Toward Development of a Vocal Fold Contact Pressure Probe: Sensor Characterization and Validation Using Synthetic Vocal Fold Models
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
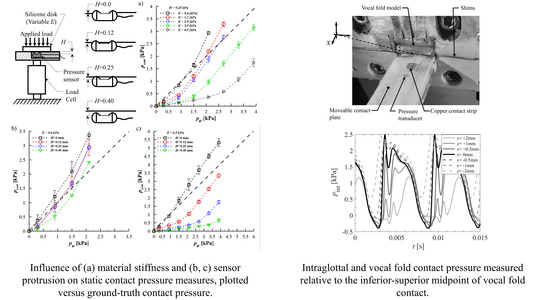
2. Influence of Sensor Intrusion on Vocal Fold Contact Pressure Accuracy
2.1. Contact Pressure Transducer Specifications
2.2. Methods
2.3. Results
2.3.1. Sensor Intrusion and Tissue Stiffness Dependency
2.3.2. Mitigating Sensor Intrusion Using a Wall-Mounted, Embedded Approach
3. Sensitivity of the Intraglottal and Vocal Fold Contact Pressures to Sensor Position
3.1. Methods
3.1.1. Synthetic Vocal Fold Model Design
3.1.2. Laryngeal Flow Facility
3.1.3. Intraglottal and Vocal Fold Contact Pressure Sensor Integration
3.1.4. Identifying the Location of Vocal Fold Contact
3.2. Results
3.2.1. Validation of Synthetic Vocal Fold Model Kinematics
3.2.2. Validation of Intraglottal and Vocal Fold Contact Pressure Measurements
3.2.3. Sensitivity of Intraglottal and Vocal Fold Contact Pressures to Sensor Position
4. Discussion and Future Work
4.1. Observations on Vocal Fold Model Development and Intraglottal and Vocal Fold Contact Pressure Measurements
4.2. Recommendations for In Vivo Assessment of Sensor Location
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AT | Adipose tissue |
| DS | Smooth-On® Dragonskin 10 |
| EF | Smooth-On® Ecoflex 0030 |
| FSO | Full scale output |
| HSV | High-speed video |
| MPC | Medial prephonatory compression |
| MPP | Medial prephonatory pressure |
| Open quotient | |
| PGO | Posterior glottal opening |
| SPL | Sound pressure level |
| Speed quotient | |
| VF | Vocal fold |
References
- Zhang, Z.; Neubauer, J.; Berry, D.A. The Influence of Subglottal Acoustics on Laboratory Models of Phonation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 120, 1558–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zañartu, M.; Mongeau, L.; Wodicka, G.R. Influence of Acoustic Loading on an Effective Single-Mass Model of the Vocal Folds. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 121, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.; Kniesburges, S.; Müller, S.; Delgado, A. Flow-Structure-Acoustic Interactions in a Human Voice Model. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erath, B.D.; Peterson, S.D.; Zañartu, M.; Wodicka, G.R.; Plesniak, M.W. A Theoretical Model of the Pressure Field Arising from Asymmetric Intraglottal Flows Applied to a Two-Mass Model of the Vocal Folds. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, R.; Erath, B.D.; Plesniak, M.W. Fluid-Dynamics of Human Phonation and Speech. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2013, 45, 436–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Södersten, M.; Lindestad, P.A. Glottal Closure and Perceived Breathiness During Phonation in Normally Speaking Subjects. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1990, 33, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titze, I.R. Principles of Voice Production; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hillman, R.E.; Holmberg, E.B.; Perkell, J.S.; Walsh, M.; Vaughan, C. Objective Assessment of Vocal Hyperfunction: An Experimental Framework and Initial Results. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1989, 32, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titze, I.R. Mechanical Stress in Phonation. J. Voice 1994, 8, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erath, B.D.; Zañartu, M.; Peterson, S.D. Modeling Viscous Dissipation During Vocal Fold Contact: The Influence of Tissue Viscosity and Thickness with Implications for Hydration. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2017, 16, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.J.; Titze, I.R. Measurement of Vocal Fold Intraglottal Pressure and Impact Stress. J. Voice 1994, 8, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, F.; Scherer, R.C. Dynamic Glottal Pressures in an Excised Hemilarynx Model. J. Voice 2000, 14, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, M.; Siegmung, T.; Mongeau, L. Determination of Superior Surface Strains and Stresses, and Vocal Fold Contact Pressure in a Synthetic Larynx Model Using Digital Image Correlation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Mongeau, L. Verification of Two Minimally Invasive Methods for the Estimation of the Contact Pressure in Human Vocal Folds During Phonation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 1618–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunter, H. A Mechanical Model of Vocal-Fold Collision with High Spatial and Temporal Resolution. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 113, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunter, H. Modeling Mechanical Stresses as a Factor in the Etiology of Benign Vocal Fold Lesions. J. Biomech. 2004, 37, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horác̆ek, J.; S̆idlof, P.; S̆vec, J.G. Numerical Simulation of Self-Oscillations of Human Vocal Folds with Hertz Model of Impact Forces. J. Fluids Struct. 2005, 20, 853–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horác̆ek, J.; Laukkanen, A.M.; S̆idlof, P.; Murphy, P.; S̆vec, J.G. Comparison of Acceleration and Impact Stress as Possible Loading Factors in Phonation: A Computer Modeling Study. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2009, 61, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, P.; Siegmund, T. A Computational Study of Systemic Hydration in Vocal Fold Collision. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 17, 1835–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, M.; Galindo, G.E.; Espinoza, V.; Zañartu, M. Vocal Fold Contact Pressure Estimation over Laryngeal High Speed Videoendoscopy Based on a Vocal Edge Tracking Method Using Kalman Filter and Hertzian Impact Model. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Voice Physiology and Biomechanics (ICVPB), Viña del Mar, Chile, 14–17 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Galindo, G.E.; Peterson, S.D.; Erath, B.D.; Castro, C.; Hillman, R.E.; Zañartu, M. Modeling the Pathophysiology of Phonotraumatic Vocal Hyperfunction with a Triangular Glottal Model of the Vocal Folds. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2017, 60, 2452–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinsasser, O. Pathogenesis of Vocal Cord Polyps. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1982, 91, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.; Titze, I.R.; Lusk, R.P. Electron Microscopy of Hyperphonated Canine Vocal Folds. J. Voice 1987, 1, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Van Deusen, M.; Jerome, W.G.; Garrett, C.G.; Sivasankar, M.P.; Novaleski, C.K.; Rousseau, B. Quantification of Acute Vocal Fold Epithelial Surface Damage with Increasing Time and Magnitude Doses of Vibration Exposure. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunter, H.; Howe, R.D.; Zeitels, S.M.; Kobler, J.B.; Hillman, R.E. Measurement of Vocal Fold Collision Forces During Phonation: Methods and Preliminary Data. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2005, 48, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Sutor, A.; Rupitsch, S.J.; Kniesburges, S.; Döllinger, M.; Lerch, R. Development of a Small Film Sensor for the Estimation of the Contact Pressure of Artificial Vocal Folds. In Proceedings of the Meetings on Acoustics, Montreal, QC, USA, 2–7 June 2013; Volume 19, p. 060307. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, M.M.; Verdolini, K.; Bierhals, W.; Mansmann, U.; Gross, M. Endolaryngeal Contact Pressures. J. Voice 1998, 12, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdolini, K.; Hess, M.M.; Titze, I.R.; Bierhals, W.; Gross, M. Investigation of Vocal Fold Impact Stress in Human Subjects. J. Voice 1999, 13, 184–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, S.L.; Mongeau, L.; Frankel, S. Aerodynamic Transfer of Energy to the Vocal Folds. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 118, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drechsel, J.S.; Thomson, S.L. Influence of Supraglottal Structures on the Glottal Jet Exiting a Two-Layer Synthetic, Self-Oscillating Vocal Fold Model. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 4434–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, B.A.; Thomson, S.L. Influence of Asymmetric Stiffness on the Structural and Aerodynamic Response of Synthetic Vocal Fold Models. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 2219–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.R.; Thomson, S.L. Synthetic, Multi-Layer, Self-Oscillating Vocal Fold Model Fabrication. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 58, 3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.R.; Thomson, S.L. Vibratory Responses of Synthetic, Self-Oscillating Vocal Fold Models. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 3428–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Zhang, Z. Influence of Embedded Fibers and an Epithelium Layer on the Glottal Closure Pattern in a Physical Vocal Fold Model. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2014, 57, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chhetri, D.K.; Zhang, Z.; Neubauer, J. Measurement of Young’s Modulus of Vocal Folds by Indentation. J. Voice 2011, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipour, F.; Vigmostad, S. Measurement of Vocal Folds Elastic Properties for Continuum Modeling. J. Voice 2012, 26, 816.e21–816.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Šidlof, P.; Švec, J.G.; Horáček, J.; Veselỳ, J.; Klepáček, I.; Havlík, R. Geometry of Human Vocal Folds and Glottal Channel for Mathematical and Biomechanical Modeling of Voice Production. J. Biomech. 2008, 41, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, M.; Sato, K. Histological Color Atlas of the Human Larynx; Singular Publishing Group: East Brunswick, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 36–57. [Google Scholar]
- Comley, K.; Fleck, N.A. The Compressive Response of Porcine Adipose Tissue from Low to High Strain. J. Biomech. Eng. 2012, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.L.; Achuthan, A.; Erath, B.D. Modal Response of a Computational Vocal Fold Model with a Substrate Layer of Adipose Tissue. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 137, EL158–EL164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, Y.B.; Titze, I.R.; Alipour-Haghighi, F. Stress-strain response of the human vocal ligament. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1995, 104, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dion, G.R.; Coelho, P.G.; Teng, S.; Janal, M.; Amin, M.R.; Branski, R.C. Dynamic Nanomechanical Analysis of the Vocal Fold Structure in Excised Larynges. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, E225–E230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syndergaard, K.L.; Dushku, S.; Thomson, S.L. Electrically Conductive Synthetic Vocal Fold Replicas for Voice Production Research. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 142, EL63–EL68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timcke, R.; von Leden, H.; Moore, P. Laryngeal Vibrations: Measurements of the Glottic Wave. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1958, 68, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, R.C. Physiology of Phonation: A Review of Basic Mechanics. In Phonosurgery: Assesment and Surgical Management of Voice Disorders; Ford, C.N., Bless, D.M., Eds.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 77–93. [Google Scholar]
- Lohscheller, J.; Švec, J.; Döllinger, M. Vocal Fold Vibration Amplitude, Open Quotient, Speed Quotient and Their Variability Along Glottal Length: Kymographic Data from Normal Subjects. Log. Phon. Vocol. 2013, 38, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kania, R.E.; Hans, S.; Hartl, D.M.; Clement, P.; Crevier-Buchman, L.; Brasnu, D.F. Variability of Electroglottographic Glottal Closed Quotients: Necessity of Standardization to Obtain Normative Values. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.R.; Thomson, S.L.; Smith, M.E. A Synthetic, Self-Oscillating Vocal Fold Model Platform for Studying Augmentation Injection. J. Voice 2014, 28, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dromey, C.; Stathopoulos, E.T.; Sapienza, C.M. Glottal Airflow and Electroglottographic Measures of Vocal Function at Multiple Intensities. J. Voice 1992, 6, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döllinger, M.; Berry, D.A. Visualization and Quantification of the Medial Surface Dynamics of an Excised Human Vocal Fold During Phonation. J. Voice. 2006, 20, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titze, I.R. Nonlinear Source-Filter Coupling in Phonation: Theory. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 2733–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.M.; Thomson, S.L.; Dromey, C.; Smith, S. Frequency Response of Synthetic Vocal Fold Models with Linear and Nonlinear Material Properties. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2012, 55, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.J. Interntal Deformation Measurements and Optimization of Synthetic Vocal Fold Models. Master’s Thesis, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, D.D.; Kobler, J.B.; Zeitels, S.M.; Hillman, R.E. In Vivo Probe for Tracking Intraglottal Pressure, Vocal Fold Collision, and Subglottal Pressure During Phonation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Voice Physiology and Biomechanics, East Lansing, MI, USA, 1–3 August 2018. [Google Scholar]















| Layer | Physiological Range () | Vocal Fold Model [Std. Dev.] () | Silicone Ratio (Type of Silicone) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adipose tissue | [39] | ||
| Body | [35,41,42] | ||
| Cover | [35,36] | ||
| Epithelium |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Motie-Shirazi, M.; Zañartu, M.; Peterson, S.D.; Mehta, D.D.; Kobler, J.B.; Hillman, R.E.; Erath, B.D. Toward Development of a Vocal Fold Contact Pressure Probe: Sensor Characterization and Validation Using Synthetic Vocal Fold Models. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153002
Motie-Shirazi M, Zañartu M, Peterson SD, Mehta DD, Kobler JB, Hillman RE, Erath BD. Toward Development of a Vocal Fold Contact Pressure Probe: Sensor Characterization and Validation Using Synthetic Vocal Fold Models. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(15):3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153002
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotie-Shirazi, Mohsen, Matías Zañartu, Sean D. Peterson, Daryush D. Mehta, James B. Kobler, Robert E. Hillman, and Byron D. Erath. 2019. "Toward Development of a Vocal Fold Contact Pressure Probe: Sensor Characterization and Validation Using Synthetic Vocal Fold Models" Applied Sciences 9, no. 15: 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153002
APA StyleMotie-Shirazi, M., Zañartu, M., Peterson, S. D., Mehta, D. D., Kobler, J. B., Hillman, R. E., & Erath, B. D. (2019). Toward Development of a Vocal Fold Contact Pressure Probe: Sensor Characterization and Validation Using Synthetic Vocal Fold Models. Applied Sciences, 9(15), 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153002