Radiomics Detection of Pulmonary Hypertension via Texture-Based Assessments of Cardiac MRI: A Machine-Learning Model Comparison—Cardiac MRI Radiomics in Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cardiac MRI (cMRI)
2.2. CMR Image Analysis
2.3. Right Heart Catheterization
2.4. Image Pre-Processing
2.5. Image Segmentation
2.6. Texture Features Extraction
2.7. Feature Selection
2.8. Model Fitting
2.9. Model Performance Evaluation
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Patient Characteristics
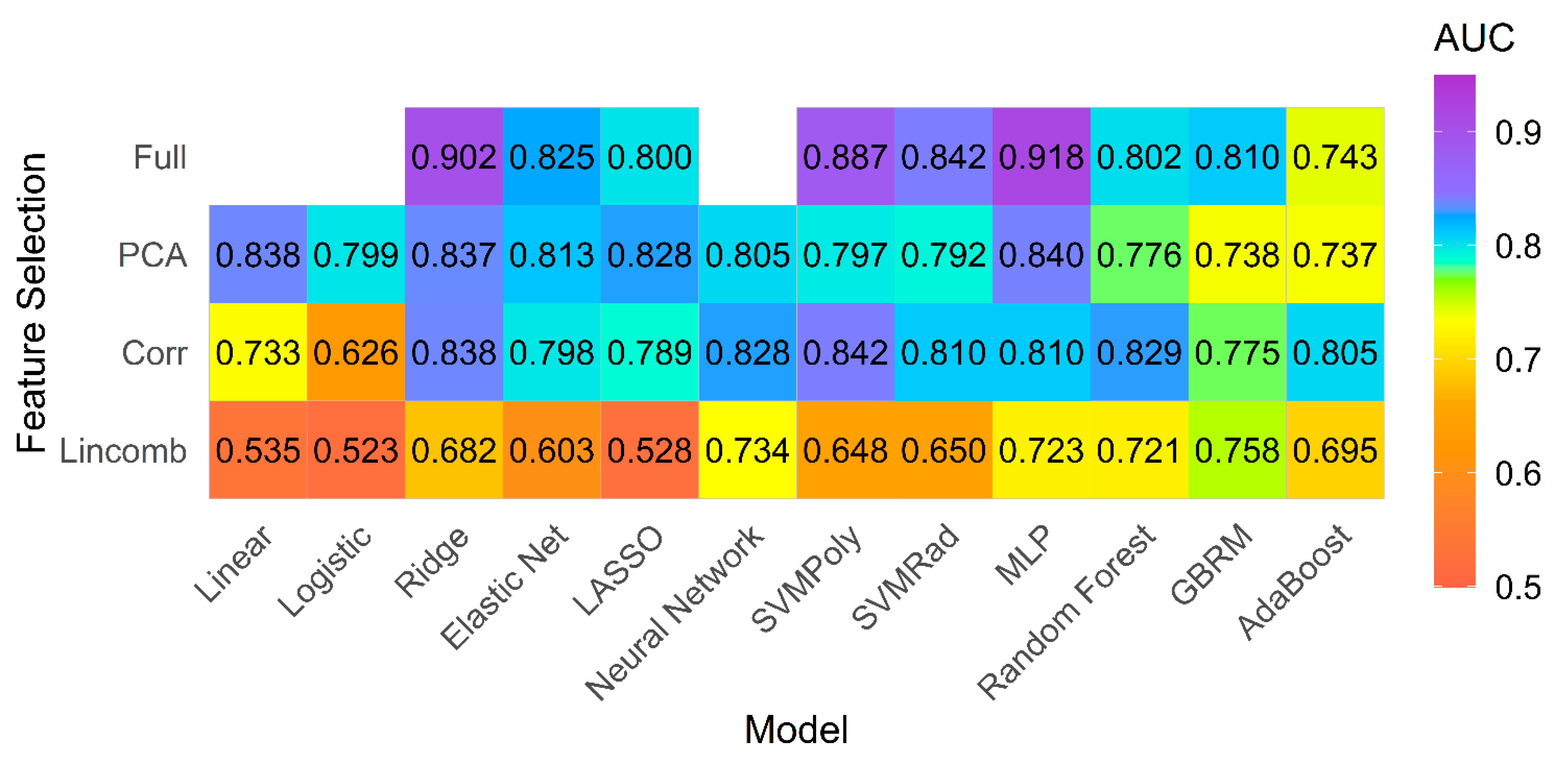
4.2. Model Performance on Primary Analysis
4.3. Model Performance on Subgroup of PH Patients with Preserved Ejection Fraction (EF)
4.4. Overall Performance for Both Groups
4.5. Feature Importance
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wijeratne, D.T.; Lajkosz, K.; Brogly, S.B.; Lougheed, M.D.; Jiang, L.; Housin, A.; Barber, D.; Johnson, A.; Doliszny, K.M.; Archer, S.L. Increasing Incidence and Prevalence of World Health Organization Groups 1 to 4 Pulmonary Hypertension: A Population-Based Cohort Study in Ontario, Canada. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2018, 11, e003973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Bogaard, H.J.; Condliffe, R.; Frantz, R.; Khanna, D.; Kurzyna, M.; Langleben, D.; Manes, A.; Satoh, T.; Torres, F.; et al. Definitions and Diagnosis of Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, D42–D50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonneau, G.; Hoeper, M.M. The revised definition of pulmonary hypertension: Exploring the impact on patient management. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2019, 21, K4–K8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesto, S.; Begic, Z.; Prevljak, S.; Pecar, E.; Kukavica, N.; Begic, E. Pulmonary Hypertension—New Trends of Diagnostic and Therapy. Med. Arch. 2016, 70, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Gerry Coghlan, J.; Khanna, D. Early detection and management of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2012, 21, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakol, M.; Ashraf, S.; Brener, S.J. Risks and complications of coronary angiography: A comprehensive review. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2012, 4, 65–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcasoy, S.M.; Christie, J.D.; Ferrari, V.A.; Sutton, M.S.; Zisman, D.A.; Blumenthal, N.P.; Pochettino, A.; Kotloff, R.M. Echocardiographic assessment of pulmonary hypertension in patients with advanced lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, S.; Shahidi, N.; Gin, K.; Swiston, J. Diagnostic accuracy of echocardiography for pulmonary hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart (Br. Card. Soc.) 2011, 97, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy-Jardin, M.; Ryerson, C.J.; Schiebler, M.L.; Leung, A.N.C.; Wild, J.M.; Hoeper, M.M.; Alderson, P.O.; Goodman, L.R.; Mayo, J.; Haramati, L.B.; et al. Imaging of Pulmonary Hypertension in Adults: A Position Paper from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2021, 298, 203108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, N.; Priya, S.; Bathla, G. Texture Analysis in Cerebral Gliomas: A Review of the Literature. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Park, J.E.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.T.; Kim, H.S. Diffusion radiomics as a diagnostic model for atypical manifestation of primary central nervous system lymphoma: Development and multicenter external validation. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, S.; Agarwal, A.; Ward, C.; Locke, T.; Monga, V.; Bathla, G. Survival prediction in glioblastoma on post-contrast magnetic resonance imaging using filtration based first-order texture analysis: Comparison of multiple machine learning models. Neuroradiol. J. 2021, 1971400921990766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthoff, J.; Nagpal, P.; Sanchez, R.; Gross, T.J.; Lee, C.; Sieren, J.C. Differentiation of non-small cell lung cancer and histoplasmosis pulmonary nodules: Insights from radiomics model performance compared with clinician observers. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.; Ward, C.; Locke, T.; Soni, N.; Maheshwarappa, R.P.; Monga, V.; Agarwal, A.; Bathla, G. Glioblastoma and primary central nervous system lymphoma: Differentiation using MRI derived first-order texture analysis—A machine learning study. Neuroradiol. J. 2021, 1971400921998979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemirli, S.G.; Chopra, S.; Priya, S.; Ward, C.; Locke, T.; Soni, N.; Srivastava, S.; Jones, K.; Bathla, G. Presurgical detection of brain invasion status in meningiomas based on first-order histogram based texture analysis of contrast enhanced imaging. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 198, 106205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neisius, U.; El-Rewaidy, H.; Nakamori, S.; Rodriguez, J.; Manning, W.J.; Nezafat, R. Radiomic Analysis of Myocardial Native T(1) Imaging Discriminates between Hypertensive Heart Disease and Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baessler, B.; Luecke, C.; Lurz, J.; Klingel, K.; Das, A.; von Roeder, M.; de Waha-Thiele, S.; Besler, C.; Rommel, K.P.; Maintz, D.; et al. Cardiac MRI and Texture Analysis of Myocardial T1 and T2 Maps in Myocarditis with Acute versus Chronic Symptoms of Heart Failure. Radiology 2019, 292, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baessler, B.; Luecke, C.; Lurz, J.; Klingel, K.; von Roeder, M.; de Waha, S.; Besler, C.; Maintz, D.; Gutberlet, M.; Thiele, H.; et al. Cardiac MRI Texture Analysis of T1 and T2 Maps in Patients with Infarctlike Acute Myocarditis. Radiology 2018, 289, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, R.; Ganeshan, B.; Fontana, M.; Nasis, A.; Castelletti, S.; Rosmini, S.; Treibel, T.A.; Manisty, C.; Endozo, R.; Groves, A.; et al. Texture analysis of cardiovascular magnetic resonance cine images differentiates aetiologies of left ventricular hypertrophy. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 74, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, S.; Pettit, S. What is ‘normal’ left ventricular ejection fraction? Heart (Br. Card. Soc.) 2020, 106, 1445–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiberg, E.; Sjogren, J.; Ugander, M.; Carlsson, M.; Engblom, H.; Arheden, H. Design and validation of Segment--freely available software for cardiovascular image analysis. BMC Med. Imaging 2010, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baessler, B.; Mannil, M.; Oebel, S.; Maintz, D.; Alkadhi, H.; Manka, R. Subacute and Chronic Left Ventricular Myocardial Scar: Accuracy of Texture Analysis on Nonenhanced Cine MR Images. Radiology 2018, 286, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczypiński, P.M.; Strzelecki, M.; Materka, A.; Klepaczko, A. MaZda—The Software Package for Textural Analysis of Biomedical Images. In Computers in Medical Activity; Kącki, E., Rudnicki, M., Stempczyńska, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alis, D.; Guler, A.; Yergin, M.; Asmakutlu, O. Assessment of ventricular tachyarrhythmia in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with machine learning-based texture analysis of late gadolinium enhancement cardiac MRI. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2020, 101, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strzelecki, M.; Szczypinski, P.; Materka, A.; Klepaczko, A. A software tool for automatic classification and segmentation of 2D/3D medical images. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2013, 702, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Wickham, H. RStudio. Recipes: Preprocessing Tools to Create Design Matrices. (2018). 2020. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/recipes/ (accessed on 28 April 2021).
- Smith, B.J. MachineShop: Machine Learning Models and Tools. R Package Version 2.5.0. 2020. Available online: https://brian-j-smith.github.io/MachineShop/ (accessed on 28 April 2021).
- Bergmeir, C.; Benítez, J.M. Neural Networks in R Using the Stuttgart Neural Network Simulator: RSNNS; American Statistical Association: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2012; Volume 46, p. 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2006; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zihni, E.; Madai, V.I.; Livne, M.; Galinovic, I.; Khalil, A.A.; Fiebach, J.B.; Frey, D. Opening the black box of artificial intelligence for clinical decision support: A study predicting stroke outcome. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amano, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Yanagisawa, F.; Omori, Y.; Matsumoto, N. Relationship between Extension or Texture Features of Late Gadolinium Enhancement and Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4092469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.-N.; Sun, Y.-J.; Xiao, K.-T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.-B.; Kou, Z.-F.; Cheng, J.-L. Texture analysis of magnetic resonance T1 mapping with dilated cardiomyopathy: A machine learning approach. Medicine 2018, 97, e12246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Normal (n = 30) | Pulmonary Hypertension (n = 42) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age a | 49.53 ± 12.72 | 54.45 ± 17.42 | 0.1706 |
| Number of Women (%) | 16 (53.3) | 23 (54.8) | 0.9045 |
| BMI a | 28.82 ± 6.51 | 34.63 ± 9.00 | 0.0022 |
| BSA a | 1.96 ± 0.35 | 2.08 ± 0.27 | 0.1490 |
| RVEF b | 55.50 (53.00–61.00) | 39.50 (29.0–47.75) | <0.0001 |
| LVEF b | 62.00 (58.00–67.00) | 45.50 (21.0–57.83) | <0.0001 |
| RVEDVI b | 72.24 (62.07–82.63) | 97.85 (73.99–120.71) | 0.0003 |
| LVEDVI b | 76.73 (65.06–86.09) | 95.21 (67.45–144.70) | 0.0511 |
| Smoking Status—n (%) | 0.1444 | ||
| Current | 2 (6.67) | 3 (7.14) | |
| Former | 7 (23.33) | 19 (45.24) | |
| Never | 21 (70.00) | 20 (47.62) | |
| DM—n (%) | 0.0663 | ||
| No | 26 (86.67) | 26 (61.90) | |
| Yes | 4 (13.33) | 15 (38.10) | |
| Number with Hypertension (%) | 14 (46.67) | 25 (59.52) | 0.2804 |
| Parameters | Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) (n = 42) |
|---|---|
| PA Pressure a | 37.00 (22–60) |
| PVR a | 2.25 (0.91–9.95) |
| PCW a | 22.00 (9–35) |
| Dur b/n RHC and Cardiac MRI (days) | 6.00 (0–30) |
| WHO Class—n (%) | |
| 1 | 3 (7) |
| 2 | 26 (62) |
| 3 | 1 (2.4) |
| 1 & 2 | 1 (2.4) |
| 1, 2 & 3 | 1 (2.4) |
| 2 & 3 | 9 (21.4) |
| 5 | 1 (2.4) |
| NYHA Class—n (%) | |
| 1 | 2 (4.76) |
| 2 | 5 (11.90) |
| 3 | 23 (54.76) |
| 4 | 6 (14.29) |
| No | 2 (4.76) |
| Not Available | 4 (9.52) |
| Model | Feature Selection | Mean | SD | Median | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLP | full | 0.862 | 0.066 | 0.852 | 0.759 | 0.862 |
| Ridge | full | 0.859 | 0.063 | 0.852 | 0.750 | 0.859 |
| RF | corr | 0.848 | 0.081 | 0.854 | 0.630 | 0.848 |
| Enet | full | 0.843 | 0.094 | 0.854 | 0.667 | 0.843 |
| SVM Poly | full | 0.840 | 0.078 | 0.852 | 0.685 | 0.840 |
| Model | Feature Selection | Mean | SD | Median | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLP | full | 0.918 | 0.089 | 0.917 | 0.708 | 1.000 |
| Ridge | full | 0.902 | 0.129 | 0.958 | 0.542 | 1.000 |
| SVM Poly | full | 0.887 | 0.152 | 0.958 | 0.417 | 1.000 |
| SVM Poly | corr | 0.842 | 0.164 | 0.875 | 0.417 | 1.000 |
| SVM Rad | full | 0.842 | 0.155 | 0.875 | 0.417 | 1.000 |
| Feature Set | Model | Feature Selection | Observed AUC | CV AUC | CV Accuracy | CV Sensitivity | CV Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LV mask (entire group) | MLP | full | 0.998 | 0.862 | 0.783 | 0.794 | 0.767 |
| LV mask (PH subgroup) | MLP | full | 1.000 | 0.918 | 0.808 | 0.740 | 0.853 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Priya, S.; Aggarwal, T.; Ward, C.; Bathla, G.; Jacob, M.; Gerke, A.; Hoffman, E.A.; Nagpal, P. Radiomics Detection of Pulmonary Hypertension via Texture-Based Assessments of Cardiac MRI: A Machine-Learning Model Comparison—Cardiac MRI Radiomics in Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091921
Priya S, Aggarwal T, Ward C, Bathla G, Jacob M, Gerke A, Hoffman EA, Nagpal P. Radiomics Detection of Pulmonary Hypertension via Texture-Based Assessments of Cardiac MRI: A Machine-Learning Model Comparison—Cardiac MRI Radiomics in Pulmonary Hypertension. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(9):1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091921
Chicago/Turabian StylePriya, Sarv, Tanya Aggarwal, Caitlin Ward, Girish Bathla, Mathews Jacob, Alicia Gerke, Eric A. Hoffman, and Prashant Nagpal. 2021. "Radiomics Detection of Pulmonary Hypertension via Texture-Based Assessments of Cardiac MRI: A Machine-Learning Model Comparison—Cardiac MRI Radiomics in Pulmonary Hypertension" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 9: 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091921
APA StylePriya, S., Aggarwal, T., Ward, C., Bathla, G., Jacob, M., Gerke, A., Hoffman, E. A., & Nagpal, P. (2021). Radiomics Detection of Pulmonary Hypertension via Texture-Based Assessments of Cardiac MRI: A Machine-Learning Model Comparison—Cardiac MRI Radiomics in Pulmonary Hypertension. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(9), 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10091921





