Review on Seat Suspension System Technology Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Passive Vibration Control Systems
3. Semi Active Vibration Control Systems
4. Active Vibration Control Systems
5. Our Contributions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seidel, H. Selected health risks caused by long-term, whole-body vibration. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1993, 23, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Schimmels, J.M. Improved Vibration Isolating Seat Suspension Designs Based on Position-Dependent Nonlinear Stiffness and Damping Characteristics. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2003, 125, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.C.; Desai, G.J.; Patwardhan, S.R.; Shirke, P.H.; Kurne, W.M.H.; Banerjee, N. Optimization of passive vehicle suspension system by genetic algorithm. Procedia Eng. 2016, 144, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkaya, N.; Goldsheyder, D.; Willems, B. Effect of operator seat design on vibration exposure. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1996, 57, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 7096. Earth-Moving Machinery—Laboratory Evaluation of Operator Seat Vibration; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Maciejewski, I.; Meyer, L.; Krzyzynski, T. Modelling and multi-criteria optimisation of passive seat suspension vibro-isolating properties. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 324, 520–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paddan, G.S.; Griffin, M.J. Evaluation of whole-body vibration in vehicles. J. Sound Vib. 2002, 253, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker-Bone, K.; Palmer, K. Musculoskeletal disorders in farmers and farm workers. Occup. Med. 2002, 52, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, T.D.; Ahn, K.K. A vibration isolation system in low frequency excitation region using negative stiffness structure for vehicle seat. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 6311–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdzik, R.; Konieczny, L. Vibration issues in passenger car. Transp. Probl. 2014, 9, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kolich, M. Automobile seat comfort: Occupant preferences vs. anthropometric accommodation. Appl. Ergon. 2003, 34, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danh, L.T.; Ahn, K.K. Active pneumatic vibration isolation system using negative stiffness structures for a vehicle seat. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 1245–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawana, M.; Shimogo, T. Active suspension of truck seat. Shock Vib. 1998, 5, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-B.; Han, Y.-M. Vibration control of electrorheological seat suspension with human-body model using sliding mode control. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 303, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Sun, S.; Du, H.; Li, W. Integrated active and semi-active control for seat suspension of a heavy duty vehicle. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 29, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmino, E.; Sireteanu, T.; Stammers, C.W.; Ghita, G.; Giuclea, M. Semi-Active Suspension Control: Improved Vehicle Ride and Road Friendliness; Springer-Verlag London: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Z.; Hillis, A.J.; Darling, J. Adaptive control of an active seat for occupant vibration reduction. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 349, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fedders, B.J. Active Seat Suspension for Watercraft. U.S. Patent US6880483B2, 19 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Karnopp, D.; Crosby, M.J.; Harwood, R. Vibration control using semi-active force generators. J. Eng. Ind. 1974, 96, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, H.; Tewari, V.; Singh, S. Discomfort, pressure distribution and safety in operator’s seat—A critical review. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2003, 5. Available online: http://www.cigrjournal.org/index.php/Ejounral/article/view/467 (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- Peng, C.; Fang, J.; Xu, X. Mismatched Disturbance Rejection Control for Voltage-Controlled Active Magnetic Bearing via State-Space Disturbance Observer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 2753–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Sun, S.; Wei, L.; Zhang, B.; Du, H.; Li, W. Vibration reduction of seat suspension using observer based terminal sliding mode control with acceleration data fusion. Mechatronics 2017, 44, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Nayfeh, S. Low order continuous-time filters for approximation of the ISO 2631-1 human vibration sensitivity weightings. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 265, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, N. Semi-active variable stiffness vibration control of vehicle seat suspension using an MR elastomer isolator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 105003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delecluse, C.; Roelants, M.; Verschueren, S. Strength increase after whole-body vibration compared with resistance training. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO. Mechanical Vibration and Shock: Evaluation of Human Exposure to Whole-Body Vibration. Part 1, General Requirements; International Standard ISO 2631-1; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, D.; Du, H.; Sun, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, B. An innovative two-layer multiple-DOF seat suspension for vehicle whole body vibration control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 1787–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morioka, M.; Griffin, M.J. Magnitude-dependence of equivalent comfort contours for fore-and-aft, lateral and vertical whole-body vibration. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 298, 755–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basri, B.; Griffin, M.J. Predicting discomfort from whole-body vertical vibration when sitting with an inclined backrest. Appl. Ergon. 2013, 44, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiemessen, I.J.; Hulshof, C.T.; Frings-Dresen, M.H. An overview of strategies to reduce whole-body vibration exposure on drivers: A systematic review. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2007, 37, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, A.; Zanoni, A.; Muscarello, V.; Cocco, A.; Quaranta, G.; Masarati, P. Biodynamic Modeling Techniques for Rotorcraft Comfort Evaluation. Aerotec. Missili Spazi. 2019, 2, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torvinen, S.; Kannus, P.; Sievänen, H.; Järvinen, T.A.; Pasanen, M.; Kontulainen, S.; Järvinen, T.L.; Järvinen, M.; Oja, P.; Vuori, I. Effect of four-month vertical whole body vibration on performance and balance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abercromby, A.F.; Amonette, W.E.; Layne, C.S.; McFarlin, B.K.; Hinman, M.R.; Paloski, W.H. Vibration exposure and biodynamic responses during whole-body vibration training. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1794–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakheja, S.; Dong, R.G.; Patra, S.; Boileau, P.-É.; Marcotte, P.; Warren, C. Biodynamics of the human body under whole-body vibration: Synthesis of the reported data. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2010, 40, 710–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Qiu, Y. A Simple Mathematical Model of a Vehicle with Seat and Occupant for Studying the Effect of Vehicle Dynamic Parameters on Ride Comfort. In Proceedings of the Conference on Human Responses to Vibration, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 9–10 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield, N.J.; Griffin, M.J. Non-linearities in apparent mass and transmissibility during exposure to whole-body vertical vibration. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T.; Nakai, K.; Tamaoki, G. Multi-body dynamics modelling of seated human body under exposure to whole-body vibration. Ind. Health 2005, 43, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Lv, G.; Han, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Biomechanical response of the musculoskeletal system to whole body vibration using a seated driver model. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2015, 45, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdet, N.; Willinger, R. Coupled head-neck-torso and seat model for car seat optimization under rear-end impact. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 313, 891–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyte, J.L.; Stirling, D.; Du, H.; Ros, M. Seated whole-body vibration analysis, technologies, and modeling: A survey. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2016, 46, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayari, H.; Thomas, M.; Doré, S.; Serrus, O. Evaluation of lumbar vertebra injury risk to the seated human body when exposed to vertical vibration. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 321, 454–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siefert, A.; Pankoke, S.; Wölfel, H.-P. Virtual optimisation of car passenger seats: Simulation of static and dynamic effects on drivers’ seating comfort. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2008, 38, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, Y.Z.; Sezgin, A.; Yagiz, N. Improving the ride comfort of vehicle passenger using fuzzy sliding mode controller. J. Vib. Control 2015, 21, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanes, R. Human Sensitivity to Whole-Body Vibration in Urban Transportation Systems: A Literature Review. J. Sound Vib. 1973, 28, 785–788. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, S. Vehicle ride comfort analysis with whole-body vibration on long-span bridges subjected to crosswind. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2016, 155, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciloglu, H.; Alziadeh, M.; Mohany, A.; Kishawy, H. Assessment of the whole body vibration exposure and the dynamic seat comfort in passenger aircraft. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2015, 45, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, A.J.; Morales, A.L.; Chicharro, J.M.; Pintado, P. An adaptive pneumatic suspension system for improving ride comfort and handling. J. Vib. Control 2016, 22, 1492–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuyama, E.; Omae, A. Improvement of ride comfort by unsprung negative skyhook damper control using in-wheel motors. SAE Int. J. Altern. Powertrains 2016, 5, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, K.; Lee, H.; Yoon, J.W.; Choi, C.; Hwang, S.H. Effectiveness evaluation of hydro-pneumatic and semi-active cab suspension for the improvement of ride comfort of agricultural tractors. J. Terramech. 2017, 69, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Rastogi, V.; Pathak, P. Simulation for whole-body vibration to assess ride comfort of a low-medium speed railway vehicle. Simulation 2017, 93, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentoni, V.; Massacci, G. Occupational exposure to whole-body vibration: Unfavourable effects due to the use of old earth-moving machinery in mine reclamation. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2013, 27, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blood, R.P.; Ploger, J.D.; Johnson, P.W. Whole body vibration exposures in forklift operators: Comparison of a mechanical and air suspension seat. Ergonomics 2010, 53, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Sun, S.; Du, H.; Li, W.; Li, W. Control of a multiple-DOF vehicle seat suspension with roll and vertical vibration. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 435, 170–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, G.; Ballo, I. Active vibration control system for the driver’s seat for off-road vehicles. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1991, 20, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, J.F.; Tang, T.Q.; Ghabra, R. Seat Folding Apparatus with a Passive Radio Frequency Link and Foreign Object Detection System. U.S. Patent US7808394B2, 5 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Baz, A.M. Method and Device for Active Constrained Layer Damping for Vibration and Sound Control. U.S. Patent US5485053A, 16 January 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Maciejewski, I.; Kiczkowiak, T.; Krzyzynski, T. Optimisation of Pneumatic Circuit Aimed at Improving the Vibro-Isolation Properties of Seat Suspension; WILEY-VCH Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2009; Volume 9, pp. 639–640. [Google Scholar]
- Valero, B.; Amirouche, F.; Mayton, A.; Jobes, C. Comparison of Passive Seat Suspension with Different Configuration of Seat Pads and Active Seat Suspension; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Krzyzynski, T.; Meyer, L. Control system synthesis of seat suspensions used for protection of working machine operators. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2014, 52, 1355–1371. [Google Scholar]
- Maciejewski, I. Control. system design of active seat suspensions. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 1291–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMickell, M.B.; Kreider, T.; Hansen, E.; Davis, T.; Gonzalez, M. Optical payload isolation using the miniature vibration isolation system (MVIS-II). In Proceedings of the Industrial and Commercial Applications of Smart Structures Technologies, San Diego, CA, USA, 11 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Metered, H.; Šika, Z. Vibration control of a semi-active seat suspension system using magnetorheological damper. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/ASME 10th International Conference on Mechatronic and Embedded Systems and Applications (MESA), Senigallia, Italy, 10–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Turnip, A.; Park, S.; Hong, K.S. Sensitivity control of a MR-damper semi-active suspension. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2010, 11, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.Z.; Yap, F.F.; Chen, G.; Li, W.; Yeo, S.H. MR damper and its application for semi-active control of vehicle suspension system. Mechatronics 2002, 12, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hege, P.; Genoux, G. The SARIB Vibration Absorber. In Proceedings of the ninth European Rotorcraft and powered lift aircraft forum, Stresa, Italy, 13–15 September 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Graf, P.; Shoureshi, R. Modeling and implementation of semi-active hydraulic engine mounts. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 1988, 110, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourzeynali, S.; Estaki, S. Optimization of the TMD parameters to suppress the vertical vibrations of suspension bridges subjected to earthquake excitations. Int. J. Eng. 2009, 22, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, D.Q.; Ahn, K.K. MR Fluid Damper and Its Application to Force Sensorless Damping Control System; INTECH Open Access Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gavin, H.P.; Alhan, C. Guidelines for low-transmissibility semi-active vibration isolation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2005, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Jing, X.; Cheng, L. Magnetorheological fluid dampers: A review on structure design and analysis. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2012, 23, 839–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-B.; Han, Y.-M. MR seat suspension for vibration control of a commercial vehicle. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2003, 31, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-T.; Wereley, N.M. Self-powered magnetorheological dampers. J. Vib. Acoust. 2009, 131, 044501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.-X.; Hu, W.; Wereley, N.M. Magnetorheological damper utilizing an inner bypass for ground vehicle suspensions. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 3422–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Christenson, R. Hyperbolic Tangent Model for 200 kN Large-Scale Magneto-Rheological Fluid (MR) Damper; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tse, K.-T.; Kwok, K.C.; Tamura, Y. Performance and cost evaluation of a smart tuned mass damper for suppressing wind-induced lateral-torsional motion of tall structures. J. Struct. Eng. 2012, 138, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.Y. Parametric design for aeroengine parts based on assembly constraint relations. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2003, 22, 710. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, J.D.; Jolly, M.R. MR fluid, foam and elastomer devices. Mechatronics 2000, 10, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, T.; Chang, C.C. Shear-Mode Rotary Magnetorheological Damper for Small-Scale Structural Control Experiments. J. Struct. Eng. 2004, 130, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaduddin, F.; Mazlan, S.A.; Zamzuri, H. A design and modelling review of rotary magnetorheological damper. Mater. Des. 2013, 51, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Ning, D.H.; Yang, J.; Du, H.; Zhang, S.W.; Li, W.H. A seat suspension with a rotary magnetorheological damper for heavy duty vehicles. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 105032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gong, X.L.; Li, W.H. Microstructures and viscoelastic properties of anisotropic magnetorheological elastomers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Li, W.H. Adaptive tuned dynamic vibration absorbers working with MR elastomers. Smart Struct. Syst. 2009, 5, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.-M.; Miao, Y.; Liao, C.R.; Chen, W.M. A new variable stiffness absorber based on magneto-rheological elastomer. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2009, 19, s611–s615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Gong, X.; Liao, G.; Chen, X. An active-damping-compensated magnetorheological elastomer adaptive tuned vibration absorber. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2010, 21, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Sung, S.H.; Jang, D.D.; Jung, H.J.; Koo, J.H. Numerical investigation of smart base isolation system employing MR elastomer. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 149, 012099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, T.F. Viscoelastic properties of MR elastomers under harmonic loading. Rheol. Acta 2010, 49, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collette, C.; Kroll, G.; Saive, G.; Guillemier, V.; Avraam, M. On magnetorheologic elastomers for vibration isolation, damping, and stress reduction in mass-varying structures. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2010, 21, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opie, S.; Yim, W. Design and control of a real-time variable stiffness vibration isolator. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Singapore, 14–17 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, D.; Sun, S.; Du, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, N. Vibration control of an energy regenerative seat suspension with variable external resistance. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 106, 94–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De, C.F.V.; Fragassa, C.; Pavlović, A.; Martignani, M. Analysis of the suspension design evolution in solar cars. FME Trans. 2017, 45, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasbullah, F.; Faris, W.F. A comparative analysis of LQR and fuzzy logic controller for active suspension using half car model. In Proceedings of the 2010 11th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics & Vision (ICARCV), Singapore, 7–10 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sam, Y.M.; Osman, J.H.S.B. Modeling and control of the active suspension system using proportional integral sliding mode approach. Asian J. Control 2005, 7, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, P.W.; Haiping, D.; Li, W.; Alici, G. Implementation of adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system controller on magneto rheological damper suspension. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Wollongong, Australia, 9–12 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi, P.; Adarsh, S.; Ramachandran, K.I. Performance Analysis of Half Car Suspension Model with 4 DOF using PID, LQR, FUZZY and ANFIS Controllers. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 115, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyan, F.; Hong, Y.F.; Tu, S.H.; Jeng, W.S. Generation of random road profiles. J. Adv. Eng. 2009, 4, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, N. Integrated seat and suspension control for a quarter car with driver model. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 3893–3908. [Google Scholar]
- Ekberg, C.; Hansson, E. Design and Simulation of Active and Semi-Active Cab Suspensions with Focus to Improve Ride Comfort of a Heavy Truck; Department of Applied Mechanics, Chalmers University of Technology: Gothenburg, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, A.; van Wynsberghe, R. Development of a 4-Point-Air Cab Suspension System for Conventional Heavy Trucks; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, D.; Sun, S.; Zhang, J.; Du, H.; Li, W.; Wang, X. An active seat suspension design for vibration control of heavy-duty vehicles. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2016, 35, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, M.; Rahman, R.A.; Mailah, M.; Gohari, M. Roll movement control of a spray boom structure using active force control with artificial neural network strategy. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2013, 32, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bi, F.; Du, H. Reduction of low frequency vibration of truck driver and seating system through system parameter identification, sensitivity analysis and active control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 105, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






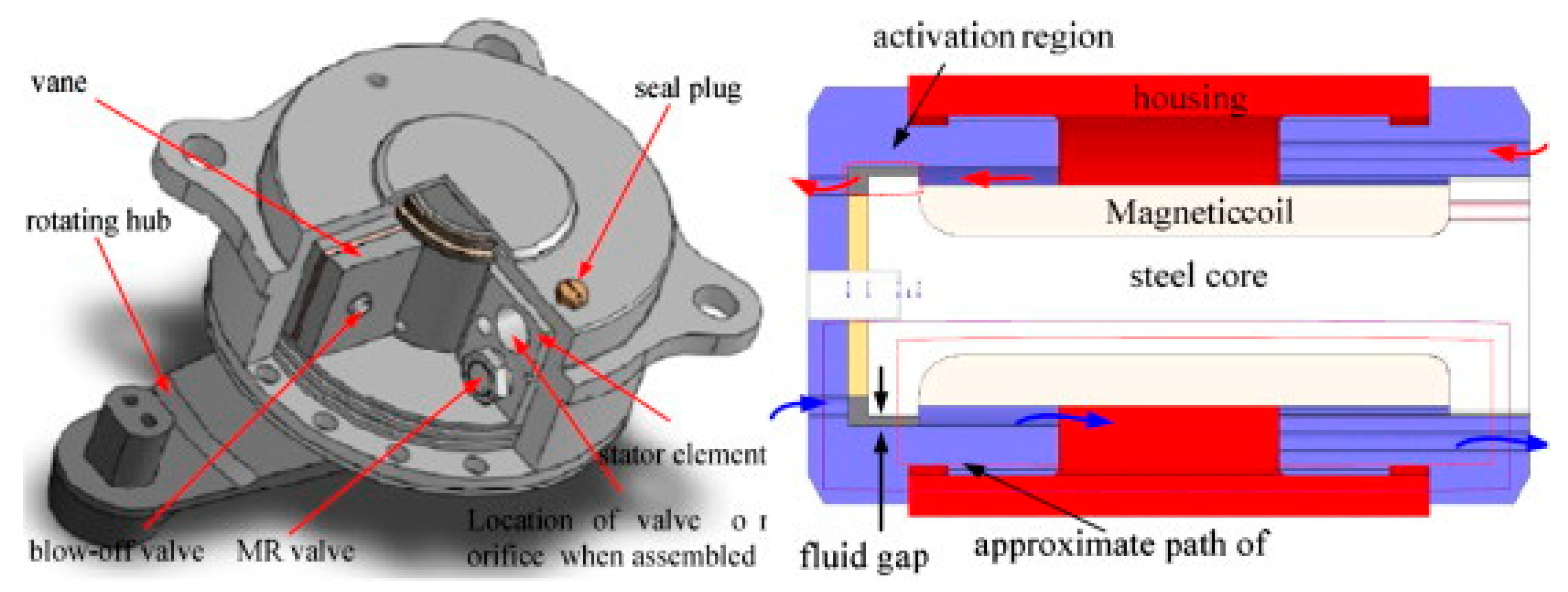
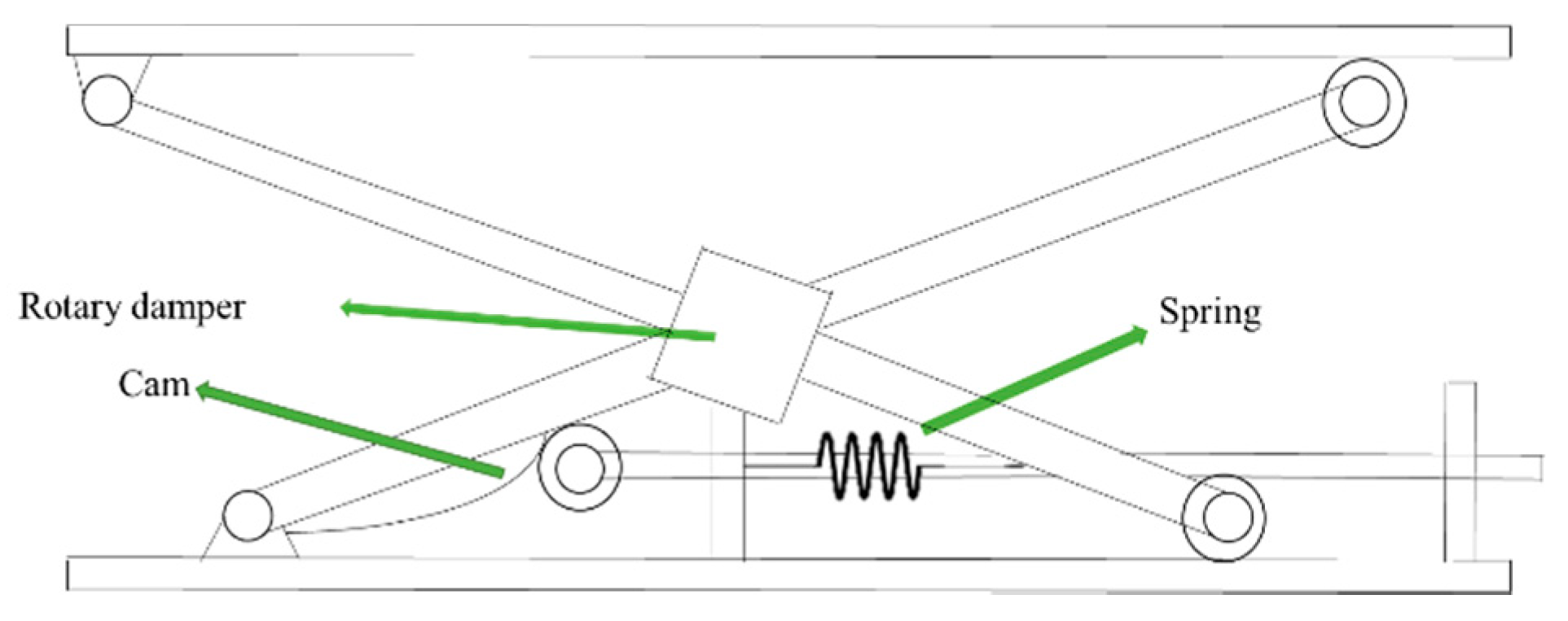





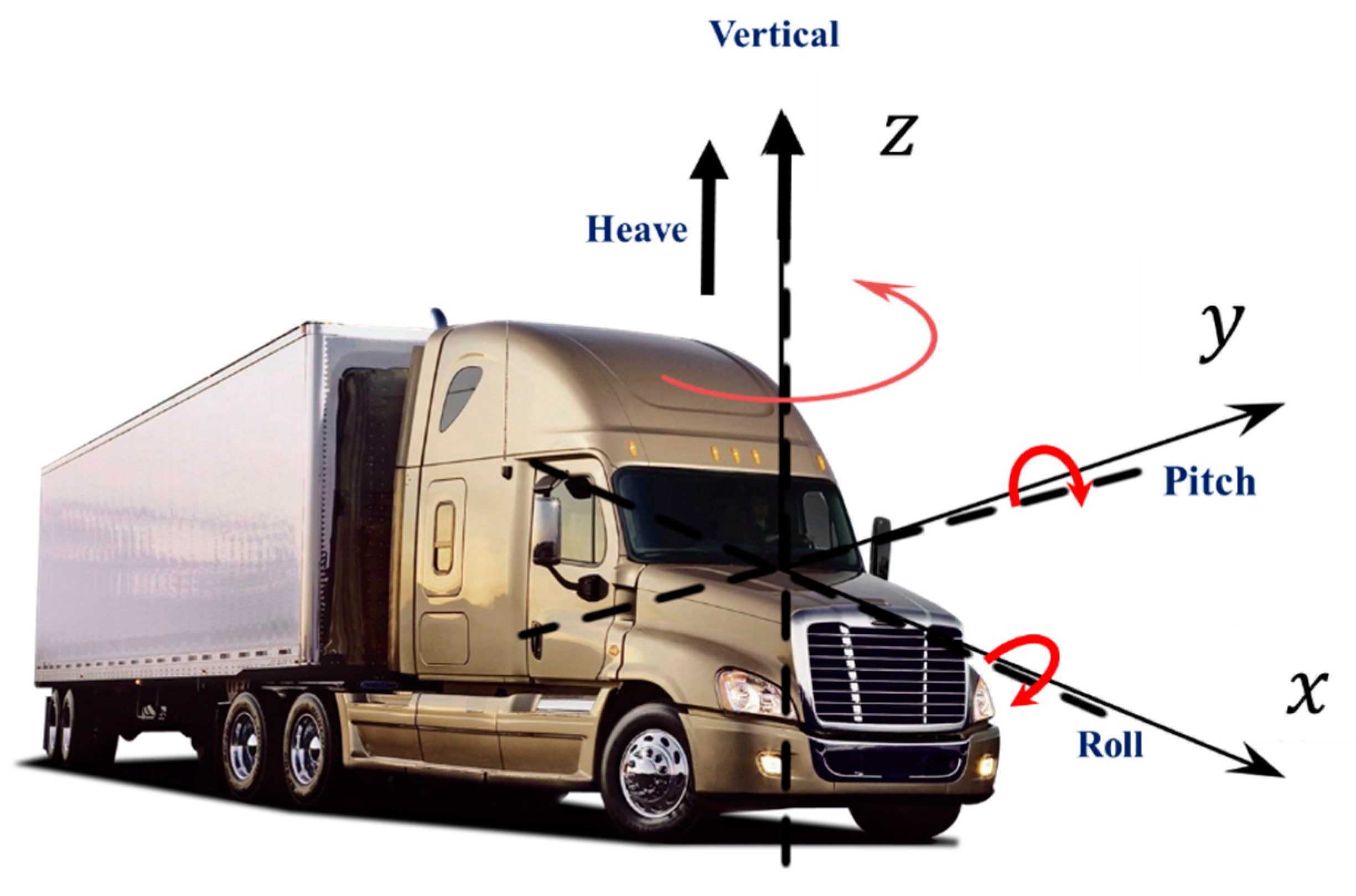






| Active | Semi-Active | Passive | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advantages |
|
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
|
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heidarian, A.; Wang, X. Review on Seat Suspension System Technology Development. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9142834
Heidarian A, Wang X. Review on Seat Suspension System Technology Development. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(14):2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9142834
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeidarian, Alireza, and Xu Wang. 2019. "Review on Seat Suspension System Technology Development" Applied Sciences 9, no. 14: 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9142834
APA StyleHeidarian, A., & Wang, X. (2019). Review on Seat Suspension System Technology Development. Applied Sciences, 9(14), 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9142834






