Pneumatic Soft Actuator with Anisotropic Soft and Rigid Restraints for Pure in-Plane Bending Motion
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design, Material, and Fabrication
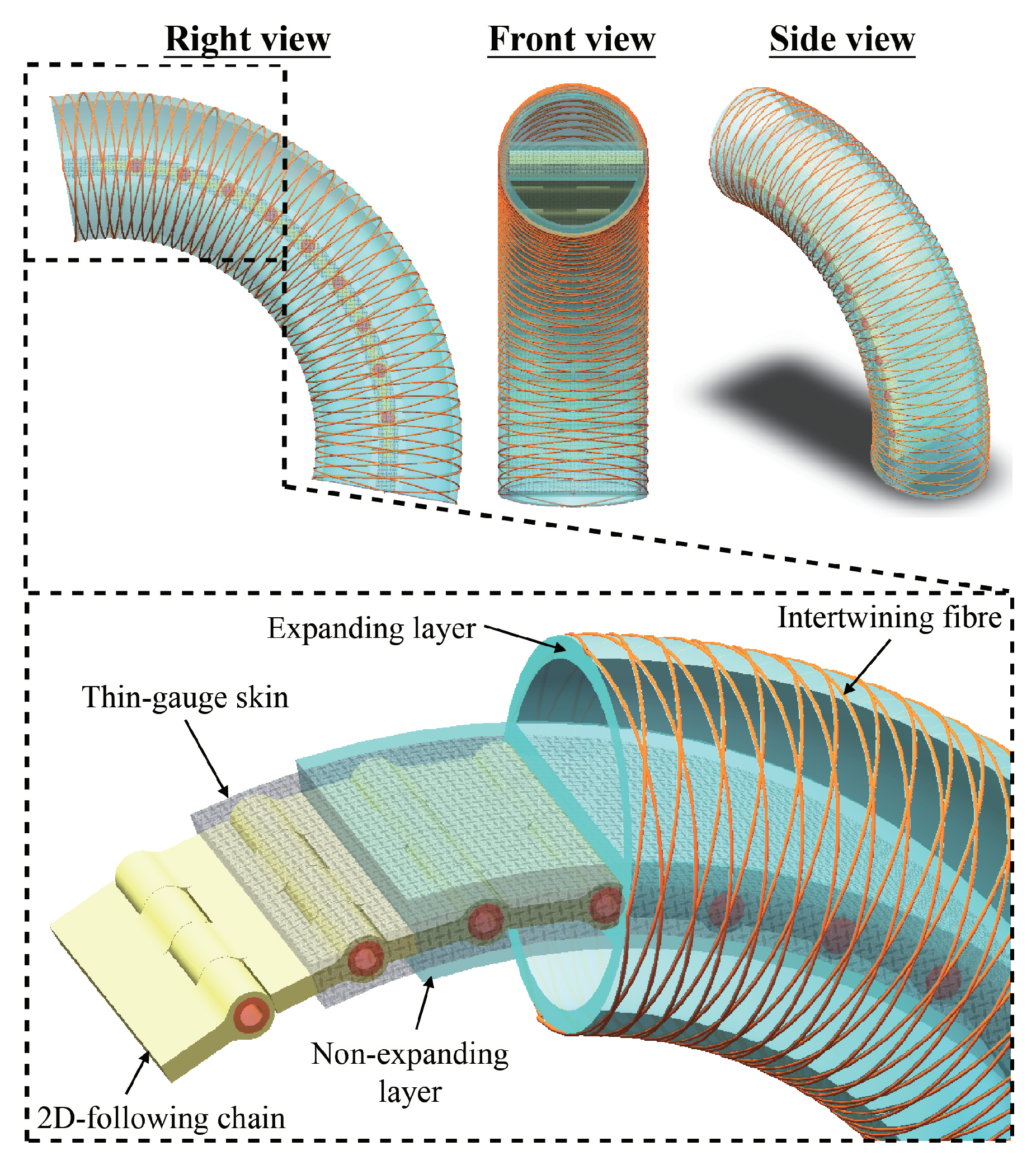
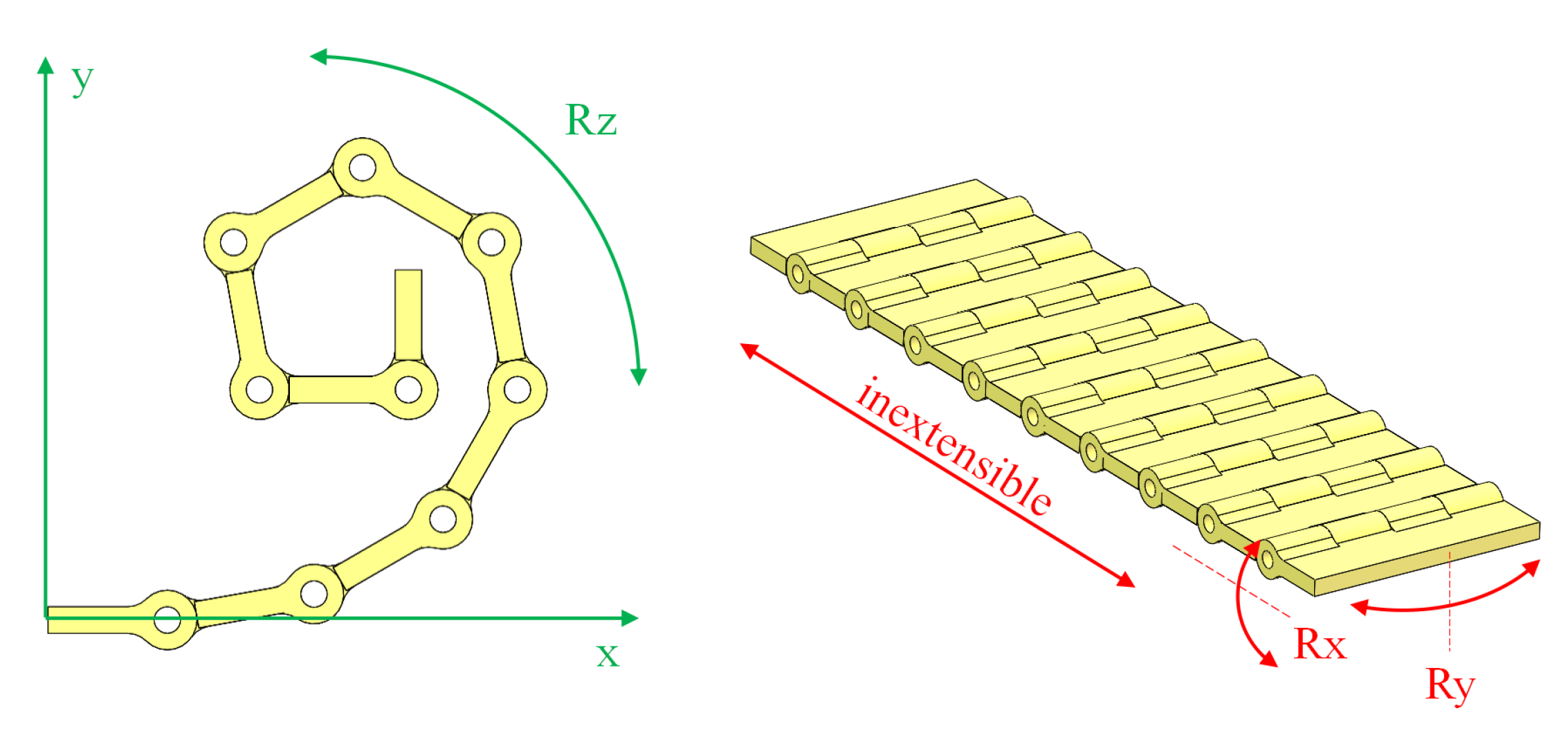
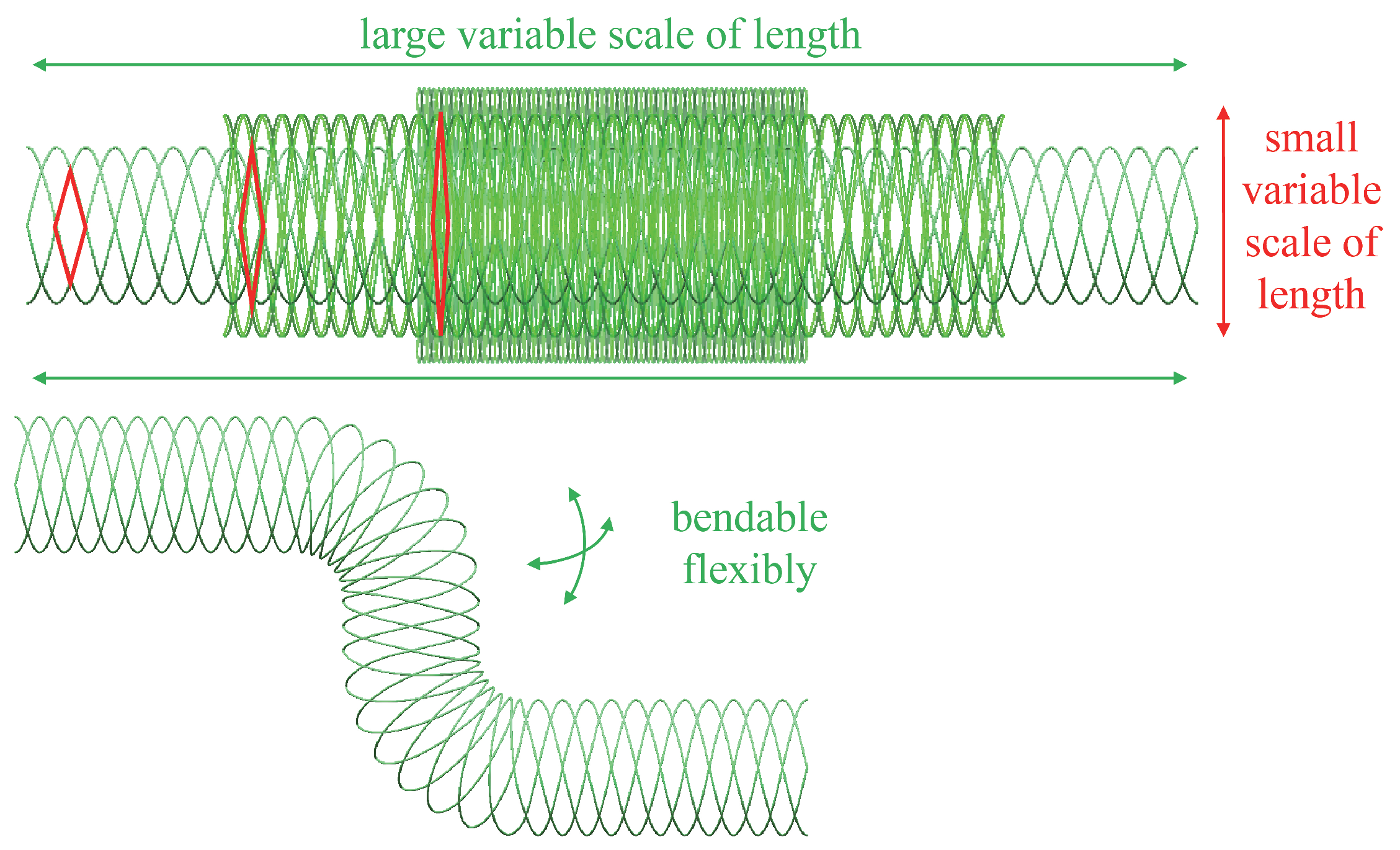
2.1. Structural Design and Analysis
2.2. Material
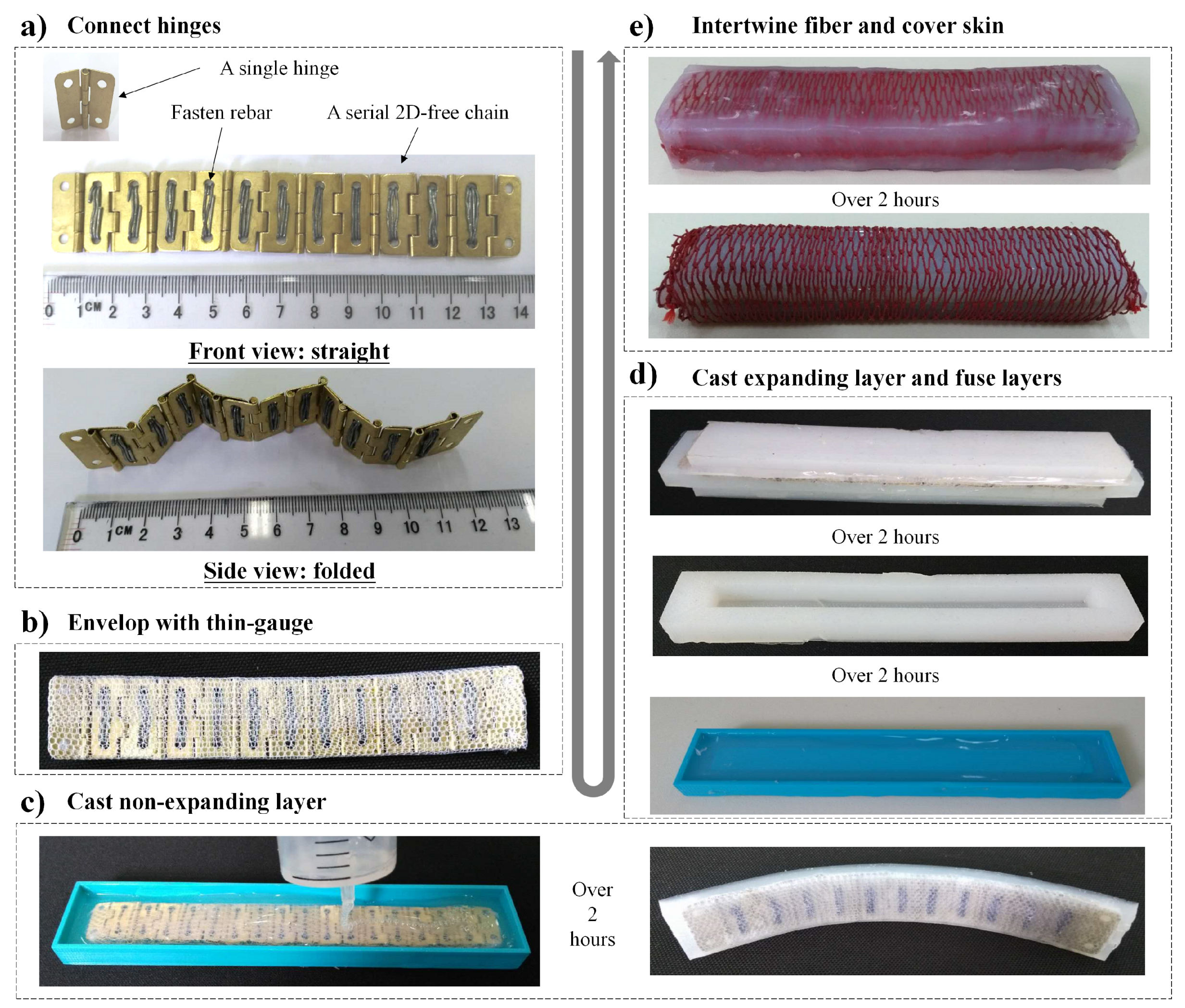
2.3. Fabrication Process
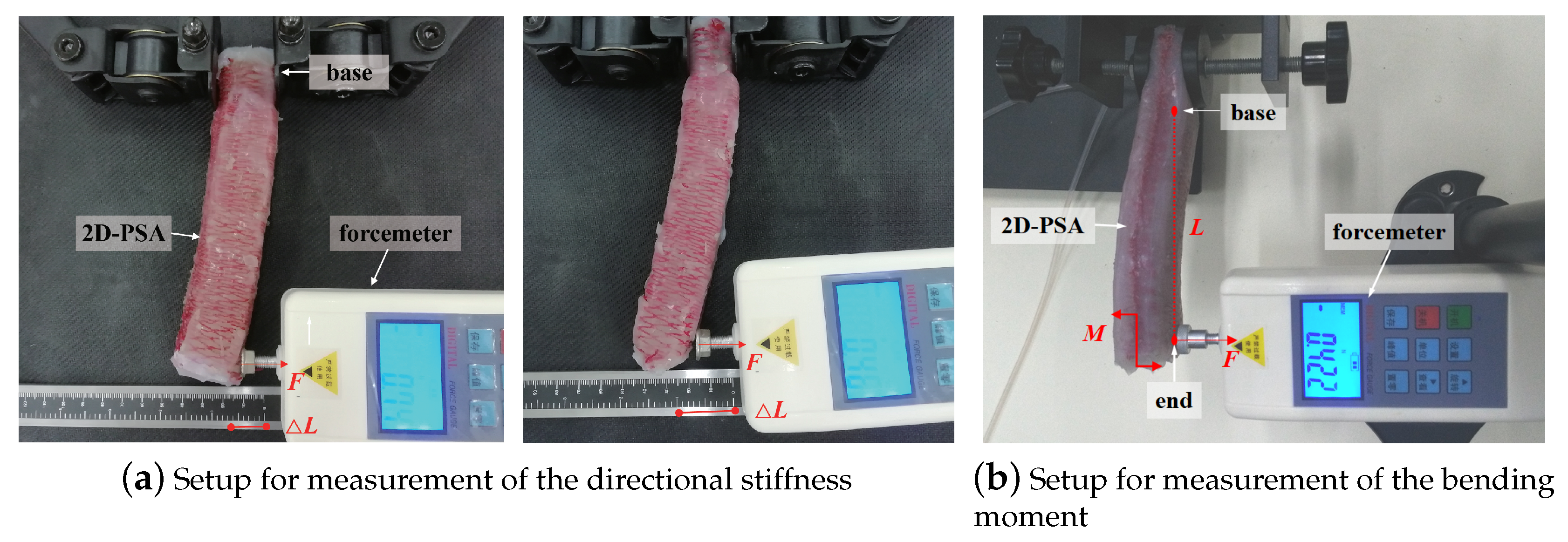
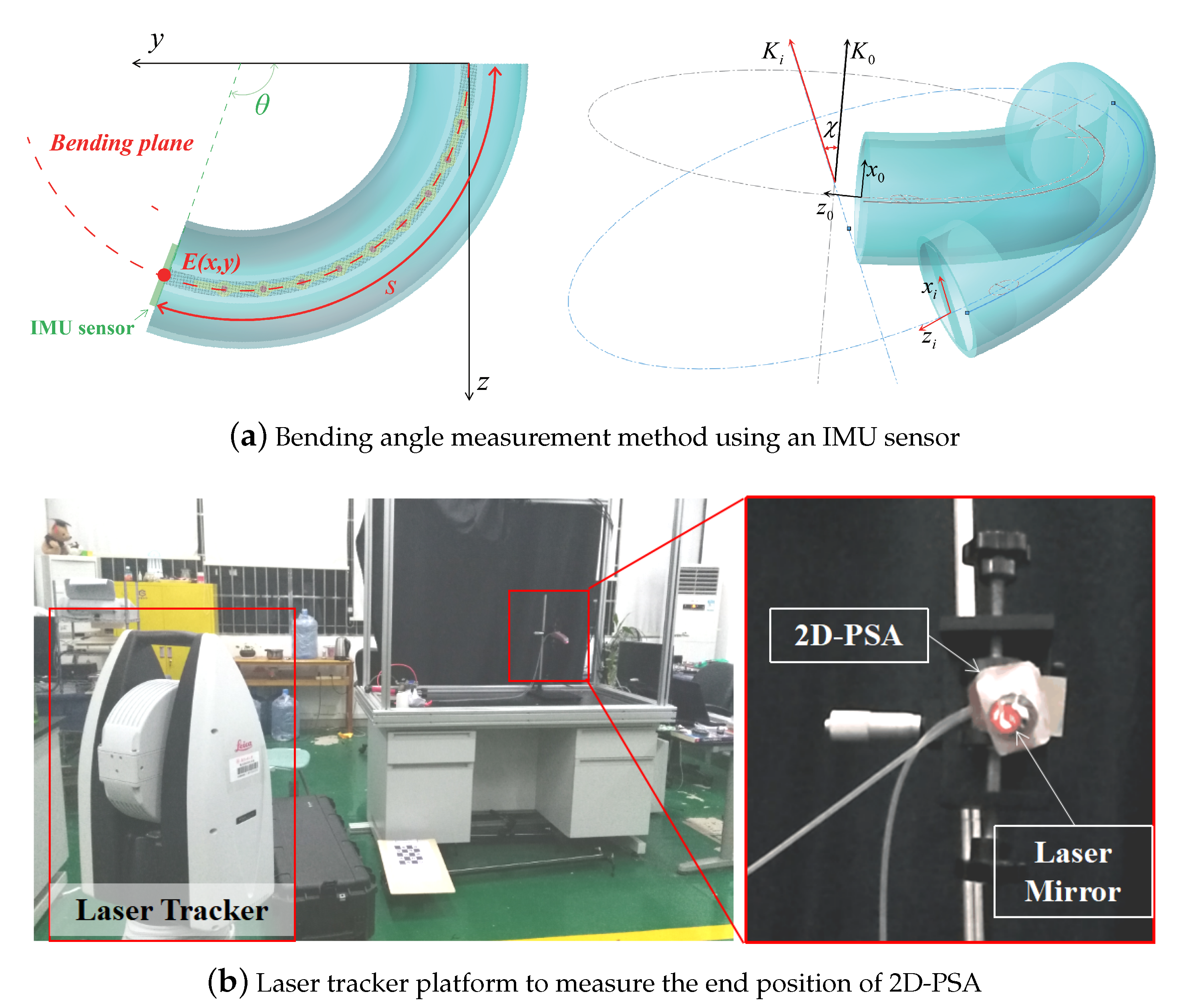
3. Experimental Setup and Test
4. Results and Discussion
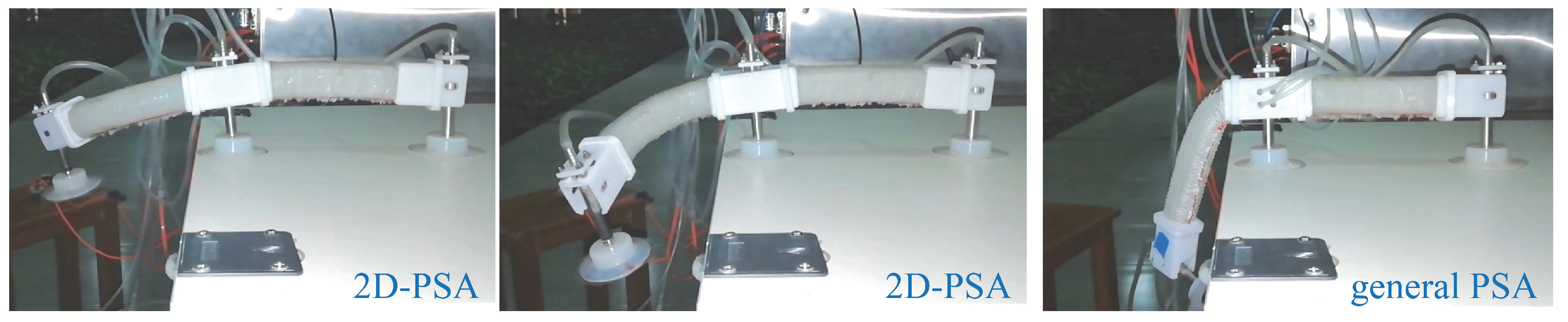
4.1. Comparative In-Plane and Out-Of-Plane Performance
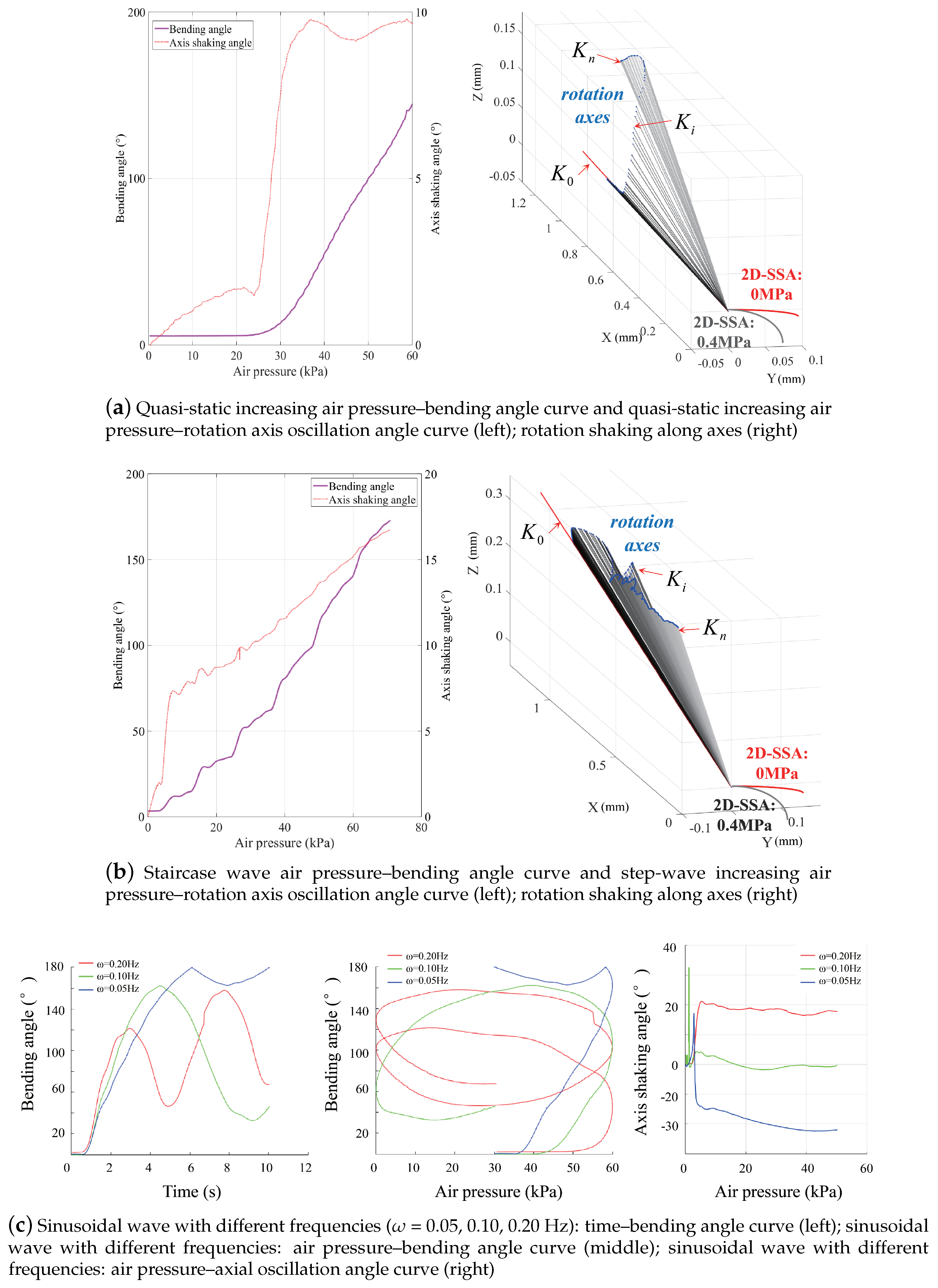
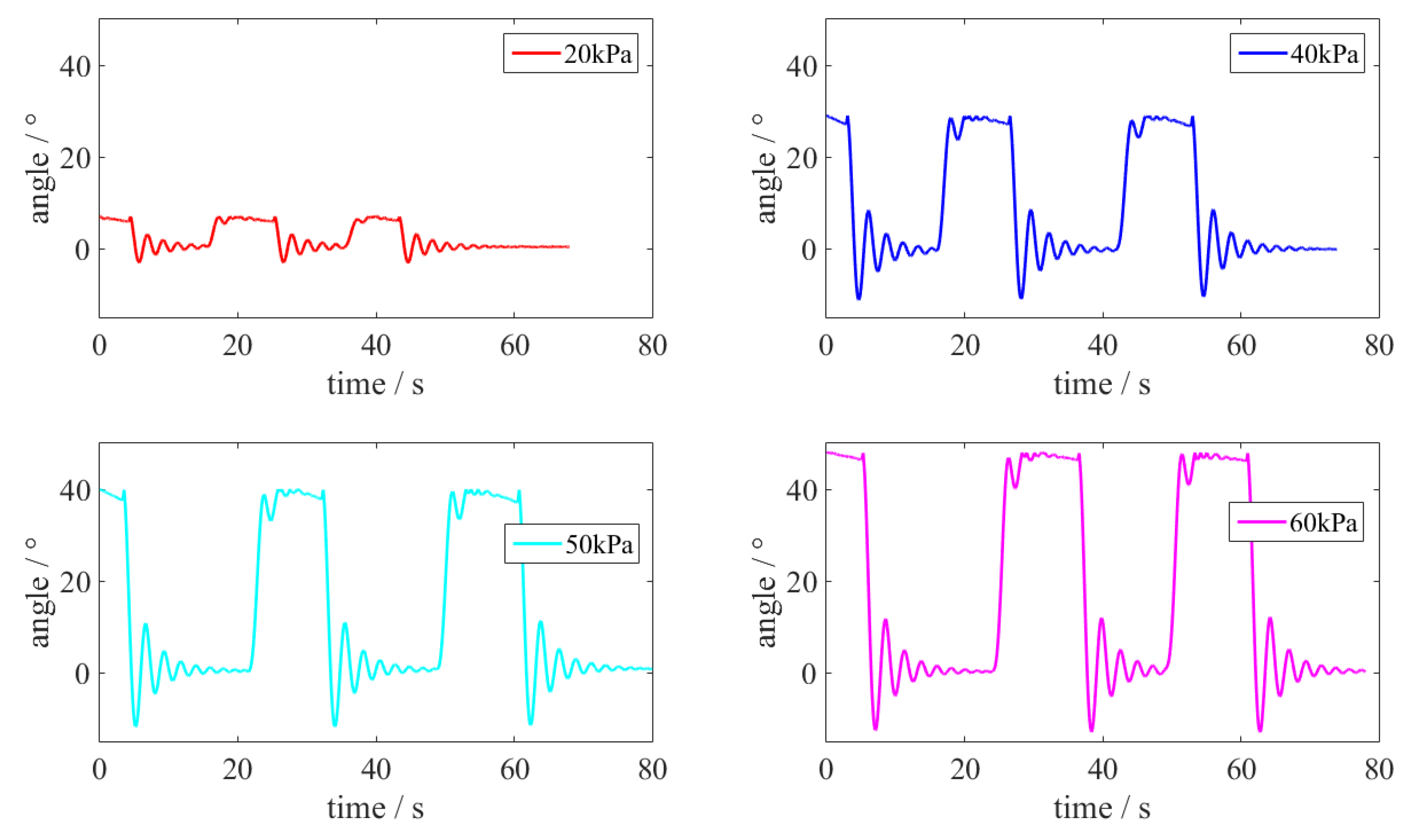
4.2. Pure Bending Motion
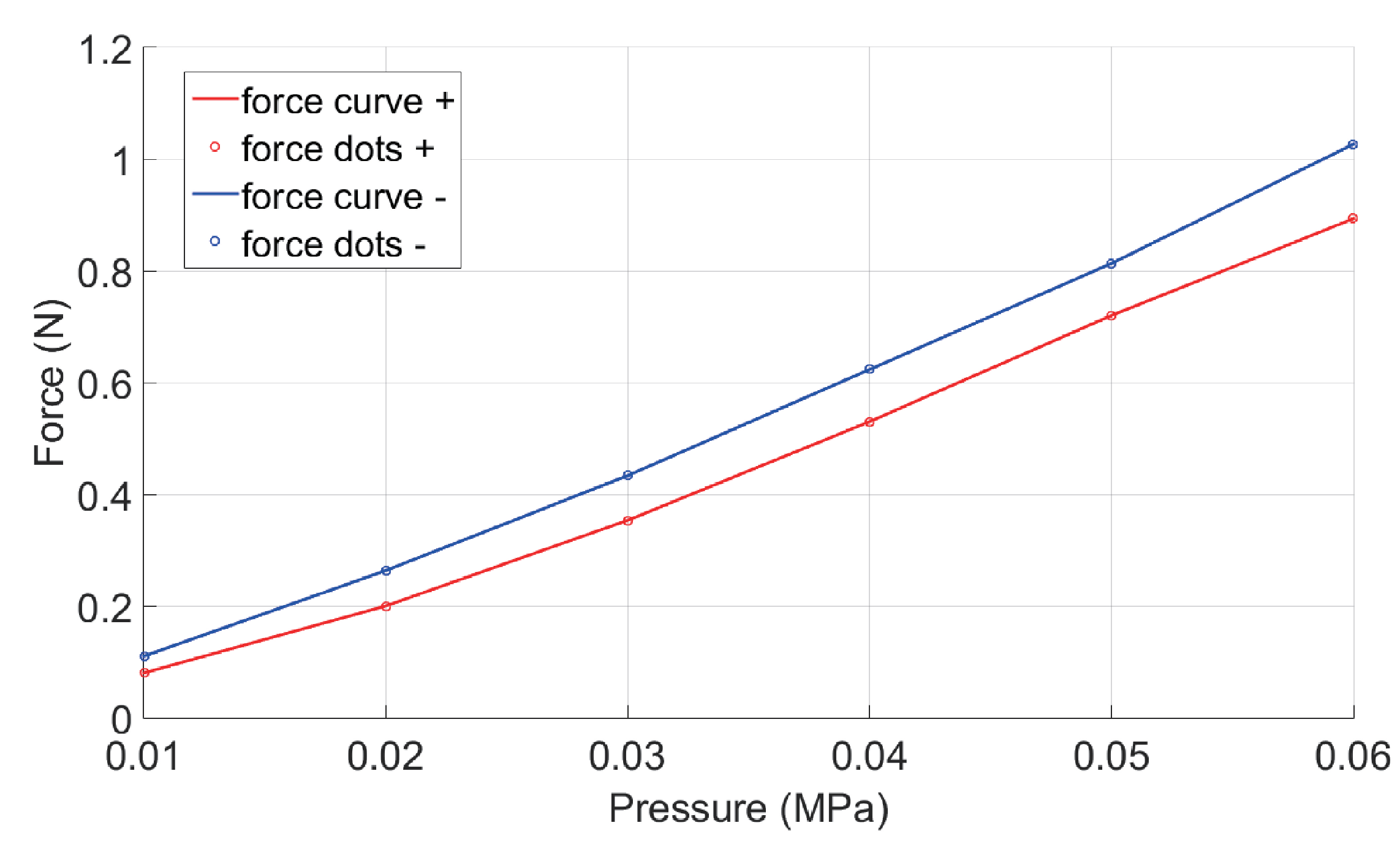
4.3. Winding Force
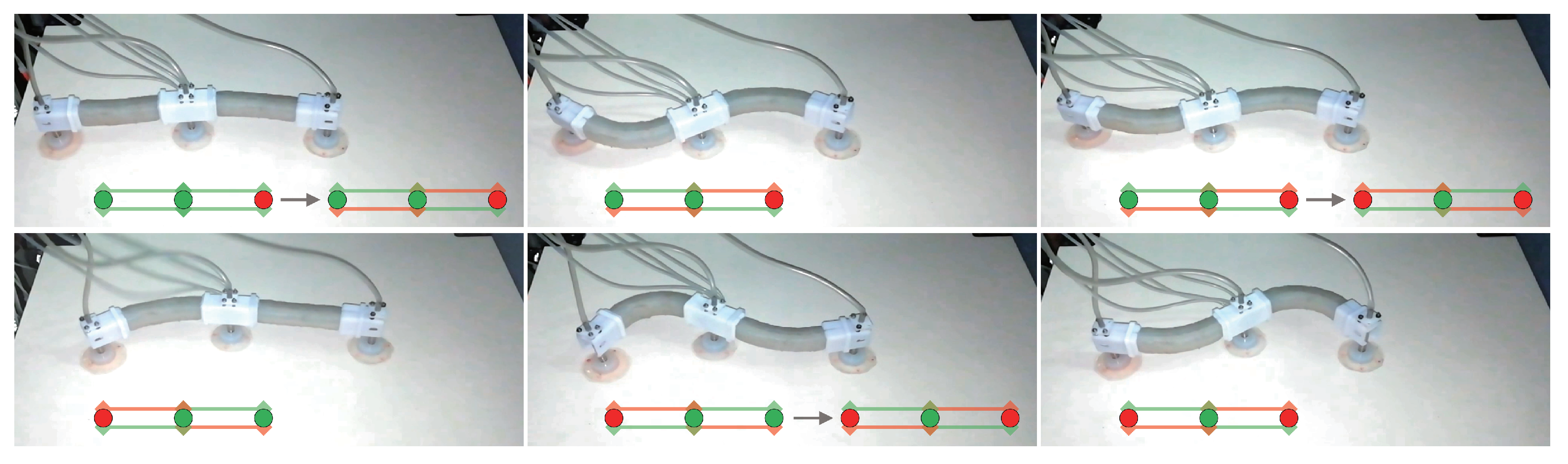
5. Application
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PSA | Pneumatic Soft Actuator |
| 2D-PSA | 2D (or in-plane) Pneumatic Soft Actuator |
References
- Carmel, M. A perspective-Current trends and prospects for the future Soft Robotics. Soft Robot. 2013, 1, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ilievski, F.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Shepherd, R.F.; Chen, X.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft Robotics for Chemists. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 123, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, R.F.; Ilievski, F.; Choi, W.; Morin, S.A.; Stokes, A.A.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Chen, X.; Wang, M.H.; Whitesides, G.M. From the Cover: Multigait soft robot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20400–20403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correll, N.; Önal, Ç.D.; Liang, H.; Schoenfeld, E.; Rus, D. Soft Autonomous Materials Using Active Elasticity and Embedded Distributed Computation. In Experimental Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 79, pp. 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Polygerinos, P.; Wang, Z.; Overvelde, J.T.B.; Galloway, K.C.; Wood, R.J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J. Modeling of Soft Fiber-Reinforced Bending Actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, R.; Alici, G.; Weihua, L. An effective methodology to solve inverse kinematics of electroactive polymer actuators modelled as active and soft robotic structures. Mech. Mach. Theory 2013, 67, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaneto, K. Research Trends of Soft Actuators based on Electroactive Polymers and Conducting Polymers. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 704, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, R.; Alici, G.; Weihua, L. Electroactive polymers as soft robotic actuators: Electromechanical modeling and identification. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Wollongong, Australia, 9–12 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.; Erbao, D.; Min, X.; Liu, C.; Alici, G.; Jie, Y. Soft and smart modular structures actuated by shape memory alloy (SMA) wires as tentacles of soft robots. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 085026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, M.; Li, M.; Xie, R.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y. A spatial soft module actuated by SMA coil. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Takamatsu, Japan, 6–9 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Godaba, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J. A Soft Jellyfish Robot Driven by a Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2016, 1, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Su, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y. PISRob: A Pneumatic Soft Robot for Climbing Like an Inchworm. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; He, B.; Yan, Z.; Shang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z. Touch Locating and Stretch Sensing Studies of Conductive Hydrogels with Applications to Soft Robots. Sensors 2018, 18, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Song, S.H.; Ahn, S.H. A turtle-like swimming robot using a smart soft composite (SSC) structure. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 014007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lee, J.Y.; Rodrigue, H.; Song, S.H.; Chu, W.S.; Ahn, S.H. Locomotion of inchworm-inspired robot made of smart soft composite (SSC). Bioinspir. Biomim. 2014, 9, 046006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onal, C.D.; Rus, D. A modular approach to soft robots. In Proceedings of the 2012 4th IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Rome, Italy, 24–27 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, R.F.; Stokes, A.A.; Freake, J.; Barber, J.; Snyder, P.W.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Cademartiri, L.; Morin, S.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Using Explosions to Power a Soft Robot. Angew. Chem. 2013, 52, 2892–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umedachi, T.; Idei, R.; Ito, K.; Ishiguro, A. A fluid-filled soft robot that exhibits spontaneous switching among versatile spatiotemporal oscillatory patterns inspired by the true slime mold. Artif. Life 2013, 19, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tondu, B.; Lopez, P. Modeling and control of McKibben artificial muscle robot actuators. IEEE Control Syst. 2000, 20, 15–38. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, K.C.; Polygerinos, P.; Walsh, C.J.; Wood, R.J. Mechanically programmable bend radius for fiber-reinforced soft actuators. In Proceedings of the 2013 16th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), Montevideo, Uruguay, 25–29 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Florijn, B.; Coulais, C.; Van Hecke, M. Programmable Mechanical Metamaterials: The Role of Geometry. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 8736–8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manti, M.; Cacucciolo, V.; Cianchetti, M. Stiffening in Soft Robotics: A Review of the State of the Art. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2016, 23, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyu, W. Soft-Material Robotics. Found. Trends Robot. 2014, 5, 191–259. [Google Scholar]
- Ranzani, T.; Gerboni, G.; Cianchetti, M.; Menciassi, A. A bioinspired soft manipulator for minimally invasive surgery. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianchetti, M. Soft robotics technologies to address shortcomings in today’s minimally invasive surgery: The stiff-flop approach. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, S.; Robertson, M.; Ijspeert, A.; Paik, J. JammJoint: A Variable Stiffness Device Based on Granular Jamming for Wearable Joint Support. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Kong, C.; Li, J.; Yang, G. Modeling of grasping force for a soft robotic gripper with variable stiffness. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 128, 254–274. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Ellenberger, B.; Sumioka, H.; Sandy, T.; Pfeifer, R. The effect of spine actuation and stiffness on a pneumatically-driven quadruped robot for cheetah-like locomotion. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Shenzhen, China, 12–14 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Groothuis, S.; Carloni, R.; Stramigioli, S. A novel variable stiffness mechanism capable of an infinite stifness range and unlimited decoupled output motion. Actuators 2014, 3, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, M.; Xie, R.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, X.; Huang, D.; Guan, Y.; Zhu, H. Pneumatic Soft Actuator with Anisotropic Soft and Rigid Restraints for Pure in-Plane Bending Motion. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9152999
Su M, Xie R, Zhang Y, Kang X, Huang D, Guan Y, Zhu H. Pneumatic Soft Actuator with Anisotropic Soft and Rigid Restraints for Pure in-Plane Bending Motion. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(15):2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9152999
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Manjia, Rongzhen Xie, Yihong Zhang, Xiaopan Kang, Dongyu Huang, Yisheng Guan, and Haifei Zhu. 2019. "Pneumatic Soft Actuator with Anisotropic Soft and Rigid Restraints for Pure in-Plane Bending Motion" Applied Sciences 9, no. 15: 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9152999
APA StyleSu, M., Xie, R., Zhang, Y., Kang, X., Huang, D., Guan, Y., & Zhu, H. (2019). Pneumatic Soft Actuator with Anisotropic Soft and Rigid Restraints for Pure in-Plane Bending Motion. Applied Sciences, 9(15), 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9152999





