Irreversible Electroporation Mediates Glioma Apoptosis via Upregulation of AP-1 and Bim: Transcriptome Evidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and IRE
2.2. Apoptosis and Necrosis Assay
2.3. RNA Extraction and Transcriptome Sequencing
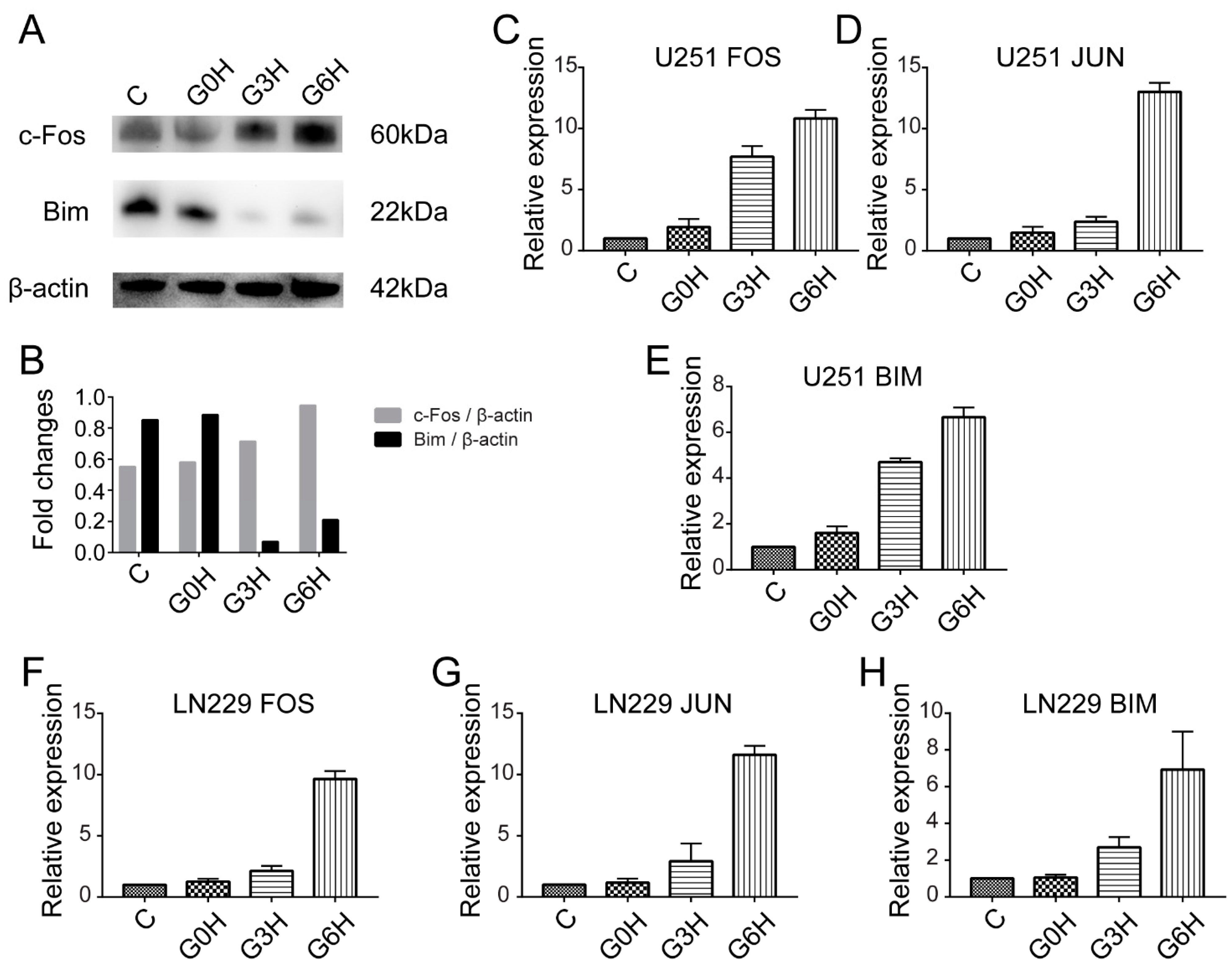
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Quantitative PCR
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Electric Field Intensity Threshold for Apoptosis/Necrosis of U251 Glioma Cell Line
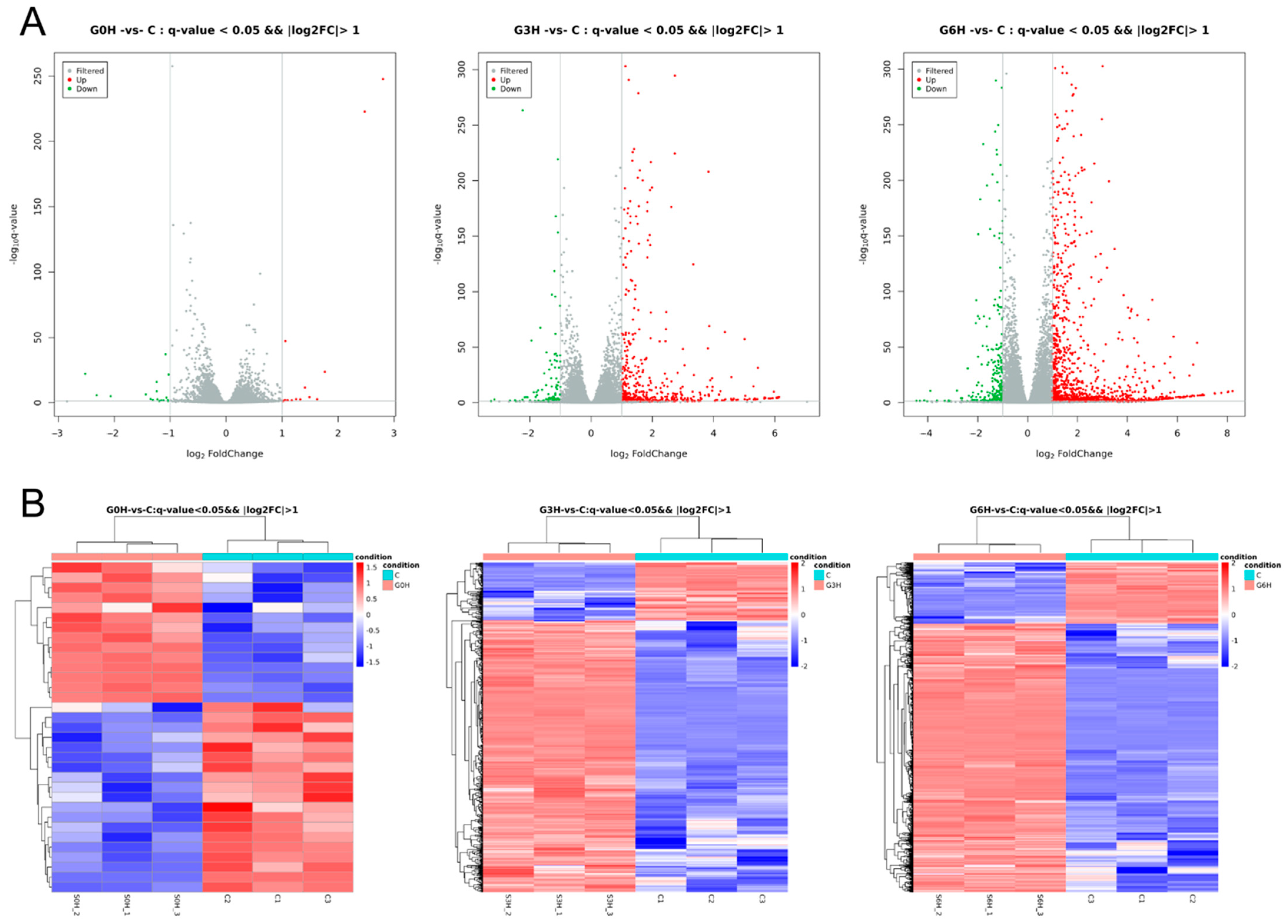
3.2. Comprehensive Regulatory Transcription Changes of IRE-Induced Apoptosis
3.3. Transcription Factors FOS and JUN Played a Major Role in the Apoptosis after IRE, Accompanied by Mixed RCD Forms
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Liao, P.; Vecchione-Koval, T.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2010–2014. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, V1–V88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchorska, B.; Weller, M.; Tabatabai, G.; Senft, C.; Hau, P.; Sabel, M.C.; Herrlinger, U.; Ketter, R.; Schlegel, U.; Marosi, C.; et al. Complete resection of contrast-enhancing tumor volume is associated with improved survival in recurrent glioblastoma-results from the DIRECTOR trial. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualetti, F.; Montemurro, N.; Desideri, I.; Loi, M.; Giannini, N.; Gadducci, G.; Malfatti, G.; Cantarella, M.; Gonnelli, A.; Montrone, S.; et al. Impact of recurrence pattern in patients undergoing a second surgery for recurrent glioblastoma. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2022, 122, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, C.; Thumann, S.; Beyer, L.; Pregler, B.; Kramer, J.; Lang, S.; Teufel, A.; Jung, E.M.; Stroszczynski, C.; Wiggermann, P. Percutaneous Irreversible Electroporation: Long-term survival analysis of 71 patients with inoperable malignant hepatic tumors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiella, S.; Butturini, G.; Frigerio, I.; Salvia, R.; Armatura, G.; Bacchion, M.; Fontana, M.; D’Onofrio, M.; Martone, E.; Bassi, C. Safety and Feasibility of Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) in Patients with Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: Results of a Prospective Study. Dig. Surg. 2015, 32, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, M.; Dickinson, L.; Ali, A.; Ramachandran, N.; Donaldson, I.; Freeman, A.; Ahmed, H.U.; Emberton, M. A prospective development study investigating focal irreversible electroporation in men with localised prostate cancer: Nanoknife Electroporation Ablation Trial (NEAT). Contemp. Clin. Trials 2014, 39, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendler, J.J.; Porsch, M.; Nitschke, S.; Kollermann, J.; Siedentopf, S.; Pech, M.; Fischbach, F.; Ricke, J.; Schostak, M.; Liehr, U.B. A prospective Phase 2a pilot study investigating focal percutaneous irreversible electroporation (IRE) ablation by NanoKnife in patients with localised renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with delayed interval tumour resection (IRENE trial). Contemp. Clin. Trials 2015, 43, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpentier, K.P.; Wolf, F.; Noble, L.; Winn, B.; Resnick, M.; Dupuy, D.E. Irreversible electroporation of the liver and liver hilum in swine. HPB 2011, 13, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Chen, L.C.; Moser, M.A.J.; Zhang, W.J.; Qin, Z.Y.; Zhang, B. Electroporation-Based Therapy for Brain Tumors: A Review. J. Biomech. Eng.-Trans. Asme 2021, 143, 100802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmeisl, J.H.; Garcia, P.A.; Pancotto, T.E.; Robertson, J.L.; Henao-Guerrero, N.; Neal, R.E.; Ellis, T.L.; Davalos, R.V. Safety and feasibility of the Nano Knife system for irreversible electroporation ablative treatment of canine spontaneous intracranial gliomas. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 1008–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.; Ding, L.; Fang, Z.; Yu, S.; Chen, L.; Moser, M.; Zhang, W.J.C.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, B. Lethal Electric Field Thresholds for Cerebral Cells with IRE and H-FIRE Protocols: An In Vitro 3D Cell Model Study. J. Biomech. Eng. 2022, 144, 101010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napotnik, T.B.; Polajzer, T.; Miklavcic, D. Cell death due to electroporation—A review. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 141, 107871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Agostinis, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Amelio, I.; Andrews, D.W.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 486–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idziorek, T.; Estaquier, J.; Debels, F.; Ameisen, J.C. Yopro-1 Permits Cytofluorometric Analysis Of Programmed Cell-Death (Apoptosis) Without Interfering With Cell Viability. J. Immunol. Methods 1995, 185, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling The False Discovery Rate—A Practical And Powerful Approach To Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Kuo, L.R.; Chang, C.L.; Hwu, Y.K.; Huang, C.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Chen, K.; Lin, S.J.; Huang, J.D.; Chen, Y.Y. In situ real-time investigation of cancer cell photothermolysis mediated by excited gold nanorod surface plasmons. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4104–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, G. The morphology of apoptosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2000, 301, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtaszczyk, A.; Caluori, G.; Pešl, M.; Melajova, K.; Stárek, Z. Irreversible electroporation ablation for atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2018, 29, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, J.T., Jr.; Wilcoxon, F. A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1949, 96, 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Eferl, R.; Wagner, E.F. AP-1: A double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voll, R.E.; Herrmann, M.; Roth, E.A.; Stach, C.; Kalden, J.R.; Girkontaite, I. Immunosuppressive effects of apoptotic cells. Nature 1997, 390, 350–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, A.G.; Hubbard, N.W.; Messmer, M.N.; Kofman, S.B.; Hagan, C.E.; Orozco, S.L.; Chiang, K.; Daniels, B.P.; Baker, D.; Oberst, A. Intratumoral activation of the necroptotic pathway components RIPK1 and RIPK3 potentiates antitumor immunity. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaaw2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Karin, M. Autophagy, Inflammation, and Immunity: A Troika Governing Cancer and Its Treatment. Cell 2016, 166, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Anti-inflammatory Agents: Present and Future. Cell 2010, 140, 935–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggi, A.; Zocchi, M.R. Mechanisms of tumor escape: Role of tumor microenvironment in inducing apoptosis of cytolytic effector cells. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2006, 54, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Shin, J.; Zhong, C.; Wang, S.; Roychowdhury, P.; Lim, J.; Kim, D.; Ming, G.L.; Song, H. Neuronal activity modifies the chromatin accessibility landscape in the adult brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, V.; Mandinova, A.; Guinea-Viniegra, J.; Hu, B.; Lefort, K.; Lambertini, C.; Neel, V.; Dummer, R.; Wagner, E.F.; Dotto, G.P. EGFR signalling as a negative regulator of Notch1 gene transcription and function in proliferating keratinocytes and cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Chan, C.S.; Wu, R.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Song, J.S.; Tang, L.H.; Levine, A.J.; Feng, Z. Negative regulation of tumor suppressor p53 by microRNA miR-504. Mol. Cell. 2010, 38, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasibhatla, S.; Brunner, T.; Genestier, L.; Echeverri, F.; Mahboubi, A.; Green, D.R. DNA damaging agents induce expression of Fas ligand and subsequent apoptosis in T lymphocytes via the activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, J.; Neame, S.J.; Paquet, L.; Bernard, O.; Ham, J. Dominant-negative c-Jun promotes neuronal survival by reducing BIM expression and inhibiting mitochondrial cytochrome c release. Neuron 2001, 29, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Lee, J.M.; Zeng, C.B.; Chen, H.; Hsu, C.Y.; Xu, J. Amyloid beta peptide increases DP5 expression via activation of neutral sphingomyelinase and JNK in oligodendrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putcha, G.V.; Le, S.; Frank, S.; Besirli, C.G.; Clark, K.; Chu, B.; Alix, S.; Youle, R.J.; LaMarche, A.; Maroney, A.C.; et al. JNK-mediated BIM phosphorylation potentiates BAX-dependent apoptosis. Neuron 2003, 38, 899–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Apoptosis | Apoptosis-Multiple Species | Autophagy-Other | Autophagy-Animal | Necroptosis | Pyroptosis | Ferroptosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa04210 | hsa04215 | hsa04136 | hsa04140 | hsa04217 | Not Available | hsa04216 |
| BIRC3 | BIRC3 | BIRC3 | N/A | / | ||
| BCL2L11 APAF1 | BCL2L11 APAF1 | |||||
| PIK3R3 EIF2AK3 | PIK3R3 EIF2AK3 | |||||
| TNFRSF10A TNF | TNFRSF10A TNF | |||||
| ATG9B | ATG9B | |||||
| DDIT4 DEPTOR | ||||||
| GADD45B MCL1 JUN DDIT3 PIDD1 GADD45A NFKBIA FOS NTRK1 GADD45G ATF4 | ||||||
| H2AC6 PLA2G4C H2AC20 PYGM JAK3 PLA2G4F IL1A USP21 TNFAIP3 ZBP1 |
| G0H-vs-C | G3H-vs-C | G6H-vs-C |
|---|---|---|
| FOS FOSB | FOS FOSB | FOS FOSB |
| MMP1 | MMP1 | |
| FERMT3 NFKBIA ITGAM MAPK13 H2BU1 ATP6V1B1 GRIN2B C5AR1 HSPA6 EGR3 SERPINC1 TNFAIP3 H2BC18 CCL2 IL17B TNFRSF10A CXCL3 C3AR1 DLL1 MYLK3 IL6 PRKCG MAP3K8 PTPN6 IL23A PECAM1 CXCL2 EGR2 BCL3 IL1A ITGAX H3C4 IL17C C9 JUN CD1D CD79A BUB1B-PAK6 IL1R2 GNB3 RASGRP2 H2BC17 JAK3 HSPA1B PLA2G4F RASSF5 CD14 HSPA1A | FERMT3 NFKBIA ITGAM MAPK13 H2BU1 ATP6V1B1 GRIN2B C5AR1 HSPA6 EGR3 SERPINC1 TNFAIP3 H2BC18 CCL2 IL17B TNFRSF10A CXCL3 C3AR1 DLL1 MYLK3 IL6 PRKCG MAP3K8 PTPN6 IL23A PECAM1 CXCL2 EGR2 BCL3 IL1A ITGAX H3C4 IL17C C9 JUN CD1D CD79A BUB1B-PAK6 IL1R2 GNB3 RASGRP2 H2BC17 JAK3 HSPA1B PLA2G4F RASSF5 CD14 HSPA1A | |
| CCL26 | ||
| HSPA2 FGG COL3A1 F3 CD74 APBB1IP | ||
| KIT TNFRSF13C H2BC6 H2BC5 H2BC4 CD34 C2 TBX21 DLL3 H3C13 SCIN CXCR4 MASP2 GRK7 GBP1 PLA2G4C FOSL1 KSR1 H2AC20 MYLK4 F2 FOXO3 H2BC11 POLR1C TNFRSF11A RUNX1 CD1A PTGS2 BDKRB2 CALML4 TNF FLT1 LCK TLR9 H2AC6 RARA DLL4 GUCY1A2 NFATC2 CLDN1 TBKBP1 TLR5 IL5RA F2RL2 POLR2H RAG1 IRF1 F2R CLDN19 NFKBIE IRF3 SERPINF2 PIK3R3 BIRC3 JAM2 THBD ITGB7 H3C3 ITGA2B H2BC8 NAMPT ZBP1 PIP5K1A BTK |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Chen, L.; Song, K.; Shu, T.; Fang, Z.; Ding, L.; Liu, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.; et al. Irreversible Electroporation Mediates Glioma Apoptosis via Upregulation of AP-1 and Bim: Transcriptome Evidence. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111465
Yu S, Chen L, Song K, Shu T, Fang Z, Ding L, Liu J, Jiang L, Zhang G, Zhang B, et al. Irreversible Electroporation Mediates Glioma Apoptosis via Upregulation of AP-1 and Bim: Transcriptome Evidence. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(11):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111465
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shuangquan, Lingchao Chen, Kun Song, Ting Shu, Zheng Fang, Lujia Ding, Jilong Liu, Lei Jiang, Guanqing Zhang, Bing Zhang, and et al. 2022. "Irreversible Electroporation Mediates Glioma Apoptosis via Upregulation of AP-1 and Bim: Transcriptome Evidence" Brain Sciences 12, no. 11: 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111465
APA StyleYu, S., Chen, L., Song, K., Shu, T., Fang, Z., Ding, L., Liu, J., Jiang, L., Zhang, G., Zhang, B., & Qin, Z. (2022). Irreversible Electroporation Mediates Glioma Apoptosis via Upregulation of AP-1 and Bim: Transcriptome Evidence. Brain Sciences, 12(11), 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12111465







