Abstract
Background: Smartphone overdependence is a type of mental disorder that requires continuous treatment for cure and prevention. A smartphone overdependence management system that is based on scientific evidence is required. This study proposes the design, development and implementation of a smartphone overdependence management system for self-control of smart devices. Methods: The system architecture of the Smartphone Overdependence Management System (SOMS) primarily consists of four sessions of mental monitoring: (1) Baseline settlement session; (2) Assessment session; (3) Sensing & monitoring session; and (4) Analysis and feedback session. We developed the smartphone-usage-monitoring application (app) and MindsCare personal computer (PC) app to receive and integrate usage data from smartphone users. We analyzed smartphone usage data using the Chi-square Automatic Interaction Detector (CHAID). Based on the baseline settlement results, we designed a feedback service to intervene. We implemented the system using 96 participants for testing and validation. The participants were classified into two groups: the smartphone usage control group (SUC) and the smartphone usage disorder addiction group (SUD). Results: The background smartphone monitoring app of the proposed system successfully monitored the smartphone usage based on the developed algorithm. The usage minutes of the SUD were higher than the usage minutes of the SUC in 11 of the 16 categories developed in our study. Via the MindsCare PC app, the data were successfully integrated and stored, and managers can successfully analyze and diagnose based on the monitored data. Conclusion: The SOMS is a new system that is based on integrated personalized data for evidence-based smartphone overdependence intervention. The SOMS is useful for managing usage data, diagnosing smartphone overdependence, classifying usage patterns and predicting smartphone overdependence. This system contributes to the diagnosis of an abstract mental status, such as smartphone overdependence, based on specific scientific indicators without reliance on consultation.
1. Introduction
The use of smartphones has increased convenience in all sectors of everyday lives. However, numerous studies in the previous have stated the following side effects of excessive smartphone usage [1,2]: Due to a lack of self-control [3], smartphone overuse interferes with daily life and sleep [4]; The side effects are severe at times and may cause depressive symptoms and social relationship failure [5]; Negative effects are valid regardless of gender, particularly in the case of hindering academic achievements [6].
The term smartphone overuse includes all addictive activities regarding the problematic use of the Internet [7], playing games, logging on to messengers, or accessing virtual communities to the extent that they neglect positive areas of life [8].
Sufficient evidence supports the fact that the overdependence of smartphones requires continuous mental treatment sessions to cure this disorder and, if possible, prevent the disorder. Both treatment and prevention should be accompanied by a systemized monitoring environment for appropriate intervention. Information technology (IT) has been extensively applied in other healthcare systems, and many variants of medical information systems (MIS), which enable efficient monitoring of health statuses, have been created [9,10,11]. Although previous studies have addressed telepsychiatry [12], they primarily rely on videoconferencing.
However, the proper management of mental-related issues is difficult compared with the management of physical illness, such as those caused by viruses or bacteria, because these issues do not accompany distinct causal biomarkers. A recent report has stated that studies about reproducible and clinically actionable markers are lacking in the general case of psychiatry, such as overdependence [13].
This is shown in past literature also, with many utilizing smartphone monitoring application on physical indicators that monitors the changes in heart activity [14], screens for hearing loss [15], or assesses mobility of the elderly [16], etc. As mentioned, mental status such as overuse is still a difficult psychological marker to monitor, with conventional treatment relying on “perceived overuse”, and not scientific evidence.
Therefore, we propose the Smartphone Overdependence Management System (SOMS), which is a smartphone overdependence management system that delivers mental medical services based on scientific evidence. The goal of the study is to develop a system that scientifically analyzes behavioral patterns that directly cause smartphone overdependence, prevents and monitors smartphone overdependence, and treats patients with integrated information. The system service was developed and implemented for potentially and currently addicted adults and adolescents.
2. Related Research
The majority of studies have focused on social scientific findings regarding the risks and causal pathways of smartphone overuse [17,18,19]. Few studies consider smartphone overuse as a psychiatric problem and apply telemedicine for intervention. Lee et al. [20] proposed the Smartphone Addiction Management System (SAMS); however, it lacked a proper automated measurement algorithm (as mentioned in their limitations) and appeared to include location information, which exhibits weak importance in the case of smartphone usage monitoring.
Telepsychiatry, which is a variant of telemedicine, has been the center of solutions in medical information systems regarding mental health. Telepsychiatry initially emerged due to the difficulty of providing mental treatment service [21] in rural and geographically isolated regions. Although it is costly and some patients from remote distances are unable to travel to urban medical centers for psychiatric treatment, the expected outcome of this IT-converged service was subjected to skepticism because many experts believed that mental status issues can be solved only with face-to-face consultation. However, previous consecutive studies indicate that telepsychiatry services, such as interactive videoconferencing, are as effective as face-to-face psychiatry treatment [12] in most psychiatry fields. Positive results were similar for adults, adolescents and children. The studies prove that telepsychiatry is a feasible and acceptable approach to providing mental medical services to youths [22] with educational effects [23].
Additional unique possibilities by applying telemedicine facilitates monitoring using up-to-date mobile technology [24]. Focusing on monitoring and preventing the relapse of alcohol addicts using smartphones, Gustafson et al. [25] proved the effectiveness of smartphone monitoring. Specialized and personalized intervention is possible only based on individually monitored specific data and evidence. This study proposes a medical information system that is based on an optimized algorithm that provides monitoring services to patients to diagnose based on objective data.
3. System Overview
3.1. Total System Architecture
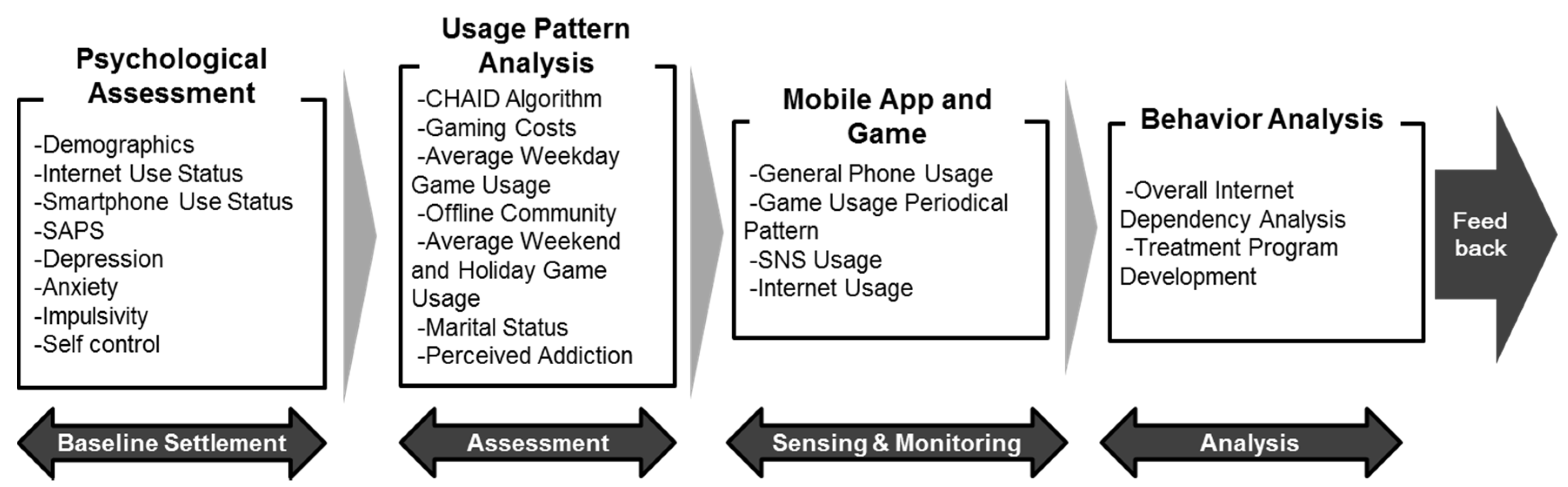
The system architecture of the SOMS consists of four main sessions of mental monitoring: (1) Baseline settlement session; (2) Assessment session; (3) Sensing & monitoring session; and (4) Analysis session. Figure 1 shows the total system architecture.
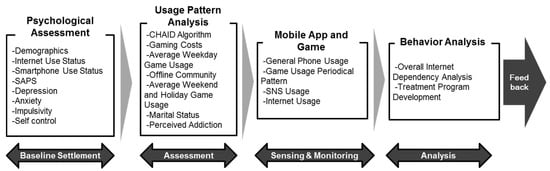
Figure 1.
Total System Architecture of the Smartphone Overdependence Management System (SOMS).
In the baseline settlement session, we obtain the psychological information of all patients using surveys and an offline medical test. The psychological information is obtained to assess the socio-demographical status, Internet usage status, smartphone usage status, Smartphone Addiction Proneness Scale (SAPS), depression status, anxiety status, impulsivity status, and self-control status of each patient. In the assessment phase, the patient information is processed using the Chi-square Automatic Interaction Detector (CHAID) algorithm [26]. Six important indicators—gaming costs, average weekday game usage, offline community, average weekend and holiday game usage, marital status, and perceived addiction—are assessed using the CHAID algorithm.
After the assessment phase, the mobile device usage behavior of the patient is sensed and monitored via the mobile application (app), which is developed as a part of the SOMS. The general device usage, game usage periodical pattern, social network service (SNS) and Internet usage are monitored to obtain usage behavior evidence.
The analysis session includes the total Internet dependency analysis of the patient. This session provides a conclusion for the overdependence usage status. Personalized feedback and treatment programs are developed.
Considering the diagnosis based on scientific indicators, the system provides a feedback service for patients when intervention is necessary. The system is implemented to randomly selected adults nationwide and willingly participating middle school and high school adolescents.
3.2. General Specifications
3.2.1. Baseline Settlement Session
We conducted a general survey to assess the psychological status of smartphone overdependence. In the case of adolescents, adolescents who accepted the terms to provide information and had their parents’ approval were provided services by the SOMS.
In all surveys, various survey tools, such as the SAPS [27], a behavioral activation system/behavioral inhibition system (BAS/BIS) [28], a short version of the smartphone addiction scale (SAS-SV) [29], depression symptom checklist-90-revision (SCL-90-R) [30], Dickman Functional and Dysfunctional Impulsivity Inventory (DFDII) [31], and belief self-control scale (BSCS) [32], were employed.
The participants were divided into two groups: the smartphone usage control (SUC) group, which included healthy and productive smartphone users, and the smartphone usage disorder (SUD) group, which included negative users with smartphone overdependence.
3.2.2. Assessment Session
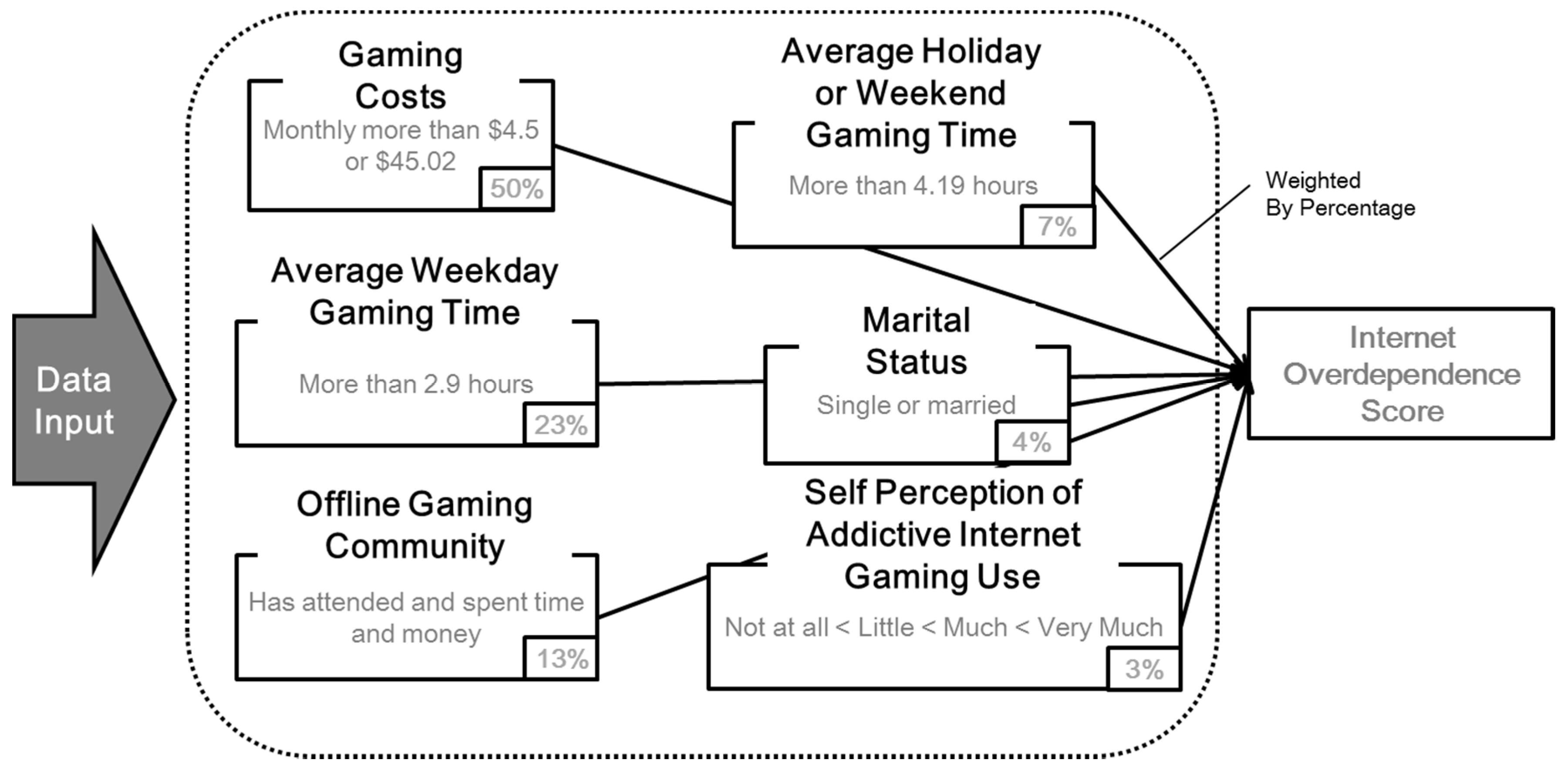
The obtained information was input to the developed algorithm based on the CHAID. In our previous study [33], an optimized algorithm to determine the Internet overdependence condition was derived from the CHAID decision tree and applied to the proposed analysis system, as shown in Figure 2.
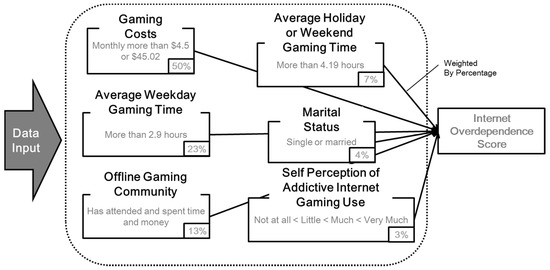
Figure 2.
Smartphone overdependence decision algorithm.
When the monitored data are input in the analysis algorithm, the following six indicators are scored and aggregated according to each weight percentage by importance: whether the user has spent more than $4.5–45.02 on gaming (50%); whether the user’s average weekday gaming time exceeds 2.9 h (23%); whether the user attends occasional events of the offline gaming community and spends his/her time and money (13%); whether the user’s average holiday or weekend gaming time exceeds 4.19 h (7%); the marital status of the user (4%); and the user’s self-perception of addictive Internet gaming use (3%). Weight differences were derived from our previous study and were applied in this algorithm. Each of the six indicators’ scores is weighted and scored. The aggregated score of the six indicators is the total smartphone over-dependency score of the individual.
3.2.3. Sensing & Monitoring Session
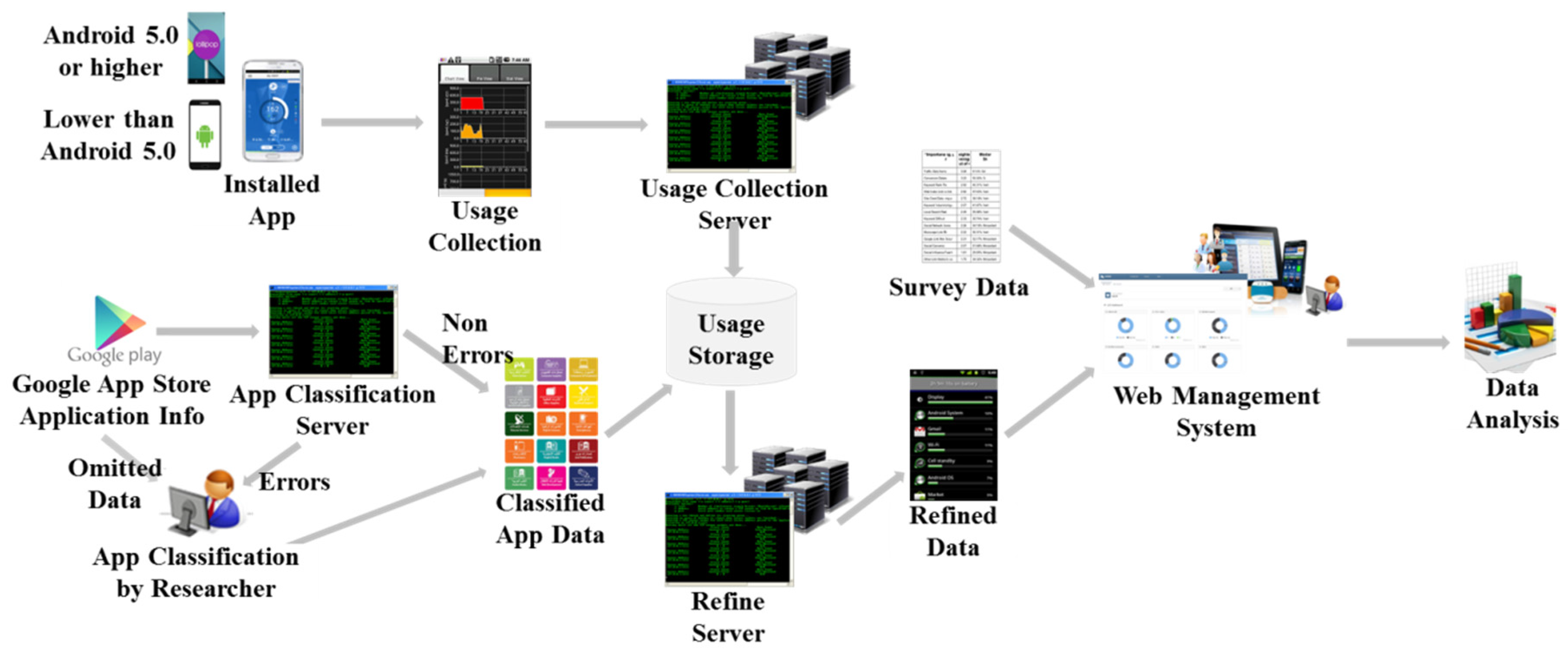
Via the mobile app of the SOMS, the mobile device usage data of the patients are collected and sent to the main server. General phone usage contains all general status information about a phone, even data regarding whether the phone is turned on or off, whether the phone is in an idle state, and whether an Internet connection exists. The most important feature is Internet, SNS, and game usage monitoring. The general application data, exact usage time and period logs are monitored via the background application. The proposed application supports only Android phones. The system architecture is shown in Figure 3.
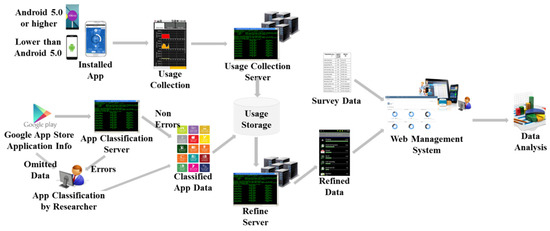
Figure 3.
System architecture of sensing and monitoring app.
The installed app collects the application usage information (amount of usage and frequency of usage) and sends it to the usage collection server. The Google app store application information is sent to the app classification server. Only the “application classification” information provided by Google is obtained. However, when the application classification information is omitted, the researcher manually types in the classification information. If data errors occur in the app classification server, the researcher manually corrects the errors. Then, the non-errors and data that are adjusted by the researcher are integrated as classified app data and sent to the usage storage. The application usage and classification information are integrated and sent to the usage storage.
These usage data are useful for analyzing individual application usage information but are not useful for data analysis. In data analysis, the data must be refined. This task is performed by the refine server, which optimizes the refined data for visualization or analysis. The refine server contains a computational algorithm to classify data into meaningful fields, as shown in Table 1. Note that one measurement occurs, for example, when the user begins a game application one time.

Table 1.
Data quality management.
In the general measurement information field, classification by day, hour, or ten minutes was conducted to adjust the periods when the smartphone was off or not in use. If the non-usage period is included, the overuse level of the patient is underestimated. The usage data can be analyzed without a smartphone non-usage period bias to manage the data quality. The management fields that are classified and defined based on the binge/chronic status enable researchers to categorize binge overuse and chronic overuse. Binge overuse accounts for people who play games in a certain short period (for example, weekends) but play a lot, whereas chronic overuse accounts for people who play a lot throughout an entire week or period.
With the survey data obtained in the baseline settlement phase, the refined data are sent to a web management system, which is specifically shown in Section 4.5. Using the data from the web management server, researchers can conduct the analysis.
3.2.4. Analysis Session
The individually targeted diagnosis that considers six indicators of a patient is provided based on an analysis. The total score of smartphone overdependence is provided (as mentioned in the assessment session), and brief specific comments are simultaneously provided. With the total smartphone overdependence score (e.g., 83.3% or 81%), comments such as “Costs for games are pretty high…” or “You tend to have many activities related to games…” are provided to account for the specific indicator(s) with which the user has a problem.
This simplified recommendation is envisioned to help patients and their physicians understand the nature of their overdependence on the smartphone, monitor the overuse, assess risk and help construct the future mental treatment.
4. Implementation
4.1. Target Population
A baseline settlement survey was conducted with 139 randomly selected participants, who agreed to install the smartphone application of the proposed system. The system was consecutively implemented using these participants. However, 43 participants were excluded due to dropout within seven days or data collection errors. As a result, 96 participants remained (69.06%). The research procedures were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The Institutional Review Board of the Catholic University of South Korea, ST. Mary’s Hospital (IRB number: KC15EISI0103).
All 96 participants were classified into two groups: the SUD group and the SUC group. The SUD and SUC groups were distinguished based on the SAPS standards. As a result, the SUD groups had 29 participants, and the SUC groups had 67 participants. The socio-demographic status for the participants in the SUD and SUC groups is listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Socio-demographic status of participants in the smartphone usage disorder (SUD) and smartphone usage control (SUC) groups.
Most participants were male (n = 86, 90.6%), and the age of most participants ranged from 10–19 (n = 72, 75.0%). Most participants had an undergraduate degree or lower level of education (n = 79, 82.3%), were unemployed (n = 81, 84.4%), and were not married (n = 86, 89.6%), which is also noted by the age demographics. Half of the participants replied that their socio-economic status (SES) was in the middle (n = 48, 50%).
4.2. Smartphone Usage Monitoring Implementation
The smartphone application of the SOMS was installed on the mobile phones of the informed participants for additional monitoring. The app monitored the smartphone usage patterns of the participants to obtain objective and specific data to provide evidence of smartphone overdependence.
The SOMS smartphone-usage-monitoring application can be downloaded and installed from app stores. It is not loaded with a user interface (UI); after it is installed and initially executed, it runs as a background app to monitor general usage events. Note that users must approve the app usage access by tapping “on” on the app usage access screen. Then, the data are sent to the personal computer (PC) application of the management servers for the analysis (Section 4.3).
4.3. Management Server: MindsCare PC Application
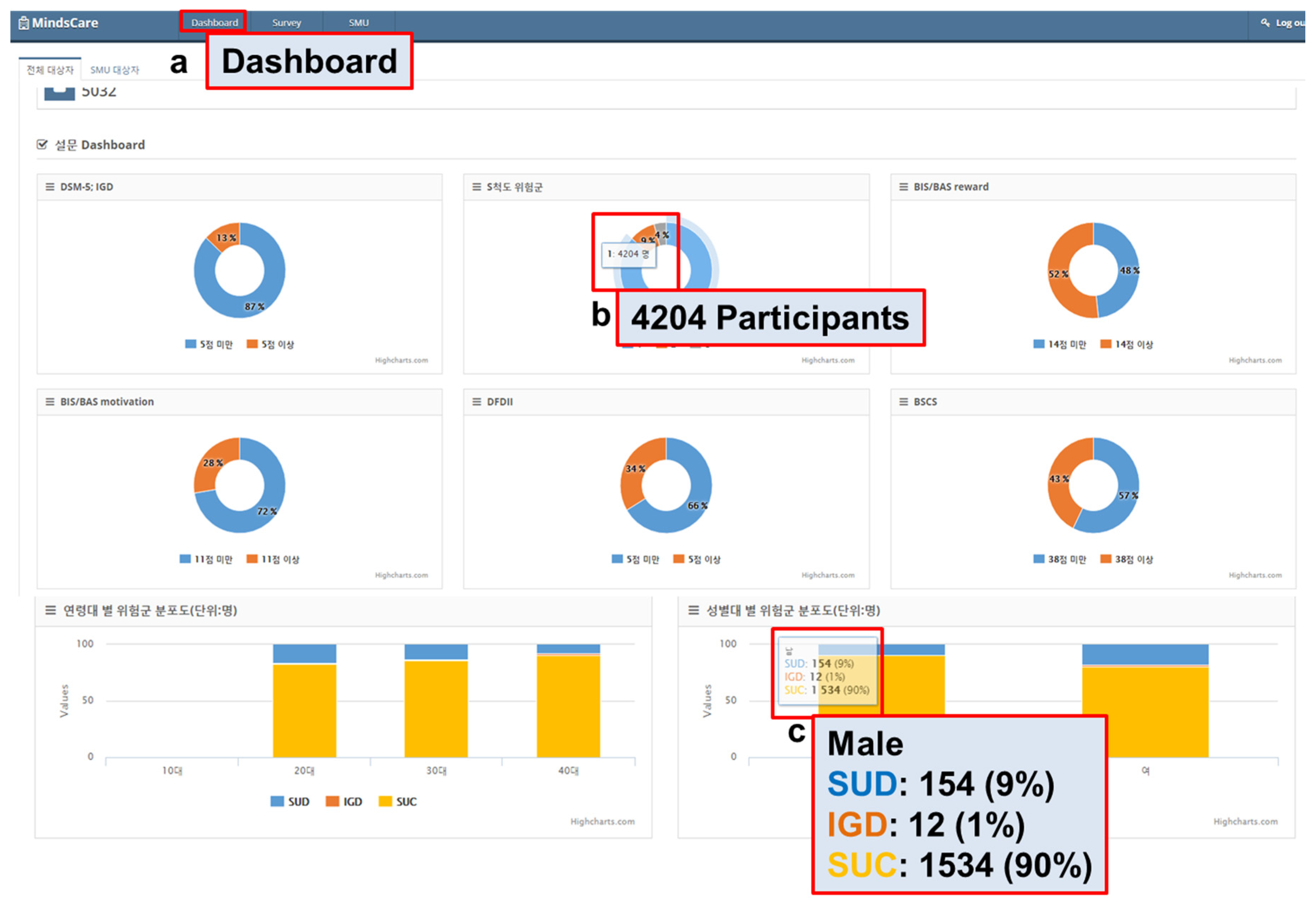
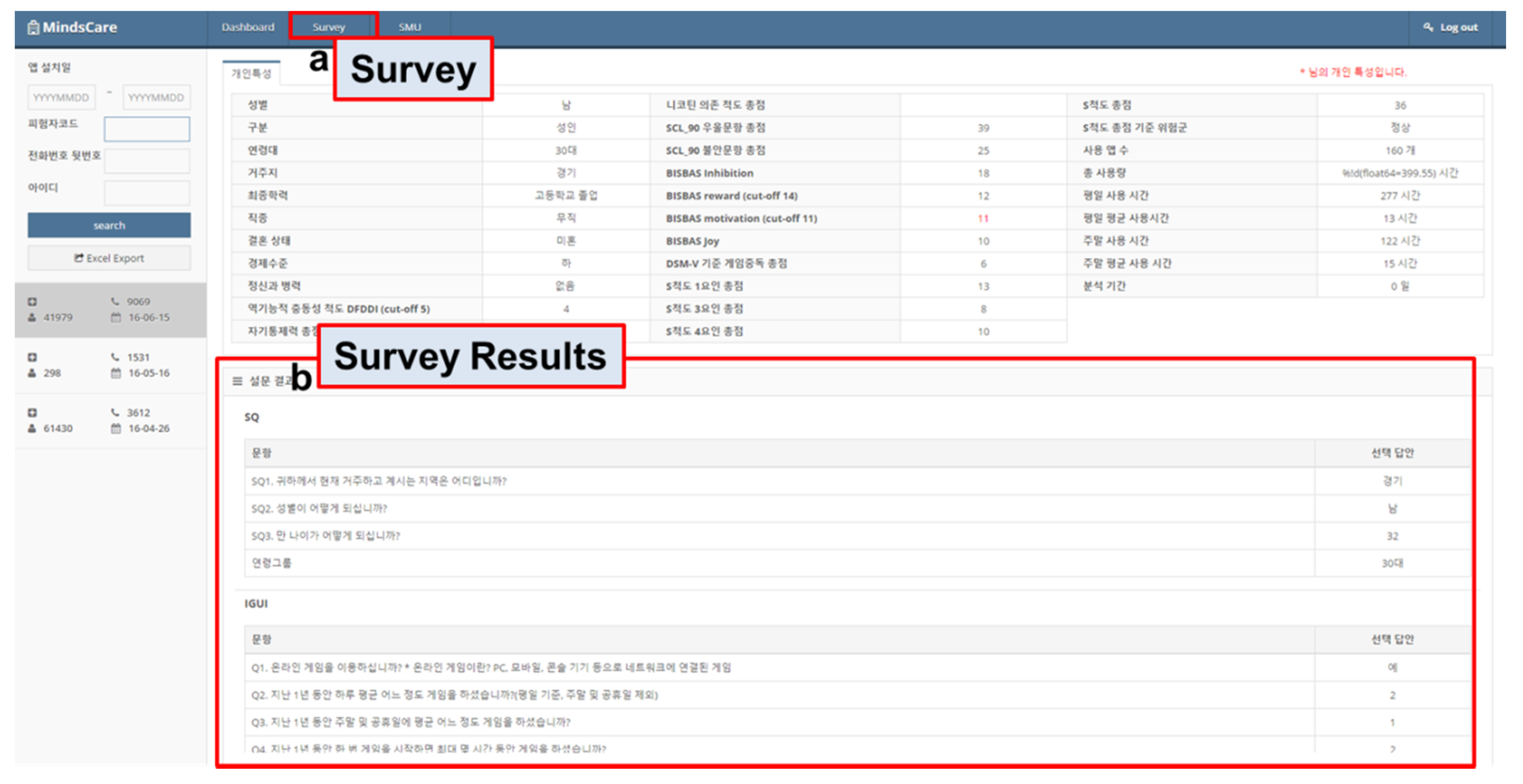
The aggregated patient data were sent to the server for monitoring. The received data were integrated and mined through the MindsCare PC application and shown as a visual UI, as illustrated in Figure 4 and Figure 5.
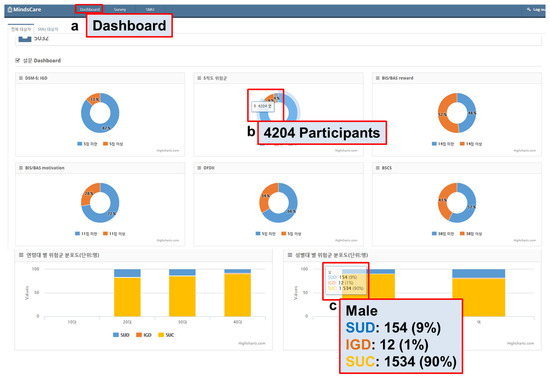
Figure 4.
Survey data mining and visualization. SUD: Smartphone Use Disorder; IGD: Internet Gaming Disorder; SUC: Smartphone Use Control.
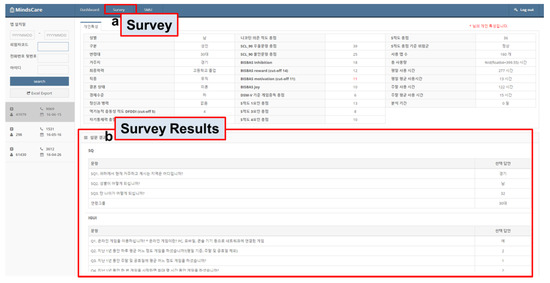
Figure 5.
Application usage monitoring.
On the Dashboard page (Figure 4a), the SUD, SAPS, BAS/BIS, DFDII, and BSCS information is shown in each visual circular chart. The users can view the number of samples when they place the mouse cursor over the circular chart (Figure 4b). The group distribution by age and sex is shown in the bar graphs, and the managers can view the number of samples when they place the mouse cursor over the bar graphs (Figure 4c).
The user smartphone application monitoring information that is obtained via the background-running app Internet Detox is observed on the Smartphone Usage (SMU) page (Figure 5a). The top five smartphone application lists are shown in a circular chart (e.g., Kakao Talk, Chrome, and Google apps). A manager can view the aggregate usage time of each application when they place the mouse cursor over the circular chart (Figure 5b).
4.4. Smartphone Usage Results
The smartphone usage monitoring results are listed in Table 3. The results were calculated based on the daily average usage. The Google Play store provides 35 category standards, and registered apps to the store are categorized. However, we identified some categories that can be integrated and reorganized. Thus, the 35 categories were reorganized into the following 16 items: finance, system, web, SNS, shopping, business, tool/productivity, entertainment, weather, transportation, photo, lifestyle, health/exercise, game, and education, as shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Daily average usage by category.
“User” refers to the number of users who have used the app of a certain category, and “usage minutes” refers to the time that the user has spent on the app of this category. The usage gap was calculated by subtracting the usage minutes of the SUC from the usage minutes of the SUD. With the exception of five categories (lifestyle, health/exercise, game, education, and decoration), the monitoring results indicate that the SUD usage minutes in all 11 categories were higher than the SUC usage minutes. The most noticeable categories were finance- and system-related apps with usage gaps of 28.0 and 25.9, respectively.
4.5. Discussion
This study attempts to design, develop, and implement a smartphone overdependence management system for self-control of smart devices. Based on the results of this study, we present the discussions below.
In the baseline settlement session, we adapt diverse psychological tools, such as SAPS, BAS/BIS, SAS-SV, SCL-90-R, DFDII, and BSCS, to assess the psychological status of smartphone overdependence. These tools support the system to correctly analyze smartphone usage. Future research may identify other psychological tools to address missing areas.
In the assessment session, we employ the CHAID Algorithm and six indicators to assess the smartphone overdependence. However, the shortcoming is that the six indicators were developed only for Internet dependence. Thus, future research may involve the development of new indicators that are more applicable in other fields.
In the sensing and monitoring session, the background smartphone app monitors specific overuse stats. In the MindsCare PC app, the data are successfully stored and integrated, which enables the monitoring of general application data, exact usage time and period logs. The limitation is that the proposed app only supports Android phones due to security issues at the stage of development, and because more than 85% of smartphone users in South Korea use Android phones. Considering worldwide users, future research should develop the usage collection app for other operating systems (OSs).
In the analysis and feedback session, medical treatment recommendations are provided based on six indicators. If the user has an impediment in two of the six indicators, recommendations are provided based on these two impediments.
Implementation results of the participants of the system indicate that the usage minutes of SUD were higher than the usage minutes of SUC in 11 categories. With the exception of five categories (lifestyle, health/exercise, game, education, and decoration), the daily-average comparison between the SUD group and the SUC group in the 16 categories that were defined from this study indicate that the usage minutes of SUD were higher than the usage minutes of SUC in all 11 categories. In the “game” category, the SUD and SUC groups did not significantly differ (SUD − SUC = −3.2). The smartphone usage time for the SUC group was higher than the smartphone usage for the SUD group. Although games can be easily associated with addiction, and this linkage is sometimes viable [34,35], the proposed results suggest the larger effect of web usage or SNS usage in the case of smartphones. The results also correspond with recent studies that emphasized the importance of considering SNS as a main factor for smartphone overuse [36,37].
A brief comparison with the SAMS is discussed because it is almost the first reference of the smartphone overuse monitoring system. Other related solutions were simple apps that were non-systematic or were not studies. The main difference is that the SAMS simply shows raw smartphone usage, whereas we developed an algorithm to filter raw information and consider the key risks or variables regarding smartphone overuse. The proposed system shows better monitored results based on weekday or weekend usage, which is an important risk factor that was discussed in previous research [38].
Another important point is that we developed 16 new categories to classify the collected app data: finance, system, web, SNS, shopping, business, tool/productivity, entertainment, weather, transportation, photo, lifestyle, health/exercise, game, and education. The previous 35 categories established by Google are overspecified, which render them inappropriate for analysis or research applications. A representative example is that Google separates “Cartoons” and “Entertainment” (based on the most recent Google category in November 2016); however, combining these two terms in the research analysis is more appropriate. It is also a shortcoming of SAMS because they do not address this part. Future related studies are recommended to follow the proposed categories in this study instead of relying on the default category settings of Google.
In the case of “Finance,” “System,” and “Decoration,” the daily average usage minutes were overmeasured because they included usage events such as background security applications and any type of application launchers. These categories may cause bias when monitoring. Thus, future research on monitoring algorithms that filter these events is necessary. A future study should include new categories depending on the app data or research topic.
5. Conclusions
This study developed and implemented the SOMS, which is an original MIS that is based on integrated personalized data for evidence-based smartphone overuse intervention. The SOMS primarily consists of four sessions of mental monitoring: (1) Baseline settlement session; (2) Assessment session; (3) Sensing & monitoring session; and (4) Analysis session. By obtaining integrated data of smartphone overdependent patients, the personalized mental service in the management server can be diagnosed. The uniqueness of the SOMS is that its services are based on specific scientific grounds, which are inferred from specific psychological data. In addition, the proposed system can provide a scientific footwork for personalized smartphone overuse management systems. Additional years of implementation of this study may provide integrated big data in the area of smartphone overdependence, which will cause the abstract mental status, such as smartphone overdependence, to be diagnosed based on specific scientific indicators instead of a dependence on verbal consultation.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), which is funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (NRF-2014M3C7A1062893). The authors thank the Trend & Innovation Company (TNIC) for their support in system development.
Author Contributions
Seo-Joon Lee and Mi-Jung Rho are both first authors who contributed equally in the article; Seo-Joon Lee wrote the article; Mi-Jung Rho is the assistant executive of the funded research project. Mi-Jung Rho also supported the writing of the article; In Hye Yook analyzed the data and performed the evaluation; Seung-Ho Park, Kwang-Soo Jang and Bum-Joon Park contributed to developing the proposed system; Dong Kyun Lee supported general implementation of the research project; Ook Lee supervised parts of the project and managed researchers; Dai-Jin Kim and In Young Choi are both corresponding authors who contributed equally to this work. SOMS is a large-scale and long-term research project worth $4.5 million, and all 10 authors substantially contributed in each of their expertise.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, L.; Yan, Z.; Tang, W.J.; Yang, F.Y.; Xie, X.D.; He, J.C. Mobile phone addiction levels and negative emotions among Chinese young adults: The mediating role of interpersonal problems. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 55, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chóliz, M. Mobile-phone addiction in adolescence: The test of mobile phone dependence (TMD). Prog. Health Sci. 2012, 2, 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Gokcearslan, S.; Mumcu, F.K.; Haslaman, T.; Çevik, Y.D. Modelling smartphone addiction: The role of smartphone usage, self-regulation, general self-efficacy and cyberloafing in university students. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 63, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavia, L.; Cavani, P.; Di Blasi, M.; Giordano, C. Smartphone Addiction Inventory (SPAI): Psychometric properties and confirmatory factor analysis. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 63, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.G.; Park, Y.; Kim, M.K.; Park, J. Mobile phone dependency and its impacts on adolescents’ social and academic behaviors. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 63, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawi, N.S.; Samaha, M. To excel or not to excel: Strong evidence on the adverse effect of smartphone addiction on academic performance. Comput. Educ. 2016, 98, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellowlees, P.M.; Marks, S. Problematic Internet use or Internet addiction? Comput. Hum. Behav. 2007, 23, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billieux, J.; Maurage, P.; Lopez-Fernandez, O.; Kuss, D.J.; Griffiths, M.D. Can disordered mobile phone use be considered a behavioral addiction? An update on current evidence and a comprehensive model for future research. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2015, 2, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamedine, D.; Khalil, M.; Marque, C. Parameters extraction and monitoring in uterine EMG signals. Detection of preterm deliveries. IRBM 2013, 34, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstam, M.A. Home monitoring should be the central element in an effective program of heart failure disease management. Circulation 2012, 125, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayalakshmi, S.R.; Muruganand, S. Real-time monitoring of ubiquitous wireless ECG sensor node for medical care using ZigBee. Int. J. Electron. 2012, 99, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, R.; Bishop, J.; Maddox, K.; Hutchinson, L.; Fisman, M.; Takhar, J. Is telepsychiatry equivalent to face-to-face psychiatry? Results from a randomized controlled equivalence trial. Psychiatr. Serv. 2007, 58, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insel, T.R. The NIMH Research Domain Criteria (RDoC) Project: Precision Medicine for Psychiatry. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliev, T.A.; Rzayeva, N.E.; Sattarova, U.E. Robust correlation technology for online monitoring of changes in the state of the heart by means of laptops and smartphones. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 31, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.Y.; Swanepoel, D.; de Jager, L.B.; Myburgh, H.C.; Eikelboom, R.H.; Hugo, J. Smartphone hearing screening in mHealth assisted community-based primary care. J. Telemed. Telecare. 2016, 22, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhushri, P.; Dzhagary, A.; Jovanov, E.; Milenkovic, A. An mHealth Tool Suite for Mobility Assessment. Information 2016, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljomaa, S.S.; Al Qudah, M.F.; Albursan, I.S.; Bakhiet, S.F.; Abduljabbar, A.S. Smartphone addiction among university students in the light of some variables. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 61, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Pyeon, A. Altered functional connectivity related smartphone overuse in adolescent. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19, 158. [Google Scholar]
- Inal, E.E.; Demirci, K.; Cetinturk, A.; Akgonul, M.; Savas, S. Effects of smartphone overuse on hand function, pinch strength, and the median nerve. Muscle Nerve 2015, 52, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Ahn, H.; Choi, S.; Choi, W. The SAMS: Smartphone Addiction Management System and verification. J. Med. Syst. 2014, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Guebaly, N.; Kingstone, E.; Rae-Grant, Q.; Fyfe, I. The geographical distribution of psychiatrists in Canada: Unmet needs and remedial strategies. Can. Psychiatr. Assoc. Rev. Assoc. Psychiatres Can. J. 1993, 38, 212–216. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, K.M.; Valentine, J.M.; Melzer, S.M. Feasibility, acceptability, and sustainability of telepsychiatry for children and adolescents. Psychiatr. Serv. 2007, 58, 1493–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesamaa, L.; Ebeling, H.; Kuusimaki, M.L.; Winblad, I.; Isohanni, M.; Moilanen, I. Videoconferencing in child and adolescent telepsychiatry: A systematic review of the literature. J. Telemed. Telecare 2004, 10, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proudfoot, J. The future is in our hands: The role of mobile phones in the prevention and management of mental disorders. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2013, 47, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, J.H.; Alagoz, E.; Dinauer, S.; Johnson, K.A.; Pe-Romashko, K.; Gustafson, D.H. Successful organizational strategies to sustain use of A-CHESS: A mobile intervention for individuals with alcohol use disorders. JMIR 2015, 17, e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.L.; Comiskey, C.M. Using chi-Squared Automatic Interaction Detection (CHAID) modelling to identify groups of methadone treatment clients experiencing significantly poorer treatment outcomes. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2013, 45, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Nam, J.K.; Chung, Y. Development of Korean smartphone addiction proneness scale for youth. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.; Kim, D.-J.; Cho, H.; Yang, S. The smartphone addiction scale: Development and validation of a short version for adolescents. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.; Choi, J.-H.; Gu, X.-Y.; Kim, D.-J. Standardization of the smart phone addiction scale (SAS). Asia Pac. Psychiatry 2012, 4, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, K.; Schaefer, M.; Stickel, A.; Binder, H.; Heinz, A.; Richter, C. The role of psychological distress in relapse prevention of alcohol addiction. Can high scores on the SCL-90-R predict alcohol relapse? Alcohol Alcohol. 2016, 51, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Jia, C. Psychometric properties of the Dickman Impulsivity Instrument in suicide victims and living controls of rural China. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 132, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, C.; Nagy, G.; Retelsdorf, J. The dimensionality of the Brief Self-Control Scale-An evaluation of unidimensional and multidimensional applications. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2015, 86, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, M.J.; Jeong, J.E.; Chun, J.W.; Cho, H.; Jung, D.J.; Choi, I.Y.; Kim, D.J. Predictors and patterns of problematic Internet game use using a decision tree model. J. Behav. Addict. 2016, 5, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Leung, L. Are you addicted to Candy Crush Saga? An exploratory study linking psychological factors to mobile social game addiction. Telemat. Inform. 2016, 33, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Miralles, R.; Ortega-Gonzalez, R.; Lopez-Moron, M.R.; Batalla-Martinez, C.; Manresa, J.M.; Montella-Jordana, N.; Chamarro, A.; Carbonell, X.; Toran-Monserrat, P. The problematic use of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) in adolescents by the cross sectional JOITIC study. BMC Pediatr. 2016, 16, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.-H.; Kim, H.; Yum, J.-Y.; Hwang, Y. What type of content are smartphone users addicted to?: SNS vs. games. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 54, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. Exercise rehabilitation for smartphone addiction. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2013, 9, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Jeong, J.E.; Cho, H.; Jung, D.J.; Kwak, M.; Rho, M.J.; Yu, H.; Kim, D.J.; Choi, I.Y. Personality factors predicting smartphone addiction predisposition: Behavioral inhibition and activation systems, impulsivity, and self-control. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).