Superiority of Direct Oral Anticoagulants over Vitamin K Antagonists in Oncological Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Analysis of Efficacy and Safety Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Process
2.3. Quality Assessment
2.4. Endpoints and Definitions
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Studies and Population
3.2. Quality of the Studies
3.3. Follow Up
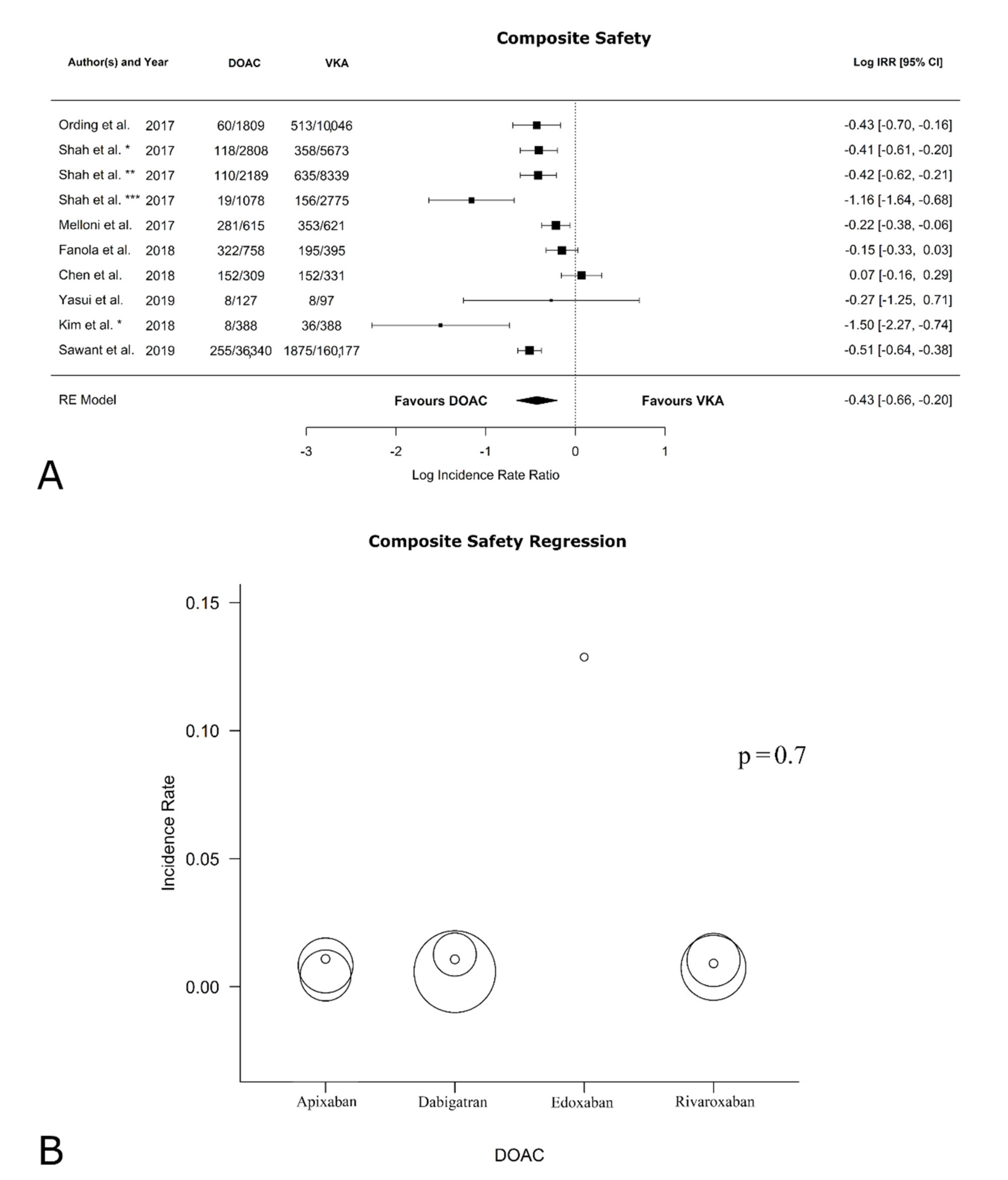
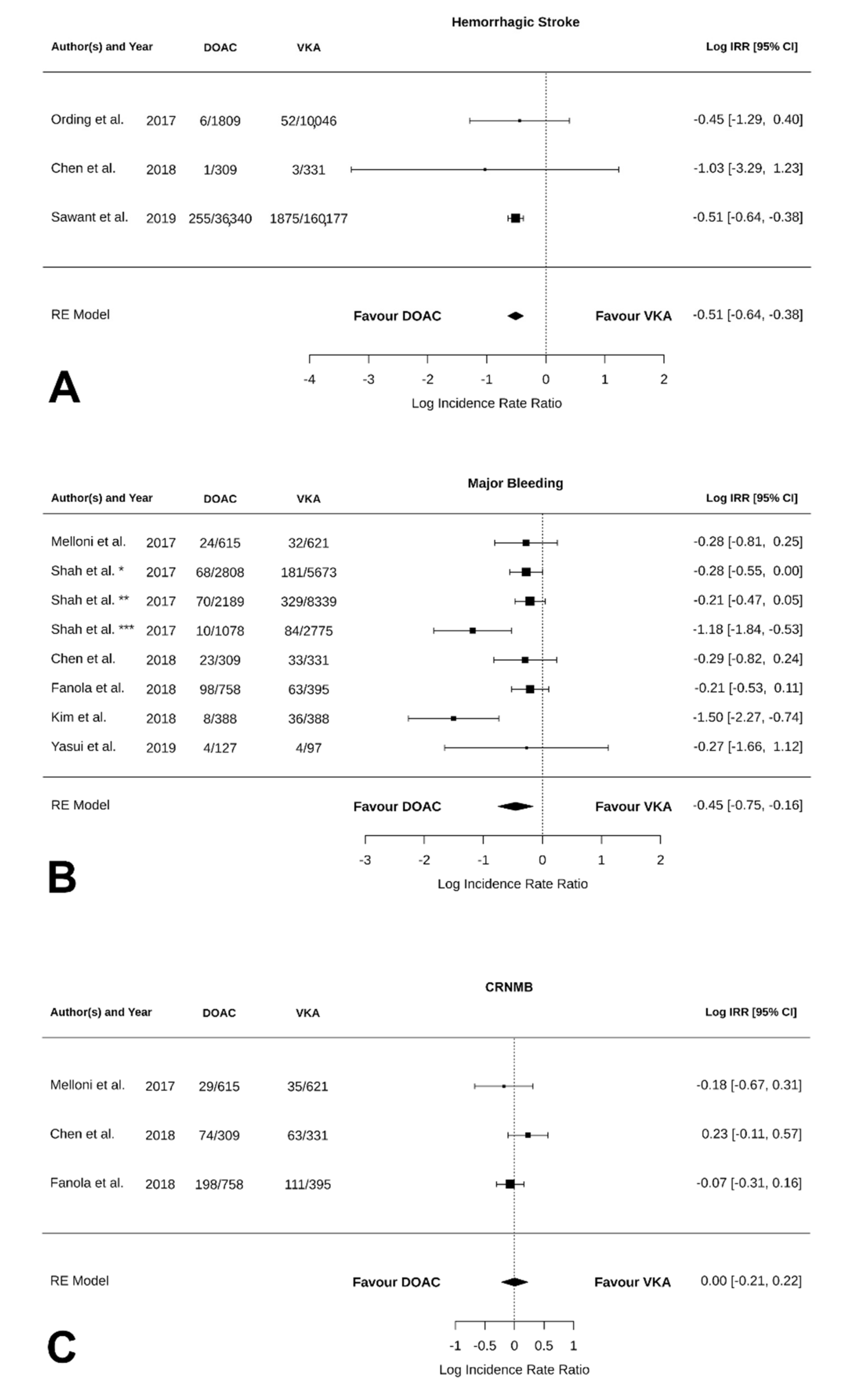
3.4. Safety Outcomes
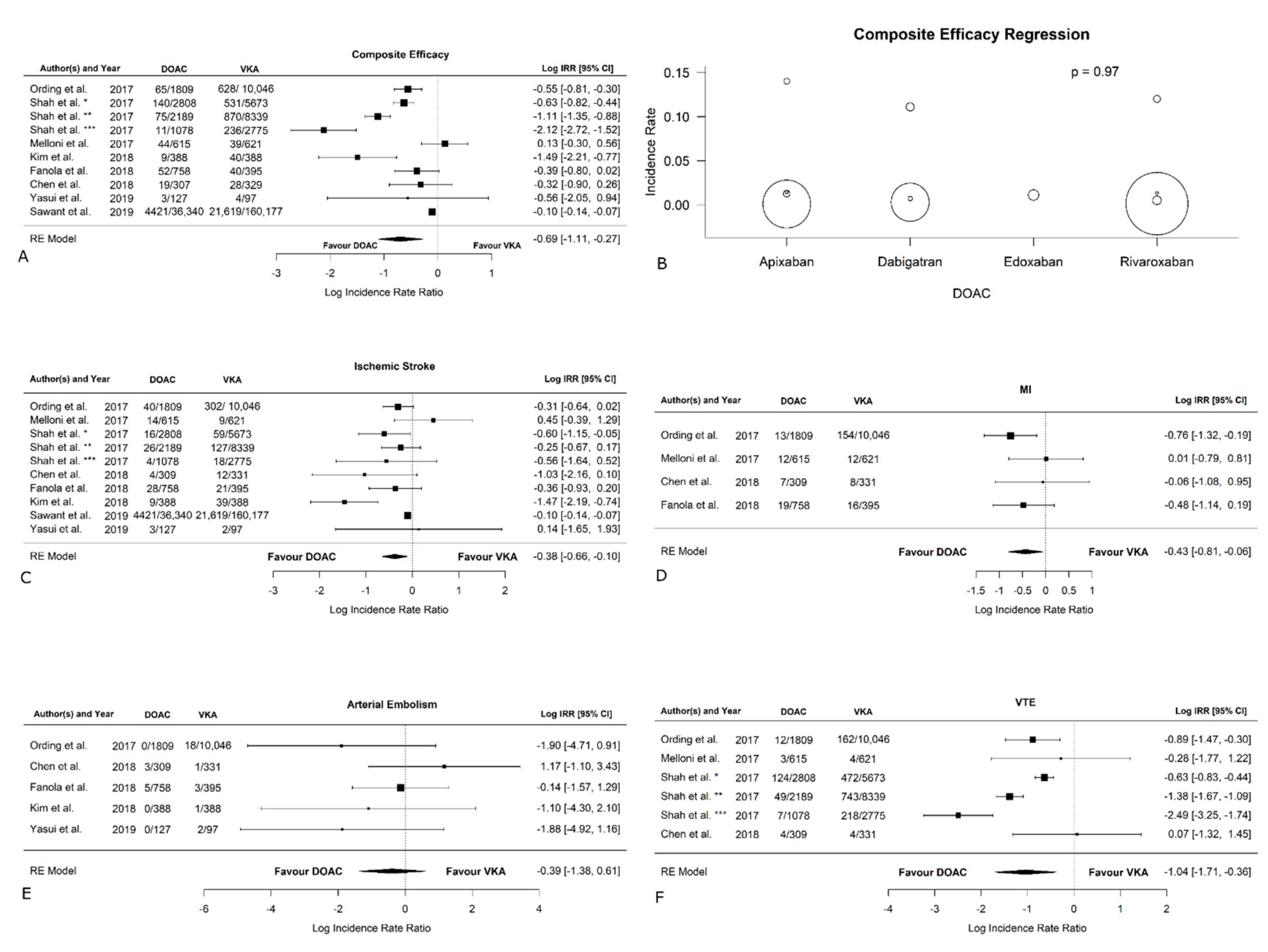
3.5. Efficacy Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vinter, N.; Christesen, A.M.S.; Fenger-Grøn, M.; Tjønneland, A.; Frost, L. Atrial Fibrillation and Risk of Cancer: A Danish Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.P.; Choi, E.K.; Han, K.D.; Park, S.H.; Jung, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Ahn, H.J.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, S.R.; Oh, S. Risk of Atrial Fibrillation According to Cancer Type: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. JACC Cardio Oncol. 2021, 3, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, G.; Versteeg, H.H.; Verschoor, A.J.; Trines, S.A.; Hemels, M.E.W.; Ay, C.; Huisman, M.V.; Klok, F.A. Atrial fibrillation and cancer—An unexplored field in cardiovascular oncology. Blood Rev. 2019, 35, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamorano, J.L.; Gottfridsson, C.; Asteggiano, R.; Atar, D.; Badimon, L.; Bax, J.J.; Cardinale, D.; Cardone, A.; Feijen, E.A.M.; Ferdinandy, P.; et al. The cancer patient and cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 2290–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmakis, D.; Parissis, J.; Filippatos, G. Insights into onco-cardiology: Atrial fibrillation in cancer. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gervaso, L.; Dave, H.; Khorana, A.A. Venous and Arterial Thromboembolism in Patients With Cancer: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review. JACC CardioOncol. 2021, 3, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucà, F.; Parrini, I.; Abrignani, M.G.; Rao, C.M.; Piccioni, L.; Di Fusco, S.A.; Ceravolo, R.; Bisceglia, I.; Riccio, C.; Gelsomino, S.; et al. Management of Acute Coronary Syndrome in Cancer Patients: It’s High Time We Dealt with It. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffel, J.; Verhamme, P.; Potpara, T.S.; Albaladejo, P.; Antz, M.; Desteghe, L.; Haeusler, K.G.; Oldgren, J.; Reinecke, H.; Roldan-Schilling, V.; et al. The 2018 European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the use of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1330–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Tong, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zou, L.; Li, S.; Chen, H. Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants Versus Warfarin in Patients With Cancer and Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.J.; Sharman, J.P.; Ozonoff, A.; Henault, L.E.; Hylek, E.M. Effectiveness of warfarin among patients with cancer. J Gen Intern. Med. 2007, 22, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirmohamed, M. Warfarin: Almost 60 years old and still causing problems. Br. J. Clin. Pharm. 2006, 62, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.K.; Lim, H.; Lee, A.Y.Y. Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Cancer and Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Cardio Oncol. 2021, 3, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Xu, Z.; Luo, J.; Yu, P.; Ma, J.; Yuan, P.; Zhu, W. Effectiveness and Safety of DOACs vs. VKAs in AF Patients with Cancer: Evidence from Randomized Clinical Trials and Observational Studies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 766377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosarla, R.C.; Vaduganathan, M.; Qamar, A.; Moslehi, J.; Piazza, G.; Giugliano, R.P. Anticoagulation Strategies in Patients with Cancer: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1336–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, S.H.; Black, N. The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1998, 52, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, M.R.; Gosain, R.; Donato, A.; Yu, H.; Katel, A.; Bhandari, Y.; Dhital, R.; Kouides, P.A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of apixaban compared to rivaroxaban in acute VTE in the real world. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanola, C.L.; Ruff, C.T.; Murphy, S.A.; Jin, J.; Duggal, A.; Babilonia, N.A.; Sritara, P.; Mercuri, M.F.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; Antman, E.M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Edoxaban in Patients With Active Malignancy and Atrial Fibrillation: Analysis of the ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 Trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyaker, M.R.; Tulman, D.B.; Dimitrova, G.T.; Pin, R.H.; Papadimos, T.J. Arterial embolism. Int. J. Crit. Illn. Inj. Sci. 2013, 3, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navi, B.B.; Howard, G.; Howard, V.J.; Zhao, H.; Judd, S.E.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Iadecola, C.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Kamel, H.; Okin, P.M.; et al. The risk of arterial thromboembolic events after cancer diagnosis. Res. Pr. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 3, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabinger, I.; Riedl, J. Direct oral anticoagulants: Now also for prevention and treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism? Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2017, 2017, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Spittal, M.J.; Pirkis, J.; Gurrin, L.C. Meta-analysis of incidence rate data in the presence of zero events. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2015, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagos, P.G.; Nikolopoulos, G.K. Mixed-effects Poisson regression models for meta-analysis of follow-up studies with constant or varying durations. Int. J. Biostat. 2009, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, A.C.; Kumar, A.; McCray, W.; Tetewsky, S.; Parone, L.; Sridhara, S.; Prakash, M.P.H.; Tse, G.; Liu, T.; Kanwar, N.; et al. Superior safety of direct oral anticoagulants compared to Warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation and underlying cancer: A national veterans affairs database study. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Becker, R.C.; Berkowitz, S.D.; Breithardt, G.; Fox, K.A.A.; Hacke, W.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Mahaffey, K.W.; et al. Efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban vs. warfarin in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and a history of cancer: Observations from ROCKET AF. Eur. Heart J. Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes 2019, 5, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melloni, C.; Dunning, A.; Granger, C.B.; Thomas, L.; Khouri, M.G.; Garcia, D.A.; Hylek, E.M.; Hanna, M.; Wallentin, L.; Gersh, B.J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Apixaban Versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and a History of Cancer: Insights from the ARISTOTLE Trial. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 1440–1448.e1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ording, A.G.; Horváth-Puhó, E.; Adelborg, K.; Pedersen, L.; Prandoni, P.; Sørensen, H.T. Thromboembolic and bleeding complications during oral anticoagulation therapy in cancer patients with atrial fibrillation: A Danish nationwide population-based cohort study. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Norby, F.L.; Datta, Y.H.; Lutsey, P.L.; MacLehose, R.F.; Chen, L.Y.; Alonso, A. Comparative effectiveness of direct oral anticoagulants and warfarin in patients with cancer and atrial fibrillation. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, T.; Shioyama, W.; Oboshi, M.; Oka, T.; Fujita, M. Oral Anticoagulants in Japanese Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Active Cancer. Intern. Med. 2019, 58, 1845–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, T.H.; Uhm, J.S.; Pak, H.N.; Lee, M.H.; Joung, B. Effect of Non-vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation Patients with Newly Diagnosed Cancer. Korean Circ. J. 2018, 48, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Stecker, E.; Warden, B.A. Direct Oral Anticoagulant Use: A Practical Guide to Common Clinical Challenges. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e017559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyakawa, T.; Fukuda, H.; Muraoka, N.; Iida, K.; Kusuhara, M. Cancer-associated cerebral infarction during direct oral anticoagulant treatment in cancer patients: A case series. Int. Cancer Conf. J. 2019, 8, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melloni, C.; Shrader, P.; Carver, J.; Piccini, J.P.; Thomas, L.; Fonarow, G.C.; Ansell, J.; Gersh, B.; Go, A.S.; Hylek, E.; et al. Management and outcomes of patients with atrial fibrillation and a history of cancer: The ORBIT-AF registry. Eur. Heart. J. Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes 2017, 3, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyamany, G.; Alzahrani, A.M.; Bukhary, E. Cancer-associated thrombosis: An overview. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2014, 8, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panageas, K.S.; DeAngelis, L.M. Cancer and Clot: A Deadly Dance. JACC CardioOncol. 2021, 3, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falanga, A.; Marchetti, M.; Vignoli, A. Coagulation and cancer: Biological and clinical aspects. J. Thromb. Haemost 2013, 11, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrugno, A.; Tormoen, G.W.; Kuhn, P.; McCarty, O.J. The prothrombotic activity of cancer cells in the circulation. Blood Rev. 2016, 30, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.G.; Monteiro, R.Q. Activation of blood coagulation in cancer: Implications for tumour progression. Biosci. Rep. 2013, 33, e00064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadir, Y.; Brenner, B.; Gingis-Velitski, S.; Levy-Adam, F.; Ilan, N.; Zcharia, E.; Nadir, E.; Vlodavsky, I. Heparanase induces tissue factor pathway inhibitor expression and extracellular accumulation in endothelial and tumor cells. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 99, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.T.; Gorzelanny, C.; Gebhardt, C.; Pantel, K.; Schneider, S.W. Interplay between coagulation and inflammation in cancer: Limitations and therapeutic opportunities. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2022, 102, 102322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Zhu, D.; Xu, X.; Shen, W.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, G.; Wu, Q. Efficacy and safety of oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation patients with cancer-a network meta-analysis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2020, 25, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Crijns, H.J. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: The euro heart survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest 2010, 137, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallari, I.; Verolino, G.; Romano, S.; Patti, G. Efficacy and Safety of Nonvitamin K Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Cancer: A Study-Level Meta-Analysis. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boriani, G.; Lee, G.; Parrini, I.; Lopez-Fernandez, T.; Lyon, A.R.; Suter, T.; Van der Meer, P.; Cardinale, D.; Lancellotti, P.; Zamorano, J.L.; et al. Anticoagulation in patients with atrial fibrillation and active cancer: An international survey on patient management. Council of Cardio-Oncology of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessler, J.D.; Grip, L.T.; Mendell, J.; Giugliano, R.P. The P-glycoprotein transport system and cardiovascular drugs. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 2495–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walenga, J.M.; Adiguzel, C. Drug and dietary interactions of the new and emerging oral anticoagulants. Int. J. Clin. Pr. 2010, 64, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.C.; Pinto, D.J.; Zhang, D. Preclinical discovery of apixaban, a direct and orally bioavailable factor Xa inhibitor. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2011, 31, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, N.; Colombo, E.; Tenconi, M.; Baldessin, L.; Corsini, A. Drug-Drug Interactions of Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs): From Pharmacological to Clinical Practice. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Skalij, P.; Tokajuk, P.; Politynska, B.; Wojtukiewicz, A.M.; Tucker, S.C.; Honn, K.V. Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Cancer Patients. Time for a Change in Paradigm. Cancers 2020, 12, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerster, K.I.; Hermann, S.; Mikus, G.; Haefeli, W.E. Drug-Drug Interactions with Direct Oral Anticoagulants. Clin. Pharm. 2020, 59, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffel, J.; Collins, R.; Antz, M.; Cornu, P.; Desteghe, L.; Haeusler, K.G.; Oldgren, J.; Reinecke, H.; Roldan-Schilling, V.; Rowell, N.; et al. 2021 European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the Use of Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Europace 2021, 23, 1612–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Author | Year | Study Design | No. of Patients | Age | M/F | Cancer (Active/Remote) | Definition of Active/Remote Cancer | Anticoagulant | Type of VKA | Type of DOAC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VKA | DOAC | W | O | A | R | D | E | |||||||||
| Ording et al. [29] | 2017 | OS | 11,855 | - | - | Active | Active: diagnosed < 2 years before the index date (=redemption date of the first reimbursed prescription of anticoagulants) | 10,046 (84.7) | 1809 (15.3) | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Shah et al. [30] | 2017 | RCS (PS-matched) | 16,096 | - | - | Active | Active: use of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or cancer surgery within 6 months prior to the start of anticoagulation | 10,021 (62.3) | 6075 (37.7) | 10,021 (100) | 0 (0) | 1078 (17.6) | 2808 (46.2) | 2189 (36.2) | 0 (0) | |
| Melloni et al. [28] | 2017 | Post-hoc analysis from ARISTOTLE Trial (RCT) | 1236 | 74 (68–80) * 75 (69–80) † | 126/31 * 1004/75 † | Active: 157 (12.7) Remote: 1079 (87.3) | Active: malignancy other than basal or squamous cell skin cancer treated within the past 1 year Remote: medical disease history question malignancy other than basal or squamous cell skin cancer | 621 (50.2) | 615 (49.8) | 621 (100) | 0 (0) | 615 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Kim et al. [32] | 2018 | RCS (PS-matched) | 776 | - | - | Active | Newly diagnosed | 388 (50) | 388 (50) | 388 (100) | 0 (0) | 138 (35.6) | 110 (28.3) | 140 (36.1) | 0 (0) | |
| Fanola et al. [19] | 2018 | Post-hoc analysis from ENGAGE-AF TIMI 48 Trial (RCT) | 1153 | 75 (68–79) | 794/359 | Active | Active: new or recurrent malignancies other than nonmelanoma localized skin cancer, benign tumors, and in situ precancerous lesions | 395 (34.3) | 758 (65.7) | 395 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 758 (100) | |
| Chen et al. [27] | 2018 | Post hoc analysis from ROCKET AF Trial (RCT) | 640 | 77 (72–81) | 423/217 | Active: 50 (7.8) Remote: 590 (92.2) | Active: patients receiving cancer treatment with hormonal or chemotherapeutic agents Remote: history of any cancer other than benign, pre-cancer, skin (except melanoma), basal, and squamous | 331 (52) | 309 (48) | 331 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 309 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Yasui et al. [31] | 2019 | RCS | 224 | 72.7 ± 7.1 | 196/28 | Active | Evidence of neoplasm on imaging or ongoing cancer therapy | 97 (43.3) | 127 (56.7) | 97 (100) | 0 (0) | 46 (36.2) | 44 (34.6) | 25 (19.7) | 12 (9.4) | |
| Sawant et al. [26] | 2019 | ROS | 196,517 | 76 ± 10 | 192,787/3730 | Active | NS | 160,177 (81.5) | 36,340 (18.5) | 160,177 (100) | 0 (0) | 9495 (4.8) | 11,877 (6) | 14,968 (7.6) | 0 (0) | |
| Characteristics of the Population | ||||||||||||||||
| Author | Age (Average) | Gender | HTN | Diabetes | CHF | Pulmonary Disease | Renal Disease | Liver Disease | Metastasis | Hematological Malignancies | ||||||
| Female | Male | |||||||||||||||
| Ording et al. [29] | VKA n = 10,046 DOAC n = 1809 | 77 (70–83) | n = 4509 45% | n = 5537 55% | n = 6012 60% | n = 1434 14% | n = 901 9.0% | n = 2802 28% | n = 474 4.7% | n = 77 0.8% | n = 278 2.8% | n = 3.4 | ||||
| Shah et al. [30] | VKA n = 10,021 | 75.4 | 40% | |||||||||||||
| DOAC n = 6075 | 74.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Melloni et al. [28] | active cancer | 74 (68–80) | n = 31 19.7% | n = 132 84.1% | n = 40 25.5% | |||||||||||
| remote cancer | 75 (69–80) | n = 374 34.7% | n = 933 86.5% | n = 303 28.1% | ||||||||||||
| VKA n = 621 DOAC n = 615 | ||||||||||||||||
| Kim et al. [32] | VKA n = 1079 | 67.5 | n = 387 31.5% | n = 804 74.5% | n = 403 37.3% | n = 295 27.3% | n = 127 11.8% | n = 153 14.2% | ||||||||
| DOAC n = 572 | 74.2 | n = 180 35.9% | n = 485 84.8% | n = 233 40.7% | n = 107 18.7% | n = 35 6.1% | n = 73 12.7% | |||||||||
| Fanola et al. [19] | VKA n = 395 DOAC n = 758 | 75 | n = 794 68.9% | n = 1091 94.6% | n = 445 38.6% | n = 594 51.5% | ||||||||||
| Chen et al. [33] | VKA n = 331 DOAK n = 309 | 77 (72–81) | n = 217 34% | n = 574 90% | n = 286 45% | n = 338 53% | 111 17% | n = 4 <0.1% | n = 33 5.2% | |||||||
| Yasui et al. [31] | VKA n = 97 DOAC n = 127 | 72.7 (±7.1) | n = 28 12.5% | n = 48 22.2% | n = 7 3.1% | |||||||||||
| Sawant et al. [26] | VKA n = 160,177 DOAC n = 36,340 | 76 (±10) | 98.1% | 91.1% | 57.0% | 38.7% | ||||||||||
| Author | Year | Ischemic Stroke | Myocardial Infarction | Venous Thromboembolism | Major Bleeding | Major or CRNM Bleeding | Any Bleeding (Major, CRNM, Minor) | Hemorrhagic Stroke | All-Cause Death | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VKA | DOAC | VKA | DOAC | VKA | DOAC | VKA | DOAC | VKA | DOAC | VKA | DOAC | VKA | DOAC | VKA | DOAC | ||
| Ording et al. [29] | 2017 | 1426 (14.2) | 188 (10.4) | 739 (7.4) | 65 (3.6) | 527 (5.2) | 30 (1.7) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 229 (2.3) | 10 (0.6) | - | - |
| Shah et al. [30] | 2017 | 59 (1.0) * 127 (1.5) † 18 (0.6) ‡ | 46 (0.8) | - | - | 472 (8.3) * 743 (8.9) † 218 (7.9) ‡ | 180 (3.0) | - | - | 2245 (39.6) * 3273 (39.2) † 551 (19.9) ‡ | 148 (2.4) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Melloni et al. [28] | 2017 | 9 (0.8) | 14 (1.3) | 12 (1.1) | 12 (1.1) | 4 (0.4) | 3 (0.3) | - | - | 67 (6.9) | 53 (5.5) | 245 (32.2) | 204 (26.5) | 9 (0.9) | 0 (0) | 42 (3.6) | 54 (4.7) |
| Kim et al. [32] | 2018 | 39 (5.5) | 9 (1.3) | - | - | - | - | 8 (1.2) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 93 (13.3) | 41 (6.1) |
| Fanola et al. [19] | 2018 | 21 (2.1) | 28 (3.7) | 16 (1.6) | 19 (2.5) | - | - | 63 (8.2) | 98 (12.9) | 174 (27.9) | 296 (39.1) | 195 (33.8) | 322 (42.5) | - | - | 120 (11.5) | 241 (31.8) |
| Chen et al. [27] | 2018 | 12 (2.0) | 4 (0.7) | 7 (1.2) | 8 (1.4) | 4 (0.6) | 4 (0.7) | 33 (6.4) | 23 (4.7) | 96 (21.6) | 97 (23.6) | 152 (40.8) | 152 (46.6) | 3 (0.6) | 1 (0.2) | 48 (8.0) | 32 (5.4) |
| Yasui et al. [31] | 2019 | 2 (2.1) | 3 (2.4) | - | - | - | - | 4 (4.1) | 4 (3.1) | - | - | - | - | 1 (1.0) | 0 (0) | - | - |
| Sawant et al. [26] | 2019 | 21,619 (13.5) | 4421 (12.2) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1875 (1.2) | 255 (0.7) | - | - |
| Active + Remote Cancer | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRR [95%CI] | p-Value IRR | I2 (%) | p-Value I2 | Egger’s Intercept [95%CI] | p-Value Egger’s Test | |
| Thromboembolic events | −0.77 [−1.22, −0.33] | 0.0007 | 92.12 | <0.0001 | −0.64 [−1.30, 0.01] | 0.01 |
| Ischemic stroke | −0.45 [−0.77, −0.13] | 0.006 | 52.59 | 0.05 | −0.26 [−0.91, 0.39] | 0.07 |
| Bleeding | −0.43 [−0.70, −0.16] | 0.002 | 89.52 | <0.0001 | 0.03 [−0.32, 0.38] | 0.01 |
| Hemorrhagic stroke | −0.52 [−1.31, 0.28] | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.64 | −0.1 [NA, NA] * | NA * |
| Active Cancer Only | ||||||
| IRR [95%CI] | p-Value IRR | I2 (%) | p-Value I2 | Egger’s Intercept [95%CI] | p-Value Egger’s Test | |
| Thromboembolic events | −0.94 [−1.36, −0.52] | <0.0001 | 89.25 | <0.0001 | −0.61 [−1.14, −0.08] | 0.00 |
| Ischemic stroke | −0.51 [−0.81, −0.21] | 0.0009 | 39.50 | 0.14 | −0.18 [−0.69, 0.32] | 0.03 |
| Bleeding | −0.50 [−0.79, −0.21] | 0.0008 | 84.76 | 0.0003 | −0.12 [−0.50, 0.26] | 0.01 |
| Hemorrhagic stroke † | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parrini, I.; Lucà, F.; Rao, C.M.; Parise, G.; Micali, L.R.; Musumeci, G.; La Meir, M.; Colivicchi, F.; Gulizia, M.M.; Gelsomino, S. Superiority of Direct Oral Anticoagulants over Vitamin K Antagonists in Oncological Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Analysis of Efficacy and Safety Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5712. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195712
Parrini I, Lucà F, Rao CM, Parise G, Micali LR, Musumeci G, La Meir M, Colivicchi F, Gulizia MM, Gelsomino S. Superiority of Direct Oral Anticoagulants over Vitamin K Antagonists in Oncological Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Analysis of Efficacy and Safety Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5712. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195712
Chicago/Turabian StyleParrini, Iris, Fabiana Lucà, Carmelo Massimiliano Rao, Gianmarco Parise, Linda Renata Micali, Giuseppe Musumeci, Mark La Meir, Furio Colivicchi, Michele Massimo Gulizia, and Sandro Gelsomino. 2022. "Superiority of Direct Oral Anticoagulants over Vitamin K Antagonists in Oncological Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Analysis of Efficacy and Safety Outcomes" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5712. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195712
APA StyleParrini, I., Lucà, F., Rao, C. M., Parise, G., Micali, L. R., Musumeci, G., La Meir, M., Colivicchi, F., Gulizia, M. M., & Gelsomino, S. (2022). Superiority of Direct Oral Anticoagulants over Vitamin K Antagonists in Oncological Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Analysis of Efficacy and Safety Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5712. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195712





