Correlation of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and the Dilation of the Basilar Artery with the Potential Role of Vascular Compromise in the Pathophysiology of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
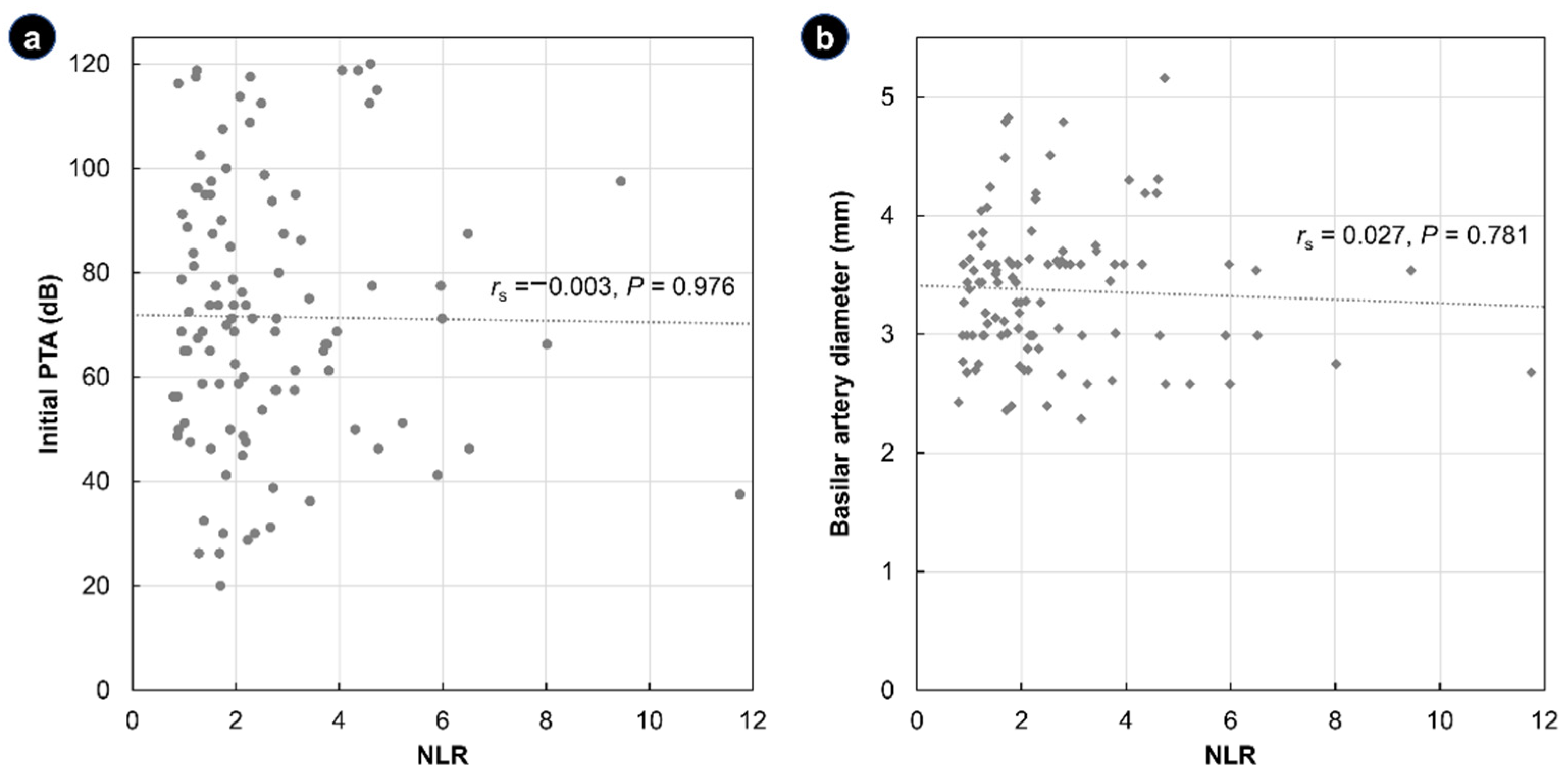
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hughes, G.B.; Freedman, M.A.; Haberkamp, T.J.; Guay, M.E. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 1996, 29, 393–405. [Google Scholar]
- Stachler, R.J.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Archer, S.M.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Schwartz, S.R.; Barrs, D.M.; Brown, S.R.; Fife, T.D.; Ford, P.; Ganiats, T.G.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 146, S1–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schreiber, B.E.; Agrup, C.; Haskard, D.O.; Luxon, L.M. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Lancet 2010, 375, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, M.; Kanzaki, S.; Minami, S.; Kikuchi, J.; Kanzaki, J.; Sato, H.; Ogawa, K. Correlations of inflammatory biomarkers with the onset and prognosis of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merchant, S.N.; Durand, M.L.; Adams, J.C. Sudden deafness: Is it viral? ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2008, 70, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, H.; Hibino, M.; Iino, M.; Matsuura, K.; Kamei, T. Unilateral hearing disturbance could be an isolated manifestation prior to ipsilateral anterior inferior cerebellar artery infarction. Intern. Med. 2008, 47, 795–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amarenco, P.; Rosengart, A.; DeWitt, L.D.; Pessin, M.S.; Caplan, L.R. Anterior inferior cerebellar artery territory infarcts. Mechanisms and clinical features. Arch. Neurol. 1993, 50, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belal, A., Jr. Pathology of vascular sensorineural hearing impairment. Laryngoscope 1980, 90, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H. Effects of circulatory disturbance on the cochlea. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 1991, 53, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Furukawa, M.; Kumagai, M.; Takahashi, E.; Matsuura, K.; Katori, Y.; Shimomura, A.; Kobayashi, T. Defibrinogenation therapy for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss in comparison with high-dose steroid therapy. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2003, 123, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, J.; Ha, R.; Sunwoo, W. Heparin therapy as adjuvant treatment for profound idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, T.; Kubo, T.; Okumura, S.; Naramura, H.; Nishimura, M.; Okusa, M.; Matsunaga, T. Hearing recovery in sudden deafness patients using a modified defibrinogenation therapy. Acta Otolaryngol. Suppl. 1993, 501, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, S.; Celik, T.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Ozturk, C.; Demirkol, S.; Aparci, M.; Iyisoy, A. The Relation Between Atherosclerosis and the Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio. Clin. Appl. Thromb./Hemost. Off. J. Int. Acad. Clin. Appl. Thromb./Hemost. 2016, 22, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chollangi, S.; Rout, N.K.; Patro, S. A Study on Correlation of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Red Cell Distribution Width with Microalbuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2022, 70, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zinellu, A.; Zinellu, E.; Pau, M.C.; Carru, C.; Pirina, P.; Fois, A.G.; Mangoni, A.A. A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonacera, A.; Stancanelli, B.; Colaci, M.; Malatino, L. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio: An Emerging Marker of the Relationships between the Immune System and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Song, S.P.; Jiang, Y.D. Association between routine hematological parameters and sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A meta-analysis. J. Otol. 2021, 16, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Wu, J. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts diagnosis and prognosis of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e12492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, J. The Roles Played by Blood Inflammatory Parameters in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Ear. Nose Throat J. 2021. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Park, B.; Choi, H.G.; Kong, I.G.; Song, H.J.; Kim, H.J. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in children with sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A retrospective study. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2017, 137, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, T.; Teli, S.; Rijal, J.; Bhat, H.; Raza, M.; Khoueiry, G.; Meghani, M.; Akhtar, M.; Costantino, T. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and cardiovascular diseases: A review. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2013, 11, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Sohn, J.H.; Choi, H.C. Vertebrobasilar angulation and its association with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Med. Hypotheses 2012, 79, 202–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.M.; Chung, C.-S.; Bang, O.Y.; Yong, S.W.; Joo, I.S.; Huh, K. Vertebral artery dominance contributes to basilar artery curvature and peri-vertebrobasilar junctional infarcts. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Miwa, K.; Okazaki, S.; Furukado, S.; Yagita, Y.; Mochizuki, H.; Kitagawa, K. Basilar artery diameter is an independent predictor of incident cardiovascular events. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2240–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Sohn, J.-H.; Jang, M.U.; Hong, S.-K.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, H.-J.; Choi, H.-C.; Lee, J.H. Ischemia as a potential etiologic factor in idiopathic unilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Analysis of posterior circulation arteries. Hear. Res. 2016, 331, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huy, P.T.; Sauvaget, E. Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss is not an otologic emergency. Otol. Neurotol. 2005, 26, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Heman-Ackah, S.E.; Shaikh, J.A.; Roehm, P.C. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A review of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Trends Amplif. 2011, 15, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forget, P.; Khalifa, C.; Defour, J.P.; Latinne, D.; Van Pel, M.C.; De Kock, M. What is the normal value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio? BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Sohn, S.I.; Jung, D.K.; Cho, Y.W.; Lim, J.G.; Yi, S.D.; Lee, S.R.; Sohn, C.H.; Baloh, R.W. Sudden deafness and anterior inferior cerebellar artery infarction. Stroke 2002, 33, 2807–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogson, J.M.; Taylor, R.L.; Young, A.S.; McGarvie, L.A.; Flanagan, S.; Halmagyi, G.M.; Welgampola, M.S. Vertigo with sudden hearing loss: Audio-vestibular characteristics. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 2086–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murofushi, T.; Tsubota, M.; Suzuki, D. Idiopathic acute high-tone sensorineural hearing loss accompanied by vertigo: Vestibulo-cochlear artery syndrome? Consideration based on VEMP and vHIT. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 2066–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vofo, G.; de Jong, M.A.; Kaufman, M.; Meyler, J.; Eliashar, R.; Gross, M. The impact of vestibular symptoms and electronystagmography results on recovery from sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, T.; Ali, S.M.; Shah, M.I.; Hussain, A.; Zaman, A.; Qamar Naqvi, S.R.; Sajid, Z. Oral Corticosteroid Therapy for Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Factors Affecting Prognosis. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad JAMC 2021, 33, 279–282. [Google Scholar]
- Eryigit, B.; Ziylan, F.; Yaz, F.; Thomeer, H. The effectiveness of hyperbaric oxygen in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A systematic review. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 275, 2893–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeng, J.S.; Yip, P.K. Evaluation of vertebral artery hypoplasia and asymmetry by color-coded duplex ultrasonography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2004, 30, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, K.S.; Gotlieb, A.I. The role of shear stress in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Lab. Investig. A J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2005, 85, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Cao, Z.; Shi, F.; Chen, B. Investigation of the prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss based on propensity score matching: A retrospective observational study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2020, 277, 2107–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.W.; Kim, M.G.; Kim, S.S.; Im, H.I.; Dong, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Yeo, S.G. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a valuable prognostic marker in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2020, 140, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, G.; Bae, Y.J.; Woo, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Koo, J.W.; Song, J.J. Vestibulocochlear Symptoms Caused by Vertebrobasilar Dolichoectasia. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 13, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbow, R.C.; Ruhl, D.S.; Hashisaki, G.T. Unilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss Associated with Vertebrobasilar Dolichoectasia. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, e56–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Qian, G.; Jiang, S.; Miao, C. Study on the Correlation between different Levels of Patients with Vertebrobasilar Dolichoectasia and Posterior Circulation Blood Perfusion. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 31, 106378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrettini, S.; Seccia, V.; Fortunato, S.; Forli, F.; Bruschini, L.; Piaggi, P.; Canapicchi, R. Analysis of the 3-dimensional fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery (3D-FLAIR) sequence in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 139, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Z.; Chi, F.L. The clinical value of three-dimensional fluid-attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance imaging in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A meta-analysis. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, O. Arterial pattern of human brainstem. Normal appearance and deformation in expanding supratentorial conditions. Neurology 1967, 17, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, Y. Anatomical analysis of the basilar artery and its branches with special reference to the arterial anastomosis, and its course and distribution on the pontine ventral surface. Nihon Ika Daigaku Zasshi 1994, 61, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Total (N = 105) | NLR ≤ 3.53 (n = 83) | NLR > 3.53 (n = 22) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 52 (27–81) | 52 (27–79) | 51.5 (34–81) | 0.816 1 |
| Sex (male/female) | 54/51 | 45/38 | 9/13 | 0.267 2 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.8 (17.4–51.0) | 24.8 (17.4–51.0) | 24.2 (19.1–35.2) | 0.634 3 |
| Hypertension | 27 (25.7%) | 62 (74.7%) | 6 (27.3%) | 0.851 2 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 17 (16.2%) | 15 (18.1%) | 2 (9.1%) | 0.515 4 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 6 (5.7%) | 5 (6.0%) | 1 (4.5%) | 1.000 4 |
| Affected side (right/left) | 56/49 | 48/35 | 8/14 | 0.073 2 |
| Initial PTA (dB) | 68.8 (20.0–120.0) | 70.0 (20.0–118.8) | 67.5 (37.5–120.0) | 0.595 3 |
| Vertigo | 21 (20%) | 13 (15.7%) | 8 (36.4%) | 0.040 4 |
| Audiometric curves | ||||
| Up-sloping type | 23 (21.9%) | 17 (20.5%) | 6 (27.3%) | 1.000 5 |
| Down-sloping type | 18 (17.1%) | 16 (19.3%) | 2 (9.1%) | |
| Flat type | 38 (36.2%) | 30 (36.1%) | 8 (36.4%) | |
| Profound | 26 (24.8%) | 20 (24.1%) | 6 (27.3%) | |
| BA diameter (mm) | 3.44 (2.29–5.16) | 3.44 (2.29–4.83) | 3.50 (2.58–5.16) | 0.850 3 |
| BA dolichoectasia | 5 (4.8%) | 4 (4.8%) | 1 (4.5%) | 1.000 4 |
| WBC (×103 cells/mm3) | 6.73 (3.57–9.72) | 6.57 (3.57–9.40) | 7.35 (4.64–9.72) | 0.015 1 |
| Neutrophil (×103 cells/mm3) | 4.21 (1.46–8.02) | 3.78 (1.46–6.44) | 5.83 (3.37–8.02) | <0.001 3 |
| Lymphocyte (×103 cells/mm3) | 1.96 (0.50–4.00) | 2.17 (1.26–4.00) | 1.15 (0.50–1.88) | <0.001 3 |
| Platelet (×103 cells/mm3) | 250.5 (130–522) | 250.3 (130–522) | 251.4 (148–329) | 0.471 3 |
| MPV (fL) | 10.1 (6.6–12.6) | 10.2 (7.5–12.6) | 9.8 (6.6–12.0) | 0.125 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, D.-W.; Kim, S.; Sunwoo, W. Correlation of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and the Dilation of the Basilar Artery with the Potential Role of Vascular Compromise in the Pathophysiology of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5943. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195943
Kang D-W, Kim S, Sunwoo W. Correlation of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and the Dilation of the Basilar Artery with the Potential Role of Vascular Compromise in the Pathophysiology of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5943. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195943
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Dae-Woong, Seul Kim, and Woongsang Sunwoo. 2022. "Correlation of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and the Dilation of the Basilar Artery with the Potential Role of Vascular Compromise in the Pathophysiology of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5943. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195943
APA StyleKang, D.-W., Kim, S., & Sunwoo, W. (2022). Correlation of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and the Dilation of the Basilar Artery with the Potential Role of Vascular Compromise in the Pathophysiology of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5943. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195943






