Mortality of NBA Players: Risk Factors and Comparison with the General US Population
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design, Subjects, and Variables
2.2. Validation of Variables: Height and Ethnicity
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
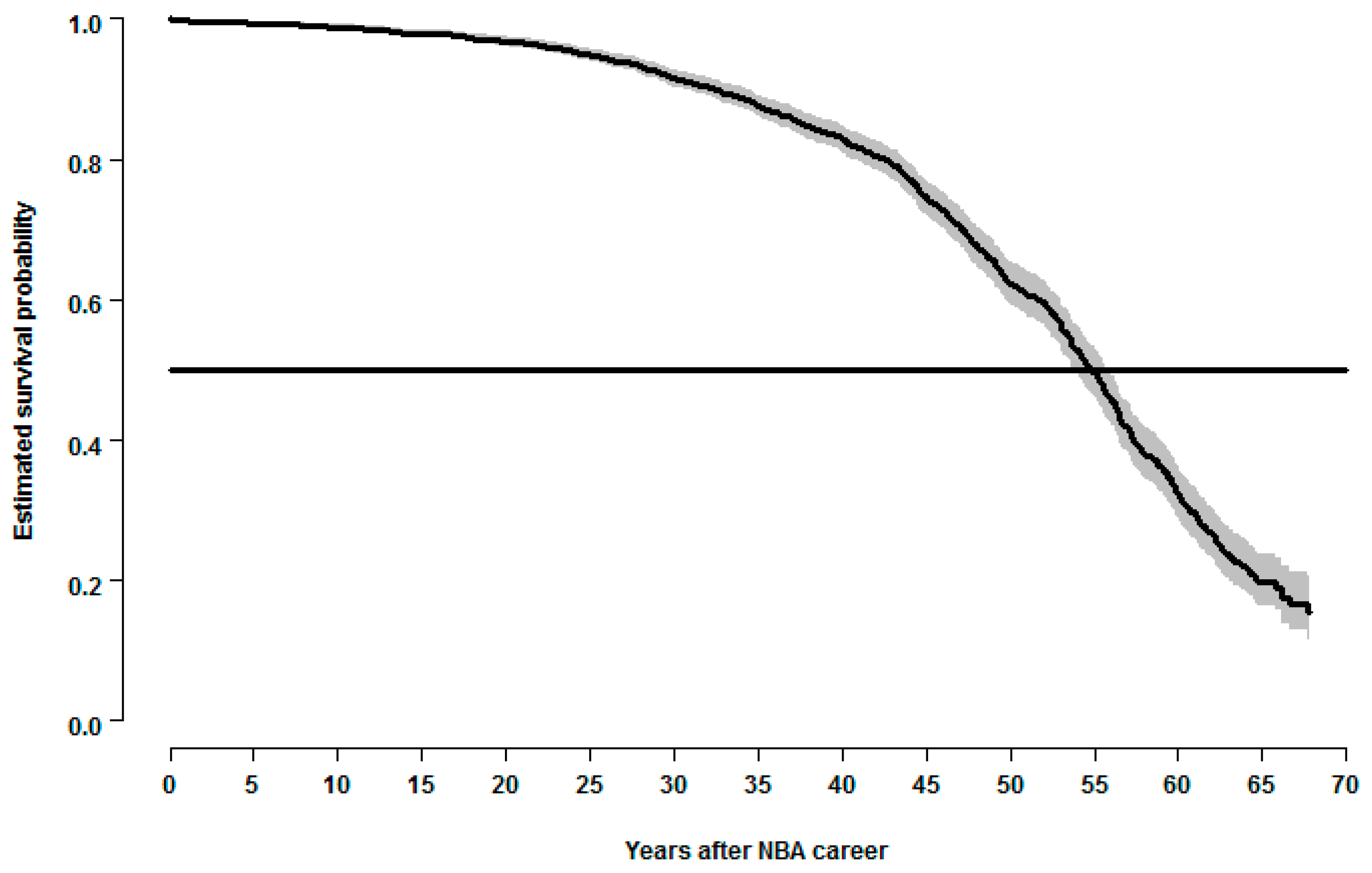
3.2. Survival Analysis
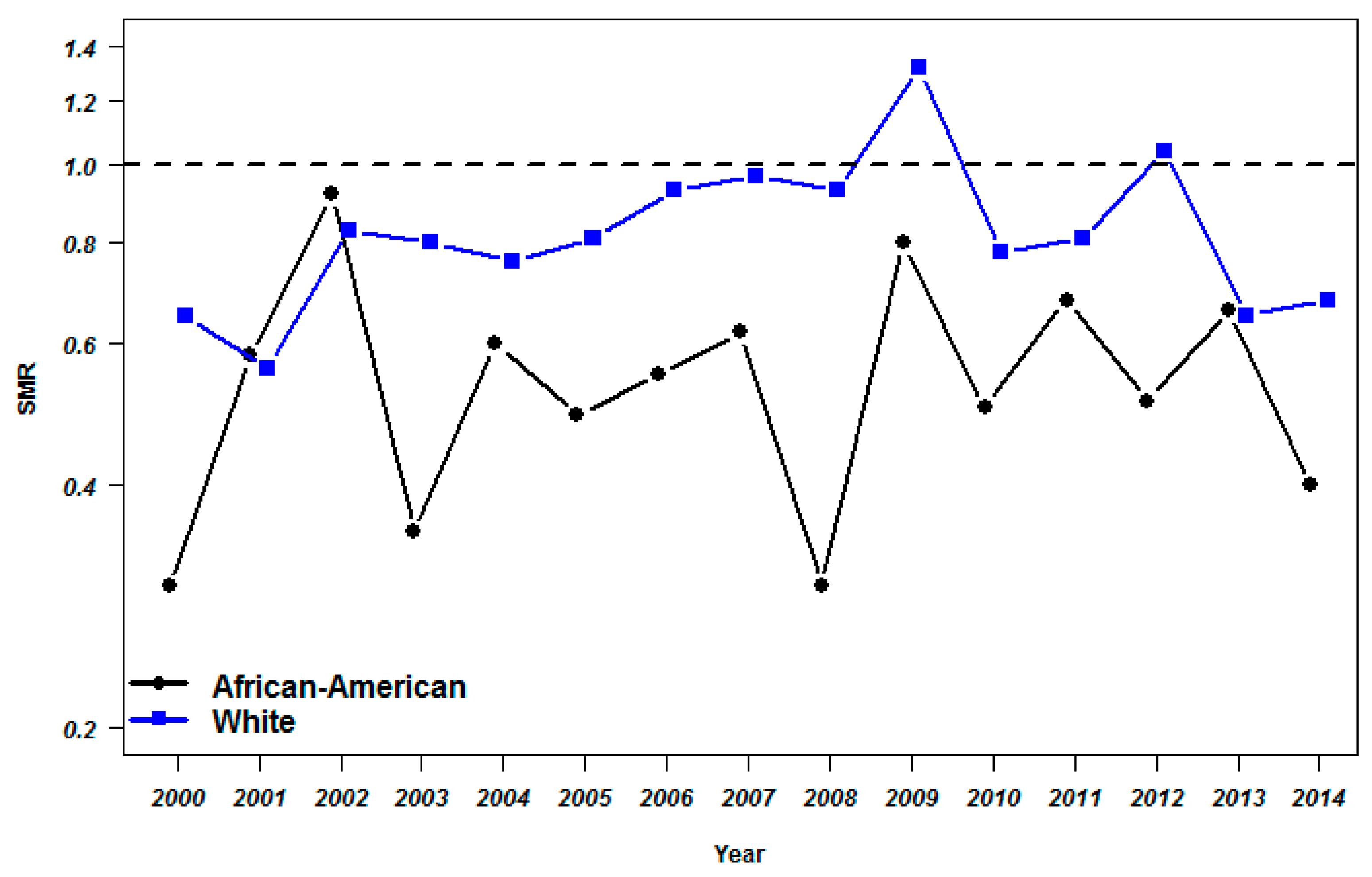
3.3. Comparison of Yearly Mortality Rates of NBA Players with the General Population
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations and Strengths
4.2. Practical Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fortington, L.V.; Finch, C.F. Death in community Australian football: A ten year national insurance claims report. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortington, L.V.; Bekker, S.; Finch, C.F. Online news media reporting of football-related fatalities in Australia: A matter of life and death. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2018, 21, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemez, S. Mortality in Professional Athletes: Examining Incidence, Predictors and Causes of Death. Ph.D. Thesis, York University, York, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lemez, S.; Baker, J. Do Elite Athletes Live Longer? A Systematic Review of Mortality and Longevity in Elite Athletes. Sports Med. Open 2015, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radonić, V.; Kozmar, D.; Počanić, D.; Jerkić, H.; Bohaček, I.; Letilović, T. Mortality and causes of death among Croatian male Olympic medalists. Croat. Med. J. 2017, 58, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Sarna, S.; Sahi, T.; Koskenvuo, M.; Kapiro, J. Increased life expectancy of world class male athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1993, 25, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fafian, J.J. Mortality experience of National Association Players. N. Am. Actuar. J. 1997, 1, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, T.P.; Lawler, F.; Gibson, J.; Murray, R. Does the African-American–White Mortality Gap Persist After Playing Professional Basketball? A 59-Year Historical Cohort Study. Ann. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, D.J.; Schwartz, A.; Homma, S. Athletic cardiac remodeling in US professional basketball players. JAMA Cardiol. 2016, 1, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabat, G.C.; Anderson, M.L.; Heo, M.; Hosgood, H.D., 3rd; Kamensky, V.; Bea, J.W.; Hou, L.; Lane, D.S.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Manson, J.E.; et al. Adult Stature and Risk of Cancer at Different Anatomic Sites in a Cohort of Postmenopausal Women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkeers Prev. 2013, 22, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khankari, N.K.; Shu, X.O.; Wen, W.; Kraft, P.; Lindström, S.; Peters, U.; Schildkraut, J.; Schumacher, F.; Bofetta, P.; Risch, A.; et al. Colorectal Transdisciplinary Study (CORECT); Discovery, Biology, and Risk of Inherited Variants in Breast Cancer (DRIVE); Elucidating Loci Involved in Prostate Cancer Susceptibility (ELLIPSE); Transdisciplinary Research in Cancer of the Lung (TRICL). Association between Adult Height and Risk of Colorectal, Lung, and Prostate Cancer: Results from Meta-analyses of Prospective Studies and Mendelian Randomization Analyses. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002118. [Google Scholar]
- Sawada, N.; Wark, P.A.; Merritt, M.A.; Tsugane, S.; Ward, H.A.; Rinaldi, S.; Weiderpass, E.; Dartois, L.; His, M.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; et al. The association between adult attained height and sitting height with mortality in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaras, T.T. How height is related to our health and longevity: A review. Nutr. Health 2012, 21, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutsea, P.L.; Folsom, A.R. Taller women are at greater risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism: The Iowa Women’s Health Study. Am. J. Hematol. 2012, 87, 716–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casals, M.; Martínez, J.A.; Cayla, J.; Martín, V. Do Basketball Players Have a High Risk of Pulmonary Embolism? A Scoping Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacMullan, J. Larry Bird Will Die Young. Available online: http://www.espn.com/nba/story/_/id/14712117/larry-bird-believes-nba-big-men-dieyoung-right (accessed on 4 February 2018).
- Spears, M.J. The NBA Seeks to Address a Spiking Problem with Heart Disease. Available online: https://theundefeated.com/features/the-nba-seeksto-address-a-spiking-problem-with-heart-disease/ (accessed on 4 February 2018).
- Teramoto, M.; Bungum, T.J. Mortality and longevity of elite athletes. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garatachea, N.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Fiuza-Luces, C.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Emanuele, E.; Lucia, A. Elite athletes live longer than the general population: A meta-analysis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettunen, J.A.; Kujala, U.M.; Kaprio, J.; Bäckmand, H.; Peltonen, M.; Eriksson, J.G.; Sarna, S. All-cause and disease-specific mortality among male, former elite athletes: An average 50-year follow-up. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontro, T.K.; Sarna, S.; Kaprio, J.; Kujala, U.M. Mortality and health-related habits in 900 Finnish former elite athletes and their brothers. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donovan, G.; Lee, I.M.; Hamer, M.; Stamatakis, E. Association of “Weekend Warrior” and Other Leisure Time Physical Activity Patterns with Risks for All-Cause, Cardiovascular Disease, and Cancer Mortality. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, P.T.; Kim, J.H. Exercise and Competitive Sport: Physiology, Adaptations, and Uncertain Long-Term Risks. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 19, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Baggish, A.L. Strenuous exercise and cardiovascular disease outcomes. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, E.L.; Meier, P. Nonparametric Estimation from Incomplete Observations. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1958, 53, 457–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.R. Regression Models and Life-Tables. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1972, 34, 187–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grambsch, P.M.; Therneau, T.M. Proportional hazards tests and diagnostics based on weighted residuals. Biometrika 1994, 81, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T. A Package for Survival Analysis in S. Version 2.43–3. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Aragon, T.J. Epitools: Epidemiology Tools. R Package Version 0.5–10. 2017. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=epitools (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Lincoln, A.E.; Vogel, R.A.; Allen, T.W.; Dunn, R.E.; Alexander, K.; Kaufman, N.D.; Tucker, A.M. Risk and causes of death among former National Football League players (1986–2012). Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, J.A. A reexamination of salary discrimination in professional basketball. Soc. Sci. Q. 1996, 77, 594–608. [Google Scholar]
- Gius, M.; Johnson, D. An empirical investigation of wage discrimination in professional basketball. Appl. Econ. Lett. 1998, 5, 703–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, V.; Rodgers, W.M., III. Black-White Wage Gaps Expand with Rising Wage Inequality; Economic Policy Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 20 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe, R.J., Jr.; Koster, A.; Bosma, H.; Harris, T.B.; Simonsick, E.M.; van Eijk, J.T.; Kempen, G.I.; Newman, A.B.; Satterfield, S.; Rubin, S.M.; et al. Health ABC Study. Racial differences in mortality in older adults: Factors beyond socioeconomic status. Ann. Behav. Med. 2012, 43, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Naito, H.; Takagi, Y. Is racial salary discrimination disappearing in the NBA? evidence from data during 1985–2015. Int. Rev. Appl. Econ. 2017, 31, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggish, A.L. Cardiac variables in professional basketball players: Looking closely at the normal big athlete (NBA). JAMA Cardiol. 2016, 1, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, N.; Papadakis, M.; Sharma, S. Cardiac adaptation in athletes of black ethnicity: Differentiating pathology from physiology. Heart 2012, 98, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemez SWattie, N.; Lawler, T.; Baker, J. Vital statistics and early death predictors of North American professional basketball players: A historical examination. J. Sports Sci. 2017, 36, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paajanen, T.A.; Oksala, N.K.J.; Kuukasjarvi, P.; Karhunen, P.J. Short stature is associated with coronary heart disease: A systematic review of the literature and a meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 1802–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofler, T.; Thériault, S.; Bossard, M.; Aeschbacher, S.; Bernet, S.; Krisai, P.; Blum, S.; Risch, M.; Risch, L.; Albert, C.M.; et al. Relationships of Measured and Genetically Determined Height with the Cardiac Conduction System in Healthy Adults. Circul. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2016, 10, e004735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miniati, M.; Bottai, M.; Pavlickova, I.; Monti, S. Body height as risk factor for emphysema in COPD. Sci. Rep. 2016, 22, 36896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, D.A.; Smith, G.D.; Shipley, M.; Strachan, D. Adult height and mortality in London: Early life, socioeconomic confounding, or shrinkage? J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1995, 49, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey Smith, G.; Hart, C.; Upton, M.; Hole, D.; Gillis, C.; Watt, G.; Hawthorne, V. Height and risk of death among men and women: Aetiological implications of associations with cardiorespiratory disease and cancer mortality. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2000, 54, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadhani, M.K.; Elias, S.G.; van Noord, P.A.; Grobbee, D.E.; Peeters, P.H.; Uiterwaal, C.S. Innate handedness and disease-specific mortality in women. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, M.A.; Gasperi, L.; Lupo, C. Performance analysis of game dynamics during the 4th game quarter of NBA close games. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2016, 16, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, B.G.; French, W.J.; Mayeda, G.S.; Burstein, S.; Economides, C.; Bhandari, A.K.; Cannom, D.S.; Kloner, R.A. Emotional stressors trigger cardiovascular events. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2012, 66, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, B.G.; McDonald, S.A.; Kloner, R.A. Super Bowl outcome’s association with cardiovascular death. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2013, 102, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkataramani, A.S.; Gandhavadi, M.; Jena, A.B. Association Between Playing American Football in the National Football League and Long-term Mortality. JAMA 2018, 319, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, P. No hay Razas Humanas, pero Abundan los Racistas. Ensayos de Filosofía. 2016, 4 (2), Artículo 6. Available online: http://www.ensayosfilosofia.es/archivos/articulo/no-hay-razas-pero-abundan-los-racistas (accessed on 10 January 2018).
- Dent, M. Moses Malone, Darryl Dawkins and the Scary Trend That’s Killing So Many Legendary NBA Bigs. Available online: https://billypenn.com/2015/10/01/moses-malone-darryl-dawkins-and-the-scary-trend-thats-killing-so-many-legendary-nba-bigs/ (accessed on 20 May 2018).

| Total 1 | Active 1 | Former 1 | Players Who Died 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 3985 | N = 481 | N = 3504 | N = 687 | |
| Position | ||||
| Center | 431 (11.0%) | 53 (11.3%) | 378 (11.0%) | 70 (18.52%) |
| Center–Forward | 177 (4.53%) | 11 (2.35%) | 166 (4.83%) | 51 (30.72%) |
| Forward | 1122 (28.7%) | 146 (31.1%) | 976 (28.4%) | 163 (16.7%) |
| Forward–Center | 326 (8.34%) | 32 (6.82%) | 294 (8.55%) | 84 (28.57%) |
| Forward–Guard | 193 (4.94%) | 20 (4.26%) | 173 (5.03%) | 50 (28.9%) |
| Guard | 1342 (34.3%) | 163 (34.8%) | 1179 (34.3%) | 178 (15.1%) |
| Guard–Forward | 317 (8.11%) | 44 (9.38%) | 273 (7.94%) | 77 (28.21%) |
| Ethnicity | ||||
| White | 1535 (38.7%) | 112 (23.3%) | 1423 (40.9%) | 517 (36.33%) |
| Mixed | 103 (2.60%) | 47 (9.79%) | 56 (1.61%) | 1 (1.79%) |
| African-American | 2324 (58.7%) | 321 (66.9%) | 2003 (57.5%) | 165 (8.24%) |
| Place | ||||
| Non-USA | 360 (9.03%) | 100 (20.8%) | 260 (7.42%) | 12 (4.62%) |
| USA | 3625 (91.0%) | 381 (79.2%) | 3244 (92.6%) | 675 (20.81%) |
| Left handed | ||||
| No | 3753 (94.2%) | 439 (91.3%) | 3314 (94.6%) | 661 (19.95%) |
| Yes | 232 (5.82%) | 42 (8.73%) | 190 (5.42%) | 26 (3.78%) |
| Age—years-at debut (mean; SD) | 23.4 (2.11) | 22.0 (1.93) | 23.6 (2.06) | 24.2 (2.34) |
| Age—years-at end of the last NBA season (mean; SD) | 28.2 (4.36) | 27.4 (4.21) 3 | 28.3 (4.37) | 27.8 (3.56) |
| Height—cm (mean; SD) | 198 (9.32) | 201 (8.75) | 198 (9.34) | 194 (8.81) |
| Weight—kg (mean; SD) | 94.8 (12.0) | 100 (12.1) | 94.1 (11.8) | 198 (22.1) |
| Number of NBA games (mean; SD) | 277 (310) | 342 (294) 3 | 268 (311) | 183 (230) |
| Model I Variables | Estimate | SE | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Height | 0.02 | 0.005 | 1.02 (1.01–1.03) | <0.001 |
| Age at end of NBA career | 0.09 | 0.011 | 1.10 (1.07–1.12) | <0.001 |
| Year of last NBA season | −0.02 | 0.005 | 0.98 (0.97–0.99) | <0.001 |
| Ethnicity (African-Americans vs. White) | 0.35 | 0.113 | 1.41 (1.13–1.76) | <0.001 |
| Model II Variables | Estimate | SE | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Height | 0.02 | 0.005 | 1.02 (1.01–1.03) | <0.001 |
| Year of first NBA season | −0.02 | 0.005 | 0.98 (0.97–0.99) | <0.001 |
| Ethnicity (African-Americans vs. White) | 0.31 | 0.109 | 1.37 (1.11–1.69) | 0.002 |
| Ethnicity | Height (cm) | Year | Median Age (Life Expectancy) | CI 95% LI | CI 95% LS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 200 | 1950 | 79.6 | 78.6 | 81.0 |
| African-American | 200 | 1950 | 76.6 | 74.2 | 79.2 |
| White | 200 | 1960 | 81.0 | 79.7 | 82.6 |
| African-American | 200 | 1960 | 78.5 | 76.5 | 80.0 |
| White | 200 | 1970 | 82.8 | 80.6 | 85.1 |
| African-American | 200 | 1970 | 79.6 | 78.4 | 81.5 |
| White | 200 | 1980 | 84.3 | 81.7 | 87.8 |
| African-American | 200 | 1980 | 81.0 | 79.2 | 84.0 |
| White | 200 | 1990 | 85.9 | 82.6 | 91.2 |
| African-American | 200 | 1990 | 82.6 | 79.9 | 86.4 |
| White | 200 | 2000 | 87.4 | 83.7 | 94.3 |
| African-American | 200 | 2000 | 84.3 | 80.6 | 89.7 |
| White | 200 | 2010 | 89.0 | 84.5 | -- |
| African-American | 200 | 2010 | 85.8 | 81.7 | 92.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez, J.A.; Langohr, K.; Felipo, J.; Casals, M. Mortality of NBA Players: Risk Factors and Comparison with the General US Population. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030500
Martínez JA, Langohr K, Felipo J, Casals M. Mortality of NBA Players: Risk Factors and Comparison with the General US Population. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(3):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030500
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez, Jose A., Klaus Langohr, Julián Felipo, and Martí Casals. 2019. "Mortality of NBA Players: Risk Factors and Comparison with the General US Population" Applied Sciences 9, no. 3: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030500
APA StyleMartínez, J. A., Langohr, K., Felipo, J., & Casals, M. (2019). Mortality of NBA Players: Risk Factors and Comparison with the General US Population. Applied Sciences, 9(3), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030500




