An Investigation of the Modulating Effects of Sensory Stimulation and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Memory-Related Brain Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
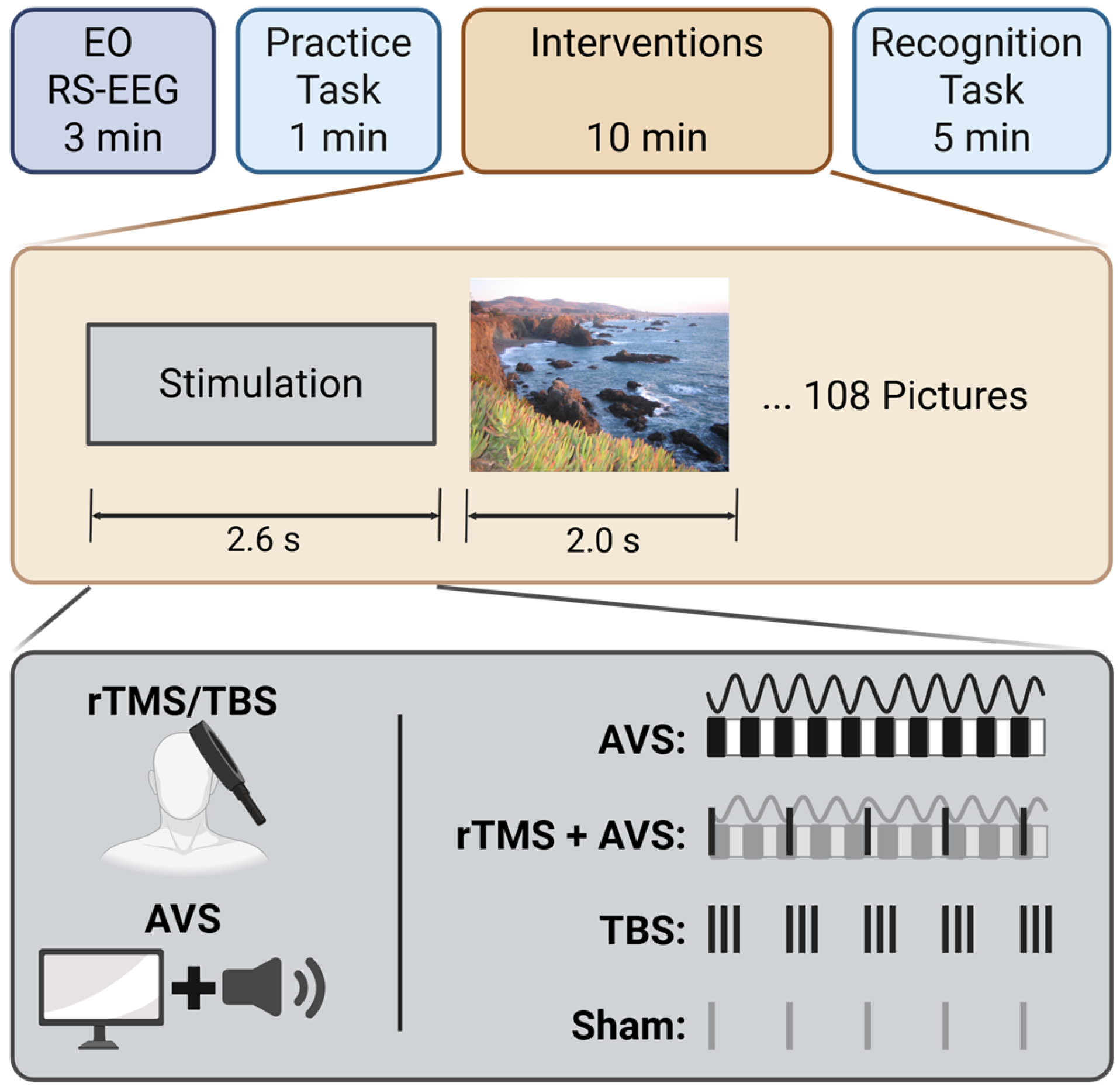
2.2. Experiment Design
Recognition Memory Task
2.3. Interventions
2.3.1. Audiovisual Stimulation (AVS)
2.3.2. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) with AVS
2.3.3. Theta Burst Stimulation (TBS)
2.3.4. Sham rTMS
2.4. Electroencephalography Data Acquisition
2.5. Electroencephalography Pre-Processing
2.6. Event-Related Synchronisation/Desynchronisation
2.7. Phase-Amplitude Coupling
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
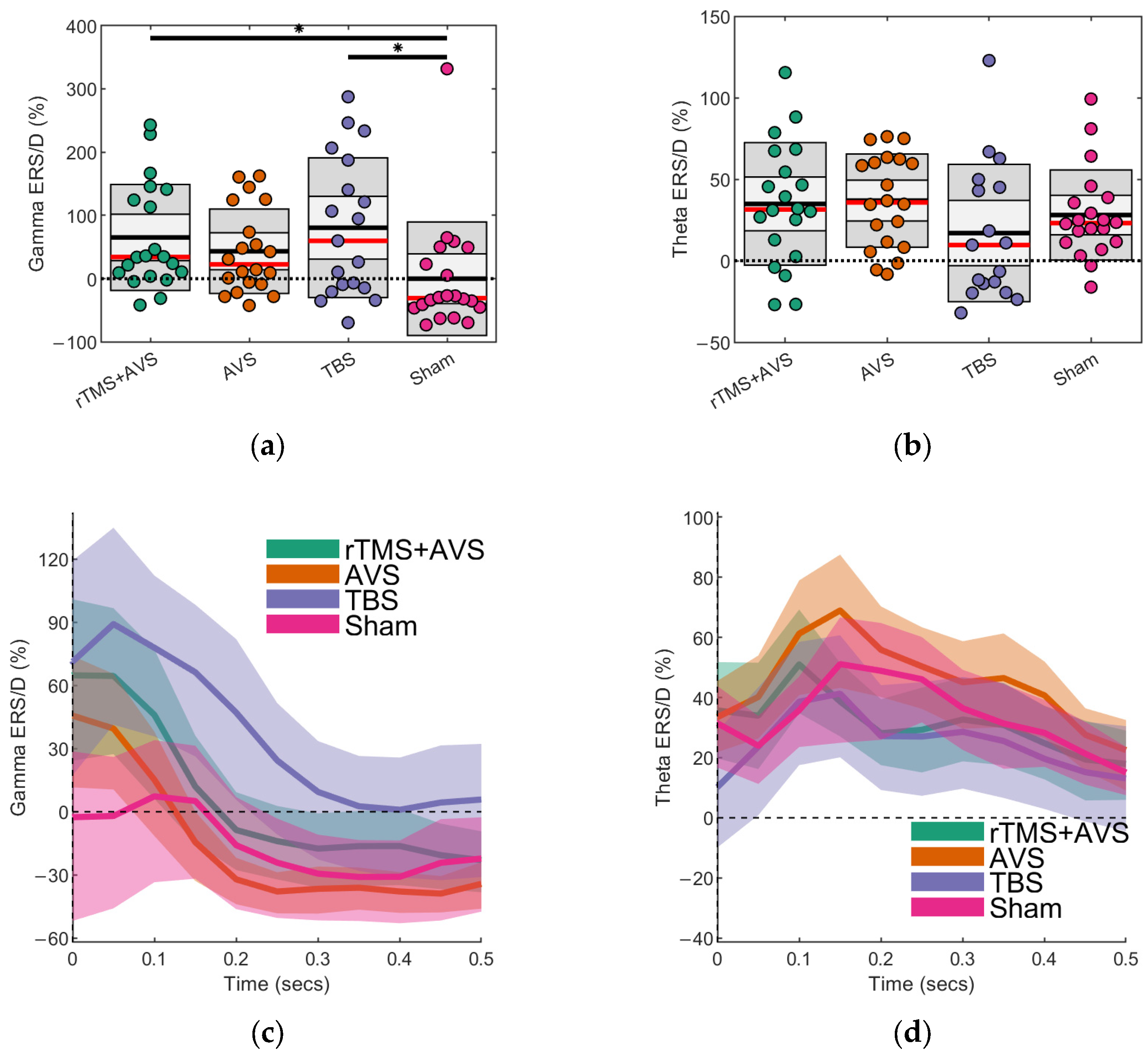
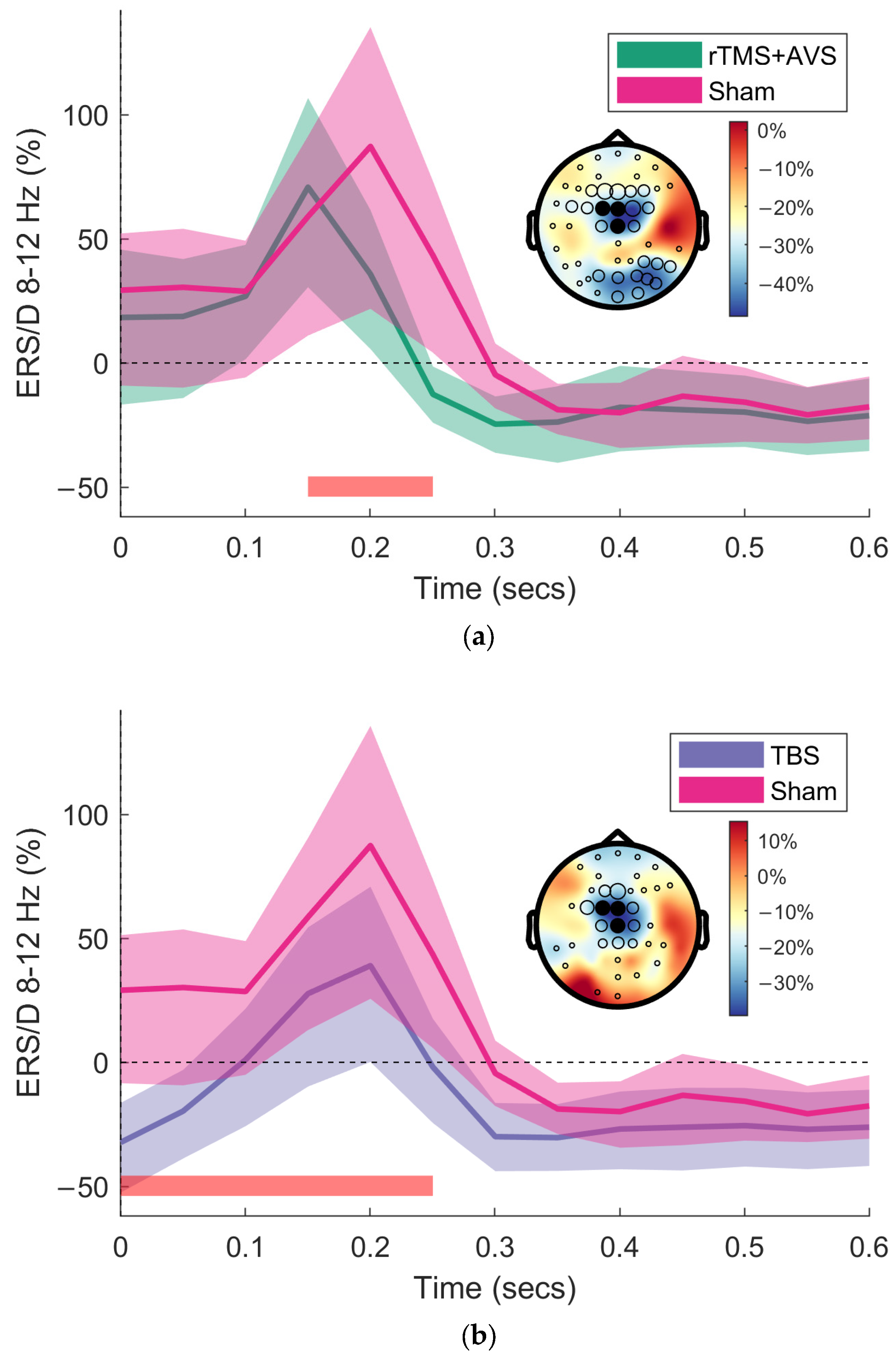
3.1. Event-Related Synchronisation/Desynchronisation
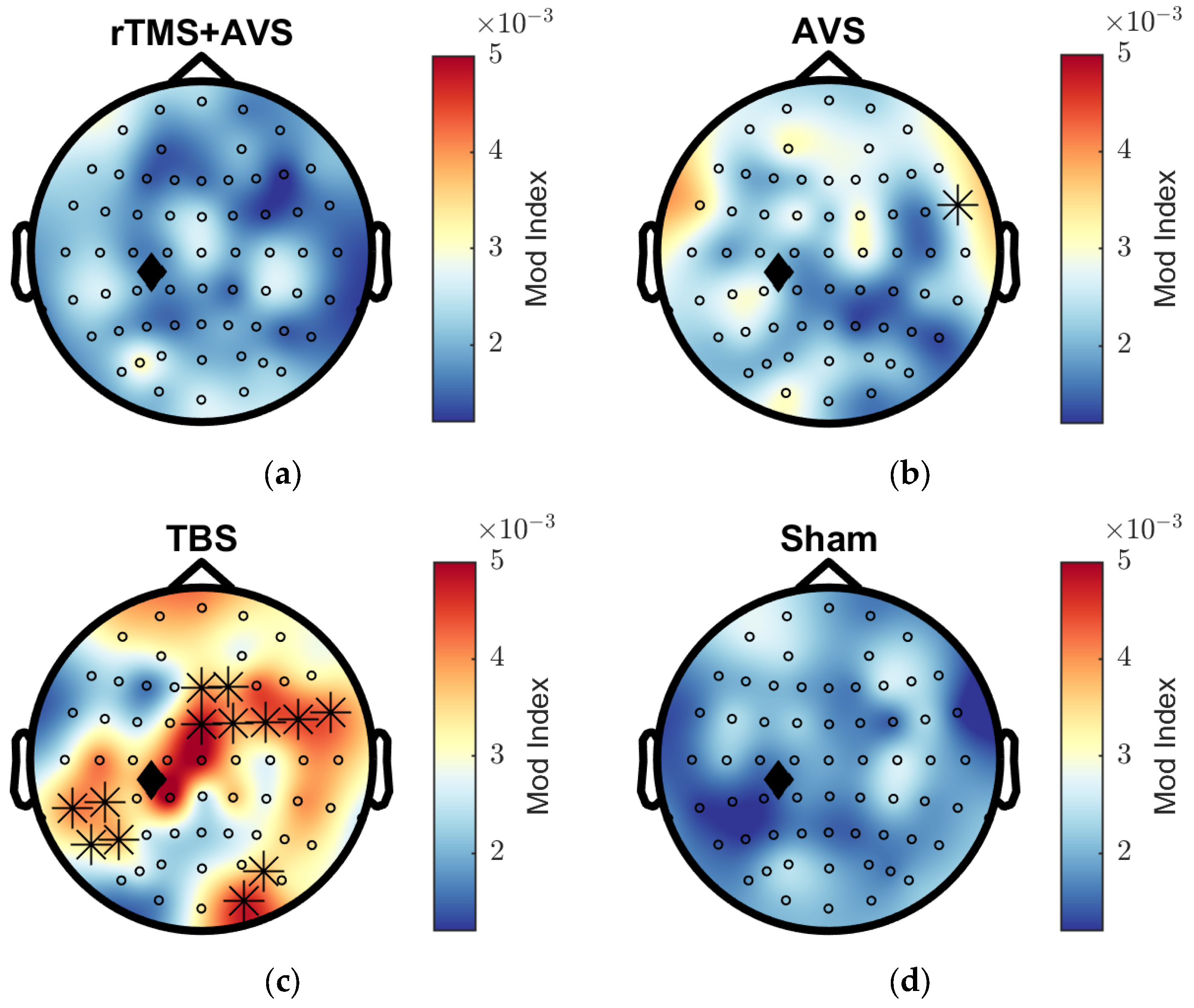
3.2. Phase-Amplitude Coupling
3.3. Recognition Memory Task Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| AVS | Audiovisual stimulation |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| ERS/D | Event-related synchronisation/desynchronisation |
| fMRI | Functional magnetic resonance imaging |
| HEAR | High-variance electrode artifact removal |
| HF-rTMS | High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation |
| ICA | Independent component analysis |
| MI | Modulation index |
| MRMM | Mixed-effect repeated measure model |
| PAC | Phase-amplitude coupling |
| RMT | Resting motor threshold |
| RS-EEG | Resting-state electroencephalography |
| rTMS | Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation |
| SOUND | Source-estimate-utilizing noise-discarding |
| STFT | Short-time Fourier transform |
| TBS | Theta burst stimulation |
| TFR | Time frequency representation |
| TMS | Transcranial magnetic stimulation |
References
- Danieli, K.; Guyon, A.; Bethus, I. Episodic Memory formation: A review of complex Hippocampus input pathways. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 126, 110757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, B.C.; Eichenbaum, H. The episodic memory system: Neurocircuitry and disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, N.T.; Mowszowski, L.; Naismith, S.L.; Chadwick, V.L.; Valenzuela, M.; Lampit, A. Computerized cognitive training in older adults with mild cognitive impairment or dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry 2017, 174, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.M.; Wollny-Huttarsch, D.; Nikolin, S.; McClintock, S.M.; Alonzo, A.; Lisanby, S.H.; Loo, C.K. Neurocognitive subgroups in major depressive disorder. Neuropsychology 2020, 34, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orygen. Cognitive Impairment in Psychosis; Landscape Report; Orygen: Parkville, VIC, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, W.; Chung, C.K.; Kim, J.S. Episodic memory in aspects of large-scale brain networks. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geib, B.R.; Stanley, M.L.; Wing, E.A.; Laurienti, P.J.; Cabeza, R. Hippocampal contributions to the large-scale episodic memory network predict vivid visual memories. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.A.; Ritchey, M. Cortico-hippocampal network connections support the multidimensional quality of episodic memory. eLife 2019, 8, e45591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Lu, J.; Yan, T.; Ding, Y.; Wang, B. The dynamic reconfiguration of the functional network during episodic memory task predicts the memory performance. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Marcantoni, E.; Clouter, A.; Shapiro, K.L.; Hanslmayr, S. Rhythmic sensory stimulation as a noninvasive tool to study plasticity mechanisms in human episodic memory. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2024, 58, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmeykina, E.; Mittner, M.; Paulus, W.; Turi, Z. Weak rTMS-induced electric fields produce neural entrainment in humans. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, C.J.; Murman, D.L.; Warren, D.E. Stimulating memory: Reviewing interventions using repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation to enhance or restore memory abilities. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutsuridis, V.; Yoshida, M. Editorial: Memory Processes in Medial Temporal Lobe: Experimental, Theoretical and Computational Approaches. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opitz, B. Memory function and the hippocampus. Front. Neurol Neurosci. 2014, 34, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camina, E.; Güell, F. The Neuroanatomical, Neurophysiological and Psychological Basis of Memory: Current Models and Their Origins. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscovitch, M.; Cabeza, R.; Winocur, G.; Nadel, L. Episodic Memory and Beyond: The Hippocampus and Neocortex in Transformation. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2016, 67, 105–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgin, L.L. Rhythms of the hippocampal network. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanslmayr, S.; Axmacher, N.; Inman, C.S. Modulating Human Memory via Entrainment of Brain Oscillations. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermiller, M.A.-O.; Karp, E.; Nilakantan, A.A.-O.; Voss, J.A.-O. Episodic memory improvements due to noninvasive stimulation targeting the cortical-hippocampal network: A replication and extension experiment. Brain Behav. 2019, 9, e01393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.A.-O.; Nilakantan, A.S.; Hermiller, M.A.-O.; Palumbo, R.A.-O.X.; VanHaerents, S.A.-O.; Voss, J.L. Selective and coherent activity increases due to stimulation indicate functional distinctions between episodic memory networks. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkow, M.B.; Burke, J.F.; Kahana, M.J. The human hippocampus contributes to both the recollection and familiarity components of recognition memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14378–14383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, K.N.; Hermiller, M.S.; Nilakantan, A.S.; Voss, J.L. Stimulating the hippocampal posterior-medial network enhances task-dependent connectivity and memory. eLife 2019, 8, e49458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilakantan, A.S.; Bridge, D.J.; Gagnon, E.P.; VanHaerents, S.A.; Voss, J.L. Stimulation of the Posterior Cortical-Hippocampal Network Enhances Precision of Memory Recollection. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, N.S.; Carpenter, S.L.; Ridout, S.J.; Sanchez, G.; Albright, S.E.; Tyrka, A.R.; Price, L.H.; Carpenter, L.L. 5Hz Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation to left prefrontal cortex for major depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 186, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambini, A.; Nee, D.E.; D’Esposito, M. Hippocampal-targeted Theta-burst Stimulation Enhances Associative Memory Formation. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 30, 1452–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermiller, M.S.; Chen, Y.F.; Parrish, T.B.; Voss, J.L. Evidence for Immediate Enhancement of Hippocampal Memory Encoding by Network-Targeted Theta-Burst Stimulation during Concurrent fMRI. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 7155–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terao, Y.; Ugawa, Y. Basic Mechanisms of TMS. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 19, 322–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Deng, X.P.; Wu, Y.Y.; Li, X.L.; Feng, Z.J.; Wang, H.X.; Jing, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zang, Y.F.; Zhang, J. High-Frequency rTMS of the Motor Cortex Modulates Cerebellar and Widespread Activity as Revealed by SVM. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, P.B.; Fountain, S.; Daskalakis, Z.J. A comprehensive review of the effects of rTMS on motor cortical excitability and inhibition. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 2584–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation: A primer. Neuron 2007, 55, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luber, B.; Lisanby, S.H. Enhancement of human cognitive performance using transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). Neuroimage 2014, 85, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Agustín, A.; Crevillén, D.; Soto-León, V.; Moreno, J.C.; Oliviero, A.; Pons, J.L. Transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with endogenous human hippocampal and motor cortical activity enhances memory. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, J.L.; Bridge, D.J.; Cohen, N.J.; Walker, J.A. A Closer Look at the Hippocampus and Memory. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2017, 21, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-Z.; Edwards, M.J.; Rounis, E.; Bhatia, K.P.; Rothwell, J.C. Theta burst stimulation of the human motor cortex. Neuron 2005, 45, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lazzaro, V.; Pilato, F.; Dileone, M.; Profice, P.; Oliviero, A.; Mazzone, P.; Insola, A.; Ranieri, F.; Meglio, M.; Tonali, P. The physiological basis of the effects of intermittent theta burst stimulation of the human motor cortex. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 3871–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lazzaro, V.; Pilato, F.; Saturno, E.; Oliviero, A.; Dileone, M.; Mazzone, P.; Insola, A.; Tonali, P.; Ranieri, F.; Huang, Y. Theta-burst repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation suppresses specific excitatory circuits in the human motor cortex. J. Physiol. 2005, 565, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischnewski, M.; Schutter, D.J. Efficacy and time course of theta burst stimulation in healthy humans. Brain Stimul. 2015, 8, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyffeler, T.; Wurtz, P.; Lüscher, H.-R.; Hess, C.W.; Senn, W.; Pflugshaupt, T.; von Wartburg, R.; Lüthi, M.; Müri, R.M. Repetitive TMS over the human oculomotor cortex: Comparison of 1-Hz and theta burst stimulation. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 409, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, T.-T.; Song, X.-B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.-H.; Cui, Z.-H.; Hao, Q.; Liu, H.L.; Lei, C.L.; Liu, J. Comparison of different stimulation parameters of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for unilateral spatial neglect in stroke patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 359, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, E.A.; Sperling, M.R.; Sharan, A.D.; Wanda, P.A.; Levy, D.F.; Lyalenko, A.; Pedisich, I.; Rizzuto, D.S.; Kahana, M.J. Theta-burst stimulation entrains frequency-specific oscillatory responses. Brain Stimul. 2021, 14, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, S.; Han, Y.; Shan, C. Gamma oscillations and application of 40-Hz audiovisual stimulation to improve brain function. Brain Behav. 2022, 12, e2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukiw, W.J. Treating Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) with Light and Sound. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Park. 2020, 10, 487. [Google Scholar]
- Suk, H.J.; Chan, D.; Jackson, B.; Fernandez, V.; Stark, D.; Milman, N.; Beach, S.; Uitermarkt, B.; Gander, P.; Boes, A.D. Sensory gamma frequency stimulation in cognitively healthy and AD individuals safely induces highly coordinated 40 hz neural oscillation: A preliminary study of non-invasive sensory stimulation for treating Alzheimer’s disease: Dementia care research (research projects; nonpharmacological)/Therapeutic strategies and interventions. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2020, 16, e041146. [Google Scholar]
- Teplan, M.; Krakovská, A.; Štolc, S. EEG responses to long-term audio–visual stimulation. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2006, 59, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.; Suk, H.J.; Jackson, B.L.; Milman, N.P.; Stark, D.; Klerman, E.B.; Kitchener, E.; Fernandez Avalos, V.S.; de Weck, G.; Banerjee, A.; et al. Gamma frequency sensory stimulation in mild probable Alzheimer’s dementia patients: Results of feasibility and pilot studies. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorell, A.J.; Paulson, A.L.; Suk, H.J.; Abdurrob, F.; Drummond, G.T.; Guan, W.; Young, J.Z.; Kim, D.N.; Kritskiy, O.; Barker, S.J.; et al. Multi-sensory Gamma Stimulation Ameliorates Alzheimer’s-Associated Pathology and Improves Cognition. Cell 2019, 177, 256–271.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaikkan, C.; Middleton, S.J.; Marco, A.; Pao, P.-C.; Mathys, H.; Kim, D.N.-W.; Gao, F.; Young, J.Z.; Suk, H.-J.; Boyden, E.S. Gamma entrainment binds higher-order brain regions and offers neuroprotection. Neuron 2019, 102, 929–943.e928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaccarino, H.F.; Singer, A.C.; Martorell, A.J.; Rudenko, A.; Gao, F.; Gillingham, T.Z.; Mathys, H.; Seo, J.; Kritskiy, O.; Abdurrob, F. Gamma frequency entrainment attenuates amyloid load and modifies microglia. Nature 2016, 540, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements-Cortes, A.; Ahonen, H.; Evans, M.; Freedman, M.; Bartel, L. Short-Term Effects of Rhythmic Sensory Stimulation in Alzheimer’s Disease: An Exploratory Pilot Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Park. 2016, 52, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Colon-Motas, K.M.; Pybus, A.F.; Piendel, L.; Seppa, J.K.; Walker, M.L.; Manzanares, C.M.; Qiu, D.; Miocinovic, S.; Wood, L.B.; et al. A feasibility trial of gamma sensory flicker for patients with prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2021, 7, e12178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Ehinger, K.A.; Hays, J.; Torralba, A.; Oliva, A. Sun database: Exploring a large collection of scene categories. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2016, 119, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostenveld, R.; Fries, P.; Maris, E.; Schoffelen, J.-M. FieldTrip: Open source software for advanced analysis of MEG, EEG, and invasive electrophysiological data. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 156869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobler, R.J.; Sburlea, A.I.; Mondini, V.; Müller-Putz, G.R. HEAR to remove pops and drifts: The high-variance electrode artifact removal (HEAR) algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 5150–5155. [Google Scholar]
- Mutanen, T.P.; Metsomaa, J.; Liljander, S.; Ilmoniemi, R.J. Automatic and robust noise suppression in EEG and MEG: The SOUND algorithm. Neuroimage 2018, 166, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köster, M.; Finger, H.; Graetz, S.; Kater, M.; Gruber, T. Theta-gamma coupling binds visual perceptual features in an associative memory task. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köster, M.; Martens, U.; Gruber, T. Memory entrainment by visually evoked theta-gamma coupling. NeuroImage 2019, 188, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tort, A.B.; Komorowski, R.; Eichenbaum, H.; Kopell, N. Measuring phase-amplitude coupling between neuronal oscillations of different frequencies. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 104, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, B. Percentage points for a generalized ESD many-outlier procedure. Technometrics 1983, 25, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schielzeth, H.; Dingemanse, N.J.; Nakagawa, S.; Westneat, D.F.; Allegue, H.; Teplitsky, C.; Réale, D.; Dochtermann, N.A.; Garamszegi, L.Z.; Araya-Ajoy, Y.G. Robustness of linear mixed-effects models to violations of distributional assumptions. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maris, E.; Oostenveld, R. Nonparametric statistical testing of EEG-and MEG-data. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 164, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernet, C.; Latinus, M.; Nichols, T.; Rousselet, G. Cluster-based computational methods for mass univariate analyses of event-related brain potentials/fields: A simulation study. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 250, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonstra, T.W.; Nikolin, S.; Meisener, A.-C.; Martin, D.M.; Loo, C.K. Change in mean frequency of resting-state electroencephalography after transcranial direct current stimulation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, A.R.; Chau, W.; Protzner, A.B. Spatiotemporal analysis of event-related fMRI data using partial least squares. Neuroimage 2004, 23, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langdon, A.J.; Boonstra, T.W.; Breakspear, M. Multi-frequency phase locking in human somatosensory cortex. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2011, 105, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, A.E.; Wehrspaun, C.C.; Sander, M.C. Item recognition and lure discrimination in younger and older adults are supported by alpha/beta desynchronization. Neuropsychologia 2020, 148, 107658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, B.J.; Martín-Buro, M.C.; Staresina, B.P.; Hanslmayr, S. Disentangling neocortical alpha/beta and hippocampal theta/gamma oscillations in human episodic memory formation. NeuroImage 2021, 242, 118454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, B.J.; Martín-Buro, M.C.; Staresina, B.P.; Hanslmayr, S.; Staudigl, T. Alpha/beta power decreases during episodic memory formation predict the magnitude of alpha/beta power decreases during subsequent retrieval. Neuropsychologia 2021, 153, 107755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, M.; Wada, Y.; Takeda, T.; Oe, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Koshino, Y. EEG harmonic responses to photic stimulation in normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease: Differences in interhemispheric coherence. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Park, Y.; Suh, S.W.; Kim, S.-S.; Kim, D.-W.; Lee, J.; Park, J.; Yoo, S.; Kim, K.W. Optimal flickering light stimulation for entraining gamma waves in the human brain. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Nikolin, S.; Samaratunga, N.; Chow, E.J.H.; Loo, C.K.; Martin, D.M. Cognitive effects following offline High-Frequency repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (HF-rTMS) in healthy populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2024, 34, 250–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, A.; Proksch, S.; Mede, B.; Comstock, D.C.; Ross, J.M.; Balasubramaniam, R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of intermittent theta burst stimulation (iTBS) on cognitive enhancement. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 135, 104587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedberg, M.V.; Reeves, J.A.; Fioriti, C.M.; Murillo, J.; Wassermann, E.M. Reproducing the effect of hippocampal network-targeted transcranial magnetic stimulation on episodic memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2022, 419, 113707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| AVS | rTMS + AVS | TBS | Sham | F(3, 60) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recognition hits | 0.70 (0.13) | 0.72 (0.15) | 0.71 (0.14) | 0.69 (0.14) | 0.55 | 0.65 |
| Lure hits | 0.73 (0.11) | 0.70 (0.14) | 0.68 (0.12) | 0.72 (0.12) | 2.07 | 0.11 |
| Recognition D-prime | 1.18 (0.51) | 1.21 (0.56) | 1.08 (0.44) | 1.15 (0.37) | 0.66 | 0.58 |
| Recognition RT (ms) | 1295 (242) | 1362 (247) | 1325 (216) | 1295 (181) | 0.94 | 0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolin, S.; Wang, M.; Moffa, A.; Huang, H.; Xu, M.; Pande, S.R.; Martin, D. An Investigation of the Modulating Effects of Sensory Stimulation and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Memory-Related Brain Activity. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111182
Nikolin S, Wang M, Moffa A, Huang H, Xu M, Pande SR, Martin D. An Investigation of the Modulating Effects of Sensory Stimulation and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Memory-Related Brain Activity. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(11):1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111182
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolin, Stevan, Matthew Wang, Adriano Moffa, Haijing Huang, Mei Xu, Siddhartha Raj Pande, and Donel Martin. 2025. "An Investigation of the Modulating Effects of Sensory Stimulation and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Memory-Related Brain Activity" Brain Sciences 15, no. 11: 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111182
APA StyleNikolin, S., Wang, M., Moffa, A., Huang, H., Xu, M., Pande, S. R., & Martin, D. (2025). An Investigation of the Modulating Effects of Sensory Stimulation and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Memory-Related Brain Activity. Brain Sciences, 15(11), 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111182






