DAGANFuse: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Differential Features Attention Generative Adversarial Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We designed a cross-modal differential features attention module to measure the activity level at the same scale. The proposed module increases the information and details contained in the fused image by effectively integrating the intermediate features of different modal images.
- We proposed a new cross-scale attentional decoder, which can enable cross-modal features of different scales to interact. Through the parallel path of differential features and fusion features, it is beneficial to extract more complementary information on the basis of maintaining detailed information.
- We proposed an end-to-end dual discriminator adversarial fusion network based on WGAN [10]. The experimental outcomes demonstrate that the proposed method achieves the SOTA performance. Compared with other conventional fusion techniques, it exhibits superiority in both qualitative visual depiction and quantitative index assessment, thereby offering a more efficient and robust approach for multi-modal image fusion tasks.
2. Related Work
2.1. AE-Based Fusion Methods
2.2. CNN-Based Fusion Methods
2.3. GAN-Based Fusion Methods
3. Methods
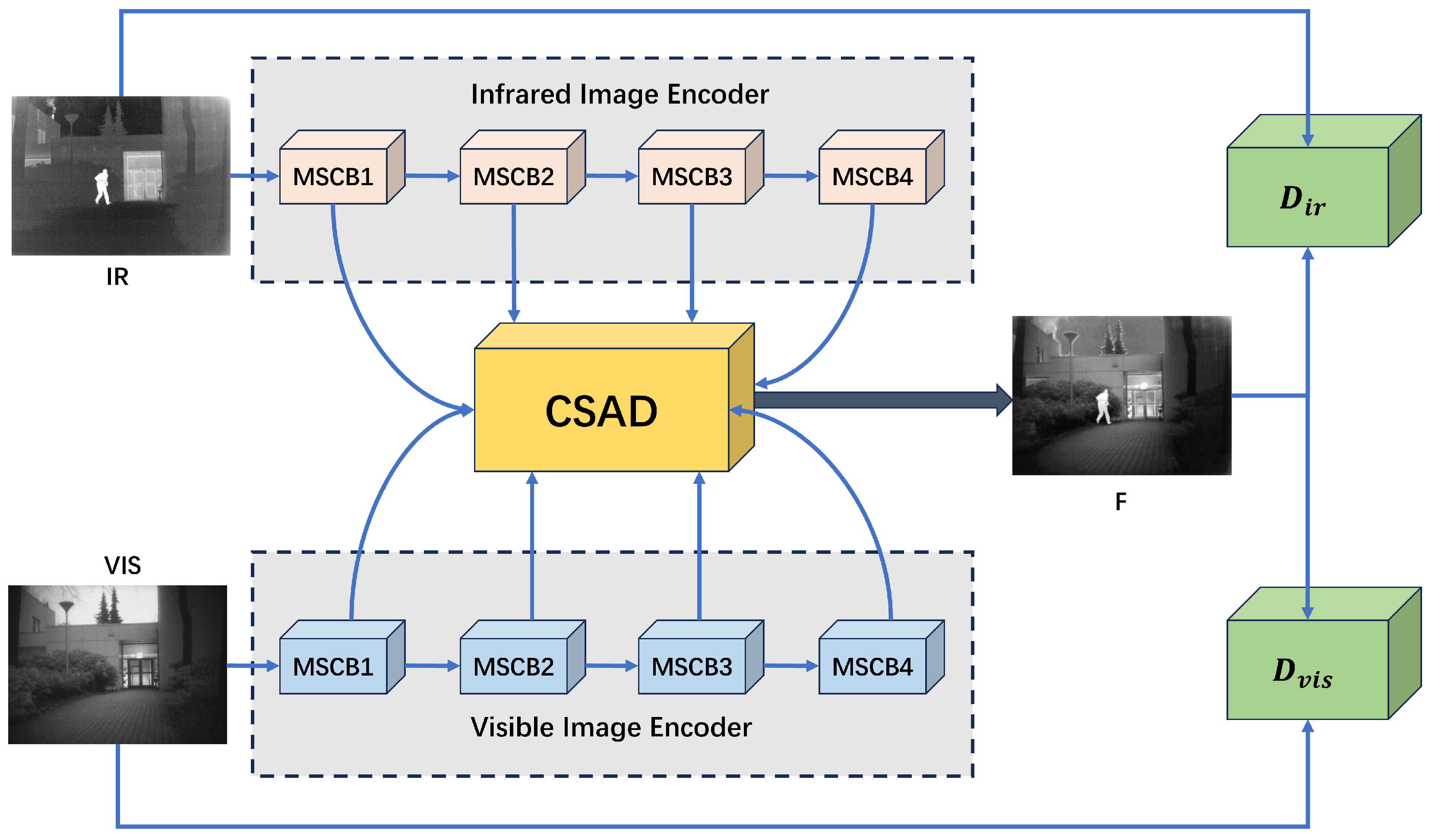
3.1. The Architecture of the Fusion Network
3.1.1. Generator Architecture
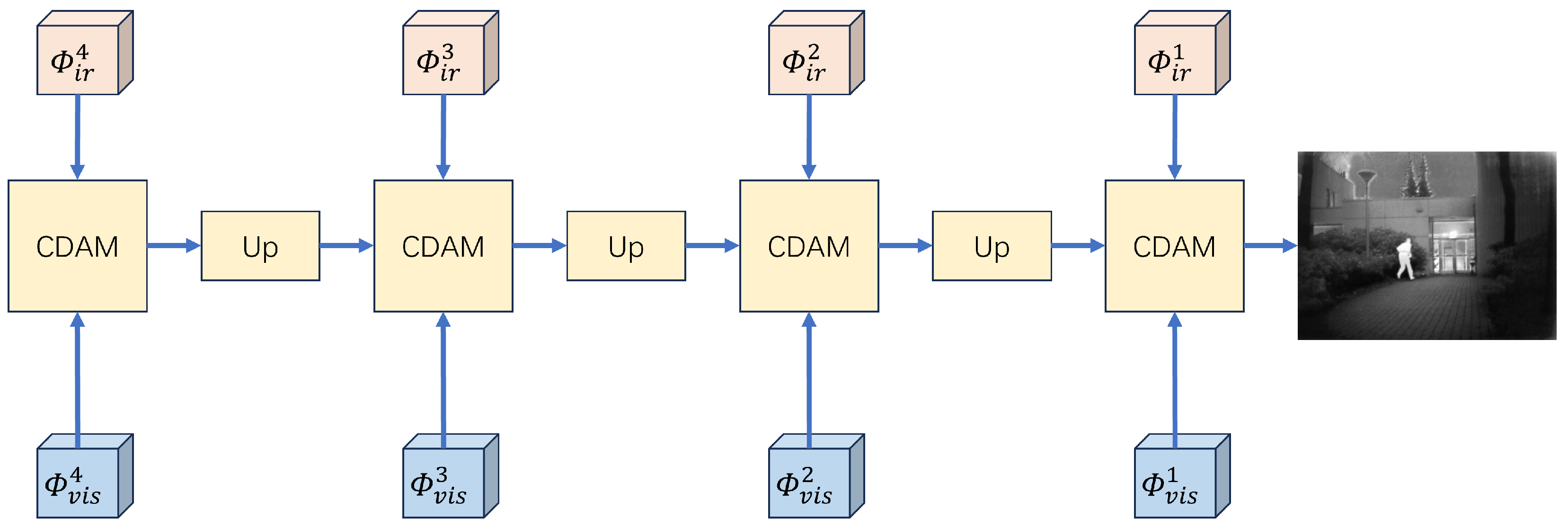
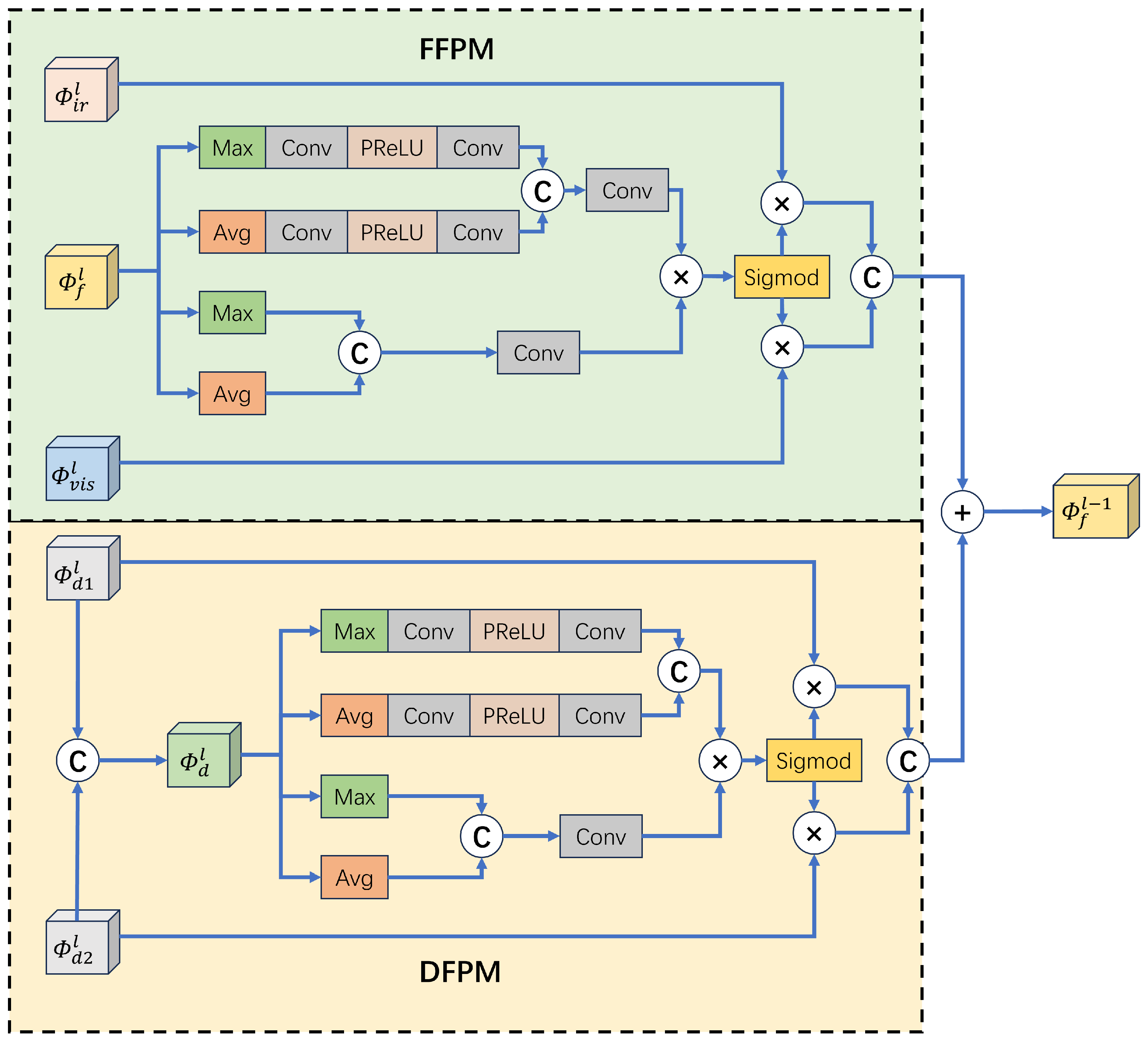
3.1.2. Cross-Modal Differential Features Attention Module (CDAM)
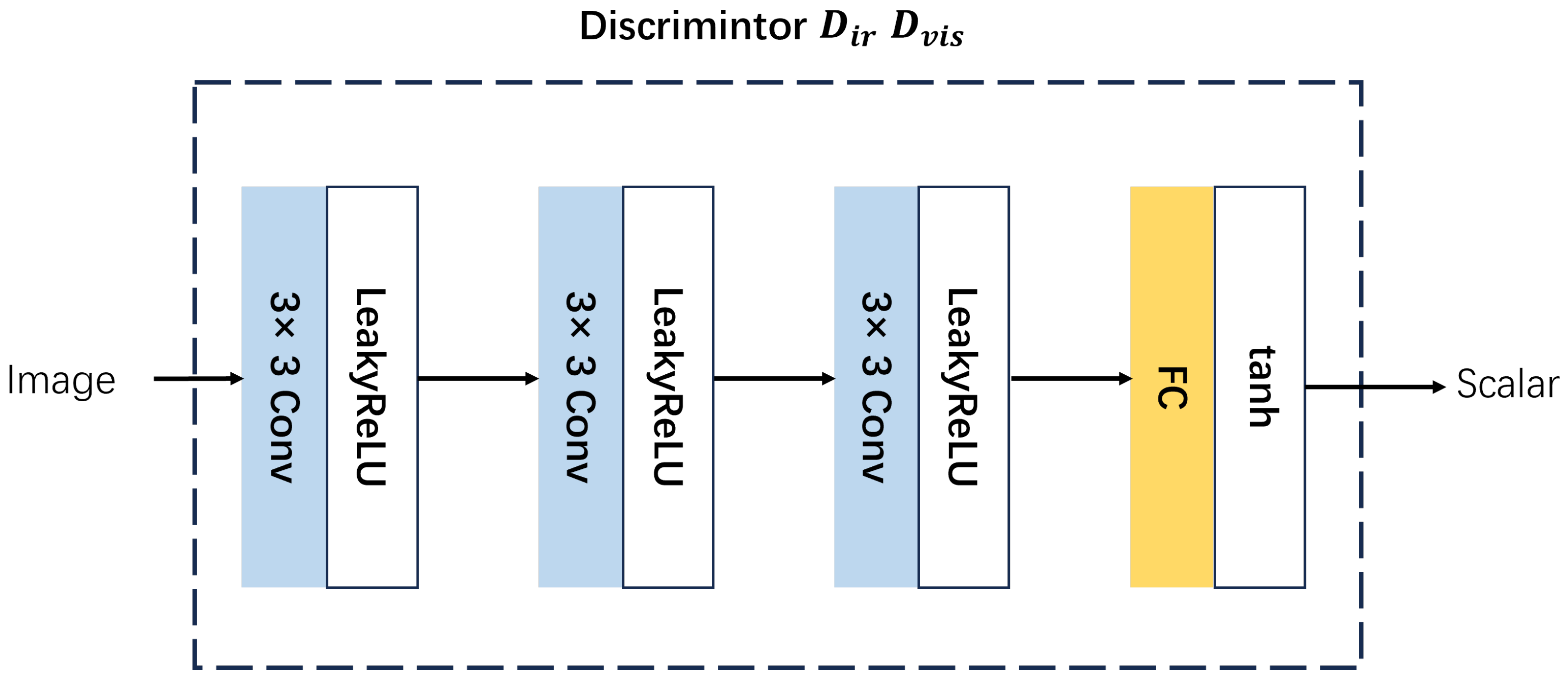
3.1.3. Discriminator Architecture
3.1.4. Loss Function
4. Experiments and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.2. Ablation Study
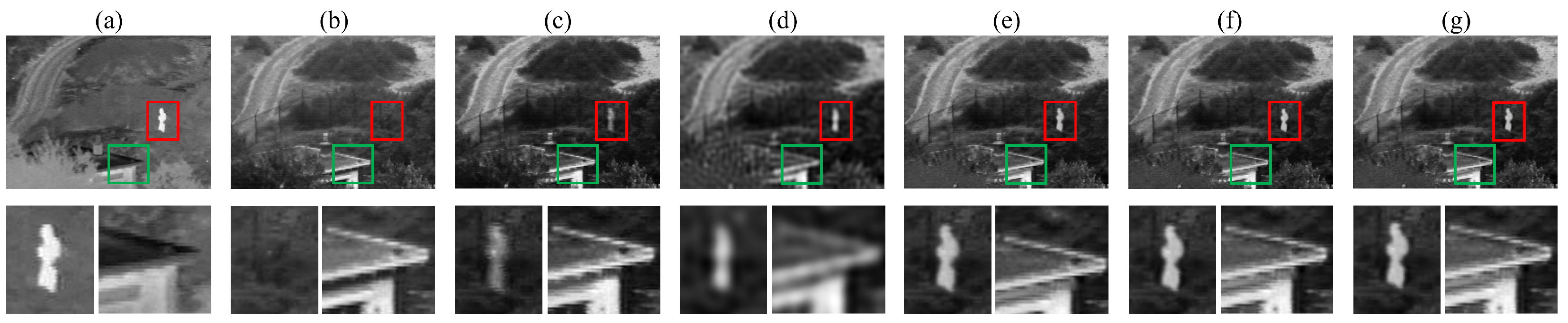
- Qualitative analysis: As can be seen from the results in Figure 5, in the absence of CDAM, the Without_CDAM model not only reduces the brightness of infrared targets but also has the problem of blurred contours. In contrast, adding the CBAM model enables the fused image to retain some infrared target information but loses some texture details. In addition, the results of the Without_DFPM model, the Without_FFPM model, and our model are similar, with no obvious differences. All of them better retain the brightness information of infrared targets and the texture information of visible images.
- Quantitative analysis: The quantitative analysis results are shown in Table 1. The red bold and underlined values indicate the optimal and sub-optimal values respectively. Compared with other models, our model obtains the optimal values under the evaluation indicators of entropy (EN), standard deviation (SD), average gradient (AG), and spatial frequency (SF), and obtains the sub-optimal values under the evaluation indicators of mutual information (MI) and visual information fidelity (VIF). In summary, every component of the differential features attention module proposed is effective.
4.3. Fusion Results on TNO Dataset
4.4. Fusion Results on Roadscene Dataset
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
- The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SOTA | State-of-the-art |
| IVIF | Infrared and visible image fusion |
| MSCB | Multi-scale convolution block |
| CSAD | Cross-scale attention decoder |
| CBAM | Convolutional block attention module |
| CDAM | Cross-modal differential features attention module |
| DFPM | Differential features fusion path module |
| FFPM | Fusion features fusion path module |
References
- Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2019, 45, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Dong, X. Region level based multi-focus image fusion using quaternion wavelet and normalized cut. Signal Process. 2014, 97, 9–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ward, R.K.; Wang, Z.J. Image Fusion with Convolutional Sparse Representation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1882–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvejic, N.; Bull, D.; Canagarajah, N. Region-Based Multimodal Image Fusion Using ICA Bases. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Zong, H. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 82, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Huang, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization. Inf. Fusion 2016, 31, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Pixel-level image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2017, 33, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-J.; Durrani, T. NestFuse: An Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Architecture Based on Nest Connection and Spatial/Channel Attention Models. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 9645–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, G. STDFusionNet: An Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Network Based on Salient Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5009513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjovsky, M.; Chintala, S.; Bottou, L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; Volume 70, pp. 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Jiang, J.; Mei, X.; Zhang, X.-P. DDcGAN: A Dual-Discriminator Conditional Generative Adversarial Network for Multi-Resolution Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4980–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Chen, X. Multi-focus image fusion with deep residual learning and focus property detection. Inf. Fusion 2022, 86–87, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-J. DenseFuse: A Fusion Approach to Infrared and Visible Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, J. DIDFuse: Deep Image Decomposition for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Yokohama, Japan, 11–17 July 2020; pp. 970–976. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Zhao, W.; Yao, L.; Liu, Y. Self-supervised feature adaption for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2021, 76, 189–203. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Jeon, G.; Gao, M.; Chisholm, D. SEDRFuse: A Symmetric Encoder–Decoder with Residual Block Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5002215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Shao, W. Res2Fusion: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Dense Res2net and Double Nonlocal Attention Models. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 5005012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. UNFusion: A Unified Multi-Scale Densely Connected Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 3360–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z. Infrared and visible image fusion with convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolut Inf. Process. 2018, 16, 1850018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Zhou, D.; Nie, R.; Liu, D.; Xiong, L.; Guo, Y.; Yu, C. VIF-Net: An Unsupervised Framework for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2020, 6, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Jia, H.; Zhong, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, Y. RXDNFuse: A aggregated residual dense network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2021, 69, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollar, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated Residual Transformations for Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 5987–5995. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Ma, J. PIAFusion: A progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware. Inf. Fusion 2022, 83–84, 79–92. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network. Inf. Fusion 2022, 82, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A Unified Unsupervised Image Fusion Network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liang, P.; Yu, W.; Chen, C.; Guo, X.; Wu, J.; Jiang, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via detail preserving adversarial learning. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Shao, Z.; Liang, P.; Xu, H. GANMcC: A Generative Adversarial Network with Multiclassification Constraints for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5005014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, X.-J.; Durrani, T. Image fusion based on generative adversarial network consistent with perception. Inf. Fusion 2021, 72, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Z.; Huang, J.; Xu, H.; Fan, F.; Ma, Y.; Mei, X.; Ma, J. UIFGAN: An unsupervised continual-learning generative adversarial network for unified image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2022, 88, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huo, H.; Li, C.; Wang, R.; Feng, Q. AttentionFGAN: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Using Attention-Based Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 23, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Ling, H. Semantic-Supervised Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Via a Dual-Discriminator Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Du, B.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J. Reluplex made more practical: Leaky ReLU. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications, Rennes, France, 7–10 July 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- TNO Image Fusion Dataset. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/TNO_Image_Fusion_Dataset/1008029 (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Roadscene Database. Available online: https://github.com/hanna-xu/RoadScene (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-J.; Kittler, J. MDLatLRR: A Novel Decomposition Method for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4733–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, X. Learning a Deep Multi-Scale Feature Ensemble and an Edge-Attention Guidance for Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.W.; van Aardt, J.; Ahmed, F. Assessment of image fusion procedures using entropy, image quality, and multispectral classification. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2008, 2, 023522. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.-J. In-fibre Bragg grating sensors. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2008, 8, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y. A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity. Inf. Fusion 2008, 14, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskicioglu, A.M.; Fisher, P.S. Image quality measures and their performance. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1995, 8, 2959–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| EN | SD | AG | MI | VIF | SF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without_CDAM | 6.9969 | 37.1377 | 1.7484 | 1.0673 | 0.1998 | 3.1063 |
| CBAM | 7.0451 | 40.5360 | 2.1700 | 1.6596 | 0.4171 | 4.1848 |
| Without_DFPM | 7.1019 | 41.5828 | 3.9443 | 2.3943 | 0.5145 | 8.2949 |
| Without_FFPM | 7.0958 | 41.6206 | 3.9841 | 2.8534 | 0.5373 | 8.4275 |
| ours | 7.1253 | 41.8938 | 4.0462 | 2.6519 | 0.5367 | 8.5184 |
| EN | SD | AG | MI | VIF | SF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FusionGAN | 6.4493 | 27.2618 | 3.0096 | 2.1065 | 0.2846 | 5.9125 |
| DDcGAN | 6.4783 | 41.6072 | 3.9393 | 1.2044 | 0.2432 | 8.1566 |
| MDLatLRR | 6.3292 | 24.0935 | 3.5845 | 1.9596 | 0.3669 | 7.0322 |
| DenseFuse | 6.2892 | 23.2344 | 3.1913 | 2.0259 | 0.3424 | 6.0231 |
| MFEIF | 6.6492 | 31.5080 | 3.4791 | 2.3943 | 0.3842 | 6.7707 |
| Res2Fusion | 6.9569 | 39.2702 | 4.0239 | 2.7047 | 0.4579 | 8.3721 |
| SDDGAN | 7.0352 | 45.8426 | 3.1325 | 1.3724 | 0.3987 | 6.4354 |
| DAGANFuse | 7.1253 | 41.8938 | 4.0462 | 2.6519 | 0.5367 | 8.5184 |
| EN | SD | AG | MI | VIF | SF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FusionGAN | 7.0087 | 37.1567 | 2.6824 | 1.8554 | 0.2914 | 5.8114 |
| DDcGAN | 7.5950 | 56.6306 | 3.5391 | 1.4670 | 0.1763 | 7.0693 |
| MDLatLRR | 7.3976 | 54.5890 | 5.3283 | 1.2881 | 0.3524 | 10.2970 |
| DenseFuse | 7.2343 | 42.0498 | 3.3448 | 1.7809 | 0.3531 | 6.8627 |
| MFEIF | 7.0695 | 38.8528 | 2.9874 | 2.1377 | 0.3787 | 6.3558 |
| Res2Fusion | 7.3308 | 46.6483 | 3.3744 | 2.3449 | 0.4073 | 7.1569 |
| SDDGAN | 7.5453 | 56.1106 | 3.2748 | 2.0076 | 0.3529 | 6.7498 |
| DAGANFuse | 7.8632 | 47.3390 | 6.4322 | 2.4970 | 0.4505 | 12.3760 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Y.; Liu, W. DAGANFuse: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Differential Features Attention Generative Adversarial Networks. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4560. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084560
Wen Y, Liu W. DAGANFuse: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Differential Features Attention Generative Adversarial Networks. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4560. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084560
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Yuxin, and Wen Liu. 2025. "DAGANFuse: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Differential Features Attention Generative Adversarial Networks" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4560. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084560
APA StyleWen, Y., & Liu, W. (2025). DAGANFuse: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Differential Features Attention Generative Adversarial Networks. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4560. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084560






