Quantitative Assessment of the Environmental Impacts of Dredging and Dumping Activities at Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
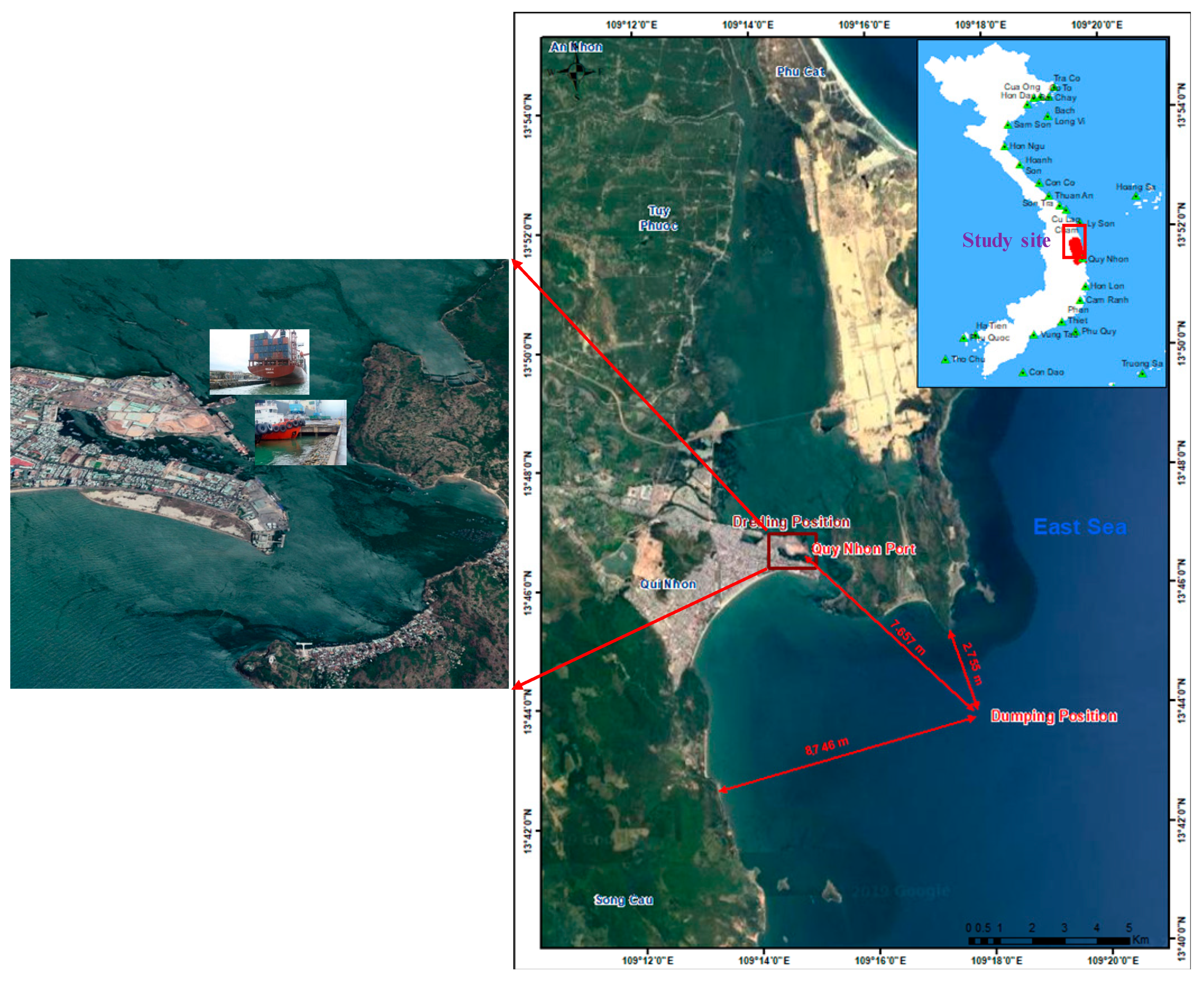
2.1. Description of Study Site
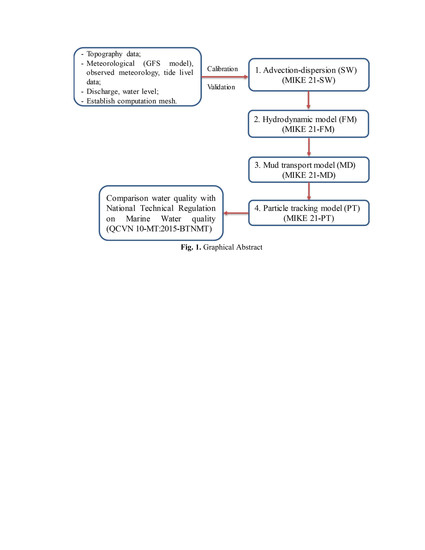
2.2. Model Description
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Wind Data Collection
2.3.2. The Regime of Tide
2.3.3. The Characteristics of Streamflow
3. Results
3.1. Calibration and Validation Spectral Wind-Wave (SW) Model
3.1.1. Establishing Mesh in SW 2D Model
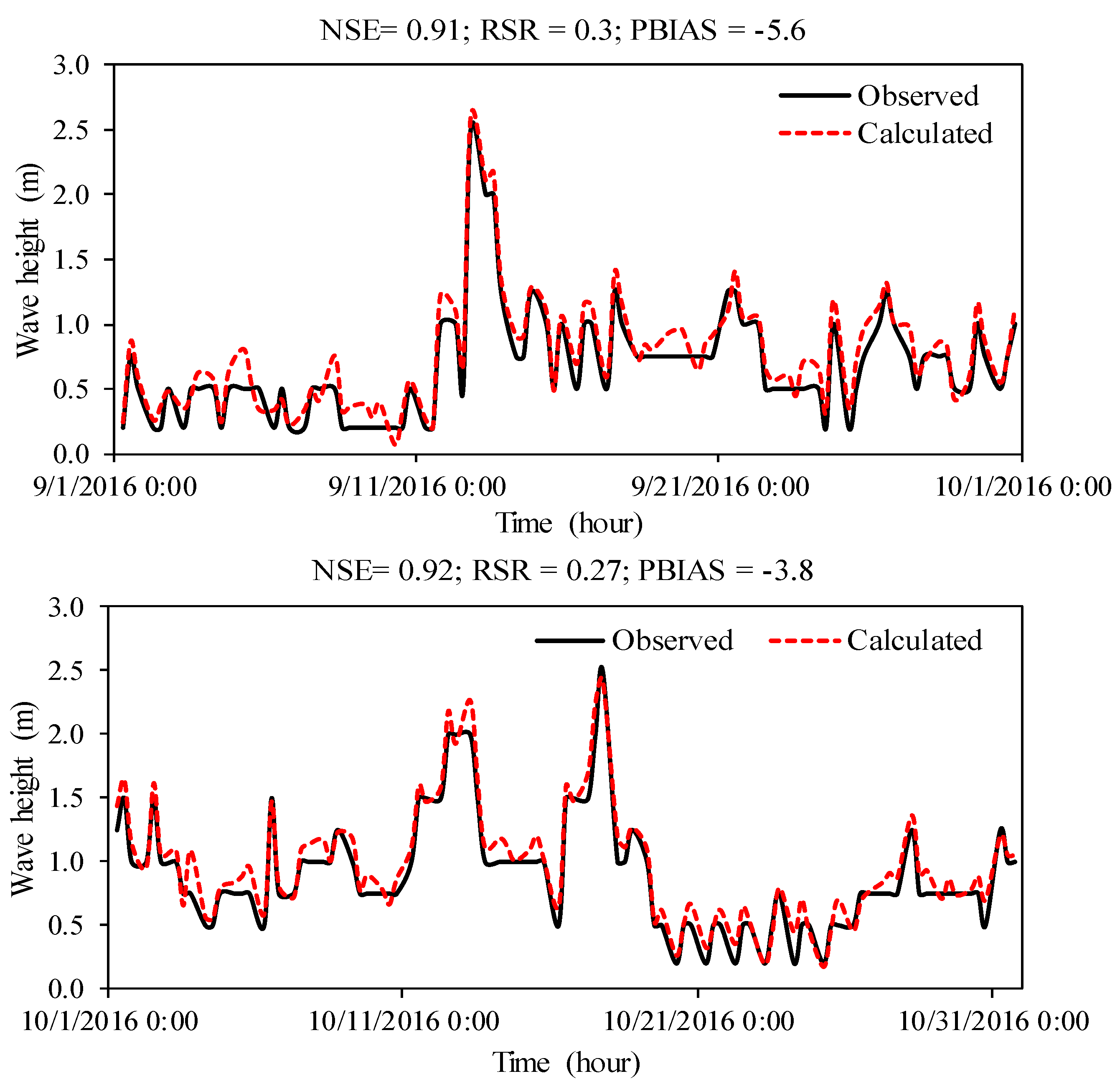
3.1.2. Calibration and Validation of Spectral Wind-Wave in 2D Model
3.2. Calibration and Validation of Hydrodynamic in 2D Model
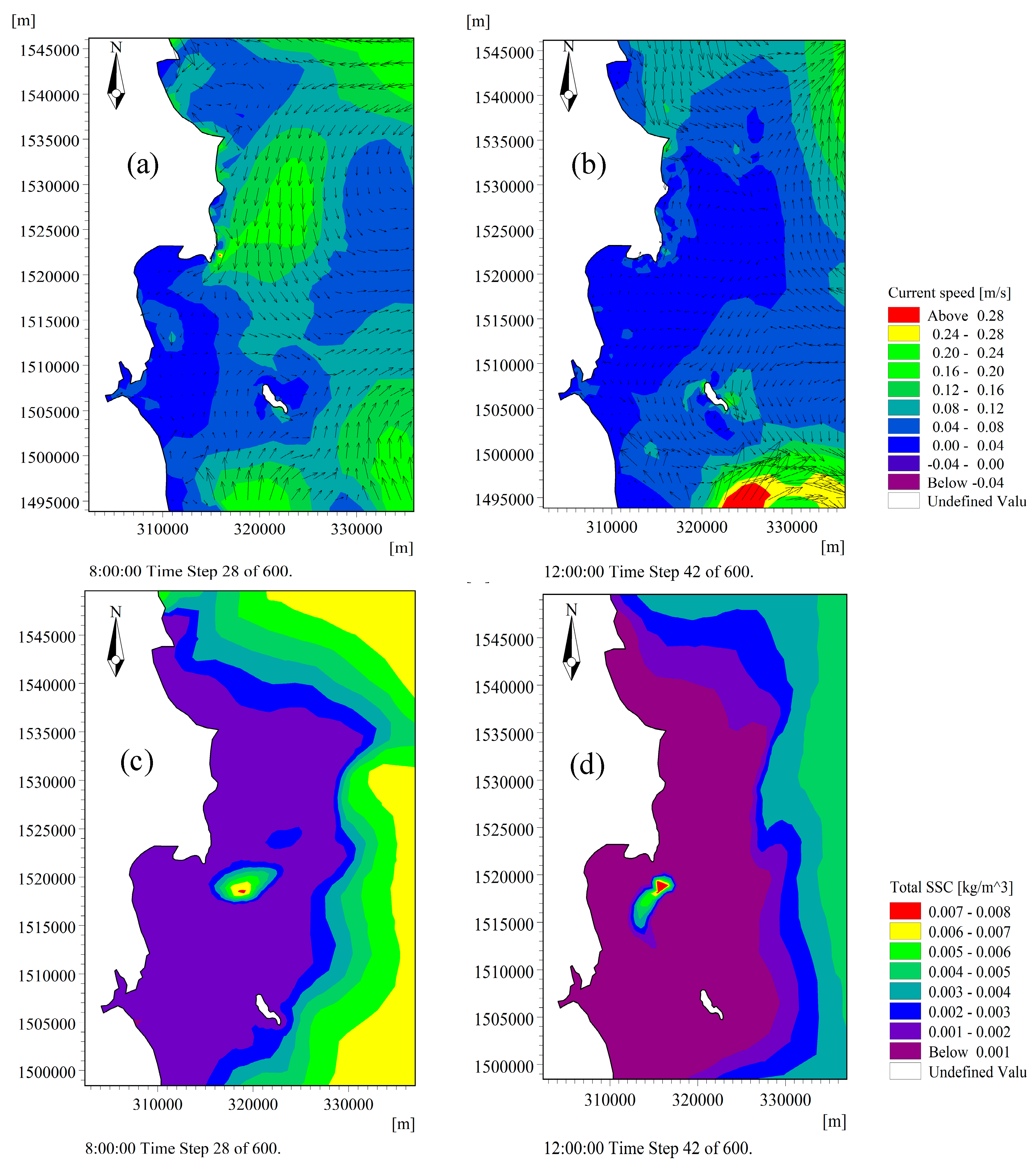
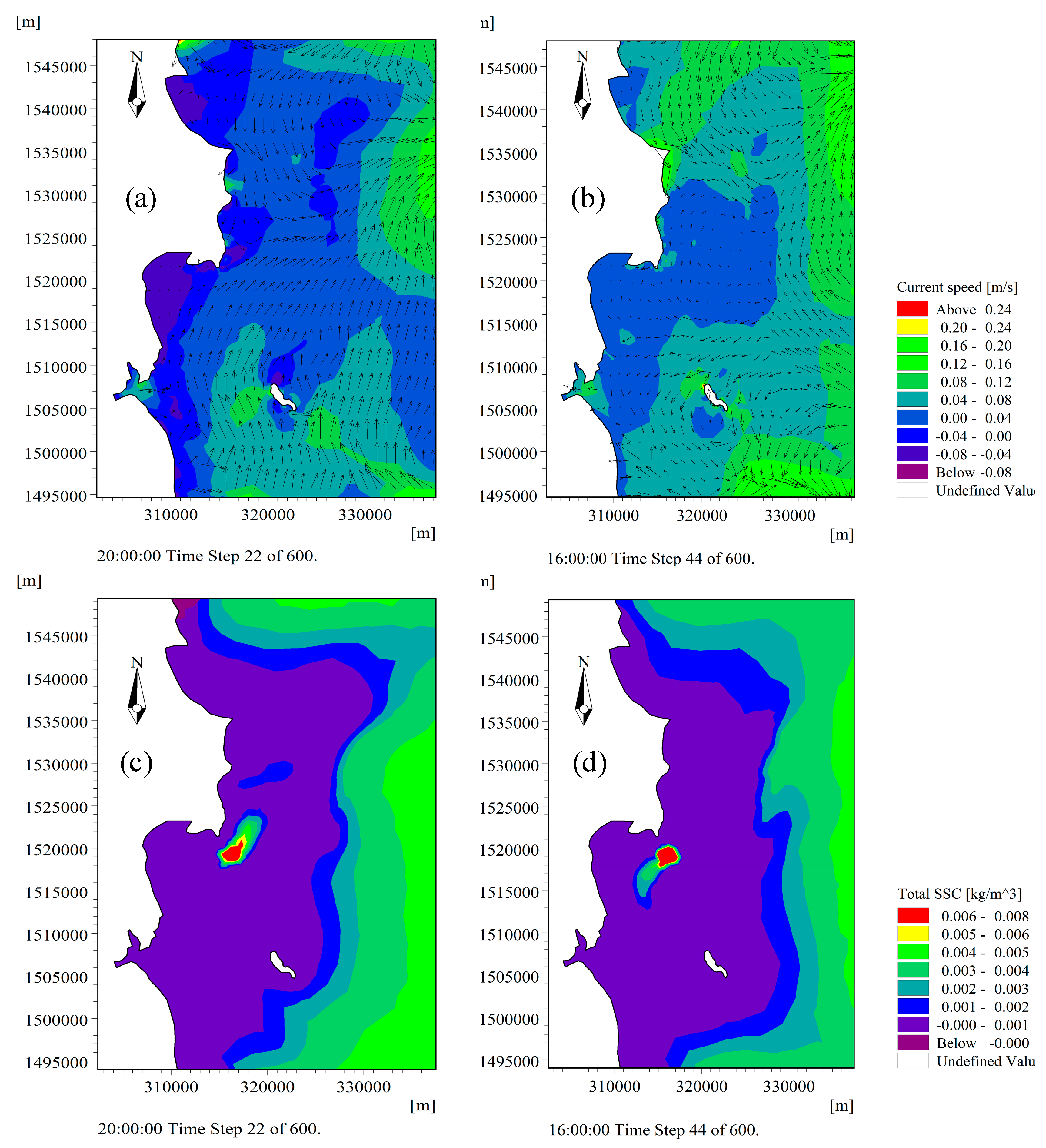
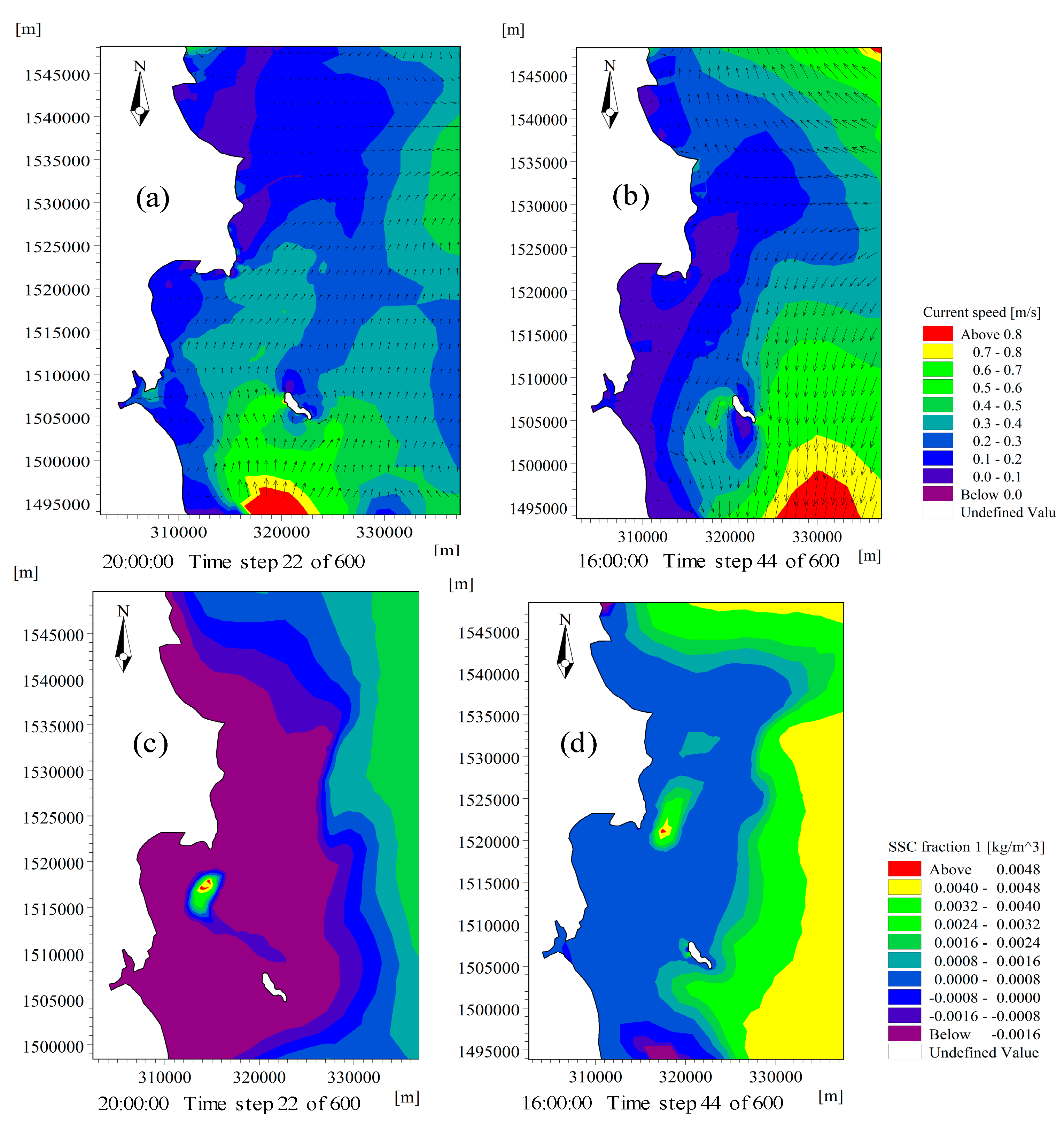
3.3. Result of Mud Transport (MT) in 2D Model
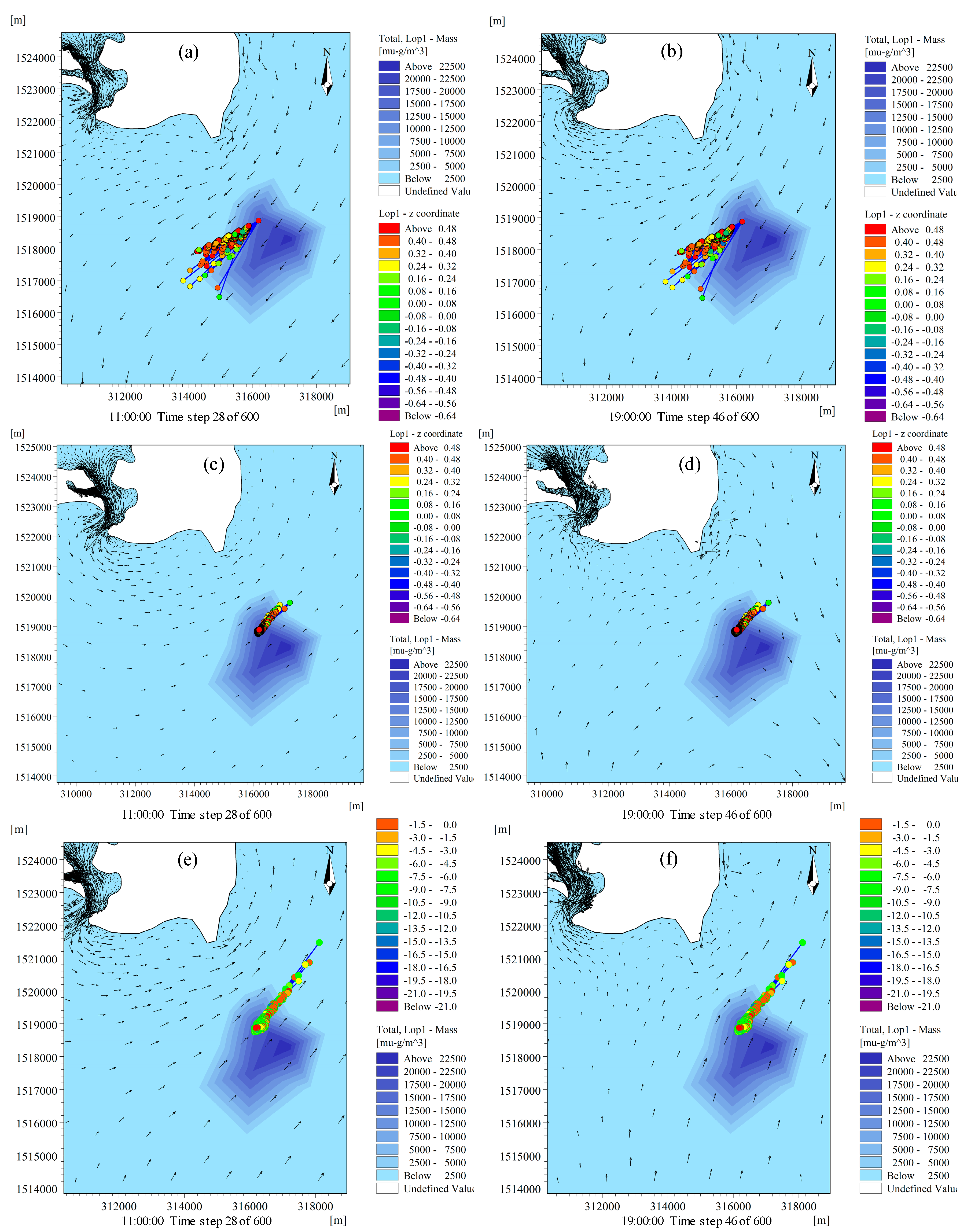
3.4. Results of Particle Tracking (PT) in 2D Model
- -
- In the case of calm wind (S2) and northeast wind (S1), the changes in seabed level due to the dumping of spoils were relatively similar.
- -
- The increase in seabed level due to the dumping of spoils over a period of approximately 180 days was between 0.08–0.16 m over 0.0285 km2.
4. Conclusions and Discussion
- -
- The computation time steps of the 2D model are currently large, although it takes approximately 4 to 5 h for one simulation of the 2D SW, HD, MT, PT model. A smaller time step can refine the results and provide more clarity, especially for sedimentation and particle tracking.
- -
- The number of calibration and validation locations in the 2D models are few. It may not be enough to evaluate the adequacy of the model in the study area.
- -
- The results of the 2D PT model only evaluate the distribution concentration and distance transmission of particles after the dredged materials. The results will be more useful and expanded if these are combined with the survey deposit patterns in the area surrounding the dump site.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolam, S.G.; Rees, H.L. Minimizing impacts of maintenance dredged material disposal in the coastal environment: A habitat approach. Environ. Manag. 2003, 32, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonini, R.; Ansaloni, I.; Cavallini, F.; Graziosi, F.; Iotti, M.; N’Siala, G.M.; Mauri, M.; Montanari, G.; Preti, M.; Prevedelli, D. Effects of long-term dumping of dredged material on macrozoobenthos at four disposal sites along the Emilia-Romagna coast (Northern Adriatic Sea, Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leipe, T.; Kersten, M.; Heise, S.; Pohl, C.; Witt, G.; Liehr, G.; Zettler, M.; Tauber, F. Ecotoxicity assessment of natural attenuation effects at a historical dumping site in the western Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, S.; Bolam, S.G.; Rees, H.L. Impact and recovery associated with the deposition of capital dredgings at UK disposal sites: Lessions for future licensing and monitoring. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsimalis, V.; Panagiotopoulos, I.; Kanellopoulos, T.; Hatzianestis, I.; Antoniou, P.; Anagnostou, C. A multi-criteria approach for the dumping of dredged material in the Thermaikos Gulf, Northern Greece. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, J.; Nieto, Ó.; Beiras, R. Integrative assessment of coastal pollution: Development and evaluation of sediment quality criteria from chemical contamination and ecotoxicological data. Cont. Self Res. 2011, 31, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarninkhof, S.; Luijendijk, A. Safe disposal of dredged material in anenvironmentally sensitive environment. Port Technol. Int. 2010, 47, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Erftemeijer, P.L.A.; Riegl, B.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Todd, P.A. Environmental impacts of dredging and other sediment disturbances on corals. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1737–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maren, D.S.; Kessel, T.; Cronin, K.; Sittoni, L. The impact of channel deepening and dredging on estuarine sediment concentration. Cont. Self Res. 2015, 95, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staniszewska, M.; Boniecka, H. Dangerous compounds in the dredged material from the sea—Assessment of the current approach to the evaluation of contaminations based on the data from the Polish coastal zone (the Baltic Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 130, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, P.; Bormann, C.; Lauenburg, B.; Bohling, B.; Bartholdy, J. Environment impact assessment of sediment dumping in the southern Baltic Sea using meiofaunal indicators. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 75, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boniecka, H.; Staniszewska, M.; Sapota, G.; Dembska, G.; Suzdalev, S. Przewodnik do wyznaczania nowych miejsc pod klapowiska. In Guideline for the Location of New Dumping Sites, ECODUMP; Maritime Institute of Gdańsk: Gdańsk, Poland, 2014; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Staniszewska, M.; Boniecka, H.; Gajecka, A. Prace pogłębiarskie w polskiej strefie przybrzeżnej-aktualne problemy (Dredging works in the polish coastal zone-actual problems). Inż. Ekol. 2014, 40, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniszewska, M.; Boniecka, H.; Cylkowska, H. Dredging works in the Polish open sea ports as an anthropogenic factor of development of sea coastal zones. Bull. Marit. Inst. Gdan. 2016, 31, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniszewska, M.; Boniecka, H. The Environmental Protection Aspects of Handling Dredged Material. BMI Bull. Marit. Inst. Gdan. 2015, 30, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniszewska, M.; Boniecka, H. Managing dredged material in the coastal zone of the Baltic Sea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arizaga, J.; Amat, J.A.; Ganuzas, M.M. The negative effect of dredging and dumping on shorebirds at a coastal wetland in northern Spain. J. Nat. Conserv. 2017, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Chen, C.W.; Ju, Y.R.; Kao, C.M.; Dong, C.D. Impact of disposal of dredged material on sediment quality in the Kaohsiung Ocean Dredged Material Disposal Site, Taiwan. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erftemeijer, P.L.A.; Lewis, R.R., III. Environmental impacts of dredging on seagrasses: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 1553–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeksema, B.W. Delineation of the Indo-Malayan Centre of maximum marine biodiversity: The Coral Triangle. In Biogeography, Time and Place. Distributions. Barriers and Islands; Renema, W., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 117–178. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.; Browne, P.B.; Fisher, R.; Klonowski, W.; Slivkoff, M. Assessing the impacts of sediments from dredging on corals. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniszewska, M.; Boniecka, H. Badania przesiewowe w ocenie stopnia zanieczyszczenia urobku. Screening methods for dredged material contamination assessment. BMI Bull. Marit. Inst. Gdan. 2016, 31, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.; Annan, J.D.; Jones, P.D.; Mann, M.E.; Mullan, B.; Renwick, J.; Salinger, J.; Schmidt, G.A.; Trenberth, K.E. Comment on “Influence of the Southern Oscillation on tropospheric temperature” by J. D. McLean, C. R. de Freitas, and R. M. Carter. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D09110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quy Nhon Port. 2012. Available online: http://www.quinhonport.com.vn/en/gioi-thieu/17/gioi-thieu-chung- (accessed on May 2011).
- Hervouet, J.M. Hydrodynamics of Free Surface Flows: Modelling with the Finite Element Method; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Maerker, C.; Malcherek, A. The Simulation Tool DredgeSim—Predicting Dredging Needs in 2- and 3-Dimensional Models to Evaluate Dredging Strategies; Dittrich, A., Koll, K., Aberle, J., Geisenhainer, P., Eds.; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11970/99824 (accessed on 26 November 2014).
- Guerrero, M.; di Federico, V.; Lamberti, A. Calibration of a 2-D morphodynamic model using water-sediment flux maps derived from an ADCP recording. J. Hydroinform. 2013, 15, 813–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paarlberg, A.J.; Guerrero, M.; Huthoff, F.; Re, M. Optimizing Dredge-and-Dump Activities for River Navigability Using a Hydro-Morphodynamic Model. Water 2015, 7, 3943–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shukla, V.K.; Konkane, V.D.; Nagendra, T.; Agrawal, J.D. Dredged Material Dumping Site Selection Using Mathematical Models. Procedia Eng. 2015, 116, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramli, A.Y.; de Lange, W.; Bryan, K.; Mullarney, J. Coupled Flow-Wave Numerical Model in Assessing the Impact of Dredging on the Morphology of Matakana Banks. In Proceedings of the Australasian Coasts & Ports Conference 2015, Auckland, New Zealand, 15–18 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Morais, M.; Dibajnia, M.; Lu, Q.; Fournier, C. 3D modelling of combined dredge and disposal plumes dispersion, ponta da madeira, Brazil. In Proceedings of the WEDA XXXIV Technical Conference & TAMU 45 Dredging Seminar, Toronto, ON, Canada, June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gaeta, M.G.; Bonaldo, D.; Samaras, A.G.; Carniel, S.; Archetti, R. Coupled Wave-2D Hydrodynamics Modeling at the Reno River Mouth (Italy) under Climate Change Scenarios. Water 2018, 10, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.; Mirfenderesk, H.; Tomlinson, R.; Szylkarski, S. Hydrodynamic, water quality and sediment transport modeling of estuarine and coastal waters on the gold coast Australia. Proc. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 56, 937–941. [Google Scholar]
- Doan, Q.T.; Nguyen, C.D.; Chen, Y.C. Trajectory Modelling of Marine Oil Spills: Case Study of Lach Huyen Port, Vietnam. Lowl. Technol. Int. 2013, 15, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, A.N.; Badano, N.D.; Lopolito, M.F.; Re, M. Water quality assessment for a coastal zone through numerical modeling. J. Appl. Water Eng. Res. 2013, 1, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z. Estuaries: Dynamics, mixing, sedimentation and morphology. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 586–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossati, M.; Piedra-Cueva, I. A 3D hydrodynamic numerical model of the Río de la Plata and Montevideo’s coastal zone. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 1310–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, Q.T.; Nguyen, C.D.; Chen, Y.C.; Pawan, K.M. Application of Environmental Sensitivity Index (ESI) Maps of Shoreline for the Coastal Oil Spills: Case Study of Cat Ba Island, Vietnam. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 3433–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntoyo; Ikhwani, H.; Zikra, M.; Sukmasari, N.A.; Angraeni, G.; Tanaka, H.; Umeda, M.; Kure, S. Modelling of the COD, TSS, Phosphate and Nitrate Distribution Due to the Sidoardjo Mud Flow into Porong River Estuary. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 14, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doan, Q.T.; Nguyen, T.M.L.; Nguyen, C.D. Using numerical modelling in the simulation of mass fish death phenomenon along the Central Coast of Vietnam. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, Q.T.; Nguyen, T.M.L.; Tran, H.T.; Kandasamy, J. Application of 1D-2D Coupled Modeling in Water Quality Assessment: A Case Study in Ca Mau Peninsula, Vietnam. Phys. Chem. Earth 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komen, G.J.; Cavaleri, L.; Doneland, M.; Hasselmann, K.; Hasselmann, S.; Janssen, P.A.E.M. Dynamics and Modeling of Ocean Waves; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; p. 560. [Google Scholar]
- Young, I.R. Wind-generated Ocean waves. In Elsevier Ocean Engineering Book Series; Bhattacharyya, R., McCormick, M.E., Eds.; 1999; Volume 2, Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/books/wind-generated-ocean-waves/young/978-0-08-043317-2 (accessed on 23 March 1999).
- Martin, J.L.; McCutcheon, S.C. Hydrodynamics and Transport for Water Quality Modeling; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, London, 1998; 816p, Available online: https://www.crcpress.com/Hydrodynamicsand-Transport-for-Water-Quality-Modeling/Martin-McCutcheon/p/book/9780873716123 (accessed on 4 May 2018).
- Krone, R.B. Flume Studies of the Transport of Sediment in Estuarial Processes; Final Report; Hydraulic Engineering Laboratory and Sanitary Engineering Research Laboratory, University of California: Barkeley, CA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, A.J.; Hayter, E.J.; Parker, W.R.; Krone, R.B.; Teeter, A.M. Cohesive sediment transport. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1989, 115, 1076–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikder, S.; Hossain, F. Assessment of the weather research and forecasting model generalized parameterization schemes for advancement of precipitation forecasting in monsoon-driven river basins. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2016, 8, 1210–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doan, Q.T.; Nguyen, T.M.L.; Quach, T.T.T.; Tran, A.P.; Nguyen, C.D. Assessment of Water Quality in Coastal Estuaries Under Impact of Industrial Zone in Hai Phong, Vietnam. Phys. Chem. Earth 2019, accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models parts I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, Y. Eddy-viscosity-type subgrid-scale model with a variable Smagorinsky coefficient and its relationship with the one-equation model in large eddy simulation. Phys. Fluids 1991, 3, 2007–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.X.; Xu, C.X.; Fang, L.F.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Z.S. A new subgrid eddy-viscosity model for large-eddy simulation of anisotropic turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 2007, 582, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romit, M.; Omer, S. Dynamic modeling of the horizontal eddy viscosity coefficient for quasigeostrophic ocean circulation problems. J. Ocean Eng. Sci. 2016, 1, 300–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Circulars 67, QCVN 10-MT/BTNMT, National Technical Regulation on Marine Water Quality. 2015. Available online: https://thuvienphapluat.vn/van-ban/Tai-nguyen-Moi-truong/Thong-tu-67-2015-TT-BTNMT-quy-chuan-ky-thuat-quoc-gia-moi-truong-301666.aspx (accessed on 21 December 2015).





| Month | Calm Wind | Direction | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North | North-East | East | South-East | South | South-West | West | North-West | ||
| 1 | 9.5 | 12.6 | 43.7 | 2.3 | 4.1 | 2 | 31.2 | 4 | |
| 2 | 14.7 | 8.9 | 41.2 | 3.5 | 10.3 | 6.1 | 26.6 | 3 | 0.1 |
| 3 | 19.6 | 6.7 | 30.2 | 6.1 | 26.2 | 11.7 | 16.2 | 2.5 | 0.4 |
| 4 | 23.6 | 5.9 | 18.1 | 9.1 | 36.7 | 19.4 | 9.1 | 1.1 | 0.6 |
| 5 | 26.1 | 5.3 | 13 | 7.5 | 32.3 | 21.4 | 11 | 7 | 2 |
| 6 | 25.3 | 2.8 | 6.5 | 6 | 25.8 | 17.4 | 16.8 | 21 | 3.6 |
| 7 | 22.6 | 2.4 | 5.9 | 2.6 | 23.9 | 12.3 | 18.1 | 31 | 3.6 |
| 8 | 22.8 | 2.3 | 7.1 | 3.3 | 19.2 | 9.5 | 19.6 | 34 | 4.2 |
| 9 | 25.6 | 5.7 | 21.6 | 4.5 | 17.1 | 11.6 | 21.4 | 3.2 | |
| 10 | 14.7 | 12.8 | 36.4 | 4.8 | 5.8 | 4 | 29.4 | 0.5 | |
| 11 | 7.9 | 13.1 | 51.6 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 26.3 | 0.1 | |
| 12 | 6.4 | 10.6 | 51 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 30.8 | ||
| Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | ||||||||||||
| 2011 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.3 | 1.9 | 3.1 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3.7 |
| 2012 | 2.0 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.3 | 2.8 | 4.2 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 2.8 |
| 2013 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.9 |
| 2014 | 2.5 | 2.7 | 1.9 | 2.7 | 1.8 | 2.7 | 2.2 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| 2015 | 3.2 | 2.9 | 3.1 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 3.1 | 3.2 | 3.3 |
| 2016 | 2.5 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 3.0 | 1.9 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 3.4 | 2.7 | 3.4 | 3.3 |
| No. | Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Flux | 8.3 | kg/s |
| 2 | Number of particles per time step | 20 | Integer |
| 3 | Decay Rate | 0.05 | /sec |
| 4 | Settling velocity data | 0.1 | m/s |
| 5 | Settling parameters | ||
| 5.1 | Minimum concentration for | 0.01 | kg/m3 |
| 5.2 | Maximum concentration for | 10 | kg/m3 |
| 5.3 | Alpha | 1.01 | |
| 6 | Dispersion coefficient formulation | 0.05 | m2/s |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quang Tri, D.; Kandasamy, J.; Cao Don, N. Quantitative Assessment of the Environmental Impacts of Dredging and Dumping Activities at Sea. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081703
Quang Tri D, Kandasamy J, Cao Don N. Quantitative Assessment of the Environmental Impacts of Dredging and Dumping Activities at Sea. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(8):1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081703
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuang Tri, Doan, Jaya Kandasamy, and Nguyen Cao Don. 2019. "Quantitative Assessment of the Environmental Impacts of Dredging and Dumping Activities at Sea" Applied Sciences 9, no. 8: 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081703
APA StyleQuang Tri, D., Kandasamy, J., & Cao Don, N. (2019). Quantitative Assessment of the Environmental Impacts of Dredging and Dumping Activities at Sea. Applied Sciences, 9(8), 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081703