A Sensor Fusion Framework for Indoor Localization Using Smartphone Sensors and Wi-Fi RSSI Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
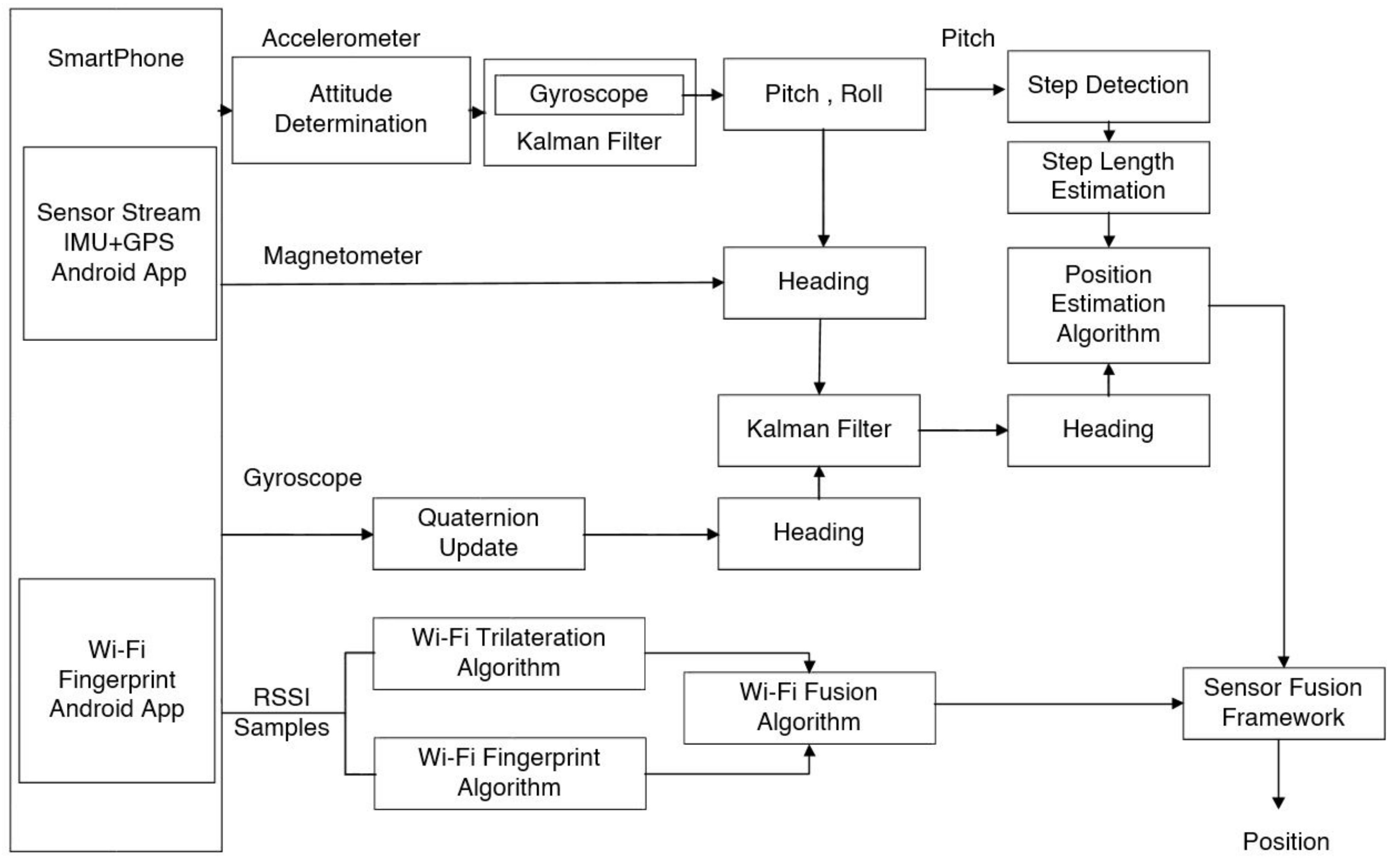
3. Proposed Sensor Fusion Framework Model Using PDR and W-Fi Localization Systems
3.1. PDR Positioning
3.2. Wi-Fi Positioning
3.2.1. Wi-Fi Trilateration Algorithm
3.2.2. Wi-Fi Fingerprint Algorithm
3.2.3. Proposed Wi-Fi Fusion Algorithm
3.3. Proposed Sensor Fusion Framework Algorithm using Wi-Fi Fusion and PDR Position Results
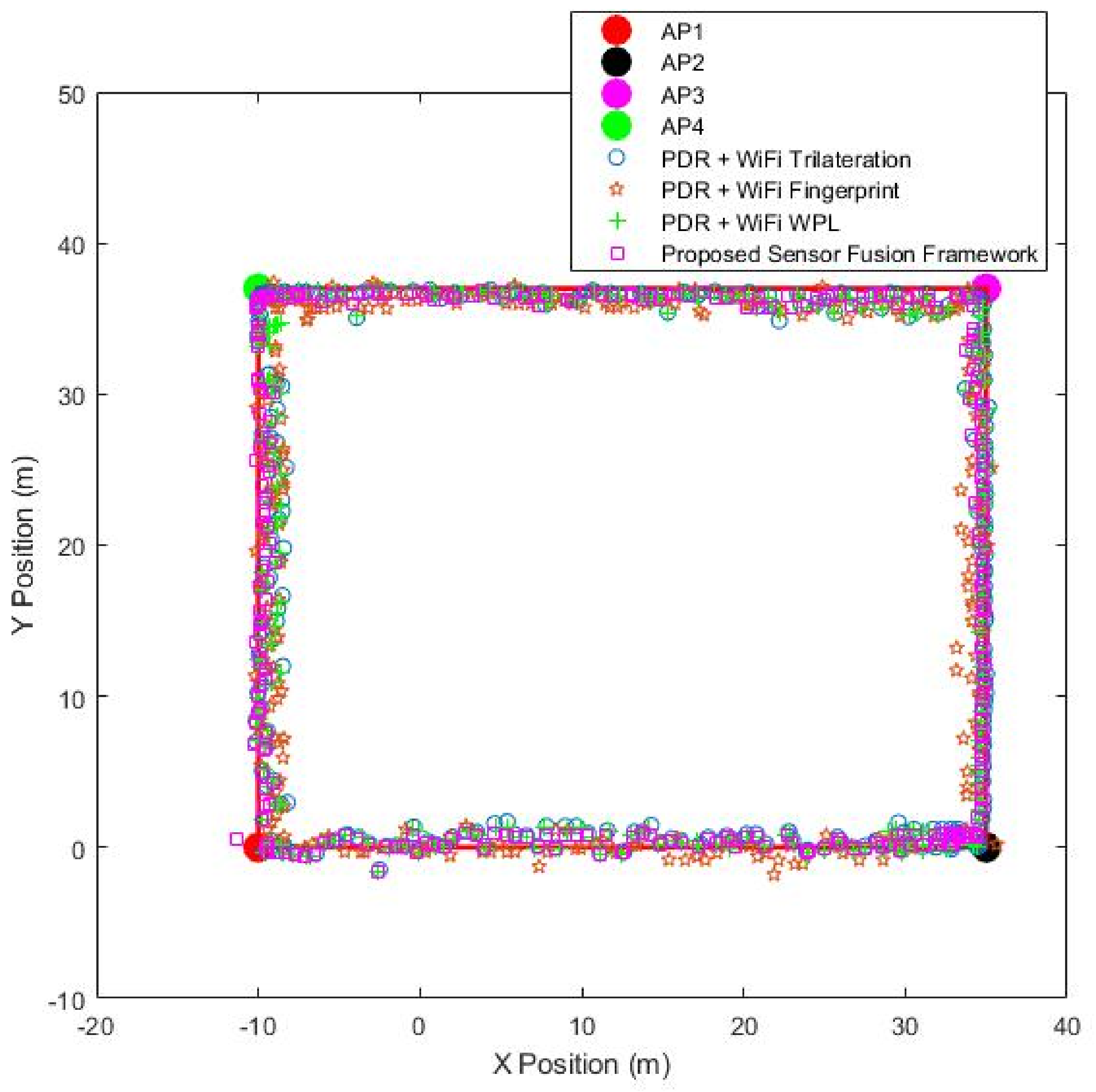
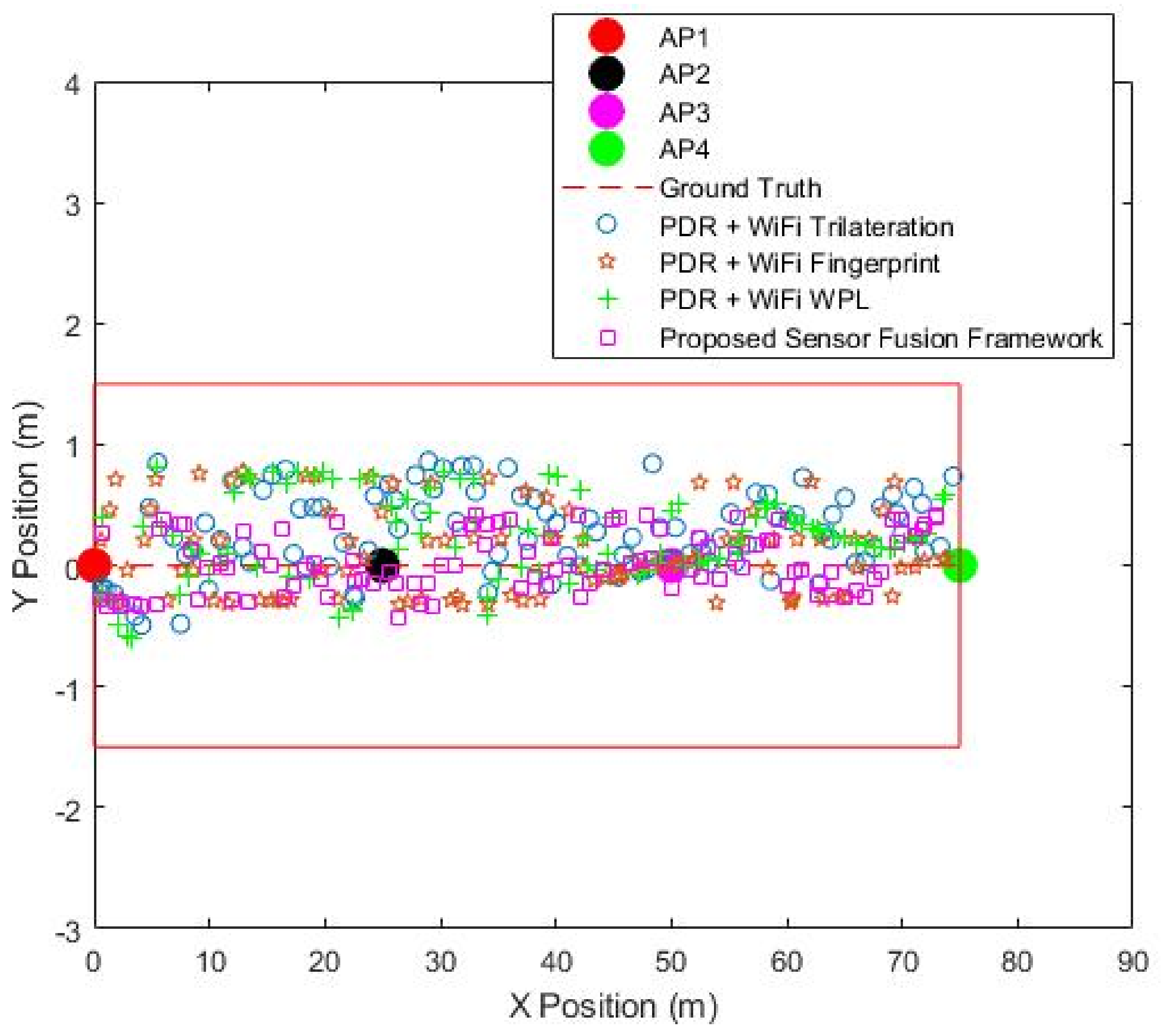
4. Experiment and Result Analysis
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, R.; Chen, W.; Xu, Y.; Ji, S. A new indoor positioning system architecture using GPS signals. Sensors 2015, 15, 10074–10087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussar, Y.; Ahriz, I.; Denby, B.; Dreyfus, G. Indoor localization based on cellular telephony RSSI fingerprints containing very large numbers of carriers. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Network. 2011, 2011, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarifi, A.; Al-Salman, A.; Alsaleh, M.; Alnafessah, A.; Al-Hadhrami, S.; Al-Ammar, M.; Al-Khalifa, H. Ultra wideband indoor positioning technologies: Analysis and recent advances. Sensors 2016, 16, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Niu, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X. Indoor positioning based on pedestrian dead reckoning and magnetic field matching for smartphones. Sensors 2018, 18, 4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saab, S.S.; Nakad, Z.S. A standalone RFID indoor positioning system using passive tags. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Qi, L.; El-Sheimy, N. Smartphone-based indoor localization with bluetooth low energy beacons. Sensors 2016, 16, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Shao, S.; Ansari, N.; Khreishah, A. Indoor localization using visible light via fusion of multiple classifiers. IEEE Photon. J. 2017, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uradzinski, M.; Guo, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, M. Advanced indoor positioning using Zigbee wireless technology. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 97, 6509–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husen, M.; Lee, S. Indoor location sensing with invariant Wi-Fi received signal strength fingerprinting. Sensors 2016, 16, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, W.; Liu, H.; Su, X. Indoor mobile localization based on Wi-Fi fingerprint’s important access point. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2015, 11, 429104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Sidhom, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ye, F. Accurate WiFi based localization for smartphones using peer assistance. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2014, 13, 2199–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Chon, Y.; Cha, H. Smartphone-based collaborative and autonomous radio fingerprinting. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C (Appl. Rev.) 2012, 42, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Ni, W.; Toh, Y.K. Integrated Wi-Fi fingerprinting and inertial sensing for indoor positioning. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Guimaraes, Portugal, 21–23 September 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Fang, X.; Zhou, M.; Li, L. Smartphone-based indoor integrated WiFi/MEMS positioning algorithm in a multi-floor environment. Micromachines 2015, 6, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrío, P.; Besada, J.A.; Casar, J.R. Fusion of RSS and inertial measurements for calibration-free indoor pedestrian tracking. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Information Fusion, Istanbul, Turkey, 9–12 July 2013; pp. 1458–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Poulose, A.; Eyobu, O.S.; Han, D.S. A Combined PDR and Wi-Fi Trilateration Algorithm for Indoor Localization. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Okinawa, Japan, 11–13 February 2019; pp. 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Poulose, A.; Eyobu, O.S.; Han, D.S. An Indoor Position-Estimation Algorithm Using Smartphone IMU Sensor Data. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 11165–11177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, N.-H.; Truong, P.; Jeong, G.-M. Step-detection and adaptive step-length estimation for pedestrian dead-reckoning at various walking speeds using a smartphone. Sensors 2016, 16, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Yu, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, G.; Liu, S. Quaternion-based unscented Kalman filter for accurate indoor heading estimation using wearable multi-sensor system. Sensors 2015, 15, 10872–10890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.; Han, Y. SmartPDR: Smartphone-based pedestrian dead reckoning for indoor localization. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 2906–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evennou, F.; Marx, F. Advanced integration of WiFi and inertial navigation systems for indoor mobile positioning. Eur. J. Appl. Signal Process. 2006, 2006, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lenz, H.; Szabo, A.; Bamberger, J.; Hanebeck, U.D. WLAN-based pedestrian tracking using particle filters and low-cost MEMS sensors. In Proceedings of the 2007 4th Workshop on pOsitioning, Navigation and Communication (WPNC), Hannover, German, 22 March 2007; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Carrera, J.L.; Zhao, Z.; Braun, T.; Li, Z. A real-time indoor tracking system by fusing inertial sensor, radio signal and floor plan. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Alcala de Henares, Spain, 4–7 October 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Knauth, S. Smartphone PDR positioning in large environments employing WiFi, particle filter, and backward optimization. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sapporo, Japan, 18–21 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, K.; Krach, B.; Catterall, N.; Robertson, P. Development and evaluation of a combined WLAN & inertial indoor pedestrian positioning system. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS, Savannah, Georgia, 22–25 September 2009; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Y.; El-Sheimy, N. Tightly-coupled integration of WiFi and MEMS sensors on handheld devices for indoor pedestrian navigation. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.-A.; Hu, Y.; Yu, J.; Na, Z. Extended Kalman filter for real time indoor localization by fusing WiFi and smartphone inertial sensors. Micromachines 2015, 6, 523–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppäkoski, H.; Collin, J.; Takala, J. Pedestrian navigation based on inertial sensors, indoor map, and WLAN signals. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2013, 71, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, P.; Yang, H. Integrated WiFi/PDR/Smartphone using an unscented kalman filter algorithm for 3D indoor localization. Sensors 2015, 15, 24595–24614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waqar, W.; Chen, Y.; Vardy, A. Incorporating user motion information for indoor smartphone positioning in sparse Wi-Fi environments. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM international conference on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems (ACM), Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–26 September 2014; pp. 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Lan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Niu, X.; El-Sheimy, N. A hybrid WiFi/magnetic matching/PDR approach for indoor navigation with smartphone sensors. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2016, 20, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Gao, J.; Li, X. An improved WiFi/PDR integrated system using an adaptive and robust filter for indoor localization. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P. Kalman Filter for Beginners: With MATLAB Examples; CreateSpace: Scotts Valley, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, E.M.; Gonzalez, A.L.M. Step detector and step length estimator for an inertial pocket navigation system. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Busan, Korea, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wen, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Gao, R.; Zhao, H. Pedestrian dead-reckoning indoor localization based on OS-ELM. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 6116–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchekotov, M. Indoor localization method based on wi-fi trilateration technique. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference of Fruct Association, Oulu, Finland, 27–31 October 2014; pp. 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Ilci, V.; Alkan, R.M.; Gülal, V.E.; Cizmeci, H. Trilateration technique for WiFi-based indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Communications (ICWMC), St. Julians, Malta, 11–16 October 2015; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, J.; Jeong, S.; Gwon, K.; Joo, J. Improvement of Kalman filters for WLAN based indoor tracking. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, J. Development of Web Services for WLAN-based Indoor Positioning and Floor Map Repositories. Int. J. Control Autom. 2014, 7, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Peuker, B.; Quan, M.; Clark, C.; Jipson, J. Wi-Fi Localization Using RSSI Fingerprinting; Citeseer, 2010. Available online: http://digitalcommons.calpoly.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1007&context=cpesp (accessed on 18 March 2019).
- Zegeye, W.K.; Amsalu, S.B.; Astatke, Y.; Moazzami, F. WiFi RSS fingerprinting indoor localization for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 7th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 20–22 October 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.; Kai, Y.D.; Gul, H.U. Indoor Wi-Fi positioning algorithm based on combination of location fingerprint and unscented Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 2017 14th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology (IBCAST), Islamabad, Pakistan, 10–14 January 2017; pp. 693–698. [Google Scholar]
- Retscher, G. Fusion of location fingerprinting and trilateration based on the example of differential wi-fi positioning. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 4, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.; Sohn, G. Indoor localization using wi-fi based fingerprinting and trilateration techiques for lbs applications. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 38, C26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.J.; Aggoun, L.; Moore, J.B. Hidden Markov Models: Estimation And Control; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 28 July 2008; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]



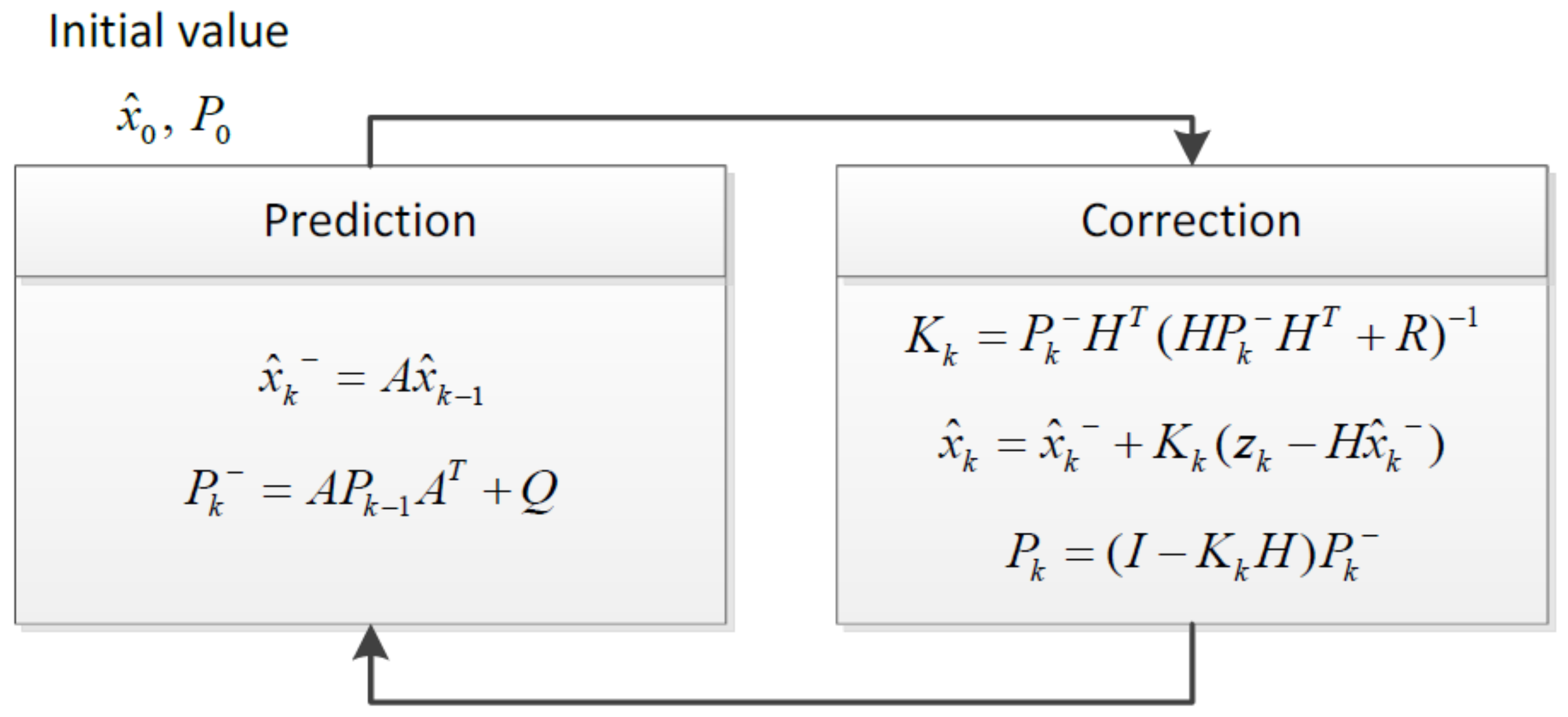




| State variable | |
| Error covariance matrix | |
| A | State transition matrix |
| k | Variable used for the recursive execution of Kalman filter |
| For internal computation | |
| Q | Noise covariance of the process |
| Kalman gain | |
| Measurement | |
| H | Matrix for calculating the predicted value in the form of a measured value |
| R | Covariance of the measurement noise |
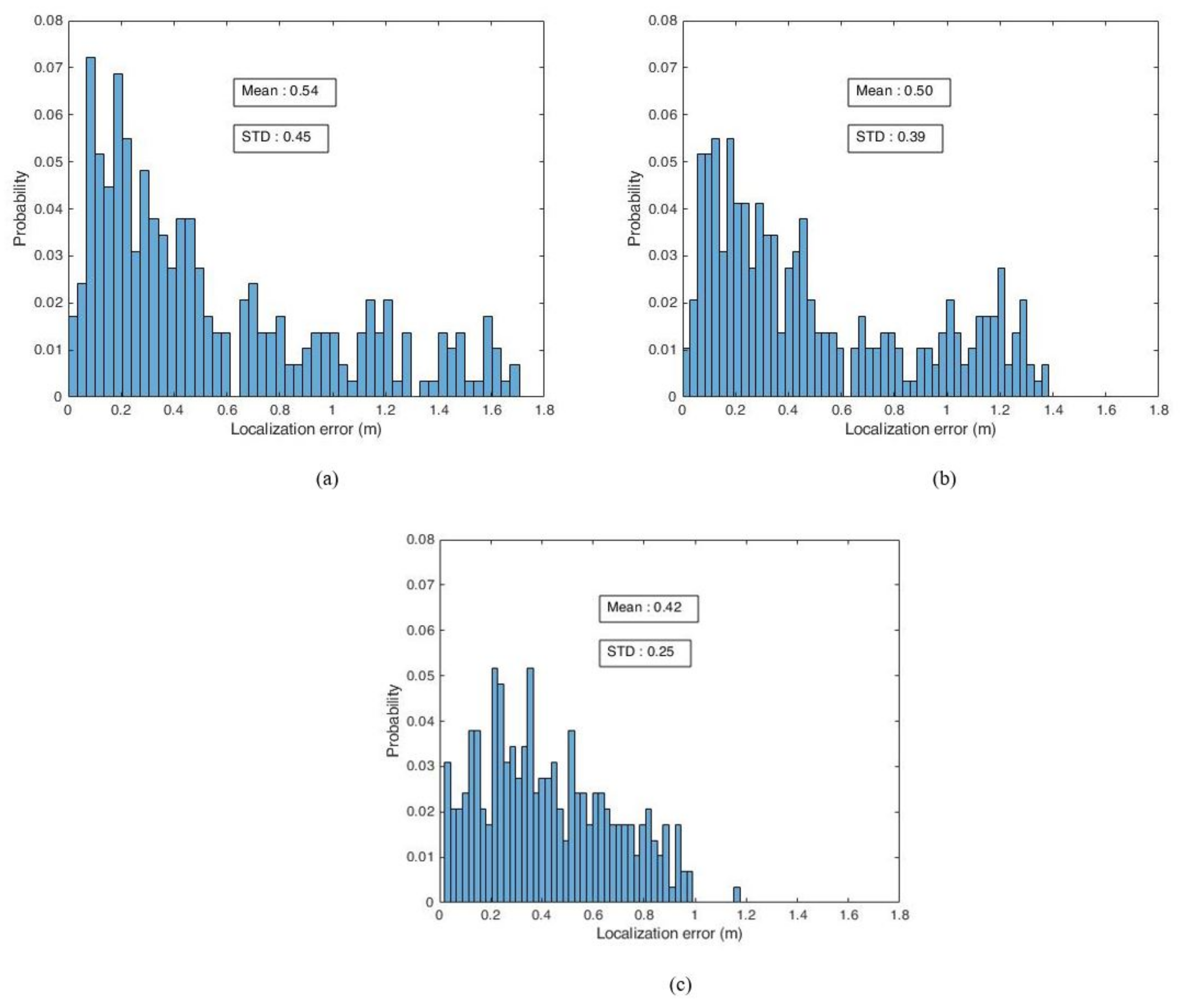
| Position Estimation Systems | Mean Error (m) | Max. Error (m) | Min. Error (m) | Standard Deviation of Error (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDR+Wi-Fi Trilateration | 0.54 | 1.7 | 0.01 | 0.45 |
| PDR+Wi-Fi Fingerprint | 0.50 | 1.38 | 0.5 | 0.39 |
| Proposed sensor fusion framework | 0.42 | 1.17 | 0.02 | 0.25 |
| Position Estimation Systems | Mean Error (m) | Max. Error (m) | Min. Error (m) | Standard Deviation of Error (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDR+Wi-Fi Trilateration | 0.35 | 0.86 | 0.04 | 0.23 |
| PDR+Wi-Fi Fingerprint | 0.30 | 0.78 | 0.008 | 0.21 |
| Proposed sensor fusion framework | 0.22 | 0.44 | 0.007 | 0.12 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poulose, A.; Kim, J.; Han, D.S. A Sensor Fusion Framework for Indoor Localization Using Smartphone Sensors and Wi-Fi RSSI Measurements. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204379
Poulose A, Kim J, Han DS. A Sensor Fusion Framework for Indoor Localization Using Smartphone Sensors and Wi-Fi RSSI Measurements. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(20):4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204379
Chicago/Turabian StylePoulose, Alwin, Jihun Kim, and Dong Seog Han. 2019. "A Sensor Fusion Framework for Indoor Localization Using Smartphone Sensors and Wi-Fi RSSI Measurements" Applied Sciences 9, no. 20: 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204379
APA StylePoulose, A., Kim, J., & Han, D. S. (2019). A Sensor Fusion Framework for Indoor Localization Using Smartphone Sensors and Wi-Fi RSSI Measurements. Applied Sciences, 9(20), 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204379








