An Overview of Nanoparticle-Based Delivery Platforms for mRNA Vaccines for Treating Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cancer Vaccines
2.1. Traditional Tumor Vaccine Types
2.2. mRNA Vaccines
3. Nanotechnology in mRNA Vaccine Platforms
3.1. Lipid-Based Nanoparticle Delivery Systems
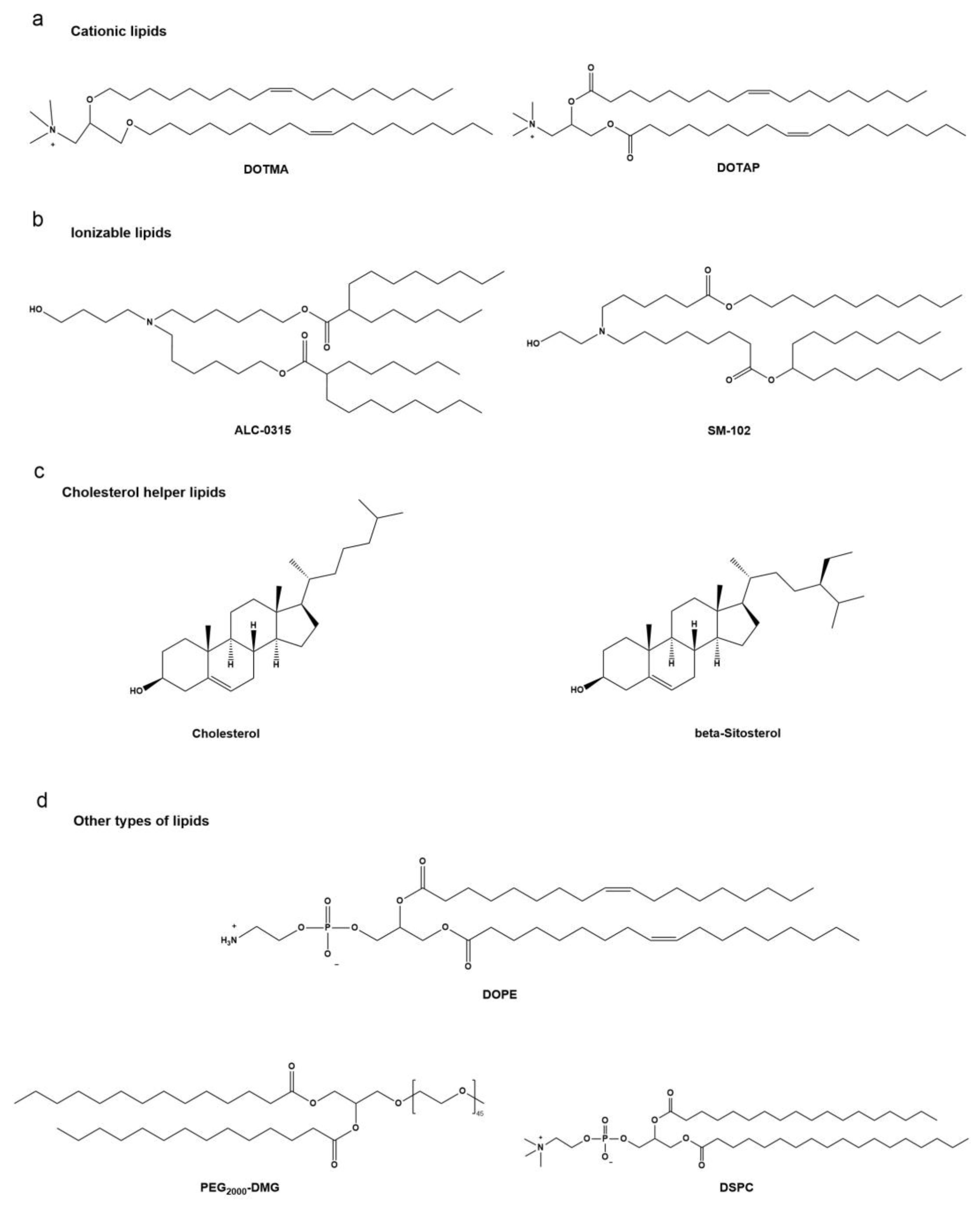
3.1.1. Composition of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles
3.1.2. Stability and Modification of Lipid-Based Nanoparticle Delivery Platforms
3.1.3. Application of Lipid-Based Nanoparticle Delivery Platforms
3.1.4. Disadvantages and Optimization of Lipid-Based Nanoparticle Delivery Platforms
3.1.5. Self-Adjuvants and Adjuvants in Lipid-Based Nanoparticle Delivery Platforms
3.2. Polymer-Based Nanoparticle Delivery Systems
3.3. Protein-Based mRNA Delivery Systems
3.4. Other Formulations Used in mRNA Delivery
3.4.1. Virus-like Particles (VLPs)
3.4.2. Inorganic-Based Nanoparticles
3.4.3. Cationic Nanoemulsions
4. Nanovaccines and Anti-Tumor Immunity
5. Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, G.; Wu, M.; Han, M.-Y. Stimuli-Responsive Hybridized Nanostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1903439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabizon, A.; Isacson, R.; Rosengarten, O.; Tzemach, D.; Shmeeda, H.; Sapir, R. An open-label study to evaluate dose and cycle dependence of the pharmacokinetics of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2008, 61, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aulic, S.; Marson, D.; Laurini, E.; Fermeglia, M.; Pricl, S. 16–Breast cancer nanomedicine market update and other industrial perspectives of nanomedicine. In Nanomedicines for Breast Cancer Theranostics; Thorat, N.D., Bauer, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 371–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Roemeling, C.; Jiang, W.; Chan, C.K.; Weissman, I.L.; Kim, B.Y.S. Breaking Down the Barriers to Precision Cancer Nanomedicine. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arevalo, C.P.; Bolton, M.J.; Le Sage, V.; Ye, N.; Furey, C.; Muramatsu, H.; Alameh, M.-G.; Pardi, N.; Drapeau, E.M.; Parkhouse, K.; et al. A multivalent nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccine against all known influenza virus subtypes. Science 2022, 378, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Duan, X.; Peng, X.; Jin, Z.; Huang, H.; Xiao, W.; Zheng, Q.; Deng, Y.; Fan, N.; Chen, K.; et al. A lipid-based LMP2-mRNA vaccine to treat nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 5357–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranz, L.M.; Diken, M.; Haas, H.; Kreiter, S.; Loquai, C.; Reuter, K.C.; Meng, M.; Fritz, D.; Vascotto, F.; Hefesha, H.; et al. Systemic RNA delivery to dendritic cells exploits antiviral defence for cancer immunotherapy. Nature 2016, 534, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorentzen, C.L.; Haanen, J.B.; Met, O.; Svane, I.M. Clinical advances and ongoing trials on mRNA vaccines for cancer treatment. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, e450–e458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paunovska, K.; Loughrey, D.; Dahlman, J.E. Drug delivery systems for RNA therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, B.B.; Conniot, J.; Avital, A.; Yao, D.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, X.; Sharf-Pauker, N.; Xiao, Y.; Adir, O.; Liang, H.; et al. Nanodelivery of nucleic acids. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.K.; Moynihan, K.D.; Irvine, D.J. Engineering New Approaches to Cancer Vaccines. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezbaruah, R.; Chavda, V.P.; Nongrang, L.; Alom, S.; Deka, K.; Kalita, T.; Ali, F.; Bhattacharjee, B.; Vora, L. Nanoparticle-Based Delivery Systems for Vaccines. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.D.; Coulie, P.G.; Van den Eynde, B.J.; Agostinis, P. Integrating Next-Generation Dendritic Cell Vaccines into the Current Cancer Immunotherapy Landscape. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.-T.; Liu, X.-H.; An, J.-X.; Liang, J.-L.; Li, C.-X.; Jin, X.-K.; Ji, P.; Zhang, X.-Z. Dendritic Cell-Based In Situ Nanovaccine for Reprogramming Lipid Metabolism to Boost Tumor Immunotherapy. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 24947–24960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malonis, R.J.; Lai, J.R.; Vergnolle, O. Peptide-Based Vaccines: Current Progress and Future Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 3210–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, L. Cancer-vaccine trials give reasons for optimism. Nature 2024, 627, S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Tang, T.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Liang, T. mRNA vaccines in disease prevention and treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, H.; Hazama, S.; Shindo, Y.; Nagano, H. Combination treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer using novel vaccine and traditional therapies. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2018, 18, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. mRNA vaccines—A new era in vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, K.; Lazzaro, S.; Lutz, J.; Rauch, S.; Heidenreich, R. mRNA Cancer Vaccines. In Current Strategies in Cancer Gene Therapy; Recent Results in Cancer Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 209, pp. 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, J.; Han, X.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. mRNA vaccine: A potential therapeutic strategy. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlake, T.; Thess, A.; Fotin-Mleczek, M.; Kallen, K.-J. Developing mRNA-vaccine technologies. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, U.; Oehm, P.; Derhovanessian, E.; Jabulowsky, R.A.; Vormehr, M.; Gold, M.; Maurus, D.; Schwarck-Kokarakis, D.; Kuhn, A.N.; Omokoko, T.; et al. An RNA vaccine drives immunity in checkpoint-inhibitor-treated melanoma. Nature 2020, 585, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Jiang, A.Y.; Raji, I.; Atyeo, C.; Raimondo, T.M.; Gordon, A.G.R.; Rhym, L.H.; Samad, T.; MacIsaac, C.; Witten, J.; et al. Enhancing the immunogenicity of lipid-nanoparticle mRNA vaccines by adjuvanting the ionizable lipid and the mRNA. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 6, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y.; He, Y.; Boucetta, H.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; He, W. Lipid carriers for mRNA delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 4105–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.S.; June, C.H.; Langer, R.; Mitchell, M.J. Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Zaks, T.; Langer, R.; Dong, Y. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1078–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Seth, A.; Wibowo, N.; Zhao, C.X.; Mitter, N.; Yu, C.; Middelberg, A.P. Nanoparticle vaccines. Vaccine 2014, 32, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.; Gonzalez-Duarte, A.; O’Riordan, W.D.; Yang, C.C.; Ueda, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Tournev, I.; Schmidt, H.H.; Coelho, T.; Berk, J.L.; et al. Patisiran, an RNAi Therapeutic, for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrowolski, C.; Paunovska, K.; Hatit, M.Z.C.; Lokugamage, M.P.; Dahlman, J.A.-O.X. Therapeutic RNA Delivery for COVID and Other Diseases. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2002022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wei, T.; Cheng, Q. Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) Enables mRNA Delivery for Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2303261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirisala, A.; Uchida, S.; Tockary, T.A.; Yoshinaga, N.; Li, J.; Osawa, S.; Gorantla, L.; Fukushima, S.; Osada, K.; Kataoka, K. Precise tuning of disulphide crosslinking in mRNA polyplex micelles for optimising extracellular and intracellular nuclease tolerability. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajj, K.A.; Whitehead, K.A. Tools for translation: Non-viral materials for therapeutic mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eygeris, Y.; Gupta, M.; Kim, J.; Sahay, G. Chemistry of Lipid Nanoparticles for RNA Delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akanda, M.; Mithu, M.D.S.H.; Douroumis, D. Solid lipid nanoparticles: An effective lipid-based technology for cancer treatment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 86, 104709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, D. Controlling the Growth of Charged-Nanoparticle Chains through Interparticle Electrostatic Repulsion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3984–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenchov, R.; Sasso, J.M.; Zhou, Q.A. PEGylated Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations: Immunological Safety and Efficiency Perspective. Bioconjugate Chem. 2023, 34, 941–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Geetha, K.M. Lipid nanoparticles in the development of mRNA vaccines for COVID-19. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 74, 103553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, L.; Gallarate, M. Lipid nanoparticles: State of the art, new preparation methods and challenges in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, W.; Mäder, K. Solid lipid nanoparticles: Production, characterization and applications. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenchov, R.; Bird, R.; Curtze, A.E.; Zhou, Q. Lipid Nanoparticles─From Liposomes to mRNA Vaccine Delivery, a Landscape of Research Diversity and Advancement. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16982–17015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, L.; Qiang, C.; Tuo, W. Surface engineering of lipid nanoparticles: Targeted nucleic acid delivery and beyond. Biophys. Rep. 2023, 9, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Ibrahim, N.M.; Cheng, K. The Importance of Apparent pKa in the Development of Nanoparticles Encapsulating siRNA and mRNA. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Dyett, B.; Kirby, N.; Cai, X.; Mohamad, M.E.; Bozinovski, S.; Drummond, C.J.; Zhai, J. pH-Dependent Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Mesophase and Ionization Behavior of Phytantriol-Based Ionizable Lipid Nanoparticles. Small 2024, 20, e2309200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Jeong, M.; Hur, S.; Cho, Y.; Park, J.; Jung, H.; Seo, Y.; Woo, H.A.; Nam, K.T.; Lee, K.; et al. Engineered ionizable lipid nanoparticles for targeted delivery of RNA therapeutics into different types of cells in the liver. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X. Ionizable Lipid Nanoparticles for mRNA Delivery. Adv. NanoBiomed Res. 2023, 3, 2300006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alameh, M.-G.; Tombácz, I.; Bettini, E.; Lederer, K.; Sittplangkoon, C.; Wilmore, J.R.; Gaudette, B.T.; Soliman, O.Y.; Pine, M.; Hicks, P.; et al. Lipid nanoparticles enhance the efficacy of mRNA and protein subunit vaccines by inducing robust T follicular helper cell and humoral responses. Immunity 2022, 55, 1136–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos da Silva, J.; Bitencourt Rodrigues, K.; Formoso Pelegrin, G.; Silva Sales, N.; Muramatsu, H.; de Oliveira Silva, M.; Porchia, B.F.M.M.; Moreno, A.C.R.; Aps, L.R.M.M.; Venceslau-Carvalho, A.A.; et al. Single immunizations of self-amplifying or non-replicating mRNA-LNP vaccines control HPV-associated tumors in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabn3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ye, Z.; Huang, C.; Qiu, M.; Song, D.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q. Lipid nanoparticle-mediated lymph node-targeting delivery of mRNA cancer vaccine elicits robust CD8+ T cell response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2207841119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appidi, T.; Sivasankaran, R.P.; Chinchulkar, S.A.; Patra, P.; Murugaiyan, K.; Veeresh, B.; Rengan, A.K. A lipo-polymeric hybrid nanosystem with metal enhanced fluorescence for targeted imaging of metastatic breast cancer. Nanotheranostics 2024, 8, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; You, X.; Wang, X.; Cui, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, F.; Li, M.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Huang, P.; et al. Delivery of mRNA vaccine with a lipid-like material potentiates antitumor efficacy through Toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2005191118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.V.; Connors, T.J.; Farber, D.L. Human T Cell Development, Localization, and Function throughout Life. Immunity 2018, 48, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitte, R.; Rabel, M.; Geczy, R.; Park, S.; Fricke, S.; Koehl, U.; Tretbar, U.S. Lipid nanoparticles outperform electroporation in mRNA-based CAR T cell engineering. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2023, 31, 101139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinlay, C.J.; Vargas, J.R.; Blake, T.R.; Hardy, J.W.; Kanada, M.; Contag, C.H.; Wender, P.A.; Waymouth, R.M. Charge-altering releasable transporters (CARTs) for the delivery and release of mRNA in living animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E448–E456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Amaya, L.; Pi, R.; Wang, S.K.; Ranjan, A.; Waymouth, R.M.; Blish, C.A.; Chang, H.Y.; Wender, P.A. Charge-altering releasable transporters enhance mRNA delivery in vitro and exhibit in vivo tropism. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z. Lipid Nanoparticle-Based Delivery System-A Competing Place for mRNA Vaccines. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 6219–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shaw, R.H.; Stuart, A.S.V.; Greenland, M.; Aley, P.K.; Andrews, N.J.; Cameron, J.C.; Charlton, S.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; Collins, A.M.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of heterologous versus homologous prime-boost schedules with an adenoviral vectored and mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (Com-COV): A single-blind, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boettler, T.; Csernalabics, B.; Salié, H.; Luxenburger, H.; Wischer, L.; Salimi Alizei, E.; Zoldan, K.; Krimmel, L.; Bronsert, P.; Schwabenland, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccination can elicit a CD8 T-cell dominant hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szebeni, J.; Storm, G.; Ljubimova, J.Y.; Castells, M.; Phillips, E.J.; Turjeman, K.; Barenholz, Y.; Crommelin, D.J.A.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A. Applying lessons learned from nanomedicines to understand rare hypersensitivity reactions to mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Meng, C.; Yi, X.; Han, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Ling, Q.; Li, H.; Gu, Z. Fluorinated Lipid Nanoparticles for Enhancing mRNA Delivery Efficiency. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 7825–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Bai, B.; Lei, J.; Yu, X.; Qi, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, F.; Tong, Z.; Yu, G. Biodegradable Lipid-Modified Poly(Guanidine Thioctic Acid)s: A Fortifier of Lipid Nanoparticles to Promote the Efficacy and Safety of mRNA Cancer Vaccines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 11679–11693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Qi, S.; Yu, X.; Gao, X.; Yang, K.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, M.; Bai, B.; Feng, Y.; Lu, M.; et al. Development of Mannosylated Lipid Nanoparticles for mRNA Cancer Vaccine with High Antigen Presentation Efficiency and Immunomodulatory Capability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202318515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Garg, A.; Varshney, V. Recent Updates on Applications of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles for Site-Specific Drug Delivery. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2022, 10, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombácz, I.; Laczkó, D.; Shahnawaz, H.; Muramatsu, H.; Natesan, A.; Yadegari, A.; Papp, T.E.; Alameh, M.-G.; Shuvaev, V.; Mui, B.L.; et al. Highly efficient CD4+ T cell targeting and genetic recombination using engineered CD4+ cell-homing mRNA-LNPs. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 3293–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilsed, C.M.; Sadiq, B.A.; Papp, T.E.; Areesawangkit, P.; Kimura, K.; Noguera-Ortega, E.; Scholler, J.; Cerda, N.; Aghajanian, H.; Bot, A.; et al. IL7 increases targeted lipid nanoparticle-mediated mRNA expression in T cells in vitro and in vivo by enhancing T cell protein translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2319856121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swingle, K.L.; Safford, H.C.; Geisler, H.C.; Hamilton, A.G.; Thatte, A.S.; Billingsley, M.M.; Joseph, R.A.; Mrksich, K.; Padilla, M.S.; Ghalsasi, A.A.; et al. Ionizable Lipid Nanoparticles for In Vivo mRNA Delivery to the Placenta during Pregnancy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 4691–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, M.; Heydarkhan-Hagvall, S.; Tangruksa, B.; González-King Garibotti, H.; Jing, Y.; Maugeri, M.; Kohl, F.; Hultin, L.; Reyahi, A.; Camponeschi, A.; et al. Lipid Nanoparticles Deliver the Therapeutic VEGFA mRNA In Vitro and In Vivo and Transform Extracellular Vesicles for Their Functional Extensions. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2206187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Delcassian, D.; Chahal, J.; Han, J.; Shi, Y.; Sadtler, K.; Gao, W.; Lin, J.; et al. Delivery of mRNA vaccines with heterocyclic lipids increases anti-tumor efficacy by STING-mediated immune cell activation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Barber, G.N. STING signaling and host defense against microbial infection. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Alameh, M.-G.; Butowska, K.; Knox, J.J.; Lundgreen, K.; Ghattas, M.; Gong, N.; Xue, L.; Xu, Y.; Lavertu, M.; et al. Adjuvant lipidoid-substituted lipid nanoparticles augment the immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2023, 18, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffman, R.L.; Sher, A.; Seder, R.A. Vaccine adjuvants: Putting innate immunity to work. Immunity 2010, 33, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, W.; Peppas, N.A. Robotic pills for gastrointestinal-tract-targeted oral mRNA delivery. Matter 2022, 5, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Tang, Z.; Huang, X.; Chen, W.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Kong, N.; Tao, W. Emerging mRNA technologies: Delivery strategies and biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 3828–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begines, B.; Ortiz, T.; Pérez-Aranda, M.; Martínez, G.; Merinero, M.; Argüelles-Arias, F.; Alcudia, A. Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Recent Developments and Future Prospects. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Deng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X. The roles of polymers in mRNA delivery. Matter 2022, 5, 1670–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi-Gaballu, F.; Dehghan, G.; Ghaffari, M.; Yekta, R.; Abbaspour-Ravasjani, S.; Baradaran, B.; Ezzati Nazhad Dolatabadi, J.; Hamblin, M.R. PAMAM dendrimers as efficient drug and gene delivery nanosystems for cancer therapy. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 12, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joubert, F.; Munson, M.J.; Sabirsh, A.; England, R.M.; Hemmerling, M.; Alexander, C.; Ashford, M.B. Precise and systematic end group chemistry modifications on PAMAM and poly(l-lysine) dendrimers to improve cytosolic delivery of mRNA. J. Control. Release 2023, 356, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong, D.; Kesharwani, P.; Deshmukh, R.; Amin, M.C.I.M.; Gupta, U.; Greish, K.; Iyer, A.K. PEGylated PAMAM dendrimers: Enhancing efficacy and mitigating toxicity for effective anticancer drug and gene delivery. Acta Biomater. 2016, 43, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guizze, F.; Serra, C.H.d.R.; Giarolla, J. PAMAM Dendrimers: A Review of Methodologies Employed in Biopharmaceutical Classification. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 2662–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharwade, R.; More, S.; Warokar, A.; Agrawal, P.; Mahajan, N. Starburst pamam dendrimers: Synthetic approaches, surface modifications, and biomedical applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 6009–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, J.S.; Khan, O.F.; Cooper, C.L.; McPartlan, J.S.; Tsosie, J.K.; Tilley, L.D.; Sidik, S.M.; Lourido, S.; Langer, R.; Bavari, S.; et al. Dendrimer-RNA nanoparticles generate protective immunity against lethal Ebola, H1N1 influenza, and Toxoplasma gondii challenges with a single dose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E4133–E4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ta, W.; Hua, R.; Song, J.; Lu, W. A Review on Increasing the Targeting of PAMAM as Carriers in Glioma Therapy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yeudall, W.A.; Yang, H. Folic acid-decorated polyamidoamine dendrimer exhibits high tumor uptake and sustained highly localized retention in solid tumors: Its utility for local siRNA delivery. Acta Biomater. 2017, 57, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, L. Modern methods for delivery of drugs across the blood-brain barrier. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 640–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, Z.; Piao, Y.; Tang, J.; Shen, Y. Glutathione-Specific and Intracellularly Labile Polymeric Nanocarrier for Efficient and Safe Cancer Gene Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 14825–14838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Cázares, H.; Tzeng, S.Y.; Young, N.P.; Abutaleb, A.O.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A.; Green, J.J. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles show high efficacy and specificity at DNA delivery to human glioblastoma in vitro and in vivo. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5141–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosta, P.; Cryer, A.M.; Dion, M.Z.; Shiraishi, T.; Langston, S.P.; Lok, D.; Wang, J.; Harrison, S.; Hatten, T.; Ganno, M.L.; et al. Investigation of the enhanced antitumour potency of STING agonist after conjugation to polymer nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2023, 18, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ma, S.; Qi, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Song, W.; Chen, X. A polyamino acid-based phosphatidyl polymer library for in vivo mRNA delivery with spleen targeting ability. Mater. Horiz. 2024, 11, 2739–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suberi, A.; Grun, M.K.; Mao, T.; Israelow, B.; Reschke, M.; Grundler, J.; Akhtar, L.; Lee, T.; Shin, K.; Piotrowski-Daspit, A.S.; et al. Polymer nanoparticles deliver mRNA to the lung for mucosal vaccination. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabq0603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, Y.; He, X.; Wei, Y.; Yu, Y.; Tian, X. Vaccine adjuvants: Mechanisms and platforms. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzebska, N.T.; Mellett, M.; Frei, J.; Kündig, T.M.; Pascolo, S. Protamine-Based Strategies for RNA Transfection. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, Q.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, M.; Yan, Y. mRNA delivery via non-viral carriers for biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 121020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäumer, N.; Scheller, A.; Wittmann, L.; Faust, A.; Apel, M.; Nimmagadda, S.C.; Geyer, C.; Grunert, K.; Kellmann, N.; Peipp, M.; et al. Electrostatic anti-CD33-antibody-protamine nanocarriers as platform for a targeted treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullard, A. Antibody–oligonucleotide conjugates enter the clinic. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 21, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Gilabert, M.; Artero, R.; López-Castel, A. The myotonic dystrophy type 1 drug development pipeline: 2022 edition. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, S.T.; A Poliskey, J.; Baumhover, N.J.; Rice, K.G. Efficient expression of stabilized mRNA PEG-peptide polyplexes in liver. Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houser, K.V.; Chen, G.L.; Carter, C.; Crank, M.C.; Nguyen, T.A.; Burgos Florez, M.C.; Berkowitz, N.M.; Mendoza, F.; Hendel, C.S.; Gordon, I.J.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a ferritin nanoparticle H2 influenza vaccine in healthy adults: A phase 1 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udhayakumar, V.K.; De Beuckelaer, A.; McCaffrey, J.; McCrudden, C.M.; Kirschman, J.L.; Vanover, D.; Van Hoecke, L.; Roose, K.; Deswarte, K.; De Geest, B.G.; et al. Arginine-Rich Peptide-Based mRNA Nanocomplexes Efficiently Instigate Cytotoxic T Cell Immunity Dependent on the Amphipathic Organization of the Peptide. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitmann, J.S.; Tandler, C.; Marconato, M.; Nelde, A.; Habibzada, T.; Rittig, S.M.; Tegeler, C.M.; Maringer, Y.; Jaeger, S.U.; Denk, M.; et al. Phase I/II trial of a peptide-based COVID-19 T-cell activator in patients with B-cell deficiency. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, X.; Wang, C.; Hua, B.; Hong, S.; Huang, X.; Lin, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, W. PEGylated pH-responsive peptide-mRNA nano self-assemblies enhance the pulmonary delivery efficiency and safety of aerosolized mRNA. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2219870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Haese, S.; Laeremans, T.; Roover, S.D.; Allard, S.D.; Vanham, G.; Aerts, J.L. Efficient Induction of Antigen-Specific CD8+ T-Cell Responses by Cationic Peptide-Based mRNA Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frietze, K.M.; Peabody, D.S.; Chackerian, B. Engineering virus-like particles as vaccine platforms. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 18, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unti, M.J.; Jaffrey, S.R. Highly efficient cellular expression of circular mRNA enables prolonged protein expression. Cell Chem. Biol. 2024, 31, 163–176.e165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Yang, S.; Hu, X.; Yin, D.; Dai, Y.; Qian, X.; Wang, D.; Pan, X.; Hong, J.; Sun, X.; et al. Lentiviral delivery of co-packaged Cas9 mRNA and a Vegfa-targeting guide RNA prevents wet age-related macular degeneration in mice. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Zha, L.; Cabral-Miranda, G.; Bachmann, M.F. Major findings and recent advances in virus-like particle (VLP)-based vaccines. Semin. Immunol. 2017, 34, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Krenger, P.; Krueger, C.C.; Zha, L.; Han, J.; Yermanos, A.; Roongta, S.; Mohsen, M.O.; Oxenius, A.; Vogel, M.; et al. TLR7 Signaling Shapes and Maintains Antibody Diversity Upon Virus-Like Particle Immunization. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 827256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.A.G.; Yang, Z.; Huey-Tubman, K.E.; Cohen, A.A.; Gnanapragasam, P.N.P.; Nakatomi, L.M.; Storm, K.N.; Moon, W.J.; Lin, P.J.C.; West, A.P., Jr.; et al. ESCRT recruitment to SARS-CoV-2 spike induces virus-like particles that improve mRNA vaccines. Cell 2023, 186, 2380–2391.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, X.; Xu, L.; Lin, H.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. Emerging trends in chiral inorganic nanomaterials for enantioselective catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, N.D.; Acar, H.; Wilhelm, S. Concepts of nanoparticle cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and kinetics in nanomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 143, 68–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OuYang, X.; Xu, X.; Qin, Q.; Dai, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Hu, L.; Xiong, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, D. Manganese-Based Nanoparticle Vaccine for Combating Fatal Bacterial Pneumonia. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2304514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, H.F.; Bruxel, F.; Fraga, M.; Schuh, R.S.; Zorzi, G.K.; Matte, U.; Fattal, E. Cationic nanoemulsions as nucleic acids delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 534, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, X.; Li, J.; Gong, L.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, G.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Structural and biochemical characteristics of mRNA nanoparticles determine anti–SARS-CoV-2 humoral and cellular immune responses. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, L.A.; Chan, M.; Shaw, C.A.; Hekele, A.; Carsillo, T.; Schaefer, M.; Archer, J.; Seubert, A.; Otten, G.R.; Beard, C.W.; et al. A cationic nanoemulsion for the delivery of next-generation RNA vaccines. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucouturier, J.; Dupuis, L.; Deville, S.; Ascarateil, S.; Ganne, V. Montanide ISA 720 and 51: A new generation of water in oil emulsions as adjuvants for human vaccines. Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2002, 1, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, R.; Hogan, M.J.; Loré, K.; Pardi, N. Innate immune mechanisms of mRNA vaccines. Immunity 2022, 55, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, G.; Rachamalla, H.K.; Arjunan, P.; Karuppusamy, K.V.; Periyasami, Y.; Mohan, A.; Subramaniyam, K.; Salma, M.; Rajendran, V.; Moorthy, M.; et al. SMART-lipid nanoparticles enabled mRNA vaccine elicits cross-reactive humoral responses against the omicron sub-variants. Mol. Ther. 2024, 32, 1284–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, E.; Ad-El, N.; Hazan-Halevy, I.; Stotsky-Oterin, L.; Peer, D. Targeting cancer with mRNA–lipid nanoparticles: Key considerations and future prospects. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 739–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pine, M.; Arora, G.; Hart, T.M.; Bettini, E.; Gaudette, B.T.; Muramatsu, H.; Tombácz, I.; Kambayashi, T.; Tam, Y.K.; Brisson, D.; et al. Development of an mRNA-lipid nanoparticle vaccine against Lyme disease. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 2702–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, E.; Pardi, N.; Parkhouse, K.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Weissman, D.; Hensley, S.E. Nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccination partially overcomes maternal antibody inhibition of de novo immune responses in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaav5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yin, Y.; Gong, L.; Liang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Ren, C.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Manganese nanodepot augments host immune response against coronavirus. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 1260–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelvanambi, M.; Fecek, R.J.; Taylor, J.L.; Storkus, W.J. STING agonist-based treatment promotes vascular normalization and tertiary lymphoid structure formation in the therapeutic melanoma microenvironment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Bao, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, J.; Chi, X.; Ni, K.; Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. Octapod iron oxide nanoparticles as high-performance T2 contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Saeed, M.; Liu, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Hou, B.; Lai, Y.; et al. Acid-Ionizable Iron Nanoadjuvant Augments STING Activation for Personalized Vaccination Immunotherapy of Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2209910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, L.A.; Sethna, Z.; Soares, K.C.; Olcese, C.; Pang, N.; Patterson, E.; Lihm, J.; Ceglia, N.; Guasp, P.; Chu, A.; et al. Personalized RNA neoantigen vaccines stimulate T cells in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2023, 618, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L. mRNA vaccine for cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, M.; van der Burg, S.H.; Melief, C.J.M.; Bhardwaj, N. Therapeutic cancer vaccines. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 360–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y. Lipid Nanoparticle–mRNA Formulations for Therapeutic Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 4283–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, K.; Liang, L.; Zhang, H. An Overview of Nanoparticle-Based Delivery Platforms for mRNA Vaccines for Treating Cancer. Vaccines 2024, 12, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12070727
Lin Y, Chen X, Wang K, Liang L, Zhang H. An Overview of Nanoparticle-Based Delivery Platforms for mRNA Vaccines for Treating Cancer. Vaccines. 2024; 12(7):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12070727
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yang, Xuehua Chen, Ke Wang, Li Liang, and Hongxia Zhang. 2024. "An Overview of Nanoparticle-Based Delivery Platforms for mRNA Vaccines for Treating Cancer" Vaccines 12, no. 7: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12070727
APA StyleLin, Y., Chen, X., Wang, K., Liang, L., & Zhang, H. (2024). An Overview of Nanoparticle-Based Delivery Platforms for mRNA Vaccines for Treating Cancer. Vaccines, 12(7), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12070727




