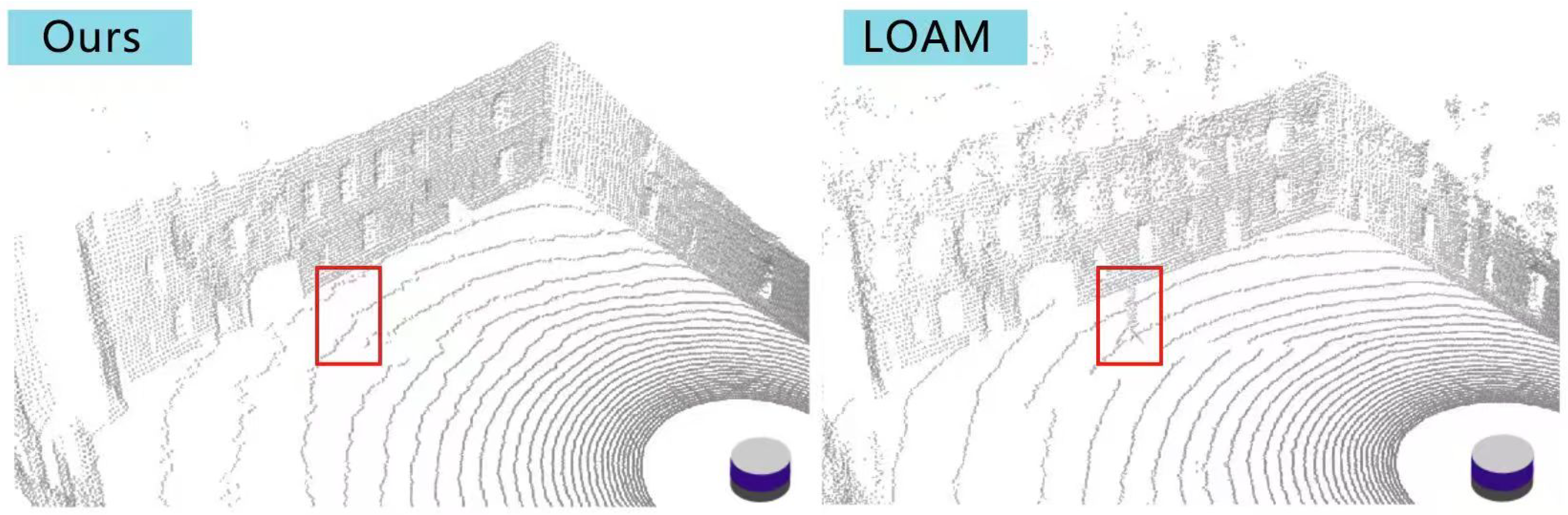
4.3. Mapping Results
4.4. Tracking Results
4.5. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Tancik, M.; Barron, J.T.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ng, R. Nerf: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. Commun. ACM 2021, 65, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosinol, A.; Leonard, J.J.; Carlone, L. Nerf-slam: Real-time dense monocular slam with neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Detroit, MI, USA, 1–5 October 2023; pp. 3437–3444. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Guo, Z.; Deng, T.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wang, H. DDN-SLAM: Real Time Dense Dynamic Neural Implicit SLAM. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.M.; Tseng, Y.C.; Hsu, Y.C.; Shi, X.Q.; Hua, Y.H.; Yeh, J.F.; Chen, W.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Hsu, W.H. Orbeez-slam: A real-time monocular visual slam with orb features and nerf-realized mapping. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 9400–9406. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Tan, L.; Li, M.; Shan, H.; Liao, P. DNIV-SLAM: Neural Implicit Visual SLAM in Dynamic Environments. In Proceedings of the Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision (PRCV), Urumqi, China, 18–20 October 2024; pp. 33–47. [Google Scholar]
- Naumann, J.; Xu, B.; Leutenegger, S.; Zuo, X. Nerf-vo: Real-time sparse visual odometry with neural radiance fields. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 7278–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Qi, J.; Pan, Y.; Fu, C.; Pan, J. Semantics-Aware Receding Horizon Planner for Object-Centric Active Mapping. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 3838–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Qu, D.; Xu, D.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, X. Gs-slam: Dense visual slam with 3D gaussian splatting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 19595–19604. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, H.; Huang, G.; Hu, Q.; Li, G.; Bao, H.; Zhang, G. Nis-slam: Neural implicit semantic rgb-d slam for 3D consistent scene understanding. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2024, 30, 7129–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuki, H.; Murai, R.; Kelly, P.H.J.; Davison, A.J. Gaussian Splatting SLAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, G.; Cheng, N.; Deng, T.; Wang, H. Sgs-slam: Semantic gaussian splatting for neural dense slam. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 163–179. [Google Scholar]
- Keetha, N.; Karhade, J.; Jatavallabhula, K.M.; Yang, G.; Scherer, S.; Ramanan, D.; Luiten, J. SplaTAM: Splat Track & Map 3D Gaussians for Dense RGB-D SLAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 21357–21366. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Wu, Q.; Chen, X.; Xia, S.; Sun, Z.; Liu, G.; Yu, W.; Pei, L. Nerf-loam: Neural implicit representation for large-scale incremental lidar odometry and mapping. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 8218–8227. [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson, S.; Kung, P.C.; Ramanagopal, M.; Vasudevan, R.; Skinner, K.A. Loner: Lidar only neural representations for real-time slam. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 8042–8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhong, X.; Wiesmann, L.; Posewsky, T.; Behley, J.; Stachniss, C. PIN-SLAM: LiDAR SLAM using a point-based implicit neural representation for achieving global map consistency. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2024, 40, 4045–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, A.; Ramanagopal, M.S.; Tseng, N.; Johnson-Roberson, M.; Vasudevan, R.; Skinner, K.A. Cloner: Camera-lidar fusion for occupancy grid-aided neural representations. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 2812–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, A.W.; Meng, T.; Caine, B.; Ngiam, J.; Peng, D.; Shen, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Le, Q.V.; et al. Deepfusion: Lidar-camera deep fusion for multi-modal 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 17182–17191. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, F.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, X.; Lv, J. Gaussian-LIC: Photo-realistic LiDAR-Inertial-Camera SLAM with 3D Gaussian Splatting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.06926. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Lin, Z.; Shan, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Yang, M.H. Drivinggaussian: Composite gaussian splatting for surrounding dynamic autonomous driving scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 21634–21643. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Cao, J.; Zhao, F.; He, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J. LetsGo: Large-scale garage modeling and rendering via LiDAR-assisted gaussian primitives. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2024, 43, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; He, J.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, C.; Shen, S. Liv-gaussmap: Lidar-inertial-visual fusion for real-time 3D radiance field map rendering. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 9765–9772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Xie, H.; Yu, K.; Xia, Z.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tang, T.; Wang, B.; Tang, Z. Bevfusion: A simple and robust lidar-camera fusion framework. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 10421–10434. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.C.; Rho, D.; Sun, X.; Ko, J.H.; Park, E. Compact 3D gaussian representation for radiance field. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 21719–21728. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Hu, L. LiV-GS: LiDAR-Vision Integration for 3D Gaussian Splatting SLAM in Outdoor Environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 10, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandström, E.; Li, Y.; Van Gool, L.; Oswald, M.R. Point-slam: Dense neural point cloud-based slam. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 18433–18444. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, P.J. Robust estimation of a location parameter. In Breakthroughs in Statistics: Methodology and Distribution; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 492–518. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Urtasun, R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? The kitti vision benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 3354–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Vizzo, I.; Chen, X.; Chebrolu, N.; Behley, J.; Stachniss, C. Poisson surface reconstruction for LiDAR odometry and mapping. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 5624–5630. [Google Scholar]
- Ramezani, M.; Wang, Y.; Camurri, M.; Wisth, D.; Mattamala, M.; Fallon, M. The newer college dataset: Handheld lidar, inertial and vision with ground truth. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 4353–4360. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.N.; Yang, Y.H.; Fischer, T.; Darrell, T.; Yu, F.; Sun, M. Monocular quasi-dense 3D object tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 1992–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, T.; Gao, L.; Wang, G.; Lao, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhao, H.; Hao, D.; Liang, X.; Salzmann, M.; Yu, K. LiDAR-NeRF: Novel lidar view synthesis via neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Melbourne, Australia, 28 October–1 November 2024; pp. 390–398. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X.; Pan, Y.; Behley, J.; Stachniss, C. Shine-mapping: Large-scale 3D mapping using sparse hierarchical implicit neural representations. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 8371–8377. [Google Scholar]




| Method | Completion ↓ | Accuracy ↓ | Chamfer-L1 Distance ↓ | F-Score ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDAR-NeRF | 5.71 | 3.81 | 4.84 | 90.16 |
| SHINE | 4.35 | 4.08 | 4.26 | 89.94 |
| NeRF-LOAM | 4.16 | 3.29 | 3.68 | 93.51 |
| LiV-GS | 3.09 | 2.58 | 2.87 | 94.52 |
| Ours | 2.67 | 2.21 | 2.35 | 96.17 |
| Method | Completion ↓ | Accuracy ↓ | Chamfer-L1 Distance ↓ | F-Score ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDAR-NeRF | 13.76 | 10.32 | 12.68 | 85.26 |
| SHINE | 14.39 | 8.57 | 11.45 | 90.43 |
| NeRF-LOAM | 16.01 | 6.95 | 10.94 | 91.85 |
| LiV-GS | 12.84 | 6.17 | 9.86 | 93.27 |
| Ours | 10.05 | 5.54 | 8.09 | 95.48 |
| Method | MaiCity | Newer College | KITTI | ROI-IND | ROI-OD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NeRF-LOAM | 0.19 | 0.14 | 9.17 | 0.53 | 0.84 |
| LiV-GS | 0.08 | 0.08 | 8.21 | 0.41 | 0.65 |
| Ours | 0.06 | 0.01 | 6.57 | 0.19 | 0.32 |
| Window Length | Completion ↓ | Accuracy ↓ | Chamfer-L1 Distance ↓ | F-Score ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Window | 3.86 | 3.18 | 3.52 | 91.34 |
| 3.25 | 2.79 | 2.71 | 94.12 | |
| 2.67 | 2.21 | 2.35 | 96.17 | |
| 3.49 | 2.54 | 2.86 | 93.58 | |
| 3.74 | 2.99 | 3.67 | 90.81 |
| Rendering Losses | Completion ↓ | Accuracy ↓ | Chamfer-L1 Distance ↓ | F-Score ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/o | 4.27 | 3.45 | 3.79 | 92.36 |
| w/o | 3.54 | 2.87 | 3.05 | 94.28 |
| w/o | 5.13 | 3.96 | 4.76 | 90.89 |
| FULL | 2.67 | 2.21 | 2.35 | 96.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Li, M.; Feng, G. The 3D Gaussian Splatting SLAM System for Dynamic Scenes Based on LiDAR Point Clouds and Vision Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084190
Zhang Y, Jiang G, Li M, Feng G. The 3D Gaussian Splatting SLAM System for Dynamic Scenes Based on LiDAR Point Clouds and Vision Fusion. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084190
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuquan, Guangan Jiang, Mingrui Li, and Guosheng Feng. 2025. "The 3D Gaussian Splatting SLAM System for Dynamic Scenes Based on LiDAR Point Clouds and Vision Fusion" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084190
APA StyleZhang, Y., Jiang, G., Li, M., & Feng, G. (2025). The 3D Gaussian Splatting SLAM System for Dynamic Scenes Based on LiDAR Point Clouds and Vision Fusion. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4190. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084190





