An Omnidirectional Near-Field Comprehensive Damage Detection Method for Composite Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ultrasonic Phased-Array Damage Imaging Method
2.1. Definition of Near Field and Far Field
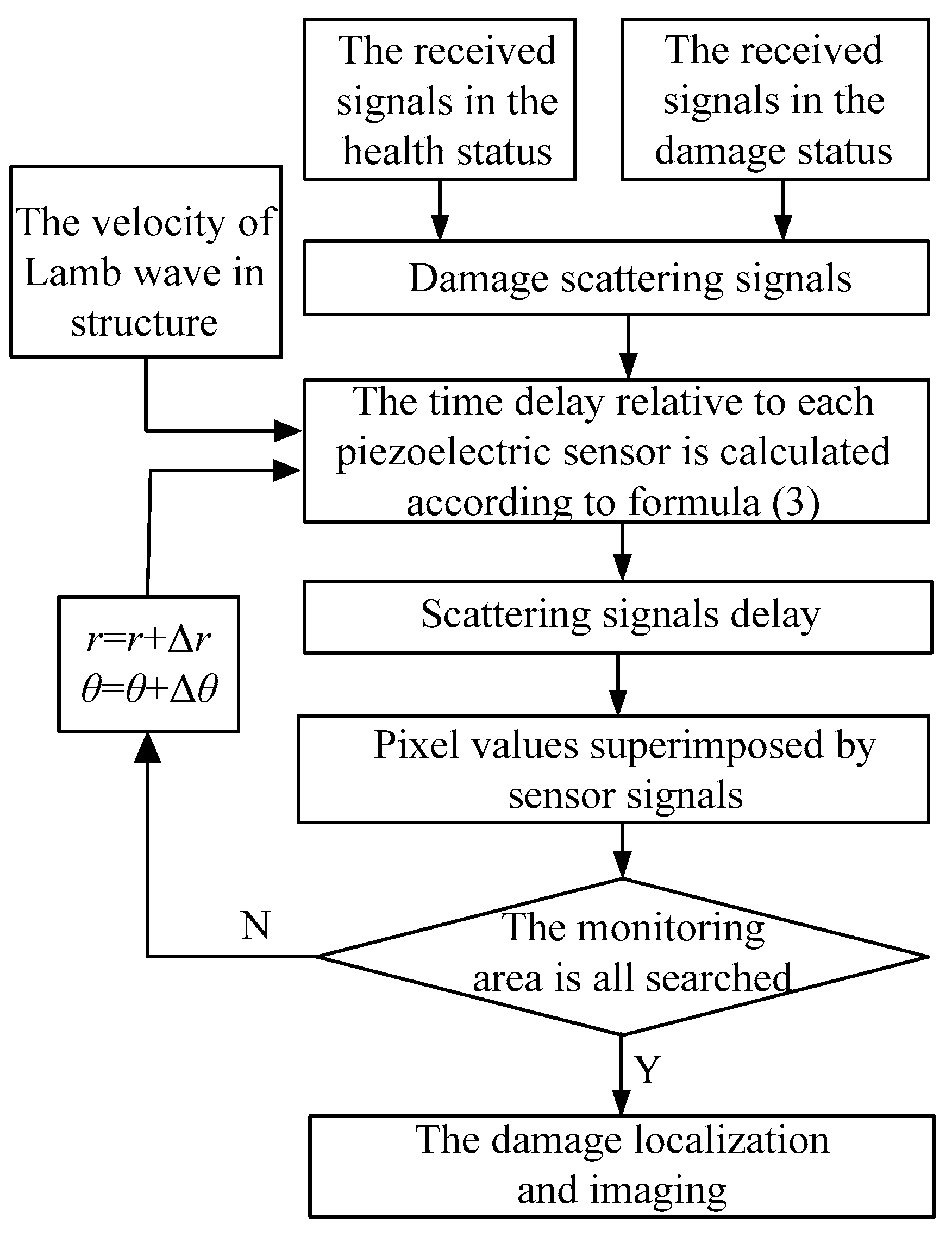
2.2. Near-Field Sampling Ultrasonic Phased-Array Damage Imaging Method
3. Experiments
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Calculation of Aviation Fuel Tank Wave Velocity
4. Experimental Results Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boller, C.; Buderath, M. Fatigue in aerostructures—Where structural health monitoring can contribute to a complex subject. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2007, 365, 561–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Ren, Y.; Qiu, L.; Mei, H. A multi-response-based wireless impact monitoring network for aircraft composite structures. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7712–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiche, C.; Coelho, C.K.; Chattopadhyay, A. A strain amplitude-based algorithm for impact localization on composite laminates. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2011, 22, 2061–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurgiutiu, V.; Bao, J.; Zhao, W. Piezoelectric wafer active sensor embedded ultrasonics in beams and plates. Exp. Mech. 2003, 43, 428–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, P.; Lowe, M.; Cawley, P. Lamb and SH wave transducer arrays for the inspection of large areas of thick plates. AIP Conf. Proc. 2000, 509, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Malinowski, P.; Wandowski, T.; Trendafilova, I.; Ostachowicz, W. A Phased Array-based Method for Damage Detection and Localization in Thin Plates. Struct. Health Monit. 2009, 8, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yuan, S.; Cai, J. Using Phased Array Technology in Structure Health Monitoring. J. Astronaut. 2008, 29, 1393–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.Y.; Tian, Z.H. Guided wave phased array beamforming and imaging in composite Plates. Ultrasonics 2016, 68, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giurgiutiu, V. Structural Health Monitoring with Piezoelectric Wafer Active Sensors; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Purekar, A.S.; Pines, D.J.; Sundararaman, S.; Adams, D.E. Directional piezoelectric phased array filters for detecting damage in isotropic plates. Smart Mater. Struct. 2004, 13, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.; Pines, D. Piezoceramic-Based 2-D Spiral Phased Array for Damage Detection of Thin Orthotropic Composite Laminates. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring, Stanford, CA, USA, 13–15 September 2011; Volume 7, pp. 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yuan, S.; Qiu, L.; Liu, B. Omni-directional damage detection and localization with a cruciform piezoelectric ultrasonic phased array. J. Vibroeng. 2015, 17, 2338–2349. [Google Scholar]
- Papulak, T.S.; Deemer, C.M. Damage detection in large scale composite rocket structures using modal acoustic emission and phased array sensing techniques. In Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring, Stanford, CA, USA, 10–12 September 2013; pp. 2314–2321. [Google Scholar]
- Dalton, R.P.; Cawley, P.; Lowe, M.J. The Potential of Guided Waves for Monitoring Large Areas of Metallic Aircraft Fuselage Structure. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2001, 20, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Yuan, S. On development of a multi-channel PZT array scanning system and its evaluating application on UAV wing box. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2009, 151, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, L.; Ricci, F.; Memmolo, V.; Monaco, E.; Boffa, N.D. Application of laser Doppler vibrometry for ultrasonic velocity assessment in a composite panel with defect. Compos. Struct. 2018, 184, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Element Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angle (°) | 32 | 40 | 80 | 120 | 140 | 160 | 180 | 206 | 270 | 316 | 345 |
| Arrival time (ms) | 0.11 775 | 0.118 | 0.1185 | 0.1335 | 0.1185 | 0.10925 | 0.11175 | 0.11925 | 0.09574 | 0.10925 | 0.10925 |
| TDOA (ms) | 0.064 | 0.06425 | 0.06475 | 0.07975 | 0.06475 | 0.0555 | 0.058 | 0.0655 | 0.0555 | 0.0555 | 0.0555 |
| Distance (mm) | 91 | 110 | 102 | 106 | 106 | 85 | 80 | 99.4 | 60 | 84 | 85.4 |
| Velocity (m/s) | 1422 | 1712 | 1575 | 1329 | 1637 | 1532 | 1379 | 1518 | 1491 | 1514 | 1539 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y. An Omnidirectional Near-Field Comprehensive Damage Detection Method for Composite Structures. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030567
Wang Z, Xiao Z, Li Y, Jiang Y. An Omnidirectional Near-Field Comprehensive Damage Detection Method for Composite Structures. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(3):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030567
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhiling, Zhenwei Xiao, Yonglin Li, and Yudong Jiang. 2019. "An Omnidirectional Near-Field Comprehensive Damage Detection Method for Composite Structures" Applied Sciences 9, no. 3: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030567
APA StyleWang, Z., Xiao, Z., Li, Y., & Jiang, Y. (2019). An Omnidirectional Near-Field Comprehensive Damage Detection Method for Composite Structures. Applied Sciences, 9(3), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030567




