Evaluation of Tip Loss Corrections to AD/NS Simulations of Wind Turbine Aerodynamic Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Axisymmetric AD/NS Method
2.1. Governing Equations
2.2. Force on Actuator Disc
3. Tip Loss Corrections
3.1. Glauert Correction
3.2. A Newly Developed Correction
4. Applying Corrections to AD/NS Simulation
4.1. Application of Glauert Tip Loss Factor F
4.1.1. Glauert-A Correction
4.1.2. Glauert-B Correction
4.1.3. Glauert-C Correction
4.2. Application of New Correction
5. Computational Setup
5.1. Flow Solver and Mesh Configuration
5.2. Simulation Cases
6. Simulation Results
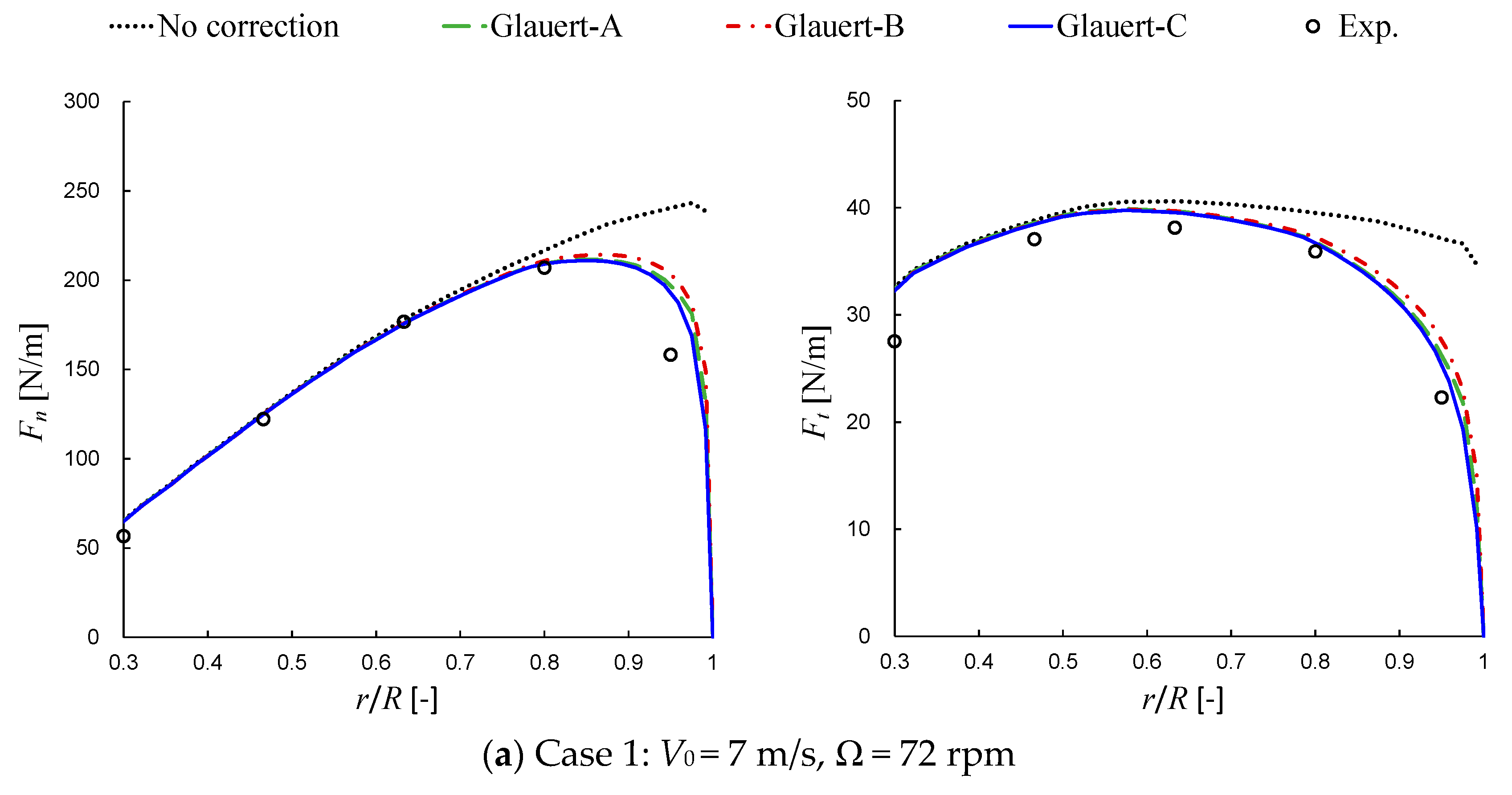
6.1. Results of Glauert-Type Corrections
6.1.1. Glauert-A/B/C Corrections
6.1.2. Comparison with BEMT Results
6.2. Results of New Tip Loss Correction
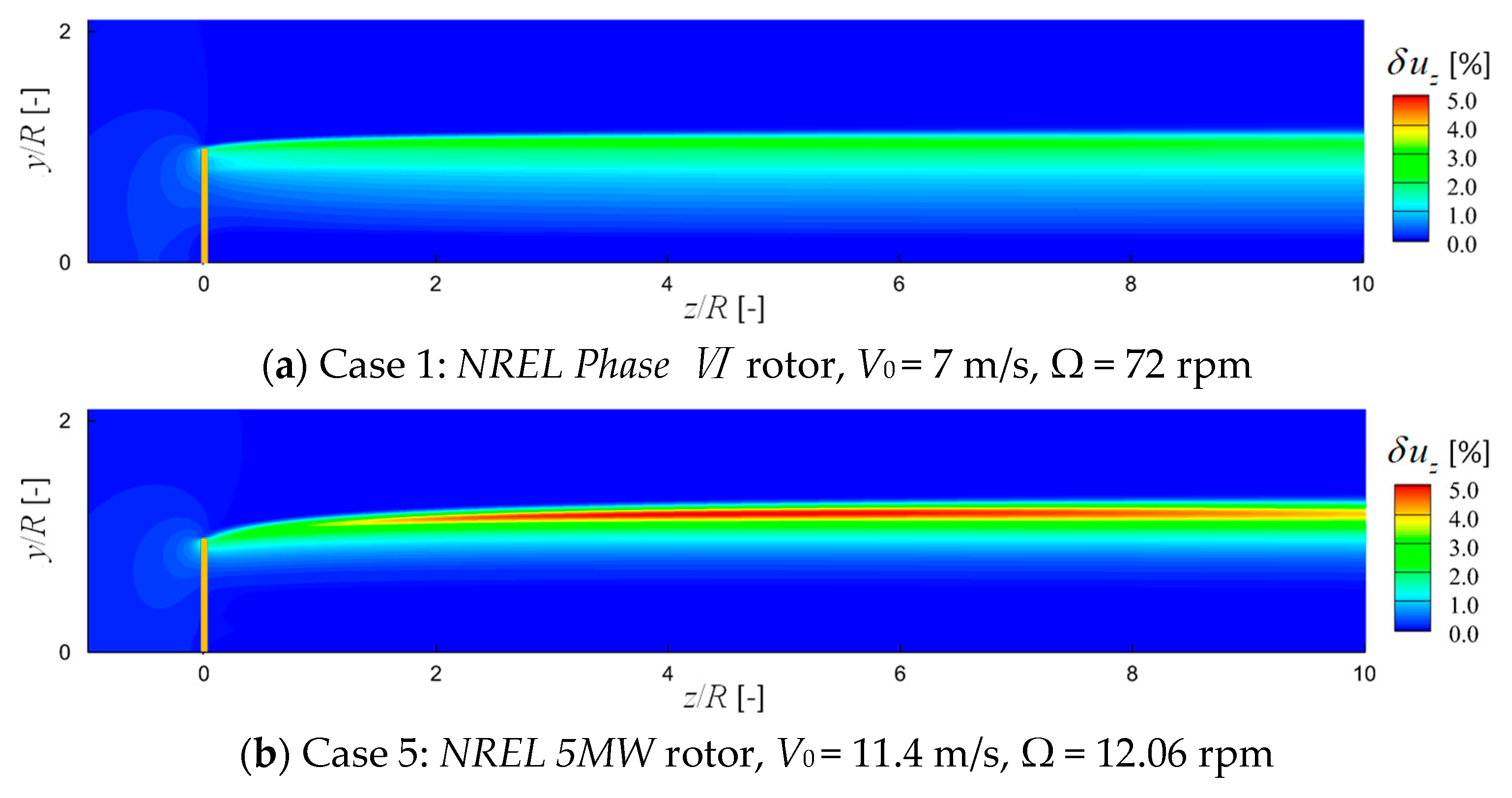
6.3. Comparison of Velocity Field
7. Conclusions
- The three different implementations of the Glauert tip loss factor showed a certain degree of difference to each other, although the relative difference in blade loads is generally no more than 4%. The Glauert-C correction, in which the tip loss factor F is directly used to be divided by the interference factors, is recommended for AD/NS simulations, since it gives results closest to the reference data in all the studied cases.
- The performance of the Glauert-C correction in AD/NS was found to be almost equal to that of the standard Glauert correction in BEMT. That provides evidence for the reasonableness of the transplantation of the tip loss correction from BEMT into AD/NS.
- The Glauert-type corrections tend to make an over-prediction of the blade tip loads. In contrast, the new correction showed superior performance in various conditions of the present study.
- A difference in tip loss correction leads to the influence of not only on the blade tip loads, but also on the velocity field around and after the rotor. The range of this influence is observed expanding in the rotor wake. In addition, the magnitude of this influence is found to be increased after the NREL 5 MW rotor.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Renewables 2019 Global Status Report; REN21: Paris, France, 2019.
- Shen, W.Z. Special issue on wind turbine aerodynamics. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.O.L. The classical blade element momentum method. In Aerodynamics of Wind Turbines, 3rd ed.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2015; pp. 38–53. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, J.N. General Momentum Theory for Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines; Springer International Publishing Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, J.; Watters, C.S.; Masson, C. CFD in wind energy: The virtual, multiscale wind tunnel. Energies 2010, 3, 989–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderse, B.; van er Pijl, S.P.; Koren, B. Review of computational fluid dynamics for wind turbine wake aerodynamics. Wind Energy 2011, 14, 799–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Alam, M.M.; Alhems, L.M.; Rafique, M.M. Horizontal axis wind turbine blade design methodologies for efficiency enhancement—A review. Energies 2018, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Tang, H.W.; Wang, T.G.; Zhu, C. Accurate RANS simulation of wind turbines stall by turbulence coefficient calibration. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.V.; Lengsfeld, C. Development of a computational system to improve wind farm layout, part I: Medel validation and near wake analysis. Energies 2019, 12, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, R.; Sørensen, J.N.; Shen, W.Z. Modelling and analysis of the flow field around a coned rotor. Wind Energy 2001, 4, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, D.J. A general momentum theory applied to an energy-extracting actuator disc. Wind Energy 2004, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, M.; Duponcheel, M.; Winckelmans, G.; Chatelain, P. An actuator disk method with tip-loss correction based on local effective upstream velocities. Wind Energy 2018, 21, 766–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simisiroglou, N.; Polatidis, H.; Ivanell, S. Wind farm power production assessment: Introduction of a new actuator disc method and comparison with existing models in the context of a case study. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, J.N.; Shen, W.Z. Numerical modeling of wind turbine wakes. J. Fluids Eng. 2002, 124, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.Z.; Zhu, W.J.; Sørensen, J.N. Actuator line/Navier-Stokes computations for the MEXICO rotor: Comparison with detailed measurements. Wind Energy 2012, 15, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Tossas, L.A.; Churchfield, M.J.; Meneveau, C. A highly resolved large-eddy simulation of a wind turbine using an actuator line model with optimal body force projection. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 753, 082014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Tossas, L.A.; Meneveau, C. Filtered lifting line theory and application to the actuator line model. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 863, 269–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, F.; Vignaroli, A. An application of the actuator disc model for wind turbine wakes calculations. Appl. Energy 2013, 101, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Porte-Agel, F. Modeling turbine wakes and power losses within a wind farm using LES: An application to the Horns Rev offshore wind farm. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessarego, M.; Shen, W.Z.; van der Laan, M.P.; Hansen, K.S.; Zhu, W.J. CFD simulations of flows in a wind farm in complex terrain and comparisons to measurements. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, G.P.N.; Saulo, A.C.; Otero, A.D. Wind farm interference and terrain interaction simulation by means of an adaptive actuator disc. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2019, 186, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargallo-Peiró, A.; Avila, M.; Owen, H.; Prieto-Godino, L.; Folcha, L. Mesh generation, sizing and convergence for onshore and offshore wind farm Atmospheric Boundary Layer flow simulation with actuator discs. J. Comput. Phys. 2018, 375, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Sørensen, J.N. Far-wake meandering induced by atmospheric eddies in flow past a wind turbine. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 846, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.J.; Shen, W.Z.; Barlas, E.; Bertagnolio, F.; Sørensen, J.N. Wind turbine noise generation and propagation modeling at DTU Wind Energy: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 88, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.Z.; Zhu, W.J.; Barlas, E; Barlas, E.; Li, Y. Advanced flow and noise simulation method for wind farm assessment in complex terrain. Renew. Energy 2019, 143, 1812–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauert, H. Airplane propellers. In Aerodynamic Theory; Durand, W.F., Ed.; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1963; pp. 169–360. [Google Scholar]
- Branlard, E. Wind Turbine Tip-Loss Corrections. Master’s Thesis, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.Z.; Mikkelsen, R.; Sørensen, J.N.; Bak, C. Tip loss corrections for wind turbine computations. Wind Energy 2005, 8, 457–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, J.N.; Dag, K.O.; Ramos-Garía, N. A new tip correction based on the decambering approach. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 524, 012097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.H.; Okulov, V.L.; Bhattacharjee, D. Direct calculation of wind turbine tip loss. Renew. Energy 2016, 95, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, S.; Maniaci, D.C. Methodology to determine a tip-loss factor for highly loaded wind turbines. AIAA J. 2017, 55, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimshurst, A.; Willden, R.H.J. Computatioanl observations of the tip loss mechanism experienced by horizontal axis rotors. Wind Energy 2018, 21, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Shen, W.Z.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. A tip loss correction model for wind turbine aerodynamic performance prediction. Renew. Energy 2020, 147, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, M.M.; Simms, D.A.; Fingersh, L.J.; Jager, D.W.; Cotrell, J.R.; Schreck, S.; Larwood, S.M. Unsteady Aerodynamics Experiment Phase Vi: Wind Tunnel Test Configurations and Available Data Campaigns; NREL/TP-500-29955; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2001.
- Jonkman, J.; Butterfield, S.; Musial, W.; Scott, G. Definition of A 5-Mw Reference Wind Turbine for Offshore System Development; Technical Report NREL/TP-500-38060; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2009.
- Prandtl, L. Applications of Modern Hydrodynamics to Aeronautics; NACA: Washington DC, USA, 1921; No. 116. [Google Scholar]
- Prandtl, L.; Betz, A. Vier Abhandlungen zur Hydrodynamik und Aerodynamik; Göttingen Nachrichten: Göttingen, Germany, 1927. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Ramdin, S.F. Prandtl Tip Loss Factor Assessed. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, R.E.; Lissaman, P.B.S. Applied Aerodynamics of Wind Power Machines; NSF/RA/N-74113; Oregon State University: Corvallis, OR, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- De Vries, O. Fluid Dynamic Aspects of Wind Energy Conversion; AGARD: Brussels, Belgium, 1979; AG-243, Chapter 4; pp. 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, J.N.; Kock, C.W. A model for unsteady rotor aerodynamics. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1995, 58, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, R. Actuator Disc Methods Applied to Wind Turbines. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.Z.; Sørensen, J.N.; Mikkelsen, R. Tip loss correction for Actuator/Navier-Stokes computations. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2005, 127, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, J.A. Basis3d—A Platform for Development of Multiblock PDE Solvers; Technical Report AFM; Technical University of Denmark: Lyngby, Denmark, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, N.N. General Purpose Flow Solver Applied Over Hills; RISØ-R-827-(EN); Risø National Laboratory: Roskilde, Denmark, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, F.R. Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.L.; Zhu, W.J.; Shen, W.Z.; Sørensen, J.N.; Zhao, N. Investigation of modified AD/RANS models for wind turbine wake predictions in large wind farm. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 524, 012151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospathopoulos, J.M.; Politis, E.S. Evaluation of the effects of turbulence model enhancements on wind turbine wake predictions. Wind Energy 2011, 14, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhu, W.; Shen, W; Sørensen, J.N.; Wang, T. Development of a CFD-based wind turbine rotor optimization tool in considering wake effects. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, J.M. Modeling of the UAE Wind Turbine for Refinement of FAST_AD; Technical Report NREL/TP-500-34755; National Renewable Energy Lab.: Golden, CO, USA, 2003.




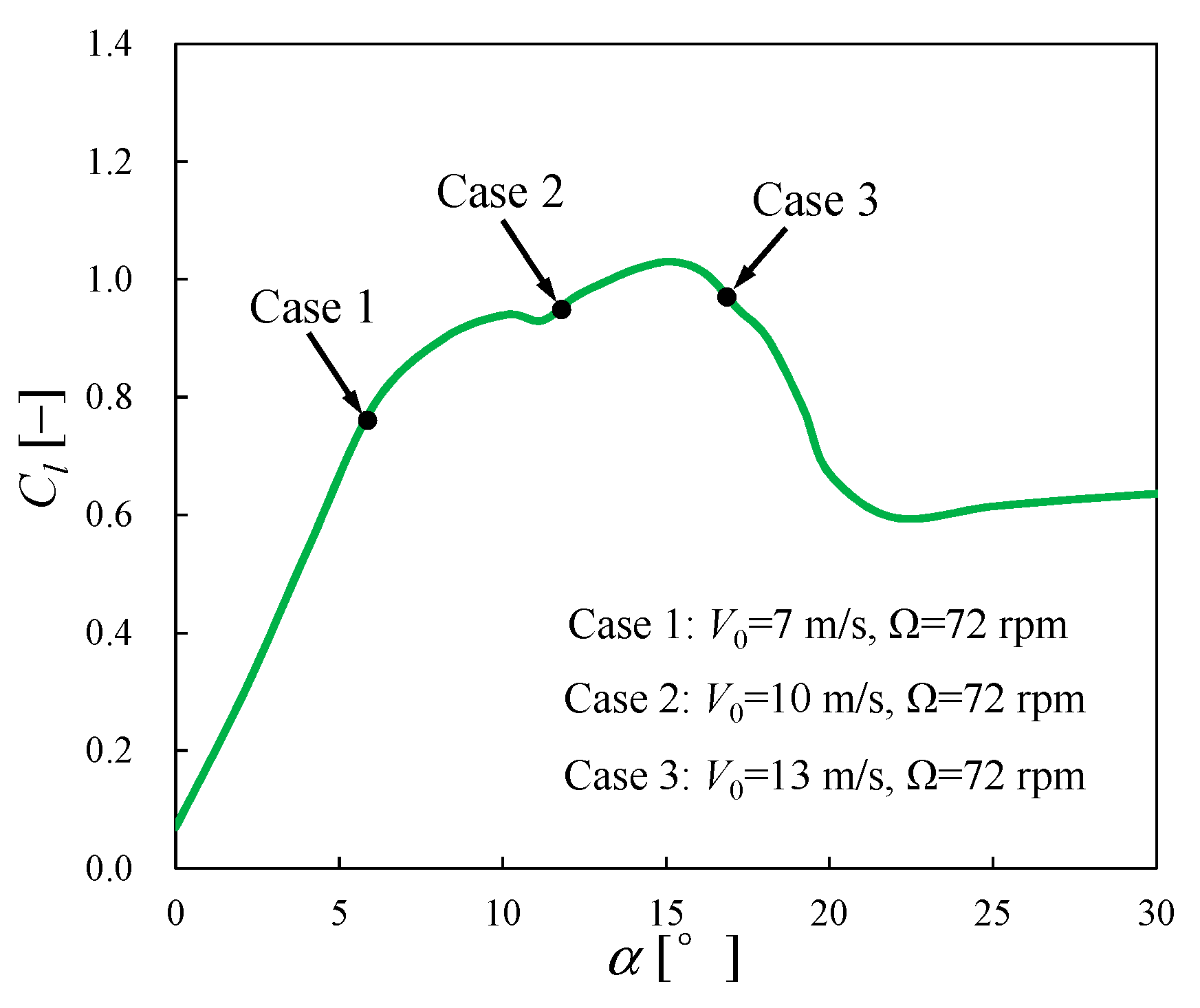




| Rotor Name | Number | Wind Speed (V0, m/s) | Rotating Speed (Ω, rpm) | Tip Speed Ratio (λ) | Tip Pitch Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NREL PhaseⅥ | 1 | 7.0 | 72 | 5.4 | 3 |
| 2 | 10.0 | 72 | 3.8 | 3 | |
| 3 | 13.0 | 72 | 2.9 | 3 | |
| NREL 5MW | 4 | 8.0 | 9.22 | 7.60 | 0 |
| 5 | 11.4 | 12.06 | 6.98 | 0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, W.; Wang, T.G.; Zhu, W.J.; Shen, W.Z. Evaluation of Tip Loss Corrections to AD/NS Simulations of Wind Turbine Aerodynamic Performance. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4919. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224919
Zhong W, Wang TG, Zhu WJ, Shen WZ. Evaluation of Tip Loss Corrections to AD/NS Simulations of Wind Turbine Aerodynamic Performance. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(22):4919. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224919
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Wei, Tong Guang Wang, Wei Jun Zhu, and Wen Zhong Shen. 2019. "Evaluation of Tip Loss Corrections to AD/NS Simulations of Wind Turbine Aerodynamic Performance" Applied Sciences 9, no. 22: 4919. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224919
APA StyleZhong, W., Wang, T. G., Zhu, W. J., & Shen, W. Z. (2019). Evaluation of Tip Loss Corrections to AD/NS Simulations of Wind Turbine Aerodynamic Performance. Applied Sciences, 9(22), 4919. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224919







