Design of Shape Memory Alloy-Based Soft Wearable Robot for Assisting Wrist Motion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of Muscle-Like Actuator Based on Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) Coil Spring
3. Design of Soft Wrist Assist (SWA)
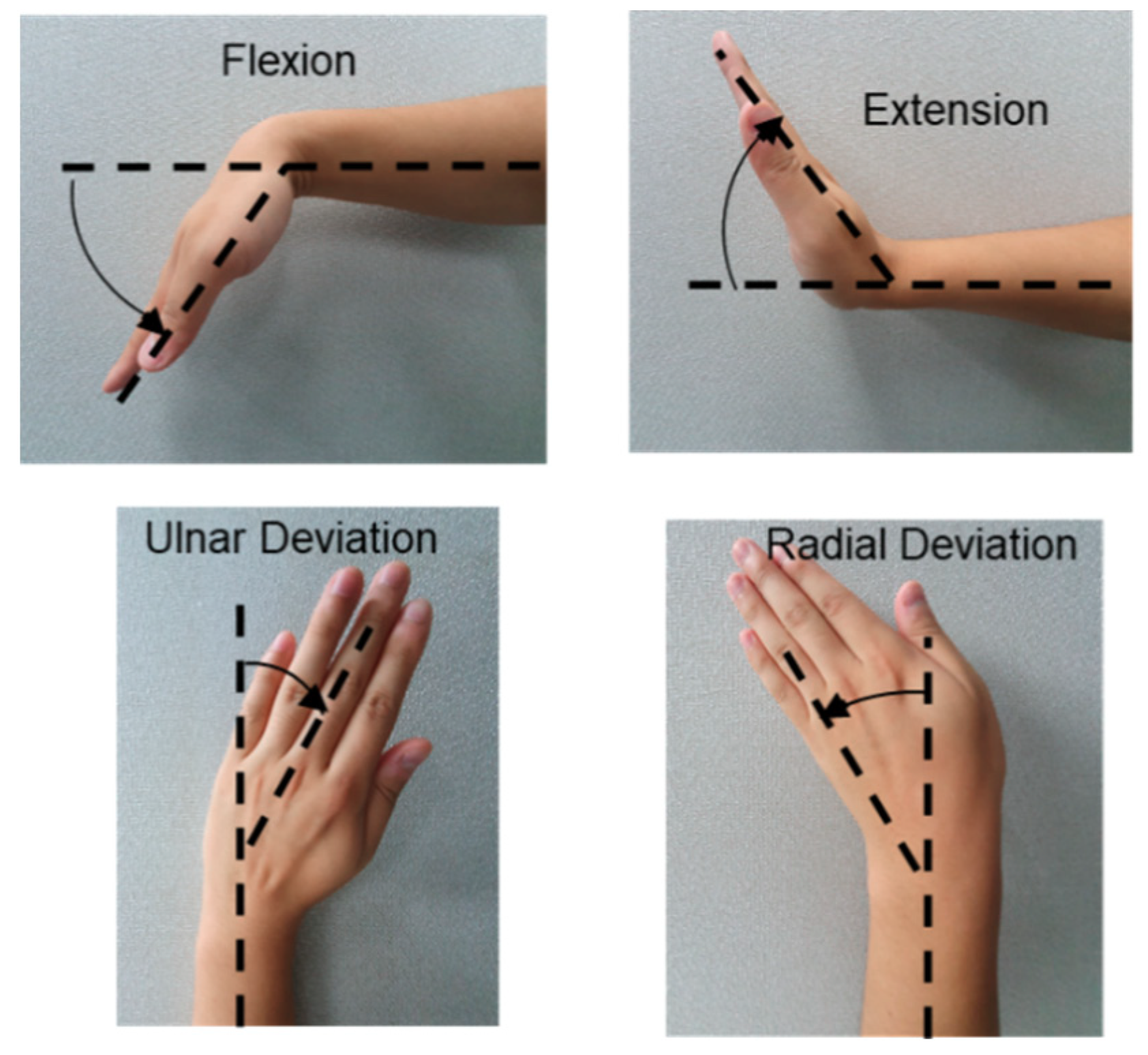
3.1. Mechanism of Wrist Motion
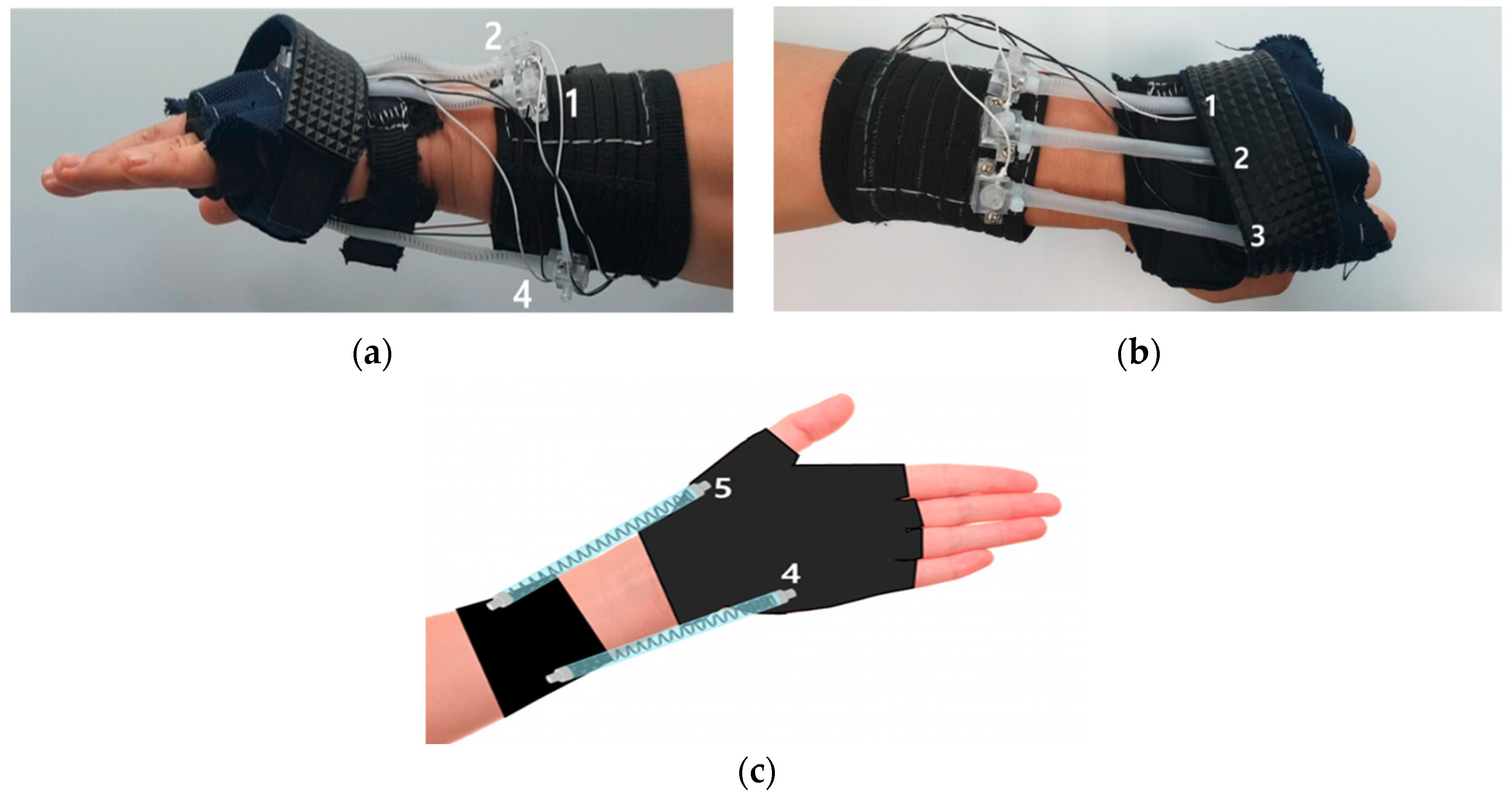
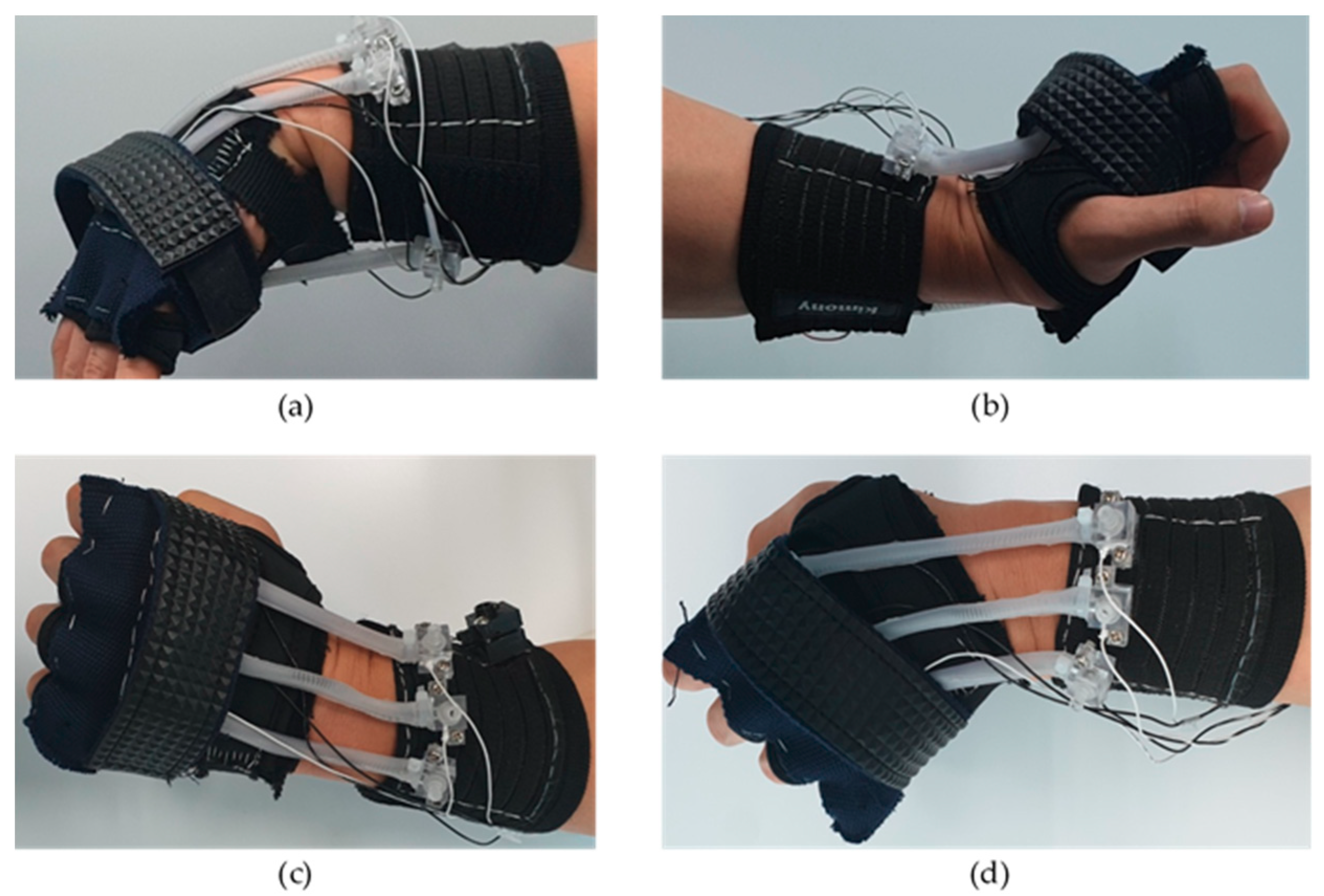
3.2. The Alignment of the Actuator
3.3. Anchor Design
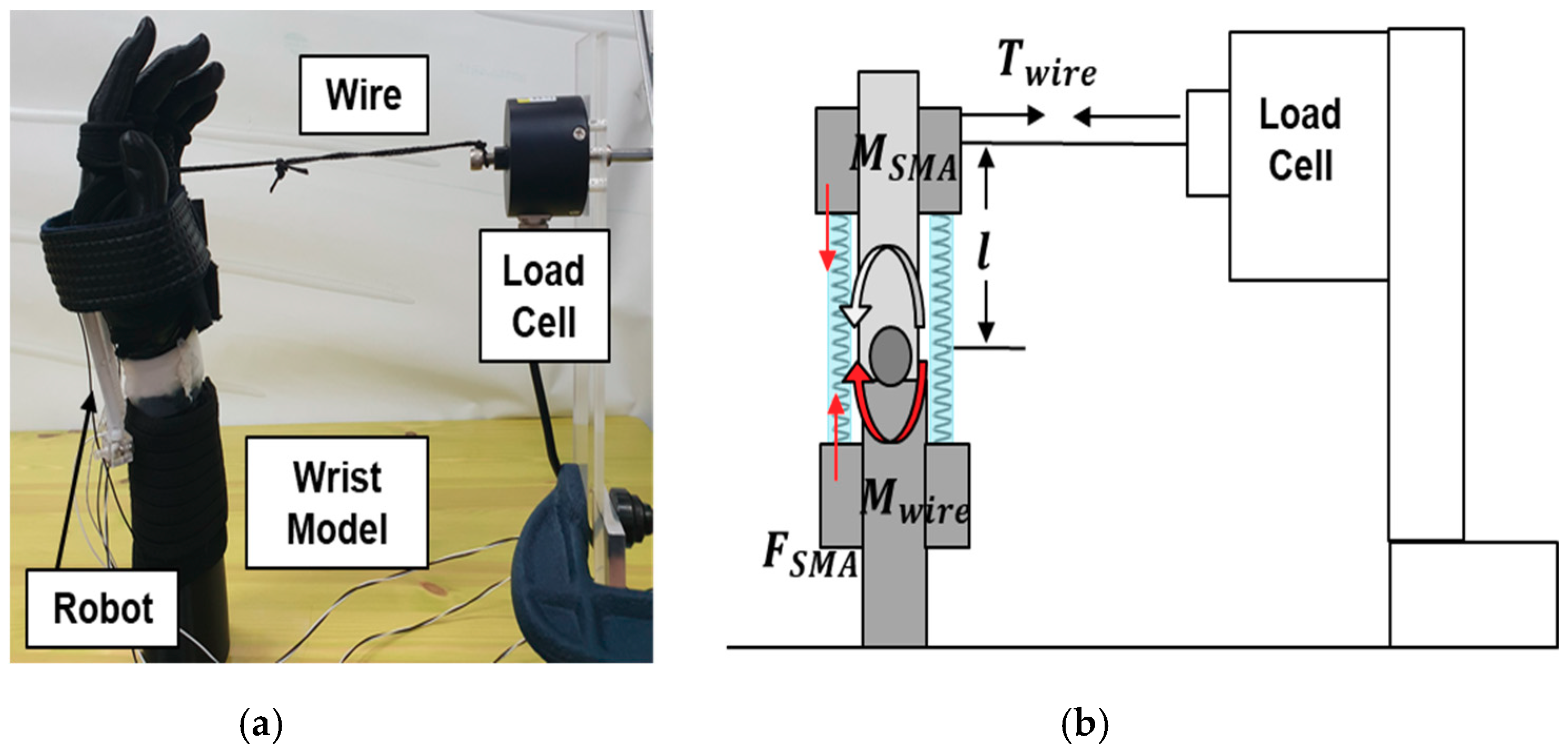
3.4. Torque Evaluation
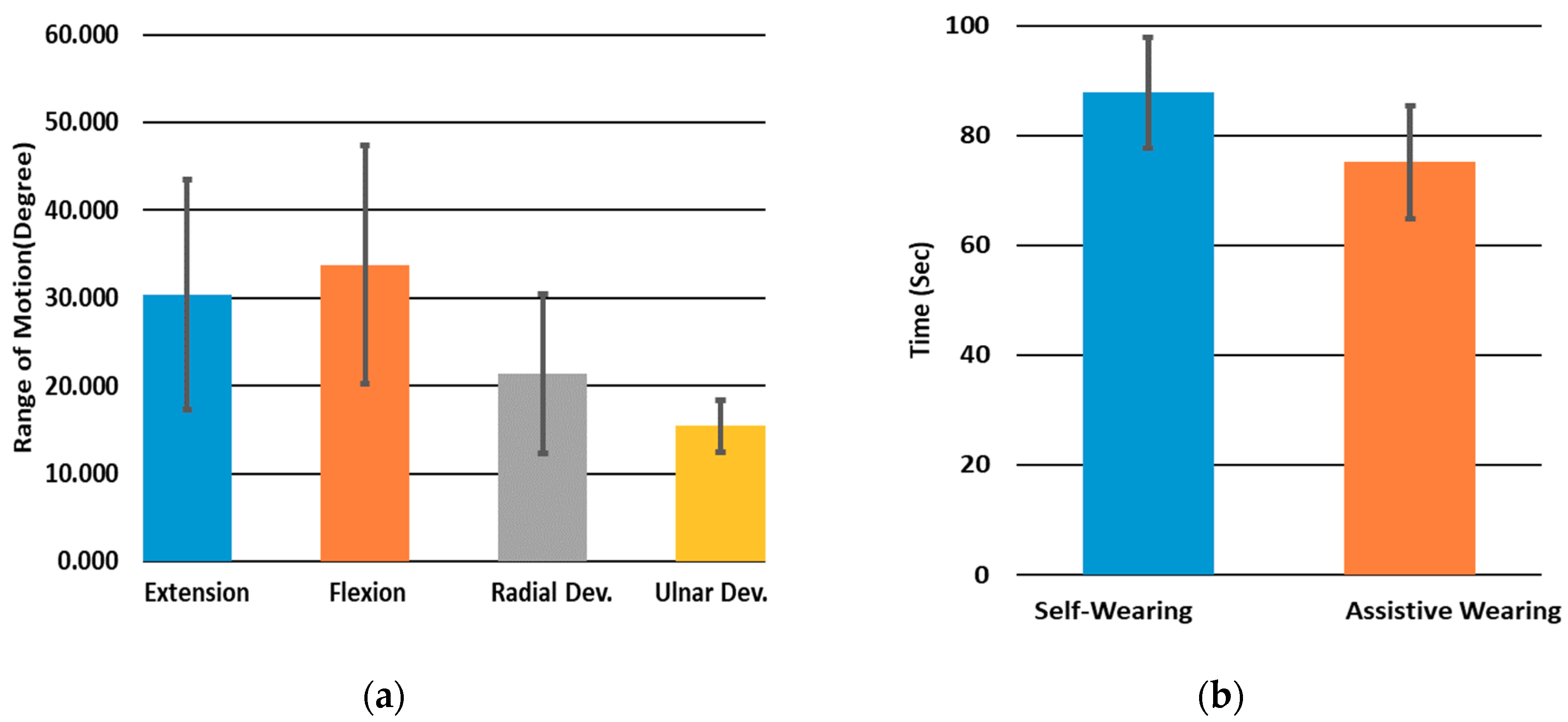
3.5. User Test
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Connell, L.A.; Lincoln, N.B.; Radford, K.A. Somatosensory impairment after stroke: Frequency of different deficits and their recovery. Clin. Rehabilit. 2008, 22, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyson, S.F.; Hanley, M.; Chillala, J.; Selley, A.B.; Tallis, R.C. Sensory loss in hospital-admitted people with stroke: Characteristics, associated factors, and relationship with function. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2008, 22, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendleton, H.M.H.; Schultz-Krohn, W. Pedretti’s Occupational Therapy: Practice Skills for Physical Dysfunction, 8th ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: San Jose, CA, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-03-2333-928-5. [Google Scholar]
- Janca, A.; Aarli, J.A.; Prilipko, L.; Dua, T.; Saxena, S.; Saraceno, B. WHO/WFN Survey of neurological services: A worldwide perspective. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 247, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathian, K.; Buxbaum, L.J.; Cohen, L.G.; Krakauer, J.W.; Lang, C.E.; Corbetta, M.; Fitzpatrick, S.M. Neurological principles and rehabilitation of action disorders: Common clinical deficits. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2011, 25, 21S–32S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemperline, J.J.; Allen, S.; Walk, D.; Rymer, W.Z. Characteristics of motor unit discharge in subjects with hemiparesis. Muscle Nerve 1995, 18, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, A.; Farmer, S.E.; Brady, M.C.; Langhorne, P.; Mead, G.E.; Mehrholz, J.; Van Wijck, F. Interventions for improving upper limb function after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlinac, M.; Feng, M. Assessment of Activities of Daily Living, Self-Care, and Independence. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2016, 31, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijima, Y.; Viegas, S.F. Wrist anatomy and biomechanics. J. Hand Surg. 2009, 34, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, B.D.; Grosland, N.M.; Murphy, D.M.; McCullough, M. Impact of impaired wrist motion on hand and upper-extremity performance. J. Hand Surg. 2003, 28, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Peppen, R.P.; Kwakkel, G.; Wood-Dauphinee, S.; Hendriks, H.J.; Van der Wees, P.J.; Dekker, J. The impact of physical therapy on functional outcomes after stroke: What’s the evidence? Clin. Rehabilit. 2004, 18, 833–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimyan, M.A.; Cohen, L.G. Neuroplasticity in the context of motor rehabilitation after stroke. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bütefisch, C.; Hummelsheim, H.; Denzler, P.; Mauritz, K.H. Repetitive training of isolated movements improves the outcome of motor rehabilitation of the centrally paretic hand. J. Neurol. Sci. 1995, 130, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liepert, J.; Miltner, W.H.R.; Bauder, H.; Sommer, M.; Dettmers, C.; Taub, E.; Weiller, C. Motor cortex plasticity during constraint-induced movement therapy in stroke patients. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 250, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakkel, G.; Kollen, B.J.; van der Grond, J.; Prevo, A.J. Probability of regaining dexterity in the flaccid upper limb: Impact of severity of paresis and time since onset in acute stroke. Stroke 2003, 34, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sörös, P.; Teasell, R.; Hanley, D.F.; Spence, J.D. Motor recovery beginning 23 years after ischemic stroke. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 118, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.; Verheyden, G.; Brinkmann, N.; Dejaeger, E.; De Weerdt, W.; Feys, H.; Gantenbein, A.R.; Walter, J.; Laenen, A.; Lincoln, N.; et al. Functional and Motor Outcome 5 Years After Stroke Is Equivalent to Outcome at 2 Months: Follow-Up of the Collaborative Evaluation of Rehabilitation in Stroke Across Europe. Stroke 2015, 46, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.; Després, J.P.; Fullerton, H.J.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 133, e38–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisen, M.L.; Krebs, H.I.; Hogan, N.; McDowell, F.; Volpe, B.T. The effect of robot-assisted therapy and rehabilitative training on motor recovery following stroke. Arch. Neurol. 1997, 54, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, B.T.; Krebs, H.I.; Hogan, N.; Edelsteinn, L.; Diels, C.M.; Aisen, M. Robot training enhanced motor outcome in patients with stroke maintained over 3 years. Neurology 1999, 53, 1874–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, H.I.; Ladenheim, B.; Hippolyte, C.; Monterroso, L.; Mast, J. Robot-assisted task-specific training in cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2009, 51, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpinella, I.; Cattaneo, D.; Bertoni, R.; Ferrarin, M. Robot training of upper limb in multiple sclerosis: Comparing protocols with or without manipulative task components. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabilit. Eng. 2012, 20, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zariffa, J.; Kapadia, N.; Kramer, J.; Taylor, P.; Alizadeh-Meghrazi, M.; Zivanovic, V.; Willms, R.; Townson, A.; Curt, A.; Popovic, M.; et al. Feasibility and efficacy of upper limb robotic rehabilitation in a subacute cervical spinal cord injury population. Spinal Cord 2012, 50, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgar, C.G.; Lum, P.S.; Shor, P.C.; Van der Loos, H.F.M. Development of robots for rehabilitation therapy: The Palo Alto VA/Stanford experience. J. Rehabilit. Res. Dev. 2000, 37, 663–673. [Google Scholar]
- Celik, O.; O’Malley, M.K.; Boake, C.; Levin, H.S.; Yozbatiran, N.; Reistetter, T.A. Normalized Movement Quality Measures for Therapeutic Robots Strongly Correlate with Clinical Motor Impairment Measures. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabilit. Eng. 2010, 18, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, N.; Krebs, H.I.; Rohrer, B.; Fasoli, S.; Stein, J.; Volpe, B.T. Recovery After Stroke; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 604–622. ISBN -13 978-0-521-82236-X. [Google Scholar]
- Fasoli, S.E.; Krebs, H.I.; Stein, J.; Frontera, W.R.; Hogan, N. Effects of robotic therapy on motor impairment and recovery in chronic stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabilit. 2003, 84, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winstein, C.J.; Stein, J.; Arena, R.; Bates, B.; Cherney, L.R.; Cramer, S.C.; Deruyter, F.; Eng, J.J.; Fisher, B.; Harvey, R.L.; et al. Guidelines for Adult Stroke Rehabilitation and Recovery: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2016, 47, e98–e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.H.; Rahman, M.J.; Cristobal, O.L.; Saad, M.; Kenné, J.P.; Archambault, P.S. Development of a whole arm wearable robotic exoskeleton for rehabilitation and to assist upper limb movements. Robotica 2015, 33, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopura, R.A.R.C.; Kiguchi, K.; Li, Y. SUEFUL-7: A 7DOF upper-limb exoskeleton robot with muscle-model-oriented EMG-based control. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2009), St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009; pp. 1126–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Nef, T.; Guidali, M.; Klamroth-Marganska, V.; Riener, R. ARMin—Exoskeleton Robot for Stroke Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Munich, Germany, 7–12 September 2009; pp. 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Carignan, C.; Tang, J.; Roderick, S.; Naylor, M. A Configuration-Space Approach to Controlling a Rehabilitation Arm Exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 10th International Rehabilitation Robotics, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 13–15 June 2007; pp. 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, J.C.; Rosen, J.; Burns, S.T. Upper-Limb Powered Exoskeleton Design. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2007, 12, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coderre, A.M.; Zeid, A.A.; Dukelow, S.P.; Demmer, M.J.; Moore, K.D.; Demers, M.J.; Bretzke, H.; Herter, T.M.; Glasgow, J.I.; Norman, K.E.; et al. Assessment of upper-limb sensorimotor function of subacute stroke patients using visually guided reaching. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2010, 24, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, M.; Gopura, R.; Jayawardena, S. 6-REXOS: Upper Limb Exoskeleton Robot with Improved pHRI. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2015, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopura, R.; Bandara, D.; Kiguchi, K.; Mann, G.; Gopura, R. Developments in hardware systems of active upper-limb exoskeleton robots: A review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 75, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, D.; Noritsugu, T.; Takaiwa, M. Development of Active Support Splint driven by Pneumatic Soft Actuator (ASSIST). In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference of Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2005, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 520–525. [Google Scholar]
- Realmuto, J.; Sanger, T. A robotic forearm orthosis using soft fabric-based helical actuators. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2nd International Conference of Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Seoul, Korea, 14–18 April 2019; pp. 591–596. [Google Scholar]
- Skorina, E.H.; Luo, M.; Onal, C.D. A Soft Robotic Wearable Wrist Device for Kinesthetic Haptic Feedback. Front. Robot. AI 2018, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fahaam, H.; Davis, S.; Nefti-Meziani, S. The design and mathematical modelling of novel extensor bending pneumatic artificial muscles (EBPAMs) for soft exoskeletons. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2018, 99, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hashimoto, M. PVC gel soft actuator-based wearable assist wear for hip joint support during walking. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 125003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Cho, K.J. Development and evaluation of a soft wearable weight support device for reducing muscle fatigue on shoulder. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, B.K.; Xiloyannis, M.; Cappello, L.; Antuvan, C.W.; Yen, S.; Masia, L. Adaptive backlash compensation in upper limb soft wearable exoskeletons. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 92, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaponov, I.; Popov, D.; Lee, S.J.; Ryu, J.H. Auxilio: A portable cable-driven exosuit for upper extremity assistance. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kang, B.B.; Jung, B.; Cho, K. Exo Wrist: A Soft Tendon Driven Wrist Wearable Robot with Active Anchor for Dart Throwing Motion in Hemiplegic Patients. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.M.; Ryu, J.; Cho, M.; Cho, K.J. Engineering Design Framework for a Shape Memory Alloy Coil Spring Actuator using a Static Two-State Model. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 055009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villoslada, A.; Flores, A.; Copaci, D.; Blanco, D.; Moreno, L. High-displacement flexible Shape Memory Alloy actuator for soft wearable robots. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2015, 73, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copaci, D.S.; Moreno, L.; Blanco, D. Wearable elbow exoskeleton actuated with shape memory alloy in antagonist movement. In Proceedings of the Joint Workshop on Wearable Robotics and Assistive Devices, International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Daejeon, Korea, 9–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hope, J.; McDaid, A. Development of Wearable Wrist and Forearm Exoskeleton with Shape Memory Alloy Actuators. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2017, 86, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertel, J.D.; Mascaro, S.A. Dynamic Thermomechanical Modeling of a Wet Shape Memory Alloy Actuator. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 2010, 132, 051006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ge, Y. Underwater Swimming Micro Robot Using IPMC Actuator. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Luoyang, China, 25–28 June 2006; pp. 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Cianchetti, M.; Mattoli, V.; Mazzolai, B.; Laschi, C.; Dario, P. A new design methodology of electrostrictive actuators for bio-inspired robotics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 142, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Ding, Z.; Wang, C.C.; Wei, J.; Purnawali, H.; Zhao, Y. Shape memory materials. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.R.; Shin, C.; Memic, A.; Shadmehr, S.; Miscuglio, M.; Jung, H.Y.; Jung, S.M.; Bae, H.; Khademhosseini, A.; Tang, X.S.; et al. Aligned carbon nanotube–based flexible gel substrates for engineering biohybrid tissue actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4486–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Ham, S.Y.; Son, Y.S. Relationship between Input Power and Power Density of SMA Spring. In Proceedings of the SPIE. Smart Structures and Materials + Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 15 April 2016; p. 9799. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.H.; Son, Y. SMA spring-based artificial muscle actuated by hot and cool water using faucet-like valve. In Proceedings of the SPIE. Smart Structures and Materials + Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, Portland, OR, USA, 11 April 2017; p. 10164. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.H.; Choi, K.J.; Son, Y.S. Shape Memory Alloy-Based Spring Bundle Actuator Controlled by Water Temperature. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 1798–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.S.; Kim, Y.; Desai, J.P. Modeling and characterization of shape memory alloy springs with water cooling strategy in a neurosurgical robot. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2017, 28, 2167–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Park, C.H. Suit-type Wearable Robot Powered by Shape-Memory-alloy-based Fabric Muscle. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, J.D.W.; Vandesteeg, N.A.; Anquetil, P.A.; Madden, P.G.A.; Takshi, A.; Pytel, R.Z.; Lafontaine, S.R.; Wieringa, P.A.; Hunter, I.W. Artificial Muscle Technology: Physical Principles and Naval Prospects. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2004, 29, 706–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, K.A.; Werner, F.W.; Palmer, A.K. Frequency Spectrum Analysis of Wrist Motion for Activities of Daily Living. J. Orthop. Res. 1989, 7, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.G.; Youm, Y. A biomechanical investigation of wrist kinematics. J. Biomech. 1979, 12, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, F.; Lee, M.M.; O’Malley, K. Design of a series elastic actuator for a compliant parallel wrist rehabilitation robot. In Proceedings of the International Conference of Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gates, D.H.; Walters, L.S.; Cowley, J.; Wilken, J.M.; Resnik, L. Range of Motion Requirements for Upper-Limb Activites of Daily Living. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2015, 70, 70013500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

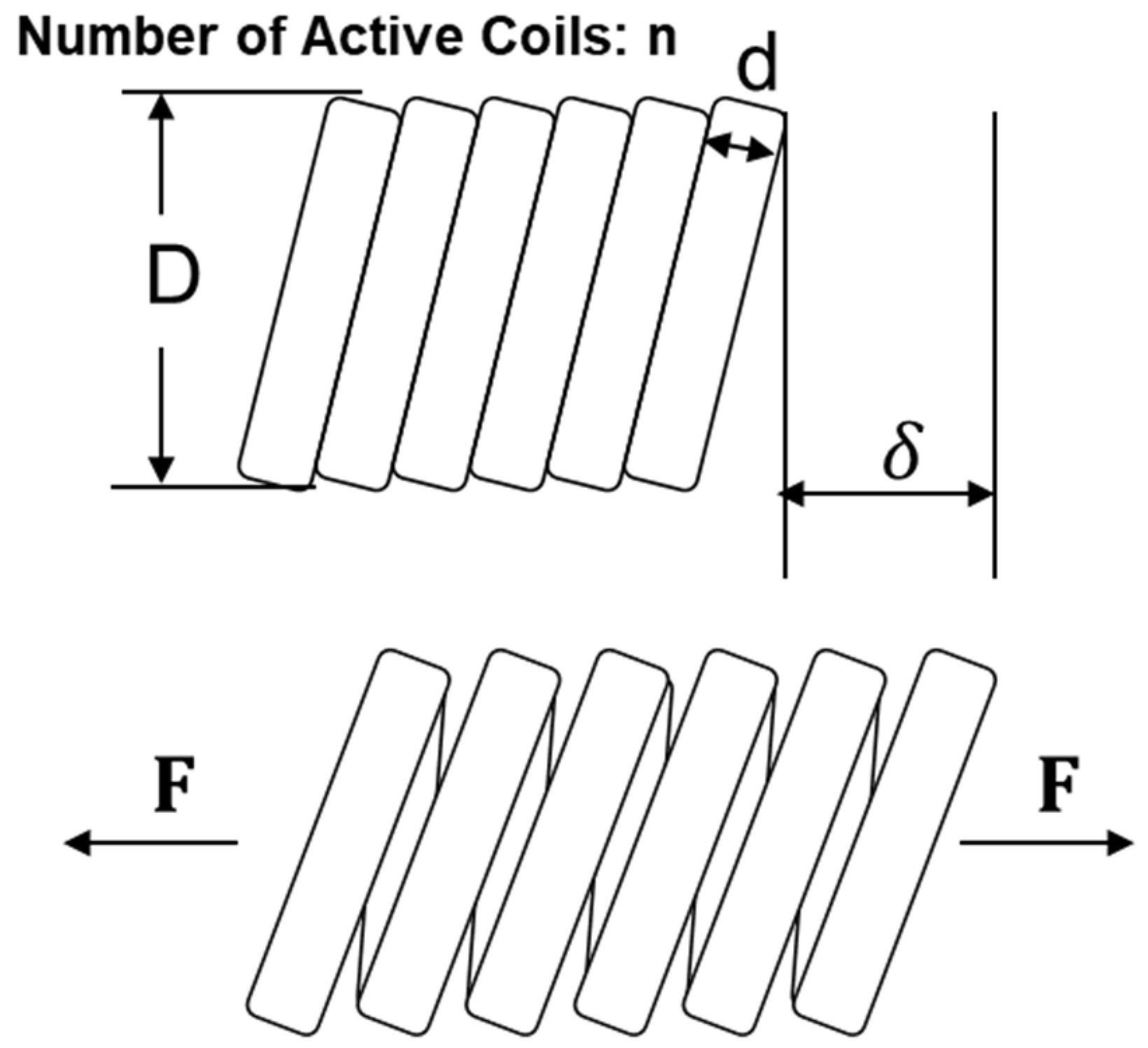
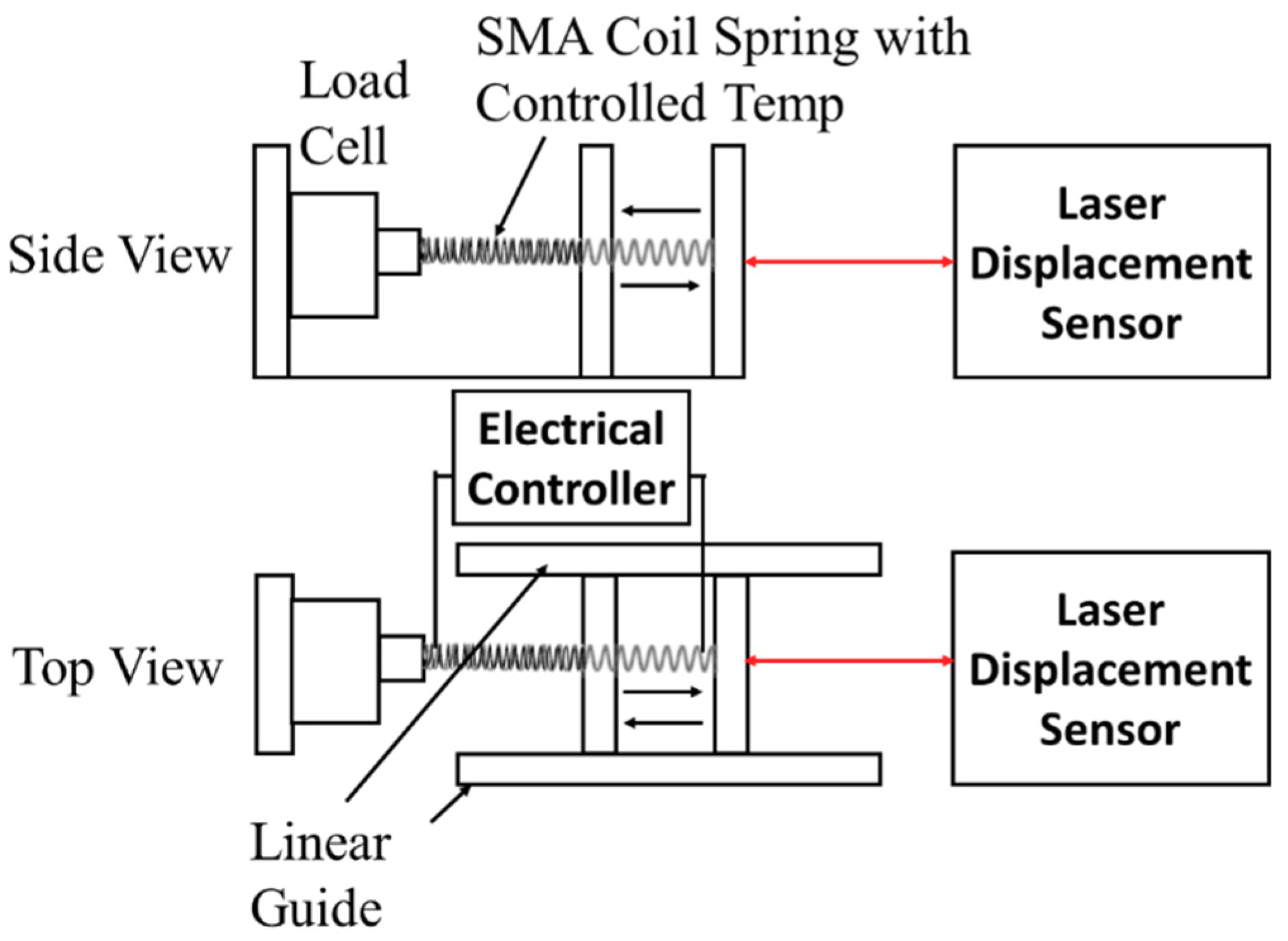
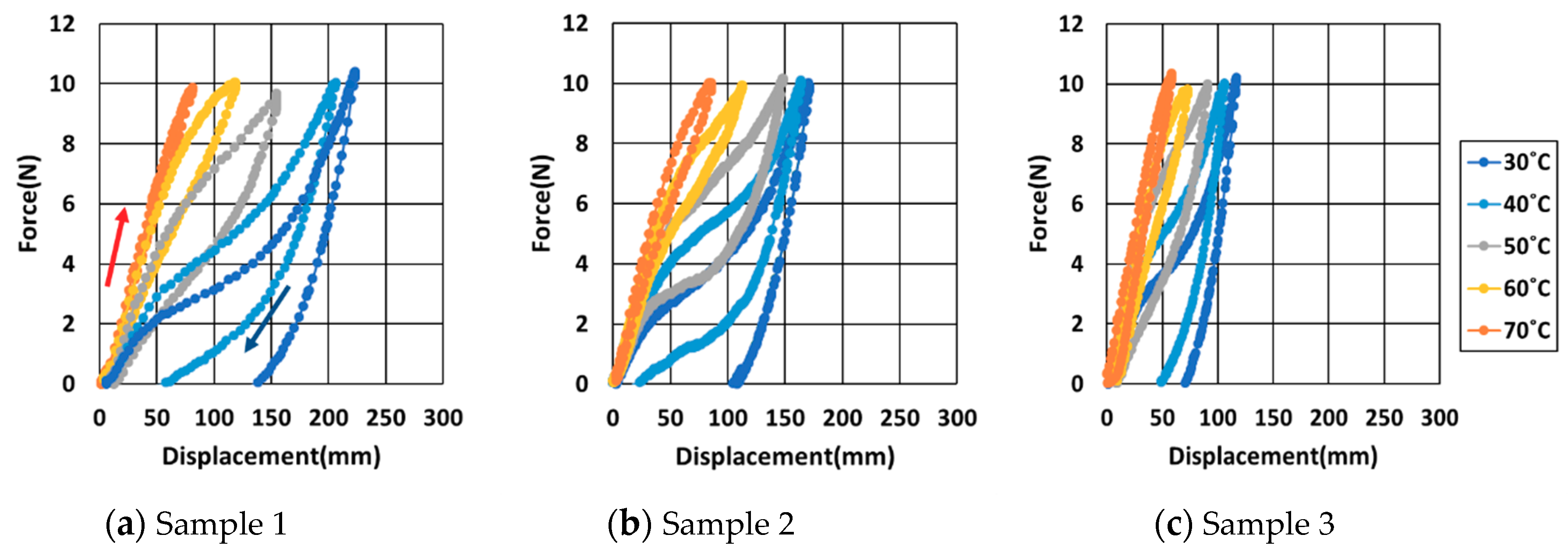

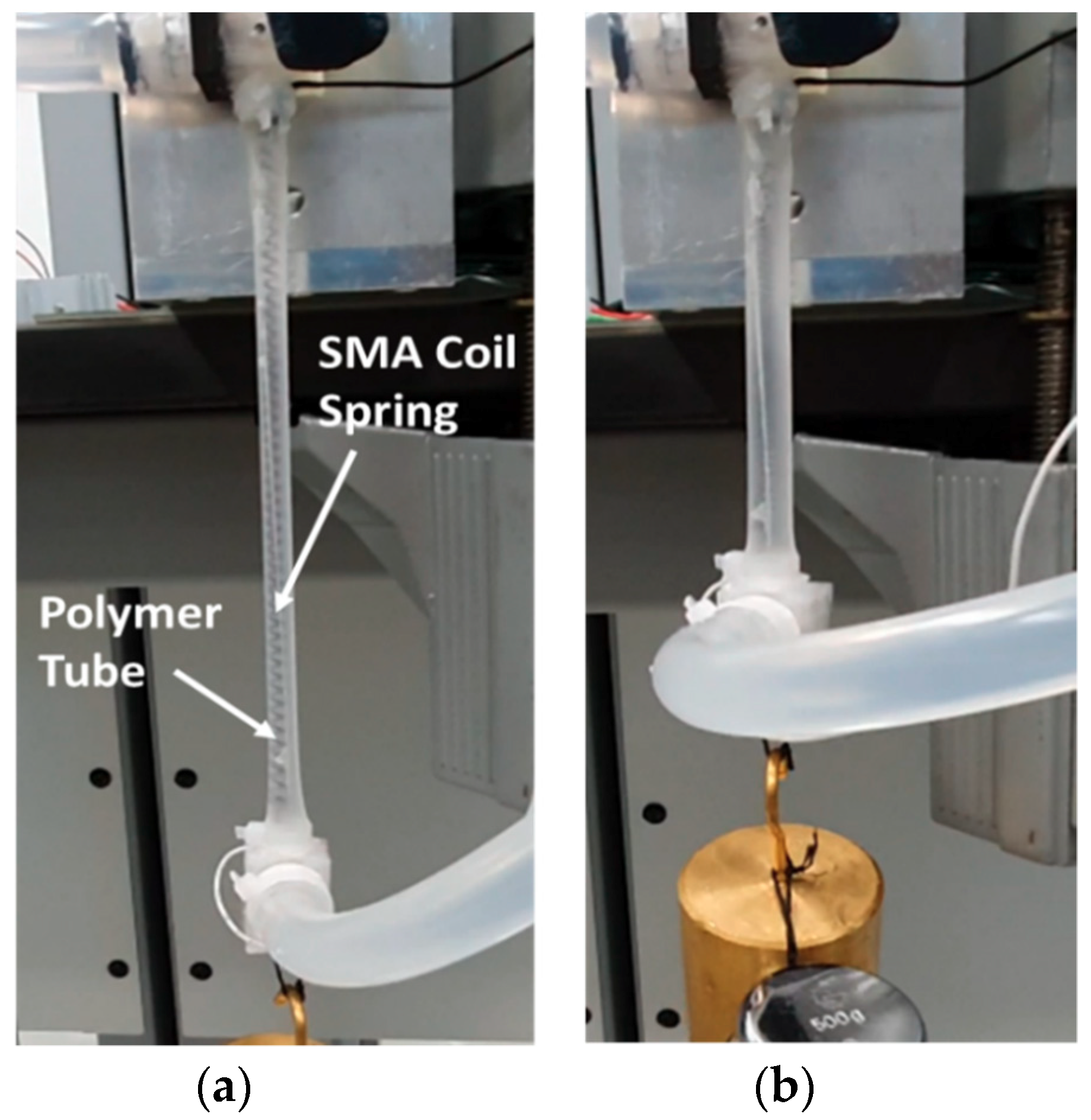
| Sample Number | SMA Materials | Spring Diameter (D) | Number of Turns (n) | Initial Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | d = 0.5 mm Transition Temperature 40 °C | 3 mm | 55 | 50 |
| 2 | 2.8 mm | 55 | 50 | |
| 3 | 2.5 mm | 55 | 50 | |
| 4 | d = 0.42 mm Transition Temperature 70 °C | 3 mm | 55 | 45 |
| 5 | 2.5 mm | 55 | 45 |
| Wrist Motion | Flexion | Extension | Radial Deviation | Ulnar Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Torque (Nm) | 0.61 | 1.32 | 0.90 | 0.62 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, J.; Yasir, I.B.; Han, J.; Park, C.H.; Bok, S.-K.; Kyung, K.-U. Design of Shape Memory Alloy-Based Soft Wearable Robot for Assisting Wrist Motion. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194025
Jeong J, Yasir IB, Han J, Park CH, Bok S-K, Kyung K-U. Design of Shape Memory Alloy-Based Soft Wearable Robot for Assisting Wrist Motion. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(19):4025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194025
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Jaeyeon, Ibrahim Bin Yasir, Jungwoo Han, Cheol Hoon Park, Soo-Kyung Bok, and Ki-Uk Kyung. 2019. "Design of Shape Memory Alloy-Based Soft Wearable Robot for Assisting Wrist Motion" Applied Sciences 9, no. 19: 4025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194025
APA StyleJeong, J., Yasir, I. B., Han, J., Park, C. H., Bok, S.-K., & Kyung, K.-U. (2019). Design of Shape Memory Alloy-Based Soft Wearable Robot for Assisting Wrist Motion. Applied Sciences, 9(19), 4025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194025







