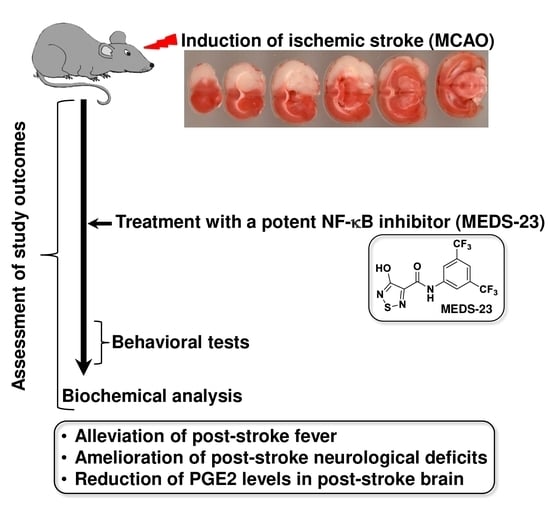
A New NF-κB Inhibitor, MEDS-23, Reduces the Severity of Adverse Post-Ischemic Stroke Outcomes in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Measurement of Body Weight (BW)
2.3. Measurement of BT
2.4. Surgical Procedures
2.5. Drug Treatment
2.6. Assessment of Neurological Score (NS)
2.7. Assessment of Mortality and General Health Condition
2.8. Behavioral Tests
2.8.1. Open Field Test (OFT)
2.8.2. Sucrose Consumption Test (SCT)
2.8.3. Elevated Plus-Maze Test (EPMT)
2.9. Blood and Tissue Collection and Preparation of Brain Homogenates
2.10. Determination of Renal, Hematological and Gastric Parameters
2.11. Measurement of Cytokines and PGE2 Levels
2.12. Statistical Analysis and Presentation of the Data
3. Results
3.1. Toxicity Experiment
3.2. Efficacy Experiments
3.2.1. Effects of MEDS-23 Treatment on BW of Post-Stroke Rats
3.2.2. Effects of MEDS-23 Treatment on BT of Post-Stroke Rats
3.2.3. Effects of MEDS-23 Treatment on Levels of Brain Inflammatory Mediators in Post-Stroke Rats
3.2.4. Effects of MEDS-23 Treatment on NS of Post-Stroke Rats
3.2.5. Effects of MEDS-23 Treatment on Mortality of Post-Stroke Rats
3.2.6. Effects of MEDS-23 Treatment on Sucrose Consumption in Post-Stroke Rats
3.2.7. Effects of MEDS-23 Treatment on Anxiety-Like Behavior in Post-Stroke Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, C.O.; Nguyen, M.; Roth, G.A.; Nichols, E.; Alam, T.; Abate, D.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abraha, H.N.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hossmann, K.A. The two pathophysiologies of focal brain ischemia: Implications for translational stroke research. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feske, S.K. Ischemic Stroke. Am. J. Med. 2021, 134, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, J.P. Endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2009, 40, S103–S106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweid, A.; Hammoud, B.; Ramesh, S.; Wong, D.; Alexander, T.D.; Weinberg, J.H.; Deprince, M.; Dougherty, J.; Maamari, D.J.-M.; Tjoumakaris, S.; et al. Acute ischaemic stroke interventions: Large vessel occlusion and beyond. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2019, 5, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arboix, A.; Jimenez, C.; Massons, J.; Parra, O.; Besses, C. Hematological disorders: A commonly unrecognized cause of acute stroke. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2016, 9, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Yin-Yi, S.; Kang-Yong, L. Autophagy and inflammation in ischemic stroke. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1388–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, B. The effect of focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury on TLR4 and NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nurmi, A.; Lindsberg, P.J.; Koistinaho, M.; Zhang, W.; Juettler, E.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.L.; Weih, F.; Frank, N.; Schwaninger, M.; Koistinaho, J. Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to infarction after permanent focal ischemia. Stroke 2004, 35, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howell, J.A.; Bidwell, G.L. Targeting the NF-κB pathway for therapy of ischemic stroke. Ther. Deliv. 2020, 11, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippione, A.C.; Federico, A.; Ducime, A.; Sainas, S.; Boschi, D.; Barge, A.; Lupino, E.; Piccinini, M.; Kubbutat, M.; Contreras, J.M.; et al. 4-Hydroxy-: N -[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,2,5-thiadiazole-3-carboxamide: A novel inhibitor of the canonical NF-κB cascade. MedChemComm 2017, 8, 1850–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ko, D.; Lee, Y.; Jang, S.; Lee, Y.; Lee, I.Y.; Kim, S. Anti-cancer activity of the novel 2-hydroxydiarylamide derivatives IMD-0354 and KRT1853 through suppression of cancer cell invasion, proliferation, and survival mediated by TMPRSS4. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kitaichi, N.; Wu, D.; Hase, K.; Satoh, M.; Iwata, D.; Namba, K.; Kanda, A.; Noda, K.; Itai, A.; et al. Attenuation of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis in mice by IKKβ inhibitor IMD-0354. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 525, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Mabarak, C.; Mitre-Aguilar, I.B.; Camacho-Carranza, R.; Arias, C.; Zentella-Dehesa, A.; Espinosa-Aguirre, J.J. Role of NF-κB in cytochrome P450 epoxygenases down-regulation during an inflammatory process in astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 129, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippione, A.C.; Sainas, S.; Boschi, D.; Lolli, M.L. Hydroxyazoles as acid isosteres and their drug design applications—Part 2: Bicyclic systems. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 2021, 134, 273–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainas, S.; Pippione, A.C.; Boschi, D.; Lolli, M.L. Hydroxyazoles as acid isosteres and their drug design applications—Part 1: Monocyclic systems. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 2021, 134, 185–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballatore, C.; Huryn, D.M.; Smith, A.B. Carboxylic Acid (Bio)Isosteres in Drug Design. ChemMedChem. 2013, 8, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pippione, A.C.; Sainas, S.; Federico, A.; Lupino, E.; Piccinini, M.; Kubbutat, M.; Contreras, J.-M.; Morice, C.; Barge, A.; Ducime, A.; et al. N-Acetyl-3-aminopyrazoles block the non-canonical NF-kB cascade by selectively inhibiting NIK. MedChemComm 2018, 9, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluk, H.; Woźniak, A.; Grześk, G.; Kołodziejska, R.; Kozakiewicz, M.; Kopkowska, E.; Grzechowiak, E.; Kozera, G. The Role of Selected Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Pathogenesis of Ischemic Stroke. Clin. Interv. Aging 2020, 15, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarnico, I.; Lanzillotta, A.; Boroni, F.; Benarese, M.; Alghisi, M.; Schwaninger, M.; Inta, I.; Battistin, L.; Spano, P.; Pizzi, M. NF-kappaB p50/RelA and c-Rel-containing dimers: Opposite regulators of neuron vulnerability to ischaemia. J. Neurochem. 2009, 108, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, M.; Nassar, A.; Kaplanski, J.; Zlotnik, A.; Sharon-Granit, Y.; Azab, A.N. Effects of Acute Lithium Treatment on Brain Levels of Inflammatory Mediators in Poststroke Rats. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 916234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rostevanov, I.S.; Boyko, M.; Ferorelli, S.; Scilimati, A.; Perrone, M.G.; Kaplanski, J.; Zlotnik, A.; Azab, A.N. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-1 does not reduce mortality in post-ischemic stroke rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 737, 135296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, M.; Zlotnik, A.; Gruenbaum, B.F.; Gruenbaum, S.E.; Ohayon, S.; Goldsmith, T.; Kotz, R.; Leibowitz, A.; Sheiner, E.; Shapira, Y.; et al. An experimental model of focal ischemia using an internal carotid artery approach. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 193, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippione, A.C.; Giraudo, A.; Bonanni, D.; Carnovale, I.M.; Marini, E.; Cena, C.; Costale, A.; Zonari, D.; Pors, K.; Sadiq, M.; et al. Hydroxytriazole derivatives as potent and selective aldo-keto reductase 1C3 (AKR1C3) inhibitors discovered by bioisosteric scaffold hopping approach. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 139, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sainas, S.; Pippione, A.C.; Giraudo, A.; Martina, K.; Bosca, F.; Rolando, B.; Barge, A.; Ducime, A.; Federico, A.; Grossert, S.J.; et al. Regioselective N-Alkylation of Ethyl 4-Benzyloxy-1,2,3-triazolecarboxylate: A Useful Tool for the Synthesis of Carboxylic Acid Bioisosteres. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2019, 56, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippione, A.C.; Sainas, S.; Goyal, P.; Fritzson, I.; Cassiano, G.C.; Giraudo, A.; Giorgis, M.; Tavella, T.A.; Bagnati, R.; Rolando, B.; et al. Hydroxyazole scaffold-based Plasmodium falciparum dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors: Synthesis, biological evaluation and X-ray structural studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Kubota, M.; Kasahara, T. Animal models of bipolar disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2007, 31, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einat, H. Establishment of a battery of simple models for facets of bipolar disorder: A practical approach to achieve increased validity, better screening and possible insights into endophenotypes of disease. Behav. Genet. 2007, 37, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaisher-Grinberg, S.; Einat, H. Strain-specific battery of tests for domains of mania: Effects of valproate, lithium and imipramine. Front. Psychiatry 2010, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, J.M.; Ferreira, D.; Melo, I.; Marques, F.; Cerqueira, J.J.; Palha, J.A.; Almeida, O.F.; Sousa, N. The mood-improving actions of antidepressants do not depend on neurogenesis but are associated with neuronal remodeling. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beyer, D.K.E.; Freund, N. Animal models for bipolar disorder: From bedside to the cage. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2017, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Sun, Z.-J.; Wu, J.-L.; Quan, W.-Q.; Xiao, W.-D.; Chew, H.; Jiang, C.-M.; Li, D. Naloxone attenuates ischemic brain injury in rats through suppressing the NIK/IKKα/NF-κB and neuronal apoptotic pathways. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2019, 40, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadass, V.; Vaiyapuri, T.; Tergaonkar, V. Small Molecule NF-κB pathway inhibitors in clinic. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, R.a.B.A. NFkB pathway and inhibition: An overview. Comput. Mol. Biol. 2016, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammersgaard, L.P.; Jørgensen, H.S.; Rungby, J.A.; Reith, J.; Nakayama, H.; Weber, U.J.; Houth, J.; Olsen, T.S. Admission body temperature predicts long-term mortality after acute stroke: The Copenhagen Stroke Study. Stroke 2002, 33, 1759–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, D.M.; Funk, S.E.; Reaven, N.L.; Ouzounelli, M.; Uman, G.C. Impact of fever on outcome in patients with stroke and neurologic injury: A comprehensive meta-analysis. Stroke 2008, 39, 3029–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudy, T.A.; Williams, J.W.; Yaksh, T.L. Antagonism by indomethacin of neurogenic hyperthermia produced by unilateral puncture of the anterior hypothalamic/preoptic region. J. Physiol. 1977, 272, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walentynowicz, K.; Szefer, M.; Wojtal, B.; Terlecki, P.; Wrotek, S.; Kozak, W. Role of prostaglandins in heme-induced fever. J. Physiol. Pharm. 2006, 57 (Suppl. 8), 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, F.; Sobrino, T.; Vieites-Prado, A.; Pérez-Mato, M.; Rodríguez-Yáñez, M.; Blanco, M.; Castillo, J. Hyperthermia in human ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: Similar outcome, different mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Li, H.; Li, K.; Fan, X.D. HDAC9 promotes brain ischemic injury by provoking IkappaBalpha/NF-kappaB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzic, M.; Djordjevic, J.; Mitic, M.; Brkic, Z.; Lukic, I.; Radojcic, M. The contribution of hypothalamic neuroendocrine, neuroplastic and neuroinflammatory processes to lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behaviour in female and male rats: Involvement of glucocorticoid receptor and C/EBP-beta. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 291, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legos, J.J.; Mangoni, A.A.; Read, S.J.; Campbell, C.A.; Irving, E.A.; Roberts, J.; Barone, F.C.; Parsons, A.A. Programmable microchip monitoring of post-stroke pyrexia: Effects of aspirin and paracetamol on temperature and infarct size in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 2002, 113, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.M.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, B.H.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, H.J.; Hong, J.T.; Min, K.R.; Kim, Y. Inhibitory action of novel aromatic diamine compound on lipopolysaccharide-induced nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB without affecting IkappaB degradation. FEBS Lett. 2004, 571, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, S.; Donnan, G.A. Time Is Penumbra: Imaging, Selection and Outcome. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 38, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, P.B. The global burden of stroke: Persistent and disabling. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 417–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luengo-Fernandez, R.; Violato, M.; Candio, P.; Leal, J. Economic burden of stroke across Europe: A population-based cost analysis. Eur. Stroke J. 2020, 5, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Zhong, P.; Fang, L.; Wu, X.; Song, Y.; Yuan, H. miR-183 inhibits microglia activation and expression of inflammatory factors in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion via NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 2540–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, O.; Baumann, B.; de Lorenzi, R.; Muhammad, S.; Zhang, W.; Kleesiek, J.; Malfertheiner, M.; Köhrmann, M.; Potrovita, I.; Maegele, I.; et al. IKK mediates ischemia-induced neuronal death. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolucci, S. Epidemiology and treatment of post-stroke depression. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2008, 4, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elhaik, E.; Zandi, P. Dysregulation of the NF-κB pathway as a potential inducer of bipolar disorder. J. Psychiatr Res. 2015, 70, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troib, A.; Azab, A.N. Effects of psychotropic drugs on Nuclear Factor kappa B. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 19, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, J.S.; Harry, G.J.; Rapoport, S.I.; Kim, H.W. Increased excitotoxicity and neuroinflammatory markers in postmortem frontal cortex from bipolar disorder patients. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munhoz, C.D.; Lepsch, L.B.; Kawamoto, E.M.; Malta, M.B.; Lima Lde, S.; Avellar, M.C.; Sapolsky, R.M.; Scavone, C. Chronic unpredictable stress exacerbates lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in the frontal cortex and hippocampus via glucocorticoid secretion. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 3813–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.; Kuts, R.; Tsenter, P.; Gruenbaum, B.F.; Grinshpun, Y.; Zvenigorodsky, V.; Shelef, I.; Natanel, D.; Brotfain, E.; Zlotnik, A.; et al. The effect of pyruvate on the development and progression of post-stroke depression: A new therapeutic approach. Neuropharmacology 2019, 155, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboix, A.; Cartanyà, A.; Lowak, M.; García-Eroles, L.; Parra, O.; Oliveres, M.; Massons, J. Gender differences and woman-specific trends in acute stroke: Results from a hospital-based registry (1986–2009). Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2014, 127, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Baseline, Mean ± SEM | After 13 Days, Mean ± SEM | |
|---|---|---|
| Sham + Vehicle (n = 10) | 1.62 ± 0.18 | 1.73 ± 0.30 |
| Sham + MEDS-23 (n = 10) | 1.97 ± 0.38 | 1.80 ± 0.18 |
| MCAO + Vehicle (n = 16) | 1.92 ± 0.56 | 0.94 ± 0.43 #,*,^ |
| MCAO + MEDS-23 (n = 16) | 1.77 ± 0.33 | 1.08 ± 0.23 #,*,^ |
| Group | Sham + Vehicle (n = 9) | Sham + MEDS23 (n = 8) | MCAO + Vehicle (n = 14) | MCAO + MEDS23 (n = 14) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time in closed arm (sec); mean ± SEM | 214.2 ± 11.2 | 213.8 ± 10.9 | 178.1 ± 15.6 *,^ | 165.3 ± 13.5 *,^ |
| Time in open arm (sec); mean ± SEM | 85.8 ± 11.2 | 86.2 ± 10.9 | 121.9 ± 15.6 *,^ | 134.7 ± 13.5 *,^ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rubin, E.; Pippione, A.C.; Boyko, M.; Einaudi, G.; Sainas, S.; Collino, M.; Cifani, C.; Lolli, M.L.; Abu-Freha, N.; Kaplanski, J.; et al. A New NF-κB Inhibitor, MEDS-23, Reduces the Severity of Adverse Post-Ischemic Stroke Outcomes in Rats. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12010035
Rubin E, Pippione AC, Boyko M, Einaudi G, Sainas S, Collino M, Cifani C, Lolli ML, Abu-Freha N, Kaplanski J, et al. A New NF-κB Inhibitor, MEDS-23, Reduces the Severity of Adverse Post-Ischemic Stroke Outcomes in Rats. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12010035
Chicago/Turabian StyleRubin, Elina, Agnese C. Pippione, Matthew Boyko, Giacomo Einaudi, Stefano Sainas, Massimo Collino, Carlo Cifani, Marco L. Lolli, Naim Abu-Freha, Jacob Kaplanski, and et al. 2022. "A New NF-κB Inhibitor, MEDS-23, Reduces the Severity of Adverse Post-Ischemic Stroke Outcomes in Rats" Brain Sciences 12, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12010035
APA StyleRubin, E., Pippione, A. C., Boyko, M., Einaudi, G., Sainas, S., Collino, M., Cifani, C., Lolli, M. L., Abu-Freha, N., Kaplanski, J., Boschi, D., & Azab, A. N. (2022). A New NF-κB Inhibitor, MEDS-23, Reduces the Severity of Adverse Post-Ischemic Stroke Outcomes in Rats. Brain Sciences, 12(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12010035