Assessment of an MnCe-GAC Treatment Process for Tetramethylammonium-Contaminated Wastewater from Optoelectronic Industries
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Wastewater Composition from Photoelectric and Semiconductor Factories
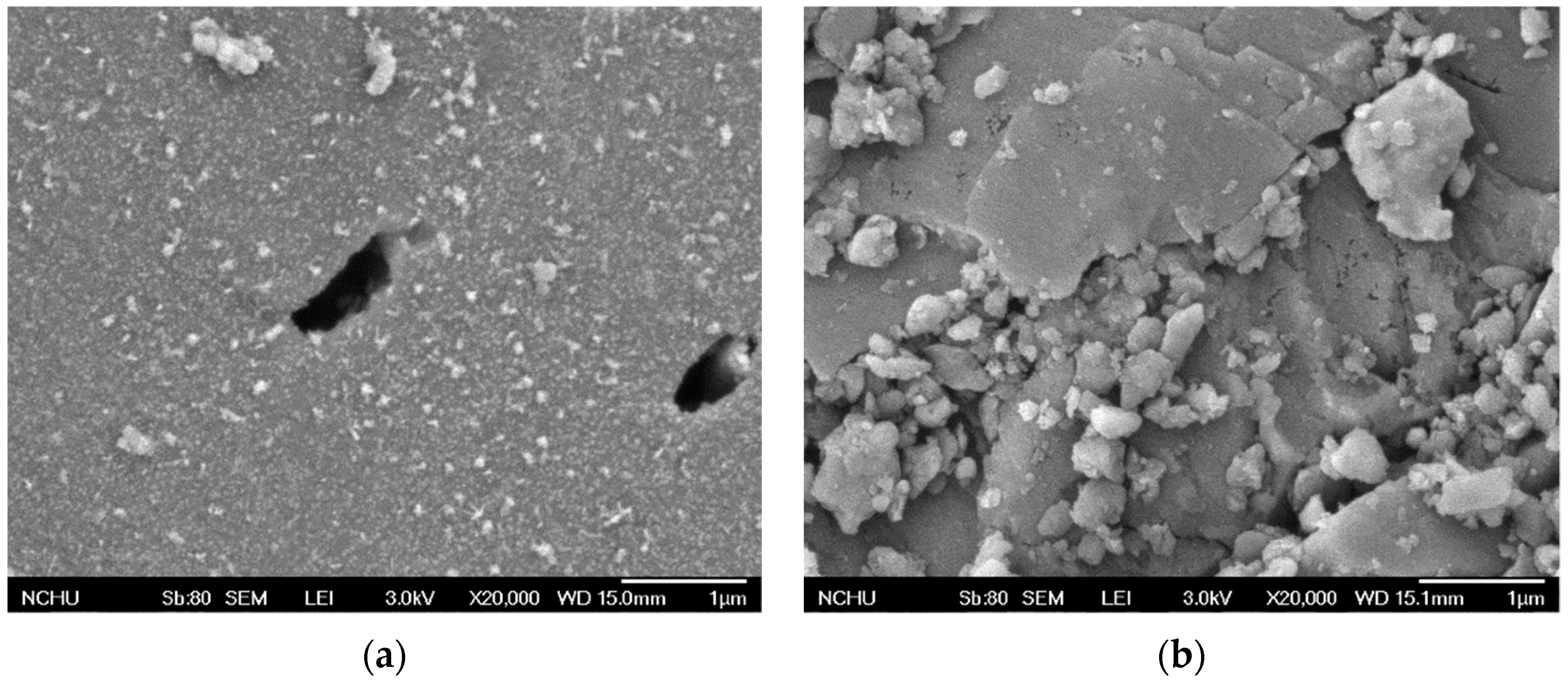
3.2. Characteristics of MnCe-GAC
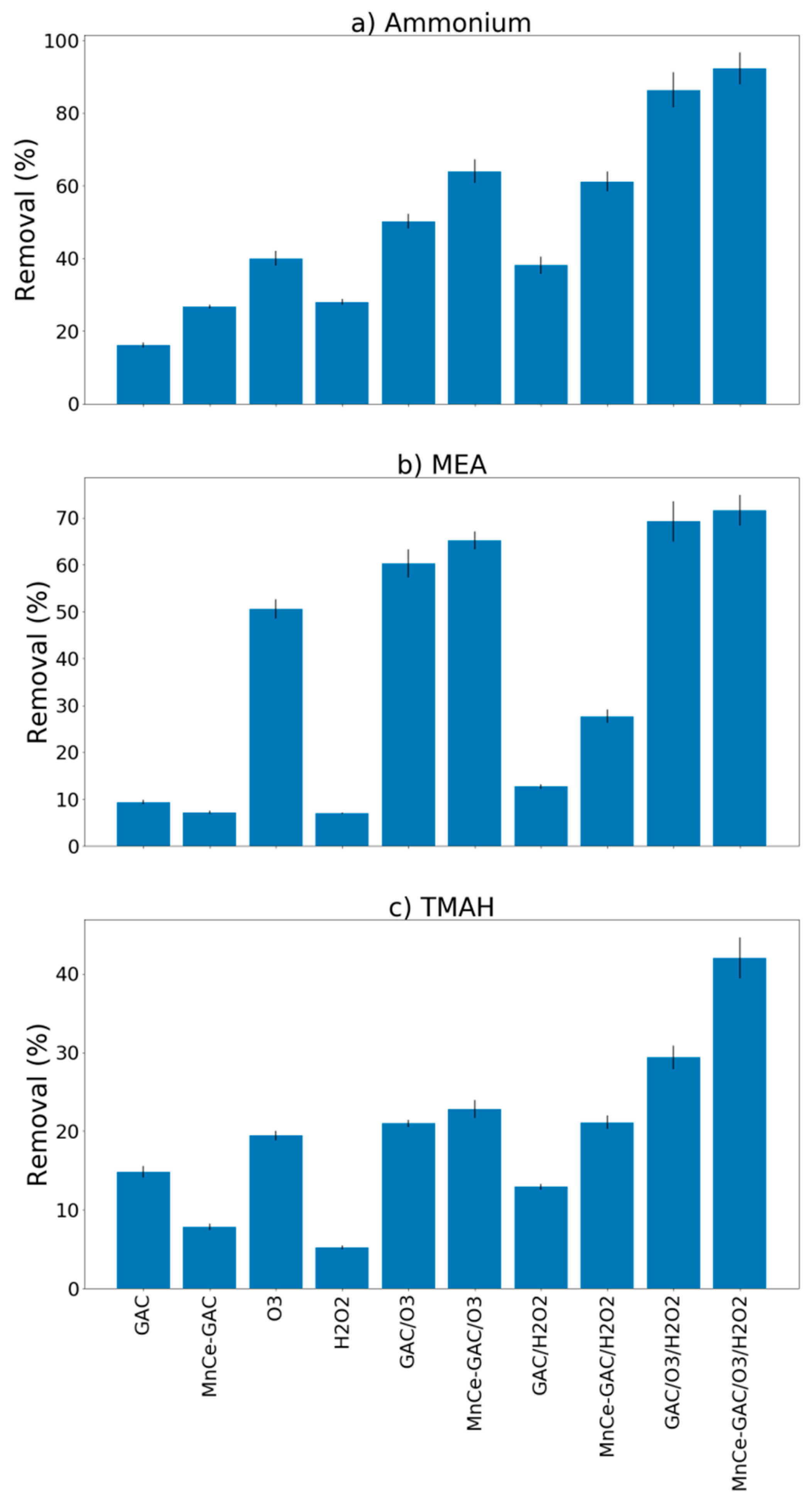
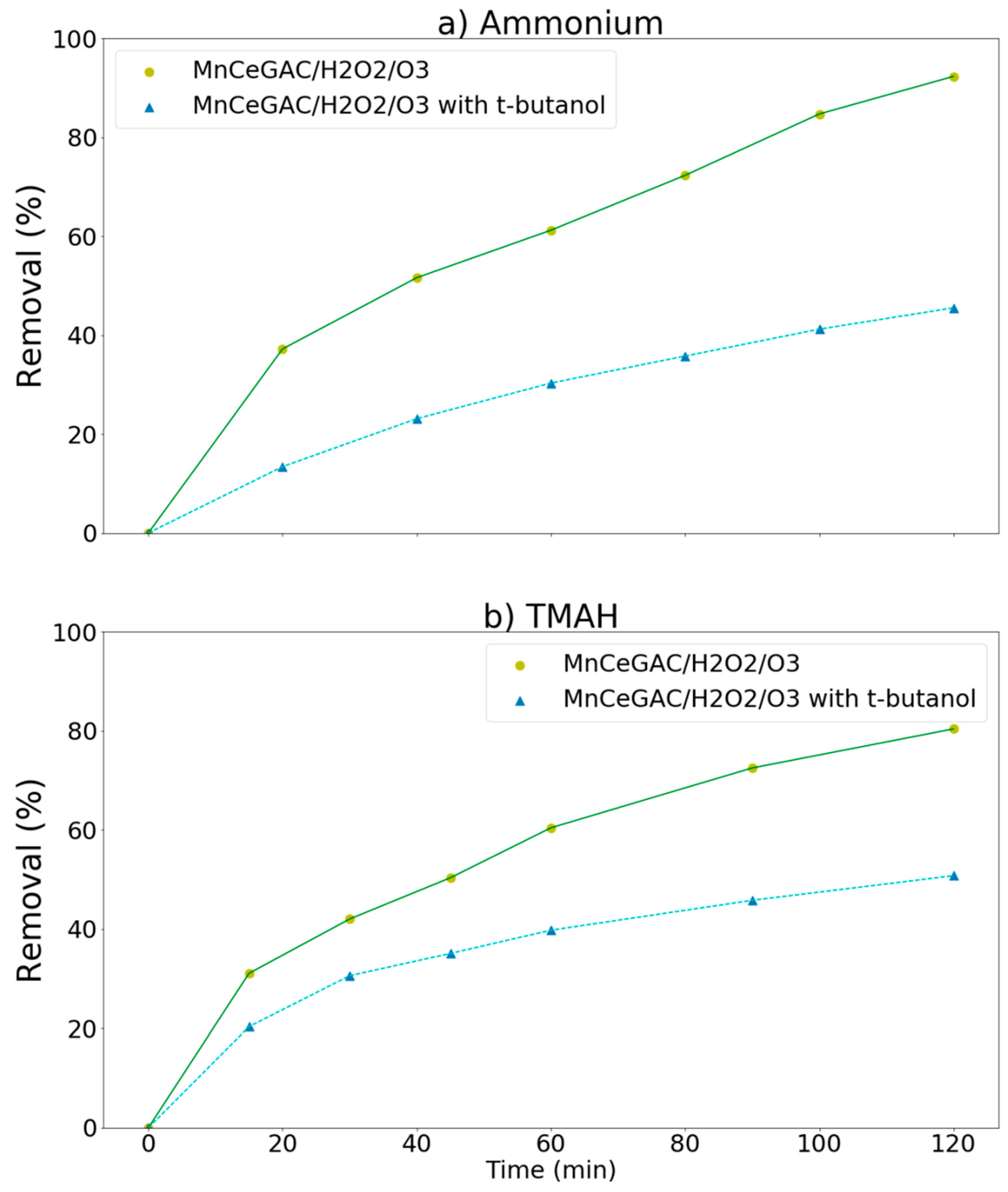
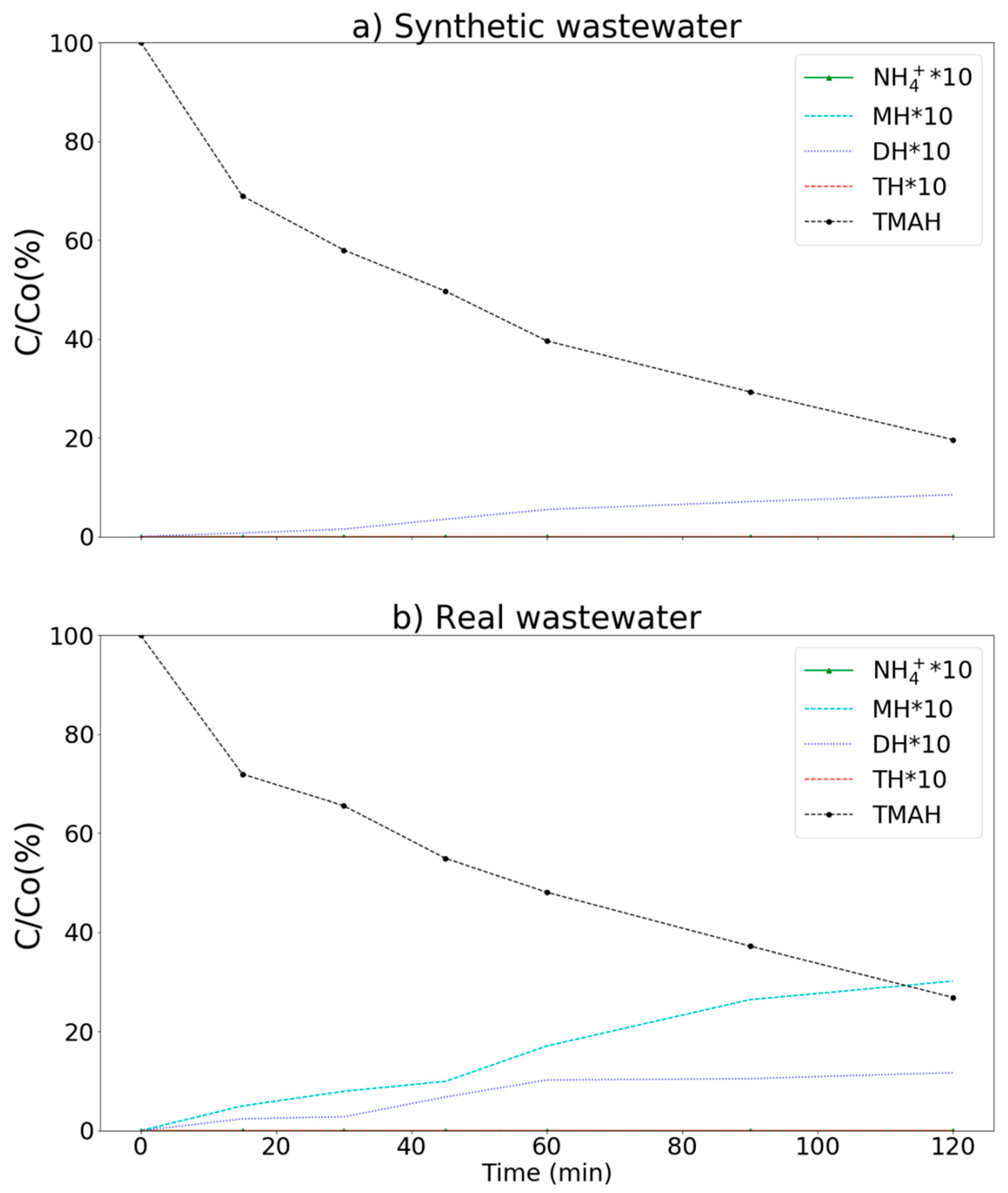
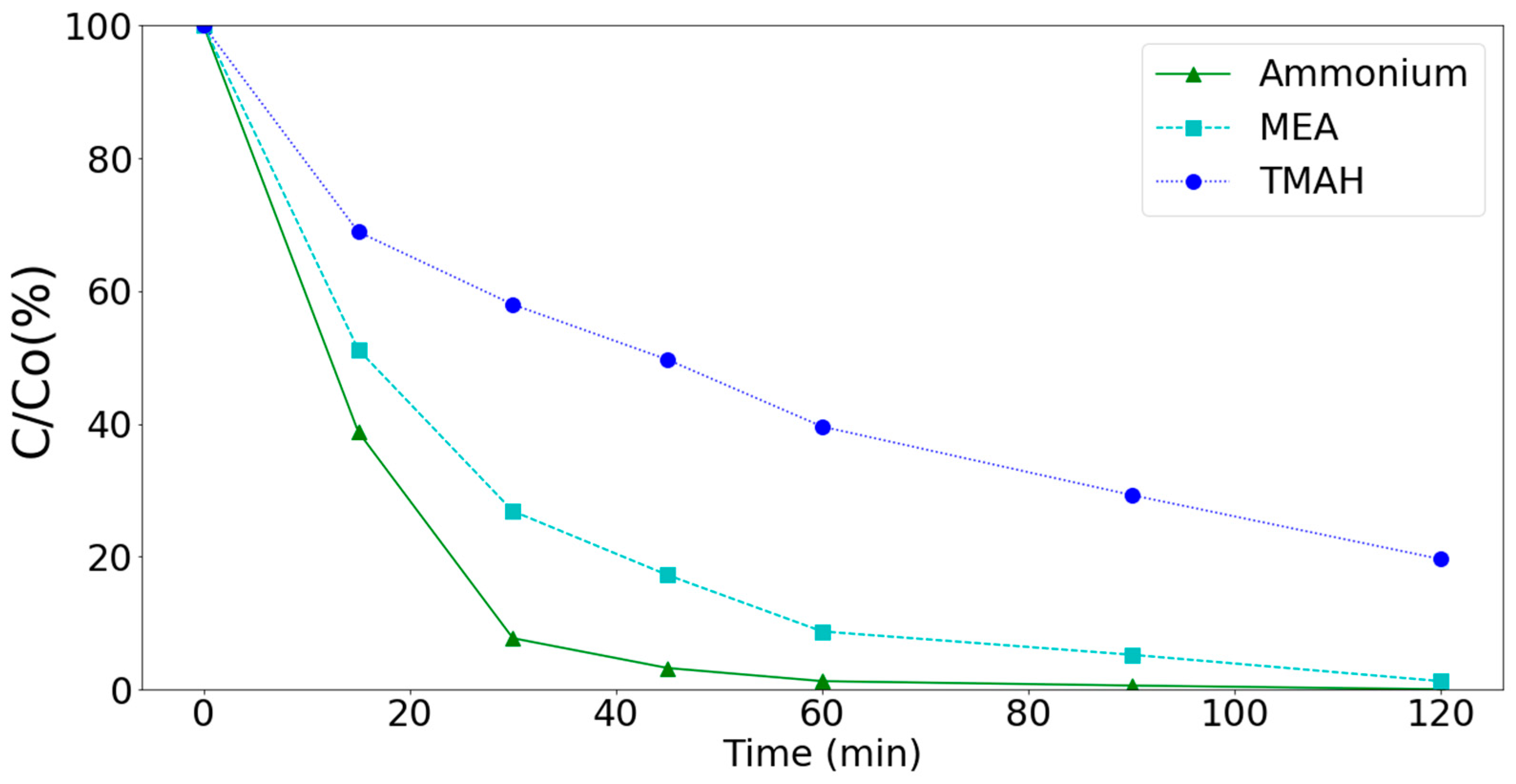
3.3. Removal of Ammonium, MEA, and TMAH by Various Processes (Synthetic Wastewater)
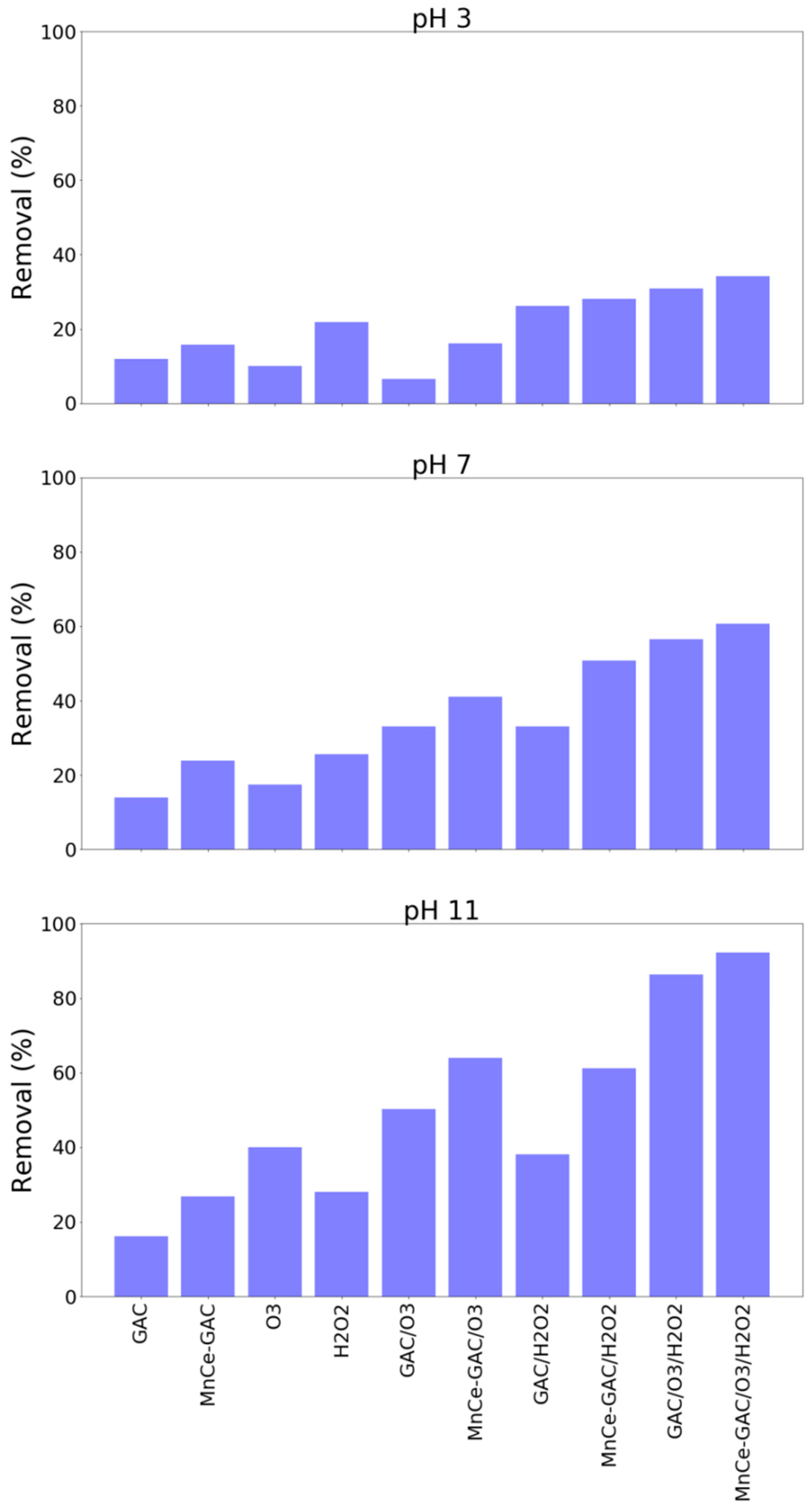
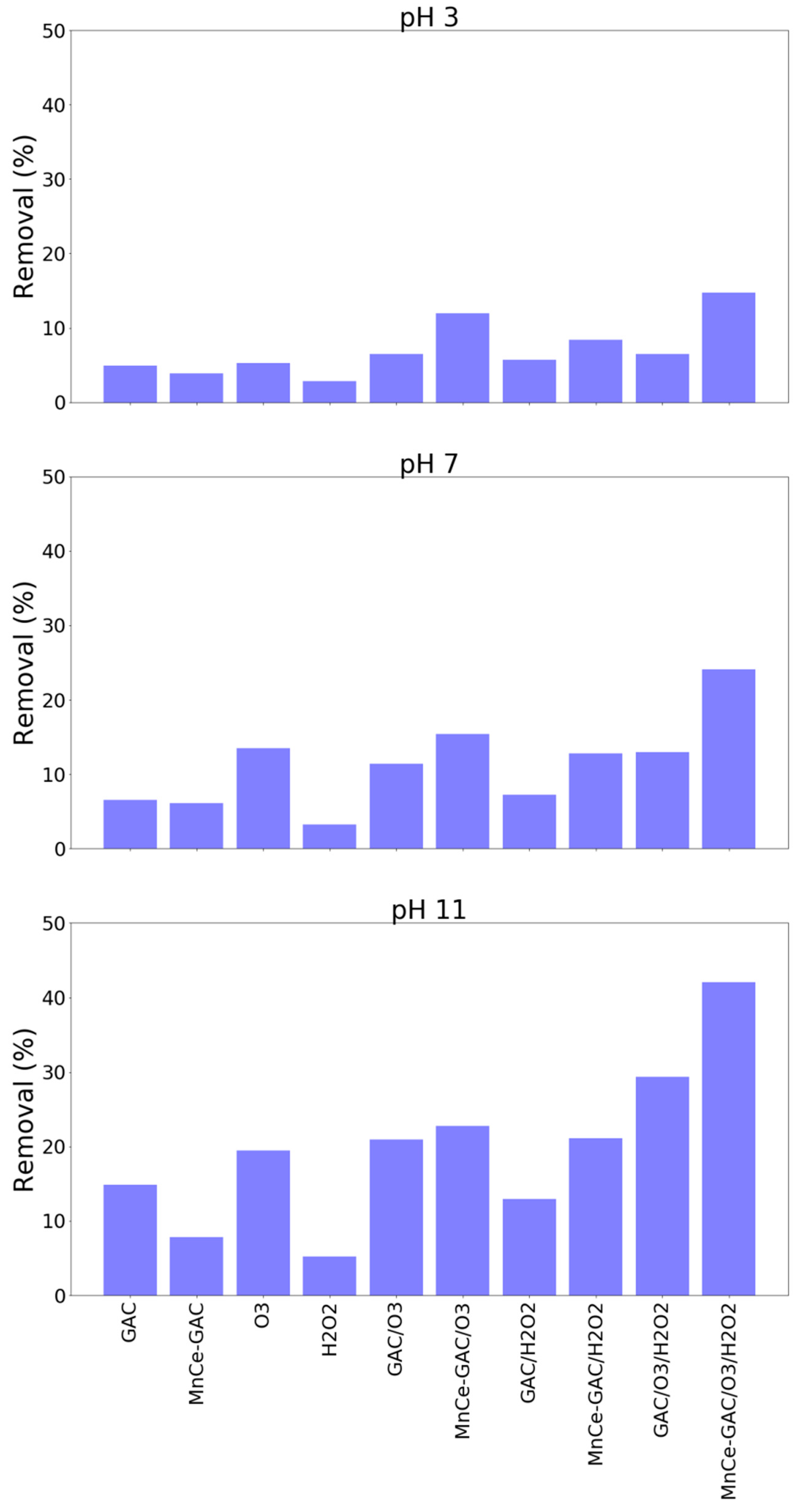
3.4. Real Wastewater
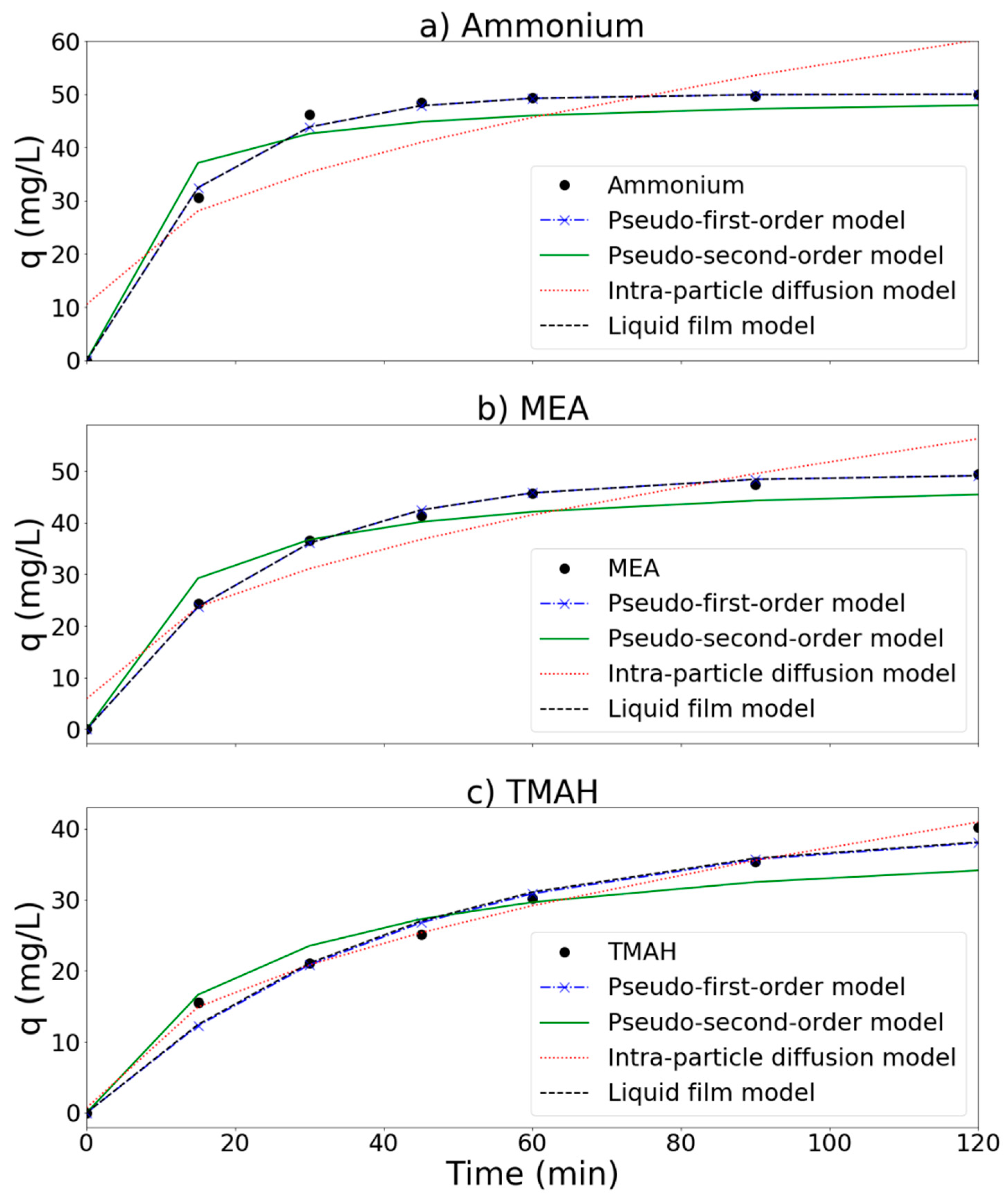
3.5. Reaction Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, C.-C.; Chen, C.-M.; Anotai, J.; Lu, M.-C. Removal of monoethanolamine and phosphate from thin-film transistor liquid crystal display (tft-lcd) wastewater by the fluidized-bed fenton process. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 222, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligaray, M.; Futalan, C.M.; de Luna, M.D.; Wan, M.-W. Removal of chemical oxygen demand from thin-film transistor liquid-crystal display wastewater using chitosan-coated bentonite: Isotherm, kinetics and optimization studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 175, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubel, I.; Kramkowska, M.; Rola, K. Silicon anisotropic etching in tmah solutions containing alcohol and surfactant additives. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 178, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhuri, V.; Son, D.-H.; Lee, D.-G.; Sakong, S.; Jeong, Y.-H.; Cho, I.-T.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-T.; Cristoloveanu, S.; Bae, Y.; et al. 1/f noise characteristics of algan/gan finfets with and without tmah surface treatment. Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 147, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan-Foo, C.; Show-Ying, Y.; Huey-Song, Y.; Pan, J.R. Anaerobic treatment of tetra-methyl ammonium hydroxide (tmah) containing wastewater. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2008, 21, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, J.; Murayama, N.; Matsumoto, S. Recovery of tetra-methyl ammonium hydroxide from waste solution by ion exchange resin. Resour. Process. 2006, 53, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hori, H.; Wachi, S.; Iwamura, K.; Sano, T. Visible light-induced decomposition of monoethanolamine in water using graphitic carbon nitride as a photocatalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2018, 351, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Su, S.B.; Chen, J.L.; Chang, C.P.; Guo, H.R. Tetramethylammonium ion causes respiratory failure related mortality in a rat model. Resuscitation 2012, 83, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yoshinaga, K.; Wu, J.-H.; Chen, W.-Y.; Terashima, M.; Goel, R.; Pangallo, D.; Yasui, H. Kinetic analysis of biological degradation for tetramethylammonium hydroxide (tmah) in the anaerobic activated sludge system at ambient temperature. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 114, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Yang, C.C.; Ger, J.; Deng, J.F.; Hung, D.Z. Tetramethylammonium hydroxide poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. (Phila) 2010, 48, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Lu, L.A.; Lin, J.G. Biodegradation of tetramethylammonium hydroxide (tmah) in completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite (canon) process. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 210, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, C.N.; Whang, L.M.; Chen, P.C. Biological treatment of thin-film transistor liquid crystal display (tft-lcd) wastewater using aerobic and anoxic/oxic sequencing batch reactors. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prahas, D.; Liu, J.C.; Ismadji, S.; Wang, M.-J. Adsorption of tetramethylammonium hydroxide on activated carbon. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 138, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Lu, C. Efficient adsorptive removal of tetramethylammonium hydroxide (tmah) from water using graphene oxide. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Lu, C.; Lin, K.-Y.A. Comparisons of kinetics, thermodynamics and regeneration of tetramethylammonium hydroxide adsorption in aqueous solution with graphene oxide, zeolite and activated carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 326, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.-S.; Chuang, K.-J.; Lin, Y.-F.; Chen, H.-W.; Ma, C.-M. Application of ozone related processes to mineralize tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide in aqueous solution. Int. J. Photoenergy 2013, 2013, 191742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, K.; Okamura, J.; Taira, T.; Sano, K.; Toyoda, A.; Ikeda, M. An efficient treatment technique for tmah wastewater by catalytic oxidation. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2001, 14, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Xu, T. Electrodialysis process for the recycling and concentrating of tetramethylammonium hydroxide (tmah) from photoresist developer wastewater. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 18356–18361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-W.; Liang, C. Oxidative degradation of tmah solution with uv persulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, K.S.; Liang, C. Oxidative degradation of tetramethylammonium hydroxide (tmah) by uv/persulfate and associated acute toxicity assessment. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2017, 52, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federation, W.E.; American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto, N.; Nakamura, E. Bromate formation characteristics of uv irradiation, hydrogen peroxide addition, ozonation, and their combination processes. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 107293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A.; Chelme-Ayala, P.; Drzewicz, P.; Martin, J.W.; Gamal El-Din, M. Effects of ozone and ozone/hydrogen peroxide on the degradation of model and real oil-sands-process-affected-water naphthenic acids. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2015, 37, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, G.; Vega, S.R.; Fick, J.; Tysklind, M.; Ledin, A.; La Cour Jansen, J.; Andersen, H.R. Removal of pharmaceuticals in wwtp effluents by ozone and hydrogen peroxide. Water SA 2014, 40, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gottschalk, C.; Libra, J.; Saupe, A. Ozonation of Water and Waste Water: A Practical Guide to Understanding Ozone and its Application; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; p. 189. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.-W.; Peng, Y.-P.; Chang, C.-N. Applying an activated carbon/silver catalyst to the decomposition of the aqueous solutions of tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 88, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.-P.; Xie, D.-M.; Wei, H.; Liu, W.-P. Degradation of sulfosalicylic acid by o3/uv o3/tio2/uv, and o3/v-o/tio2: A comparative study. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2005, 27, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rischbieter, E.; Stein, H.; Schumpe, A. Ozone solubilities in water and aqueous salt solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2000, 45, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotelo, J.L.; Beltrán, F.J.; González, M.; Domínguez, J. Effect of high salt concentrations on ozone decomposition in water. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2008, 24, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenson, H.K.; Yaminsky, V.V. Solute effects on bubble coalescence. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.B.; Tsouris, C.; DePaoli, D.W.; Thomas Klasson, K. Ozonation of soluble organics in aqueous solutions using microbubbles. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2001, 23, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncz, M.A.; Bruning, H.; Rulkens, W.H.; Zuilhof, H.; Sudhölter, E.J.R. The effect of salts on ozone oxidation processes. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2005, 27, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoigné, J. Chemistry of aqueous ozone and transformation of pollutants by ozonation and advanced oxidation processes. In Quality and Treatment of Drinking Water II; Hrubec, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; pp. 83–141. [Google Scholar]
- Tizaoui, C.; Bouselmi, L.; Mansouri, L.; Ghrabi, A. Landfill leachate treatment with ozone and ozone/hydrogen peroxide systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 140, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, A.L.C.; Silva, M.B.; Izário Filho, H.J. Leachate treatment process at a municipal stabilized landfill by catalytic ozonation: An exploratory study from taguchi orthogonal array. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 26, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.V.; Greenstock, C.L.; Helman, W.P.; Ross, A.B. Critical review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 513–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Khan, H.M.; Sayed, M.; Cooper, W.J. Advanced oxidation for the treatment of chlorpyrifos in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-M.; Lu, C.-S.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chang, D.T.; Fan, H.-J. Landfill leachate treatment with mn and ce oxides impregnated gac–ozone treatment process. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 482, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, W. Kinetics and mechanisms of photocatalytic degradation of (ch3)nnh4-n+ (0 ≤ n ≤ 4) in tio2 suspension: The role of oh radicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2019–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sayari, A.; Adnot, A.; Larachi, F. Composition-activity effects of mn–ce–o composites on phenol catalytic wet oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 32, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczak, A.; Keinath, T.M. Kinetics of sorption and desorption of copper (ii) and lead (ii) on activated carbon. Water Environ. Res. 1993, 65, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.J.; Shu, H.Y.; Tajima, K. Decolorization of acid black 24 by the fegac/h2o2 process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 128, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, N.; Sundaram, M.M. Kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue by adsorption on various carbons—A comparative study. Dye. Pigment. 2001, 51, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onundi, Y.B.; Mamun, A.A.; Al khatib, M.; Ahmed, Y.M. Adsorption of copper, nickel and lead ions from synthetic semiconductor industrial wastewater by palm shell activated carbon. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khateeb, L.A.; Almotiry, S.; Salam, M.A. Adsorption of pharmaceutical pollutants onto graphene nanoplatelets. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 248, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Plant (1) | Product | pH | Cond. (2) | SS | COD | BOD | Nitrate | Sulfate | NH3-N | TMAH | Discharge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μS/cm | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | CMD | |||
| Plant 1 | LCD-GS | 7.1 | 1351 | 32.7 | 82.2 | 38.44 | 6.84 | 130.46 | 2.12 | 35.03 | 5447 |
| Plant 2 | PV, TFT-LCD | 6.8 | 2255 | 40.4 | 80 | 36.65 | 30.42 | 156.59 | 3.24 | 127.86 | 9892 |
| Plant 3 | TFT-LCD | 6.9 | 3588 | 79.4 | 296.6 | 169.43 | 42.18 | 160.32 | 9.78 | 100.21 | 12,381 |
| Plant 4 | TFT-LCD | 6.7 | 3254 | 82.0 | 205.1 | 70.31 | 15.25 | 309.75 | 1.73 | 64.97 | 8738 |
| Plant 5 | FM, DRAM | 6.9 | 1546 | 16.1 | 28.8 | 14.78 | 8.01 | 281.31 | 6.87 | 39.76 | 5691 |
| Plant 6 | IC | 6.5 | 7390 | 6.4 | 150.1 | 35.70 | 188.16 | 1876.62 | 12.54 | 91.19 | 3565 |
| Plant 7 | IC | 6.5 | 7394 | 4.8 | 148.7 | 31.03 | 274.28 | 1850.13 | 9.75 | 84.41 | 3503 |
| Plant 8 | IC | 6.4 | 10,941 | 6.5 | 137.3 | 37.87 | 96.99 | 3167.68 | 13.96 | 109.43 | 4062 |
| Plant 9 | IC | 6.5 | 10,643 | 25.0 | 335.7 | 139.33 | 166.73 | 1212.35 | ND (3) | 84.38 | 17,778 |
| Plant 10 | IC-P&T | 7.2 | 1568 | 33.3 | 40.3 | 13.65 | 78.31 | 337.31 | ND | 27.33 | 3586 |
| Adsorbate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | Ammonium | MEA | TMAH | |
| Pseudo-first-order model | K1 | 0.161 | 0.101 | 0.056 |
| RMSE | 1.31 | 0.43 | 2.61 | |
| Pseudo-second-order model | K2 | 0.00383 | 0.00196 | 0.00117 |
| RMSE | 12.81 | 8.89 | 8.15 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion model | Kp | 4.54 | 4.60 | 3.68 |
| Cp | 10.51 | 5.91 | 0.70 | |
| RMSE | 60.25 | 22.28 | 0.38 | |
| Liquid film model | KL | 0.0698 | 0.0437 | 0.0247 |
| RMSE | 1.31 | 0.43 | 2.58 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, D.T.; Park, D.; Zhu, J.-J.; Fan, H.-J. Assessment of an MnCe-GAC Treatment Process for Tetramethylammonium-Contaminated Wastewater from Optoelectronic Industries. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4578. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214578
Chang DT, Park D, Zhu J-J, Fan H-J. Assessment of an MnCe-GAC Treatment Process for Tetramethylammonium-Contaminated Wastewater from Optoelectronic Industries. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(21):4578. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214578
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Da Tian, Daeryong Park, Jun-Jie Zhu, and Huan-Jung Fan. 2019. "Assessment of an MnCe-GAC Treatment Process for Tetramethylammonium-Contaminated Wastewater from Optoelectronic Industries" Applied Sciences 9, no. 21: 4578. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214578
APA StyleChang, D. T., Park, D., Zhu, J.-J., & Fan, H.-J. (2019). Assessment of an MnCe-GAC Treatment Process for Tetramethylammonium-Contaminated Wastewater from Optoelectronic Industries. Applied Sciences, 9(21), 4578. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214578








