Featured Application
Authors are encouraged to provide a concise description of the specific application or a potential application of the work. This section is not mandatory.
Abstract
The main objective of the study was to investigate the thermal performance of five (open and closed) bicycle helmets for convective and evaporative heat transfer using a nine-zone thermal manikin. The shape of the thermal manikin was obtained by averaging the 3D-point coordinates of the head over a sample of 85 head scans of human subjects, obtained through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and 3D-printed. Experiments were carried out in two stages, (i) a convective test and (ii) an evaporative test, with ambient temperature maintained at 20.5 ± 0.5 °C and manikin skin temperature at 30.5 ± 0.5 °C for both the tests. Results showed that the evaporative heat transfer contributed up to 51%–53% of the total heat loss from the nude head. For the convective tests, the open helmet A1 having the highest number of vents among tested helmets showed the highest cooling efficiency at 3 m/s (100.9%) and at 6 m/s (101.6%) and the closed helmet (A2) with fewer inlets and outlets and limited internal channels showed the lowest cooling efficiency at 3 m/s (75.6%) and at 6 m/s (84.4%). For the evaporative tests, the open helmet A1 showed the highest cooling efficiency at 3 m/s (97.8%), the open helmet A4 showed the highest cooling efficiency at 6 m/s (96.7%) and the closed helmet A2 showed the lowest cooling efficiency at 3 m/s (79.8%) and at 6 m/s (89.9%). Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) showed that the zonal heat-flux values for the two tested velocities were significantly different (p < 0.05) for both the modes of heat transfer. For the convective tests, at 3 m/s, the frontal zone (256–283 W/m2) recorded the highest heat flux for open helmets, the facial zone (210–212 W/m2) recorded the highest heat flux for closed helmets and the parietal zone (54–123 W/m2) recorded the lowest heat flux values for all helmets. At 6 m/s, the frontal zone (233–310 W/m2) recorded the highest heat flux for open helmets and the closed helmet H1, the facial zone (266 W/m2) recorded the highest heat flux for the closed helmet A2 and the parietal zone (65–123 W/m2) recorded the lowest heat flux for all the helmets. For evaporative tests, at 3 m/s, the frontal zone (547–615 W/m2) recorded the highest heat flux for all open helmets and the closed helmet H1, the facial zone (469 W/m2) recorded the highest heat flux for the closed helmet A2 and the parietal zone (61–204 W/m2) recorded the lowest heat flux for all helmets. At 6 m/s, the frontal zone (564–621 W/m2) recorded highest heat flux for all the helmets and the parietal zone (97–260 W/m2) recorded the lowest heat flux for all helmets.
1. Introduction
Cycling is popular, healthy, and environment-friendly. However, cycling is reported to be the third most dangerous mode of transport, resulting in injuries and mortalities. Head injuries are the most typical injuries observed among fatalities reported [1,2,3]. Studies have shown that these head-related injuries can be significantly reduced by the usage of helmets [4,5,6]. Emphasis on user safety has resulted in significant increase in research pertaining to safety [7,8,9]. However, these developments have not resulted in an increased number of helmet users among cyclists. This finding points to the existence of different influencing parameters when it comes to helmet usage by cyclists. Further research indicates that the reluctance of users to wear helmets stems from thermal discomfort [10,11,12]. For instance, helmet usage in northern and southern Italy during the summer months ranged from 93% and 60%, respectively [13], which indicated that environmental temperature may play an important role in thermal comfort or discomfort, and thus impact helmet usage.
Thermal comfort is the condition of the mind that expresses satisfaction with the thermal environment and is assessed by subjective evaluation [14]. This perception of thermal comfort widely depends on the extent to which the clothing or, in this case, the helmet ensemble allows for heat transfer between head and the environment. Therefore, the heat transfer characteristics of the helmet design that has a major influence on the user comfort must be evaluated. The heat transfer characteristics of the helmet design and the influencing parameters, has been evaluated using subject studies or objective studies. Subject studies used human participants to assess helmet-wearing effects, and focused mainly on physiology, comfort, and thermal sensation. Various studies include analyzing body heat storage using controlled chambers [15], water-perfused suits [16], or water immersion [17] to understand heat transfer between body and environment. Although subject studies provided realistic results, testing using subjects is time consuming and individual differences between subjects result in repeatability issues [18,19]. Objective studies or biophysical methods deploy anatomically correct head-forms or thermal manikins to simulate heat and mass transfer from the head and thereby evaluate the helmet performance. Thermal manikins are based on constant surface-temperature methodology to study heat and mass transfer between head and environment. The surface of the manikin was set to a constant temperature and the total power needed to maintain this temperature over a steady period of time was recorded. Total power accounts for combined heat loss by convection, radiation, and evaporation, depending on the modes of transfer being studied.
Several manikins have been developed and used to evaluate thermal performance for different applications [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. Among the developed head-forms, some are commercially available for testing and experiments, such as head-forms from Thermetrics—Measurement Technology Northwest (Seattle, WA, USA) and UCS d.o.o (Ljubljana, Slovenia). The developed head-forms differ in terms of the number of measurement segments, sweating technique, local heat-transfer data, testing duration, and measurement methodology [29]. However, there is little to no information on the shape and size of the manikin that have been developed and used in the studies and hence it can be assumed that the manikins were developed from a standard window manikin [19] or may be from a head-scan of an individual and thus may not represent the average head shape of the user population. The shape and size of the manikin controls the fitment between the head and the helmet and thereby the gaps and contact zones between the head and the helmet and thus influences the heat transfer between the head and the environment. Since the user can feel even small difference in heat loss as less as 1 W [30], it is paramount that the manikin used in evaluation of helmet performance represents the actual human head-shape as close as possible such that a realistic performance validation can be performed. Hence, a need for an anthropometrically developed biofidelic thermal manikin was identified. The developed biofidelic thermal manikin should provide more segmentation and high spatial resolution [31] such that the zonal heat-transfer characteristics can be studied in detail, which could be more useful in understanding the heat-transfer mechanisms specific to local zones. Hence, as suggested by this study [31], the manikin used in this study was modelled with nine measurement zones representing nine zones of human head.
Thermal manikins have been consistently used to analyze different heat-transfer modes. The convective characteristics of helmets have been studied in detail using manikins: To assess the influence of comfort-angle on helmet ventilation [30], to evaluate the global and local characteristics of bicycle helmets [31], to evaluate helmet-design parameters [32], to understand rowing head-gear characteristics [33], for local ventilation-efficiency quantification [34], to quantify variation among helmets and helmet-ventilation efficiency [35], convective characteristics of cricket helmets [36], and ventilation changes in full-face motorcycle helmets [37] and industrial helmets [23,27]. Thermal manikins were also used in evaluating the radiant heat-transfer characteristics of rowing head gear [33] and bicycle helmets [38] in combination with forced convection. Evaporative heat-transfer helmet characteristics were also studied using thermal manikins in pure evaporation studies for cricket helmets [36], and in combination with convection for industrial helmets [23,27]. However, combined convective and evaporative heat-transfer studies using a biofidelic thermal manikin have not been performed. Hence, the focus of this study was to perform both a convective, and a combined convective and evaporative heat-transfer study to evaluate the influence of evaporation on helmet thermal performance.
Most of the studies mentioned in this section dealt with evaluating different kinds of headgear, such as rowing headgear [33], motorcycle helmets [37], industrial helmets [23,27], and the convective characteristics of bicycle helmets [31,32,33,34,35,38]. In this study, the focus is on bicycle helmets, since helmet thermal performance plays a vital role in aiding users’ decision-making process on whether to wear a helmet or not. Hence, in this research, we aimed to evaluate the combined convective and evaporative performance of bicycle helmets using an anthropometrically developed nine-zone biofidelic thermal manikin depicting an average European head shape. Results from this study can be used to establish the heat- and mass-transfer properties of helmet ensembles that could result in improved bicycle helmets for thermal comfort.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Helmets
Five bicycle-helmet designs, listed in Table 1, were tested in this study. These helmet designs were selected to understand the heat transfer characteristics of helmets with maximum and minimum vent openings, and with and without internal channels. A1-Z1, A2-Armor, A3-Blade, and A4-Century are commercial bicycle helmets from the Lazer brand. The tested helmets were classified into open (A1-Z1, A3-Blade and A4-Century) and closed (A2-Armor and H1) based on the design characteristics. A1-Z1 was considered as an open helmet in this study because of the presence of many vent openings on the helmet surface and internal channels underneath the interior surface resulting in large exposure to incoming air flow. A3-Blade and A4-Century are similar to open helmet A1-Z1, but differ in terms of vent number and location, and the presence of prominent internal channels. H1 is not a commercial helmet and was used in this study to evaluate a closed helmet design with prominent internal channels and no vents in the front and sides. A2-Armor has fewer inlet/outlet openings and limited internal channels compared to the other three Lazer helmets.

Table 1.
Helmets tested in the study and their properties.
2.2. Thermal Manikin
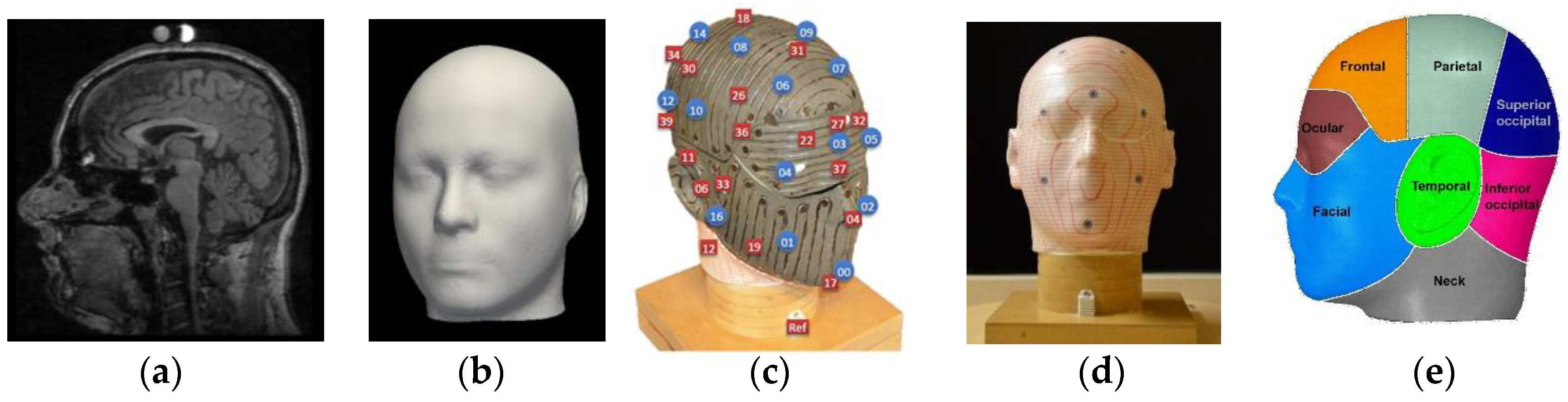
The convective and evaporative performance of the 5 bicycle helmets (Table 1) were measured using a sweating thermal manikin (Figure 1d) that was electrically heated such that the manikin surface-temperature remained constant in an environmental chamber. The thermal manikin used for this purpose was developed in-house based on an average head shape (Figure 1b), obtained by averaging the 3D point coordinates of the head over a population sample.
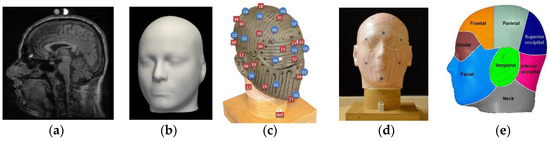
Figure 1.
(a) Slice of head scan [32]; (b) average head shape obtained from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans using shape-modeling approach; (c) manikin inner layer with marked thermal-sensor locations and sweat openings; (d) thermal manikin; (e) manikin measurement zones.
The 3D point coordinates were acquired from 85 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T1-weighted fast field echo (FFE) scans (male and female (Figure 1a) from the International Consortium for Brain Mapping (ICBM) database) [40]. The population average was obtained in two steps. In the first step, a correspondence was built between the surfaces in the population by registering a template surface via elastic-surface deformation to each individual head, thereby representing it with a fixed number of (semi)landmarks that were at the corresponding locations. In the second step, a population average was derived from the corresponded surfaces by averaging the location of each landmark over the set of surfaces [40]. The ear shape obtained from the scans was distorted due to fixtures used while scanning, so the ears on the final head shape were reconstructed using standard ear shapes available in meshmixer.
The average head-form shape was 3D-printed in a VisiJet PXL core on a ProJet CJP 660Pro and strengthened with Colorbond infiltrate. The manikin was constructed with two layers (Figure 1c), a 2 mm thick outer layer for zone visualization and sweat-duct placement, and a 2.5 mm thick inner layer for heating elements and the installation of 0.5 mm thick thermal sensors. The inner layer was lined with heating elements (Figure 1c) (Cu–Ni alloy) connected to a power source to simulate different metabolic heat-output rates. In addition to the heating elements, 40 NTC 10 k coated temperature-measurement sensors were installed in every measurement-zone location, as marked in Figure 1c. The temperature sensors provide zonal-temperature feedback that allows to control power input to maintain a constant zone temperature. The heating and feedback system were controlled using a dedicated proportional integral derivative (PID) controller for each zone.
The outer layer of the thermal manikin head was provided with 16 openings (Figure 1c) on the surface to simulate sweat. These openings were connected to an automated pumping mechanism that was programmed to pump sweat/fluid at a defined sweat rate to simulate sweating. Although a mixture of salt and water can be used to simulate realistic sweat, the fluid used in this study was water at room temperature to prevent scale formation during evaporation on the manikin surface that could inhibit heat transfer. The surface-heat loss of individual zones was determined through zonal power output over time. The surface temperature and power reading for each zone were measured at a frequency of 1 Hz for 60 min. The manikin included nine measurement regions (Figure 1e), in line with the test requirements, namely: Frontal (scalp1), parietal (scalp2), superior occipital (scalp-rear1), inferior occipital (scalp-rear2), facial (face), ocular (forehead), ears (left and right temporal), and neck. The surface area of the measurement zones is listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Manikin measurement zone and surface area.
2.3. Experiment Procedure
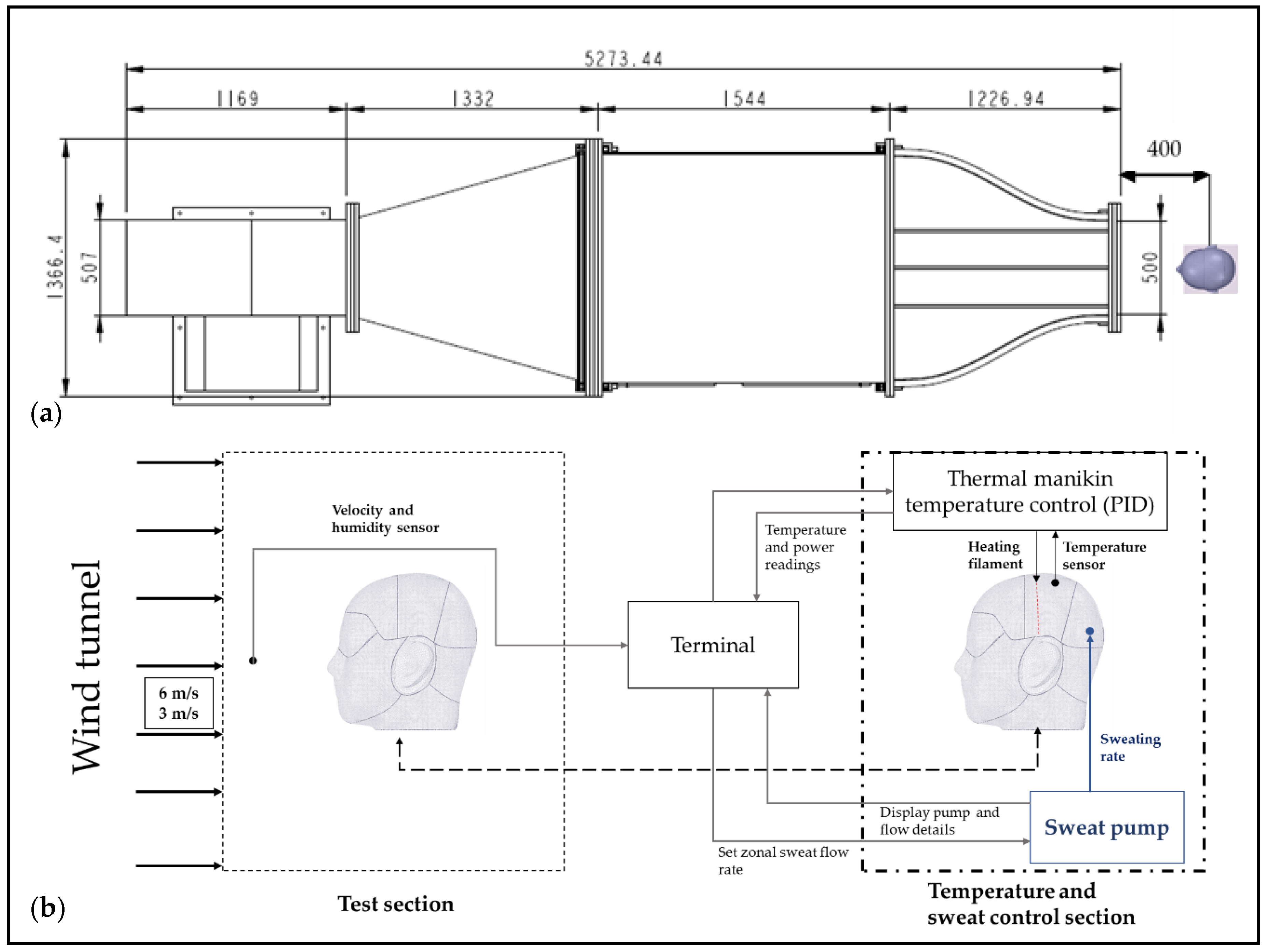
The tests were conducted in controlled laboratory conditions as specified in the test standard [41,42]. Convective-heat-transfer and evaporative-heat-transfer tests were conducted with a nude manikin (Figure 1d), and five helmets at two different velocities to evaluate helmet convective and evaporative performance, and the influence of air velocity on helmet resistance and heat-transfer characteristics. The experiments were conducted in an open-loop wind tunnel (Figure 2a) enclosed in a climate chamber at air velocities 3 ± 0.1 m/s (10.8 km/h) and 6 ± 0.1 m/s (21.6 km/h) to simulate low and moderate cycling speeds. These two air velocities were selected to simulate the studies from previous research for low [32,43] and moderate speeds [30]. A flowchart depicting the process flow and the test setup is shown in Figure 2b.
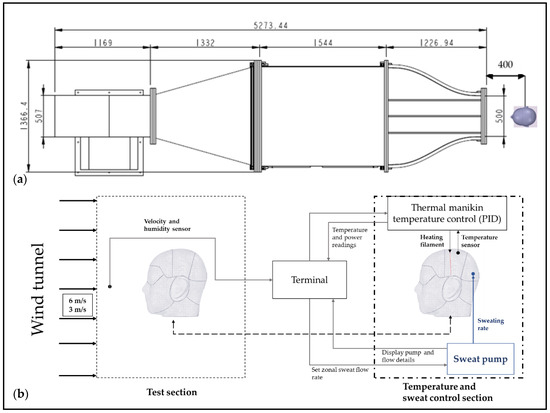
Figure 2.
(a) Schematic of open-loop wind tunnel used for simulating tested velocities with thermal manikin; (b) schematic and process flow of convective and evaporative testing.
2.3.1. Convective Heat-Loss Tests
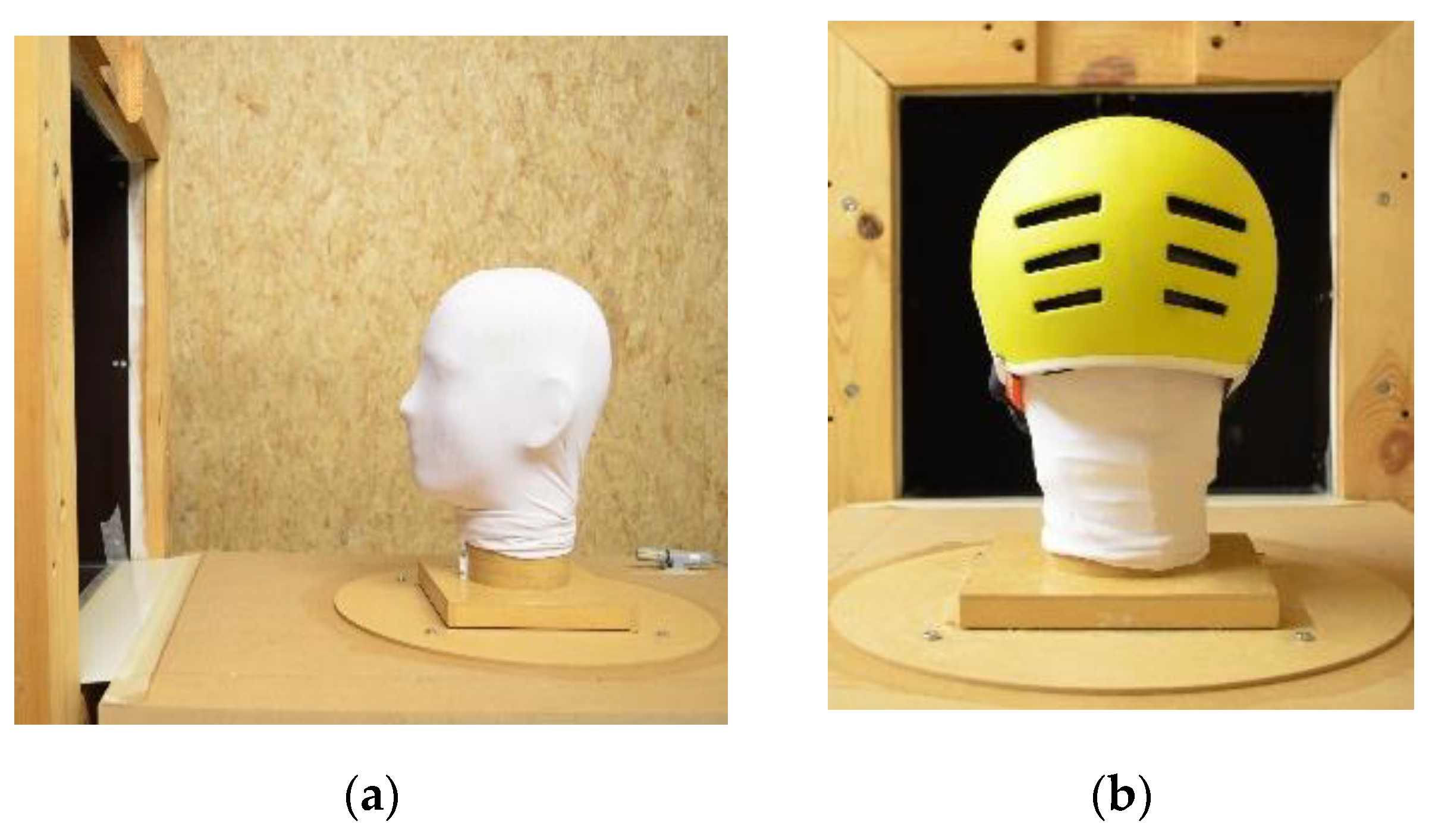
Convective (or dry) heat-transfer testing was done to evaluate the heat-transfer characteristics of selected bicycle helmets for convective heat-transfer mode. Tests were carried out as specified in the test standard [41] except for the temperature setting. The manikin surface was maintained at 30.5 ± 0.5 °C instead of 35 °C, to maintain a temperature difference (∆T) of 10 °C, as done in the previous studies [19,43] as well as to mimic the thermal responses of the human head during cycling [28]. In dry tests, the manikin was covered with a skin suit (Figure 3). The skin suit covering the head was made from 80% polyamide and 20% Lycra. The dry conditions were simulated by maintaining the environmental temperature at 20.5 ± 0.5 °C. For every test set, heat loss from the nude manikin was measured and used in the calculation of heat fluxes and thermal resistance.
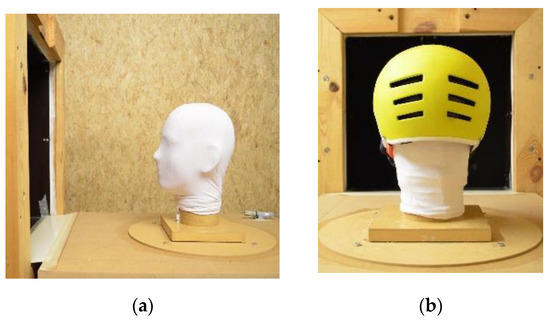
Figure 3.
(a) Manikin head with skin suit at wind-tunnel exit; (b) thermal manikin with skin suit and helmet ensemble.
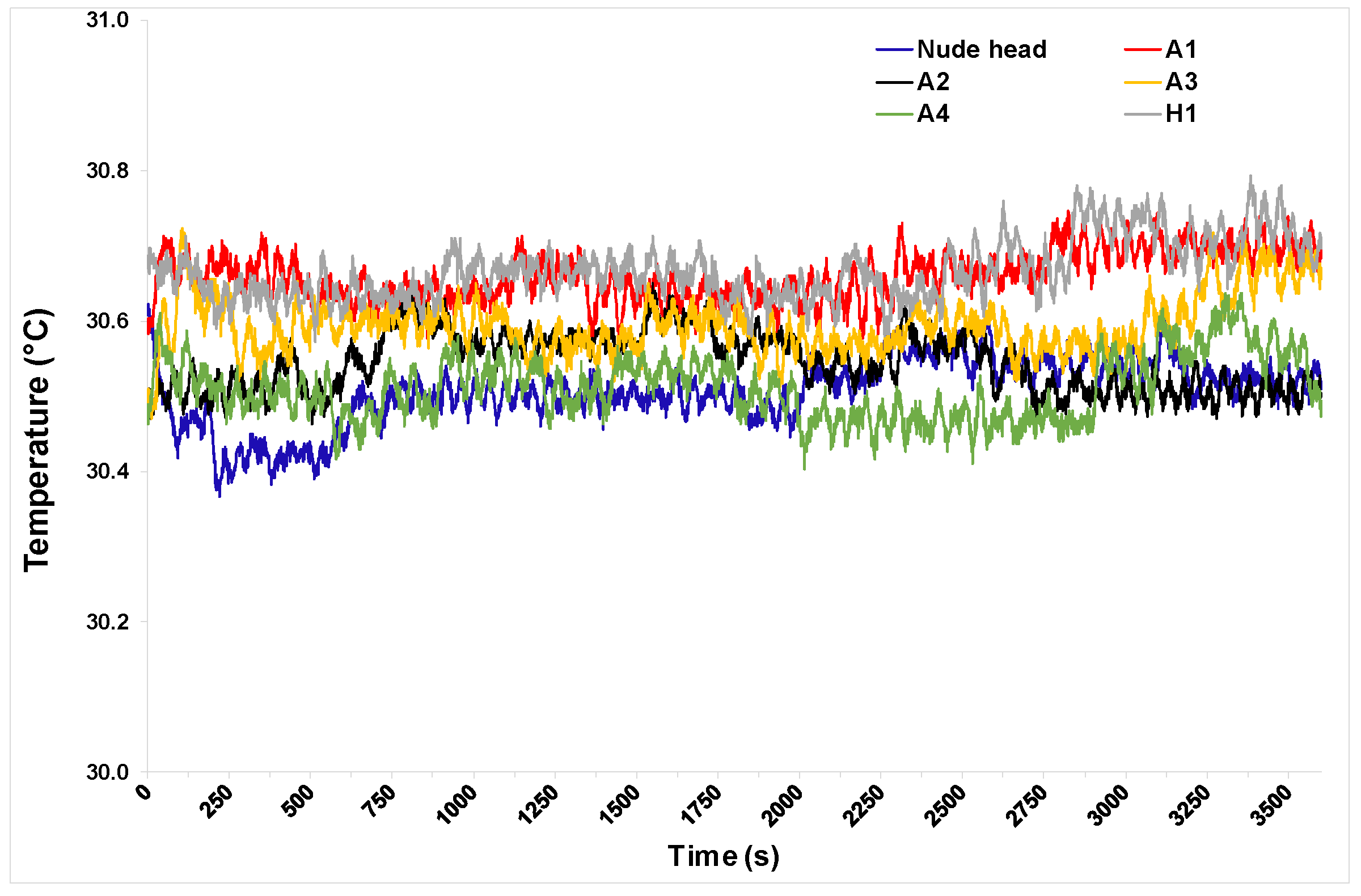
The surface temperature of the manikin zones measured using temperature sensors during the entire test duration is plotted in Figure 4. Head-surface temperature reached a steady state approximately 20 min after the start, after which temperature was in the range of 30.5 °C, with a standard deviation of ± 0.5°C for the remaining duration of the test.
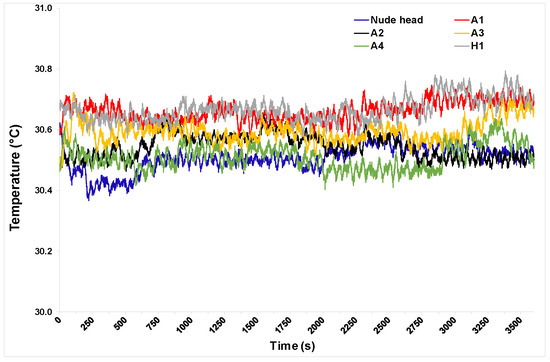
Figure 4.
Surface temperature of thermal manikin measured at 39 locations (locations shown in Figure 1c) by temperature sensors during test.
2.3.2. Latent Heat-Loss Tests
Latent heat-loss testing was carried out as per the standard [42] to determine the combined convective and evaporative heat-transfer characteristics of the helmets under the influence of sweating at different air velocities. Manikin surface temperature (Tsk) and ambient temperature (Ta) were maintained as for the convective tests. The skin fabric that covered the head was pre-wetted by spraying water before the start of every test to ensure reasonably homogeneous water distribution on the fabric. During testing, perspiration rate was set to 550 g/(m2.h) [18,44] through a pumping mechanism that was controlled through an independent controller that pumped water onto the manikin surface every three min to simulate continuous sweating.
2.4. Methods—Theoretical Background
2.4.1. Body and Environment
Thermal discomfort that arises while using helmets is directly related with body thermoregulation. The head plays an important role in human-body thermoregulation. Studies show that the human head shows high heat sensitivity [45] and unique biology due to which, under forced convection, the head can contribute up to one-third of total metabolic body-heat dissipation [29]. Helmets are constructed from high-strength materials like polymers such as plastics or composites and inner foam material to protect users from impact-related injuries. However, helmet shells made from high-strength materials act as an insulating layer for heat and moisture transfer from the head, resulting in thermal discomfort. Hence it is vital to understand the influence of helmet design on the thermoregulation of the human head.
To understand the thermal factors influencing thermal comfort, the thermophysiological response of the human body must be understood. The core temperature of the human body is maintained at approximately 37 °C, which indicates that there exist heat-transfer mechanisms between body and environment such that heat is dissipated when in surplus and retained when in deficit. The relationship between heat generation in the body and transfer to the environment is dynamic, resulting in a heat balance that is described by the heat-balance equation [46]:
where M (W) is the body metabolic rate and W (W) is work rate, quantifying the rate of heat production. Heat loss/gain is the result of evaporation (E) (W), convection (C) (W), conduction (K) (W), and radiation (R) (W). Evaporation and convection occur through respiration (res) (W) and skin (sk) (W), and S (W) is heat storage in the human body. Heat storage/dissipation by the human body plays a vital role in maintaining energy balance in the body. However, the rate of heat production is not always equal to the rate of heat dissipation, resulting in changes in thermal balance. A basic understanding of what this concept would be, if heat storage S = 0 or S ~ 0, i.e., generated heat is approximately equal to dissipated heat (M = W + heat-transfer modes), energy balance is attained, which results in thermal balance and vice versa. Heat transfer through conduction (K) is studied in combination with convective components since heat-transfer-through-conduction mode is relatively small due to little or no direct contact between head and helmet, and because of the much bigger contributions from evaporation, convection, and radiant exchange.
Researchers have often used dry (or sensible) heat transfer and wet (or evaporative) heat transfer when describing the heat-transfer mechanisms between head and environment. Dry heat transfer is the combination of heat transfer by convection (natural and forced) and radiation. The convective component is primarily influenced by the ∆T that exists between head surface and environment. Convective heat transfer is defined by [47]
where, (W) is the convective heat transfer per unit of time, A (m2) is the surface area of the object, hc (W/m2.K) is the convective heat-transfer coefficient, Tsk (K) is the temperature of head surface and Ta (K) is the temperature of air/fluid. Wet or evaporative heat transfer is related with heat transfer because of sweat evaporation and is primarily influenced by the difference in partial vapor pressure between skin surface and environment, and is defined as [48]
where, (W) is evaporative heat transfer per unit of time, A (m2) is the surface area of the object, he (W/m2.Pa) is the evaporative heat-transfer coefficient, Psk (Pa) is the partial vapor pressure of skin and Pa (Pa) is the partial vapor pressure of the surrounding air/fluid. (W) is the value measured in convective tests and ( + ) (W) is the value measured in combined convective and evaporative tests.
The cooling efficiency (%) of a helmet informs about the ability of a helmet to dissipate heat from the head to the environment, relative to a nude head. It can be calculated as follows:
The main helmet property that influences convective heat transfer between head and environment is the helmet thermal resistance (Rct) [49].
2.4.2. Thermal Resistance (Rct)
In dry heat-transfer conditions, the total thermal resistance of the helmet ensemble, i.e., between head surface and the environment (thus including the effect of the air layer around the manikin surface) is quantified using thermal resistance (Rct) (m2 °C/W), and is calculated using the following formula [49]:
where Tsk (°C) is the zone average skin temperature, Ta (°C) is the ambient environment temperature, and Q/A (W/m2) is the area-weighted heat flux.
2.4.3. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out on the test results using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) to determine if the differences between the heat-flux values for each variable (measurement zones, helmets) were significant. Null hypothesis stated that there exists no significant difference (p > 0.05), and the alternative hypothesis stated there existed significant difference (p < 0.05). Post hoc analysis was performed (Bonferroni) to identify zones and helmets with statistically significant variation. The above-mentioned statistical analyses were carried out for a 95% confidence interval.
2.5. Limitations and Considerations
To the best knowledge of the authors, experimental methodology to determine the combined convective and evaporative thermal-performance characteristics of bicycle helmets using an anthropometrically developed biofidelic thermal manikin has not yet been published. Aiming to address this limitation, the present study was based on available standard experimental methodologies [41,42] to quantify factors affecting the dry and wet thermal performance of several different helmets. However, the study also has some limitations that are discussed in this section.
The test standards [41,42] followed in this study prescribe ambient room temperature (Ta) of 23 °C and manikin surface temperature (Tsk) of 35 °C. However, in this study, ambient temperature (Ta) was maintained at 20.5 ± 0.5 °C, and surface temperature (Tsk) at 30.5 ± 0.5 °C. This change was done to enable the comparison with results from previous studies [19,43]. Testing was carried out at two velocities (3 m/s and 6 m/s) that are different from the air velocity prescribed in the test standards (0.08 m/s). This study considered higher velocities in order to investigate the effects of low and moderate velocities on the thermal and evaporative characteristics of bicycle helmets. Several works in the literature [50,51,52] show the effect of air flow on heat transfer between body and environment, and its importance in understanding thermal performance. The chosen conditions are a closer representation of the real-use conditions of helmets because, as indicated in another study [36], resistance values obtained in static conditions are likely overestimations of actual resistances surrounding a rider’s head during normal bicycle use.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Convective Heat-Transfer Characteristics of Head-Helmet Ensembles
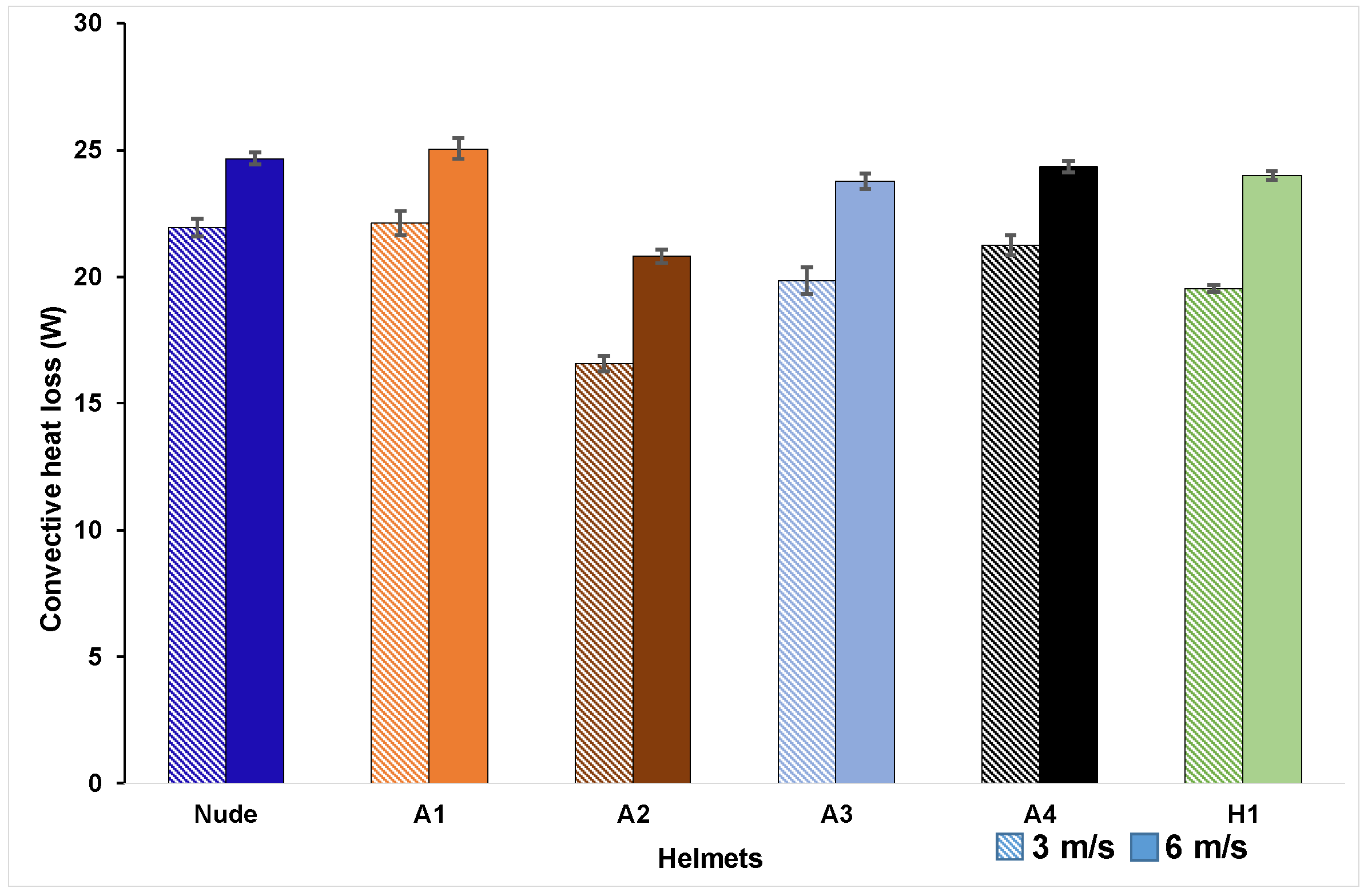
The convective loss from the nude manikin and the manikin with the helmets at 3 m/s and 6 m/s are shown in Figure 5. The convective heat loss increased from 16.6–22.1 W at 3 m/s to 20.8–25.1 W at 6 m/s, showing that heat transfer is strongly influenced by air velocity. Convective heat flux for the nude head-form was 192 ± 2.5 W/m2 at 3 m/s and 216 ± 2.5 W/m2 at 6 m/s. These values are approximately 25% lower than the theoretical heat flux calculated using heat-transfer coefficient values obtained from this study [53] for low (hc(3) = 24.8 W/m2.K) and moderate (hc(6) = 28.5 W/m2.K) velocities in Equation (2). Further investigation indicated that temperature-measurement sensors in the manikin were placed between the two layers, and the reported measurements are the temperature readings between the inner layer and outer layer plus fabric. The outer layer (thickness: 2 mm) acts as an insulation skin resulting in the external fabric layer temperature (measured using an IR thermometer) 2–2.5° C lower than the temperature measured by the sensors resulting in reduction in heat flux values recorded in the tests. The heat flux from nude head (216 ± 2.5 W/m2) recorded at 6 m/s is comparable with the heat flux values recorded in these studies [31,35].
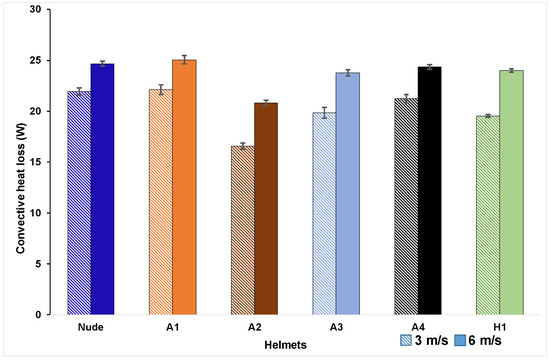
Figure 5.
Convective heat loss of helmet ensembles at tested velocities (confidence intervals obtained for a 95% confidence level and a sample size of three).
Dry heat losses with the tested helmet ensembles (Table 3) were 11%–25% lower than those of the nude head for all helmets except A1, indicating that most helmets hampered heat transfer from the head by serving as a thermal resistance to heat transfers. The cooling efficiency of the helmets (Table 3) ranged 75%–101% at 3 m/s and 84%–101% at 6 m/s, with Helmets A1 and A2, showing the highest and the lowest efficiency, respectively, for the two tested velocities. Total heat transfer from Helmet A1 was recorded to be higher than the nude head. To understand the reason behind this behavior a zonal heat flux investigation using two-way ANOVA was carried out on total heat flux values. The analysis of the total heat fluxes obtained with the different helmets at two tested velocities showed that all obtained heat fluxes were statistically different (p < 0.05) from those obtained with the nude head except for Helmet A1 (p = 1.0) thus indicating that the heat flux values of helmet A1 and nude head are comparable. Hence, analysis of zonal heat-flux values was performed using two-way ANOVA combined with post hoc (Bonferroni) analysis since helmet classification based on total heat flux may not correspond to classification based on the heat fluxes of the individual zones, as indicated in [31].

Table 3.
(a) Convective heat-loss values at 3 m/s. (b) Convective heat-loss values at 6 m/s.
Zonal Heat Transfer Characteristics
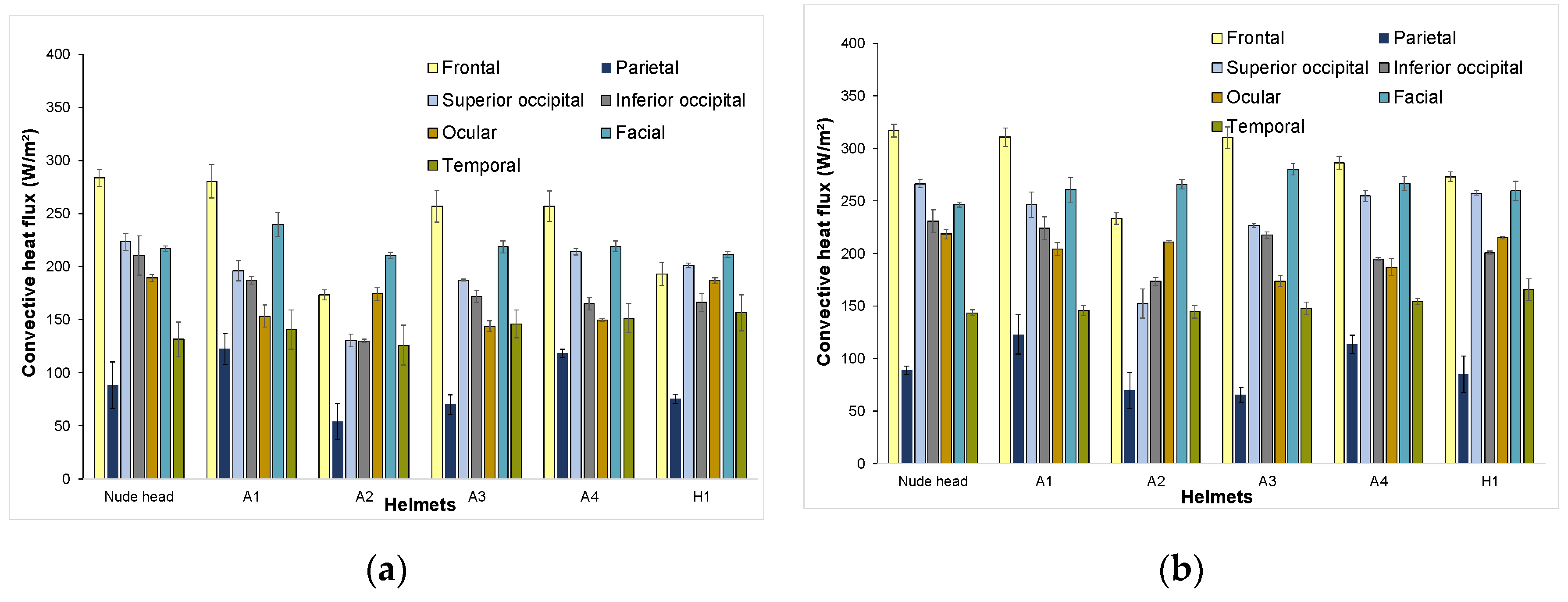
Frontal zone: Frontal-zone heat fluxes when wearing helmets were statistically different from values obtained for the same zone without a helmet except for Helmet A1 (p = 1.0). From the plots (Figure 6), it was inferred that Helmets A1, A3, and A4 depicted similar frontal heat-transfer behavior due to design features. Results also showed that heat flux from the frontal zones decreased for closed helmets.
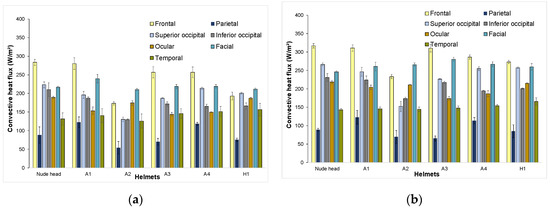
Figure 6.
Zonal convective heat-flux distribution at (a) 3 m/s; (b) 6 m/s.
Parietal zone: For parietal zones, no significant difference was observed between the nude head and Helmets A3 and H1 but heat-flux values for the nude head and Helmet A1 were significantly different (p < 0.05). Further investigation showed that the parietal zone of the manikin head with Helmet A1 recorded higher heat transfer than the nude head. This is because, at the parietal zones under Helmet A1, the gap between head and helmet at the vent outlet was smaller than the inlet, resulting in the Venturi effect, as observed in this study [54], causing higher local velocity profiles, which, in turn resulted in higher heat transfer from that zone. A similar effect was observed in helmet A4, which has a similar profile as helmet A1 resulting in helmets A1 and A4 dissipating 28%–39% more heat than from parietal zone the nude head. The parietal zone showed minimal difference in the measured heat flux for 3 and 6 m/s (Figure 6).
Occipital zones: The superior occipital zone of the helmets when compared to the nude head showed that all helmets were significantly different (p < 0.05). Helmets H1 and A4 showed the highest cooling efficiency for this zone. Helmet H1 had outlet vent openings at occipital zones resulting in unrestricted air flow. Moreover, there was no retention system interacting with the occipital region of the head during helmet H1 usage. Hence, resistance to heat transfer in this region was lower. The retention system of Helmet A4 was present but did not block air flow in the mentioned zone, as observed in other helmets. It is important to note that Helmet A1, with the highest overall cooling efficiency (slightly above 100%), transferred only 87%–93% of heat from the superior occipital region due to the retention system blocking air flow in that zone. When compared to the nude head, the inferior occipital zone of the helmets showed that all helmets were significantly different (p < 0.05) except for A1. The cooling efficiency of Helmet A1 for the inferior occipital zone was the highest among the tested helmets. Helmet A4, which showed 97%–98% overall cooling efficiency for the tested velocities, dissipated 73%–82% of heat from the inferior occipital zone due to the presence of a retention system blocking air flow in that zone. Helmet A2 performed poorly between the tested helmets because of the helmet design that reduced air flow into the helmet.
Ocular, Facial and Temporal zone characteristics: The ocular region of the helmets, when compared to the nude thermal manikin, showed no significant difference for Helmet H1 (p = 1.0). For this particular region, Helmet H1 also showed the highest heat loss among the tested helmets for both tested velocities. This is because the design of the helmet H1 favors the air flow in the ocular region. The gap between ocular region and the inner side of Helmet H1 was also found to be bigger when compared to the other helmets. It was also observed in all helmets that the gap between ocular region and helmet inner side was directly proportional to heat loss in the region, i.e., the higher the gap was, the higher the heat loss would be, and vice versa. The facial and temporal regions of the manikin with the helmets showed no significant difference when compared to the facial and temporal regions of the nude manikin for both velocities, which is logical since the helmets did not cover these regions of the head. However, the facial zone under helmet A1 recorded higher heat transfer from facial zone (Figure 6) than the nude head. This is due to the helmet front profile that directs more air flow onto the facial region as observed in this study [35], where some helmets showed more heat transfer from the facial zone than the mean value of the facial zone heat transfer from the nude head.
Thermal Resistance: Dry thermal resistances were obtained for the nude manikin and the manikin with the helmet ensembles in steady-state conditions at 3 m/s and 6 m/s as shown in Table 3a,b, respectively. From the resistance values, it is evident that Helmet A2 exhibited high resistance to heat transfer and helmet A1 recorded the lowest. Between the Rct values of the tested helmets, A2 recorded the highest resistances at both 3 m/s and 6 m/s, resulting in the lowest heat dissipation and cooling efficiency among the tested helmets.
Although the range of the obtained total thermal resistances was found to be narrow, results indicated that even a small change in resistance values could impact heat-transfer values. For example, Rct at 6 m/s for Helmets A2 and A3 was 0.055 and 0.048 (°C.m2/W), respectively. This shows that a reduction of about 14% in the total thermal resistance of the mentioned helmets implied an increase in cooling efficiency, from 85% (A2) to 96% (A3).
3.2. Evaporative-Heat-Transfer Characteristics of Helmet Ensembles
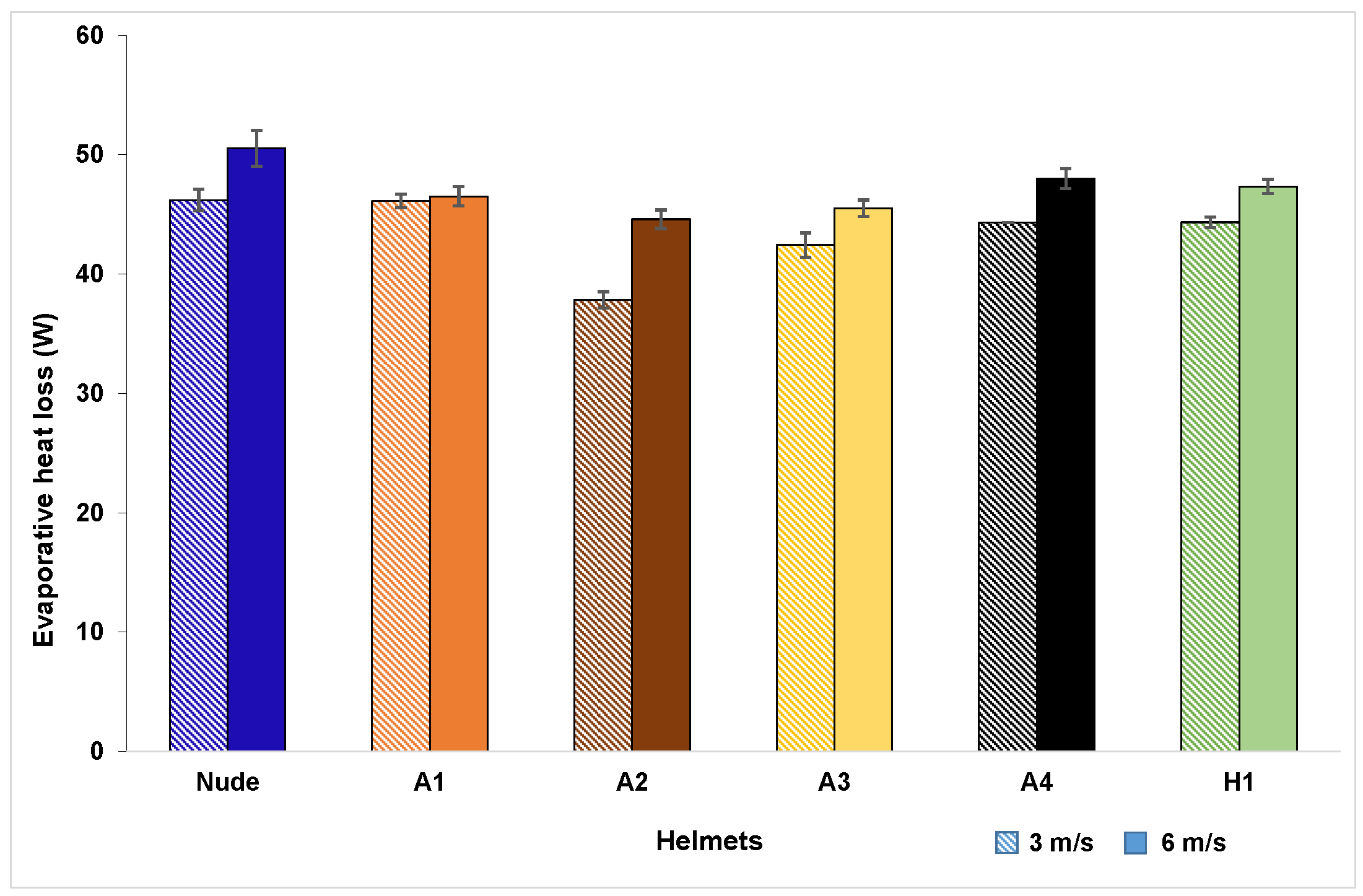
Heat losses registered by the manikin with and without helmets during the combined convective-evaporative tests at 3 m/s and 6 m/s are shown in Figure 7. Apparent evaporative heat loss was in the range of 37.8–47.4 W at 3 m/s and 44.6–50.5 W at 6 m/s (Table 4). From the test results, it is evident that convection combined with evaporation results in 51–54% higher heat transfer than pure convection demonstrating the importance of evaporation mode in heat transfer between head and helmet. The apparent evaporative heat flux value recorded in this study for nude head at 3 m/s is comparable to that reported in this study [27]. A comparison of cooling efficiency of helmets (Table 4) indicated that, at 3 m/s, helmet A1 recorded the highest (97.3%) and helmet A2 recorded the lowest (79.8%). At 6 m/s, helmet A4 recorded the highest (96.7%) and helmet A2 recorded the lowest (89.9%). Furthermore, a global analysis on the total heat flux values was carried out using two-way ANOVA that showed, in comparison with the nude head, Helmets A1, A4, and H1 were statistically not different (p > 0.05). However, as indicated in this study [31], classification based on overall heat transfer is not sufficient and, hence, zonal heat-transfer characteristics were also studied.
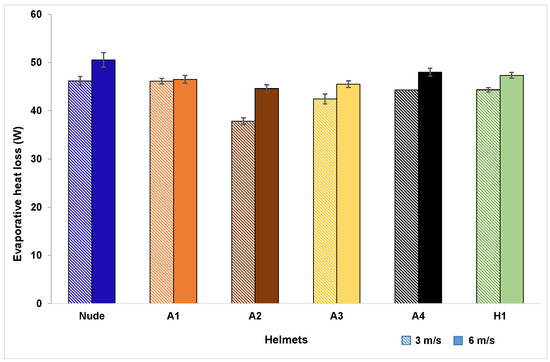
Figure 7.
Apparent evaporative heat loss of helmet ensembles at tested velocities (confidence intervals obtained for a 95% confidence level and a sample size of three).

Table 4.
(a) Apparent evaporative-heat-loss values at 3 m/s. (b) Apparent evaporative-heat-loss values at 6 m/s.
Zonal Heat Transfer Characteristics
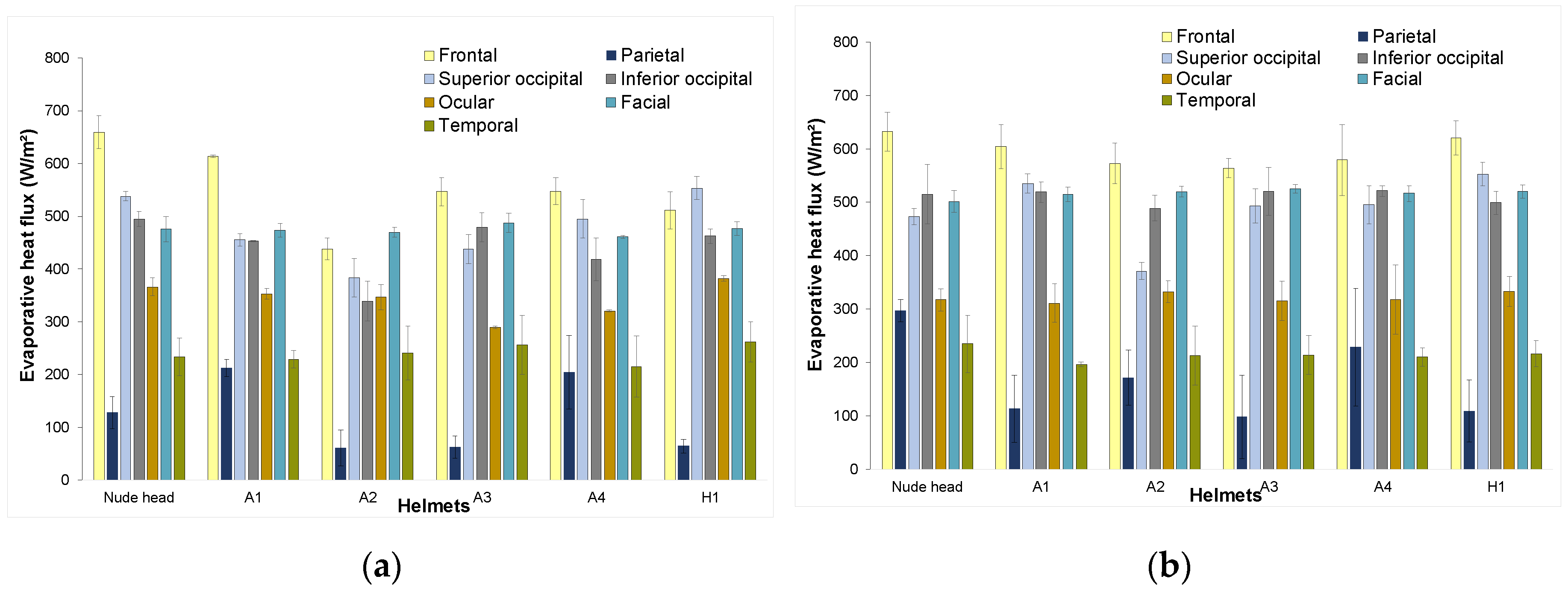
Frontal zone: In comparison with the evaporative heat losses of the nude manikin, losses from the frontal zone of Helmets A1, A4 and H1 were not statistically different (p > 0.05). However, plots indicate that the heat flux from the frontal zone of nude head at 3 m/s was, surprisingly, 2% higher than the heat flux from the frontal zone at 6 m/s (Figure 8). During the experiments, it was observed that, at 6 m/s, the fabric used to retain the fluid simulating sweat had dry spots in the frontal zone, which implied a lower surface area with evaporation, and thus lower heat losses in the zone in question. In opposition, at 3 m/s, the fabric was relatively wet, and hence implied more evaporation and higher heat losses than for 6 m/s. The same effect was observed on the fabric for Helmet A1 tests, resulting in higher frontal-region heat fluxes at the lower velocity.
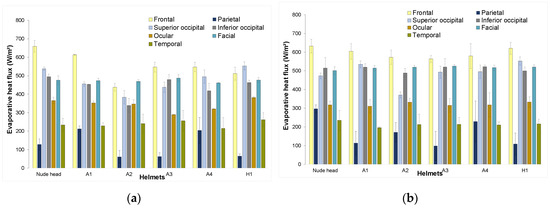
Figure 8.
Zonal apparent evaporative heat-flux distribution at (a) 3 m/s; (b) 6 m/s.
Parietal zone: When covered with helmet, the parietal zone had 2–15% lower evaporative losses when compared to nude manikin. Statistical analysis showed that the parietal region of Helmets A1, A2 and A4 was not statistically different when compared to that of the nude manikin. Heat-flux transfer from the parietal region at 3 m/s was lower than heat flux at 6 m/s for all helmets except for A1 (Figure 8). It could be considered that the high parietal cooling efficiency of Helmet A1 caused the ‘dry-fabric effect’ as observed in frontal zone resulted in lower power consumption at 6 m/s than at 3 m/s.
Occipital zones: The occipital region of Helmets A1, A3, A4 and H1 shows no significant difference when compared to the nude head (p > 0.05). The occipital regions are located on the leeward side of the air flow. Hence, the effect of air speed on this region was not very pronounced, as shown in statistical analysis. However, Helmet A2 showed the lowest heat transfer from the occipital region (8%–31% lower than nude head) for both velocities, and this can be attributed to helmet design (which implies a snug fit in the occipital region).
Ocular, facial and temporal zone characteristics: The facial region of the nude manikin with and without helmets showed no significant difference for both velocities (p > 0.05). Interaction between facial region and the helmets was minimal during helmet usage; hence, no difference was observed. Heat-flux values from the ocular region of the thermal manikin with and without helmets showed no significant difference (p > 0.05). However, heat flux values for low air velocity (3 m/s) were found to be 4–12% higher than the heat-flux values for moderate speed (6 m/s). It was assumed that the existence of dry spots in the fabric during the tests at moderate speeds (6 m/s) resulted in low power consumption, as observed in parietal region. The temporal region showed no significant difference when compared to the nude head for both tested velocities.
From the frontal zonal evaporative-heat-loss plots (Figure 8), it can be observed that the helmets transmitted 70%–85% of the evaporative heat at 3 m/s and 88–98% at 6 m/s (as compared to nude manikin). These values are comparable with the evaporative-heat-transfer results from a study [36] on cricket helmets that showed helmets dissipated 68–78% of the evaporative heat. Considering that the study [36] was carried out at a very low velocity (0.2 m/s) for cricket helmets (different from bicycle helmets), it can be presumed that high evaporative-heat-dissipation values recorded in the current study from the scalp and face zones are due to higher air velocities used in testing.
4. Conclusions
The thermal performance of five bicycle helmets for convective and evaporative heat transfer was studied using an anthropometrically developed nine-zone biofidelic thermal manikin for low (3 m/s) and moderate velocities (6 m/s). In-depth analysis of helmet-design effectiveness was done using zonal heat-transfer values obtained from thermal-manikin experiments. The results showed that evaporative heat transfer plays a vital role in helmet performance. The combined convective and evaporative helmet performance can be different from that of convective performance, as shown by the overall cooling-efficiency values of helmets for different air velocities. It was also observed that global heat transfer characteristics and zonal heat transfer characteristics differed significantly and this difference in characteristics was influenced by zone position with respect to incoming air flow and helmet design features. The major findings of this study are as follows:
- Evaporative heat-transfer mode accounts for 51%–53% of total heat transferred from the nude head, demonstrating the significant role played by sweat in heat transfer and thermal performance.
- At low velocity (3 m/s), open Helmet A1 showed the highest overall cooling efficiency due to high heat transfer from parietal and facial zones and closed Helmet A2 showed the lowest overall cooling efficiency due to low heat transfer from all the zones for both convective and evaporative heat transfer.
- At moderate velocity (6 m/s), for convection, open Helmet A1 recorded the highest cooling efficiency due to high heat transfer from parietal zone and closed Helmet A2 showed lowest cooling efficiency due to low heat transfer from all the zones as a result of it shell-like design. For evaporation, open Helmet A4 recorded the highest cooling efficiency as a result of high parietal zone heat transfer.
- Overall cooling efficiency of closed helmet with prominent internal channels and outlets (H1) was better than the closed helmets with inlets and outlets (A2) depicting the influence of internal channels on heat transfer.
- Among the zonal heat flux values for the zones under the helmet, frontal zones recorded the highest heat transfer and the parietal zone recorded the lowest heat transfer for all the tested helmets. Further research into the parameters influencing these zonal heat transfer characteristics would provide valuable insight on improving the zonal thermal performance of helmets.
This research provides a description of combined convective and evaporative helmet characteristics tested using a sweating thermal-manikin head and confirms the need for evaporative-heat-transfer tests and their influence on the cooling efficiency of bicycle helmets. It is recommended that the future research on this topic should study/examine zonal design parameters affecting the evaporative heat transfer characteristics of helmets. The results of this study could be complemented by conducting real field trials or subject studies using the same helmets to investigate both the thermal and physiological aspects of bicycle helmets.
Author Contributions
S.M., K.K., and G.D.B. developed the experimental methodology. S.M., J.V., and T.H. developed the thermal manikin used in the experiments. T.S.M., G.D.B., K.K., and T.H. helped to review and edit the original draft.
Funding
This research was funded by European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Grant Agreement No. 645770, SmartHELMET: Intersectoral Network for Innovation on Smart Thermal Solutions for Bicycle Helmets and Flanders Innovation and Entrepreneurship (VLAIO) under Grant Agreement 140881, Phyt: Physical and thermal comfort of helmets. The APC was funded by the product development research group.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Grant Agreement No. 645770, SmartHELMET: Intersectoral Network for Innovation on Smart Thermal Solutions for Bicycle Helmets. Additionally, we acknowledge the support from Flanders Innovation and Entrepreneurship (VLAIO) under Grant Agreement 140881, Phyt: Physical and thermal comfort of helmets. The authors express their gratitude to Werner Coppieters for his invaluable time and help with the statistical analysis study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wood, T.; Milne, P. Head-injuries to pedal cyclists and the promotion of helmet use in Victoria, Australia. Accid. Anal. Prev. 1988, 20, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoye, A. Bicycle helmets—To wear or not to wear? A meta-analysis of the effects of bicycle helmets on injuries. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 117, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, B.; Azim, A.; Haider, A.A.; Kulvatunyou, N.; O’Keeffe, T.; Hassan, A.; Gries, L.; Tran, E.; Latifi, R.; Rhee, P. Bicycle helmets work when it matters the most. Am. J. Surg. 2017, 213, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, E.R. Safety standards for bicycle helmets. Physician Sportsmed. 1988, 16, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier, J.; Creighton, P. Bicycle injuries and helmet use: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cripton, P.A.; Dressler, D.M.; Stuart, C.A.; Dennison, C.R.; Richards, D. Bicycle helmets are highly effective at preventing head injury during head impact: Head-form accelerations and injury criteria for helmeted and unhelmeted impacts. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2014, 70, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, N.J.; Gilchrist, A. Oblique impact testing of bicycle helmets. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2008, 35, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliven, E.; Rouhier, A.; Tsai, S.; Willinger, R.; Bourdet, N.; Deck, C.; Madey, S.M.; Bottlang, M. Evaluation of a novel bicycle helmet concept in oblique impact testing. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2019, 124, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, K.; Dau, N.; Feist, F.; Deck, C.; Willinger, R.; Madey, S.M.; Bottlang, M. Angular Impact Mitigation system for bicycle helmets to reduce head acceleration and risk of traumatic brain injury. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2013, 59, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.; Mohan, D. An improved motorcycle helmet design for tropical climates. Appl. Ergon. 1993, 24, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-L.; Li, L.-P.; Cai, Q.-E. Motorcycle helmet use in southern china: An observational study. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2008, 9, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalkidou, A.; Petridou, E.; Papadopoulos, F.C.; Dessypris, N.; Trichopoulos, D. Factors affecting motorcycle helmet use in the population of Greater Athens, Greece. Inj. Prev. 1999, 5, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servadei, F.; Begliomini, C.; Gardini, E.; Giustini, M.; Taggi, F.; Kraus, J. Effect of Italy’s motorcycle helmet law on traumatic brain injuries. Inj. Prev. 2003, 9, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASHRAE. ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 55 2010—Thermal Environmental Conditions for Human Occupancy; ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Reardon, F.D.; Leppik, K.E.; Wegmann, R.; Webb, P.; Ducharme, M.B.; Kenny, G.P. The Snellen human calorimeter revisited, re-engineered and upgraded: Design and performance characteristics. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2006, 44, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hambraeus, L.; Sjodin, A.; Webb, P.; Forslund, A.; Hambraeus, K.; Hambraeus, T. A suit calorimeter for energy-balance studies on humans during heavy exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1994, 68, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, G.L.; Flouris, A.D.; Plyley, M.J.; Cheung, S.S. The effect of a covert manipulation of ambient temperature on heat storage and voluntary exercise intensity. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 105, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruyne, G.; Aerts, J.M.; Van Der Perre, G.; Goffin, J.; Verpoest, I.; Berckmans, D. Spatial differences in sensible and latent heat losses under a bicycle helmet. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhwiler, P.A. Heated, perspiring manikin headform for the measurement of headgear ventilation characteristics. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2003, 14, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.; Tai, C.; Chen, T. Improving thermal properties of industrial safety helmets. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2000, 26, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysekera, J.D.A.; Holmer, I.; Dupuis, C. Heat-transfer characteristics of industrial safety helmets. In Towards Human Work. Solutions to Problems in Occupational Health and Safety; Taylor and Francis Group: London, UK, 1991; pp. 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Osczevski, R.J. Design and Evaluation of a Three-Zone Thermal Manikin Head; Defense and Civil Institute of Environmental Medicine: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1996; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.X.; Holmer, I. Evaporative heat-transfer characteristics of industrial safety helmets. Appl. Ergon. 1995, 26, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.; Wang, E.L. A system for quantifying the cooling effectiveness of bicycle helmets. J. Biomech. Eng.-Trans. Asme 2000, 122, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghani, S.; Elbialy, E.M.A.A.; Bakochristou, F.; Gamaledin, S.M.A.; Rashwan, M.M. The effect of forced convection and PCM on helmets’ thermal performance in hot and arid environments. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 111, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, N.; Psikuta, A.; Corberan, J.M.; Rossi, R.M.; Annaheim, S. Multi-sector thermo-physiological head simulator for headgear research. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, S.; Sawada, S. Effects of ventilation openings in industrial safety helmets on evaporative heat dissipation. J. Occup. Health 2019, 61, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, L.; Vircondelet, C.; Jermy, M. Thermal comfort and drag of a streamlined cycling helmet as a function of ventilation hole placement. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part P-J. Sports Eng. Technol. 2018, 232, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogerd, C.P.; Aerts, J.-M.; Annaheim, S.; Bröde, P.; De Bruyne, G.; Flouris, A.D.; Kuklane, K.; Sotto Mayor, T.; Rossi, R.M. A review on ergonomics of headgear: Thermal effects. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2015, 45, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhwiler, P.A.; Ducas, C.; Huber, R.; Bishop, P.A. Bicycle helmet ventilation and comfort angle dependence. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 92, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, N.; Psikuta, A.; Rossi, R.M.; Corberan, J.M.; Annaheim, S. Global and local heat transfer analysis for bicycle helmets using thermal head manikins. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2016, 53, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhwiler, P.A. Role of the visor in forced convective heat loss with bicycle helmets. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2009, 39, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogerd, C.P.; Bruhwiler, P.A.; Heus, R. The effect of rowing headgear on forced convective heat loss and radiant heat gain on a thermal manikin headform. J. Sport Sci. 2008, 26, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyne, G.; Aerts, J.M.; Vander Sloten, J.; Goffin, J.; Verpoest, I.; Berckmans, D. Quantification of local ventilation efficiency under bicycle helmets. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2012, 42, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhwiler, P.A.; Buyan, M.; Huber, R.; Bogerd, C.P.; Sznitman, J.; Graf, S.F.; Rosgen, T. Heat transfer variations of bicycle helmets. J. Sport Sci. 2006, 24, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, T.Y.; Subic, A.; Takla, M.; Pang, T.Y.; Subic, A.; Takla, M. Evaluation of thermal and evaporative resistances in cricket helmets using a sweating manikin. Appl. Ergon. 2014, 45, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogerd, C.P.; Bruhwiler, P.A. Heat loss variations of full-face motorcycle helmets. Appl. Ergon. 2009, 40, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruhwiler, P.A. Radiant heat transfer of bicycle helmets and visors. J. Sport Sci. 2008, 26, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljaste, H.; Kuklane, K.; Heidmets, S. Better bicycle helmets for commuters—Evaluation of ventilation. In Proceedings of the International Cycling Safety Conference 2014, Gothenburg, Sweden, 18–19 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Danckaers, F.; Lacko, D.; Verwulgen, S.; De Bruyne, G.; Huysmans, T.; Sijbers, J. A combined statistical shape model of the scalp and skull of the human head. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2018, 591, 538–548. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. ASTM F1291-16. Standard Test Method for Measuring the Thermal Insulation of Clothing Using a Heated Manikin; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. ASTM F2370-16. Standard Test Method for Measuring the Evaporative Resistance of Clothing Using a Sweating Manikin; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mukunthan, S.; Kuklane, K.; Huysmans, T.; De Bruyne, G. A comparison between physical and virtual experiments of convective heat transfer between head and bicycle helmet. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2018, 591, 517–527. [Google Scholar]
- Weiner, J.S. The regional distribution of sweating. J. Physiol. 1945, 104, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadel, E.R.; Mitchell, J.W.; Stolwijk, J.A.J. Control of local and total sweating during exercise transients. Int. J. Biometeorol. 1971, 15, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IUPS. Glossary of terms for thermal physiology. Jpn. J. Physiol. 2001, 51, 245–280. [Google Scholar]
- Fanger, P.O. Thermal Comfort: Analysis and Applications in Environmental Engineering; McGraw-Hill Book Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.E.; Edholm, O.G. Man and his thermal environment. J. Am. Soc. Nav. Eng. 1958, 70, 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.W.; Paskaluk, S.; Sati, R.; Crown, E.M.; Dale, J.D.; Ackerman, M. Thermal protective performance of protective clothing used for low radiant heat protection. Text. Res. J. 2011, 81, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccullough, E.A. Factors Affecting the resistance to heat-transfer provided by clothing. J. Therm. Biol. 1993, 18, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havenith, G.; Holmer, I.; Parsons, K. Personal factors in thermal comfort assessment: Clothing properties and metabolic heat production. Energy Build. 2002, 34, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.M.; Fan, J.T. Interactions of the surface heat and moisture transfer from the human body under varying climatic conditions and walking speeds. Appl. Ergon. 2006, 37, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osczevski, R.J. The Basis of Wind Chill. Arctic 1995, 48, 313–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishodia, B.S.; Sanghi, S.; Mahajan, P. Computational and subjective assessment of ventilated helmet with venturi effect and backvent. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2018, 68, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).