Multichannel Active Noise Control Based on Filtered-x Affine Projection-Like and LMS Algorithms with Switching Filter Selection
Abstract
1. Introduction
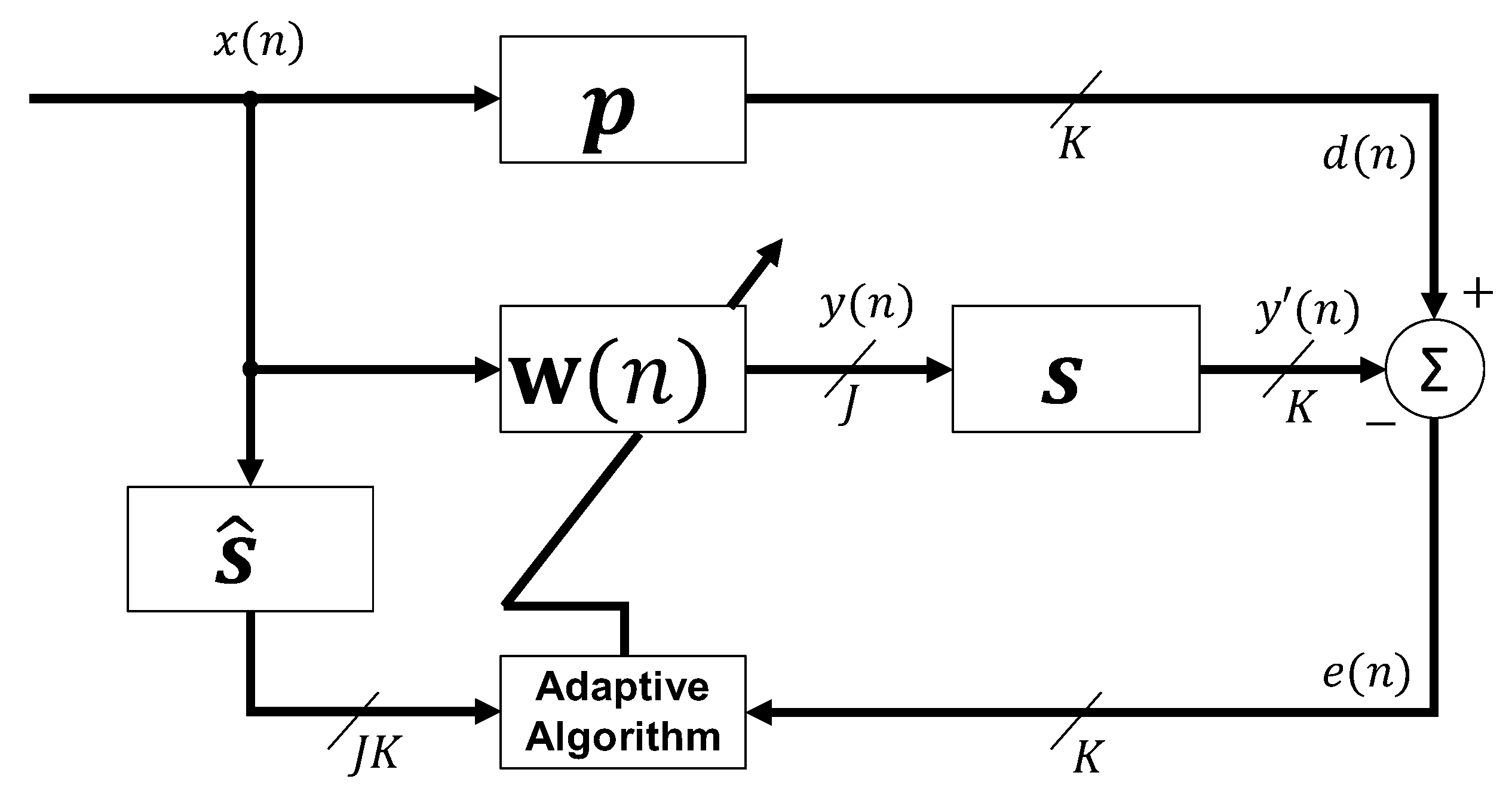
2. A Brief Introduction to the Multichannel Filtered-x Affine Projection-Like (FXAPL-I) and Filtered-x Least Mean Square (FXLMS) Algorithms
- FXLMSThe FXLMS algorithm updates the coefficients as follows:where is a fixed value between [0,1] and is usually chosen by trial and error. The FXLMS algorithm is widely used because of its simplicity, robustness and steady-state MSE. However, its convergence speed is low, which can restrict its use in some practical applications. The algorithms based on AP overcome the aforementioned problem because its convergence speed is very fast by paying a penalty in terms of computational complexity and a large MSE at the steady state.
- FXAPL-ITo calculate the coefficient update of the FXAPL-I algorithm, the filtered-x signals are arranged in a matrix, as follows:where represents the filtered-x signals as follows:Based on Equation (7), the filter update for the FXAPL-I algorithm is as follows:where step size is calculated using the following expression:where is a scaling factor used to compensate the mismatch between and . Commonly, the value of can be defined in the interval , and the designer can choose it by trial and error.A critical parameter of the existing FXAPL-I algorithm is the scaling factor because the convergence can be affected by choosing a wrong value by the designer. Until now, there has been no established method to determine the scaling factor. The following section presents a new method to dynamically adjust this parameter to optimize the design time.
Dynamic Adjustment of the Scaling Factor
3. Proposed Scheme with Switching Filter Selection
4. Analysis of Computational Complexity
4.1. Analysis of Computational Complexity under Single Channel ANC System Configuration
4.2. Analysis of Computational Complexity under Multichannel ANC System Configuration
5. Simulation Results
- A multitonal input with frequencies 200, 300, and 400 Hz. We added white Gaussian noise with an SNR of 30 dB to to validate the robustness of the proposed filtering scheme.
- A white Gaussian noise signal with variance .
5.1. Simulation of a Single-Channel ANC System
- First experiment: Multitonal noise input
- Second experiment: Gaussian noise input
5.2. Simulation of a Multi-Channel ANC System
- First experiment: Multitonal noise input
- Second experiment: Gaussian noise input
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
- We use the filtered-x affine projection-like (FXAPL-I) algorithm to achieve fast convergence.
- We employ a filtered-x least mean square (FXLMS) algorithm to guarantee a low steady-state MSE.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kajikawa, Y.; Gan, W.S.; Kuo, S.M. Recent advances on active noise control: Open issues and innovative applications. APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process. 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, N.V.; Panda, G. Advances in active noise control: A survey, with emphasis on recent nonlinear techniques. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeki, K.; Umeda, T. An adaptive filtering algorithm using an orthogonal projection to an affine subspace and its properties. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 1984, 67, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Albu, F.; Ferrer, M.; de Diego, M. Evolutionary and variable step size strategies for multichannel filtered-x affine projection algorithms. IET Signal Process. 2013, 7, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.M.; Park, P. An optimal variable step-size affine projection algorithm for the modified filtered-x active noise control. Signal Process. 2015, 114, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalos, J.G.; Rodriguez, A.; Martinez, H.M.; Sanchez, J.C.; Perez, H.M. Multichannel Filtered-X Error Coded Affine Projection-Like Algorithm with Evolving Order. Shock Vib. 2017, 2017, 3864951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arablouei, R.; Doğançay, K. Affine projection algorithm with selective projections. Signal Process. 2012, 92, 2253–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Ferrer, A.; de Diego, M.; Pinero, M. An affine projection algorithm with variable step size and projection order. Digit. Signal Process. 2012, 22, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas-Garcia, J.; Azpicueta-Ruiz, L.A.; Silva, M.T.; Nascimento, V.H.; Sayed, A.H. Combinations of adaptive filters: Performance and convergence properties. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2016, 33, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.W. Adaptive combination of Affine projection and NLMS algorithms. Signal Process. 2014, 100, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z. Adaptive combination of affine projection and NLMS algorithms based on variable step-sizes. Digit. Signal Process. 2016, 59, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, M.; Gonzalez, A.; de Diego, M.; Pinero, G. Convex combination filtered-x algorithms for active noise control systems. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2013, 21, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, N.V.; Gonzalez, A. Convex combination of nonlinear adaptive fil- ters for active noise control. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 76, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Omour, A.M.; Zidouri, A.; Iqbal, N.; Zerguine, A. Filtered-x least mean fourth (FXLMF) and leaky FXLMF adaptive algorithms. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2016, 1, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhao, H. Filtered-x generalized mixed norm (FXGMN) algorithm for active noise control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 107, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, A.; Maya, X.; Avalos, J.G.; Sánchez, G.; Sánchez, J.C.; Pérez, H.M.; Sácnhez, G. A Time-Efficient Method for Determining an Optimal Scaling Factor and the Encoder Resolution in the Multichannel FXECAP-L Algorithm with Evolving Order for Active Noise Control. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.C.; Sayed, A.H.; Song, W.J. Variable step-size NLMS and affine projection algorithms. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2004, 11, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.E.; Song, W.J. An alternating selection for parallel affine projection filters. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 2011, 94, 1576–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhotto, M.Z.A.; Antoniou, A. Affine-Projection-Like Adaptive-Filtering Algorithms Using Gradient-Based Step Size. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2014, 61, 2048–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.M.; Morgan, D.R. Active Noise Control Systems: Algorithms and DSP Implementations; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]





| Algorithm | Multiplications | Typical Case |
|---|---|---|
| FXLMS | 330 | |
| FXAPL-I | 2061 | |
| FXA-AP | 6921 | |
| FXAPL-I with switching selection | 2384 | |
| FXLMS with switching selection | 780 |
| Algorithm | Additions | Typical Case |
|---|---|---|
| FXLMS | 326 | |
| FXAPL-I | 2461 | |
| FXA-AP | 6062 | |
| FXAPL-I with switching selection | 2698 | |
| FXLMS with switching selection | 692 |
| Algorithm | Memory |
|---|---|
| FXLMS | |
| FXAPL-I | |
| FXA-AP | |
| Proposed algorithm with fixed scaling factor | |
| Proposed algorithm with dynamic scaling factor |
| Algorithm | Multiplications | Typical Case |
|---|---|---|
| FXLMS | 1116 | |
| FXAPL-I | 8444 | |
| FXA-AP | 26,748 | |
| FXAPL-I with switching selection | 10,128 | |
| FXLMS with switching selection | 3510 |
| Algorithm | Additions | Typical Case |
|---|---|---|
| FXLMS | 1106 | |
| FXAPL-I | 8956 | |
| FXA-AP | 23,628 | |
| FXAPL-I with switching selection | 10,244 | |
| FXLMS with switching selection | 4108 |
| Algorithm | Memory |
|---|---|
| FXLMS | |
| FXAPL-I | |
| FXA-AP | |
| Proposed algorithm with fixed scaling factor | |
| Proposed algorithm with dynamic scaling factor |
| Parameters | Single-Channel ANC | Multi-Channel ANC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Tonal Input | Gaussian Noise Input | Multi-Tonal Input | Gaussian Noise Input | |
| 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.001 | 0.01 | |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 0.00001 | 0.0006 | 0.00001 | 0.0007 | |
| Algorithm | Multiplications | Additions |
|---|---|---|
| FXLMS | 660,000,000 | 652,000,000 |
| FXAPL-I | 4,122,000,000 | 4,922,000,000 |
| FXA-AP | 13,842,000,000 | 12,124,000,000 |
| Proposed algorithm with fixed scaling factor | 1,601,824,300 | 1,436,306,450 |
| Proposed algorithm with dynamic scaling factor | 1,631,122,340 | 1,502,695,020 |
| Algorithm | Multiplications | Additions |
|---|---|---|
| FXLMS | 660,000,000 | 652,000,000 |
| FXAPL-I | 4,122,000,000 | 4,922,000,000 |
| FXA-AP | 13,842,000,000 | 12,124,000,000 |
| Proposed algorithm with fixed scaling factor | 1,678,715,530 | 1,581,390,400 |
| Proposed algorithm with dynamic scaling factor | 1,717,833,600 | 1,582,122,590 |
| Algorithm | Multiplications | Additions |
|---|---|---|
| FXLMS | 2,232,000,000 | 2,212,000,000 |
| FXAPL-I | 16,888,000,000 | 17,912,000,000 |
| FXA-AP | 53,496,000,000 | 47,256,000,000 |
| Proposed algorithm with fixed scaling factor | 6,390,450,195 | 8,017,950,030 |
| Proposed algorithm with dynamic scaling factor | 8,023,620,846 | 10,456,255,000 |
| Algorithm | Multiplications | Additions |
|---|---|---|
| FXLMS | 2,232,000,000 | 2,212,000,000 |
| FXAPL-I | 16,888,000,000 | 17,912,000,000 |
| FXA-AP | 53,496,000,000 | 47,256,000,000 |
| Proposed algorithm with fixed scaling factor | 7,925,438,400 | 9,779,913,600 |
| Proposed algorithm with dynamic scaling factor | 10,558,618,612 | 12,000,526,248 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vázquez, Á.A.; Pichardo, E.; Avalos, J.G.; Sánchez, G.; Martínez, H.M.; Sánchez, J.C.; Pérez, H.M. Multichannel Active Noise Control Based on Filtered-x Affine Projection-Like and LMS Algorithms with Switching Filter Selection. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214669
Vázquez ÁA, Pichardo E, Avalos JG, Sánchez G, Martínez HM, Sánchez JC, Pérez HM. Multichannel Active Noise Control Based on Filtered-x Affine Projection-Like and LMS Algorithms with Switching Filter Selection. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(21):4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214669
Chicago/Turabian StyleVázquez, Ángel A., Eduardo Pichardo, Juan G. Avalos, Giovanny Sánchez, Hugo M. Martínez, Juan C. Sánchez, and Héctor M. Pérez. 2019. "Multichannel Active Noise Control Based on Filtered-x Affine Projection-Like and LMS Algorithms with Switching Filter Selection" Applied Sciences 9, no. 21: 4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214669
APA StyleVázquez, Á. A., Pichardo, E., Avalos, J. G., Sánchez, G., Martínez, H. M., Sánchez, J. C., & Pérez, H. M. (2019). Multichannel Active Noise Control Based on Filtered-x Affine Projection-Like and LMS Algorithms with Switching Filter Selection. Applied Sciences, 9(21), 4669. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214669





