Differential Cell Death Pathways Induced by Oxidative Stress in Multi-Organs of Amur Grayling (Thymallus grubii) Under Gradient Ammonia Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Acute Toxicity Test (96 h Lethal Concentration of 50%, LC50)
2.3. Ammonia Exposure Experiment and Sample Collection
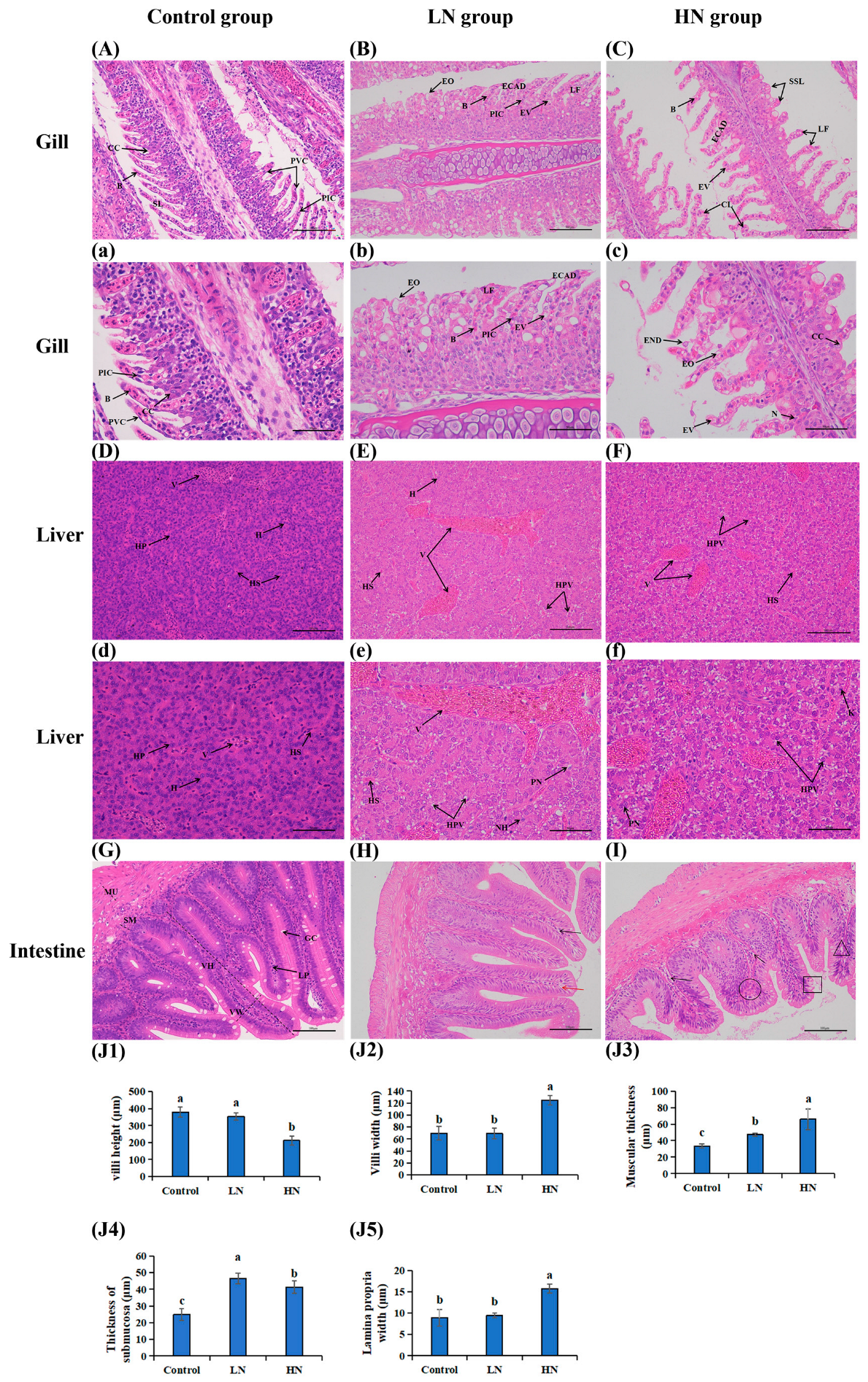
2.4. Histopathological Observation of the Liver, Gill and Intestine
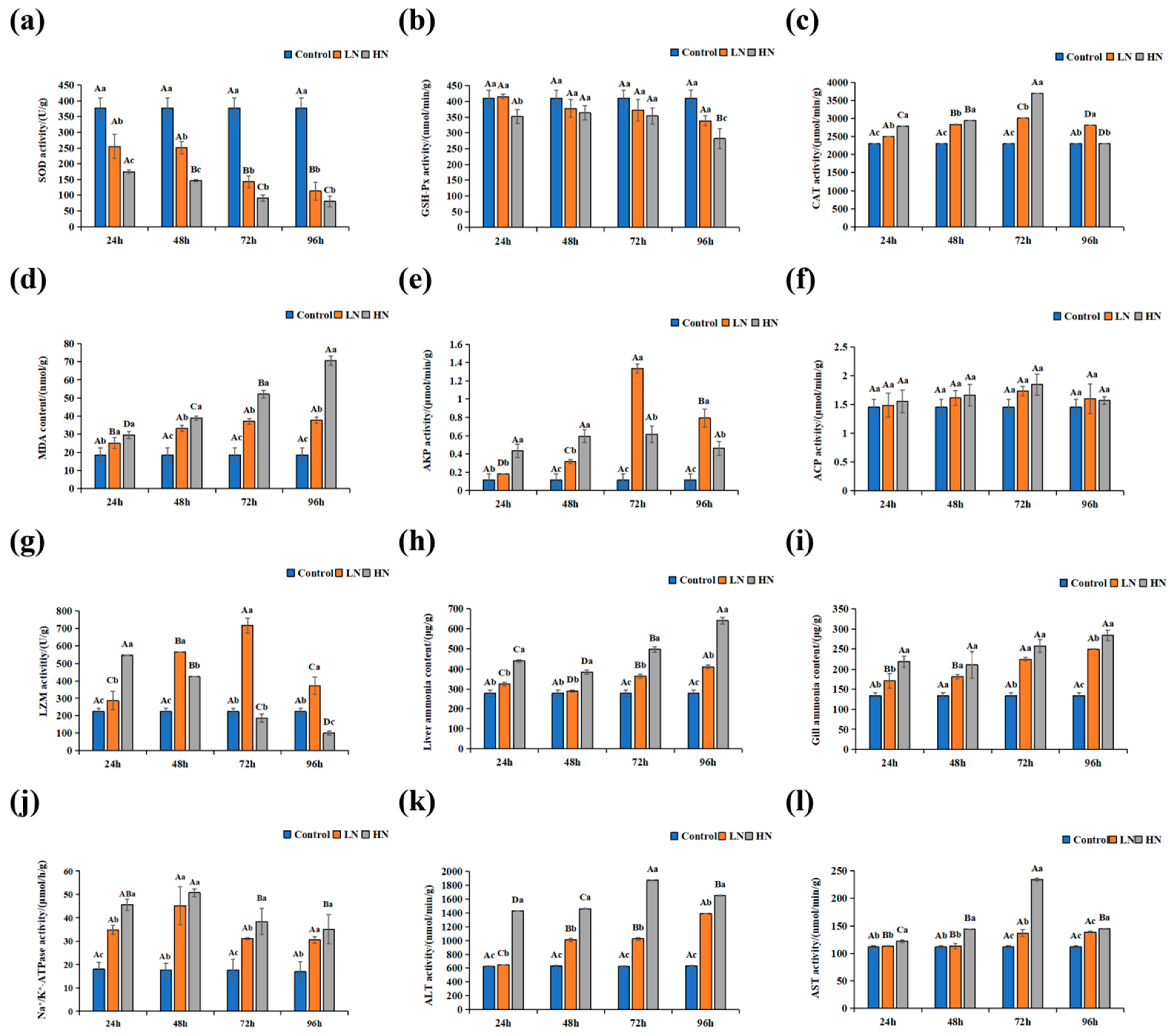
2.5. Biochemical Analysis Measurement
2.6. cDNA Library Construction and Transcriptome Sequencing
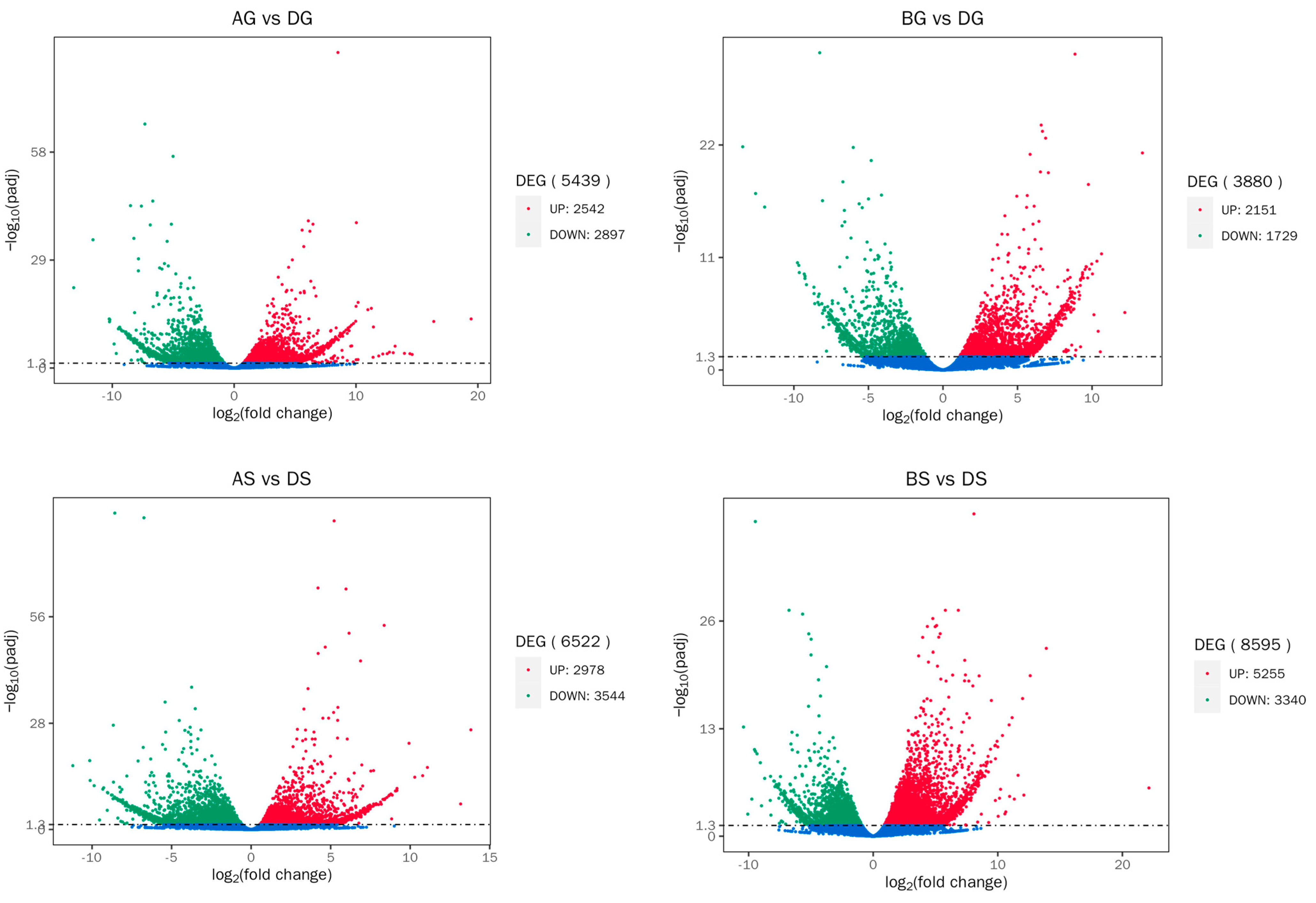
2.7. Quantification and Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) Analysis
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Verification
2.9. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis
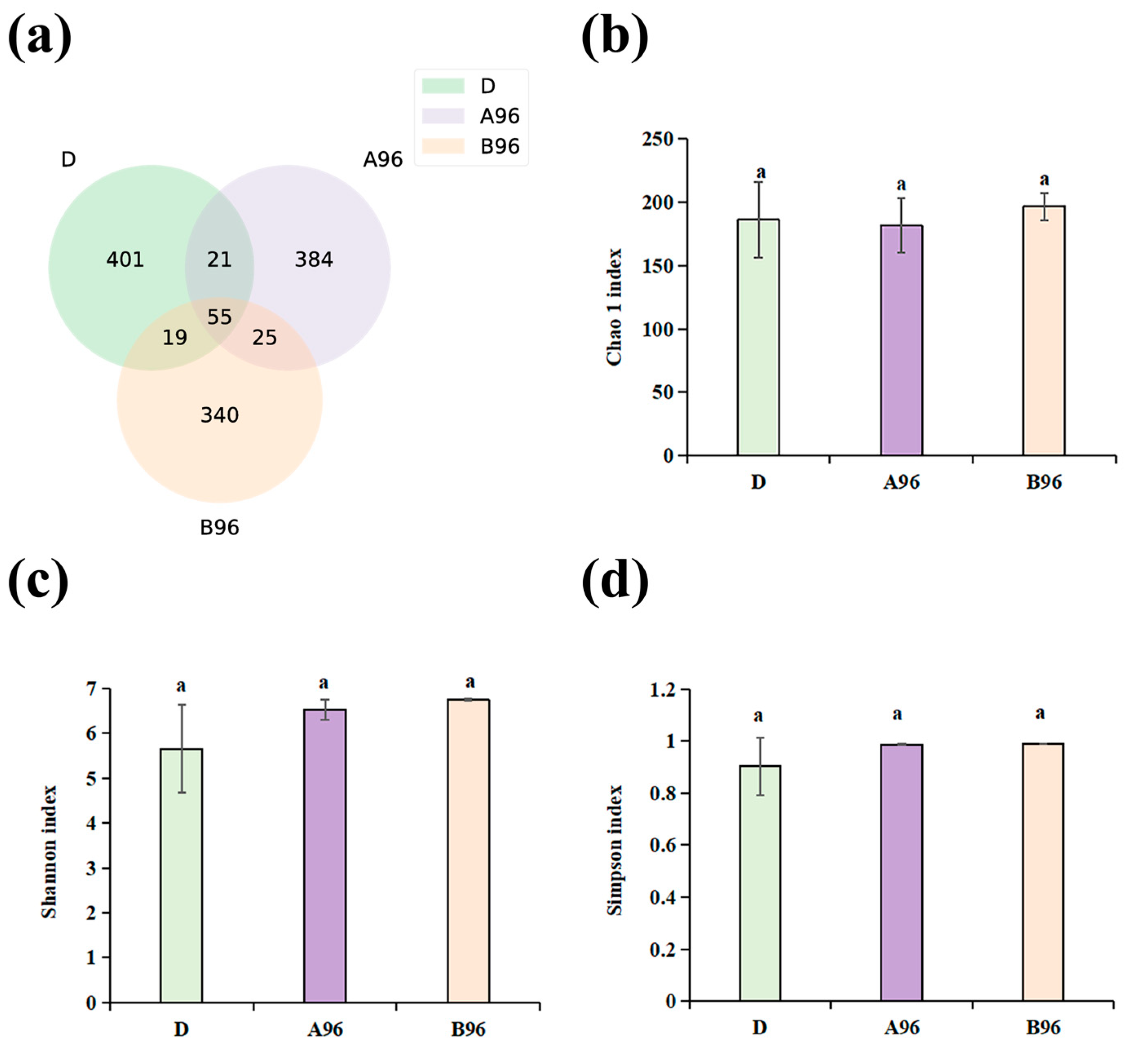
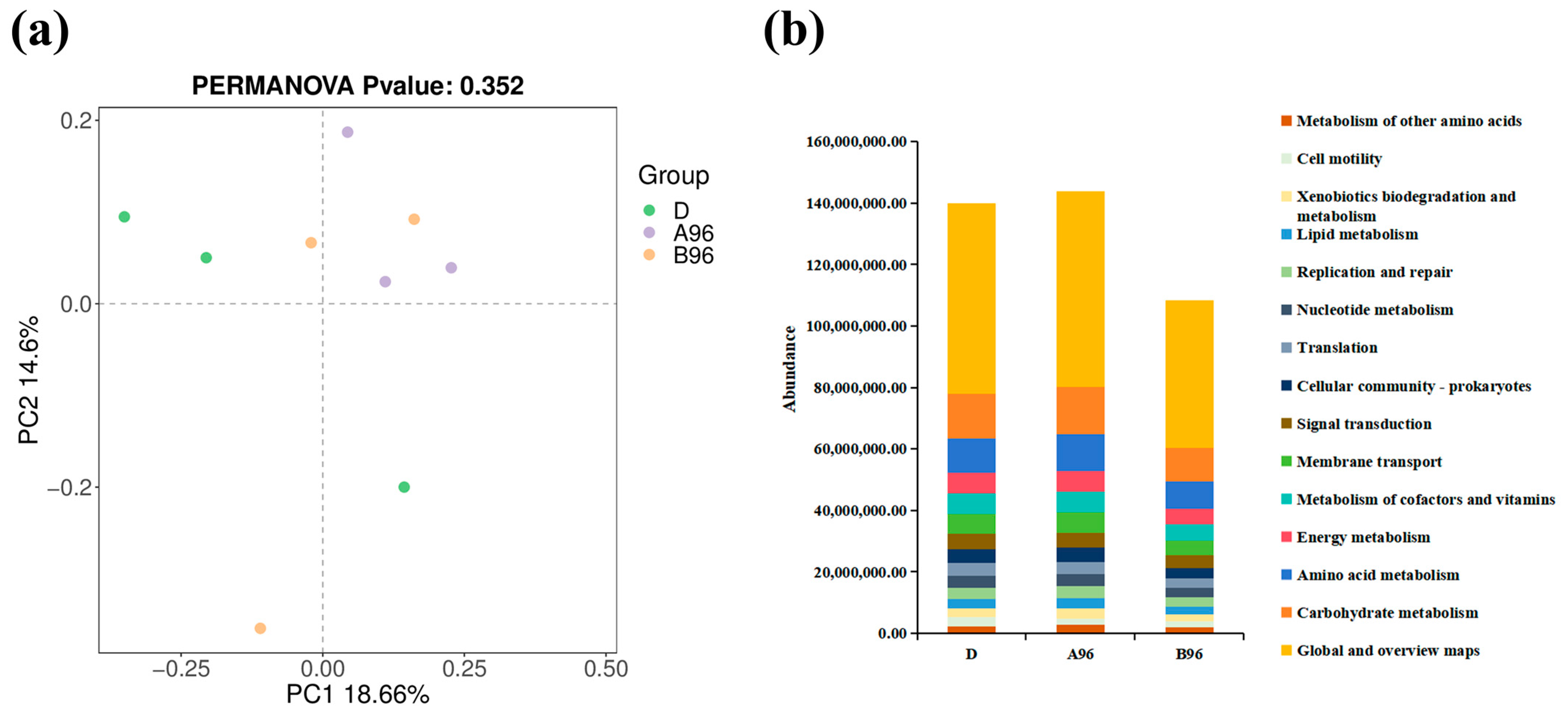
2.10. 16S Ribosomal DNA Sequencing and Gut Microbiome Analysis
2.11. Immunohistochemistry Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Acute Toxicity (96 h LC50) Experiments
3.2. Histopathology Observation for Gill, Liver and Intestine Tissues
3.3. Physiological and Biochemical Indices in Liver and Gill
3.4. Transcriptome Profiling and Annotation
3.5. DEGs Analysis
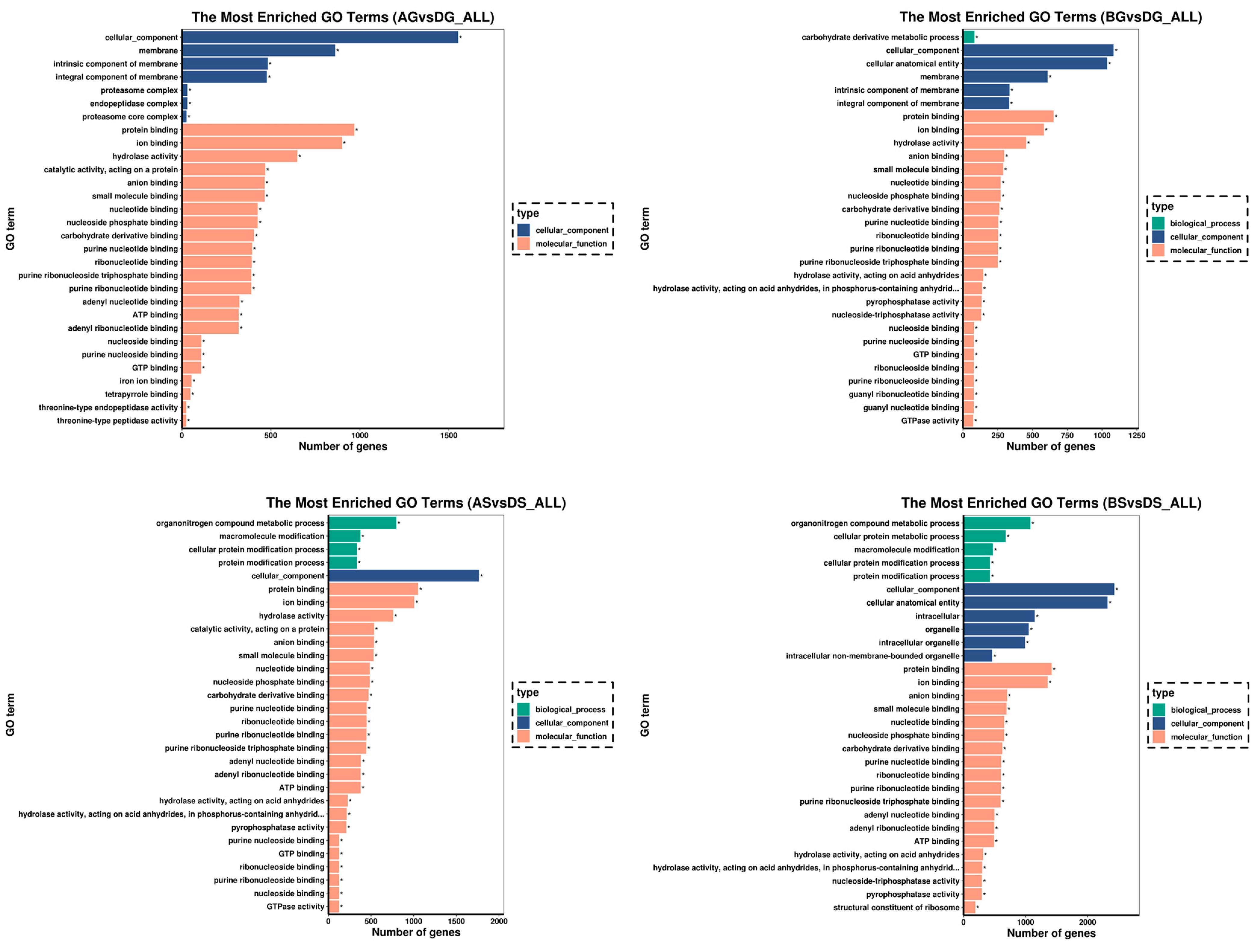
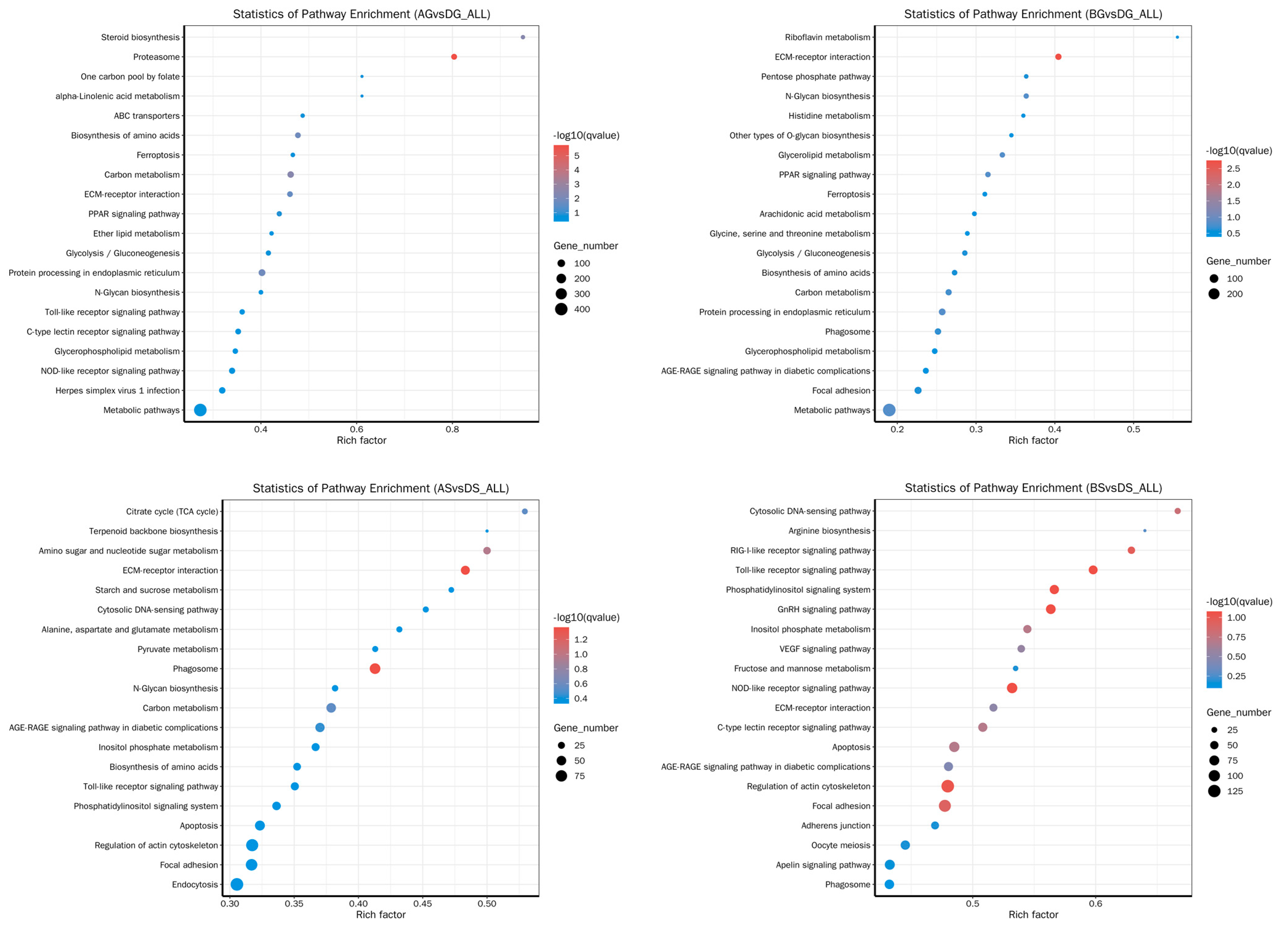
3.6. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis for DEGs
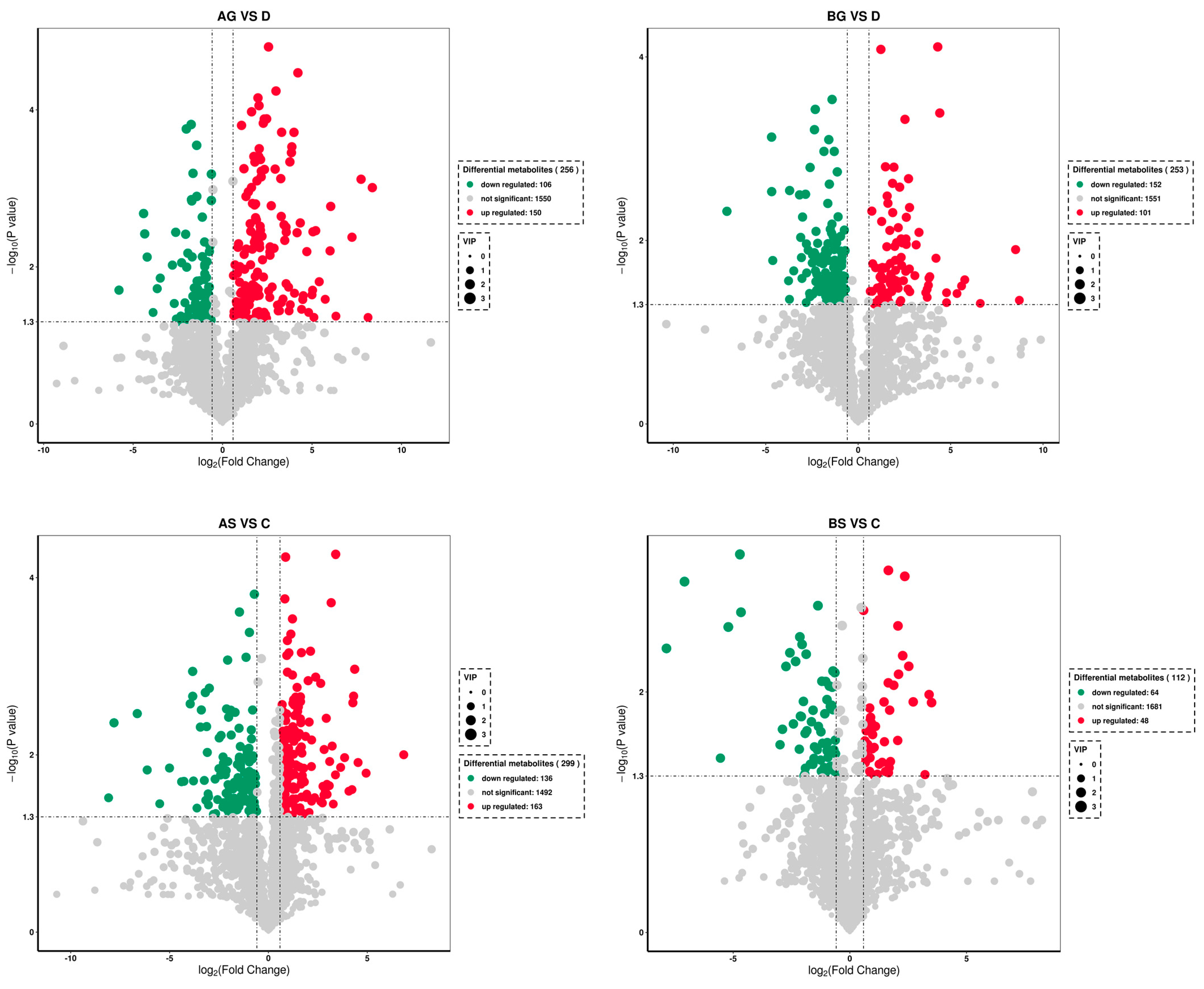
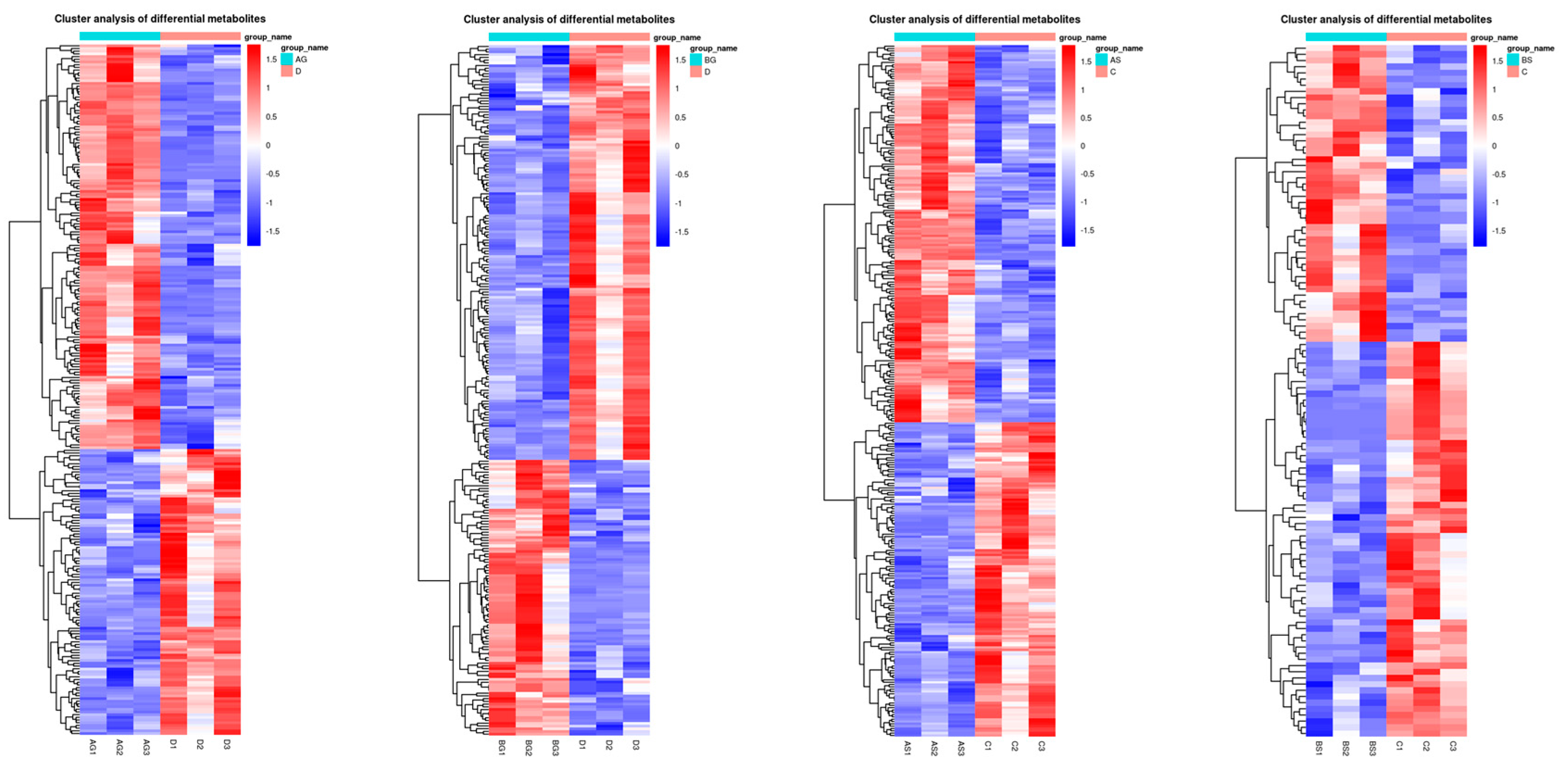
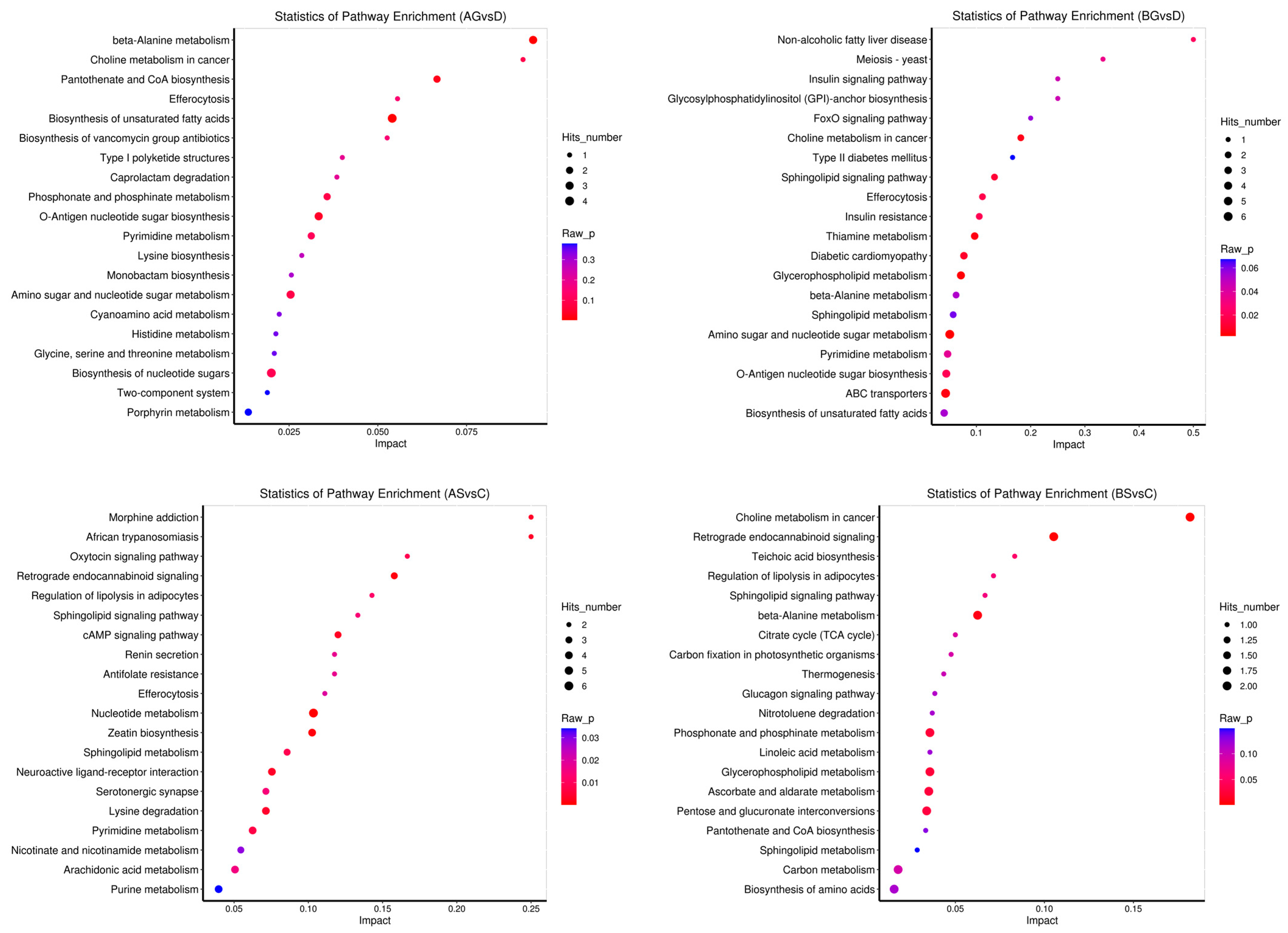
3.7. Changes in Metabolite Levels in Fish Live and Gills
3.8. Intestinal Microbe Composition of Grouper After Stress
3.9. Validation for RNA-Seq Profiling
3.10. Differential Cell Death Pathways Induced by Low/High Concentration Ammonia Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. cDNA Library Construction and Transcriptome Sequencing
Appendix B. Quantification and Differentially Expressed Gene (DEG) Analysis
Appendix C. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Verification
Appendix D. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis
Appendix E. 16S Ribosomal DNA Sequencing and Gut Microbiome Analysis
References
- Xia, H.; Song, T.; Wang, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, W. Effects of dietary toxic cyanobacteria and ammonia exposure on immune function of blunt snout bream (megalabrama amblycephala). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 78, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.L.; Liew, H.J.; Diricxa, M.; Blust, R.; Boeck, G.D. The interactive effects of ammonia exposure, nutritional status and exercise on metabolic and physiological responses in gold fish (Carassius auratus L.). Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 109, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, A.; Siikavuopio, S.I.; Sæther, B.S.; Evensen, T.H. Effect of chronic ammonia exposure on growth in juvenile Atlantic cod. Aquaculture 2004, 237, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.K.; Cao, J.; Qin, X.M.; Qiu, W.Q.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Toxic effects on bioaccumulation, hematological parameters, oxidative stress, immune responses and tissue structure in fish exposed to Ammonia nitrogen: A review. Animals 2021, 11, 3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, M.Z.; Qian, Y.X.; Shi, G.; Wang, R.X. Ammonia toxicity in the yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco), the mechanistic insight from physiological detoxification to poisoning. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 102, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.W.; Xia, Y.T.; Hu, A.; Xiong, G.Q.; Wu, W.J.; Shi, L.; Chen, L.; Guo, X.J.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, C.S.; et al. Difference in muscle metabolism caused by metabolism disorder of rainbow trout liver exposed to ammonia stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Shi, W.J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.K.; Pan, Z.J.; Xue, C.P.; Li, J.L. Identification of genes and signaling pathways associated with immune response of Hemibarbus maculatus (Bleeker, 1871) to ammonia stress. Aquaculture 2020, 524, 735265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yu, Y.B.; Choi, J.H. Toxic effects on bioaccumulation, hematological parameters, oxidative stress, immune responses and neurotoxicity in fish exposed to microplastics: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Fu, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.H. The effects of acute ammonia stress on liver antioxidant, immune and metabolic responses of juvenile yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2024, 297, 111707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.X.; Sun, S.M.; Ge, X.P.; Xia, S.L.; Zhu, J.; Miao, L.H.; Lin, Y.; Liang, H.L.; Pan, W.J.; Su, Y.L.; et al. Acute effects of ammonia exposure on the plasma and haematological parameters and histological structure of the juvenile blunt snout bream, megalobrama amblycephala, and post-exposure recovery. Aquac. Res. 2017, 49, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.H.; Yang, F.F.; Ling, R.Z.; Liao, S.A.; Miao, Y.T.; Ye, C.X.; Wang, A.L. Effects of ammonia exposure on apoptosis, oxidative stress and immune response in puffer fish (Takifugu obscurus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 164, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Quan, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Z.; Ding, J.; Shang, T.; Wu, J. Combined transcriptomics and metabolomics to reveal the effects of copper exposure on the liver of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 284, 116996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, W.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Lan, Y.; Du, Z. Study on the physiological responses and tolerance mechanisms to subchronic carbonate alkalinity exposure in the gills of Paramisgurnus dabryanus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 287, 117319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazi, M.M.; Attia, Z.I.; Ashour, O.A. Oxidative stress and antioxidant enzymes in liver and white muscle of Nile tilapia juveniles in chronic ammonia exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 99, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Jo, A.H.; Lee, D.C.; Choi, C.Y.; Kang, J.C.; Kim, J.H. Review ofcadmium toxicity effects onfish: Oxidative stress andimmune responses. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozougwu, J.C. The role of reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in oxidative stress. Int. J. Res. 2016, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.Y.; Dong, B.; Chen, Q.Z.; Wang, Y.; Han, D.; Zhu, X.M.; Liu, H.K.; Zhang, Z.M.; Yang, Y.X.; Xie, S.Q.; et al. Effects of curcumin on oxidative stress and ferroptosis in acute ammonia stress-induced liver injury in gibel carp (Carassius gibelio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, K. The intestinal microbiota and its role in human health and disease. J. Med. Investig. 2016, 63, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Nie, L.; Zhu, G.; Xiang, L.; Shao, J. Advances in research of fish immune-relevant genes: A comparative overview of innate and adaptive immunity in teleosts. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 39, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.D.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.Z.; Jiang, H.B.; Wang, R.X.; Qian, Y.X.; Ming, L. Ammonia stress disrupts intestinal microbial community and amino acid metabolism of juvenile yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, G.M.; Wang, Q.S. China Red Data Book of Endangered Animals; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 204–206. [Google Scholar]
- Buhl, K.J.; Hamilton, S.J. Relative sensitivity of early life stages of arctic grayling, coho salmon, and rainbow trout to nine inorganics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1991, 22, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2010/63/EU, Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010.
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Methods for Measuring the Acute Toxicity of Effluents and Receiving Waters to Freshwater and Marine Organisms; USEPA Report 821-R-02-012; Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory, Office of Research and Development, US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Thurston, R.V.; Russo, R.C. Acute toxicity of ammonia to rainbow trout. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1983, 112, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaage, B.; Myrick, C. The effects of acute and chronic exposure of ammonia on juvenile burbot (Lota lota) growth and survival. Aquaculture 2021, 542, 736891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Councilon Animal Care Guidelines; Care and Use Fish Res. Teach. Testing: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2005; 87p.
- Li, Y.; Pan, L.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Xing, H.; Bao, J. Ammonia exposure causes the imbalance of the gut-brain axis by altering gene networks associated with oxidative metabolism, inflammation and apoptosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 224, 112668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Cai, T.; Olyarchuk, J.G.; Wei, L. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.T.; Wang, J.; Xing, H.J.; Bao, J. Selenium mitigates ammonia-induced neurotoxicity by suppressing apoptosis, immune imbalance, and gut microbiota-driven metabolic disturbance in fattening pigs. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 3341–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widman, J.C.; Meseck, S.L.; Sennefelder, G.; Veilleux, D.J. Toxicity of un-ionized ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate to juvenile bay scallops, Argopecten irradians irradians. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 54, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasiri, A.K.; Fernandes, J.M.; Kiron, V. Glutamine synthetase activity and the expression of three glul paralogues in zebrafish during transport. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 163, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, W.F.; Castro, T.F.D.; Reichel, T.; de Castro Uzeda, P.L.; Martínez-Palacios, C.A.; Murgas, L.D.S. Diets containing Arthrospira platensis increase growth, modulate lipid metabolism, and reduce oxidative stress in pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus) exposed to ammonia. Aquaculture 2022, 547, 737402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenzado, C.E.; Morales, A.E.; Palma, J.M.; Higuera, M.D.L. Blood antioxidant defenses and hematological adjustments in crowded/uncrowded rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed on diets with different levels of antioxidant vitamins and HUFA. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 149, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zheng, S.; Pu, Y.; Shu, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, W.; Fu, Z. Cypermethrin has the potential to induce hepatic oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2011, 82, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, M. Enhancement of autophagy can alleviate oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis induced by ammonia stress in yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2024, 149, 109582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Liu, Q.; Cai, J.Z.; Yang, J.; Shen, Q.; Xu, S.W. Chlorpyrifos exposure in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) leads to oxidative stress and immune responses. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 67, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.H.; Peng, R.B.; Jiang, M.W.; Jiang, X.M.; Han, Q.X.; Han, Z.R. Effects of ammonia nitrogen stress on the blood cell immunity and liver antioxidant function of Sepiapharaonis. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Xi, Q.Y.; Yang, L.; Li, H.Y.; Jiang, Q.Y.; Shu, G.; Wang, S.B.; Gao, P.; Zhu, X.T.; Zhang, Y.L. The effect of dietary Panax ginseng polysaccharide extract on the immune responses in white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2011, 30, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Han, D.; Jin, J.; Xie, S. Effect of dietary lysozyme on growth, immune response, intestine microbiota, intestine morphology and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophilia in gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Aquac. Nutr. 2014, 20, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Deng, Q.F.; Zhang, Q.R.; Zhou, X.; Chen, R.H.; Li, S.Y.; Wu, Q.; Chen, H.G. Hazards of microplastics exposure to liver function in fishes: A systematic review and meta- analysis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 196, 106423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Liu, B.L.; Han, C.; Huang, B.; Lei, J.L. Effects of ammonia exposure on stress and immune response in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 3149–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinas, G.; Becattini, B. JNK at the crossroad of obesity, insulin resistance, and cell stress response. Mol. Met. 2016, 6, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kültz, D.; Kristina, A. Mitogen-activated protein kinases are in vivo transducers of osmosensory signals in fish gill cells. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 129, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.X.; Guo, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.P.; Lin, P.X.; Lin, C.Q.; Chen, M.X.; Zhu, S.Y.; Huang, L.Y.; He, J.W.; Zhang, L.F. MiR-223-3p alleviates trigeminal neuropathic pain in the male mouse by targeting MKNK2 and MAPK/ERK signaling. Brain Behav. 2022, 12, e2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Signaling to NF-κB by Toll-like receptors. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, F.W.S.; Wu, S.Y.; Lin, S.J.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, Y.M.; Wang, H.C.; Chen, T.Y.; Lin, H.T.; Lin, J.H.Y. The expression of two novel orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) TNF genes in peripheral blood leukocytes, various organs, and fish larvae. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2011, 30, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.T.; Liu, T.B.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Lian, C.Y.; Wang, L. HO-1 activation contributes to cadmium-induced ferroptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells via increasing the labile iron pool and promoting mitochondrial ROS generation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2024, 399, 111152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, S.K.; Chen, S.E.; Chang, L.C. The role of HO-1 and its crosstalk with oxidative stress in cancer cell survival. Cells 2021, 10, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttner, D.M.; Dennery, P.A. Reversal of HO-1 related cytoprotection with increased expression is due to reactive iron. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Synthetic lethal screening identifies compounds activating iron-dependent, nonapoptotic cell death in oncogenic-RAS-harboring cancer cells. Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ran, Q.; He, X.; Peng, D.; Xiong, A.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Bai, L.; Liu, S.; et al. HO-1 upregulation promotes mitophagy-dependent ferroptosis in PM2.5-exposed hippocampal neurons. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 277, 116314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.T.; Panka, D.J.; Cui, H.; Ettinger, R.; el-Khatib, M.; Sherr, D.H.; Stanger, B.Z.; Marshak-Rothstein, A. Fas (CD95)/FasL interactions required for programmed cell death after T-cell activation. Nature 1995, 373, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idriss, H.T.; Naismith, J.H. TNF alpha and the TNF receptor superfamily: Structure-function relationship(s). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2000, 50, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe-Fukunaga, R.; Brannan, C.I.; Itoh, N.; Yonehara, S.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A.; Nagata, S. The cDNA structure, expression, and chromosomal assignment of the mouse Fas antigen. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 1274–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, S. Apoptosis by death factor. Cell 1997, 88, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.F.; Gao, Q.; Wang, R.; Fu, Y.R.; Zheng, L.W.; Yu, H. Transcriptome investigation and in vitro verification of curcumin-induced HO-1 as a feature of ferroptosis in breast cancer cells. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 3469840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Jia, S.; Gao, B.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, J. Application of proteomics and metabolomics to assess ammonia stress response and tolerance mechanisms of juvenile ornate rock lobster Panulirus ornatus. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Jayasundara, N.; Zhang, J.; Ren, X.; Gao, B.; Li, J.; Liu, P. Integrated physiological, transcriptome and metabolome analyses of the hepatopancreas of the female swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus under ammonia exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 228, 113026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, Y.K.; Chew, S.F.; Wilson, J.M.; Randall, D.J. Defences against ammonia toxicity in tropical air-breathing fishes exposed to high concentrations of environmental ammonia: A review. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2004, 174, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.K.; Giblen, T.; AbdElgawad, H.; De Rop, M.; Asard, H.; Blust, R.; De Boeck, G. Regulation of amino acid metabolism as a defensive strategy in the brain of three freshwater teleosts in response to high environmental ammonia exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 130, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, J.; Gadd, G.M. Interactions of Cs+ and other monovalent cations (Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, NH4+) with K+-dependent pyruvate kinase and malate dehydrogenase from the yeasts Rhodotorula rubra and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mycol. Res. 1996, 100, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliarani, A.; Bandiera, P.; Ventrella, V.; Trombetti, F.; Manuzzi, M.P.; Pirini, M.; Borgatti, A.R. Response of Na(+)-dependent ATPase activities to the contaminant ammonia nitrogen in Tapes philippinarum: Possible atpase involvement in ammonium transport. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 55, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.H.; Amenyogbe, E.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Lu, Y.; Xie, R.T.; Droepenu, E.K.; Huang, J.S. Effects of ammonia nitrogen stress on the physiological, biochemical, and metabolic levels of the gill tissue of juvenile four-finger threadfin (Eleutheronema tetradactylum). Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 274, 107049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Štrukelj, B. The influence of probiotics on the firmicutes/ bacteroidetes ratio in the treatment of obesity and inflammatory bowel disease. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, M.; Csak, T.; Nath, B.; Szabo, G.; Medicine, D.O. Lipopolysaccharide induces and activates the Nalp3 inflammasome in the liver. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 4772–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Liu, S.Y.; Chen, B.P.; Li, F.L.; Deng, Y.Q.; Huang, X.L.; Geng, Y.; Yang, P.O.; Chen, D.F. Chronic ammonia stress caused disorder of intestinal microbiota and damaged intestinal structure and function in yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Aquaculture 2024, 581, 740428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klase, G.; Lee, S.; Liang, S.; Kim, J.; Zo, Y.G.; Lee, J. The microbiome and antibiotic resistance in integrated fishfarm water: Implications of environmental public health. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirpuri, J.; Raetz, M.; Sturge, C.R.; Wilhelm, C.L.; Benson, A.; Savani, R.C.; Hooper, L.V.; Yarovinsky, F. Proteobacteria-specific IgA regulates maturation of the intestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xue, C.; Sun, H.; Zheng, Y.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, X. Carbohydrate catabolic capability of a Flavobacteriia bacterium isolated from hadal water. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 42, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ng, D.H.; Wu, Y.; Cao, B. Microbial community composition and putative biogeochemical functions in the sediment and water of tropical granite quarry lakes. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargreaves, J.A.; Kucuk, S. Effects of diel un-ionized ammonia fluctuation on juvenile hybrid striped bass, channel catfish, and blue tilapia. Aquaculture 2001, 195, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; He, Z.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Kempher, M.L.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Liao, L.; et al. Environmental filtering decreases with fish development for the assembly of gut microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4739–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolina, K.; Michal, W.; Samuel, P.; Frank, O.; Chrissy, C.; Lee, J.P. The effect of first feeding exposure of larval largemouth bass to a formulated soybean meal-based or soy saponin-supplemented diet on fish growth performance and gut microbiom. N. Am. J. Aquacult. 2021, 83, 312–326. [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; McGinnity, P.; Dionne, M.; Letourneau, J.; Thonier, F.; Carvalho, G.R.; Creer, S.; Derome, N. The biogeography of the atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) gut microbiome. ISME. J. 2016, 10, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Target T-AN (mg/L) | Measured T-AN (mg/L) | Mortality (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Range finding experiment | ||
| 20 | 20.06 ± 0.08 | 0% |
| 420 | 419.88 ± 0.22 | 50% |
| 820 | 820.06 ± 0.09 | 100% |
| 1120 | 1120.02 ± 0.13 | 100% |
| 1520 | 1520.01 ± 0.1 | 100% |
| Modified range experiment | ||
| 20 | 20.04 ± 0.07 a | 0% |
| 220 | 220.08 ± 0.38 b | 25% |
| 420 | 419.83 ± 0.47 c | 50% |
| 620 | 619.81 ± 0.40 d | 66.70% |
| 820 | 819.81 ± 0.39 e | 100% |
| Gene | Name | Log2FC | p-Value (×10−5) | Change | KEGG Pathway | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS vs. DS | suclg2 | succinyl-CoA ligase | 1.0355 | 88.689 | up | Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) |
| cs | citrate synthase | 1.486 | 2.300 | up | ||
| aco2 | aconitate hydratase | 0.90375 | 52.668 | up | ||
| ogdh | 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase-like | 1.2881 | 117.650 | up | ||
| BS vs. DS | suclg2 | succinyl-CoA ligase | 2.1689 | 324.200 | up | Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) |
| ogdh | 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase-like | 2.4386 | 2.368 | up | ||
| dusp | dual specificity protein phosphatase 3 | 1.4402 | 281.330 | up | MAPK signaling pathway | |
| tnfa | tumor necrosis factor a | 6.6264 | 13.803 | up | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |
| glul | glutamate-ammonia ligase | 1.4799 | 259.480 | up | Arginine biosynthesis | |
| AG vs. DG | hk | hexokinase | −2.4433 | 381.370 | down | Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis |
| gck | glucokinase | −9.673 | 0.387 | down | ||
| fbp1b | fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase | −1.9719 | 0.000 | down | ||
| pgm1 | phosphoglucomutase-1 | −2.2693 | 20.512 | down | ||
| pfkma | 6-phosphofructokinase | −2.1265 | 11.893 | down | ||
| gcl | glutamate--cysteine ligase | 1.4309 | 98.206 | up | Ferroptosis | |
| gpx4 | glutathione peroxidase 4 | −4.7869 | 0.000 | down | ||
| BG vs. DG | hk | hexokinase | −2.2626 | 100.890 | down | Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis |
| pgm1 | phosphoglucomutase-1 | −2.4723 | 123.090 | down | ||
| pfkma | 6-phosphofructokinase | −2.2945 | 75.656 | down | ||
| hmox | heme oxygenase 1 | 2.3756 | 18.129 | up | Ferroptosis | |
| fthl | ferritin | 4.6697 | 0.076 | up | ||
| glul | glutamate-ammonia ligase | 2.2101 | 80.732 | up | Arginine biosynthesis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, B. Differential Cell Death Pathways Induced by Oxidative Stress in Multi-Organs of Amur Grayling (Thymallus grubii) Under Gradient Ammonia Stress. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040499
Zhai C, Li Y, Wang R, Zhang Y, Ma B. Differential Cell Death Pathways Induced by Oxidative Stress in Multi-Organs of Amur Grayling (Thymallus grubii) Under Gradient Ammonia Stress. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(4):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040499
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Cunhua, Yutao Li, Ruoyu Wang, Ying Zhang, and Bo Ma. 2025. "Differential Cell Death Pathways Induced by Oxidative Stress in Multi-Organs of Amur Grayling (Thymallus grubii) Under Gradient Ammonia Stress" Antioxidants 14, no. 4: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040499
APA StyleZhai, C., Li, Y., Wang, R., Zhang, Y., & Ma, B. (2025). Differential Cell Death Pathways Induced by Oxidative Stress in Multi-Organs of Amur Grayling (Thymallus grubii) Under Gradient Ammonia Stress. Antioxidants, 14(4), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14040499






