A Novel Hybrid Fuzzy Grey TOPSIS Method: Supplier Evaluation of a Collaborative Manufacturing Enterprise
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Preliminaries
3.1. The λ-Fuzzy-Measure and the Choquet Integral
3.2. The Correlation Coefficients
3.3. The Triangle Fuzzy Number
3.4. The Entropy Weight Method
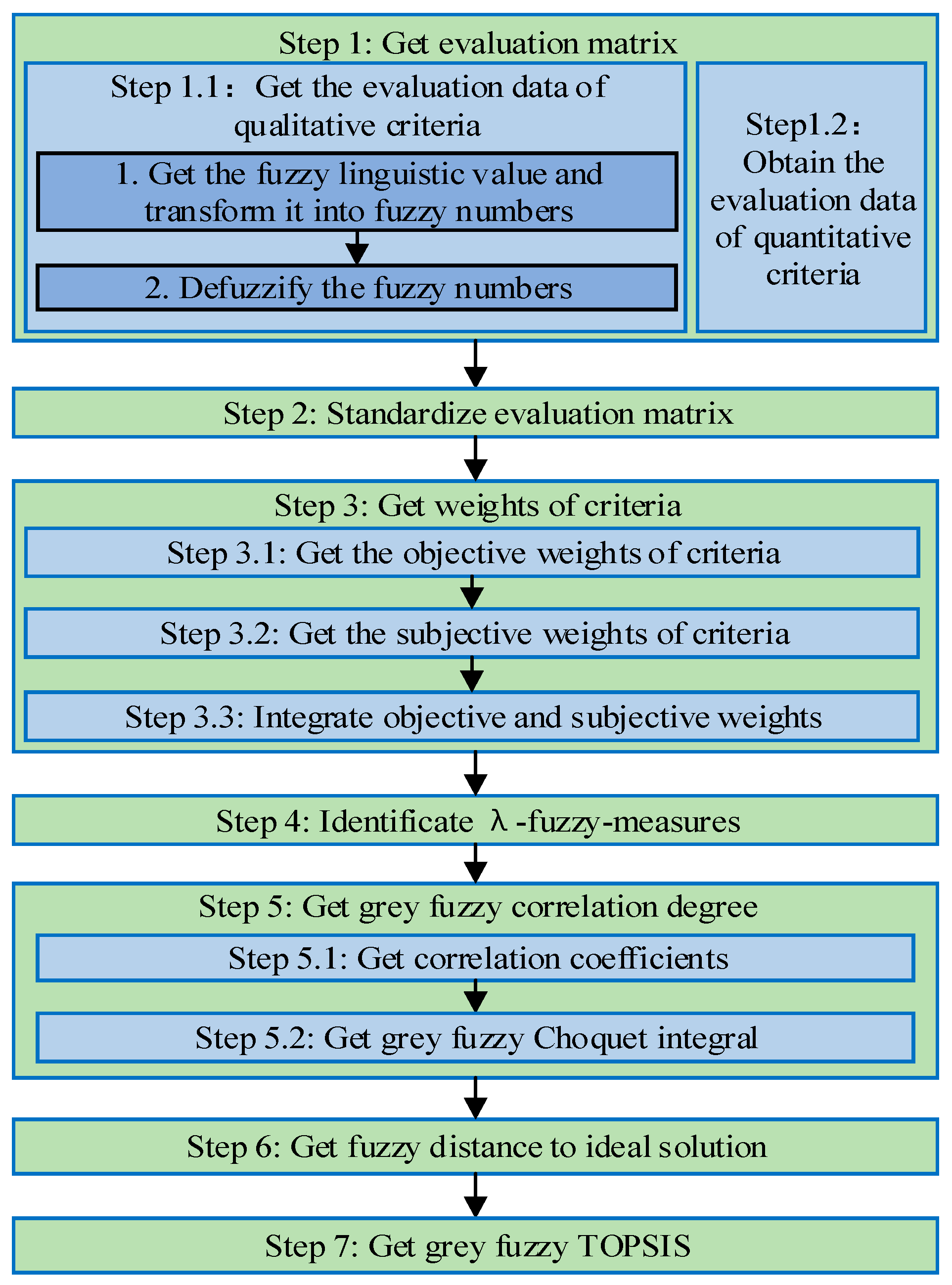
4. The Fuzzy Grey TOPSIS Method
4.1. Background
4.2. The Procedure of Fuzzy Grey TOPSIS
4.2.1. Obtain the Fuzzy Linguistic Value and Transform it into Fuzzy Numbers
4.2.2. Defuzzify the Fuzzy Numbers
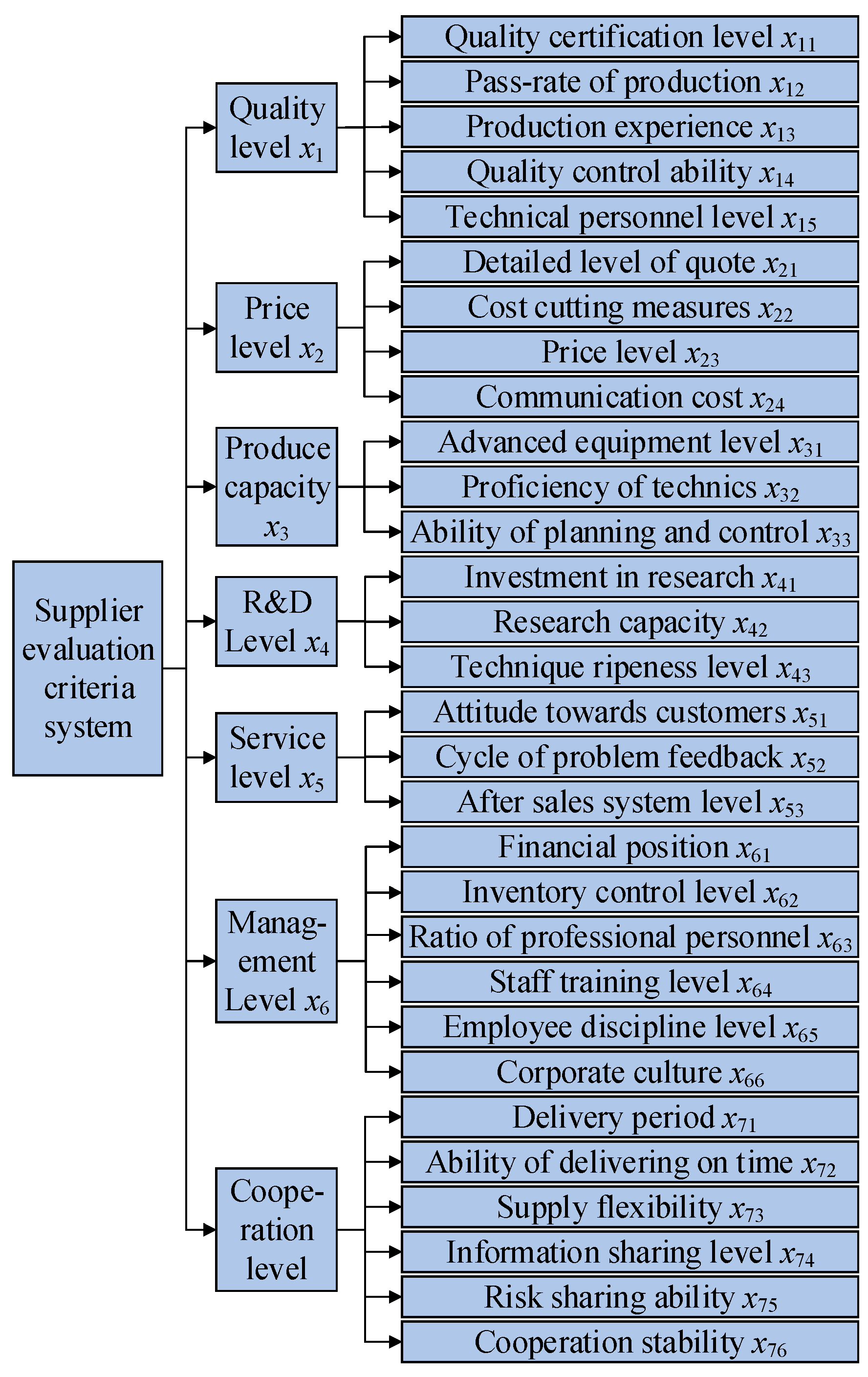
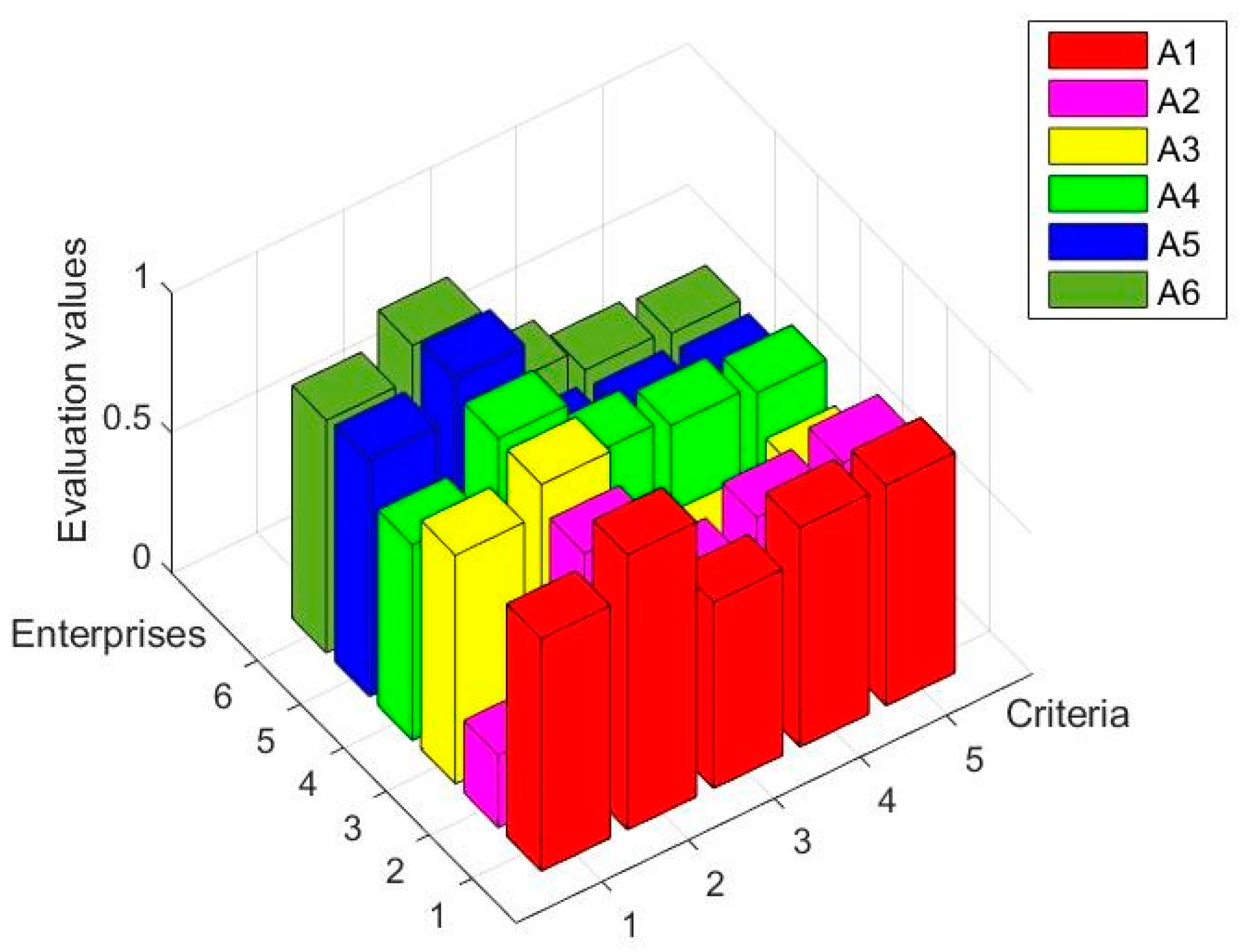
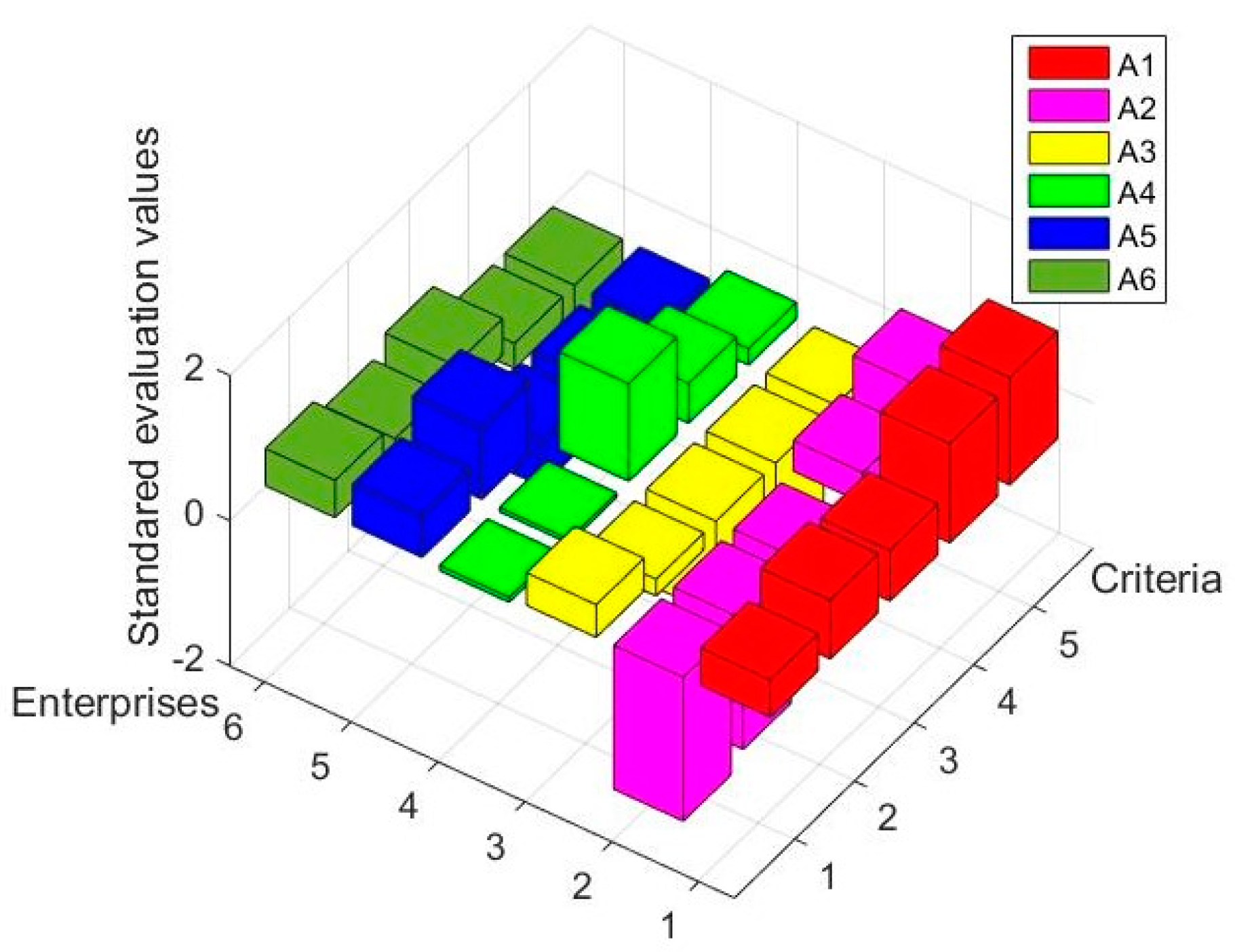
5. An Illustrative Example
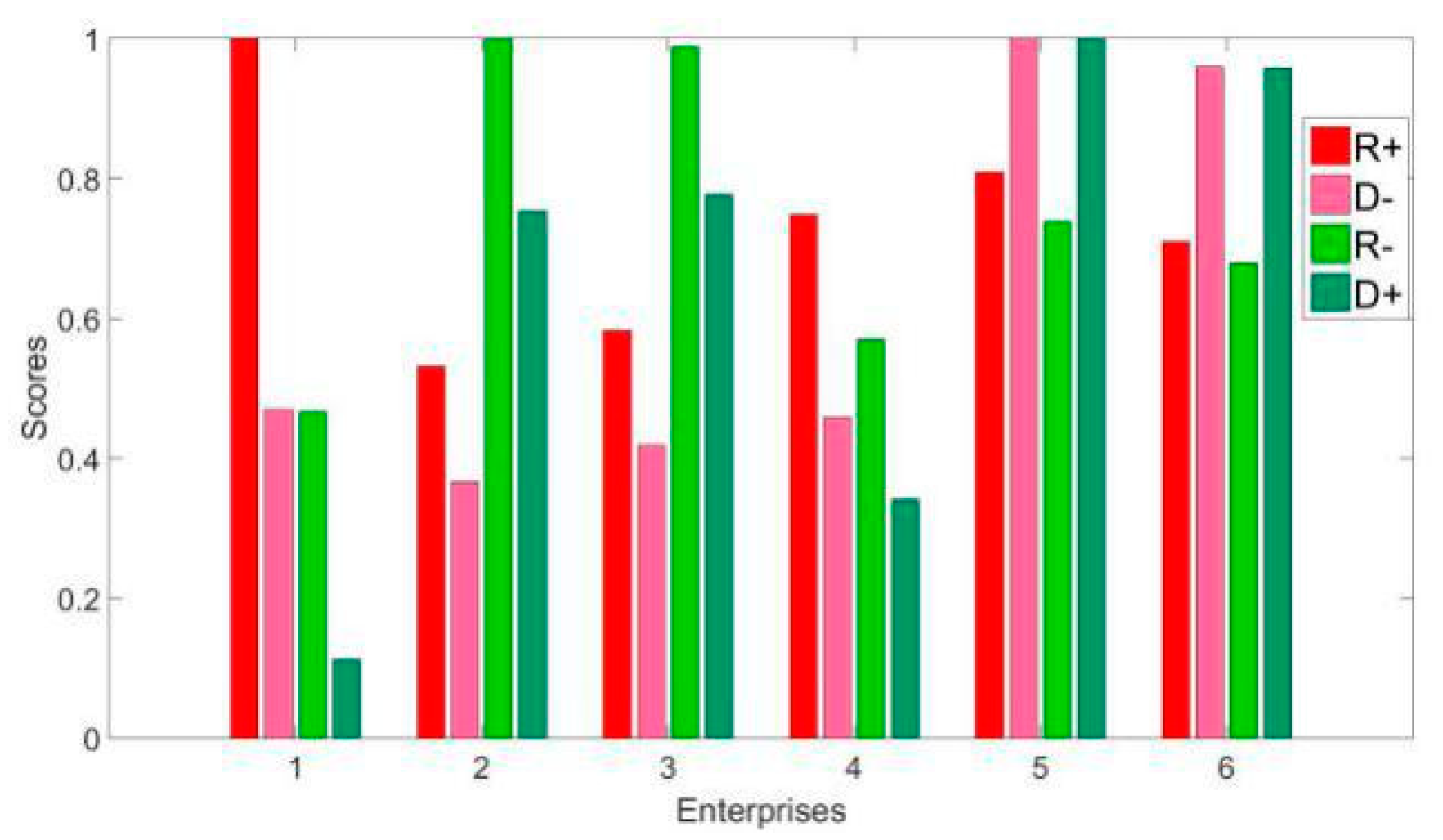
5.1. Conducting the Proposed Method
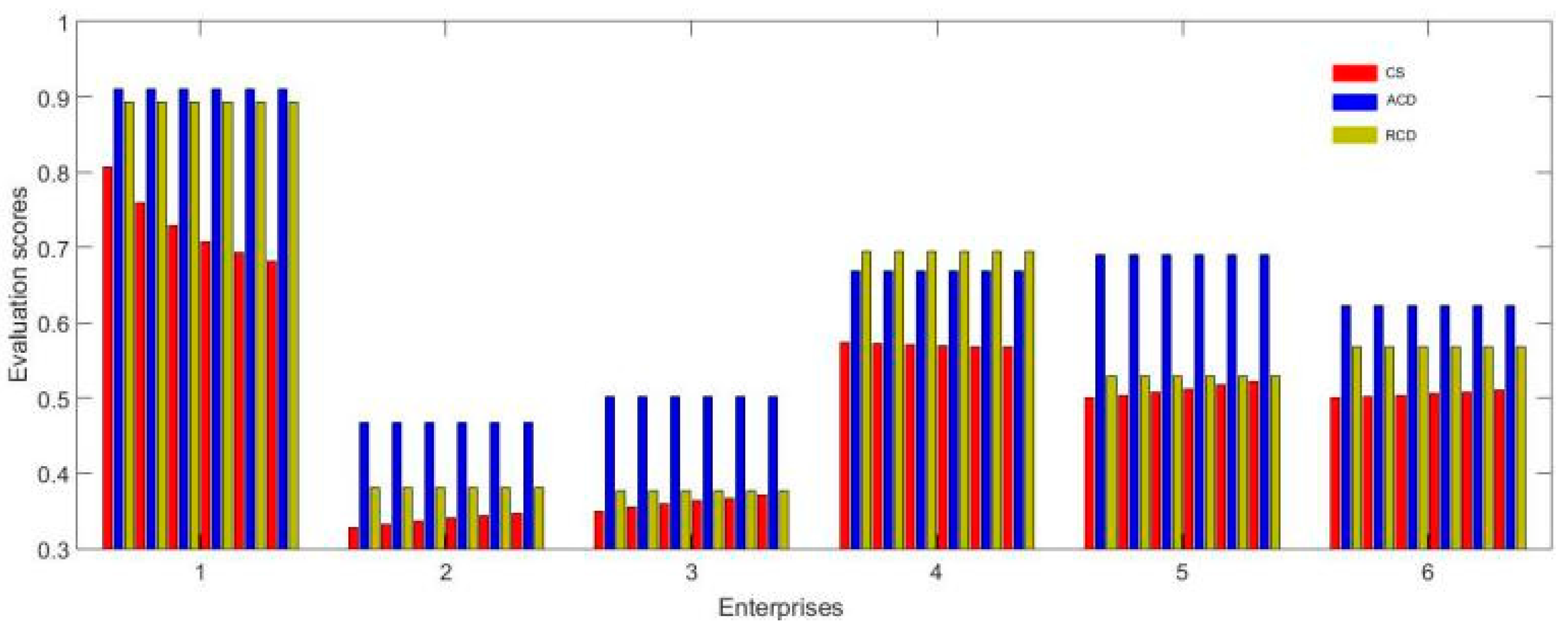
5.2. Comparisons and Sensitivity Analysis
5.3. Result Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Notations and Nomenclature
| The objects set. | |
| The criterion set. | |
| The evaluation value of the i-th object on the k-th qualitative criterion in the form of fuzzy number, . For the convenience, is presented in a simplified form as . | |
| The numerical results of defuzzification of through methods 1, 2, and 3. | |
| Numerical evaluation matrix of qualitative criteria. | |
| The evaluation value of the i-th object on the k-th criterion, . | |
| Evaluation matrix. | |
| The standardized evaluation value of the i-th object on the k-th criterion, . | |
| Standardized evaluation matrix. | |
| Positive ideal solution scheme. | |
| Negative ideal solution scheme. | |
| Positive correlation matrix. | |
| Negative correlation matrix. | |
| Objective weights vector. | |
| Subjective weights vector. | |
| Comprehensive weights vector. | |
| λ | Parameter of λ-fuzzy-measures. |
| The fuzzy measure of the subset of power set of . For example, represents a set consisting of . For convenience, is presented in a simplified form as . | |
| Positive grey fuzzy integral vector. | |
| Negative grey fuzzy integral vector. | |
| Positive fuzzy ideal solution distance. | |
| Negative fuzzy ideal solution distance. | |
| Positive comprehensive proximity degree vector. | |
| Negative comprehensive proximity degree vector. | |
| Comprehensive evaluation vector. |
References
- Gumus, S.; Egilmez, G.; Kucukvar, M.; Shin Park, Y. Integrating expert weighting and multi-criteria decision making into eco-efficiency analysis: The case of US manufacturing. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2016, 67, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.X.; You, J.X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, H.C. An integrated linguistic MCDM approach for robot evaluation and selection with incomplete weight information. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2016, 110, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.Y.; Hu, S.K.; Tzeng, G.H. Financial modeling and improvement planning for the life insurance industry by using a rough knowledge based hybrid MCDM model. Inf. Sci. 2017, 375, 296–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Kannan, D.; Shankar, M. Evaluation of green manufacturing practices using a hybrid mcdm model combining danp with promethee. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.J.; Tamošaitienė, J.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Tzeng, G.H. New hybrid COPRAS-G MADM model for improving and selecting suppliers in green supply chain management. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 263, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Parkan, C. A preemptive goal programming method for aggregating OWA operator weights in group decision making. Inf. Sci. 2007, 177, 1867–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.F.; Lin, F.M. An application of multi-attribute value theory to patient-bed assignment in hospital admission management: An empirical study. J. Healthc. Eng. 2014, 5, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrance, G.W.; Boyle, M.H.; Horwood, S.P. Application of multi-attribute utility theory to measure social preferences for health states. Oper. Res. 1982, 30, 1043–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Hu, H.; Yu, K.; Li, Z. Research on self-healing restoration strategy of urban power grid based on multi-agent technology. In 2011 International Conference on Advanced Power System Automation and Protection; IEEE: Piscatville, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1215–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Serv. Sci. 2008, 1, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, W.D. Data envelopment analysis: A comprehensive text with models, applications, references and DEA-solver software. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2001, 52, 1408–1409. [Google Scholar]
- Boran, F.E.; Genç, S.; Kurt, M.; Akay, D. A multi-criteria intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making for supplier selection with TOPSIS method. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 11363–11368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.D.; Zhang, H.H.; Feng, Y.; Jia, H.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, P. Operation patterns analysis of automotive components remanufacturing industry development in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 64, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Chen, S.F.; Sun, Y.; Qi, X. Study and implementation on the grey comprehensive evaluation support system of ecocity. J. Southeast Univ. (Engl. Ed.) 2002, 18, 356–360. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, L.; Jin, C. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation for carrying capacity of regional water resources. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 2505–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfield, J.J. Artificial neural networks. IEEE Circuits Devices Mag. 1988, 4, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, N.; Sahu, A.K.; Datta, S.; Mahapatra, S.S. Evaluation and selection of suppliers considering green perspectives: Comparative analysis on application of FMLMCDM and fuzzy-TOPSIS. Benchmarking 2016, 23, 1579–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Torabi, S.A.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. A hierarchical group decision-making approach for new product selection in a fuzzy environment. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2013, 38, 3233–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Jolai, F.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Vahdani, B. A fuzzy grey model based on the compromise ranking for multi-criteria group decision making problems in manufacturing systems. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2013, 24, 819–827. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Vahdani, B.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Tajik, N. Soft computing based on a fuzzy grey compromise solution approach with an application to the selection problem of material handling equipment. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2014, 27, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Mirdamadi, S.; Siadat, A.; Dantan, J.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. An intuitionistic fuzzy grey model for selection problems with an application to the inspection planning in manufacturing firms. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2015, 39, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Vahdani, B. Cross-docking location selection in distribution systems: A new intuitionistic fuzzy hierarchical decision model. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2016, 9, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, H.; Bazargan, J.; Mousavi, S.M. A compromise ratio method with an application to water resources management: An intuitionistic fuzzy set. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2029–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V.; Auriol, G. Hipel, K.W. Multicriteria decision-making methodology for systems engineering. IEEE Syst. J. 2016, 10, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.; Zhang, S.; Lee, L.H.; Chew, E.P.; Chen, C.H. Improving analytic hierarchy process expert allocation using optimal computing budget allocation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2016, 46, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, H.B.; Bashar, M.A.; Hipel, K.W.; Kilgour, D.M. Grey-based preference in a graph model for conflict resolution with multiple decision makers. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2015, 45, 1254–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özpeynirci, Ö.; Özpeynirci, S.; Kaya, A. An interactive approach for multiple criteria selection problem. Compu. Oper. Res. 2017, 78, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Shi, P.; Liu, H.; Xu, S. Neural-network-based decentralized adaptive output-feedback control for large-scale stochastic nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 2012, 42, 1608–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.A.M. An interactive Bi-criteria heuristic algorithm for the coherent system assembly. In 2014 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management; IEEE: Piscatville, NJ, USA, 2015; Volume 25, pp. 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.; Xu, Z.; Zeng, X.J. Hesitant fuzzy linguistic vikor method and its application in qualitative multiple criteria decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 23, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, A.F.; Cheng, W.W.; Hullermeier, E. Preference learning using the Choquet integral: The case of multipartite ranking. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2012, 20, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Wu, L.; Shi, P.; Song, Y.D. H-infinity model reduction of takagi–sugeno fuzzy stochastic systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 2012, 42, 1574–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Induced generalized hesitant fuzzy Shapley hybrid operators and their application in multi-attribute decision making. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 28, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Geng, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H. Study of decision framework of wind farm project plan selection under intuitionistic fuzzy set and fuzzy measure environment. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 87, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugeno, M. Fuzzy measure and fuzzy integral. Trans. Soc. Instrum. Control Eng. 1972, 2, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesiar, R.; Mesiarova-Zemenkova, A. Ahmad, K. Level-dependent Sugeno integral. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2009, 17, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Chen, H.C. Choquet integral-based hierarchical networks for evaluating customer service perceptions on fast food stores. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 7880–7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z. Fuzzy Measure and Fuzzy Integral and Its Application in Classifier Technology; Science Publishing Company: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Chen, J.F.; Yuan, X.Q.; Li, J. Choquet fuzzy integral aggregation based on g-lambda fuzzy measure. In 2007 International Conference on Wavelet Analysis and Pattern Recognition; IEEE: Piscatville, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Dymova, L.; Sevastjanov, P.; Tikhonenko, A. An interval type-2 fuzzy extension of the topsis method using alpha cuts. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 83, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, K.; Jiang, Q. Optimization of a straw ring-die briquetting process combined analytic hierarchy process and grey correlation analysis method. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 152, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzarour-Amokrane, Y.; Tchangani, A.; Peres, F. A bipolar consensus approach for group decision making problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 1759–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tchangani, A.P. Bipolar aggregation method for fuzzy nominal classification using Weighted Cardinal Fuzzy Measure (WCFM). J. Uncertain Syst. 2013, 7, 138–151. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.H.; Peng, Y.; Hou, L.; Tian, G.D.; Li, Z.W. A hybrid multi-objective optimization approach for energy-absorbing structures in train collisions. Inf. Sci. 2019, 481, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi-Nasab, S.H.; Sotoudeh-Anvari, A. A new multi-criteria decision making approach for sustainable material selection problem: A critical study on rank reversal problem. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 466–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.N.; Hawas, Y.E.; Ahmed, K. A multi-dimensional framework for evaluating the transit service performance. Trans. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2013, 50, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazançoğlu, Y.; Kazançoğlu, İ. Benchmarking service quality performance of airlines in Turkey. Eskişehir Osman. Üniversitesi İktis. ve İdari Bilim. Derg. 2013, 8, 59–91. [Google Scholar]
- Bagočius, V.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z. Selecting a location for a liquefied natural gas terminal in the Eastern Baltic Sea. Transport 2014, 29, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayla, A.Y.; Oztekin, A.; Gumus, A.T.; Gunasekaran, A. A hybrid data analytic methodology for 3PL transportation provider evaluation using fuzzy multi-criteria decision making. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 6094–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Yang, Z.; Riahi, R.; Wang, J. Application of a collaborative modelling and strategic fuzzy decision support system for selecting appropriate resilience strategies for seaport operations. J. Traffic Trans. Eng. 2014, 1, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanian, A.; Savadogo, O. TOPSIS multiple-criteria decision support analysis for material selection of metallic bipolar plates for polymer electrolyte fuel cell. J. Power Source 2006, 159, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.L. Comparison of weights in TOPSIS models. Math. Comput. Model. 2004, 40, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Yeh, C.H.; Willis, R.J. Inter-company comparison using modified TOPSIS with objective weights. Comput. Oper. Res. 2000, 27, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukozkan, G.; Cifci, G. A combined fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS based strategic analysis of electronic service quality in healthcare industry. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 2341–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Susinskas, S.; Daniunas, A.; Turskis, Z.; Sivilevicius, H. Multiple criteria selection of pile-column construction technology. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2012, 18, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukozkan, G.; Cifci, G. A novel hybrid MCDM approach based on fuzzy DEMATEL, fuzzy ANP and fuzzy TOPSIS to evaluate green suppliers. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 3000–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z.; Volvaciovas, R.; Kildiene, S. Multi-criteria assessment model of technologies. Stud. Inform. Control 2013, 22, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z.; Tamosaitiene, J. Risk assessment of construction projects. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2010, 16, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Payam, A.F. A comparative study on material selection of micro-electromechanical systems electrostatic actuators using Ashby, VIKOR and TOPSIS. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, S.; Matarazzo, B.; Slowinski, R. Rough sets theory for multicriteria decision analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 129, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakoulaki, D.; Karangelis, F. Multi-criteria decision analysis and cost-benefit analysis of alternative scenarios for the power generation sector in Greece. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohekar, S.; Ramachandran, M. Application of multi-criteria decision making to sustainable energy planning-a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2004, 8, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; Jia, H. Green decoration materials selection under interior environment characteristics: a grey-correlation based hybrid MCDM Method. Renew. Sustain. Energy. Rev. 2018, 81, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.H.; Karimi, A.; Aghakhani, N.; Kalantar, P. A grey-besed carbon management model for green supplier selection. In 2013 IEEE International Conference on Grey systems and Intelligent Services (GSIS); IEEE: Piscatville, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 26, pp. 402–405. [Google Scholar]
- Sarucan, A.; Baysal, M.E.; Kahraman, C.; Engin, O. A hierarchy grey relational analysis for selecting the renewable electricity generation technologies. Lect. Notes Eng. Comput. Sci. 2011, 2, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Keshavarz, A. Prime mover selection for a residential micro CCHP by using two multi-criteria decision-making methods. Energy Build. 2012, 55, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Jing, Y.; Zheng, G. Using the fuzzy multi-criteria model to select the optimal cool storage system for air conditioning. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 2059–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J. Review on multi-criteria decision analysis aid in sustainable energy decision-making. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2263–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Lin, Y. Evaluating and ranking energy performance of office buildings using grey relational analysis. Energy 2011, 36, 2551–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhang, L.B.; Hameedullah, M. Determination of optimum parameters for multi-performance characteristics in turning by using grey relational analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 63, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydin, N.; Celik, E.; Gumus, A.T. A hierarchical customer satisfaction framework for evaluating rail transit systems of Istanbul. Trans. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2015, 77, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, E.; Aydin, N.; Gumus, A.T. A multiattribute customer satisfaction evaluation approach for rail transit network: a real case study for Istanbul, Turkey. Transp. Policy 2014, 36, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Tian, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, J. Target disassembly sequencing and scheme evaluation for CNC machine tools using improved multiobjective ant colony algorithm and fuzzy integral. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Hao, N.; Zhou, M.; Pedrycz, W.; Zhang, C.; Ma, F.; Li, Z. Fuzzy Grey Choquet Integral for Evaluation of Multicriteria Decision Making Problems with Interactive and Qualitative Indices. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.L.; Liu, Y.T.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Chuang, C.H.; Lin, C.T. Fuzzy integral with particle swarm optimization for a Motor-Imagery-Based Brain-Computer interface. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 25, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhu, C.X.; Zhang, X.Z. Method for hesitant fuzzy multi-attribute decision making based on rough sets. Control Decis. 2014, 29, 1335–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Zhao, J. Multiple attribute making method based on hesitation institution fuzzy number. Syst. Eng. 2014, 32, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Lee, P.; Chang, T.; Ting, H. Multi-attribute group decision making model under the condition of uncertain information. Autom. Constr. 2008, 17, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, L.H. Method based on fuzzy integral about construction and optimization of supply chain networks. Comput. Eng. Appl. 1983, 9, 173–175. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, T.; Feng, S.; Bi, X.L. Chang, L. Grey correlation analysis and applications of drill stem failure in drilling engineering. In 2010 Seventh International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery; IEEE: Piscatville, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 4, pp. 1699–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J. Study on Measuring and Evaluating Product Innovation of Small and Medium Enterprises; Harbin University of Science and Technology: Harbin, China, 2003. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, A.; Romero, I. Environmental conflict analysis using an integrated grey clustering and entropy-weight method: A case study of a mining project in Peru. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 77, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.; Herrera, F.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Martinez, L. Combining numerical and linguistic information in group decision making. Inf. Sci. 1998, 107, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, F.; Martinez, L. An approach for combining linguistic and numerical information based on the 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model in decision-making. Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness Knowl. Based Syst. 2011, 8, 539–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, B.J.; Xu, W.; Jin, G.; Zhang, X. Application and suitability analysis of the key technologies in nearly zero energy buildings in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy. Rev. 2019, 101, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Zhou, M.; Li, P. Disassembly sequence planning considering fuzzy component quality and varying operational cost. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2018, 15, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, A.F.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M. Red Deer Algorithm (RDA); a new optimization algorithm inspired by Red Deers’ mating. In International Conference on Industrial Engineering; IEEE: Piscatville, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume 12, pp. 331–342. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C.; Li, Z.W.; Wu, N.Q.; Khalgui, M.; Qu, T.; Al-Ahmari, A. Improved multi-step look-ahead control policies for automated manufacturing systems. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 68824–68838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. The social engineering optimizer (SEO). Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 72, 267–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M. A set of efficient heuristics and metaheuristics to solve a two-stage stochastic bi-level decision-making model for the distribution network problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 123, 378–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. A bi-objective green home health care routing problem. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Tian, G.; Li, Z.; Hu, H.; Zheng, H. Flexible process planning and end-of-life decision-making for product recovery optimization based on hybrid disassembly. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2019, 16, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Ren, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, H.; Tan, J. Modeling and Planning for Dual-Objective Selective Disassembly Using AND/OR Graph and Discrete Artificial Bee Colony. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 2456–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Typical Reference | Tool Type | Advantage | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hassan et al. [46] | TOPSIS | Flexible framework | Experts have too many rights |
| Kazançoğlu et al. [47] | Fuzzy TOPSIS | Simple | Hard to describe complex systems |
| Bagočius et al. [48] | TOPSIS and COPRAS, SAW | Various comparison | Hard to describe complex systems |
| Yayla et al. [49] | Fuzzy TOPSIS and Fuzzy-AHP | More realistic and reliable | Complicated and abstract models |
| John et al. [50] | Fuzzy TOPSIS and Fuzzy-AHP | More realistic and reliable | Complicated and abstract models |
| Shanian and Savadogo [51] | Ordinary and Block TOPSIS | Simple and fast | Complicated |
| Olson [52] | TOPSIS | Simple and fast | Not accurate enough |
| Deng et al. [53] | Weighted Euclidean distances TOPSIS | Simple and direct | Not accurate enough |
| Buyukozkan and Cifci [54,55] | Fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS | Solving the uncertainty problem of score evaluation | Hard to describe complex systems |
| Zavadskas et al. [56,57,58] | TOPSIS, COPRAS, and ARAS | Aggregate both quantitative and qualitative criteria | Complicated and abstract models |
| Yazdani and Payam [59] | Ashby, VIKOR, and TOPSIS | Various comparison | Complicated and abstract models |
| Typical Reference | Tool Type | Advantage | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greco et al. [60] | Rough sets theory and MCDA | The use of the decision rule model and the capacity | Too simple |
| Diakoulaki and Karangelis [61] | MCDA and CBA | Broadening the evaluation perspective | Each method is often disputed |
| Pohekar and Ramachandran [62] | MCDM, PROMETHEE, and ELECTRE | Compare in a variety of ways | Thinking not deep enough |
| Tian et al. [63] | GRA and AHP | Simple and fast | Dependent on index selection |
| Hashemi et al. [64] | Improved grey relational analysis | Novel and convenient | Hard to describe complex systems |
| Sarucan et al. [65] | AHP and GRA | More realistic and reliable | Complicated and abstract models |
| Ebrahimi and Keshavarz [66] | FA and GIA | Two-phase comparison results are consistent | Complicated and abstract models |
| Wang et al. [67,68] | Fuzzy and weighting method | More realistic and reliable | Theory still flawed |
| Lee and Lin [69] | GRA | Reasonable and efficient | The reference factor is not enough |
| Abhang and Hameedullah [70] | Grey relational analysis | Effectively improve accuracy | Complicated and abstract models |
| Typical Reference | Tool Type | Advantage | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aydin et al. [71] | Fuzzy-AHP, Choquet integral and trapezoidal fuzzy sets | Realistic and reliable | Complicated and abstract models |
| Celik et al. [72] | VIKOR and interval type-2 fuzzy sets | Effectively improve accuracy | Complicated and abstract models |
| Feng et al. [73] | Fuzzy integral | Convenient | Complicated |
| Tian et al. [74] | Choquet fuzzy integral | Effectively improve accuracy | Complicated |
| Wu et al. [75] | Fuzzy Integral with Particle Swarm Optimization | Solving the uncertainty problem | Dependent on index selection |
| Zhu et al. [76] | Fuzzy multi-attribute decision making | Novel and convenient | Dependent on index selection |
| Fu and Zhao [77] | Hesitation institution fuzzy number | More realistic and reliable | Complicated and abstract model |
| Lin et al. [78] | TOPSIS and aggregation approach | Efficient and robust, realistic and reasonable | Complicated and abstract model |
| Superb (S) | (0.8, 0.9, 0.9) |
| Good (G) | (0.6, 0.7, 0.8) |
| Normal (N) | (0.4, 0.5, 0.6) |
| Bad (B) | (0.2, 0.3, 0.4) |
| Terrible (T) | (0.1, 0.1, 0.2) |
| Sets | Measures | Sets | Measures | Sets | Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2103 | 2 | 0.4069 | 3 | 0.2119 |
| 4 | 0.2404 | 5 | 0.2405 | 12 | 0.5722 |
| 13 | 0.3988 | 14 | 0.4241 | 15 | 0.4242 |
| 23 | 0.5734 | 24 | 0.5958 | 25 | 0.5959 |
| 34 | 0.4255 | 35 | 0.4256 | 45 | 0.4504 |
| 123 | 0.7203 | 124 | 0.7402 | 125 | 0.7402 |
| 134 | 0.5888 | 135 | 0.5888 | 145 | 0.6109 |
| 234 | 0.7413 | 235 | 0.7413 | 245 | 0.7609 |
| 345 | 0.6121 | 1234 | 0.8696 | 1235 | 0.8696 |
| 1245 | 0.8870 | 1345 | 0.7547 | 2345 | 0.8880 |
| 12345 | 1.0000 |
| p | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 | Sequence | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 0 | 0.8073 | 0.3274 | 0.3498 | 0.5737 | 0.5000 | 0.5003 | 1,4,6,5,3,2 |
| ACD | 0 | 0.9097 | 0.4677 | 0.5022 | 0.6684 | 0.6907 | 0.6228 | 1,5,4,6,3,2 |
| RCD | 0 | 0.8929 | 0.3807 | 0.3769 | 0.6949 | 0.5286 | 0.5685 | 1,4,6,5,2,3 |
| CS | 0.2 | 0.7588 | 0.3324 | 0.3550 | 0.5718 | 0.5037 | 0.5020 | 1,4,5,6,2,3 |
| ACD | 0.2 | 0.9097 | 0.4677 | 0.5022 | 0.6684 | 0.6907 | 0.6228 | 1,5,4,6,3,2 |
| RCD | 0.2 | 0.8929 | 0.3807 | 0.3769 | 0.6949 | 0.5286 | 0.5685 | 1,4,6,5,2,3 |
| CS | 0.4 | 0.7286 | 0.3368 | 0.3596 | 0.5704 | 0.5077 | 0.5039 | 1,4,5,6,3,2 |
| ACD | 0.4 | 0.9098 | 0.4677 | 0.5022 | 0.6684 | 0.6907 | 0.6228 | 1,5,4,6,3,2 |
| RCD | 0.4 | 0.8929 | 0.3807 | 0.3769 | 0.6949 | 0.5286 | 0.5685 | 1,4,6,5,2,3 |
| CS | 0.6 | 0.7081 | 0.3406 | 0.364 | 0.5692 | 0.5122 | 0.5060 | 1,4,5,6,3,2 |
| ACD | 0.6 | 0.9098 | 0.4677 | 0.5022 | 0.6684 | 0.6907 | 0.6228 | 1,5,4,6,3,2 |
| RCD | 0.6 | 0.8929 | 0.3807 | 0.3769 | 0.6949 | 0.5286 | 0.5685 | 1,4,6,5,2,3 |
| CS | 0.8 | 0.6932 | 0.3440 | 0.3675 | 0.5682 | 0.5172 | 0.5084 | 1,4,5,6,3,2 |
| ACD | 0.8 | 0.9098 | 0.4677 | 0.5022 | 0.6684 | 0.6907 | 0.6228 | 1,5,4,6,3,2 |
| RCD | 0.8 | 0.8929 | 0.3807 | 0.3769 | 0.6949 | 0.5286 | 0.5685 | 1,4,6,5,2,3 |
| CS | 1 | 0.6819 | 0.3470 | 0.3708 | 0.5674 | 0.5228 | 0.5112 | 1,4,5,6,3,2 |
| ACD | 1 | 0.9098 | 0.4677 | 0.5022 | 0.6684 | 0.6907 | 0.6228 | 1,5,4,6,3,2 |
| RCD | 1 | 0.8929 | 0.3807 | 0.3769 | 0.6949 | 0.5286 | 0.5685 | 1,4,6,5,2,3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, G.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Hao, N.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Tan, J. A Novel Hybrid Fuzzy Grey TOPSIS Method: Supplier Evaluation of a Collaborative Manufacturing Enterprise. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9183770
Feng Y, Zhang Z, Tian G, Fathollahi-Fard AM, Hao N, Li Z, Wang W, Tan J. A Novel Hybrid Fuzzy Grey TOPSIS Method: Supplier Evaluation of a Collaborative Manufacturing Enterprise. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(18):3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9183770
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yixiong, Zhifeng Zhang, Guangdong Tian, Amir Mohammad Fathollahi-Fard, Nannan Hao, Zhiwu Li, Wenjie Wang, and Jianrong Tan. 2019. "A Novel Hybrid Fuzzy Grey TOPSIS Method: Supplier Evaluation of a Collaborative Manufacturing Enterprise" Applied Sciences 9, no. 18: 3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9183770
APA StyleFeng, Y., Zhang, Z., Tian, G., Fathollahi-Fard, A. M., Hao, N., Li, Z., Wang, W., & Tan, J. (2019). A Novel Hybrid Fuzzy Grey TOPSIS Method: Supplier Evaluation of a Collaborative Manufacturing Enterprise. Applied Sciences, 9(18), 3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9183770










