Long-Term Results of Immunogenicity of Booster Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 (Hybrid COV-RAPEL TR Study) in Turkiye: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled, Multicenter Phase 2 Clinical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Procedures
2.2. Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.3. Viral Isolation and Microneutralization Test Technique
2.4. Measurement of Anti-Spike IgG Level
2.5. Statistical Analysis
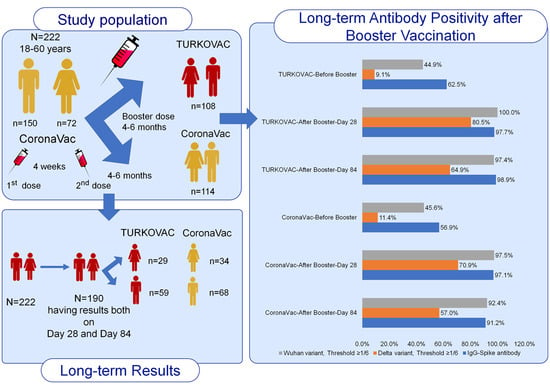
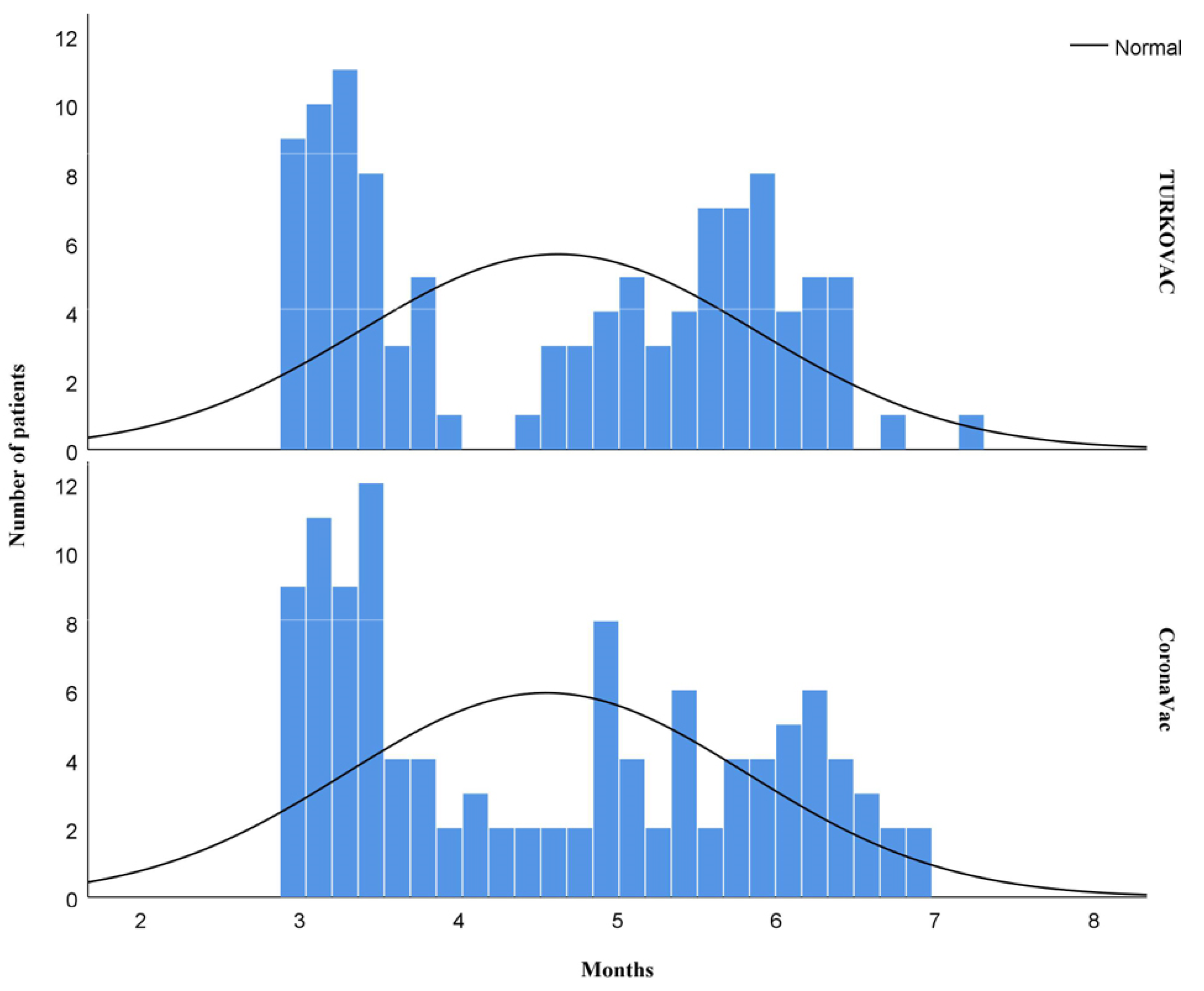
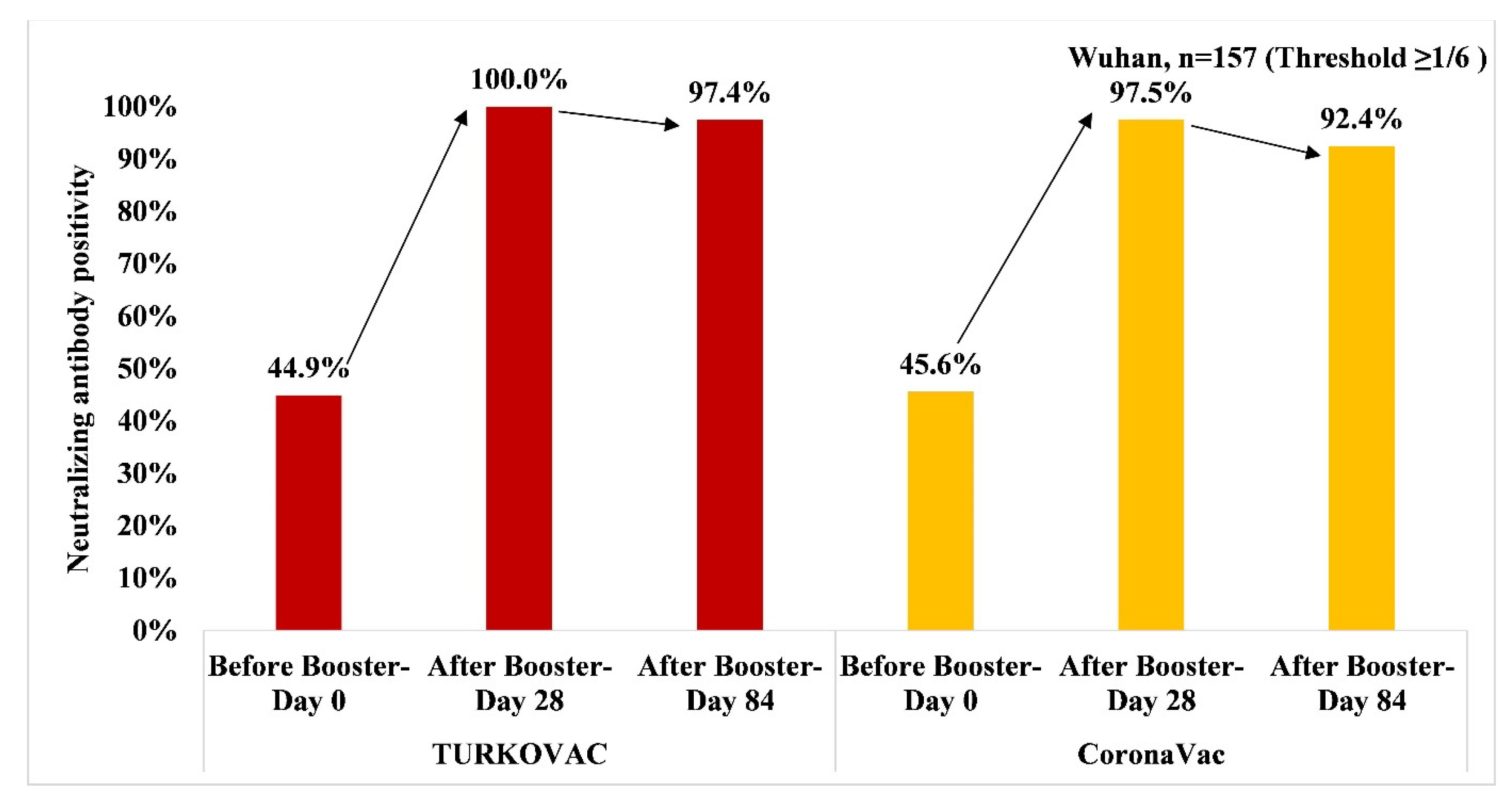
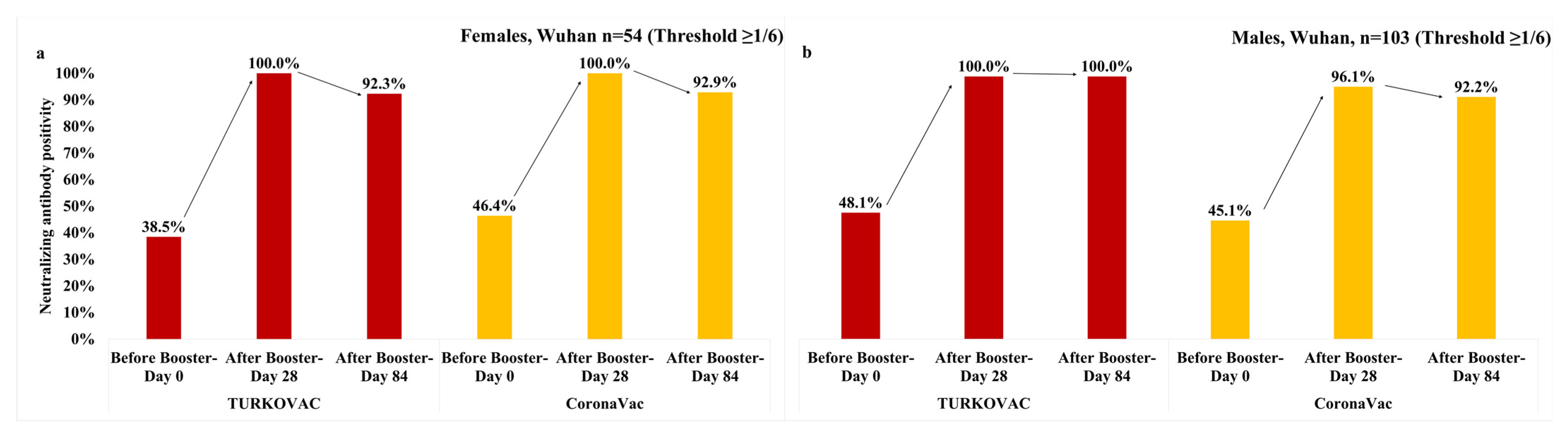
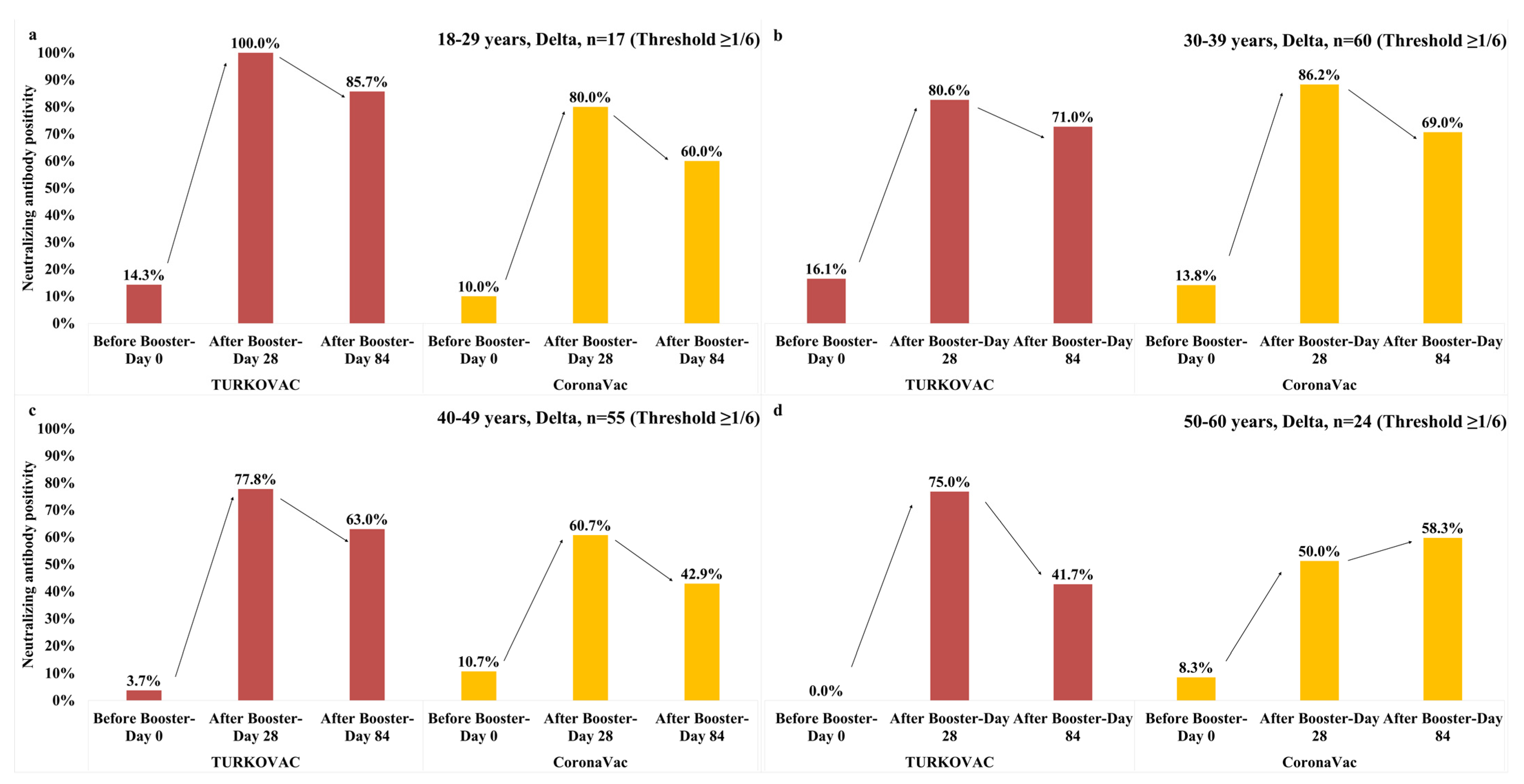
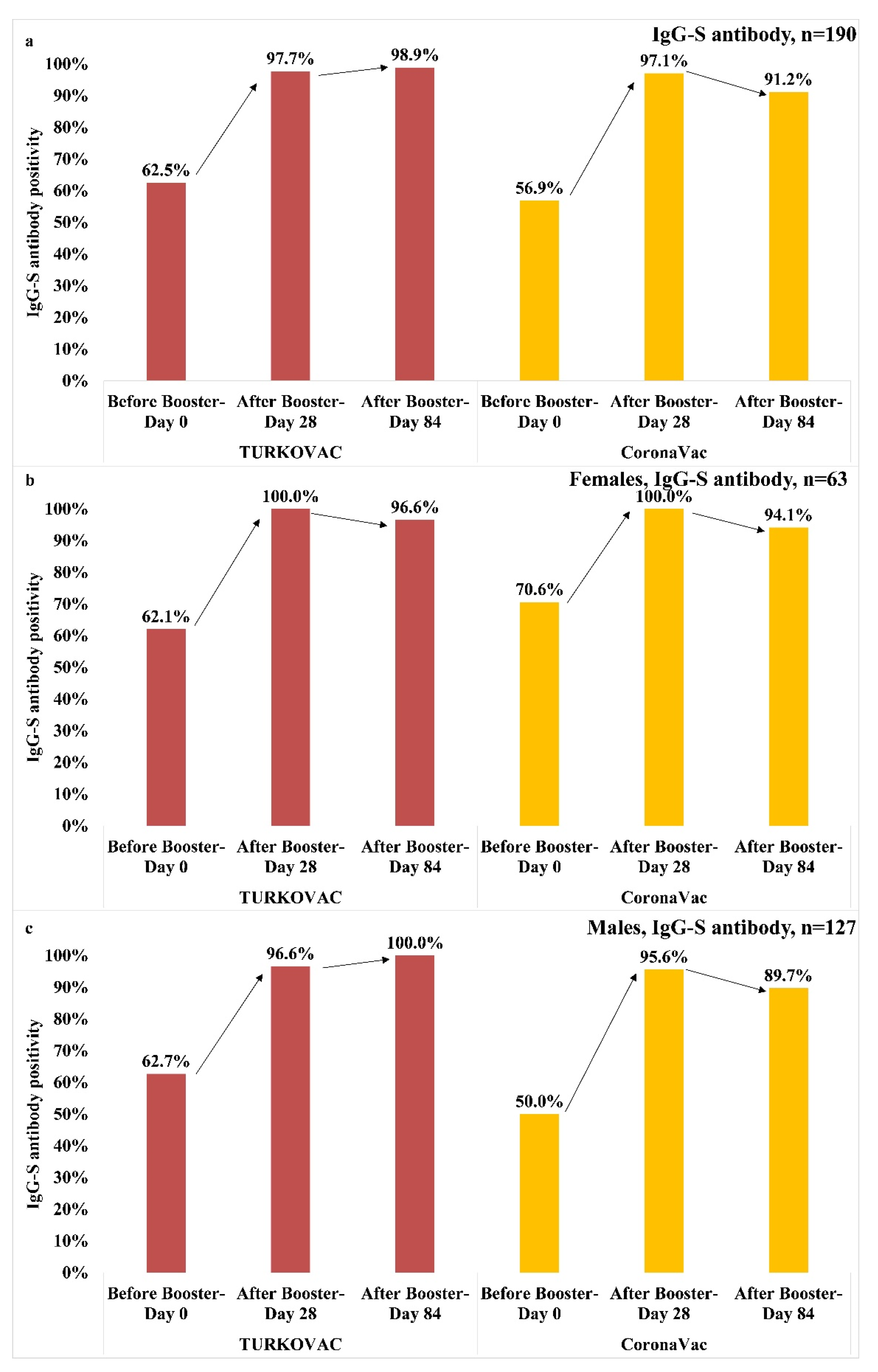
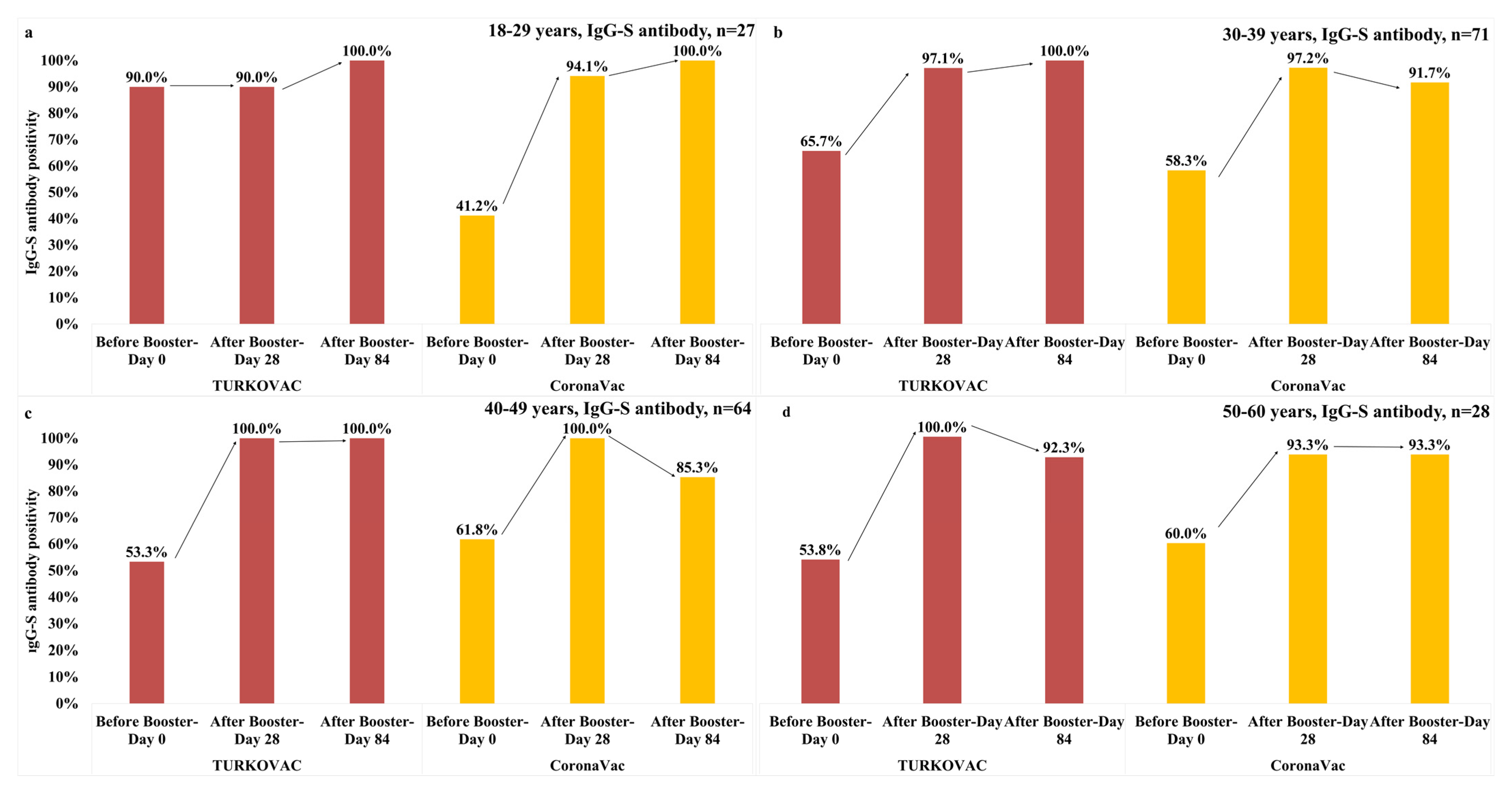
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CDC Museum COVID-19 Timeline. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/museum/timeline/covid19.html (accessed on 3 June 2023).
- COVID19 Vaccine Tracker. Available online: https://covid19.trackvaccines.org (accessed on 3 June 2023).
- Watson, O.J.; Barnsley, G.; Toor, J.; Hogan, A.B.; Winskill, P.; Ghani, A.C. Global impact of the first year of COVID-19 vaccination: A mathematical modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 3 June 2023).
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Türkiye. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/region/euro/country/tr (accessed on 3 June 2023).
- Tanriover, M.D.; Doğanay, H.L.; Akova, M.; Güner, H.R.; Azap, A.; Akhan, S.; Köse, Ş.; Erdinç, F.Ş.; Akalın, E.H.; Tabak, Ö.F.; et al. Efficacy and safety of an inactivated whole-virion SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac): Interim results of a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial in Turkey. Lancet 2021, 398, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozdarendeli, A.; Sezer, Z.; Pavel, S.T.I.; Inal, A.; Yetiskin, H.; Kaplan, B.; Uygut, M.A.; Bayram, A.; Mazicioglu, M.; Unuvar, G.K.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated whole virion SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, TURKOVAC, in healthy adults: Interim results from randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1 and 2 trials. Vaccine 2023, 41, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, S.; Yetiskin, H.; Uygut, M.A.; Aslan, A.F.; Aydın, G.; Inan, Ö.; Kaplan, B.; Ozdarendeli, A. Development of an inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.D.; Chi, W.Y.; Su, J.H.; Ferrall, L.; Hung, C.F.; Wu, T.C. Coronavirus vaccine development: From SARS and MERS to COVID-19. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omma, A.; Batirel, A.; Aydin, M.; Yilmaz Karadag, F.; Erden, A.; Kucuksahin, O.; Armagan, B.; Güven, S.C.; Karakas, O.; Gokdemir, S.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of inactive vaccines as booster doses for COVID-19 in Türkiye: A randomized trial. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2022, 18, 2122503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Pan, H.; Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Chu, K.; Han, W.; Chen, Z.; Tang, R.; Yin, W.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18-59 years: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, A.; Undurraga, E.A.; González, C.; Paredes, F.; Fontecilla, T.; Jara, G.; Pizarro, A.; Acevedo, J.; Leo, K.; Leon, F.; et al. Effectiveness of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in Chile. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kaabi, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, S.; Yang, Y.; Al Qahtani, M.M.; Abdulrazzaq, N.; Al Nusair, M.; Hassany, M.; Jawad, J.S.; Abdalla, J.; et al. Effect of 2 inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines on symptomatic COVID-19 infection in adults: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2021, 326, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widge, A.T.; Rouphael, N.G.; Jackson, L.A.; Anderson, E.J.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, L.J.; Pruijssers, A.J.; et al. Durability of responses after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, D. Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccine booster shot compared with non-booster: A meta-analysis. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, A.J.; Bijker, E.M. A guide to vaccinology: From basic principles to new developments. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO SAGE Roadmap for Prioritizing Uses of COVID-19 Vaccines. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/351138/WHO-2019-nCoV-Vaccines-SAGE-Prioritization-2022.1-eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- COVID-19 Vaccine (VeroCell), Inactivated. Available online: https://extranet.who.int/pqweb/sites/default/files/documents/COR-WHO-Adu-40_vials-insert.pdf#:~:text=Active%20ingredient%3A%20Inactivated%20SARS-CoV,No%20preservative%20in%20this%20product (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- Pavel, S.T.I.; Yetiskin, H.; Aydin, G.; Holyavkin, C.; Uygut, M.A.; Dursun, Z.B.; Celik, İ.; Cevik, C.; Ozdarendeli, A. Isolation and characterization of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in Turkey. PLoS ONE 2020, 5, e0238614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Xin, Q.; Pan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Chu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Q. Neutralizing antibody responses to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in Coronavirus Disease 2019 in patients and convalescent patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2688–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent end points. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Gao, L.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, K.; Sun, F. Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.G.; Lustig, Y.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Doolman, R.; Asraf, K.; Mendelson, E.; Ziv, A.; et al. Waning immune humoral response to BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine over 6 months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feikin, D.R.; Higdon, M.M.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Andrews, N.; Araos, R.; Goldberg, Y.; Groome, M.J.; Huppert, A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Smith, P.G.; et al. Duration of effectiveness of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease: Results of a systematic review and meta-regression. Lancet 2022, 399, 924–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VaccinesWork. Prioritise First Doses of COVID-19 Vaccines Over Boosters, Say WHO Experts. Available online: https://www.gavi.org/vaccineswork/prioritise-first-doses-covid-19-vaccines-over-boosters-say-who-experts (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- WHO. Interim Statement on the Use of Additional Booster Doses of Emergency Use Listed mRNA Vaccines against COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/17-05-2022-interim-statement-on-the-use-of-additional-booster-doses-of-emergency-use-listed-mrna-vaccines-against-covid-19 (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- Massonnaud, C.R.; Roux, J.; Colizza, V.; Crépey, P. Evaluating COVID-19 booster vaccination strategies in a partially vaccinated population: A modeling study. Vaccines 2022, 10, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronavirüs Bilim Kurulu Toplantısına İlişkin Açıklama (5 January 2022). Available online: https://www.saglik.gov.tr/TR,87061/koronavirus-bilim-kurulu-toplantisina-iliskin-aciklama-05012022.html (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- COVID-19 Aşısı Ulusal Uygulama Stratejisi. Available online: https://covid19asi.saglik.gov.tr/TR-77706/covid-19-asisi-ulusal-uygulama-stratejisi.html (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- Regev-Yochay, G.; Gonen, T.; Gilboa, M.; Mandelboim, M.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Meltzer, L.; Asraf, K.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; et al. Efficacy of a fourth dose of Covid-19 mRNA vaccine against Omicron. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, R.; Kitchen, S.A.; Nguyen, L.; Buchan, S.A.; Wilson, S.E.; Costa, A.P.; Kwong, J.C. Effectiveness of a fourth dose of covid-19 mRNA vaccine against the omicron variant among long term care residents in Ontario, Canada: Test negative design study. BMJ 2022, 378, e071502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Highlights from the Meeting of the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on Immunization 20–22 March 2023. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/immunization/sage/2023/march-2023/sage_march_2023_meeting_highlights.pdf?sfvrsn=a8e5be9_4 (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- Vadrevu, K.M.; Ganneru, B.; Reddy, S.; Jogdand, H.; Raju, D.; Sapkal, G.; Yadav, P.; Reddy, P.; Verma, S.; Singh, C.; et al. Persistence of immunity and impact of third dose of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine against emerging variants. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, G.; Wu, Q.; Pan, H.; Li, M.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, D.; Deng, X.; Chu, K.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of a third dose of CoronaVac, and immune persistence of a two-dose schedule, in healthy adults: Interim results from two single-centre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 clinical trials. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menni, C.; May, A.; Polidori, L.; Louca, P.; Wolf, J.; Capdevila, J.; Hu, C.; Ourselin, S.; Steves, C.J.; Valdes, A.M.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine waning and effectiveness and side-effects of boosters: A prospective community study from the ZOE COVID Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.Y.; Cheung, P.P. Effectiveness of heterologous and homologous covid-19 vaccine regimens: Living systematic review with network meta-analysis. BMJ 2022, 377, e069989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmezer, M.C.; Dizman, G.T.; Erul, E.; Sahin, T.K.; Saricaoglu, T.; Alp, A.; Tanriover, M.D.; Uzun, O.; Unal, S.; Akova, M. Relative vaccine effectiveness of the third dose of CoronaVac or BNT162b2 following a two-dose CoronaVac regimen: A prospective observational cohort study from an adult vaccine center in Turkey. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Xie, T.; Yang, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, T.; Li, H.; et al. Antibody response elicited by a third boost dose of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine can neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2021, 10, 2125–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zou, Y.; Hu, Z. Advances in aluminum hydroxide-based adjuvant research and its mechanism. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2015, 11, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.J.; Xue, M.; Zheng, P.; Lyu, J.; Zhan, Z.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Sun, B. Factors affecting the antibody immunogenicity of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2: A focused review. Vaccines 2021, 9, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Factors that influence the immune response to vaccination. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00084–e00118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Xie, T.; Yang, T.; Zhou, J.; Chen, H.; Zhu, H.; Li, H.; Xiang, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; et al. A third booster dose may be necessary to mitigate neutralizing antibody fading after inoculation with two doses of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.; Fuentes, M.; Alarcón, M.; Palomo, I. Immune system dysfunction in the elderly. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2017, 89, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera, A.; Campos, C.; López, N.; Hassouneh, F.; Alonso, C.; Tarazona, R.; Solana, R. Immunosenescence: Implications for response to infection and vaccination in older people. Maturitas 2015, 82, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, N.; Tessier, E.; Stowe, J.; Gower, C.; Kirsebom, F.; Simmons, R.; Gallagher, E.; Thelwall, S.; Groves, N.; Dabrera, G.; et al. Duration of protection against mild and severe disease by Covid-19 vaccines. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAGE. Highlights from the Meeting of the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on Immunization. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/immunization/sage/2021/october/sage_oct2021_meetinghighlights.pdf?sfvrsn=3dcae610 (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- Keskin, A.U.; Bolukcu, S.; Ciragil, P.; Topkaya, A.E. SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody responses after third CoronaVac or BNT162b2 vaccine following two-dose CoronaVac vaccine regimen. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, A.; Afsharyzad, Y.; Vaezi, A.; Meysamie, A. Importance of the COVID-19 vaccine booster dose in protection and immunity. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, E.B.; Gümüş, S.; Bektöre, B.; Bozkurt, H.; Gözalan, A. Evaluation of antibody response after COVID-19 vaccination of healthcare workers. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartsch, Y.C.; Tong, X.; Kang, J.; Avendaño, M.J.; Serrano, E.F.; García-Salum, T.; Pardo-Roa, C.; Riquelme, A.; Cai, Y.; Renzi, I.; et al. Omicron variant Spike-specific antibody binding and Fc activity are preserved in recipients of mRNA or inactivated COVID-19 vaccines. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabn9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Male | Female | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18–39 Years | 40–60 Years | 18–39 Years | 40–60 Years | Total | |
| CoronaVac (n) | 40 | 35 | 20 | 16 | 111 |
| TURKOVAC (n) | 40 | 35 | 20 | 16 | 111 |
| Total | 80 | 70 | 40 | 32 | 222 |
| TURKOVAC | CoronaVac | Total | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female | 34 (31.5) | 38 (33.3) | 72 (32.4) | 0.768 |
| Male | 74 (68.5) | 76 (66.7) | 150 (67.6) | ||
| Total | 108 (100) | 114 (100) | 222 (100) | ||
| Age groups, years | 18–29 | 13 (12.0) | 20 (17.5) | 33 (14.9) | 0.587 |
| 30–39 | 44 (40.7) | 39 (34.2) | 83 (37.4) | ||
| 40–49 | 37 (34.3) | 38 (33.3) | 75 (33.8) | ||
| 50–60 | 14 (13.0) | 17 (14.9) | 31 (14.0) | ||
| Total | 108 (100) | 114 (100) | 222 (100) | ||
| COVID-19 (+) | No | 84 (77.8) | 83 (72.8) | 167 (75.2) | 0.391 |
| Yes | 24 (22.2) | 31 (27.2) | 55 (24.8) | ||
| Total | 108 (100) | 114 (100) | 222 (100) | ||
| COVID-19 (+) participants after the booster dose | Day 0–28 | 4 | 3 | 4 | |
| Day 28–84 | 7 | 7 | 14 | ||
| Day ≥ 84 | 13 | 24 | 37 |
| TURKOVAC | CoronaVac | Total | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |||
| Female | <4-fold | 3 (9.1) | 11 (28.9) | 14 (19.7) | 0.036 |
| ≥4-fold | 30 (90.9) | 27 (71.1) | 57 (80.3) | ||
| Male | <4-fold | 15 (21.4) | 29 (38.2) | 44 (30.1) | 0.028 |
| ≥4-fold | 55 (78.6) | 47 (61.8) | 102 (69.9) | ||
| Total | 103 (47.46) | 114 (52.53) | 217 (100) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ates, I.; Batirel, A.; Aydin, M.; Karadag, F.Y.; Erden, A.; Kucuksahin, O.; Armagan, B.; Guven, S.C.; Karakas, O.; Gokdemir, S.; et al. Long-Term Results of Immunogenicity of Booster Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 (Hybrid COV-RAPEL TR Study) in Turkiye: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled, Multicenter Phase 2 Clinical Study. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071234
Ates I, Batirel A, Aydin M, Karadag FY, Erden A, Kucuksahin O, Armagan B, Guven SC, Karakas O, Gokdemir S, et al. Long-Term Results of Immunogenicity of Booster Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 (Hybrid COV-RAPEL TR Study) in Turkiye: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled, Multicenter Phase 2 Clinical Study. Vaccines. 2023; 11(7):1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071234
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtes, Ihsan, Ayse Batirel, Mehtap Aydin, Fatma Yilmaz Karadag, Abdulsamet Erden, Orhan Kucuksahin, Berkan Armagan, Serdar Can Guven, Ozlem Karakas, Selim Gokdemir, and et al. 2023. "Long-Term Results of Immunogenicity of Booster Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 (Hybrid COV-RAPEL TR Study) in Turkiye: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled, Multicenter Phase 2 Clinical Study" Vaccines 11, no. 7: 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071234
APA StyleAtes, I., Batirel, A., Aydin, M., Karadag, F. Y., Erden, A., Kucuksahin, O., Armagan, B., Guven, S. C., Karakas, O., Gokdemir, S., Altunal, L. N., Buber, A. A., Gemcioglu, E., Zengin, O., Inan, O., Sahiner, E. S., Korukluoglu, G., Sezer, Z., Ozdarendeli, A., ... Kara, A. (2023). Long-Term Results of Immunogenicity of Booster Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 (Hybrid COV-RAPEL TR Study) in Turkiye: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled, Multicenter Phase 2 Clinical Study. Vaccines, 11(7), 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071234