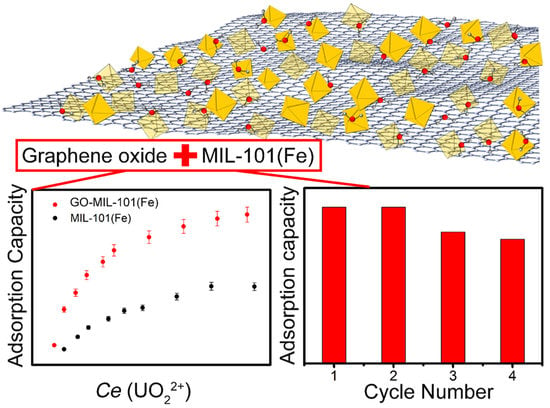
Facile Preparation of Graphene Oxide-MIL-101(Fe) Composite for the Efficient Capture of Uranium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Fabrication of the GO-MIL-101(Fe) Composite with Different GO Contents
2.4. Batch Sorption Experiments
2.5. Desorption and Reusing Studies
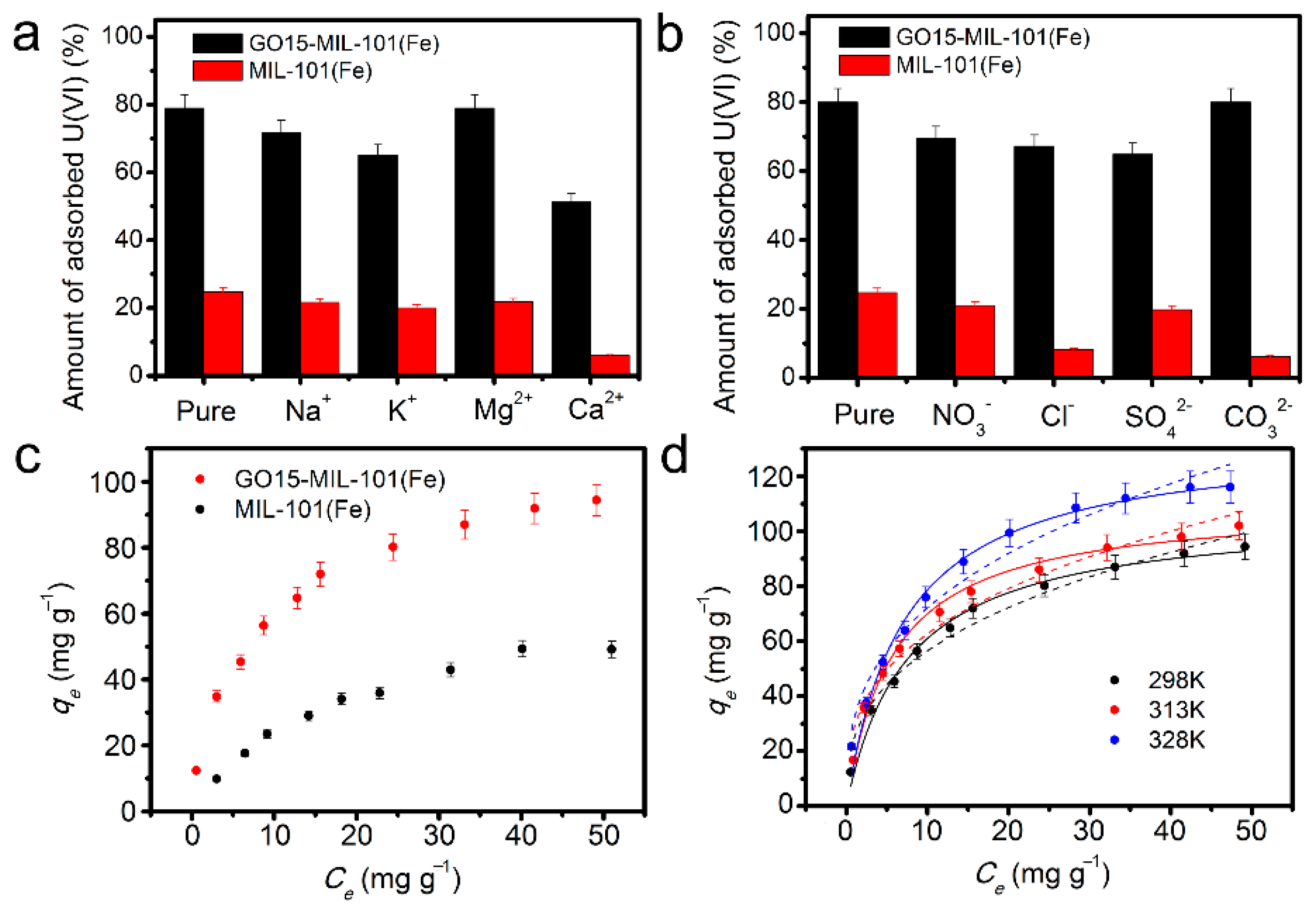
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of GO-MIL-101(Fe) Composite
3.2. U(VI) Adsorption on the GO-MIL-101(Fe)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Domingo, J.L. Reproductive and developmental toxicity of natural and depleted uranium: A review. Reprod. Toxicol. 2001, 15, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdway, D.A. Uranium toxicity to two species of Australian tropical fish. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 125, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.L.; Hogan, A.C.; Parry, D.L.; Markich, S.J.; Harford, A.J.; van Dam, R.A. Uranium toxicity and speciation during chronic exposure to the tropical freshwater fish, mogurnda mogurnda. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.; Geng, J.X.; Jin, Y.D.; Wang, C.L.; Li, S.Q.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.S.; Li, S.J. Sorption of uranium(VI) using oxime-grafted ordered mesoporous carbon cmk-5. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, J.R.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Yoon, H.-S. A brief review on solvent extraction of uranium from acidic solutions. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2011, 40, 77–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manos, M.J.; Kanatzidis, M.G. Layered metal sulfides capture uranium from seawater. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16441–16446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abney, C.W.; Mayes, R.T.; Saito, T.; Dai, S. Materials for the recovery of uranium from seawater. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13935–14013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, Z.; Shi, W. Uranium(VI) adsorption on graphene oxide nanosheets from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 210, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Gu, T.; Ding, D.; Ling, L.; Zhang, W.-X. Effect of bicarbonate on aging and reactivity of nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI) toward uranium removal. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Wang, X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhong, J.; Chu, M.; Tang, H.; Luo, L.; Xie, D. Facile fabrication of magnetic cucurbit [6]uril/graphene oxide composite and application for uranium removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ding, C.; Cheng, W.; Wang, X. Simultaneous adsorption and reduction of U(VI) on reduced graphene oxide-supported nanoscale zerovalent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizescu, C.; Podolean, I.; Albero, J.; Parvulescu, V.I.; Coman, S.M.; Bucur, C.; Puche, M.; Garcia, H. N-doped graphene as a metal-free catalyst for glucose oxidation to succinic acid. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1999–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, F.; Cseri, L.; Szekely, G.; Blanford, C.F. Robust covalently cross-linked polybenzimidazole/graphene oxide membranes for high-flux organic solvent nanofiltration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16140–16147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Liu, Q.; Jing, X.; Liu, J.; Song, D.; Hu, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, J. Removal of uranium(VI) ions from aqueous solution by magnetic cobalt ferrite/multiwalled carbon nanotubes composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasfous, I.I.; Dawoud, J.N. Uranium (VI) sorption by multiwalled carbon nanotubes from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 259, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Liu, Z.; Chao, L.; Wu, X.; Lei, X.; Chang, Z.; Sun, X. Adsorption and desorption of U(VI) on functionalized graphene oxides: A combined experimental and theoretical study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 3, 3667–3675. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Zhang, E.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, X. Hydrothermal carbon superstructures enriched with carboxyl groups for highly efficient uranium removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Yan, L.; Liu, C.; Su, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Lan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lai, L.; Liu, X.; et al. Non-covalent functionalized graphene oxide (GO) adsorbent with an organic gelator for co-adsorption of dye, endocrine-disruptor, pharmaceutical and metal ion. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierz, A.; Zänker, H. Aqueous suspensions of carbon nanotubes: Surface oxidation, colloidal stability and uranium sorption. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.B.; Shao, D.D.; Chen, C.; Yang, S.B.; Wang, X.K. Highly efficient enrichment of radionuclides on graphene oxide-supported polyaniline. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9904–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Jing, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Song, D. Enhanced adsorption of uranium (VI) using a three-dimensional layered double hydroxide/graphene hybrid material. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-J.; Wang, L.; Yuan, L.-Y.; Xiao, C.-L.; Mei, L.; Zheng, L.-R.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.-H.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Zhu, Z.-T.; et al. Efficient removal of uranium from aqueous solution by zero-valent iron nanoparticle and its graphene composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 290, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Maghrabi, H.H.; Abdelmaged, S.M.; Nada, A.A.; Zahran, F.; El-Wahab, S.A.; Yahea, D.; Hussein, G.M.; Atrees, M.S. Magnetic graphene based nanocomposite for uranium scavenging. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Shao, D.; Wang, X. Plasma-induced grafting of polyacrylamide on graphene oxide nanosheets for simultaneous removal of radionuclides. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Shao, D.; Wang, X. Graphene oxide/polypyrrole composites for highly selective enrichment of U(VI) from aqueous solutions. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 6207–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linghu, W.; Yang, H.; Sun, Y.; Sheng, G.; Huang, Y. One-pot synthesis of LDH/GO composites as highly effective adsorbents for decontamination of U(VI). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5608–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-R.; Kuppler, R.J.; Zhou, H.-C. Selective gas adsorption and separation in metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1477–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Shen, K.; Mao, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Nanoreactor of MOF-derived yolk–shell Co@C–N: Precisely controllable structure and enhanced catalytic activity. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towsif Abtab, S.M.; Alezi, D.; Bhatt, P.M.; Shkurenko, A.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Aggarwal, H.; Weseliński, Ł.J.; Alsadun, N.; Samin, U.; Hedhili, M.N.; et al. Reticular chemistry in action: A hydrolytically stable MOF capturing twice its weight in adsorbed water. Chem 2018, 4, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Jing, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Song, D. Superior removal of arsenic from water with zirconium metal-organic framework UiO-66. Sci. Rep. 2015, 259, 752–760. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.L.; Huang, L.; Ma, L.J.; Shim, Y.; Islam, S.M.; Wang, P.L.; Zhao, L.D.; Wang, S.C.; Sun, G.B.; Yang, X.J.; et al. Functionalized metal-organic framework as a new platform for efficient and selective removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 137, 3670–3677. [Google Scholar]
- Karmakar, S.; Dechnik, J.; Janiak, C.; De, S. Aluminium fumarate metal-organic framework: A super adsorbent for fluoride from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 303, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.; Burgal, J.D.S.; Szekely, G.; Davies, R.P.; Braddock, D.C.; Livingston, A. Hybrid polymer/MOF membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN): Chemical modification and the quest for perfection. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 503, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboni, M.; Abney, C.W.; Liu, S.; Lin, W. Highly porous and stable metal-organic frameworks for uranium extraction. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 2396–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Pournara, A.; Kim, K.-H.; Bansal, V.; Rapti, S.; Manos, M.J. Metal-organic frameworks: Challenges and opportunities for ion-exchange/sorption applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 86, 25–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.N.; Ma, W.; Shen, S.S.; Huang, H.X.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H.W. A combined experimental and theoretical study on the extraction of uranium by amino-derived metal–organic frameworks through post-synthetic strategy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 31032–31041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Decker, J.; Folens, K.; De Clercq, J.; Meledina, M.; Van Tendeloo, G.; Du Laing, G.; Van Der Voort, P. Ship-in-a-bottle CMPO in MIL-101(Cr) for selective uranium recovery from aqueous streams through adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 335, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Decker, J.; Rochette, J.; De Clercq, J.; Florek, J.; Van Der Voort, P. Carbamoylmethylphosphine oxide-functionalized MIL-101(Cr) as highly selective uranium adsorbent. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5678–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; Liu, L.; Wang, J. Interfacial growth of a metal-organic framework (UiO-66) on functionalized graphene oxide (GO) as a suitable seawater adsorbent for extraction of uranium(VI). J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 17933–17942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.Q.; Yuan, L.Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Z.R.; Chu, S.Q.; Zheng, L.R.; Zhang, J.; Chai, Z.F.; Shi, W.Q. Introduction of amino groups into acid-resistant MOFs for enhanced U(VI) sorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, V.; Veleta, J.M.; Zarei-Chaleshtori, M.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.; Villagrán, D. Green synthesis of magnetic MOF@GO and MOF@CNT hybrid nanocomposites with high adsorption capacity towards organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petit, C.; Bandosz, T.J. MOF–graphite oxide nanocomposites: Surface characterization and evaluation as adsorbents of ammonia. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6521–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karel, F.; Karen, L.; Ricci, N.N.; Maria, M.; Stuart, T.; Gustaaf, V.T.; Du, L.G.; Pascal, V.D.V. Fe3O4@MIL-101—A selective and regenerable adsorbent for the removal of as species from water. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2016, 4395–4401. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Burrows, A.D.; Edler, K.J. Size-controlled synthesis of MIL-101(Cr) nanoparticles with enhanced selectivity for CO2 over N2. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 6916–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konkena, B.; Vasudevan, S. Understanding aqueous dispersibility of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide through pKa measurements. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, W.; Shi, J.; Zhao, Z.; Xia, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Z. A novel mof/graphene oxide composite GrO@MIL-101 with high adsorption capacity for acetone. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 4722–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, M.; Saikia, L. Sulfonic acid-functionalized MIL-101(Cr) as a highly efficient heterogeneous catalyst for one-pot synthesis of 2-amino-4H-chromenes in aqueous medium. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 15846–15853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Li, C.-Y.V.; Yung, H.; Chan, K.-Y. A functionalized MIL-101(Cr) metal-organic framework for enhanced hydrogen release from ammonia borane at low temperature. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10629–10631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Xia, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Synthesis and adsorption performance of MIL-101(Cr)/graphite oxide composites with high capacities of n-hexane. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 239, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Liu, H. Quinone-modified NH2-MIL-101(Fe) composite as a redox mediator for improved degradation of bisphenol A. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Ning, L.; Zheng, S.; Tao, M.; Shi, Y.; He, Y. Adsorption of carbon dioxide by MIL-101(Cr): Regeneration conditions and influence of flue gas contaminants. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Shu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, L.; Hua, D. Highly efficient removal of uranium (VI) from aqueous solutions using poly(acrylic acid)-functionalized microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 253, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-T.; Chen, S.; Chang, Y.; Cao, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by graphene oxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 359, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wager, C.D.; Riggs, W.H.; Davis, L.E.; Moulder, J.F.; Meilenberg, G.E. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Perkin-Elmer Coorperation: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- VG Scientific Auger Handbook; VG Scientific Limited: West Sussex, UK, 1989.
- Makarova, L.G.; Shabanova, I.N.; Kodolov, V.I.; Besogonov, Y.V. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy as a method to control the received metal–carbon nanostructures. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2004, 137–140, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.B.; Campbell, C.T.; Graham, D.J.; Ratner, B.D. Surface characterization of hydroxyapatite and related calcium phosphates by XPS and tof-sims. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 2886–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhankhar, S.; Bhalerao, G.; Ganesamoorthy, S.; Baskar, K.; Singh, S. Growth and comparison of single crystals and polycrystalline brownmillerite Ca2Fe2O5. J. Cryst. Growth 2017, 468, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzyk, A.P. The influence of activated carbon surface chemical composition on the adsorption of acetaminophen (paracetamol) in vitro: Part II. TG, FTIR, and XPS analysis of carbons and the temperature dependence of adsorption kinetics at the neutral pH. Colloids Surf. A 2001, 177, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, B.; Rao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Gong, J.R. Strong two-photon-induced fluorescence from photostable, biocompatible nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for cellular and deep-tissue imaging. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2436–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, E.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. Three dimensional hierarchically porous ZIF-8 derived carbon/LDH core-shell composite for high performance supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 263, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredych, M.; Petit, C.; Tamashausky, A.V.; Bandosz, T.J. Role of graphite precursor in the performance of graphite oxides as ammonia adsorbents. Carbon 2009, 47, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, K.F.; Papelis, C.; Leckie, J.O. Modeling ionic strength effects on anion adsorption at hydrous oxide/solution interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1988, 125, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, S. Kinetic models of sorption: A theoretical analysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 276, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, Y.; Ishida, H.; Tanaka, S.; Kolev, S.D. Theoretical analysis of the pseudo-second order kinetic model of adsorption. Application to the adsorption of Ag(I) to mesoporous silica microspheres functionalized with thiol groups. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Ball, W.P.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Stone, A.T.; Bai, J.; Zachara, J.M. Influence of calcite and dissolved calcium on uranium(VI) sorption to a hanford subsurface sediment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7949–7955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, J.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Grambow, B.; Wang, X. A strategically designed porous magnetic N-doped Fe/Fe3C@C matrix and its highly efficient uranium(VI) remediation. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Shi, W.; Guo, L.; Leong, Z.Y.; Baji, A.; Yang, H.Y. Rational design and synthesis of monodispersed hierarchical SiO2@layered double hydroxide nanocomposites for efficient removal of pollutants from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 5, 6113–6121. [Google Scholar]





| C0 (mg L−1) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | qe (mg g−1) | R2 | k2 (g mg−1 min−1) | qe (mg g−1) | R2 | |
| MIL-101(Fe) | 0.361 | 18.40 | 0.577 | 0.0485 | 18.88 | 0.999 |
| GO15-MIL-101(Fe) | 0.179 | 36.93 | 0.961 | 0.0117 | 38.46 | 0.999 |
| T (K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg g−1) | b (L mg−1) | R2 | KF (mol1−n Ln g−1) | n | R2 | |
| MIL-101(Fe) | 68.93 | 0.053 | 0.991 | 7.66 | 2.03 | 0.969 |
| GO15-MIL-101(Fe) | 106.89 | 0.132 | 0.989 | 24.96 | 2.824 | 0.973 |
| T (K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg g−1) | b (L mg−1) | R2 | KF (mol1−n Ln g−1) | n | R2 | |
| 298 | 106.89 | 0.13 | 0.989 | 24.97 | 2.82 | 0.973 |
| 313 | 110.15 | 0.17 | 0.988 | 28.85 | 2.96 | 0.901 |
| 328 | 133.83 | 0.14 | 0.986 | 32.20 | 2.85 | 0.929 |
| Adsorbents | ΔG0 (kJ mol−1) | ΔH0 (kJ mol−1) | ΔS0 (J mol−1 K−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 K | 313 K | 328 K | |||
| GO15-MIL-101(Fe) | −23.16 | −24.71 | −26.29 | 7.96 | 104.34 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, B.; Zhang, E.; Cheng, G. Facile Preparation of Graphene Oxide-MIL-101(Fe) Composite for the Efficient Capture of Uranium. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2270. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8112270
Han B, Zhang E, Cheng G. Facile Preparation of Graphene Oxide-MIL-101(Fe) Composite for the Efficient Capture of Uranium. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(11):2270. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8112270
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Bing, Enyao Zhang, and Gong Cheng. 2018. "Facile Preparation of Graphene Oxide-MIL-101(Fe) Composite for the Efficient Capture of Uranium" Applied Sciences 8, no. 11: 2270. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8112270
APA StyleHan, B., Zhang, E., & Cheng, G. (2018). Facile Preparation of Graphene Oxide-MIL-101(Fe) Composite for the Efficient Capture of Uranium. Applied Sciences, 8(11), 2270. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8112270