Intranasal Sendai Virus Vaccination of Seropositive Children 1 to 2 Years of Age in a Phase I Clinical Trial Boosts Immune Responses Toward Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. Vaccine
2.3. Tests for SeV and Human Pathogens in Nasal Swabs
2.4. Measurement of Serum and Nasal Antibody Levels
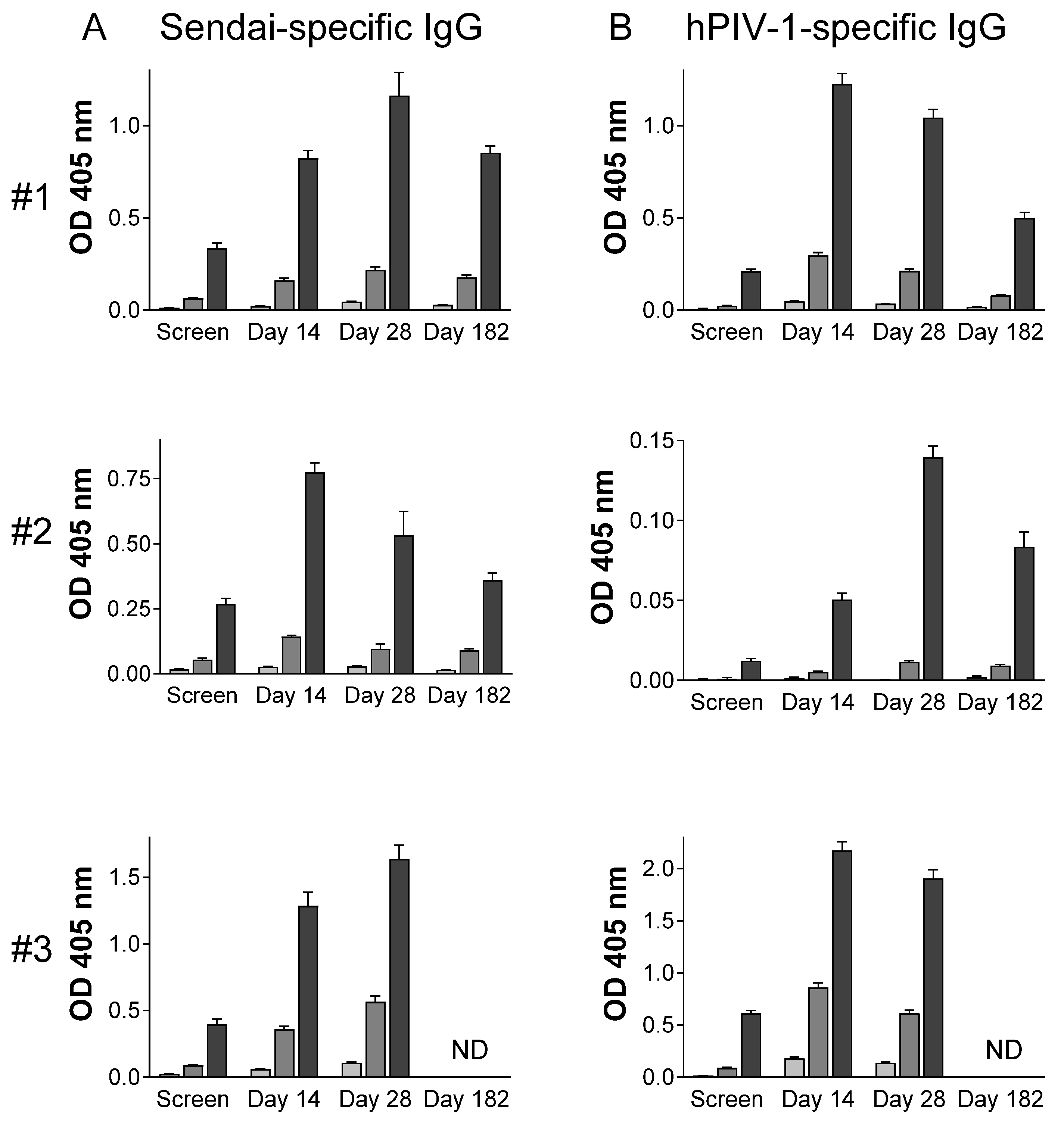
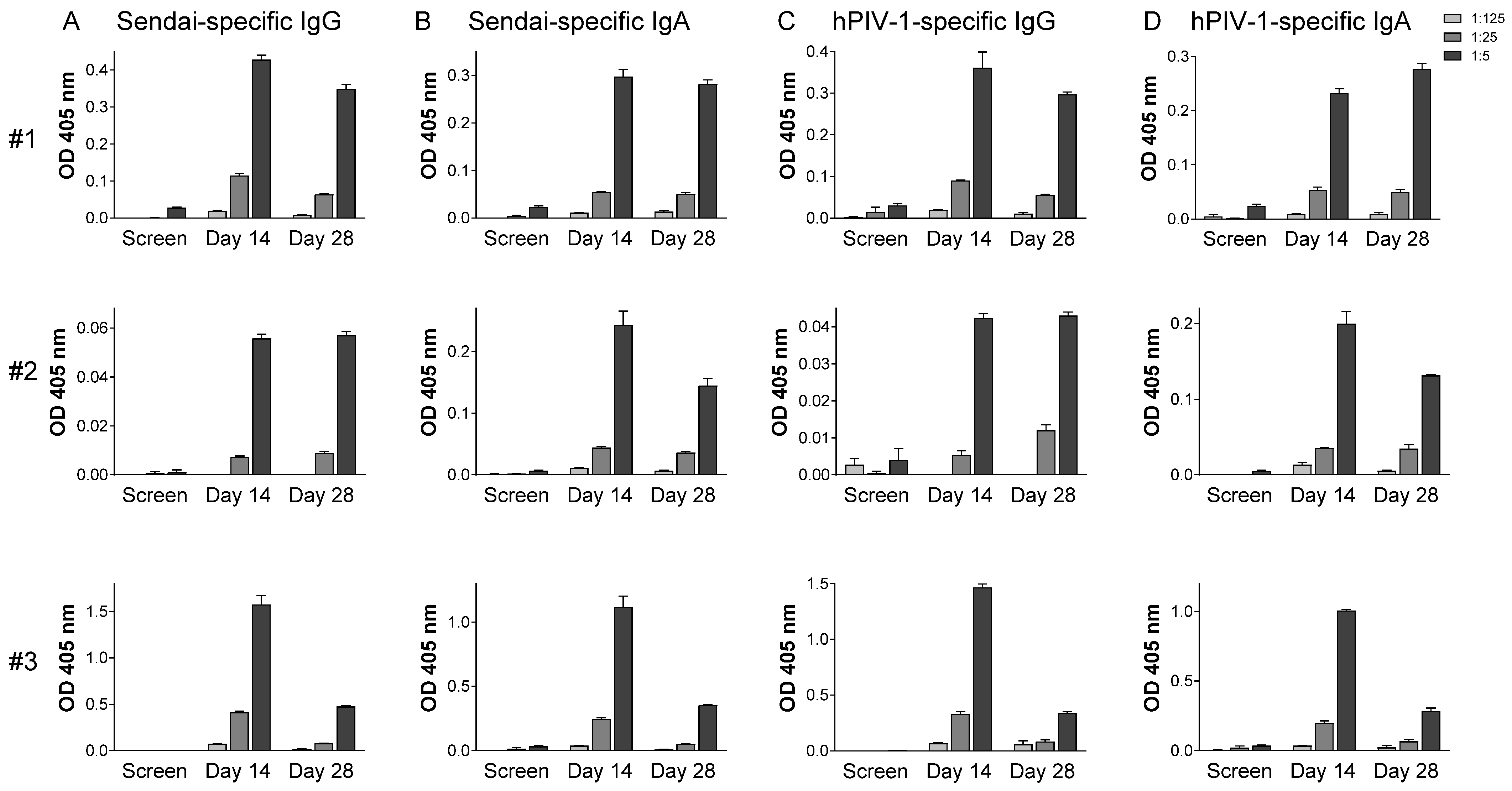
3. Results
3.1. SeV Vaccinations
3.2. Safety Data
3.3. Immunogenicity
4. Discussion
4.1. Vaccine-Induced Immune Responses in Systemic and Mucosal Tissues
4.2. SeV Immunogenicity in the Context of Pre-Existing Immunity
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khales, P.; Razizadeh, M.H.; Ghorbani, S.; Moattari, A.; Saadati, H.; Tavakoli, A. Prevalence of respiratory viruses in children with respiratory tract infections during the COVID-19 pandemic era: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2025, 25, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaunt, E.R.; Harvala, H.; McIntyre, C.; Templeton, K.E.; Simmonds, P. Disease burden of the most commonly detected respiratory viruses in hospitalized patients calculated using the disability adjusted life year (DALY) model. J. Clin. Virol. 2011, 52, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Counihan, M.E.; Shay, D.K.; Holman, R.C.; Lowther, S.A.; Anderson, L.J. Human parainfluenza virus-associated hospitalizations among children less than five years of age in the United States. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2001, 20, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.J.; Hurwitz, J.L. Sendai Virus-Vectored Vaccines That Express Envelope Glycoproteins of Respiratory Viruses. Viruses 2021, 13, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedi, G.R.; Prill, M.M.; Langley, G.E.; Wikswo, M.E.; Weinberg, G.A.; Curns, A.T.; Schneider, E. Estimates of Parainfluenza Virus-Associated Hospitalizations and Cost Among Children Aged Less Than 5 Years in the United States, 1998-2010. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2016, 5, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denny, F.W.; Murphy, T.F.; Clyde, W.A., Jr.; Collier, A.M.; Henderson, F.W. Croup: An 11-year study in a pediatric practice. Pediatrics 1983, 71, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, H.; Nokes, D.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Dherani, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Singleton, R.J.; O’Brien, K.L.; Roca, A.; Wright, P.F.; Bruce, N.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; McAllister, D.A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Madhi, S.A.; Gessner, B.D.; Polack, F.P.; Balsells, E.; Acacio, S.; Aguayo, C.; et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: A systematic review and modelling study. Lancet 2017, 390, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Deloria-Knoll, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Cohen, C.; Ali, A.; Basnet, S.; Bassat, Q.; Brooks, W.A.; Chittaganpitch, M.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infection associated with human metapneumovirus in children under 5 years in 2018: A systematic review and modelling study. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e33–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Deloria-Knoll, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Cohen, C.; Arguelles, V.L.; Basnet, S.; Bassat, Q.; Brooks, W.A.; Echavarria, M.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infection associated with human parainfluenza virus in children younger than 5 years for 2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e1077–e1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbi, H. Nirsevimab: A Review. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2024, 37, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makan-Murphy, N.; Madhi, S.A.; Dangor, Z. Safety, Efficacy, and Effectiveness of Maternal Vaccination against Respiratory Infections in Young Infants. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evong, Y.; Luo, J.; Ye, L.; Fahey, J.; Breeze, J.; Attenborough, R.; Wong, K.; Langley, J.M. Increased respiratory syncytial virus-associated hospitalizations and ambulatory visits in very preterm infants in the first year of life following discontinuation of access to palivizumab. Am. J. Perinatol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumfelt, K.E.; Pike, M.; Stolarczuk, J.E.; Lekander, A.; Lauring, A.S.; Eckert, L.O.; Englund, J.A.; Martin, E.T.; Kachikis, A.B. Maternal-Infant Respiratory Syncytial Virus and Influenza A Virus Antibody Transfer in Preterm and Full-term Infants. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2025, 12, ofae723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gans, H.; DeHovitz, R.; Forghani, B.; Beeler, J.; Maldonado, Y.; Arvin, A.M. Measles and mumps vaccination as a model to investigate the developing immune system: Passive and active immunity during the first year of life. Vaccine 2003, 21, 3398–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, E.J.; Amaro-Carambot, E.; Surman, S.R.; Newman, J.T.; Collins, P.L.; Murphy, B.R.; Skiadopoulos, M.H. Human parainfluenza virus type I (HPIV1) vaccine candidates designed by reverse genetics are attenuated and efficacious in African green monkeys. Vaccine 2005, 23, 4631–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.; Magoffin, R.L.; Shearer, L.A.; Schieble, J.H.; Lennette, E.H. Field evaluation of a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine and a trivalent parainfluenza virus vaccine in a pediatric population. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1969, 89, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulginiti, V.A.; Eller, J.J.; Sieber, O.F.; Joyner, J.W.; Minamitani, M.; Meiklejohn, G. Respiratory virus immunization. I. A field trial of two inactivated respiratory virus vaccines; an aqueous trivalent parainfluenza virus vaccine and an alum-precipitated respiratory syncytial virus vaccine. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1969, 89, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapikian, A.Z.; Mitchell, R.H.; Chanock, R.M.; Shvedoff, R.A.; Stewart, C.E. An epidemiologic study of altered clinical reactivity to respiratory syncytial (RS) virus infection in children previously vaccinated with an inactivated RS virus vaccine. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1969, 89, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Canchola, J.G.; Brandt, C.D.; Pyles, G.; Chanock, R.M.; Jensen, K.; Parrott, R.H. Respiratory syncytial virus disease in infants despite prior administration of antigenic inactivated vaccine. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1969, 89, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karron, R.A.; San Mateo, J.; Thumar, B.; Schaap-Nutt, A.; Buchholz, U.J.; Schmidt, A.C.; Bartlett, E.J.; Murphy, B.R.; Collins, P.L. Evaluation of a Live-Attenuated Human Parainfluenza Type 1 Vaccine in Adults and Children. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2015, 4, e143–e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamed Vp, A.; Choudhari, S.G.; Mudey, A.; Joshi, A. Jenner’s Legacy: How Edward Jenner’s Smallpox Vaccine Changed Public Health. Cureus 2024, 16, e68594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, J.M. Mass vaccination and surveillance/containment in the eradication of smallpox. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 304, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, W.J.; Rota, P.A. Biological feasibility of measles eradication. Virus Res. 2011, 162, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Rizvi, M.A.; Fahim, Z.; Ehsan, M.; Javed, M.; Raza, M.A. Global polio eradication; can we replicate the smallpox success story? Rev. Med. Virol. 2023, 33, e2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, P.D. The polio-eradication programme and issues of the end game. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, G.K.; Bao, Y.; Basler, C.F.; Bavari, S.; Beer, M.; Bejerman, N.; Blasdell, K.R.; Bochnowski, A.; Briese, T.; Bukreyev, A.; et al. Taxonomy of the order Mononegavirales: Update 2017. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2493–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudraraju, R.; Surman, S.; Jones, B.; Sealy, R.; Woodland, D.L.; Hurwitz, J.L. Phenotypes and functions of persistent Sendai virus-induced antibody forming cells and CD8+ T cells in diffuse nasal-associated lymphoid tissue typify lymphocyte responses of the gut. Virology 2011, 410, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sealy, R.; Jones, B.G.; Surman, S.L.; Hurwitz, J.L. Robust IgA and IgG-producing antibody forming cells in the diffuse-NALT and lungs of Sendai virus-vaccinated cotton rats associate with rapid protection against human parainfluenza virus-type 1. Vaccine 2010, 28, 6749–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, N.; Homma, M. Sendai virus. Adv. Virus Res. 1978, 23, 349–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, K.H.; Roberts, A.D.; Woodland, D.L. Cutting edge: Effector memory CD8+ T cells in the lung airways retain the potential to mediate recall responses. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 3338–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanock, R.M.; Murphy, B.R.; Collins, P.L. Parainfluenza viruses. In Fields Virology, 4th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; pp. 1341–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Karron, R.A.; Collins, P.L. Parainfluenza Viruses. In Fields Virology; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Griffin, D.E., Lamb, R.A., Martin, M.A., Roizman, B., Straus, S.E., Eds.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 1497–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Kano, M.; Matano, T.; Kato, A.; Nakamura, H.; Takeda, A.; Suzaki, Y.; Ami, Y.; Terao, K.; Nagai, Y. Primary replication of a recombinant Sendai virus vector in macaques. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousse, T.; Chambers, R.L.; Scroggs, R.A.; Portner, A.; Takimoto, T. Human parainfluenza virus type 1 but not Sendai virus replicates in human respiratory cells despite IFN treatment. Virus Res. 2006, 121, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, E.J.; Cruz, A.M.; Esker, J.; Castano, A.; Schomacker, H.; Surman, S.R.; Hennessey, M.; Boonyaratanakornkit, J.; Pickles, R.J.; Collins, P.L.; et al. Human parainfluenza virus type 1 C proteins are nonessential proteins that inhibit the host interferon and apoptotic responses and are required for efficient replication in nonhuman primates. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8965–8977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Chan Mine, E.; Gaifas, L.; Leyrat, C.; Volchkova, V.A.; Baudin, F.; Martinez-Gil, L.; Volchkov, V.E.; Karlin, D.G.; Bourhis, J.M.; et al. Orthoparamyxovirinae C Proteins Have a Common Origin and a Common Structural Organization. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.S.; Carmichael, J.; Watkinson, R.; Kowdle, S.; Reis, R.A.; Hamane, K.; Jang, J.; Park, A.; Pernet, O.; Khamaikawin, W.; et al. A temperature-sensitive and interferon-silent Sendai virus vector for CRISPR-Cas9 delivery and gene editing in primary human cells. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemitsu, Y.; Ueda, Y.; Kinoh, H.; Hasegawa, M. Immunostimulatory virotherapy using recombinant Sendai virus as a new cancer therapeutic regimen. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 4953–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, M.; Matano, T.; Kato, A.; Shioda, T.; Nagai, Y. Induction of HIV-1-specific neutralizing antibodies in mice vaccinated with a recombinant Sendai virus vector. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 55, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudrov, G.A.; Zainutdinov, S.S.; Grazhdantseva, A.A.; Shipovalov, A.V.; Sivolobova, G.F.; Semenova, A.V.; Merkuleva, I.A.; Shcherbakov, D.N.; Taranov, O.S.; Zaykovskaya, A.V.; et al. [Intranasal vaccine against COVID-19 based on a recombinant variant of the Sendai virus (Paramyxoviridae: Respirovirus) strain Moscow]. Vopr. Virusol. 2023, 68, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Gu, L.; Qiao, D.; Shu, T.; Lowrie, D.B.; Lu, S.H.; Fan, X.Y. Heterologous prime-boost vaccination against tuberculosis with recombinant Sendai virus and DNA vaccines. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.G.; Chen, X.Y.; Qian, P.; Chen, H.C.; Li, X.M. Immunogenicity of a recombinant Sendai virus expressing the capsid precursor polypeptide of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 104, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.V.; Mironova, E.; Garcin, D.; Compans, R.W. Induction of influenza-specific mucosal immunity by an attenuated recombinant Sendai virus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Yonemitsu, Y.; Chou, B.; Yoshida, K.; Tanaka, S.; Hasegawa, M.; Tetsutani, K.; Ishida, H.; Himeno, K.; Hisaeda, H. Efficient protective immunity against Trypanosoma cruzi infection after nasal vaccination with recombinant Sendai virus vector expressing amastigote surface protein-2. Vaccine 2009, 27, 6154–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Hurwitz, J.L.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Takimoto, T.; Boyd, K.; Scroggs, R.A.; Surman, S.; Portner, A.; Slobod, K.S. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) fusion protein expressed by recombinant Sendai virus elicits B-cell and T-cell responses in cotton rats and confers protection against RSV subtypes A and B. Vaccine 2007, 25, 8782–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.G.; Sealy, R.E.; Rudraraju, R.; Traina-Dorge, V.L.; Finneyfrock, B.; Cook, A.; Takimoto, T.; Portner, A.; Hurwitz, J.L. Sendai virus-based RSV vaccine protects African green monkeys from RSV infection. Vaccine 2012, 30, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.G.; Sealy, R.E.; Surman, S.L.; Portner, A.; Russell, C.J.; Slobod, K.S.; Dormitzer, P.R.; DeVincenzo, J.; Hurwitz, J.L. Sendai virus-based RSV vaccine protects against RSV challenge in an in vivo maternal antibody model. Vaccine 2014, 32, 3264–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adderson, E.; Branum, K.; Sealy, R.E.; Jones, B.G.; Surman, S.L.; Penkert, R.; Freiden, P.; Slobod, K.S.; Gaur, A.H.; Hayden, R.T.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an intranasal Sendai virus-based human parainfluenza virus type 1 vaccine in 3- to 6-year-old children. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. CVI 2015, 22, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, R.N.; Cherry, W.R.; Tritch, O.J. Growth characteristics of monkey kidney cell strains LLC-MK1, LLC-MK2, and LLC-MK2(NCTC-3196) and their utility in virus research. J. Exp. Med. 1962, 115, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sealy, R.; Webby, R.J.; Crumpton, J.C.; Hurwitz, J.L. Differential localization and function of antibody-forming cells responsive to inactivated or live-attenuated influenza virus vaccines. Int. Immunol. 2013, 25, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Bomsel, M.; Casanova, J.; Vaerman, J.P.; Mostov, K. Stimulation of transcytosis of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor by dimeric IgA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaras, G.D.; Plotkin, S.A. Complex immune correlates of protection in HIV-1 vaccine efficacy trials. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 275, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszlofy, C.; Fazekas, G.; Barath, Z.; Vajo, Z. Evaluation of Vaccine Immunogenicity-Correlates to Real-World Protection: Influenza. Viruses 2024, 16, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.H.; Min, D.H.; Beom Park, W. Limitations of neutralizing antibody titers in COVID-19 vaccine efficacy trials and a call for additional correlates of protection. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2025, 21, 2473795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britto, C.; Alter, G. The next frontier in vaccine design: Blending immune correlates of protection into rational vaccine design. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2022, 78, 102234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotkin, S.A. Updates on immunologic correlates of vaccine-induced protection. Vaccine 2020, 38, 2250–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunskole Hummel, I.; Huber, B.; Wenzel, J.J.; Jilg, W. Markers of Protection in Children and Adolescents Six to Fourteen Years After Primary Hepatitis B Vaccination in Real Life: A Pilot Study. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bissinger, T.; Genzel, Y.; Liu, X.; Reichl, U.; Tan, W.S. High cell density perfusion process for high yield of influenza A virus production using MDCK suspension cells. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Luo, J.; Li, B.; Ye, Q.; Xu, W.; Gao, F.; Zhou, L.; Lu, W.; Tan, W.S.; Li, X. Reduction in Interferon-Stimulated Genes Contributes to High-Yield Production of Influenza Virus in Suspension MDCK Cells. Vaccines 2024, 12, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adderson, E.; Allison, K.J.; Branum, K.; Sealy, R.E.; Jones, B.G.; Surman, S.L.; Penkert, R.R.; Hayden, R.T.; Russell, C.J.; Portner, A.; et al. Intranasal Sendai Virus Vaccination of Seropositive Children 1 to 2 Years of Age in a Phase I Clinical Trial Boosts Immune Responses Toward Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 1. Vaccines 2025, 13, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040430
Adderson E, Allison KJ, Branum K, Sealy RE, Jones BG, Surman SL, Penkert RR, Hayden RT, Russell CJ, Portner A, et al. Intranasal Sendai Virus Vaccination of Seropositive Children 1 to 2 Years of Age in a Phase I Clinical Trial Boosts Immune Responses Toward Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 1. Vaccines. 2025; 13(4):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040430
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdderson, Elisabeth, Kim J. Allison, Kristen Branum, Robert E. Sealy, Bart G. Jones, Sherri L. Surman, Rhiannon R. Penkert, Randall T. Hayden, Charles J. Russell, Allen Portner, and et al. 2025. "Intranasal Sendai Virus Vaccination of Seropositive Children 1 to 2 Years of Age in a Phase I Clinical Trial Boosts Immune Responses Toward Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 1" Vaccines 13, no. 4: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040430
APA StyleAdderson, E., Allison, K. J., Branum, K., Sealy, R. E., Jones, B. G., Surman, S. L., Penkert, R. R., Hayden, R. T., Russell, C. J., Portner, A., Slobod, K. S., & Hurwitz, J. L. (2025). Intranasal Sendai Virus Vaccination of Seropositive Children 1 to 2 Years of Age in a Phase I Clinical Trial Boosts Immune Responses Toward Human Parainfluenza Virus Type 1. Vaccines, 13(4), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13040430





