Temporally Programmable Hybrid MOPA Laser with Arbitrary Pulse Shape and Frequency Doubling
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MOPA Setup
3. MOPA Laser with Arbitrary Pulse Shape
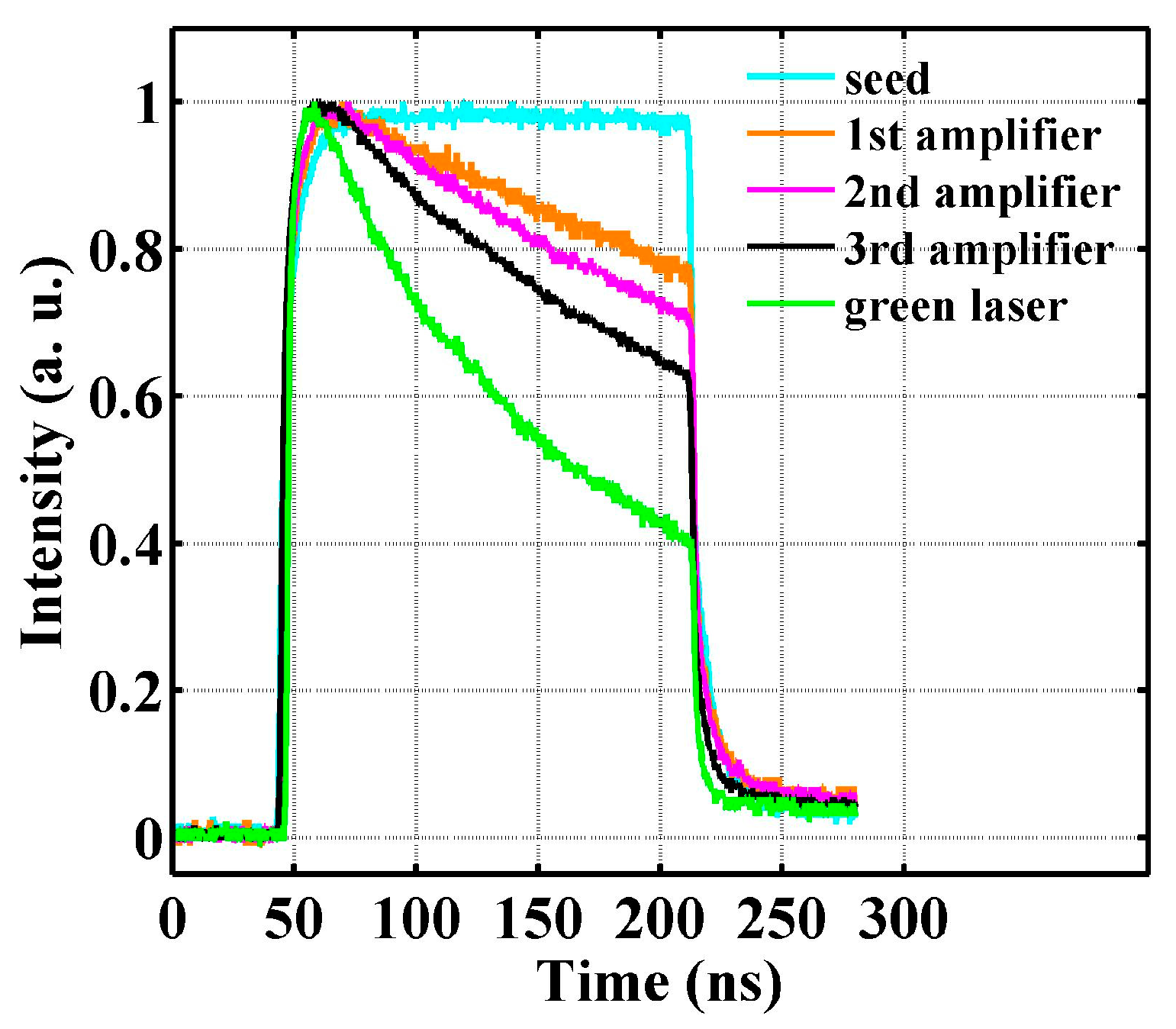
3.1. Fiber Amplifier Stage
3.2. Arbitrary Pulse Shape Output for the First Nd:YVO4 Amplifier
3.3. Arbitrary Pulse Shape Output for the MOPA System
4. Second Harmonic Generation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biswas, A.; Hemmati, H.; Lesh, J.R. High data rate laser transmission for free space laser communications. SPIE Rev. 1999, 3615, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Abshire, J.B.; Collatz, G.J.; Sun, X.; Riris, H.; Andrews, A.E.; Krainak, M. Laser sounder technique for remotely measuring atmospheric CO2 concentrations. In Proceedings of the American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–14 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, D.; Young, C.Y.; Andrews, L.C. Temporal broadening of ultrashort space-time Gaussian pulses with applications in laser satellite communication. SPIE Rev. 1998, 3266, 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati, H.; Wright, M.; Esproles, C. High efficiency pulsed laser transmitters for deep space communications. SPIE Rev. 2000, 3932, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, P.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Amzajerdian, F. Pulse shaping fiber laser at 1.5 μm. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegman, A.E. Lasers; University Science Books: Sausalito, CA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, K.T.; Malinowski, A.; Richardson, D.J.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Hickey, L.M.B.; Zervas, M.N. Adaptive pulse shape control in a diode-seeded nanosecond fiber MOPA system. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 10996–11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimpf, D.N.; Ruchert, C.; Nodop, D.; Limpert, J.; Tuennermann, A.; Salin, F. Compensation of pulse-distortion in saturated laser amplifiers. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 17637–17646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinowski, A.; Vu, K.T.; Chen, K.K.; Nilsson, J.; Jeong, Y.; Alam, S.; Lin, D.; Richardson, D.J. High power pulsed fiber MOPA system incorporating electro-optic modulator based adaptive pulse shaping. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 20927–20937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobon, G.; Kaczmarekm, P.; Antonczak, A.A.; Sotor, J.; Waz, A.; Abramski, K.M. Pulsed dual-stage fiber MOPA source operating at 1550 nm with arbitrarily shaped output pulses. Appl. Phys. B 2011, 105, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidt, A.M.; Li, Z.; Richardson, D.J. High Power Diode-Seeded Fiber Amplifiers at 2 μm—From Architectures to Applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2014, 20, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.G. Optical power handling capacity of low loss optical fibers as determined by stimulated Raman and Brillouin scattering. Appl. Opt. 1972, 11, 2489–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, M.; Williams, W.; House, R.; Haynam, C. Laser Performance Operations Model (LPOM). In Inertial Confinement Fusion Semiannual Report; Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory: Livermore, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Morice, O. Miró: Complete modeling and software for pulse amplification and propagation in high-power laser systems. Opt. Eng. 2003, 42, 1530–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegman, A.E. Design considerations for laser pulse amplifiers. J. Appl. Phys. 1964, 35, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yu, L.; Chu, Y.; Gan, Z.; Liang, X. Temporal compensation method of pulse distortion in saturated laser amplifiers. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Cao, X.; Liu, Q.; Ji, E.; Fu, X. 100 μJ pulse energy in burst-mode-operated hybrid fiber-bulk amplifier system with envelope shaping. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 13557–13566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, M.; Liu, Q.; Ji, E.; Gong, M. High peak power hybrid MOPA laser with tunable pulse repetition frequency and pulse duration. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 3457–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, M.; Liu, Q.; Ji, E.; Cao, X.; Fu, X.; Gong, M. Design of High-Gain Single-Stage and Single-Pass Nd:YVO4 Amplifier Pumped by Fiber-Coupled Laser Diodes: Simulation and Experiment. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2016, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delen, X.; Balembois, F.; Georges, P. Temperature dependence of the emission cross section of Nd:YVO4 around 1064 nm and consequences on laser operation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2011, 28, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Taira, T. Temperature dependencies of stimulated emission cross section for Nd-doped solid-state laser materials. Opt. Mater. Express 2012, 2, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Liu, Q.; Ji, E.; Gong, M. Gain change by adjusting the pumping wavelength in an end-pumped Nd:YVO4 amplifier. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 8383–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, G.; Bidin, N. Determination of a stimulated emission cross section gradient on the basis of the performance of a diode-end-pumped NdYVO4 lase. Laser Phys. Lett. 2013, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.; Jenssen, H.; Cassanho, A. Investigation of the Spectroscopic Properties of Nd:YVO4. In Proceedings of the Advanced Solid-State Lasers (Optical Society of America, 2002), Québec City, QC, Canada, 3 February 2002; pp. 294–298. [Google Scholar]







| Amplifier | Peak Power (kW) | Linewidth (nm) | Exp or Theo 1 | Arbitrary Waveform | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fiber | 2.6 | 3 | theo | yes | [7] |
| 1.5 | - | theo | yes | [8] | |
| 18 | 0.3 | exp | yes | [9] | |
| solid-state | - | - | exp | yes | [13] |
| 1.34×108 | narrow | exp | no | [16] |
| Pulse Shape | 100 kHz, 41.4 W | 40 kHz, 38.3 W | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leading Edge (ns) | Falling Edge (ns) | Pulse Duration (ns) | Power of Green Laser (W) | Leading Edge (ns) | Falling Edge (ns) | Pulse Duration (ns) | Power of Green Laser (W) | |
| square | 9 (1.53) 1 | 15 (5.7) | 168 (166.8) | 3.63 | 6.6 (2.4) | 8.6 (3.6) | 39 (38) | 14.5 |
| Gaussian | 45 (32.6) | 51 (37.9) | 63 (47.2) | 5.3 | 16 (11.7) | 20 (13.7) | 23 (17.5) | 16.3 |
| parabolic | 49 (57.2) | 54 (64.4) | 123.4 (96) | 4.19 | 14 (14.4) | 18 (13.2) | 29 (24.7) | 16.0 |
| multiple-step | 8 (2.0) | 12 (7.5) | 111 (-) | 4.23 | - | - | - | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nie, M.; Liu, Q.; Ji, E.; Cao, X.; Fu, X. Temporally Programmable Hybrid MOPA Laser with Arbitrary Pulse Shape and Frequency Doubling. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7090892
Nie M, Liu Q, Ji E, Cao X, Fu X. Temporally Programmable Hybrid MOPA Laser with Arbitrary Pulse Shape and Frequency Doubling. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(9):892. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7090892
Chicago/Turabian StyleNie, Mingming, Qiang Liu, Encai Ji, Xuezhe Cao, and Xing Fu. 2017. "Temporally Programmable Hybrid MOPA Laser with Arbitrary Pulse Shape and Frequency Doubling" Applied Sciences 7, no. 9: 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7090892
APA StyleNie, M., Liu, Q., Ji, E., Cao, X., & Fu, X. (2017). Temporally Programmable Hybrid MOPA Laser with Arbitrary Pulse Shape and Frequency Doubling. Applied Sciences, 7(9), 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7090892





