Evidence-Based Surgical Treatment Algorithm for Unstable Syndesmotic Injuries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Importance of anatomic reduction
- Closed versus open reduction under direct visualization
- Role of reduction clamps
- Role of syndesmotic screws
- Role of flexible dynamic stabilization techniques
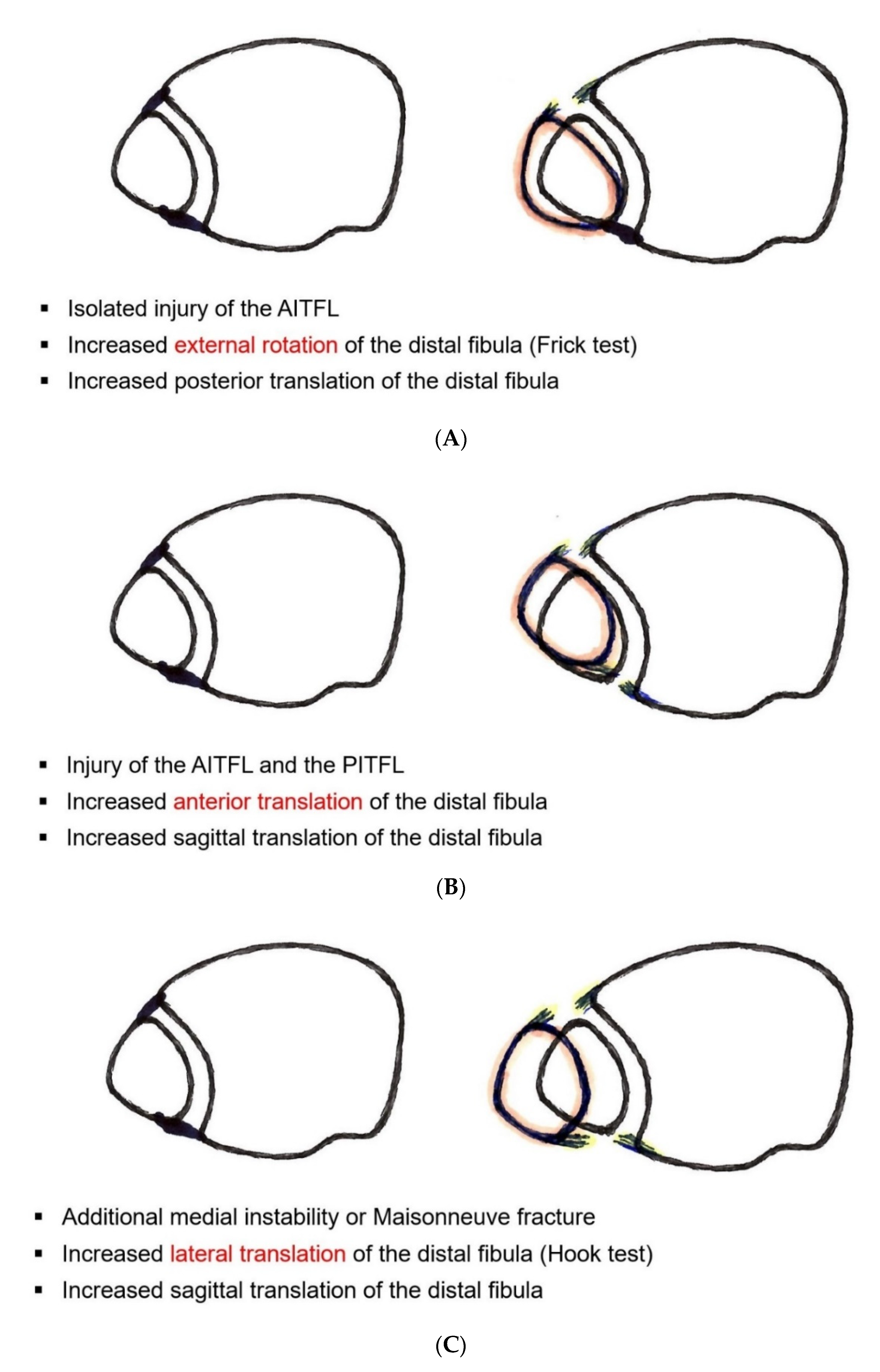
- Role of the AITFL
- Role of the posterolateral malleolus
3. Results
3.1. Importance of Anatomic Reduction
3.2. Closed vs. Open Reduction under Direct Visualization
3.3. Role of Reduction Clamps
3.4. Role of Syndesmotic Screws
3.5. Role of Flexible Dynamic Stabilization Techniques
3.6. Role of the AITFL
3.7. Role of the Posterior Malleolus
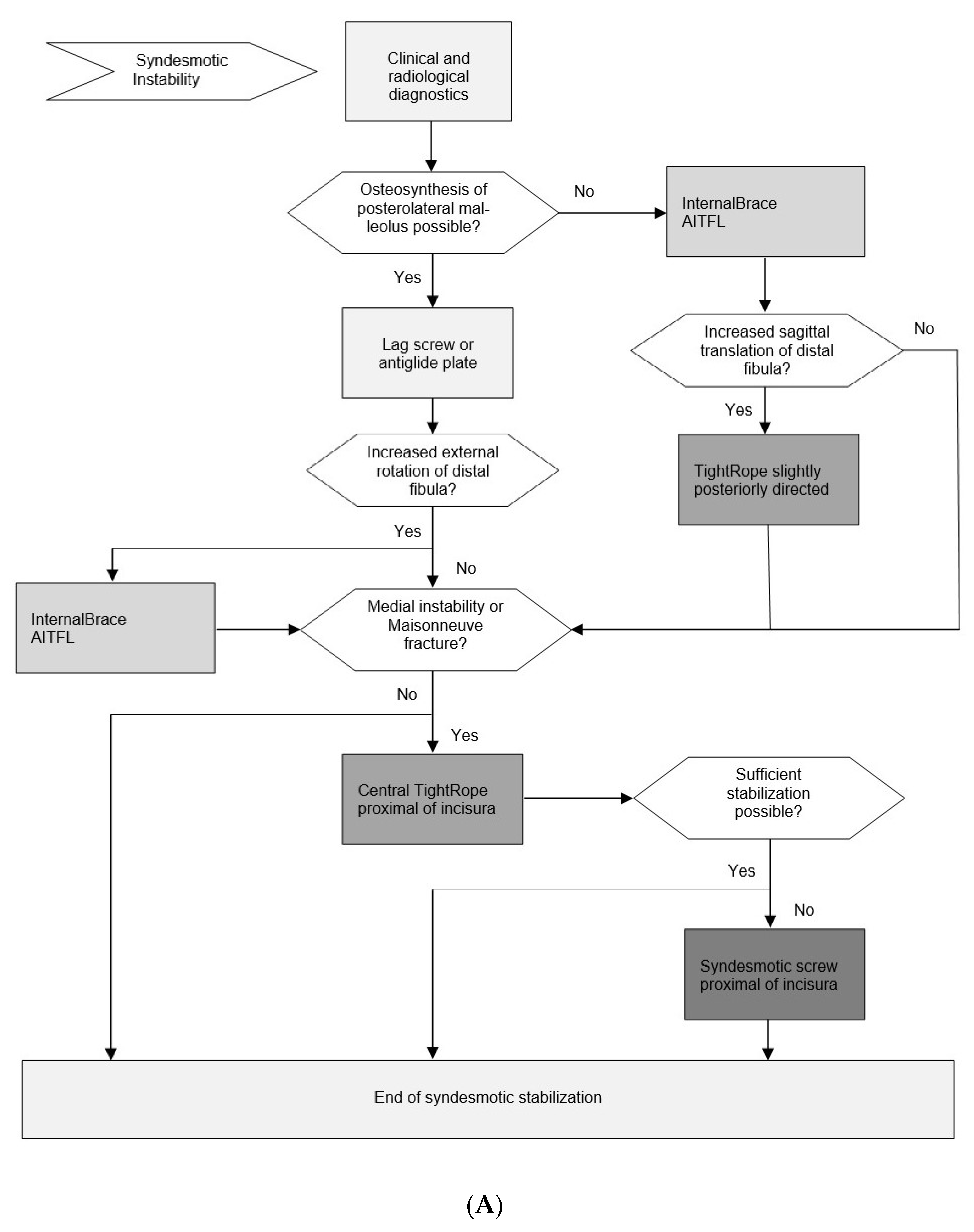
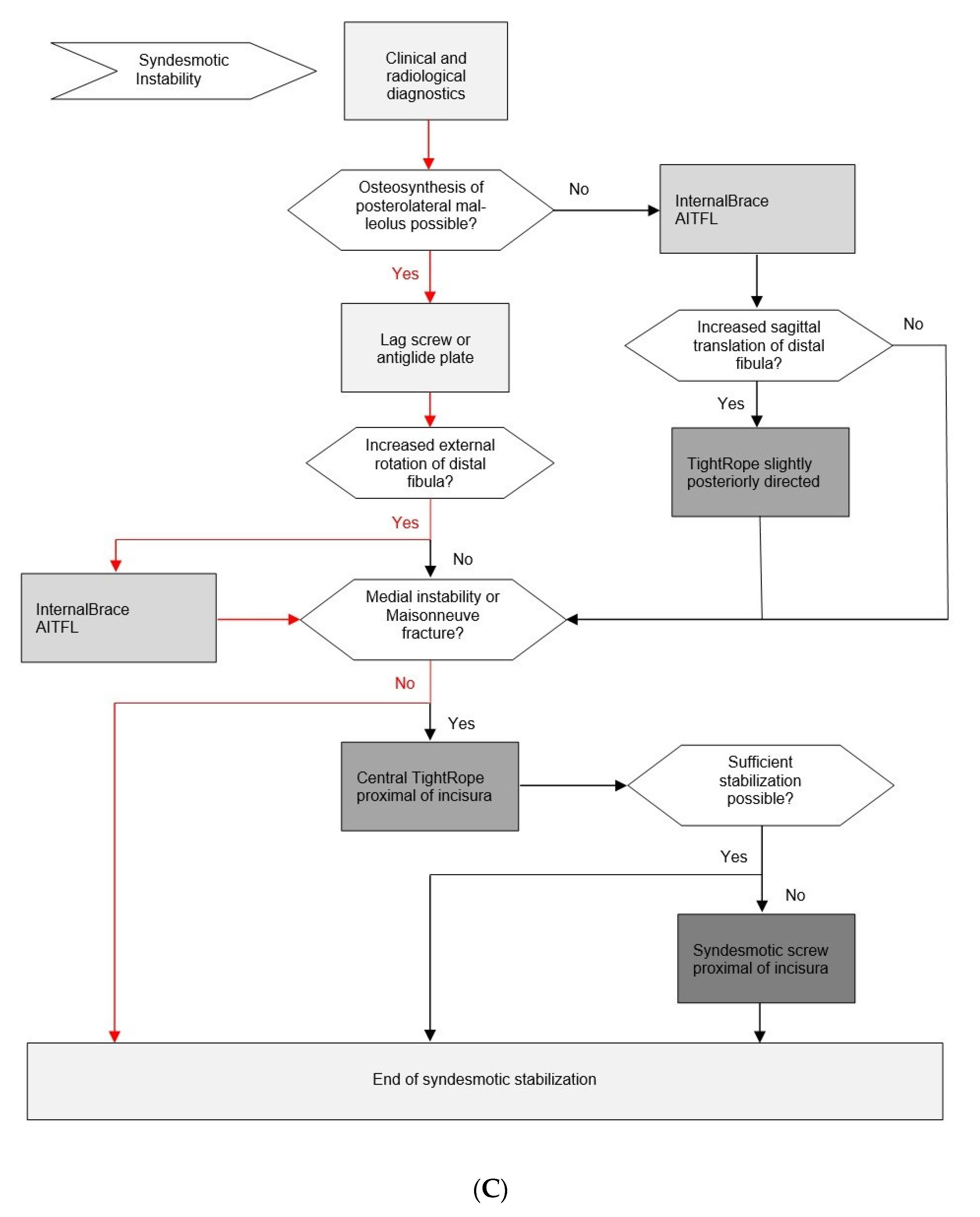
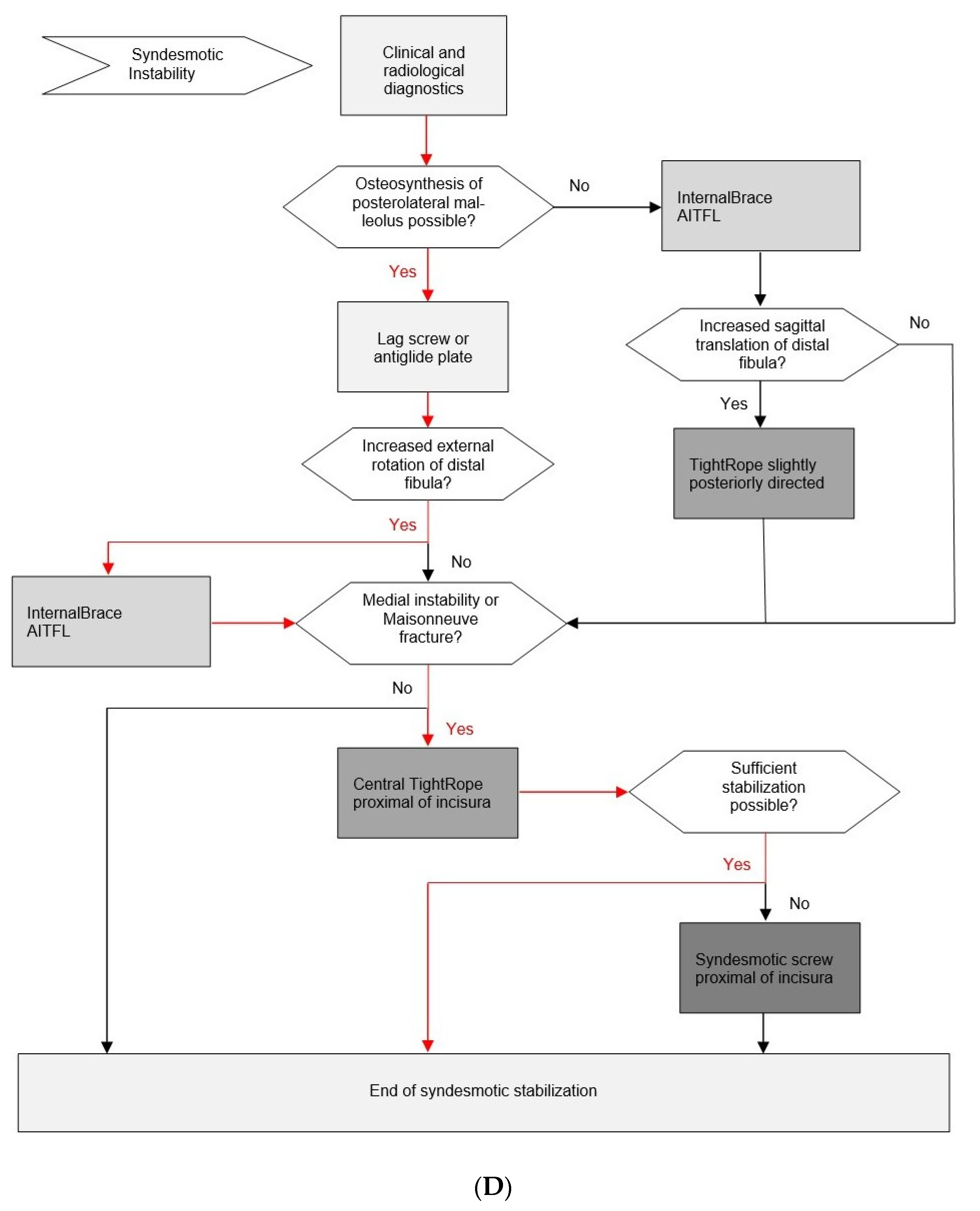
3.8. Recommended Principles for the Surgical Treatment of Unstable Syndesmotic Injuries
- Anatomic reduction is crucial for the long-term results;
- Open reduction by direct visualization is strongly recommended;
- Repair what is injured;
- Bony avulsion fragments must be identified and reduced (when big enough) and can serve as landmarks for anatomic reduction;
- The use of reduction clamps or forceps should be avoided whenever possible;
- Fix the posterolateral malleolus directly from posterior whenever possible;
- When fixing the posterolateral malleolus, start with this procedure;
- The AITFL is an important stabilizer especially for rotational stability;
- An unstable AITFL should be repaired and augmented;
- Use flexible dynamic stabilization techniques whenever possible; and
- Use syndesmotic screws only as a salvage procedure.
3.9. Evidence-Based Surgical Treatment Algorithm for Unstable Syndesmotic Injuries
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abarquero-Diezhandino, A.; Luengo-Alonso, G.; Alonso-Tejero, D.; Sánchez-Morata, E.J.; Olaya-Gonzalez, C.; Vilá Y Rico, J. Study of the relation between the posterior malleolus fracture and the development of osteoarthritis. Rev. Esp. Cir. Ortop. Traumatol. 2020, 64, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoh, C.C.; Phisitkul, P. Anatomic Ligament Repairs of Syndesmotic Injuries. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 50, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Rasgado, T.; Jimenez-Cruz, D.; Karski, M. 3-D computer modelling of malunited posterior malleolar fractures: Effect of fragment size and offset on ankle stability, contact pressure and pattern. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2017, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amendola, A.; Williams, G.; Foster, D. Evidence-based approach to treatment of acute traumatic syndesmosis (high ankle) sprains. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2006, 14, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Wei, R.; Patel, A.; Vedi, V.; Allardice, G.; Anand, B.S. Tightrope fixation of syndesmotic injuries in Weber C ankle fractures: A multicentre case series. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2017, 27, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.A. Anatomy of Ankle Syndesmotic Ligaments: A Systematic Review of Cadaveric Studies. Foot Ankle Spec. 2020, 13, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.R.; Diep, L.M.; Frihagen, F.; Castberg Hellund, J.; Madsen, J.E.; Figved, W. Importance of Syndesmotic Reduction on Clinical Outcome After Syndesmosis Injuries. J. Orthop. Trauma 2019, 33, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.R.; Figved, W. Use of Suture Button in the Treatment of Syndesmosis Injuries. JBJS Essent. Surg. Tech. 2018, 8, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.R.; Frihagen, F.; Hellund, J.C.; Madsen, J.E.; Figved, W. Randomized Trial Comparing Suture Button with Single Syndesmotic Screw for Syndesmosis Injury. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2018, 100, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.R.; Frihagen, F.; Madsen, J.E.; Figved, W. High complication rate after syndesmotic screw removal. Injury 2015, 46, 2283–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.J.; Kang, S.B.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Go, T.W. Reduction and fixation of anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament avulsion fracture without syndesmotic screw fixation in rotational ankle fracture. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060519882550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bafna, K.R.; Jordan, R.; Yatsonsky, D., 2nd; Dick, S.; Liu, J.; Ebraheim, N.A. Revision of Syndesmosis Screw Fixation. Foot Ankle Spec. 2020, 13, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Zhang, W.; Guan, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, P. Syndesmotic malreduction may decrease fixation stability: A biomechanical study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartoníček, J.; Rammelt, S.; Kostlivý, K.; Vaněček, V.; Klika, D.; Trešl, I. Anatomy and classification of the posterior tibial fragment in ankle fractures. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2015, 135, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoníček, J.; Rammelt, S.; Tuček, M. Posterior Malleolar Fractures: Changing Concepts and Recent Developments. Foot Ankle Clin. 2017, 22, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumbach, S.F.; Böcker, W.; Polzer, H. Arthroscopically assisted fracture treatment and open reduction of the posterior malleolus: New strategies for management of complex ankle fractures. Unfallchirurg 2020, 123, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumbach, S.F.; Herterich, V.; Damblemont, A.; Hieber, F.; Böcker, W.; Polzer, H. Open reduction and internal fixation of the posterior malleolus fragment frequently restores syndesmotic stability. Injury 2019, 50, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bava, E.; Charlton, T.; Thordarson, D. Ankle fracture syndesmosis fixation and management: The current practice of orthopedic surgeons. Am. J. Orthop. (Belle Mead NJ) 2010, 39, 242–246. [Google Scholar]
- Best, R.; Mauch, F.; Bauer, G. Evidence for treatment of acute syndesmosis injuries in sports. Unfallchirurg 2013, 116, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, M.F.N.; van Schilt, K.L.J.; Sanders, F.R.K.; Kloen, P.; Schepers, T. Anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament avulsion fractures in operatively treated ankle fractures: A retrospective analysis. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2019, 139, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, R.P.; Meijer, D.T.; de Muinck Keizer, R.O.; Stufkens, S.A.S.; Sierevelt, I.N.; Schepers, T.; Kerkhoffs, G.M.M.J.; Goslings, J.C.; Doornberg, J.N. Posterior malleolar fracture morphology determines outcome in rotational type ankle fractures. Injury 2019, 50, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candal-Couto, J.J.; Burrow, D.; Bromage, S.; Briggs, P.J. Instability of the tibio-fibular syndesmosis: Have we been pulling in the wrong direction? Injury 2004, 35, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassinelli, S.J.; Harris, T.G.; Giza, E.; Kreulen, C.; Matheny, L.M.; Robbins, C.M.; Clanton, T.O. Use of Anatomical Landmarks in Ankle Arthroscopy to Determine Accuracy of Syndesmotic Reduction: A Cadaveric Study. Foot Ankle Spec. 2020, 13, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Guerrero, D.E.; Rosas-Medina, J.A. Residual ankle instability in patients with syndesmosis lesions without fracture treated with situational screws. Acta Ortop. Mex. 2019, 33, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Qi, W.; Ji, B.; Liu, Y.; Liow, M.H.L. Novel anatomical reconstruction of distal tibiofibular ligaments restores syndesmotic biomechanics. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2017, 25, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherney, S.M.; Haynes, J.A.; Spraggs-Hughes, A.G.; McAndrew, C.M.; Ricci, W.M.; Gardner, M.J. In Vivo Syndesmotic Overcompression After Fixation of Ankle Fractures With a Syndesmotic Injury. J. Orthop. Trauma 2015, 29, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chissell, H.R.; Jones, J. The influence of a diastasis screw on the outcome of Weber type-C ankle fractures. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1995, 77, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clanton, T.O.; Williams, B.T.; Backus, J.D.; Dornan, G.J.; Liechti, D.J.; Whitlow, S.R.; Saroki, A.J.; Turnbull, T.L.; LaPrade, R.F. Biomechanical Analysis of the Individual Ligament Contributions to Syndesmotic Stability. Foot Ankle Int. 2017, 38, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clanton, T.O.; Whitlow, S.R.; Williams, B.T.; Liechti, D.J.; Backus, J.D.; Dornan, G.J.; Saroki, A.J.; Turnbull, T.L.; LaPrade, R.F. Biomechanical Comparison of 3 Current Ankle Syndesmosis Repair Techniques. Foot Ankle Int. 2017, 38, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clanton, T.O.; Paul, P. Syndesmosis injuries in athletes. Foot Ankle Clin. 2002, 7, 529–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, M.P.; Berkowitz, M.J. Revision Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Ankle and Syndesmosis Malunions. Instr. Course Lect. 2019, 68, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee, J.; Ebeling, P. Treatment of syndesmoses disruptions: A prospective, randomized study comparing conventional screw fixation vs TightRope fiber wire fixation—Medium term results. S. Afr. Orthop. J. 2009, 8, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee, J.; Ebeling, P. Treatment of syndesmosis disruptions with TightRope fixation. Tech. Foot Ankle Surg. 2008, 7, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colcuc, C.; Blank, M.; Stein, T.; Raimann, F.; Weber-Spickschen, S.; Fischer, S.; Hoffmann, R. Lower complication rate and faster return to sports in patients with acute syndesmotic rupture treated with a new knotless suture button device. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 3156–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.C.; Grossman, J.P.; Zulauf, E.E.; Coyer, M.A. Syndesmotic Ligament Allograft Reconstruction for Treatment of Chronic Diastasis. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020, 59, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, C.T.; Putnam, S.M.; Cherney, S.M.; Ricci, W.M.; Spraggs-Hughes, A.; McAndrew, C.M.; Gardner, M.J. Medial Clamp Tine Positioning Affects Ankle Syndesmosis Malreduction. J. Orthop. Trauma 2017, 31, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costigan, P.G. Treatment of true widening ankle mortise. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1953, 69, 310–313. [Google Scholar]
- Cottom, J.M.; Hyer, C.F.; Philbin, T.M.; Berlet, G.C. Treatment of syndesmotic disruptions with the Arthrex Tightrope: A report of 25 cases. Foot Ankle Int. 2008, 29, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Las-Heras Romero, J.; Alvarez, A.M.L.; Sanchez, F.M.; Garcia, A.P.; Porcel, P.A.G.; Sarabia, R.V.; Torralba, M.H. Management of syndesmotic injuries of the ankle. EFORT Open Rev. 2017, 2, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hooghe, P.; Cruz, F.; Alkhelaifi, K. Return to Play After a Lateral Ligament Ankle Sprain. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2020, 13, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hooghe, P.; Grassi, A.; Alkhelaifi, K.; Calder, J.; Baltes, T.P.A.; Zaffagnini, S.; Ekstrand, J. Return to play after surgery for isolated unstable syndesmotic ankle injuries (West Point grade IIB and III) in 110 male professional football players: A retrospective cohort study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1168–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Hooghe, P.; York, P.J.; Kaux, J.F.; Hunt, K.J. Fixation Techniques in Lower Extremity Syndesmotic Injuries. Foot Ankle Int. 2017, 38, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drijfhout van Hooff, C.C.; Verhage, S.M.; Hoogendoorn, J.M. Influence of fragment size and postoperative joint congruency on long-term outcome of posterior malleolar fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2015, 36, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egol, K.A.; Pahk, B.; Walsh, M.; Tejwani, N.C.; Davidovitch, R.I.; Koval, K.J. Outcome after unstable ankle fracture: Effect of syndesmotic stabilization. J. Orthop. Trauma 2010, 24, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelbrecht, E. Treatment of tibio-fibular syndesmosis rupture using the syndesmosis hook. Chirurg 1971, 42, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, E.; Goetz, J.E.; Sittapairoj, T.; Hosuru Siddappa, V.; Femino, J.E.; Phisitkul, P. Effect of Posterior Malleolus Fracture on Syndesmotic Reduction: A Cadaveric Study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2018, 100, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förschner, P.F.; Beitzel, K.; Imhoff, A.B.; Buchmann, S.; Feuerriegel, G.; Hofmann, F.; Karampinos, D.C.; Jungmann, P.; Pogorzelski, J. Five-Year Outcomes After Treatment for Acute Instability of the Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Using a Suture-Button Fixation System. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2017, 5, 2325967117702854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan, K.; Xu, D.; Hu, K.; Wu, W.; Shen, Y. Dynamic fixation is superior in terms of clinical outcomes to static fixation in managing distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2020, 28, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, K.; Zhou, K.; Hu, K.; Lu, L.; Gu, S.; Shen, Y. Dynamic Fixation Versus Static Fixation for Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Injuries: A Meta-Analysis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, M.J.; Brodsky, A.; Briggs, S.M.; Nielson, J.H.; Lorich, D.G. Fixation of posterior malleolar fractures provides greater syndesmotic stability. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2006, 447, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, M.J.; Demetrakopoulos, D.; Briggs, S.M.; Helfet, D.L.; Lorich, D.G. Malreduction of the tibiofibular syndesmosis in ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2006, 27, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, M.J.; Graves, M.L.; Higgins, T.F.; Nork, S.E. Technical Considerations in the Treatment of Syndesmotic Injuries Associated With Ankle Fractures. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2015, 23, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goetz, J.E.; Szabo, N.; Rudert, M.J.; Karam, M.D.; Phisitkul, P. Achilles Tension Mitigates Fibular Malalignment Measured in Cadaveric Studies of Syndesmotic Clamping. Foot Ankle Int. 2019, 40, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, J.E.; Rungprai, C.; Rudert, M.J.; Warth, L.C.; Phisitkul, P. Screw fixation of the syndesmosis alters joint contact characteristics in an axially loaded cadaveric model. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019, 25, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, J.E.; Davidson, N.P.; Rudert, M.J.; Szabo, N.; Karam, M.D.; Phisitkul, P. Biomechanical Comparison of Syndesmotic Repair Techniques During External Rotation Stress. Foot Ankle Int. 2018, 39, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grass, R.; Rammelt, S.; Biewener, A.; Zwipp, H. Peroneus longus ligamentoplasty for chronic instability of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Foot Ankle Int. 2003, 24, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, A.; Samuelsson, K.; D’Hooghe, P.; Romagnoli, M.; Mosca, M.; Zaffagnini, S.; Amendola, A. Dynamic Stabilization of Syndesmosis Injuries Reduces Complications and Reoperations as Compared With Screw Fixation: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Sports Med. 2020, 48, 1000–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajewski, C.J.; Duchman, K.; Goetz, J.; Femino, J. Anatomic Syndesmotic and Deltoid Ligament Reconstruction with Flexible Implants: A Technique Description. Iowa Orthop. J. 2019, 39, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.; Fallat, L. Effects of isolated Weber B fibular fractures on the tibiotalar contact area. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2004, 43, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, J.; Cherney, S.; Spraggs-Hughes, A.; McAndrew, C.M.; Ricci, W.M.; Gardner, M.J. Increased Reduction Clamp Force Associated With Syndesmotic Overcompression. Foot Ankle Int. 2016, 37, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkemeyer, H.; Püschel, R.; Burri, C. Experimental studies on the biomechanics of syndesmosis. Langenbecks Arch. Chir. 1975, 369–371. [Google Scholar]
- Hermans, J.J.; Beumer, A.; de Jong, T.A.; Kleinrensink, G.J. Anatomy of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis in adults: A pictorial essay with a multimodality approach. J. Anat. 2010, 217, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.J. Syndesmosis injuries. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2013, 6, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunt, K.J.; Phisitkul, P.; Pirolo, J.; Amendola, A. High Ankle Sprains and Syndesmotic Injuries in Athletes. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2015, 23, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.J.; Goeb, Y.; Behn, A.W.; Criswell, B.; Chou, L. Ankle Joint Contact Loads and Displacement with Progressive Syndesmotic Injury. Foot Ankle Int. 2015, 36, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinek, J.A.; Porter, D.A. Management of unstable ankle fractures and syndesmosis injuries in athletes. Foot Ankle Clin. 2009, 14, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, R.A. Stabilization of ankle syndesmosis injuries with a syndesmosis screw. Foot Ankle 1989, 9, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, S.; Tajima, G.; Sugawara, A.; Yan, J.; Maruyama, M.; Oikawa, S.; Saigo, T.; Oikawa, R.; Doita, M. Characteristic features of the insertions of the distal tibiofibular ligaments on three-dimensional computed tomography- cadaveric study. J. Exp. Orthop. 2020, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klitzman, R.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L.Q.; Strohmeyer, G.; Vora, A. Suture-button versus screw fixation of the syndesmosis: A biomechanical analysis. Foot Ankle Int. 2010, 31, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knops, S.P.; Kohn, M.A.; Hansen, E.N.; Matityahu, A.; Marmor, M. Rotational malreduction of the syndesmosis: Reliability and accuracy of computed tomography measurement methods. Foot Ankle Int. 2013, 34, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocadal, O.; Yucel, M.; Pepe, M.; Aksahin, E.; Aktekin, C.N. Evaluation of Reduction Accuracy of Suture-Button and Screw Fixation Techniques for Syndesmotic Injuries. Foot Ankle Int. 2016, 37, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortekangas, T.; Savola, O.; Flinkkilä, T.; Lepojärvi, S.; Nortunen, S.; Ohtonen, P.; Katisko, J.; Pakarinen, H. A prospective randomised study comparing TightRope and syndesmotic screw fixation for accuracy and maintenance of syndesmotic reduction assessed with bilateral computed tomography. Injury 2015, 46, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krähenbühl, N.; Weinberg, M.W.; Hintermann, B.; Haller, J.M.; Saltzman, C.L.; Barg, A. Surgical outcome in chronic syndesmotic injury: A systematic literature review. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019, 25, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Goel, L.; Chouhan, D.; Agnihotri, A.; Chauhan, S.; Passey, J. Malleolar tips as reference points for positioning of syndesmotic screw: A preliminary CT based analysis. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Passey, J.; Goel, L.; Chouhan, D.; Agnihotri, A.; Chauhan, S.; Gupta, S.; Khan, R. New landmarks for ideal positioning of syndesmotic screw: A computerised tomography based analysis and radiographic simulation. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflamme, M.; Belzile, E.L.; Bédard, L.; van den Bekerom, M.P.; Glazebrook, M.; Pelet, S. A prospective randomized multicenter trial comparing clinical outcomes of patients treated surgically with a static or dynamic implant for acute ankle syndesmosis rupture. J. Orthop. Trauma 2015, 29, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlechild, J.; Mayne, A.; Harrold, F.; Chami, G. A cadaveric study investigating the role of the anterior inferior tibio-fibular ligament and the posterior inferior tibio-fibular ligament in ankle fracture syndesmosis stability. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020, 26, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Chen, L.; Gong, M.; Xing, F.; Xiang, Z. Clinical Evidence for Treatment of Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Injury: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019, 58, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.T.; Ryan, E.; Gustafson, E.; VanPelt, M.D.; Raspovic, K.M.; Lalli, T.; Wukich, D.K.; Xi, Y.; Chhabra, A. Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Characterization of Normal Anatomic Morphology and Variations of the Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2018, 57, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, G.M.; Blyth, M.J.; Anthony, I.; Hopper, G.P.; Ribbans, W.J. A review of ligament augmentation with the InternalBrace™: The surgical principle is described for the lateral ankle ligament and ACL repair in particular, and a comprehensive review of other surgical applications and techniques is presented. Surg. Technol. Int. 2015, 26, 239–255. [Google Scholar]
- Magan, A.; Golano, P.; Maffulli, N.; Khanduja, V. Evaluation and management of injuries of the tibiofibular syndesmosis. Br. Med. Bull. 2014, 111, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahapatra, P.; Rudge, B.; Whittingham-Jones, P. Is It Possible to Overcompress the Syndesmosis? J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2018, 57, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, A.C.; Hesselholt, K.E.; Larsen, M.S.; Schmal, H. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Treatment of Ankle Fractures With Syndesmotic Rupture: Suture-Button Fixation Versus Cortical Screw Fixation. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019, 58, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; McDonald, T.C.; Graves, M.L.; Spitler, C.A.; Russell, G.V.; Jones, L.C.; Replogle, W.; Wise, J.A.; Hydrick, J.; Bergin, P.F. Stability of the Syndesmosis After Posterior Malleolar Fracture Fixation. Foot Ankle Int. 2018, 39, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.N.; Barei, D.P.; Iaquinto, J.M.; Ledoux, W.R.; Beingessner, D.M. Iatrogenic syndesmosis malreduction via clamp and screw placement. J. Orthop. Trauma 2013, 27, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.N.; Carroll, E.A.; Parker, R.J.; Helfet, D.L.; Lorich, D.G. Posterior malleolar stabilization of syndesmotic injuries is equivalent to screw fixation. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, A.N.; Carroll, E.A.; Parker, R.J.; Boraiah, S.; Helfet, D.L.; Lorich, D.G. Direct visualization for syndesmotic stabilization of ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2009, 30, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.L.; Skalak, T. Evaluation and treatment recommendations for acute injuries to the ankle syndesmosis without associated fracture. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, W.; Takao, M. Management of chronic disruption of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. World J. Orthop. 2011, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizel, M.S. Technique tip: A revised method of the Cotton test for intra-operative evaluation of syndesmotic injuries. Foot Ankle Int. 2003, 24, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.W.; Rice, P.; Schneider, T.E. Distal tibiofibular syndesmosis reconstruction using a free hamstring autograft. Foot Ankle Int. 2009, 30, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Metcalfe, A.; Guha, A.R.; Mohanty, K.; Hemmadi, S.; Lyons, K.; O’Doherty, D. Malreduction of—Are we considering the anatomical variation? Injury 2011, 42, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahey, M.K.; Bernhardson, A.S.; Murphy, C.P.; Chang, A.; Zajac, T.; Sanchez, G.; Sanchez, A.; Whalen, J.M.; Price, M.D.; Clanton, T.O.; et al. The Epidemiology of Ankle Injuries Identified at the National Football League Combine, 2009–2015. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2018, 6, 2325967118786227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, G.A.; Cunningham, P.; Lynch, B.; Galvin, R.; Awan, N. Fixation of ankle syndesmotic injuries: Comparison of tightrope fixation and syndesmotic screw fixation for accuracy of syndesmotic reduction. Am. J. Sports Med. 2012, 40, 2828–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, G.A.; Shafqat, A.; Awan, N. Tightrope fixation of ankle syndesmosis injuries: Clinical outcome, complications and technique modification. Injury 2012, 43, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, M.L.; Gascon, L.; Hébert-Davies, J.; Leduc, S.; Laflamme, G.Y.; Kramer, D. Modification of Distal Tibiofibular Relationship After a Mild Syndesmotic Injury. Foot Ankle Spec. 2017, 10, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.C.; Jensen, M.K. The treatment of trimalleolar fractures of the ankle. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1940, 71, 509–514. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, O.A. Examination and repair of the AITFL in transmalleolar fractures. J. Orthop. Trauma 2006, 20, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, T.J.; Mueller, B.; Ly, T.V.; Jacobson, A.R.; Nelson, E.R.; Cole, P.A. “A to p” screw versus posterolateral plate for posterior malleolus fixation in trimalleolar ankle fractures. J. Orthop. Trauma 2015, 29, e151–e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovaska, M.T.; Mäkinen, T.J.; Madanat, R.; Kiljunen, V.; Lindahl, J. A comprehensive analysis of patients with malreduced ankle fractures undergoing re-operation. Int. Orthop. 2014, 38, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pakarinen, H.; Flinkkilä, T.; Ohtonen, P.; Hyvönen, P.; Lakovaara, M.; Leppilahti, J.; Ristiniemi, J. Intraoperative assessment of the stability of the distal tibiofibular joint in supination-external rotation injuries of the ankle: Sensitivity, specificity, and reliability of two clinical tests. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2011, 93, 2057–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, E.Q.; Bedigrew, K.; Palanca, A.; Behn, A.W.; Hunt, K.J.; Chou, L. Ankle joint contact loads and displacement in syndesmosis injuries repaired with Tightropes compared to screw fixation in a static model. Injury 2019, 50, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, E.Q.; Coughlan, M.; Bonaretti, S.; Finlay, A.; Bellino, M.; Bishop, J.A.; Gardner, M.J. Assessment of Open Syndesmosis Reduction Techniques in an Unbroken Fibula Model: Visualization Versus Palpation. J. Orthop. Trauma 2019, 33, e14–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S. Surgical Stabilization of Syndesmotic Injuries With Accelerated Return to Play in High-Level Athletes. Foot Ankle Int. 2020, 41, 497–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.K.; Murphy, C.I.; Pfeiffer, T.R.; Naendrup, J.H.; Zlotnicki, J.P.; Debski, R.E.; Hogan, M.V.; Musahl, V. Sagittal instability with inversion is important to evaluate after syndesmosis injury and repair: A cadaveric robotic study. J. Exp. Orthop. 2020, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.S.; Chapman, W.D.; Hyer, C.F.; Berlet, G.C. Maintenance of reduction with suture button fixation devices for ankle syndesmosis repair. Foot Ankle Int. 2015, 36, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phisitkul, P.; Ebinger, T.; Goetz, J.; Vaseenon, T.; Marsh, J.L. Forceps reduction of the syndesmosis in rotational ankle fractures: A cadaveric study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2012, 94, 2256–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.A.; Jaggers, R.R.; Barnes, A.F.; Rund, A.M. Optimal management of ankle syndesmosis injuries. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2014, 5, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Press, C.M.; Gupta, A.; Hutchinson, M.R. Management of ankle syndesmosis injuries in the athlete. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2009, 8, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qamar, F.; Kadakia, A.; Venkateswaran, B. An anatomical way of treating ankle syndesmotic injuries. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2011, 50, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ræder, B.W.; Figved, W.; Madsen, J.E.; Frihagen, F.; Jacobsen, S.B.; Andersen, M.R. Better outcome for suture button compared with single syndesmotic screw for syndesmosis injury: Five-year results of a randomized controlled trial. Bone Jt. J. 2020, 102-B, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammelt, S.; Manke, E. Syndesmosis injuries at the ankle. Unfallchirurg 2018, 121, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammelt, S.; Obruba, P. An update on the evaluation and treatment of syndesmotic injuries. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2015, 41, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammelt, S.; Zwipp, H.; Grass, R. Injuries to the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: An evidence-based approach to acute and chronic lesions. Foot Ankle Clin. 2008, 13, 611–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, D.C.; Friess, D.M. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Syndesmotic Screw versus Suture Button Fixation in Tibiofibular Syndesmotic Injuries. J. Orthop. Trauma 2018, 32, e198–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, P.L.; Hamilton, W. Changes in tibiotalar area of contact caused by lateral talar shift. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1976, 58, 356–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raspovic, K.M.; Anigian, K.; Kapilow, J.; Tisano, B. Flexible Fixation in Foot and Ankle Surgery. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2019, 36, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, R.; Koohnejad, N.; Clement, N.D.; Keenan, G.F. Ankle fractures with syndesmotic stabilisation are associated with a high rate of secondary osteoarthritis. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019, 25, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regauer, M.; Mackay, G.; Lange, M.; Kammerlander, C.; Böcker, W. Syndesmotic InternalBraceTM for anatomic distal tibiofibular ligament augmentation. World J. Orthop. 2017, 8, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigby, R.B.; Cottom, J.M. Does the Arthrex TightRope® provide maintenance of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis? A 2-year follow-up of 64 TightRopes® in 37 patients. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2013, 52, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushing, C.J.; Spinner, S.M.; Armstrong, A.V., Jr.; Hardigan, P. Comparison of Different Magnitudes of Applied Syndesmotic Clamp Force: A Cadaveric Study. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020, 59, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustenburg, C.; Blom, R.; Stufkens, S.; Kerkhoffs, G.; Emanuel, K. Invisible injuries in ankle fractures: A biomechanical analysis of the ankle syndesmosis. Orthop. Proc. 2018, 100-B, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Sagi, H.C.; Shah, A.R.; Sanders, R.W. The functional consequence of syndesmotic joint malreduction at a minimum 2-year follow-up. J. Orthop. Trauma 2012, 26, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, D.; Schneider, P.; Taylor, M.; Tieszer, C.; Lawendy, A.R.; Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Improved Reduction of the Tibiofibular Syndesmosis With TightRope Compared with Screw Fixation: Results of a Randomized Controlled Study. J. Orthop. Trauma 2019, 33, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, T. Acute distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury: A systematic review of suture-button versus syndesmotic screw repair. Int. Orthop. 2012, 36, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnetzke, M.; Vetter, S.Y.; Beisemann, N.; Swartman, B.; Grützner, P.A.; Franke, J. Management of syndesmotic injuries: What is the evidence? World J. Orthop. 2016, 7, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schon, J.M.; Brady, A.W.; Krob, J.J.; Lockard, C.A.; Marchetti, D.C.; Dornan, G.J.; Clanton, T.O. Defining the three most responsive and specific CT measurements of ankle syndesmotic malreduction. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2019, 27, 2863–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schon, J.M.; Mikula, J.D.; Backus, J.D.; Venderley, M.B.; Dornan, G.J.; LaPrade, R.F.; Clanton, T.O. 3D Model Analysis of Ankle Flexion on Anatomic Reduction of a Syndesmotic Injury. Foot Ankle Int. 2017, 38, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schon, J.M.; Williams, B.T.; Venderley, M.B.; Dornan, G.J.; Backus, J.D.; Turnbull, T.L.; LaPrade, R.F.; Clanton, T.O. A 3-D CT Analysis of Screw and Suture-Button Fixation of the Syndesmosis. Foot Ankle Int. 2017, 38, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schottel, P.C.; Baxter, J.; Gilbert, S.; Garner, M.R.; Lorich, D.G. Anatomic Ligament Repair Restores Ankle and Syndesmotic Rotational Stability as Much as Syndesmotic Screw Fixation. J. Orthop. Trauma 2016, 30, e36–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G. Surgical treatment of ankle fractures with comminuted supramalleolar fracture. Zentralbl. Chir. 1955, 80, 542–546. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, W.H., Jr.; Bachner, E.J.; Abram, L.J.; Postak, P.; Polando, G.; Brooks, D.B.; Greenwald, A.S. Repair of the tibiofibular syndesmosis with a flexible implant. J. Orthop. Trauma 1991, 5, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, M.; Donmez, F.; Mahirogullari, M.; Cakmak, S.; Mutlu, S.; Guler, O. Comparison of screw fixation with elastic fixation methods in the treatment of syndesmosis injuries in ankle fractures. Injury 2015, 46 (Suppl. 2), S19–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimozono, Y.; Hurley, E.T.; Myerson, C.L.; Murawski, C.D.; Kennedy, J.G. Suture Button Versus Syndesmotic Screw for Syndesmosis Injuries: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 2764–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, H.; Teramoto, A.; Suzuki, D.; Okada, Y.; Sakakibara, Y.; Matsumura, T.; Suzuki, T.; Watanabe, K.; Yamashita, T. Suture-button fixation and anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament augmentation with suture-tape for syndesmosis injury: A biomechanical cadaveric study. Clin. Biomech. 2018, 60, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, K.; Adhikary, R.; Zou, L.; Yao, H.; Yang, H.; Adhikary, K.; Yang, Y.; Bao, T. The Assessment of the Reduction Algorithm in the Treatment for “Logsplitter” Injury. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 4139028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sman, A.D.; Hiller, C.E.; Rae, K.; Linklater, J.; Black, D.A.; Refshauge, K.M. Prognosis of ankle syndesmosis injury. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solan, M.C.; Davies, M.S.; Sakellariou, A. Syndesmosis Stabilisation: Screws Versus Flexible Fixation. Foot Ankle Clin. 2017, 22, 35–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soreide, E.; Denbeigh, J.M.; Lewallen, E.A.; Thaler, R.; Xu, W.; Berglund, L.; Yao, J.J.; Martinez, A.; Nordsletten, L.; van Wijnen, A.J.; et al. In vivo assessment of high-molecular-weight polyethylene core suture tape for intra-articular ligament reconstruction: An animal study. Bone Jt. J. 2019, 101-B, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, A.; Shoji, H.; Sakakibara, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Watanabe, K.; Yamashita, T. Suture-Button Fixation and Mini-Open Anterior Inferior Tibiofibular Ligament Augmentation Using Suture Tape for Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Injuries. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2018, 57, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teramoto, A.; Suzuki, D.; Kamiya, T.; Chikenji, T.; Watanabe, K.; Yamashita, T. Comparison of different fixation methods of the suture-button implant for tibiofibular syndesmosis injuries. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 2226–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornes, B.; Shannon, F.; Guiney, A.M.; Hession, P.; Masterson, E. Suture-button syndesmosis fixation: Accelerated rehabilitation and improved outcomes. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2005, 431, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornetta, P., 3rd; Yakavonis, M.; Veltre, D.; Shah, A. Reducing the Syndesmosis Under Direct Vision: Where Should I Look? J. Orthop. Trauma 2019, 33, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tosun, B.; Selek, O.; Gok, U.; Ceylan, H. Posterior Malleolus Fractures in Trimalleolar Ankle Fractures: Malleolus versus Transyndesmal Fixation. Indian J. Orthop. 2018, 52, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourné, Y.; Molinier, F.; Andrieu, M.; Porta, J.; Barbier, G. Diagnosis and treatment of tibiofibular syndesmosis lesions. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2019, 105, S275–S286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacas-Sánchez, E.; Olaya-González, C.; Abarquero-Diezhandino, A.; Sánchez-Morata, E.; Vilá-Rico, J. How to address the posterior malleolus in ankle fractures? A decision-making model based on the computerised tomography findings. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, N.G.; Vance, R.C.; Chandler, W.T.; Panchbhavi, V.K. Can Syndesmosis Screws Displace the Distal Fibula? Foot Ankle Spec. 2021, 14, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bekerom, M.P.; Kloen, P.; Luitse, J.S.; Raaymakers, E.L. Complications of distal tibiofibular syndesmotic screw stabilization: Analysis of 236 patients. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2013, 52, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bekerom, M.P. Diagnosing syndesmotic instability in ankle fractures. World J. Orthop. 2011, 2, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Heuvel, S.B.; Dingemans, S.A.; Gardenbroek, T.J.; Schepers, T. Assessing Quality of Syndesmotic Reduction in Surgically Treated Acute Syndesmotic Injuries: A Systematic Review. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019, 58, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vlijmen, N.; Denk, K.; van Kampen, A.; Jaarsma, R.L. Long-term Results After Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries. Orthopedics 2015, 38, e1001–e1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Rüden, C.; Hackl, S.; Woltmann, A.; Friederichs, J.; Bühren, V.; Hierholzer, C. The Postero-Lateral Approach—An Alternative to Closed Anterior-Posterior Screw Fixation of a Dislocated Postero-Lateral Fragment of the Distal Tibia in Complex Ankle Fractures. Z. Orthop. Unfall. 2015, 153, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhage, S.M.; Krijnen, P.; Schipper, I.B.; Hoogendoorn, J.M. Persistent postoperative step-off of the posterior malleolus leads to higher incidence of post-traumatic osteoarthritis in trimalleolar fractures. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2019, 139, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verhage, S.M.; Hoogendoorn, J.M.; Krijnen, P.; Schipper, I.B. When and how to operate the posterior malleolus fragment in trimalleolar fractures: A systematic literature review. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2018, 138, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhage, S.M.; Boot, F.; Schipper, I.B.; Hoogendoorn, J.M. Open reduction and internal fixation of posterior malleolar fractures using the posterolateral approach. Bone Jt. J. 2016, 98-B, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, S.Y.; Beisemann, N.; Keil, H.; Schnetzke, M.; Swartman, B.; Franke, J.; Grützner, P.A.; Privalov, M. Comparison of three different reduction methods of the ankle mortise in unstable syndesmotic injuries. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopat, M.L.; Vopat, B.G.; Lubberts, B.; DiGiovanni, C.W. Current trends in the diagnosis and management of syndesmotic injury. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2017, 10, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, J.; Martin, K.D. Syndesmosis Injury from Diagnosis to Repair: Physical Examination, Diagnosis, and Arthroscopic-assisted Reduction. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 28, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weening, B.; Bhandari, M. Predictors of functional outcome following transsyndesmotic screw fixation of ankle fractures. J. Orthop. Trauma 2005, 19, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Q.; Lin, C.; Liu, Y.; Dai, G.; Lutchooman, V.; Hong, J. Biomechanical Analysis of a Novel Syndesmotic Plate Compared With Traditional Screw and Suture Button Fixation. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020, 59, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermann, R.W.; Rungprai, C.; Goetz, J.E.; Femino, J.; Amendola, A.; Phisitkul, P. The effect of suture-button fixation on simulated syndesmotic malreduction: A cadaveric study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2014, 96, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willenegger, H. Treatment of luxation fractures of the tibiotarsal joint according to biomechanical viewpoints. Helv. Chir. Acta 1961, 28, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willenegger, H.; Weber, G.B. Malleolar fractures. Langenbecks Arch. Klin. Chir. 1965, 313, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.T.; Ahrberg, A.B.; Goldsmith, M.T.; Campbell, K.J.; Shirley, L.; Wijdicks, C.A.; LaPrade, R.F.; Clanton, T.O. Ankle syndesmosis: A qualitative and quantitative anatomic analysis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.R.; Arshad, S.A.; Kim, H.; Stewart, D. Kinematic Analysis of Combined Suture-Button and Suture Anchor Augment Constructs for Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries. Foot Ankle Int. 2020, 41, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, H.; Miao, J.; Zhou, Q.; Lian, K.; Zhai, W.; Liu, Q. Novel Elastic Syndesmosis Hook Plate Fixation versus Routine Screw Fixation for Syndesmosis Injury. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2018, 57, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasui, Y.; Takao, M.; Miyamoto, W.; Innami, K.; Matsushita, T. Anatomical reconstruction of the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament for chronic disruption of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2011, 19, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ge, D.; Yan, J.; Jiang, C.; Liang, B. Treatment of a high-energy transsyndesmotic ankle fracture: A case report of “logsplitter injury”. Medicine 2020, 99, e19380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.S.; Lin, Y.B.; Xiong, G.S.; Xu, H.B.; Liu, Y.Y. Diagnosis and treatment of ankle syndesmosis injuries with associated interosseous membrane injury: A current concept review. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 2539–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Yan, X.; Xia, R.; Cheng, T.; Luo, C. Anterior-inferior tibiofibular ligament anatomical repair and augmentation versus trans-syndesmosis screw fixation for the syndesmotic instability in external-rotation type ankle fracture with posterior malleolus involvement: A prospective and comparative study. Injury 2016, 47, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liang, Y.; He, J.; Fang, Y.; Chen, P.; Wang, J. A systematic review of suture-button versus syndesmotic screw in the treatment of distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosi, R.; Di Silvestri, C.; Manzi, L.; Indino, C.; Maccario, C.; Usuelli, F.G. Post-traumatic ankle osteoarthritis: Quality of life, frequency and associated factors. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2019, 9, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

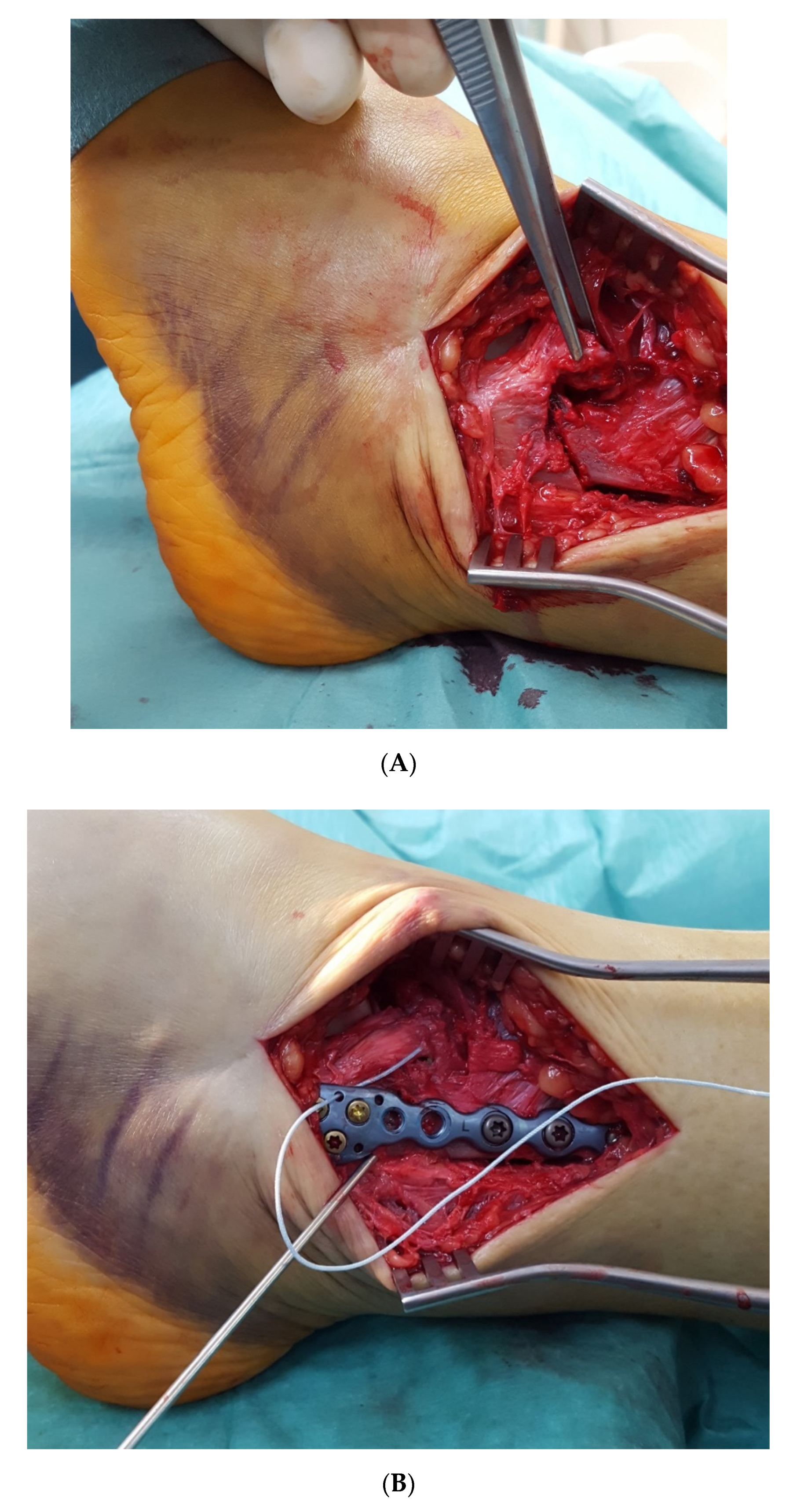
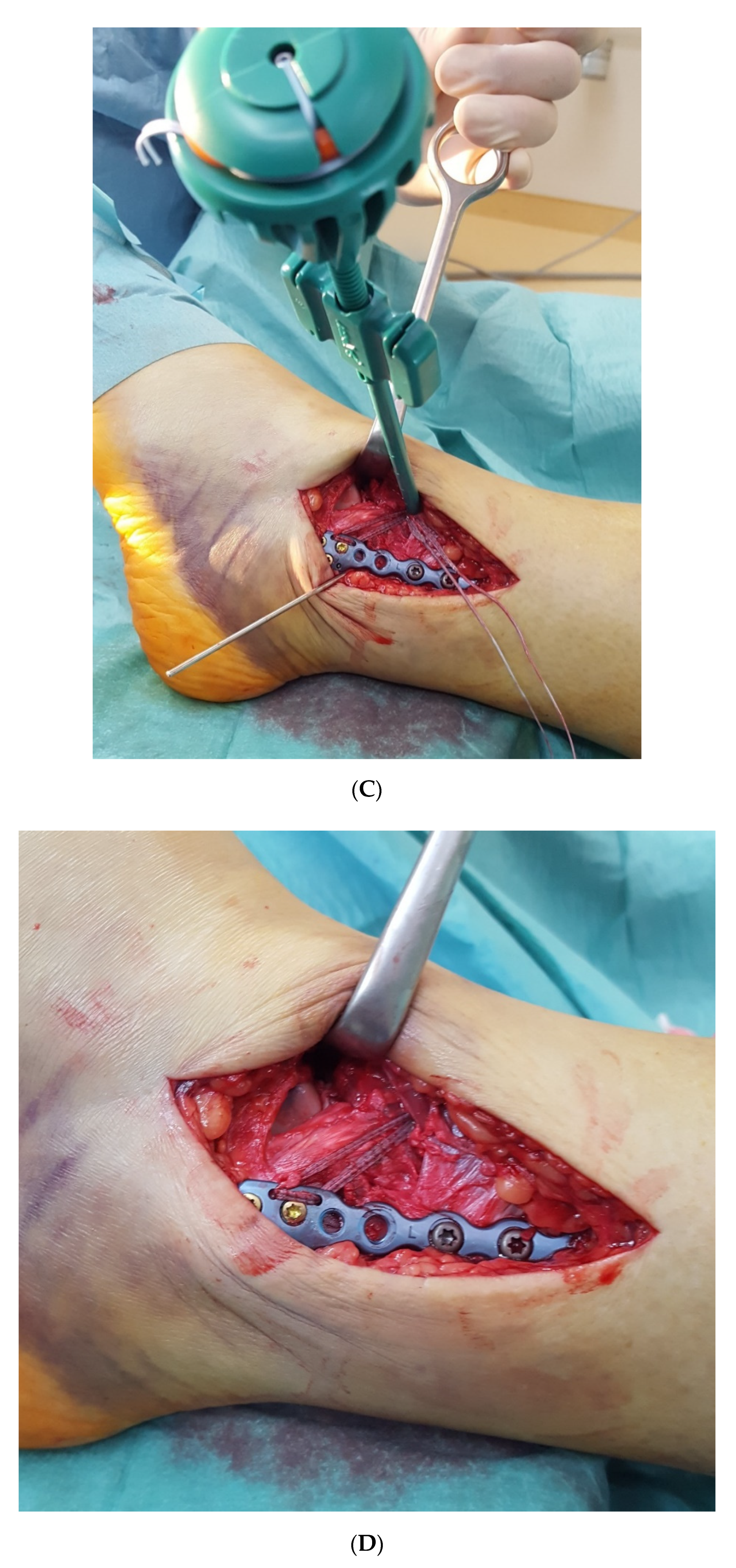
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Regauer, M.; Mackay, G.; Nelson, O.; Böcker, W.; Ehrnthaller, C. Evidence-Based Surgical Treatment Algorithm for Unstable Syndesmotic Injuries. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11020331
Regauer M, Mackay G, Nelson O, Böcker W, Ehrnthaller C. Evidence-Based Surgical Treatment Algorithm for Unstable Syndesmotic Injuries. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(2):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11020331
Chicago/Turabian StyleRegauer, Markus, Gordon Mackay, Owen Nelson, Wolfgang Böcker, and Christian Ehrnthaller. 2022. "Evidence-Based Surgical Treatment Algorithm for Unstable Syndesmotic Injuries" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 2: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11020331
APA StyleRegauer, M., Mackay, G., Nelson, O., Böcker, W., & Ehrnthaller, C. (2022). Evidence-Based Surgical Treatment Algorithm for Unstable Syndesmotic Injuries. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(2), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11020331





