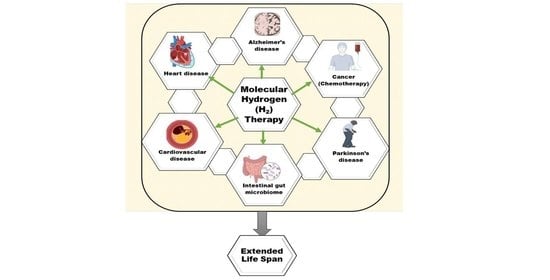
Redox-Mechanisms of Molecular Hydrogen Promote Healthful Longevity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Mechanism of Action of H2
3. The Anti-Oxidative Effects of H2 That Extend Life Span
4. The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of H2
5. H2 and Redox Mechanism of Oxidative Stress
6. Age-Related Diseases and Redox Mechanisms
7. Effects of Hydrogen Gas on Inflammatory Cytokines
8. Hydrogen Gas Relieves Adverse Effects of Chemotherapy
9. Hydrogen and Intestinal Microbiome
10. Protective Effects of H2 on the Cardiovascular System
11. Therapeutic Effects of H2 on Parkinson’s Disease (PD) and Co-Relation with Intestinal Microbiome
12. Therapeutic and Preventive Effect of H2 on AD and Co-Relation with Intestinal Microbiome
13. Effects of H2 in Heart Diseases
14. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 8-OHdG | 8-hydroxy-desoxyguanosine |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| Aβ | Amyloid beta |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| ET-1 | Endothelin-1 |
| GHSR1-α | Growth hormone secretagogue receptor |
| GSC | Glioma stem-like cell |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| H2 | Molecular Hydrogen |
| HRW | Hydrogen rich water |
| H2S | Hydrogen sulfide |
| HMGB-1 | High-mobility group box 1 |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| IL | Interleukin |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| LRP1 | Low-density lipoprotein receptor 1 |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| MMP3 | Matrix metalloproteinase 3 |
| MS | Metabolic syndrome |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
References
- Calder, P.C.; Carding, S.R.; Christopher, G.; Kuh, D.; Langley-Evans, S.C.; McNulty, H. A Holistic Approach to Healthy Ageing: How Can People Live Longer, Healthier Lives? J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 31, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, H.; Miyazawa, T.; Miyazawa, T. Effects of Dietary Food Components on Cognitive Functions in Older Adults. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidaček, N.Š.; Nanić, L.; Ravlić, S.; Sopta, M.; Gerić, M.; Gajski, G.; Garaj-Vrhovac, V.; Rubelj, I. Telomeres, Nutrition, and Longevity: Can We Really Navigate Our Aging? J. Gerontol.-Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, M.; Kim, C.S.; Shon, W.J.; Lee, Y.K.; Choi, E.Y.; Shin, D.M. Hydrogen-Rich Water Reduces Inflammatory Responses and Prevents Apoptosis of Peripheral Blood Cells in Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi-Fukatsu, A.; Yamanaka-Okumura, H.; Naniwa-Kuroki, Y.; Nishida, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Taketani, Y.; Takeda, E. Natto and Viscous Vegetables in a Japanese-Style Breakfast Improved Insulin Sensitivity, Lipid Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in Overweight Subjects with Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, K.; Sasaki, A.; Ebisu, K.; Tajima, K.; Kajimoto, O.; Nojima, J.; Kuratsune, H.; Hori, H.; Watanabe, Y. Hydrogen-Rich Water for Improvements of Mood, Anxiety, and Autonomic Nerve Function in Daily Life. Med. Gas Res. 2017, 7, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Hehemann, J.H.; Correc, G.; Barbeyron, T.; Helbert, W.; Czjzek, M.; Michel, G. Transfer of Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes from Marine Bacteria to Japanese Gut Microbiota. Nature 2010, 464, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y. Antioxidant Bioactivity of Molecular Hydrogen Gas Produced by Intestinal Bacteria with Undigested Carbohydrates. Acta Sci. Nutr. Health 2018, 2, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zanini, D.; Todorovic, N.; Korovljev, D.; Stajer, V.; Ostojic, J.; Purac, J.; Kojic, D.; Vukasinovic, E.; Djordjievski, S.; Sopic, M.; et al. The Effects of 6-Month Hydrogen-Rich Water Intake on Molecular and Phenotypic Biomarkers of Aging in Older Adults Aged 70 Years and over: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 155, 111574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A Core Gut Microbiome in Obese and Lean Twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani, A.B.; Nezami, B.G.; Gewirtz, A.; Srinivasan, S. Obesity and Its Associated Disease: A Role for Microbiota? Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, M.; Sobue, S.; Ito, M.; Ito, M.; Hirayama, M.; Ohno, K. Beneficial Biological Effects and the Underlying Mechanisms of Molecular Hydrogen—Comprehensive Review of 321 Original Articles. Med. Gas Res. 2015, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, T.; Hamada, N.; Terazawa, R.; Ito, M.; Ohno, K.; Ichihara, M.; Nozawa, Y.; Ito, M. Molecular Hydrogen Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide/Interferon γ-Induced Nitric Oxide Production through Modulation of Signal Transduction in Macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 411, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Zong, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yao, S.; Jiao, P.; Tian, H.; Zhai, L.; Zhao, H.; Tian, S.; et al. Molecular Hydrogen Stabilizes Atherosclerotic Plaque in Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Knockout Mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 87, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xie, K.; Chen, H.; Wang, G.; Yu, Y. Hydrogen Gas Inhibits High-Mobility Group Box 1 Release in Septic Mice by Upregulation of Heme Oxygenase 1. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 196, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohs, S.J. The Role of Free Radicals in Toxicity and Disease. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharm. 1995, 6, 205–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, T.; Wakabayashi, N.; Shigemura, N.; Huang, C.S.; Masutani, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Noda, K.; Peng, X.; Takahashi, T.; Billiar, T.R.; et al. Hydrogen Gas Reduces Hyperoxic Lung Injury via the Nrf2 Pathway in Vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2013, 304, L646–L656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Yamafuji, M.; Tachibana, T.; Nakabeppu, Y.; Noda, M.; Nakaya, H. Oral “hydrogen Water” Induces Neuroprotective Ghrelin Secretion in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbodio, J.I.; Snyder, S.H.; Paul, B.D. Redox Mechanisms in Neurodegeneration: From Disease Outcomes to Therapeutic Opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 1450–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.I.; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Hydrogen Acts as a Therapeutic Antioxidant by Selectively Reducing Cytotoxic Oxygen Radicals. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Shen, J.; Chuai, Y.; Cai, J. Hydrogen as a New Class of Radioprotective Agent. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Seike, T.; Yutsudo, N.; Ohno, M.; Yamada, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Sakumi, K.; Yamakawa, Y.; Kido, M.A.; Takaki, A.; et al. Hydrogen in Drinking Water Reduces Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss in the 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Chen, J.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M.; Jia, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, S. Protective Effect of Molecular Hydrogen Following Different Routes of Administration on D-Galactose-Induced Aging Mice. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 5541–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, B.J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. The Evolution of Molecular Hydrogen: A Noteworthy Potential Therapy with Clinical Significance. Med. Gas Res. 2013, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Yang, M.; Yang, N.N.; Yin, X.X.; Song, W.G. Molecular Hydrogen: A Preventive and Therapeutic Medical Gas for Various Diseases. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 102653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mascio, P.; Martinez, G.R.; Miyamoto, S.; Ronsein, G.E.; Medeiros, M.H.G.; Cadet, J. Singlet Molecular Oxygen Reactions with Nucleic Acids, Lipids, and Proteins. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2043–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, A.; Kohama, K.; Aoyama-Ishikawa, M.; Yamashita, H.; Fujisaki, N.; Yamada, T.; Yumoto, T.; Nosaka, N.; Naito, H.; Tsukahara, K.; et al. Intraperitoneally Administered, Hydrogen-Rich Physiologic Solution Protects against Postoperative Ileus and Is Associated with Reduced Nitric Oxide Production. Surgery 2016, 160, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, Y.; Ito, M.; Oshima, T.; Kojima, S.; Ohno, K. Hydrogen-Rich Water Ameliorates Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) in Newborn Rats. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2016, 51, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, M.; Zhang, S.; Wu, L.; Huan, L.; Huang, F.; Cui, Y.; Lin, Z. Hydrogen Gas Inhalation Attenuates Seawater Instillation-Induced Acute Lung Injury via the Nrf2 Pathway in Rabbits. Inflammation 2016, 39, 2029–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Dong, Y.; He, Q.; Zhu, P.; Zhuang, Q.; Shen, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M. Hydrogen: A Novel Option in Human Disease Treatment. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, A.; Liu, R.; Miao, Z.G.; Zhang, X.; Cao, P.F.; Chen, T.X.; Li, C.Y.; Shi, L.; Jiang, A.L.; Zhao, M.W. Hydrogen-Rich Water Regulates Effects of ROS Balance on Morphology, Growth and Secondary Metabolism via Glutathione Peroxidase in Ganoderma Lucidum. Env. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 566–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraini, J.H.; Gardette-Chauffour, M.C.; Martinez, E.; Rostain, J.C.; Lemaire, C. Psychophysiological Reactions in Humans during an Open Sea Dive to 500 m with a Hydrogen-Helium-Oxygen Mixture. J. Appl. Physiol. 1994, 76, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanari, P.; Badier, M.; Guillot, C.; Tomei, C.; Burnet, H.; Gardette, B.; Jammes, Y. Changes in Maximal Performance of Inspiratory and Skeletal Muscles during and after the 7.1-MPa Hydra 10 Record Human Dive. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 81, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, K.; Nakashima-Kamimura, N.; Mikami, T.; Ohsawa, I.; Ohta, S. Consumption of Molecular Hydrogen Prevents the Stress-Induced Impairments in Hippocampus-Dependent Learning Tasks during Chronic Physical Restraint in Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Ito, M.; Fujita, Y.; Ito, M.; Ichihara, M.; Masuda, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Maesawa, S.; Kajita, Y.; Hirayama, M.; et al. Molecular Hydrogen Is Protective against 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Nigrostriatal Degeneration in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 453, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, L.; Zhou, W.; Hu, L.; Li, L.; Tu, Q.; Chang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Sun, X.; Wu, M.; et al. The Protective Role of Hydrogen-Rich Saline in Experimental Liver Injury in Mice. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Li, D.; Hu, J.; Mei, H.; Shu, J.; Long, Z.; Yuan, L.; Li, D.; Guan, R.; Li, Y.; et al. Hydrogen Gas Inhalation Protects against Cigarette Smokeinduced COPD Development in Mice. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 3232–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.F.; Zhang, J. Saturated Hydrogen Saline Attenuates Endotoxin-Induced Acute Liver Dysfunction in Rats. Physiol. Res. 2013, 62, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, B.; Hanna, S.; Abdallahi, O.M.S.; Lepidi, H.; Gardette, B.; De Reggi, M. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Molecular Hydrogen: Investigation on Parasite-Induced Liver Inflammation. Comptes Rendus L’academie Sci.-Ser. III-Sci. Vie 2001, 324, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, Y.P.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.W.; Xiang, H.G.; Fan, L.Y.; Sun, Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Cai, J.M.; Ruan, C.P.; et al. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Ameliorates the Severity of l-Arginine-Induced Acute Pancreatitis in Rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 393, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, A.; Wu, H.; Hong, Y.; Tu, S.; Sun, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, J. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuated Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Early Brain Injury in Rats by Suppressing Inflammatory Response: Possible Involvement of NF-ΚB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 3462–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.C.; Xie, F.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhu, Y.L.; Chen, K.; Tan, H.M.; Hu, B.S.; Yang, J.M.; Tan, J.W. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuates Postoperative Liver Failure after Major Hepatectomy in Rats. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2014, 38, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Yu, S.; Qin, M.; Mao, Y.; Jin, L.; Che, N.; Liu, S.; Ge, R. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Ameliorates Allergic Rhinitis by Reversing the Imbalance of Th1/Th2 and Up-Regulation of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+Regulatory T Cells, Interleukin-10, and Membrane-Bound Transforming Growth Factor-β in Guinea Pigs. Inflammation 2018, 41, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yin, H.; Duan, Y.; Lai, P.; Cai, Y.; Wei, Y. Pre-Inhalation of Hydrogen-Rich Gases Protect against Caerulein-Induced Mouse Acute Pancreatitis While Enhance the Pancreatic Hsp60 Protein Expression. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, K.; Sun, Q.; Liu, W.; Xu, W.; Denoble, P.; Sun, X. Consumption of Hydrogen Water Reduces Paraquat-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, M.; Ito, M.; Minato, T.; Yoritaka, A.; Lebaron, T.; Ohno, K. Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas Elevates Urinary 8-Hydroxy-2′-Deoxyguanine in Parkinson’s Disease. Med. Gas Res. 2018, 8, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, K.; Hua, X.; Fang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Dai, W.; Cui, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Effect of Shikonin on Spinal Cord Injury in Rats Via Regulation of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, E.W.; Fridovich, I. Liposome Oxidation and Erythrocyte Lysis by Enzymically Generated Superoxide and Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 6721–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stibich, M. The Wear and Tear Theory of Aging; Verywell Health: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- HARMAN, D. Aging: A Theory Based on Free Radical and Radiation Chemistry. J. Gerontol. 1956, 11, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, R.S.; Weindruch, R. Oxidative Stress, Caloric Restriction, and Aging. Science 1996, 273, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtman, E.R. Protein Oxidation and Aging. Free Radic. Res. 2006, 40, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkwood, T.B.L.; Kowald, A. The Free-Radical Theory of Ageing—Older, Wiser and Still Alive: Modelling Positional Effects of the Primary Targets of ROS Reveals New Support. BioEssays 2012, 34, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iuchi, K.; Nishimaki, K.; Kamimura, N.; Ohta, S. Molecular Hydrogen Suppresses Free-Radical-Induced Cell Death by Mitigating Fatty Acid Peroxidation and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Can. J. Physiol. Pharm. 2019, 97, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, T. Therapeutic Efficacy of Molecular Hydrogen: A New Mechanistic Insight. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.L.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Liew, W.P.P.; Rahman, H.S. Antioxidant and Oxidative Stress: A Mutual Interplay in Age-Related Diseases. Front. Pharm. 2018, 9, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, P.; Jaquet, V.; Marcucci, F.; Schmidt, H.H.H.W. The Oxidative Stress Theory of Disease: Levels of Evidence and Epistemological Aspects. Br. J. Pharm. 2017, 174, 1784–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.S.; Kabir, M.T.; Rahman, M.H.; Alim, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Khatkar, A.; Al Mamun, A.; Rauf, A.; Mathew, B.; Ashraf, G.Md. Exploring the Multifunctional Neuroprotective Promise of Rasagiline Derivatives for Multi-Dysfunctional Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 4690–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Bajgai, J.; Fadriquela, A.; Sharma, S.; Thi, T.T.; Akter, R.; Goh, S.H.; Kim, C.S.; Lee, K.J. Redox Effects of Molecular Hydrogen and Its Therapeutic Efficacy in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Processes 2021, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Ibi, T.; Sahashi, K.; Ichihara, M.; Ito, M.; Ohno, K. Open-Label Trial and Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial of Hydrogen-Enriched Water for Mitochondrial and Inflammatory Myopathies. Med. Gas Res. 2011, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Nakano, H.; Hamada, H.; Itami, N.; Nakazawa, R.; Ito, S. A Novel Bioactive Haemodialysis System Using Dissolved Dihydrogen (H2) Produced by Water Electrolysis: A Clinical Trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 3026–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.D.; Sá, R.; Monteiro, M.P.; Barros, A.; Sousa, M.; Carvalho, R.A.; Silva, B.M.; Oliveira, P.F.; Alves, M.G. Ghrelin Acts as Energy Status Sensor of Male Reproduction by Modulating Sertoli Cells Glycolytic Metabolism and Mitochondrial Bioenergetics. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 434, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, G.L. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Chronic Disease: Treatment with Natural Supplements. Integr. Med. (Boulder) 2014, 13, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, H.Y.; Cesari, M.; Anton, S.; Marzetti, E.; Giovannini, S.; Seo, A.Y.; Carter, C.; Yu, B.P.; Leeuwenburgh, C. Molecular Inflammation: Underpinnings of Aging and Age-Related Diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2009, 8, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennicke, C.; Rahn, J.; Lichtenfels, R.; Wessjohann, L.A.; Seliger, B. Hydrogen Peroxide—Production, Fate and Role in Redox Signaling of Tumor Cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2015, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailloux, R.J. Mitochondrial Antioxidants and the Maintenance of Cellular Hydrogen Peroxide Levels. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, J.; Soehnlein, O. Atherosclerosis—A Matter of Unresolved Inflammation. Semin. Immunol. 2015, 27, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.L.; Lindner, A.B. Protein Posttranslational Modifications: Roles in Aging and Age-Related Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, J.A.; Vieira, V.J.; Keylock, K.T. Exercise, Inflammation, and Innate Immunity. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2009, 29, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.A.; Miljkovic, M.D.; Conlon, K.C. Interleukin-15 (Dys)Regulation of Lymphoid Homeostasis: Implications for Therapy of Autoimmunity and Cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.Y.P.; Lu, X.J.D.; Zhu, Y.S.; Le, N.; Kim, H.; Poh, C.F. Plasma-Derived Inflammatory Proteins Predict Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, G.C.; Accardi, G.; Monastero, R.; Nicoletti, F.; Libra, M. Ageing: From Inflammation to Cancer. Immun. Ageing 2018, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liao, R.; Sheng, X.; Luo, X.; Zhang, X.; Wen, X.; Zhou, J.; Peng, K. Hydrogen Gas in Cancer Treatment. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardill, H.R.; Mander, K.A.; Van Sebille, Y.Z.A.; Gibson, R.J.; Logan, R.M.; Bowen, J.M.; Sonis, S.T. Cytokine-Mediated Blood Brain Barrier Disruption as a Conduit for Cancer/Chemotherapy-Associated Neurotoxicity and Cognitive Dysfunction. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 2635–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaria, M.; O’Leary, M.N.; Chang, J.; Shao, L.; Liu, S.; Alimirah, F.; Koenig, K.; Le, C.; Mitin, N.; Deal, A.M.; et al. Cellular Senescence Promotes Adverse Effects of Chemotherapy and Cancer Relapse. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padoan, A.; Plebani, M.; Basso, D. Inflammation and Pancreatic Cancer: Focus on Metabolism, Cytokines, and Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.H.; Shen, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.W.; Liang, H.; Zhang, X.T.; Tang, L.; Xin, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.J.; et al. The Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO): Clinical Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastric Cancer. Cancer Commun. 2019, 39, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, C.; Karachaliou, N.; Bulotta, A.; Viganó, M.; Mirabile, A.; Brioschi, E.; Santarpia, M.; Gianni, L.; Rosell, R.; Gregorc, V. Combination of Immunotherapy with Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy in Lung Cancer: Is This the Beginning of the End for Cancer? Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susanne, K.; Michael, F.; Thomas, S.; Peter, E.; Andreas, H. Predictors of Fatigue in Cancer Patients: A Longitudinal Study. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 3463–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghdoust, A.; Mofid, B.; Peyghambarlou, P. Predictors of Chemotherapy-Induced Severe Anemia in Cancer Patients Receiving Chemotherapy. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Wang, J.Q.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Ren, L.; Gupta, P.; Wei, L.; Ashby, C.R.; Yang, D.H.; Chen, Z.S. Modulating ROS to Overcome Multidrug Resistance in Cancer. Drug Resist. Updat. 2018, 41, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.-Y.; Chen, C.; Xu, Y.-F.; Shen, J.-J.; Guo, H.-M.; Li, H.-F.; Li, X.-N.; Kang, D.; Shao, Y.-H.; Zhu, Z.-P.; et al. Is the Combinational Administration of Doxorubicin and Glutathione a Reasonable Proposal? Acta Pharm. Sin 2019, 40, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wen, G.; Yang, L.; Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Ma, F.; Xiao, L.; et al. Dual-Targeted and PH-Sensitive Doxorubicin Prodrug-Microbubble Complex with Ultrasound for Tumor Treatment. Theranostics 2017, 7, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Matsushita, T.; Fujinawa, H.; Murase, K. Experimental Verification of Protective Effect of Hydrogen-Rich Water against Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced CT. Br. J. Radiol. 2010, 83, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Kusakabe, Y.; Kitamura, A.; Okada, S.; Murase, K. Investigation of Protective Effect of Hydrogen-Rich Water against Cisplatininduced Nephrotoxicity in Rats Using Blood Oxygenation Level-Dependent Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2011, 29, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, G.; Yu, Y.; Xie, K. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuates Chemotherapy-Induced Ovarian Injury via Regulation of Oxidative Stress. Exp. Med. 2015, 10, 2277–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.M.; Kang, Y.N.; Choi, I.B.; Gu, Y.; Kawamura, T.; Toyoda, Y.; Nakao, A. Effects of Drinking Hydrogen-Rich Water on the Quality of Life of Patients Treated with Radiotherapy for Liver Tumors. Med. Gas Res. 2011, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, H.; Fan, Y.; Li, L.; Fang, J.; Yang, W. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuates Cardiac and Hepatic Injury in Doxorubicin Rat Model by Inhibiting Inflammation and Apoptosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Jin, Z.; Chen, Q.; Yang, T.; Chen, D.; Meng, J.; Lu, X.; Gu, Z.; He, Q. Local Generation of Hydrogen for Enhanced Photothermal Therapy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Xie, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.T.; Ma, S.N.; Zhao, P.X.; Zhang, X.; Lebaron, T.W.; Yan, X.L.; Ma, X.M. Molecular Hydrogen Suppresses Glioblastoma Growth via Inducing the Glioma Stem-like Cell Differentiation. Stem. Cell Res. 2019, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima-Kamimura, N.; Mori, T.; Ohsawa, I.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Molecular Hydrogen Alleviates Nephrotoxicity Induced by an Anti-Cancer Drug Cisplatin without Compromising Anti-Tumor Activity in Mice. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2009, 64, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Xie, F.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhao, P.; Ma, X.; Lebaron, T.W. Therapeutic Potential of Molecular Hydrogen in Ovarian Cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ji, G.; Pan, R.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, P. Protective Effect of Hydrogen-Rich Water on Liver Function of Colorectal Cancer Patients Treated with MFOLFOX6 Chemotherapy. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 7, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Lin, B.; Wang, P.; Pan, T.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Cheng, S.; Liu, S. The Healing Effect of Hydrogen-Rich Water on Acute Radiation-Induced Skin Injury in Rats. J. Radiat. Res. 2019, 60, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Tonaki, K.; Terasaki, M.; Kuwahara, N.; Ohsiro, J.; Iketani, M.; Takahashi, M.; Hamanoue, M.; Kajimoto, Y.; et al. Molecular Hydrogen Attenuates Gefitinib-Induced Exacerbation of Naphthalene-Evoked Acute Lung Injury through a Reduction in Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Lab. Investig. 2019, 99, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, D.; Takaki, A.; Nakatsuka, A.; Wada, J.; Tamaki, N.; Yasunaka, T.; Koike, K.; Tsuzaki, R.; Matsumoto, K.; Miyake, Y.; et al. Hydrogen-Rich Water Prevents Progression of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Accompanying Hepatocarcinogenesis in Mice. Hepatology 2012, 56, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provasi, S.; Cattaneo, A.; Cattane, N.; Galluzzi, S.; Lopizzo, N.; Plazzotta, G.; Boccardi, M.; Frisoni, G. Association of Brain Amyloidosis with Pro-Inflammatory Gut Bacterial Strains and Peripheral Inflammation Markers in Cognitively Impaired Elderly. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 26, S649–S650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simrén, M.; Öhman, L.; Olsson, J.; Svensson, U.; Ohlson, K.; Posserud, I.; Strid, H. Clinical Trial: The Effects of a Fermented Milk Containing Three Probiotic Bacteria in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome—A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Study. Aliment. Pharm. 2010, 31, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, W.; Pimentel, M. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth and Irritable Bowel Syndrome—An Update. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marthinsen, D.; Fleming, S.E. Excretion of Breath and Flatus Gases by Humans Consuming High-Fiber Diets. J. Nutr. 1982, 112, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebaron, T.W.; Singh, R.B.; Fatima, G.; Kartikey, K.; Sharma, J.P.; Ostojic, S.M.; Gvozdjakova, A.; Kura, B.; Noda, M.; Mojto, V.; et al. The Effects of 24-Week, High-Concentration Hydrogen-Rich Water on Body Composition, Blood Lipid Profiles and Inflammation Biomarkers in Men and Women with Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinane, C.M.; Cotter, P.D. Role of the Gut Microbiota in Health and Chronic Gastrointestinal Disease: Understanding a Hidden Metabolic Organ. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.W.; Li, Y.; Luo, D.; Dong, J.L.; Zhou, L.X.; Zhao, S.Y.; Zheng, Q.S.; Wang, H.C.; Cui, M.; Fan, S.J. Hydrogen-Water Ameliorates Radiation-Induced Gastrointestinal Toxicity via Myd88′s Effects on the Gut Microbiota. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, e433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, W. Intestinal Microbiota Ecological Response to Oral Administrations of Hydrogen-Rich Water and Lactulose in Female Piglets Fed a Fusarium Toxin-Contaminated Diet. Toxins 2018, 10, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, J.-B.; Zhang, S.S.; Lu, Y.M.; Gong, W.J.; Jiang, X.P.; Wang, J.J.; Qiao, T.L.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhao, M.Q.; Wang, D.P.; et al. Effects of the Long-Term Consumption of Hydrogen-Rich Water on the Antioxidant Activity and the Gut Flora in Female Juvenile Soccer Players from Suzhou, China. Med. Gas Res. 2018, 8, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.Y.; Bi, J.B.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, S.M.; Gu, J.X.; Qu, K.; Liu, C. Hydrogen-Rich Water Protects against Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Mice by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Promoting Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, W.; Yao, W. Morphological and Molecular Response of Small Intestine to Lactulose and Hydrogen-Rich Water in Female Piglets Fed Fusarium Mycotoxins Contaminated Diet. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamimura, N.; Nishimaki, K.; Ohsawa, I.; Ohta, S. Molecular Hydrogen Improves Obesity and Diabetes by Inducing Hepatic FGF21 and Stimulating Energy Metabolism in Db/Db Mice. Obesity 2011, 19, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Kiuchi, M.; Higashimura, Y.; Naito, Y.; Koyama, K. The Effects of Ingestion of Hydrogen-Dissolved Alkaline Electrolyzed Water on Stool Consistency and Gut Microbiota: A Double-Blind Randomized Trial. Med. Gas Res. 2021, 11, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yang, T.; Tan, L.; Lv, P.; Xu, Q.; Tao, G.; Qin, S.; Lu, X.; He, Q. Nanocapsule-Mediated Sustained H2 Release in the Gut Ameliorates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 121030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Ye, Q.; Sun, M.; Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Wu, G. Saturated Hydrogen Improves Lipid Metabolism Disorders and Dysbacteriosis Induced by a High-Fat Diet. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenpreis, E.D.; Swamy, R.S.; Zaitman, D.; Noth, I. Short Duration Exercise Increases Breath Hydrogen Excretion after Lactulose Ingestion: Description of a New Phenomenon. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 2798–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaskell, S.K.; Taylor, B.; Muir, J.; Costa, R.J.S. Impact of 24-h High and Low Fermentable Oligo-, Di-, Monosaccharide, and Polyol Diets on Markers of Exercise-Induced Gastrointestinal Syndrome in Response to Exertional Heat Stress. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 45, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Ye, F.; Rong, W.; Song, Y.; Wu, F.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Siqin, T.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L.; et al. Nomogram to Assist in Surgical Plan for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Prediction Model for Microvascular Invasion. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2019, 23, 2372–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsanathan, R.; Jain, S.K. Hydrogen Sulfide Regulates Circadian-Clock Genes in C2C12 Myotubes and the Muscle of High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mice. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 672, 108054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.M.; Abano, J.B.; Egan, T.M. Nitric Oxide Ventilation of Rat Lungs from Non-Heart-Beating Donors Improves Posttransplant Function. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 2707–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, K.S.; Yoshida, J.; Ueki, S.; Pettigrew, G.L.; Ghonem, N.; Sico, R.M.; Lee, L.Y.; Shapiro, R.; Lakkis, F.G.; Pacheco-Silva, A.; et al. Carbon Monoxide Inhibits Apoptosis during Cold Storage and Protects Kidney Grafts Donated after Cardiac Death. Transpl. Int. 2012, 25, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBaron, T.W.; Kura, B.; Kalocayova, B.; Tribulova, N.; Slezak, J. A New Approach for the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disorders. Molecular Hydrogen Significantly Reduces the Effects of Oxidative Stress. Molecules 2019, 24, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, I.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Ishikawa, M.; Ohta, S. Consumption of Hydrogen Water Prevents Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E Knockout Mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 377, 1195–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Xue, M.; Ji, A.; Li, Y. Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, A.; Nosaka, N.; Yumoto, T.; Knaup, E.; Naito, H.; Nishiyama, C.; Yamakawa, Y.; Tsukahara, K.; Terado, M.; Sato, K.; et al. The Clinical Application of Hydrogen as a Medical Treatment. Acta Med. Okayama 2016, 70, 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Amilan Jose, D.; Sharma, N.; Sakla, R.; Kaushik, R.; Gadiyaram, S. Fluorescent Nanoprobes for the Sensing of Gasotransmitters Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S), Nitric Oxide (NO) and Carbon Monoxide (CO). Methods 2019, 168, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Cao, F.; Cui, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chuai, Y.; Zaho, L.; Jiang, H.; Cai, J. The Potential Cardioprotective Effects of Hydrogenin Irradiated Mice. J. Radiat. Res. 2010, 51, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashida, K.; Sano, M.; Kamimura, N.; Yokota, T.; Suzuki, M.; Ohta, S.; Fukuda, K.; Hori, S. Hydrogen Inhalation during Normoxic Resuscitation Improves Neurological Outcome in a Rat Model of Cardiac Arrest Independently of Targeted Temperature Management. Circulation 2014, 130, 2173–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, A.; Toyoda, Y.; Sharma, P.; Evans, M.; Guthrie, N. Effectiveness of Hydrogen Rich Water on Antioxidant Status of Subjects with Potential Metabolic Syndrome—An Open Label Pilot Study. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 46, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, S. Molecular Hydrogen as a Preventive and Therapeutic Medical Gas: Initiation, Development and Potential of Hydrogen Medicine. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, T. Hydrogen Therapy in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases: From Bench to Bedside. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Li, M.; Sang, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Yao, S.; Yu, Y.; Zong, C.; Xue, Y.; Qin, S. Hydrogen -Rich Water Decreases Serum LDL-Cholesterol Levels and Improves HDL Function in Patients with Potential Metabolic Syndrome. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1884–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H. Application of Hydrogen in Ophthalmology. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 27, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Sano, M.; Hayashida, K.; Ohsawa, I.; Ohta, S.; Fukuda, K. Are the Effects of α-Glucosidase Inhibitors on Cardiovascular Events Related to Elevated Levels of Hydrogen Gas in the Gastrointestinal Tract? FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 2157–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Sato, B.; Hara, K.; Hara, Y.; Naritomi, Y.; Koyanagi, S.; Hara, H.; Nagao, T.; Ishibashi, T. Consumption of Water Containing over 3.5 Mg of Dissolved Hydrogen Could Improve Vascular Endothelial Function. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2014, 10, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojic, S.M.; Stojanovic, M.D. Hydrogen-Rich Water Affected Blood Alkalinity in Physically Active Men. Res. Sports Med. 2014, 22, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajiyama, S.; Hasegawa, G.; Asano, M.; Hosoda, H.; Fukui, M.; Nakamura, N.; Kitawaki, J.; Imai, S.; Nakano, K.; Ohta, M.; et al. Supplementation of Hydrogen-Rich Water Improves Lipid and Glucose Metabolism in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes or Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoritaka, A.; Takanashi, M.; Hirayama, M.; Nakahara, T.; Ohta, S.; Hattori, N. Pilot Study of H2 Therapy in Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Liu, W.; Zeng, D.; Zhu, L.; Sun, X.; Sun, X. Effect of Hydrogen-Rich Water on Oxidative Stress, Liver Function, and Viral Load in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2013, 6, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, T.; Sato, B.; Rikitake, M.; Seo, T.; Kurokawa, R.; Hara, Y.; Naritomi, Y.; Hara, H.; Nagao, T. Consumption of Water Containing a High Concentration of Molecular Hydrogen Reduces Oxidative Stress and Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Open-Label Pilot Study. Med. Gas Res. 2012, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Nakao, A.; Adachi, T.; Matsui, Y.; Miyakawa, S. Pilot Study: Effects of Drinking Hydrogen-Rich Water on Muscle Fatigue Caused by Acute Exercise in Elite Athletes. Med. Gas Res. 2012, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatani, K.; Nawashiro, H.; Takeuchi, S.; Tomura, S.; Otani, N.; Osada, H.; Wada, K.; Katoh, H.; Tsuzuki, N.; Mori, K. Safety of Intravenous Administration of Hydrogen-Enriched Fluid in Patients with Acute Cerebral Ischemia: Initial Clinical Studies. Med. Gas Res. 2013, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kato, S.; Matsuoka, D.; Tanaka, H.; Miwa, N. Hydrogen Water Intake via Tube-Feeding for Patients with Pressure Ulcer and Its Reconstructive Effects on Normal Human Skin Cells in Vitro. Med. Gas Res. 2013, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojic, S.M.; Vukomanovic, B.; Calleja-Gonzalez, J.; Hoffman, J.R. Effectiveness of Oral and Topical Hydrogen for Sports-Related Soft Tissue Injuries. Postgrad. Med. 2014, 126, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, T.R.; Debelius, J.W.; Thron, T.; Janssen, S.; Shastri, G.G.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Challis, C.; Schretter, C.E.; Rocha, S.; Gradinaru, V.; et al. Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor Deficits and Neuroinflammation in a Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Cell 2016, 167, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Hirayama, M.; Yamai, K.; Goto, S.; Ito, M.; Ichihara, M.; Ohno, K. Drinking Hydrogen Water and Intermittent Hydrogen Gas Exposure, but Not Lactulose or Continuous Hydrogen Gas Exposure, Prevent 6-Hydorxydopamine-Induced Parkinson’s Disease in Rats. Med. Gas Res. 2012, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohi, K.; Satoh, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Momma, S.; Fukuda, K.; Higuchi, R.; Ohtaki, H.; Banks, W.A. Molecular Hydrogen in the Treatment of Acute and Chronic Neurological Conditions: Mechanisms of Protection and Routes of Administration. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2017, 61, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoritaka, A.; Abe, T.; Ohtsuka, C.; Maeda, T.; Hirayama, M.; Watanabe, H.; Saiki, H.; Oyama, G.; Fukae, J.; Shimo, Y.; et al. A Randomized Double-Blind Multi-Center Trial of Hydrogen Water for Parkinson’s Disease: Protocol and Baseline Characteristics. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Shannon, K.M.; Kordower, J.H.; Voigt, R.M.; Shaikh, M.; Jaglin, J.A.; Estes, J.D.; Dodiya, H.B.; Keshavarzian, A. Increased Intestinal Permeability Correlates with Sigmoid Mucosa Alpha-Synuclein Staining and Endotoxin Exposure Markers in Early Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Ito, M.; Hamaguchi, T.; Mori, H.; Takeda, Y.; Baba, R.; Watanabe, T.; Kurokawa, K.; Asakawa, S.; Hirayama, M.; et al. Quantification of Hydrogen Production by Intestinal Bacteria That Are Specifically Dysregulated in Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheperjans, F.; Aho, V.; Pereira, P.A.B.; Koskinen, K.; Paulin, L.; Pekkonen, E.; Haapaniemi, E.; Kaakkola, S.; Eerola-Rautio, J.; Pohja, M.; et al. Gut Microbiota Are Related to Parkinson’s Disease and Clinical Phenotype. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, J.L.; Sonnenburg, E.D. Vulnerability of the Industrialized Microbiota. Science 2019, 366, eaaw9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illiano, P.; Brambilla, R.; Parolini, C. The Mutual Interplay of Gut Microbiota, Diet and Human Disease. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 833–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.; Mulak, A. Brain-Gut-Microbiota Axis in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Paula, V.d.J.R.; Forlenza, A.S.; Forlenza, O.V. Relevance of Gutmicrobiota in Cognition, Behaviour and Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharm. Res 2018, 136, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.T.; Rahman, M.H.; Shah, M.; Jamiruddin, M.R.; Basak, D.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Bhatia, S.; Ashraf, G.M.; Najda, A.; El-kott, A.F.; et al. Therapeutic Promise of Carotenoids as Antioxidants and Anti-Inflammatory Agents in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, A.; Chahal, R.; Rao, R.; Rahman, M.H.; Kaushik, D.; Akhtar, M.F.; Saleem, A.; Khalifa, S.M.A.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Kamel, M.; et al. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Potential of Various Sesquiterpene Analogues for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fujino, M.; Ichimaru, N.; Kurokawa, R.; Hirano, S.; Mou, L.; Takahara, S.; Takahara, T.; Li, X.K. Molecular Hydrogen Protects against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in a Mouse Fatty Liver Model via Regulating HO-1 and Sirt1 Expression. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut Microbiota in Human Metabolic Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostojic, S.M. Hydrogen-Rich Water as a Modulator of Gut Microbiota? J. Funct. Foods 2021, 78, 104360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, J.Y.; Meng, X.L.; Yang, D.; Fan, L.H.; Xiang, L.; Wang, P. Traditional Chinese Medicine: Role in Reducing β-Amyloid, Apoptosis, Autophagy, Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Dysfunction of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharm. 2020, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.T. Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction-Linked Neurodegenerative Disorders. Neurol. Res. 2017, 39, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriakose, M.; Younger, D.; Ravula, A.R.; Alay, E.; Rama Rao, K.V.; Chandra, N. Synergistic Role of Oxidative Stress and Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability as Injury Mechanisms in the Acute Pathophysiology of Blast-Induced Neurotrauma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Kishimoto, Y.; Grammatikakis, I.; Gottimukkala, K.; Cutler, R.G.; Zhang, S.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Bohr, V.A.; Misra Sen, J.; Gorospe, M.; et al. Senolytic Therapy Alleviates Aβ-Associated Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cell Senescence and Cognitive Deficits in an Alzheimer’s Disease Model. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, M.A.; Dohi, K.; Banks, W.A. Neuroinflammation: A Common Pathway in CNS Diseases as Mediated at the Blood-Brain Barrier. Neuroimmunomodulation 2012, 19, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Yang, R.; Zhang, J.H.; Cao, Y.P.; Sun, X.J. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Reduces Oxidative Stress and Inflammation by Inhibit of JNK and NF-ΚB Activation in a Rat Model of Amyloid-Beta-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 491, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.H.; Cai, J.M.; Cao, Y.P.; Sun, X.J. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Improves Memory Function in a Rat Model of Amyloid-Beta-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease by Reduction of Oxidative Stress. Brain Res. 2010, 1328, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Huang, C.S.; Inoue, T.; Yamashita, T.; Ishida, T.; Kang, K.M.; Nakao, A. Drinking Hydrogen Water Ameliorated Cognitive Impairment in Senescence-Accelerated Mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 46, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimaki, K.; Asada, T.; Ohsawa, I.; Nakajima, E.; Ikejima, C.; Yokota, T.; Kamimura, N.; Ohta, S. Effects of Molecular Hydrogen Assessed by an Animal Model and a Randomized Clinical Study on Mild Cognitive Impairment. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Recent Progress toward Hydrogen Medicine: Potential of Molecular Hydrogen for Preventive and Therapeutic Applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Molecular Hydrogen Is a Novel Antioxidant to Efficiently Reduce Oxidative Stress with Potential for the Improvement of Mitochondrial Diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashida, K.; Sano, M.; Ohsawa, I.; Shinmura, K.; Tamaki, K.; Kimura, K.; Endo, J.; Katayama, T.; Kawamura, A.; Kohsaka, S.; et al. Inhalation of Hydrogen Gas Reduces Infarct Size in the Rat Model of Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 373, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirone, L.; Forte, M.; Palmerio, S.; Yee, D.; Nocella, C.; Angelini, F.; Pagano, F.; Schiavon, S.; Bordin, A.; Carrizzo, A.; et al. A Review of the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Development and Progression of Cardiac Remodeling. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 3920195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.-J.; Li, H. Targeting Interferon Regulatory Factor for Cardiometabolic Diseases: Opportunities and Challenges. Curr. Drug Targets 2017, 18, 1754–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; He, B.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Hydrogen-Rich Saline in a Rat Model of Regional Myocardial Ischemia and Reperfusion. Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 148, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Long, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Sun, P.; Li, P.; Wang, T. Hydrogen (H2) Inhibits Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy via Antioxidative Pathways. Front. Pharm. 2016, 7, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Long, Z.; Xu, J.; Tan, S.; Zhang, N.; Li, A.; Wang, L.; Wang, T. Hydrogen Inhibits Isoproterenol-Induced Autophagy in Cardiomyocytes in Vitro and in Vivo. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 8253–8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.S.; Zheng, H. Chronic Hydrogen-Rich Saline Treatment Reduces Oxidative Stress and Attenuates Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Spontaneous Hypertensive Rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 365, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Route of Administration Category | Application Purpose | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2-rich saline | Cisplatin-induced damage to ovarian cortex | Stimulation of Nrf2 pathway | [86] |
| Improvement of cardiac dysfunction caused by Doxorubicin | Inhibition of ROS, Inflammatory cytokines and apoptosis | [88] | |
| H2 Pd nanocrystals | synergistic impact with thermal therapy | Provocation of ROS | [89] |
| H2 inhalation | Development of inhibition and improvement of survival rate in glioblastoma | Inhibition of cancer stem cell properties | [90] |
| Reversal of renal toxicity due to cisplatin | Inhibition of apoptosis and ROS | [91] | |
| suppression of tumor growth | Arrest and induction of apoptosis | [92] | |
| H2-rich water | Improvement of mFOLFOX6 regimen-induced liver toxicity | Inhibition of oxidative stress | [93] |
| 44Gy electronic beam reversal of skin damage created | Inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress reduction | [94] | |
| inhibition of cancer stem cells | Inhibition of angiogenesis | [92] | |
| Prevention of gefitinib-induced lung injury | Cytokines inflammatory and oxidative stress reduction | [95] | |
| Prevention of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity | Elimination of oxygen radicals | [73] | |
| Reversal of mortality and body-weight loss caused by cisplatin | Inhibition of ROS | [73] | |
| Incidence of tumors and suppression of growth | Inhibition of inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress, Induction of apoptosis | [96] | |
| Improved quality of life | Action of antioxidants | [73] |
| Authors | Category of Disease | Sample Size | Route of Administration | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sakai et al. | Vascular feature of the endothelium | 34 | Water | Vasomotor activity | [131] |
| Ostojic et al. | Metabolic acidosis caused by exercise | 52 | Water | Increased alkalinity of blood in men who are physically active | [132] |
| Kajiyama et al. | Type II diabetes mellitus | 30 | Water | Improvement in LDL-cholesterol fractions and glucose tolerance test | [133] |
| Nakao et al. | Metabolic Syndrome | 20 | Water | Enhancement of oxidative stress urinary markers | [125] |
| Yoritaka et al. | PD | 17 | Water | Improvement of Total Unified PD | [134] |
| Nakayama et al. | Chronic renal insufficiency | 29 | Dialysis | Improved markers for inflammation and oxidative stress | [61] |
| Kang et al. | Adverse effects of radiation-induced liver tumors | 49 | Water | Improved quality of life ratings during radiotherapy | [87] |
| Xia et al. | Chronic hepatitis B | 60 | Water | Reduced oxidative stress | [135] |
| Ishibashi et al. | Rheumatoid arthritis | 20 | Water | Improved rheumatoid arthritis activity score | [136] |
| Aoki et al. | Fatigue in the muscles | 10 | Water | Improvement in muscle tiredness among young athletes | [137] |
| Nagatani et al. | Ischemia of the cerebrum | 38 | Intravenous infusion | Decrease in a subset of patients of MDA-LDL, an oxidative stress serum marker | [138] |
| Li et al. | Skin pressure ulcer | 22 | Water | Reduction in wound size and early recovery from skin pressure ulcers | [139] |
| Ostojic et al. | Soft tissue damage linked to sports | 36 | H2-rich tablets and topical H2 packs | Decrease in the viscosity of plasma | [140] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, M.H.; Jeong, E.-S.; You, H.S.; Kim, C.-S.; Lee, K.-J. Redox-Mechanisms of Molecular Hydrogen Promote Healthful Longevity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12050988
Rahman MH, Jeong E-S, You HS, Kim C-S, Lee K-J. Redox-Mechanisms of Molecular Hydrogen Promote Healthful Longevity. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(5):988. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12050988
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Md. Habibur, Eun-Sook Jeong, Hae Sun You, Cheol-Su Kim, and Kyu-Jae Lee. 2023. "Redox-Mechanisms of Molecular Hydrogen Promote Healthful Longevity" Antioxidants 12, no. 5: 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12050988
APA StyleRahman, M. H., Jeong, E.-S., You, H. S., Kim, C.-S., & Lee, K.-J. (2023). Redox-Mechanisms of Molecular Hydrogen Promote Healthful Longevity. Antioxidants, 12(5), 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12050988