Determination of pH in Powdered Concrete Samples or in Suspension
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
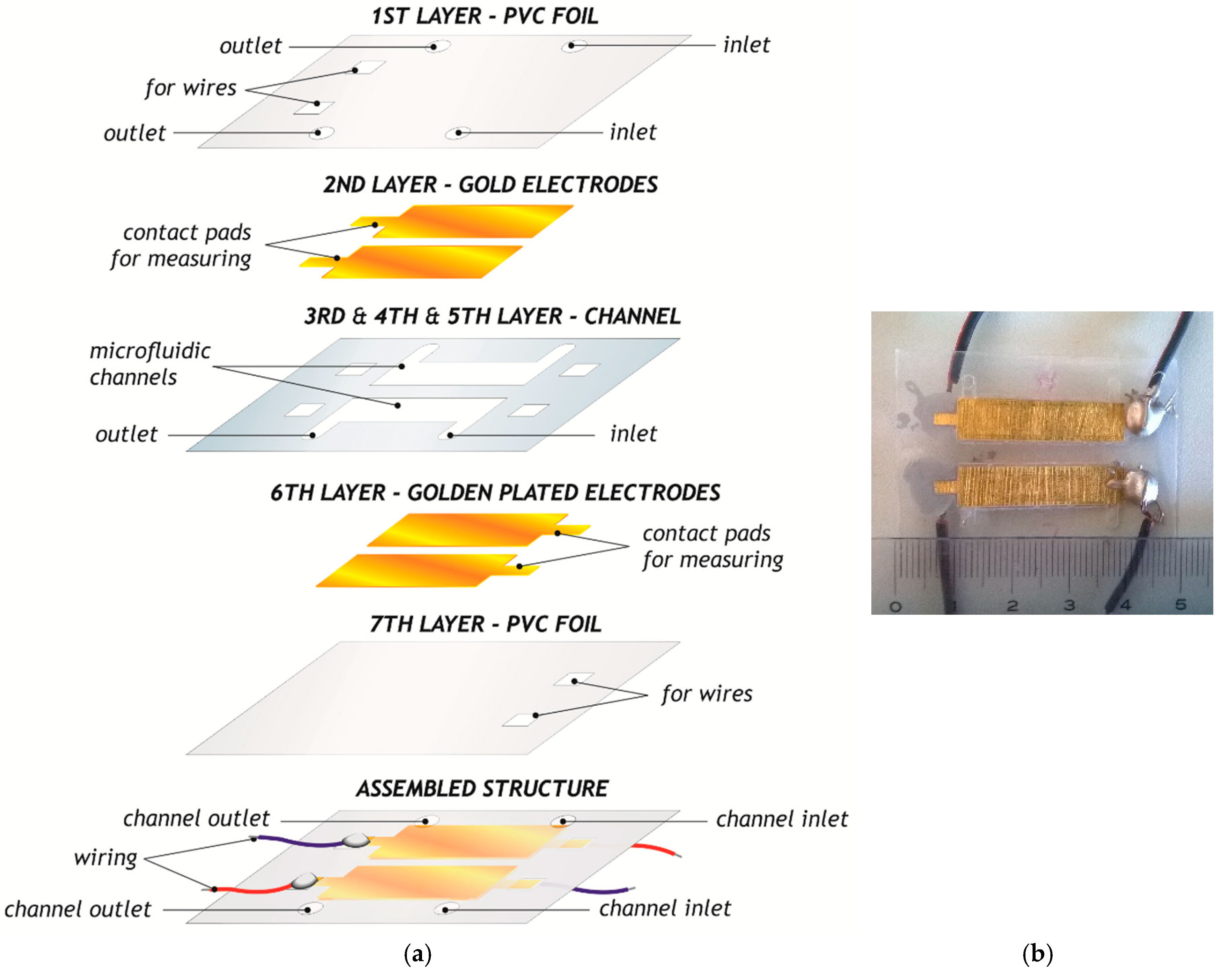
2.1. Microfluidics-Based Platform
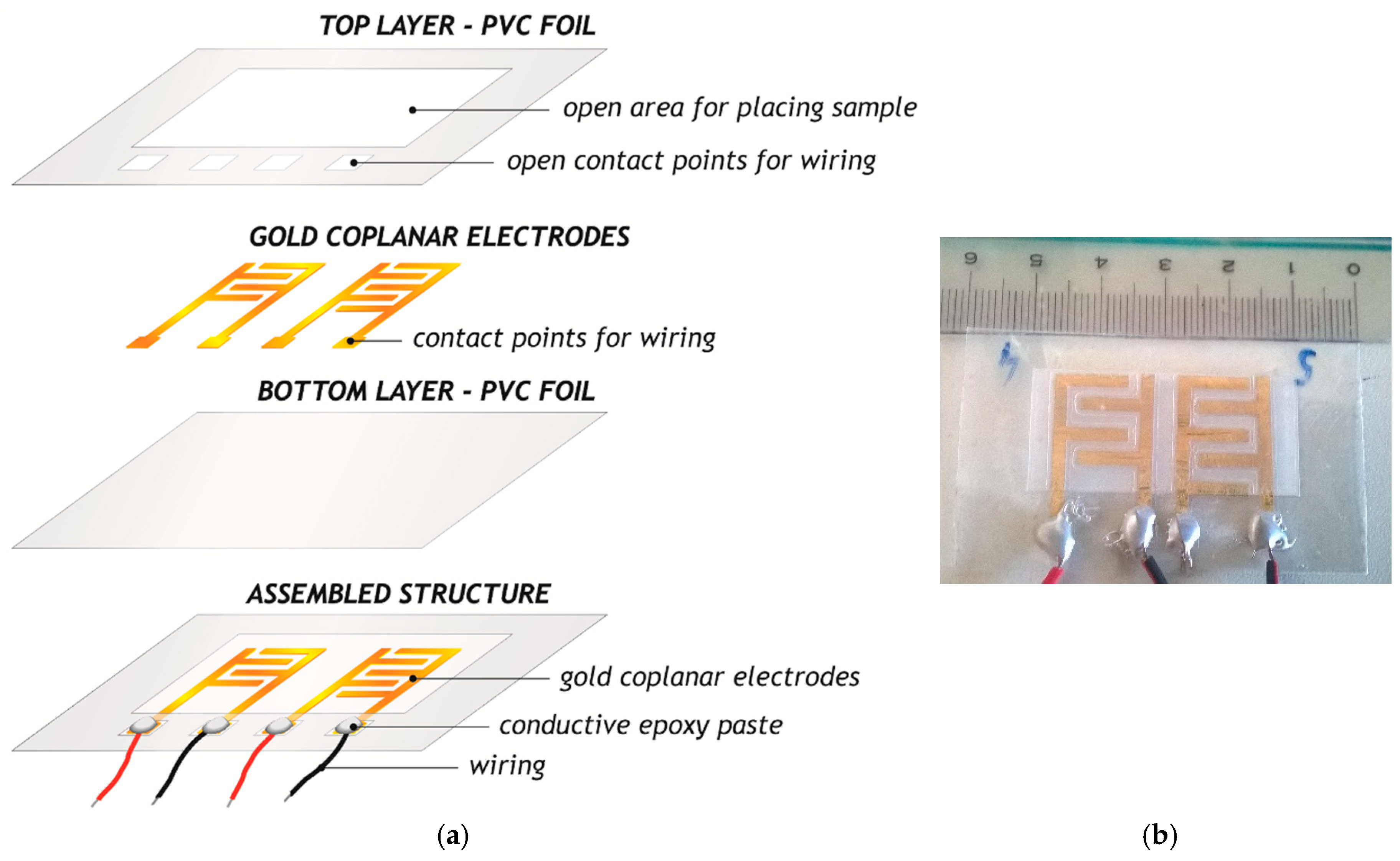
2.2. Interdigitated Electrodes-Based Platform
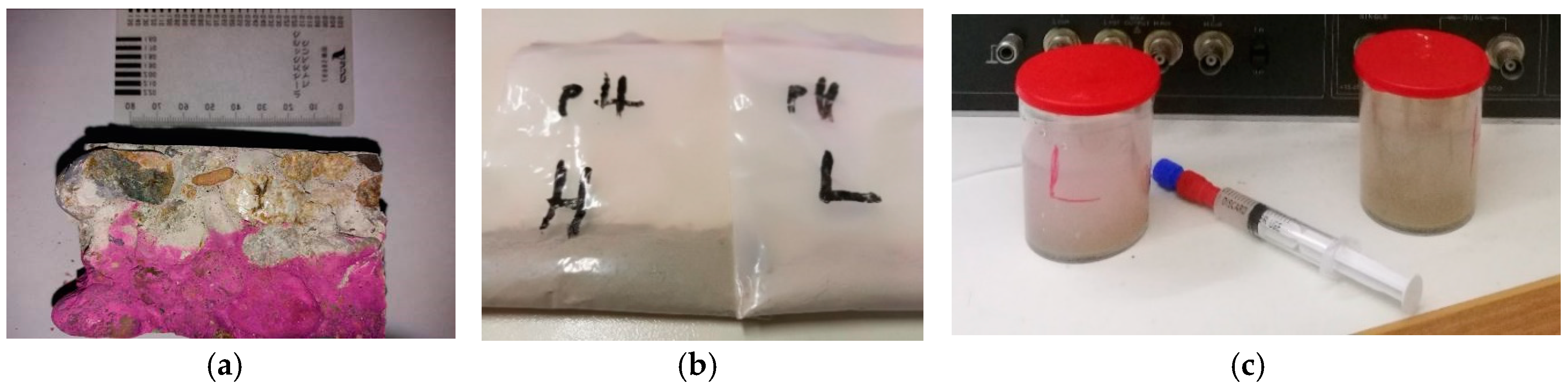
2.3. Sample Preparations and Instruments
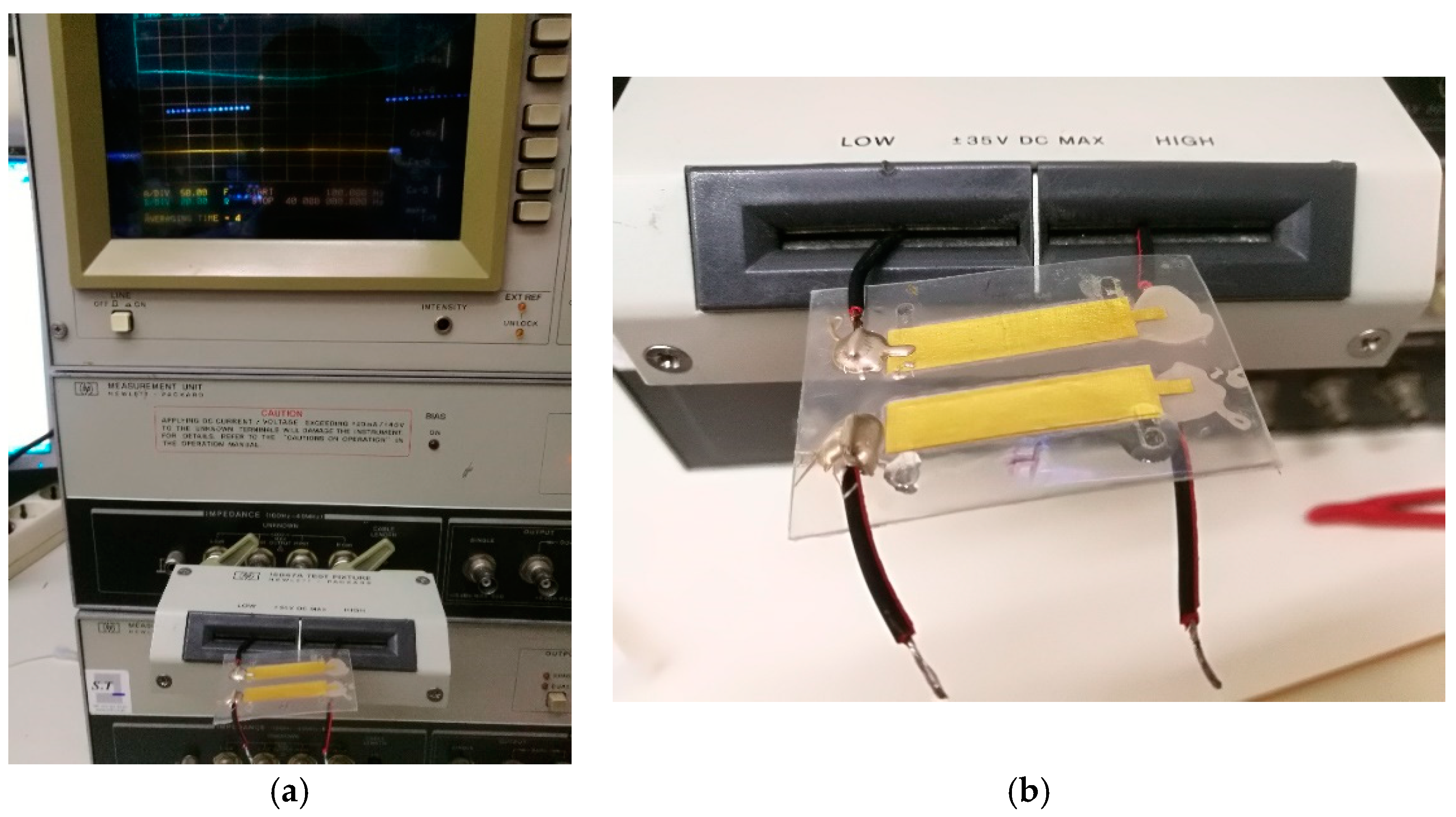
2.4. Experimental Setup
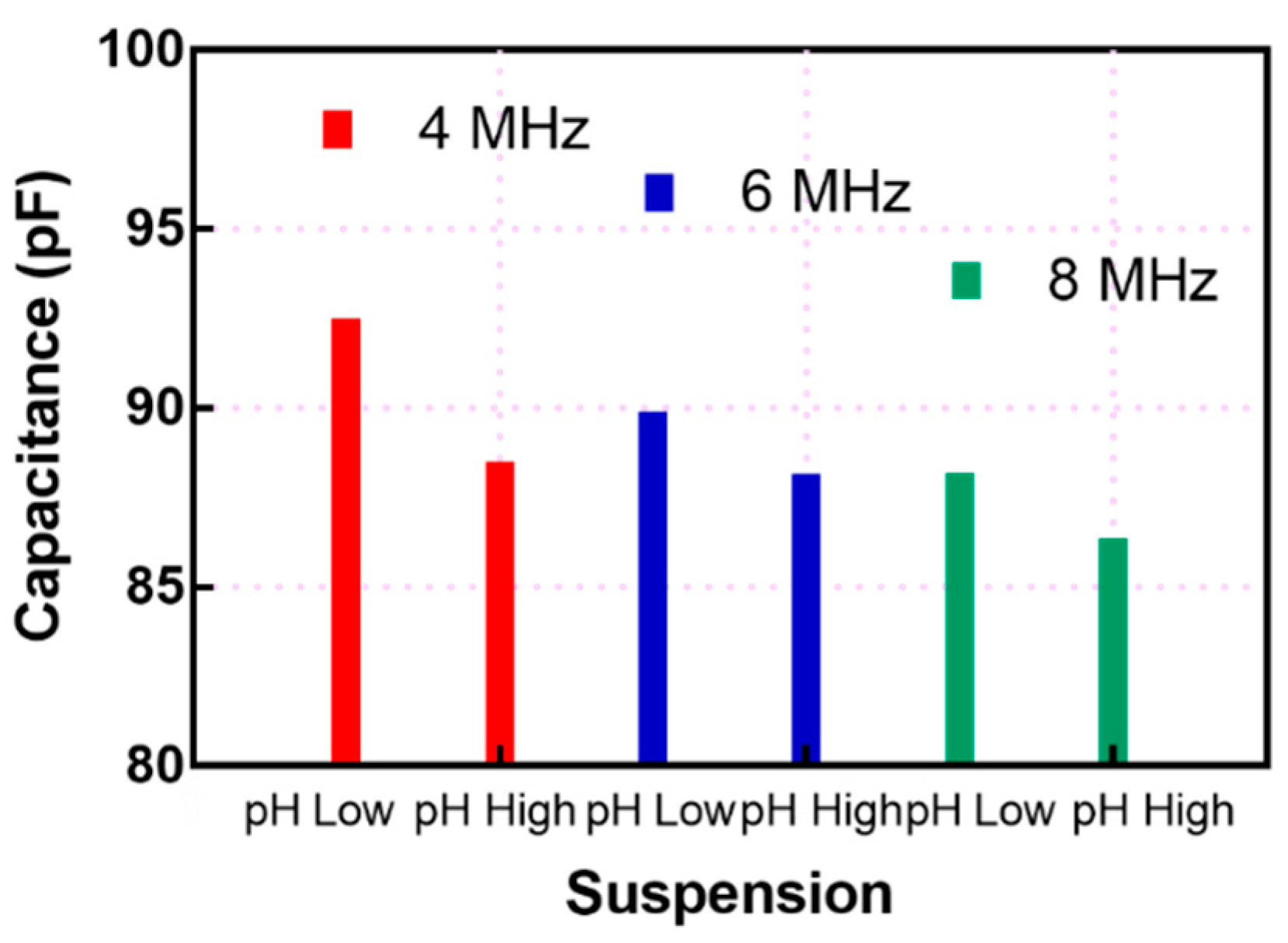
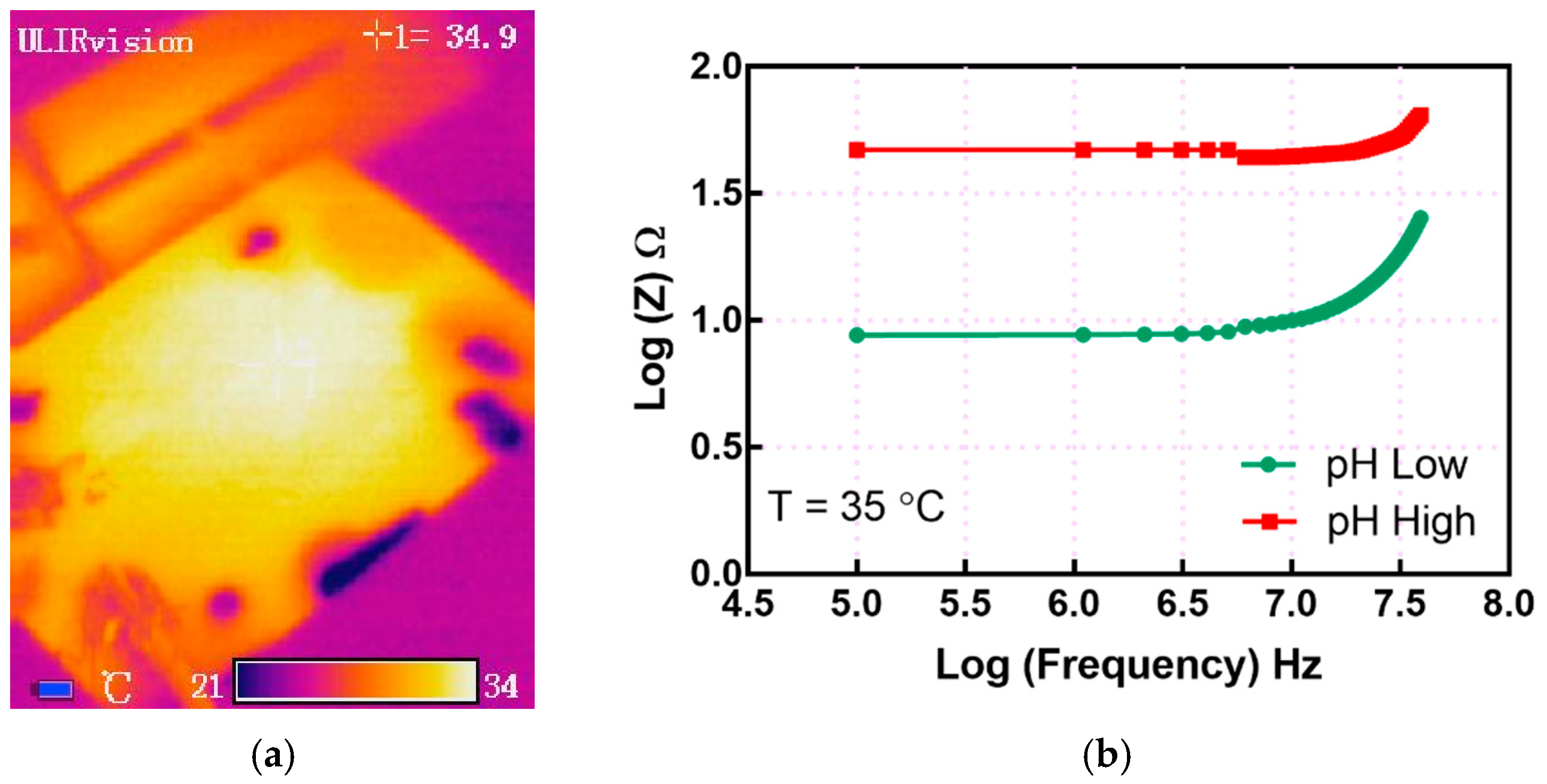
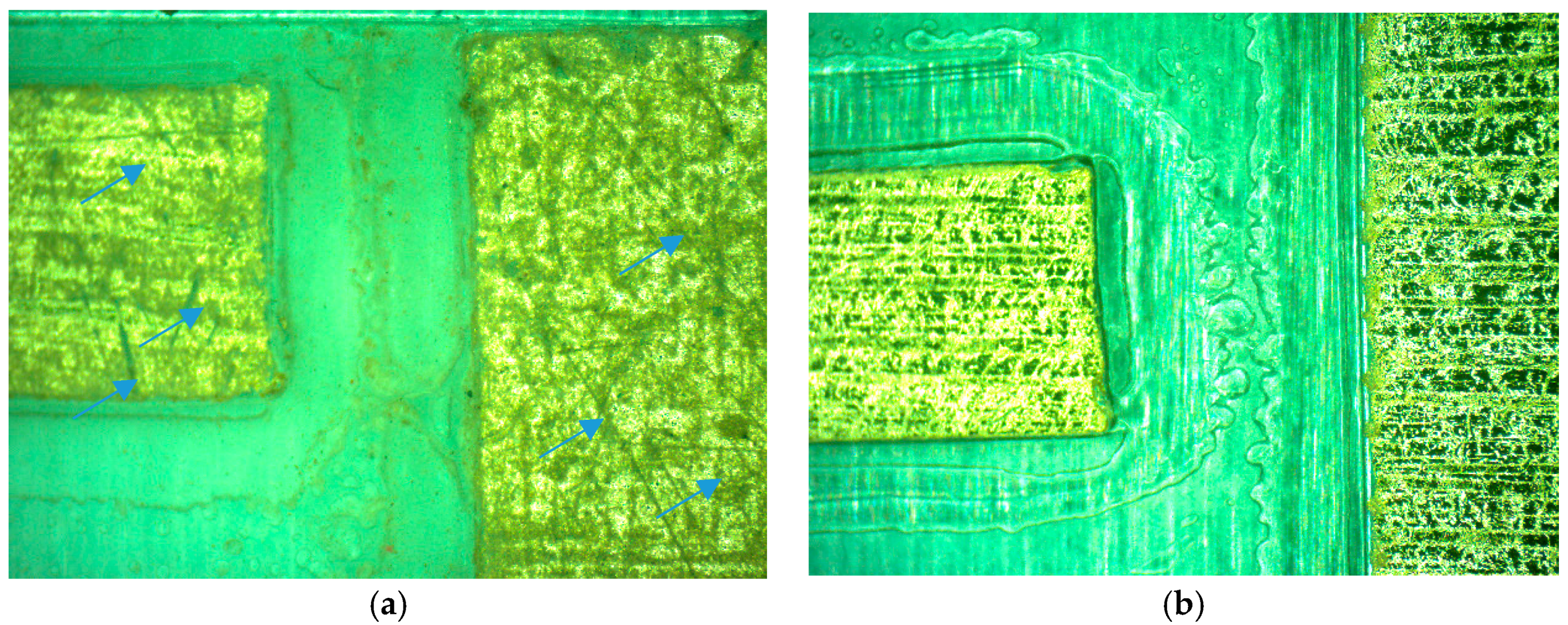
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christopher, K.Y.; Leung, K.T.W.; Chen, L. A Novel Optical Fiber Sensor for Steel Corrosion in Concrete Structure. Sensors 2008, 8, 1960–1976. [Google Scholar]
- Deschner, F.; Winnefeld, F.; Lothenbach, B.; Seufert, S.; Schwesig, P.; Dittrich, S.; Goetz-Neunhoeffer, F.; Neubauer, J. Hydration of Portland cement with high replacement by siliceous fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Niu, D.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Fu, Q. Pore Solution pH for the Corrosion Initiation of Rebars Embedded in Concrete under a Long-Term Natural Carbonation Reaction. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagues, A.A.; Moreno, E.I.; Andrade, C. Evolution of pH during in-situ leaching in small concrete cavities. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnood, A.; Tittelboom, K.V.; De Belie, N. Methods for measuring pH in concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 105, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Every, E.V.; Deyhim, A.; Faridazar, F. Embedded sensors for life-time monitoring of concrete. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Structural Health Monitoring on Intelligent Infrastructure (SHMII-4), Zurich, Switzerland, 22–24 July 2009; pp. 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, S.G.; Lin, C.J.; Hu, R.G.; Li, L.Q.; Du, R.G. Effective monitoring of corrosion in reinforcing steel in concrete constructions by a multifunctional sensor. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Venugopala, T.; Chen, S.; Sun, T.; Grattan, K.T.V.; Taylor, S.E.; Basheer, P.A.M.; Long, A.E. Fluorescence based fibre optic pH sensor for the pH 10–13 range suitable for corrosion monitoring in concrete structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 191, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumentritt, M.; Melhorn, K.; Flachsbarth, J.; Kroener, M.; Kowalsky, W.; Johannes, H.H. A novel fabrication method of fiber-optical planar transmission sensors for monitoring pH in concrete structures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 131, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertron, A.; Duchesne, J.; Escadeillas, G. Accelerated tests of hardened cement pastes alteration by organic acids: Analysis of the pH effect. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-del-Rio, J.J.; Alejandre, F.J.; Marquez, G.; Blasco, F.J. An argument for using alizarine yellow R and indigo carmine to determine in situ the degree of alkalinity in reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso, S.; Aguado, A. A review of sample preparation and its influence on pH determination in concrete samples. Mater. Construcción 2017, 67, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubb, J.A.; Limaye, H.S.; Kakade, A.M. Testing pH of concrete, need for a standard procedure. Concr. Int. 2007, 29, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ghandehari, M.; Liu, E.; Brückner, C.; Khalil, G.; Worlinsky, J.; Hyland, M. Full field imaging of high pH levels in concrete. In Optical Phenomenology and Applications, Smart Sensors, Measurement and Instrumentation; Ghandehari, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Heng, M.; Murata, K. Aging of concrete buildings and determining the pH value on the surface of concrete by using a handy semi-conductive pH-meter. Anal. Sci. 2004, 20, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Jin, W. A New Corrosion Sensor to Determine the Start and Development of Embedded Rebar Corrosion Process at Coastal Concrete. Sensors 2013, 13, 13258–13275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gandía-Romero, J.M.; Campos, I.; Valcuende, M.; García-Breijo, E.; Marcos, M.D.; Paya, J.; Soto, J. Potentiometric thick-film sensors for measuring the pH of concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 68, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femenias, Y.S.; Angst, U.; Moro, F.; Elsener, B. Development of a Novel Methodology to Assess the Corrosion Threshold in Concrete Based on Simultaneous Monitoring of pH and Free Chloride Concentration. Sensors 2018, 18, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Niu, D.; Li, X.; Lv, Y. Effects of Ca(OH)2–CaCO3 concentration distribution on the pH and pore structure in natural carbonated cover concrete: A case study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huan, Y.; Zhang, W. Passivation and Corrosion Behavior of P355 Carbon Steel in Simulated Concrete Pore Solution at pH 12.5 to 14. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 10402–10420. [Google Scholar]
- Goudar, S.K.; Das, B.B.; Arya, S.B. Combined Effect of Marine Environment and pH on the Impedance of Reinforced Concrete Studied by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy, B. B. Das and N. Neithalath (eds.), Sustainable Construction and Building Materials. Lect. Notes Civ. Eng. 2019, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, D., Jr. The measurement of the dielectric constant of three different shapes of concrete blocks. IJRRAS 2015, 25, 82–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ogunsola, A.; Reggian, U.; Sandrolini, L. Shielding effectiveness of concrete buildings. In Proceedings of the IEEE 6th International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility and Electromagnetic Ecology, Saint Petersburg, Russia, 21–24 June 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, M.; Manjakkal, L.; Zaraska, K.; Stojanović, G.M.; Ravinder, D. TiO2-Based Thick Film pH Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stojanović, G.; Radovanović, M.; Krstić, D.; Ignjatović, I.; Dragaš, J.; Carević, V. Determination of pH in Powdered Concrete Samples or in Suspension. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9163257
Stojanović G, Radovanović M, Krstić D, Ignjatović I, Dragaš J, Carević V. Determination of pH in Powdered Concrete Samples or in Suspension. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(16):3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9163257
Chicago/Turabian StyleStojanović, Goran, Milan Radovanović, Dejan Krstić, Ivan Ignjatović, Jelena Dragaš, and Vedran Carević. 2019. "Determination of pH in Powdered Concrete Samples or in Suspension" Applied Sciences 9, no. 16: 3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9163257
APA StyleStojanović, G., Radovanović, M., Krstić, D., Ignjatović, I., Dragaš, J., & Carević, V. (2019). Determination of pH in Powdered Concrete Samples or in Suspension. Applied Sciences, 9(16), 3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9163257






