Feline Infectious Peritonitis mRNA Vaccine Elicits Both Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.2. In Vitro Transcription and mRNA Purification
2.3. Measurement of Nucleocapsid mRNA Stability by Quantitative Reverse-Transcriptase PCR (q-RT PCR)
2.4. Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. LNP Encapsulation
2.7. Mouse Vaccination and Safety Assays
2.8. IgG-Specific Nucleoprotein Antigen ELISA
2.9. Splenocyte Stimulation Assay
2.10. Flow Cytometry
2.11. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
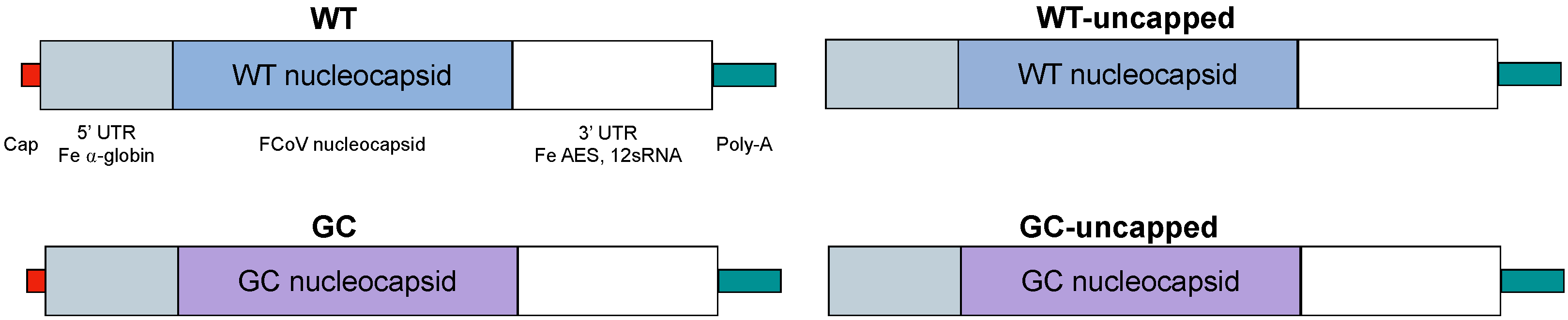
3.1. Vaccine Design
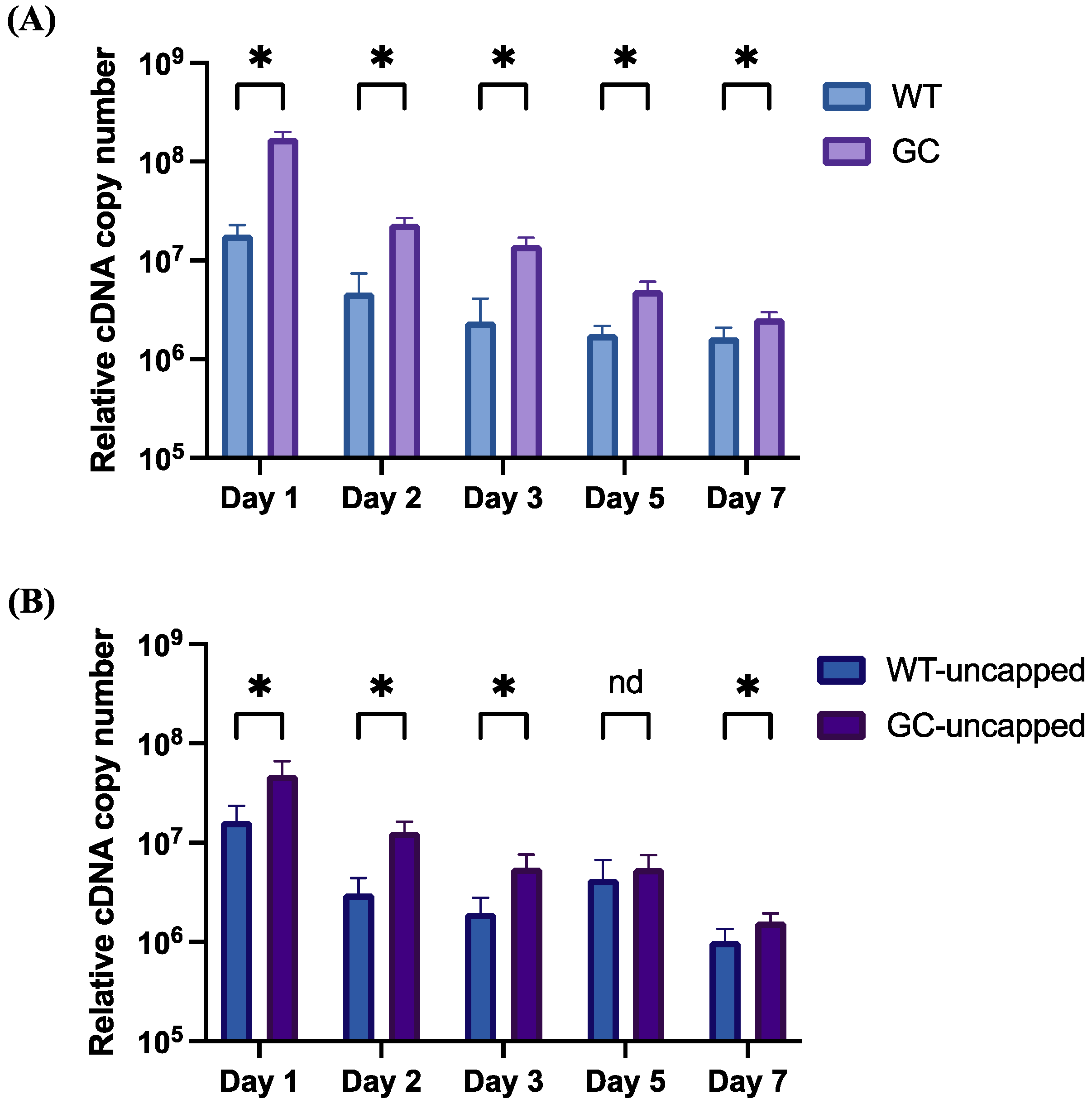
3.2. mRNA Stability and Expression In Vitro
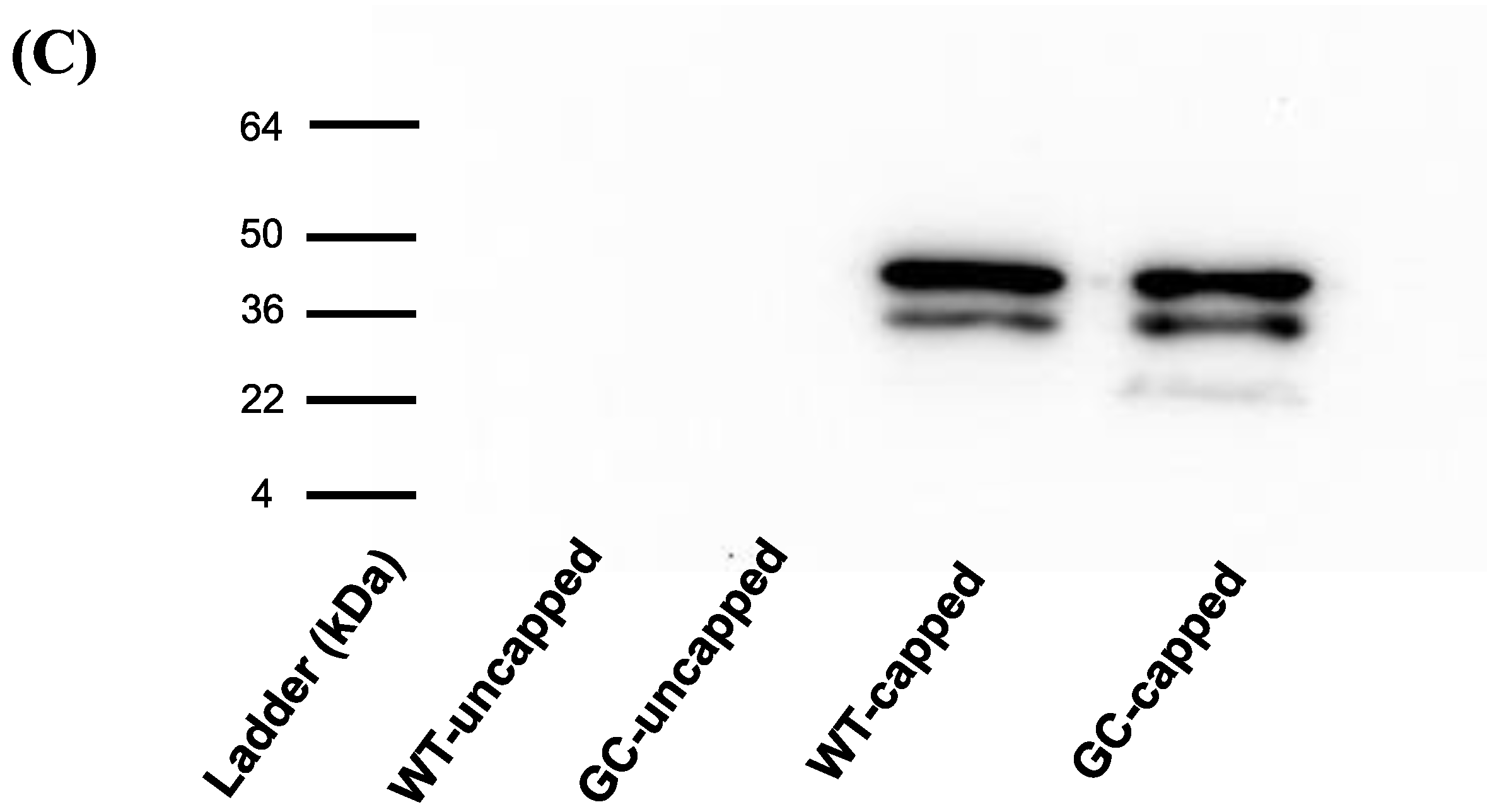
3.3. Protein Production In Vitro
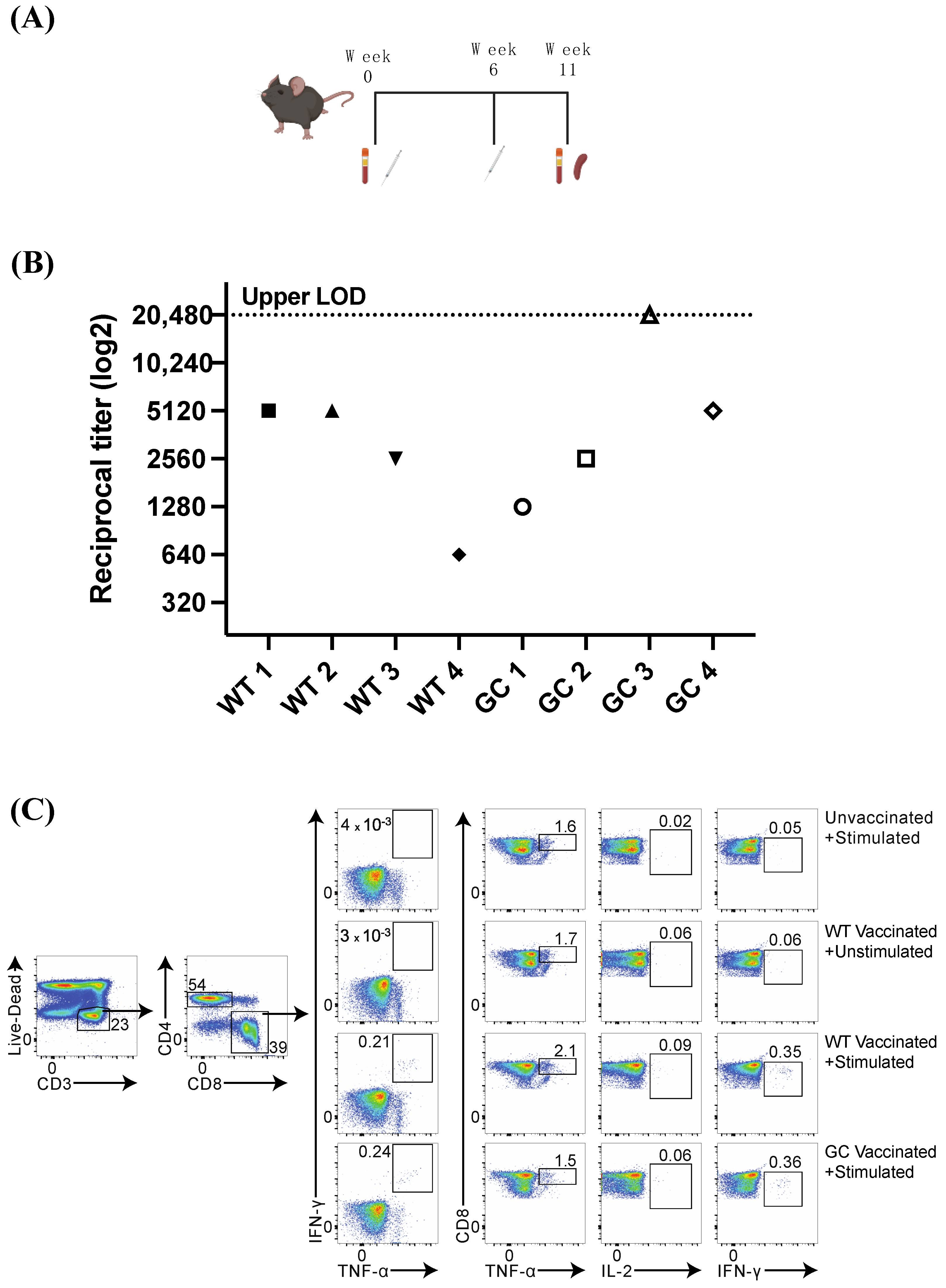
3.4. Mouse Vaccination and Humoral Immune Response
3.5. Nucleocapsid-Specific CD8+ T Cell Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pedersen, N.C. A Review of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus Infection: 1963-2008. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 225–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLachlan, N.; Dubovi, E. Coronaviridae; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jaimes, J.A.; Whittaker, G.R. Feline Coronavirus: Insights into Viral Pathogenesis Based on the Spike Protein Structure and Function. Virology 2018, 517, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuanthap, S.; Chiteafea, N.; Rattanasrisomporn, J.; Choowongkomon, K. Comparative Sequence Analysis of the Accessory and Nucleocapsid Genes of Feline Coronavirus Strains Isolated from Cats Diagnosed with Effusive Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 2779–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Poder, S. Feline and Canine Coronaviruses: Common Genetic and Pathobiological Features. Adv. Virol. 2011, 2011, 609465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstens, E.B. Ratification Vote on Taxonomic Proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2009). Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Li, B.; Yoo, D.; Qin, T.; Zhang, X.; Jia, Y.; Cui, S. Animal Coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1097–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.L. Origin and Evolution of Pathogenic Coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underdahl, N.R.; Mebus, C.A.; Torres Medina, A. Recovery of Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus from Chronically Infected Experimental Pigs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1975, 36, 1473–1476. [Google Scholar]
- Addie, D.D.; Schaap IA, T.; Nicolson, L.; Jarrett, O. Persistence and Transmission of Natural Type I Feline Coronavirus Infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2735–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, H.Y. Porcine Enteric Coronaviruses: An Updated Overview of the Pathogenesis, Prevalence, and Diagnosis. Vet. Res. Commun. 2021, 45, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhe, P.; Verma, S. Evolution, Interspecies Transmission, and Zoonotic Significance of Animal Coronaviruses. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 719834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timurkan, M.O.; Aydin, H.; Dincer, E.; Coskun, N. Molecular Characterization of Canine Coronaviruses: An Enteric and Pantropic Approach. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licitra, B.N.; Duhamel, G.E.; Whittaker, G.R. Canine Enteric Coronaviruses: Emerging Viral Pathogens with Distinct Recombinant Spike Proteins. Viruses 2014, 6, 3363–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drechsler, Y.; Alcaraz, A.; Bossong, F.J.; Collisson, E.W.; Diniz, P.P.V.P. Feline Coronavirus in Multicat Environments. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 41, 1133–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berliner, E.A. Feline Coronavirus and Feline Infectious Peritonitis. In Infectious Disease Management in Animal Shelters, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 367–392. ISBN 9781119294382. [Google Scholar]
- Healey, E.A.; Andre, N.M.; Miller, A.D.; Whitaker, G.R.; Berliner, E.A. Outbreak of Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP) in Shelter-Housed Cats: Molecular Analysis of the Feline Coronavirus S1/S2 Cleavage Site Consistent with a ‘Circulating Virulent–Avirulent Theory’ of FIP Pathogenesis. J. Feline Med. Surg. Open Rep. 2022, 8, 205511692210742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.; Janeczko, S.; Hurley, K. Infectious Disease Management in Animal Shelters; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Addie, D.D.; Toth, S.; Murray, G.D.; Jarrett, O. Risk of Feline Infectious Peritonitis in Cats Naturally Infected with Feline Coronavirus. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1995, 56, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tizard, I.R. Vaccination against Coronaviruses in Domestic Animals. Vaccine 2020, 38, 5123–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C. An Update on Feline Infectious Peritonitis: Virology and Immunopathogenesis. Vet. J. 2014, 201, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Li, W.; Schuurman, N.; Van Kuppeveld, F.; Bosch, B.-J.; Egberink, H. Serological Screening for Coronavirus Infections in Cats. Viruses 2019, 8, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohdatsu, T.; Okada, S.; Ishizuka, Y.; Yamada, H.; Koyama, H. The Prevalence of Types I and II Feline Coronavirus Infections in Cats. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1992, 54, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černá, P.; Lobová, D.; Bubeníková, J.; Vrábelová, J.; Molínková, D.; Hořín, P. Shedding Persistency and Intensity Patterns of Feline Coronavirus (FCoV) in Feces of Cats Living in Breeding Catteries in the Czech Republic. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 152, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felten, S.; Klein-Richers, U.; Unterer, S.; Bergmann, M.; Zablotski, Y.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Hartmann, K. Patterns of Feline Coronavirus Shedding and Associated Factors in Cats from Breeding Catteries. Viruses 2023, 15, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaro, N.; Mari, V.; Lanave, G.; Lorusso, E.; Lucente, M.S.; Desario, C.; Colaianni, M.L.; Elia, G.; Ferringo, F.; Alfano, F.; et al. Mutation Analysis of the Spike Protein in Italian Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus and Feline Enteric Coronavirus Sequences. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 135, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Liu, H.; Dodd, K.A.; Pesavento, P.A. Significance of Coronavirus Mutants in Feces and Diseased Tissues of Cats Suffering from Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Viruses 2009, 1, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bank-Wolf, B.R.; Stallkamp, I.; Wiese, S.; Moritz, A.; Tekes, G.; Thiel, H.J. Mutations of 3c and Spike Protein Genes Correlate with the Occurrence of Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 173, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, F.W. Evaluation of Risks and Benefits Associated with Vaccination against Coronavirus Infections in Cats. Adv. Vet. Med. 1999, 41, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, N.C.; Pollock, R.V.; Thurber, E.T. Long-Term Follow-up Study of Cats Vaccinated with a Temperature-Sensitive Feline Infectious Peritonitis Vaccine. Cornell Vet. 1992, 82, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Takano, T.; Kawakami, C.; Yamada, S.; Satoh, R.; Hohdatsu, T. Antibody-Dependent Enhancement Occurs Upon Re-Infection with the Identical Serotype Virus in Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus Infection. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2008, 70, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, T.; Yamada, S.; Doki, T.; Hohdatsu, T.; Vopat, T. Pathogenesis of Oral Type I Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus (FIPV) Infection: Antibody-Dependent Enhancement Infection of Cats with Type I FIPV via the Oral Route. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedeurwaerder, A.; Desmarets, L.M.; Olyslaegers, D.A.J.; Vermeulen, B.L.; Dewerchin, H.L.; Nauwynck, H.J. The Role of Accessory Proteins in the Replication of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus in Peripheral Blood Monocytes. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cham, T.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Tsai, P.S.; Wu, C.H.; Chen, H.W.; Jeng, C.R.; Pang, V.F.; Chang, H.W. Determination of the Cell Tropism of Serotype 1 Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus Using the Spike Affinity Histochemistry in Paraffin-Embedded Tissues. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 61, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohdatsu, T.; Yamato, H.; Ohkawa, T.; Kaneko, M.; Motokawa, K.; Kusuhara, H.; Kaneshima, T.; Arai, S.; Koyama, H. Vaccine Efficacy of a Cell Lysate with Recombinant Baculovirus-Expressed Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP) Virus Nucleocapsid Protein against Progression of FIP. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 97, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasmoen, T.L.; Kadakia, N.P.; Unfer, R.C.; Fickbohm, B.L.; Cook, C.P.; Chu, H.J.; Acree, W.M. Protection of Cats from Infectious Peritonitis by Vaccination with a Recombinant Raccoon Poxvirus Expressing the Nucleocapsid Gene of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1995, 380, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Deng, X.; Song, J.; Zhu, J.; Yu, L.; Li, G.; Liu, G. An Adenovirus-Vectored Vaccine Based on the N Protein of Feline Coronavirus Elicit Robust Protective Immune Responses. Antivir. Res. 2024, 223, 105825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustaffa-Kamal, F.; Liu, H.; Pedersen, N.C.; Sparger, E.E. Characterization of Antiviral T Cell Responses during Primary and Secondary Challenge of Laboratory Cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus (FIPV). BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.C.; Sekhon, S.S.; Shin, W.R.; Ahn, G.; Cho, B.K.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Modifications of MRNA Vaccine Structural Elements for Improving MRNA Stability and Translation Efficiency. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2022, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asrani, K.H.; Farelli, J.D.; Stahley, M.R.; Miller, R.L.; Cheng, C.J.; Subramanian, R.R.; Brown, J.M. Optimization of MRNA Untranslated Regions for Improved Expression of Therapeutic MRNA. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyler, D.E.; Franco, M.K.; Batool, Z.; Wu, M.Z.; Dubuke, M.L.; Dobosz-Bartoszek, M.; Jones, J.D.; Polikanov, Y.S.; Roy, B.; Koutmou, K.S. Pseudouridinylation of MRNA Coding Sequences Alters Translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 23068–23074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiersdörfer, M.; Boros, G.; Muramatsu, H.; Mahiny, A.; Vlatkovic, I.; Sahin, U.; Karikó, K. A Facile Method for the Removal of DsRNA Contaminant from In Vitro-Transcribed MRNA. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 15, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, A.; Di Canzio, J.; Zurakowski, D. A Statistically Defined Endpoint Titer Determination Method for Immunoassays. J. Immunol. Methods 1998, 221, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, J.D.; Pfeiffer, N.E.; Ingersoll, J.D.; Christianson, K.K.; Landon, R.M.; Selzer, N.L.; Beckenhauer, W.H. Characterization of an Attenuated Temperature Sensitive Feline Infectious Peritonitis Vaccine Virus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1990, 276, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, J.D.; Ingersoll, J.D.; Gast, A.M.; Christianson, K.K.; Selzer, N.L.; Landon, R.M.; Pfeiffer, N.E.; Sharpee, R.L.; Beckenhauer, W.H. Protection against Feline Infectious Peritonitis by Intranasal Inoculation of a Temperature-Sensitive FIPV Vaccine. Vaccine 1990, 8, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombácz, I.; Weissman, D.; Pardi, N. Vaccination with Messenger RNA: A Promising Alternative to DNA Vaccination. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2197, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.W.; Valkenburg, S.A.; Poon, L.L.M.; Wang, L.F. Broad-Spectrum Pan-Genus and Pan-Family Virus Vaccines. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, R.R.; Painter, M.M.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Mathew, D.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; Lundgreen, K.A.; Reynaldi, A.; Khoury, D.S.; Pattekar, A.; et al. MRNA Vaccines Induce Durable Immune Memory to SARS-CoV-2 and Variants of Concern. Science 2021, 374, abm0829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geers, D.; Shamier, M.C.; Bogers, S.; den Hartog, G.; Gommers, L.; Nieuwkoop, N.N.; Schmitz, K.S.; Rijsbergen, L.C.; van Osch, J.A.T.; Dijkhuizen, E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Partially Escape Humoral but Not T-Cell Responses in COVID-19 Convalescent Donors and Vaccinees. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabj1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belik, M.; Liedes, O.; Vara, S.; Haveri, A.; Pöysti, S.; Kolehmainen, P.; Maljanen, S.; Huttunen, M.; Reinholm, A.; Lundberg, R.; et al. Persistent T Cell-Mediated Immune Responses against Omicron Variants after the Third COVID-19 MRNA Vaccine Dose. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1099246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, A.; Lesichkova, S.; Baleva, M.; Nikolova-Vlahova, M.; Kundurzhiev, T.; Kolevski, A.; Naumova, E. Durability of Humoral and Cell-Mediated Immune Response after SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccine Administration. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, D.; Holznagel, E.; Bolla, S.; Hauser, B.; Herrewegh, A.A.P.M.; Horzinek, M.C.; Lutz, H. Placebo-Controlled Evaluation of a Modified Life Virus Vaccine against Feline Infectious Peritonitis: Safety and Efficacy under Field Conditions. Vaccine 1997, 15, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArdle, F.; Tennant, B.; Bennett, M.; Kelly, D.; Gaskell, C. Independent Evaluation of a Modified Live FIPV Vaccine under Experimental Conditions (University of Liverpool Experience). Feline Pract. 1995, 23, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, F.; Corapi, W.; Olsen, C. Independent Evaluation of a Modified Live FIPV Vaccine under Experimental Conditions (Cornell Experience). Feline Pract. 1995, 23, 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- Scherk, M.A.; Ford, R.B.; Gaskell, R.M.; Hartmann, K.; Hurley, K.F.; Lappin, M.R.; Levy, J.K.; Little, S.E.; Nordone, S.K.; Sparkes, A.H. 2013 AAFP Feline Vaccination Advisory Panel Report. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2013, 15, 785–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.L.; Lv, F.L.; Xu, L.D.; Huang, Y.W. Surface Display of Peptides Corresponding to the Heptad Repeat 2 Domain of the Feline Enteric Coronavirus Spike Protein on Bacillus Subtilis Spores Elicits Protective Immune Responses Against Homologous Infection in a Feline Aminopeptidase-N-Transduced Mouse Model. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 925922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Fan, B.; Song, X.; Gao, J.; Guo, R.; Yi, C.; He, Z.; Hu, H.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, L.; et al. PEDV-Spike-Protein-Expressing MRNA Vaccine Protects Piglets against PEDV Challenge. mBio 2024, 15, e02958-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paarlberg, P.L. Updated Estimated Economic Welfare Impacts of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (Pedv); Purdue University: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, D.W.; Lexchin, J. The Costs of Coronavirus Vaccines and Their Pricing. J. R. Soc. Med. 2021, 114, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Vaccine | N/P Ratio | Average Diameter DLS (nm) | Polydispersity Index DLS | Average Diameter NTA (nm) | Encapsulation Efficiency Ribogreen (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 5 | 96.8 | 0.199 | 100.5 | 96.3 |
| 6 | 86.6 | 0.173 | 94.7 | 94.6 | |
| GC | 5 | 122.8 | 0.174 | 96.7 | 93.9 |
| 6 | 117.8 | 0.186 | 95.9 | 96.8 |
| Vaccine–Mouse | IFN-γ | TNF-α | IL-2 | TNF-α + IFN-γ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT-1 | 0.31 | 1.94 | 0.07 | 0.18 |
| WT-2 | 1.78 | 3.22 | 0.2 | 1.59 |
| WT-3 | 0.35 | 1.27 | 0.05 | 0.23 |
| WT-4 | 0.17 | 1.50 | 0.06 | 0.10 |
| GC-1 | 0.14 | 1.71 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| GC-2 | 0.31 | 1.25 | 0.06 | 0.19 |
| GC-3 | 0.54 | 3.72 | 0.04 | 0.39 |
| GC-4 | 0.18 | 1.32 | 0.05 | 0.09 |
| PBS-1 | 0.05 | 1.64 | 0.02 | 0.004 |
| PBS-2 | 0.14 | 2.47 | 0.02 | 0.016 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brostoff, T.; Savage, H.P.; Jackson, K.A.; Dutra, J.C.; Fontaine, J.H.; Hartigan-O’Connor, D.J.; Carney, R.P.; Pesavento, P.A. Feline Infectious Peritonitis mRNA Vaccine Elicits Both Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses in Mice. Vaccines 2024, 12, 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12070705
Brostoff T, Savage HP, Jackson KA, Dutra JC, Fontaine JH, Hartigan-O’Connor DJ, Carney RP, Pesavento PA. Feline Infectious Peritonitis mRNA Vaccine Elicits Both Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses in Mice. Vaccines. 2024; 12(7):705. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12070705
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrostoff, Terza, Hannah P. Savage, Kenneth A. Jackson, Joseph C. Dutra, Justin H. Fontaine, Dennis J. Hartigan-O’Connor, Randy P. Carney, and Patricia A. Pesavento. 2024. "Feline Infectious Peritonitis mRNA Vaccine Elicits Both Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses in Mice" Vaccines 12, no. 7: 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12070705
APA StyleBrostoff, T., Savage, H. P., Jackson, K. A., Dutra, J. C., Fontaine, J. H., Hartigan-O’Connor, D. J., Carney, R. P., & Pesavento, P. A. (2024). Feline Infectious Peritonitis mRNA Vaccine Elicits Both Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses in Mice. Vaccines, 12(7), 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12070705






