Risk Factors for Maxillary Sinus Pathology after Surgery for Midfacial Fracture: A Multivariate Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Factors of Interest and Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Bokhamseen, M.; Salma, R.; Al-Bodbaij, M. Patterns of maxillofacial fractures in Hofuf, Saudi Arabia: A 10-year retrospective case series. Saudi Dent. J. 2019, 31, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelin, S.P.; Giot, J.P. Epidemiology of Maxillofacial Traumatisms in French Alps Metropole (Grenoble) Specificity for the mountain sports and evolution in the last 40 years. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 122, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlAli, A.M.; Ibrahim, H.; Algharib, A.; Alsaad, F.; Rajab, B. Characteristics of pediatric maxillofacial fractures in Kuwait: A single-center retrospective study. Dent. Traumatol. 2021, 37, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabalag, M.S.; Wasiak, J.; Andrew, N.E.; Tang, J.; Kirby, J.C.; Morgan, D.J. Epidemiology and management of maxillofacial fractures in an Australian trauma centre. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2014, 67, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boffano, P.; Roccia, F.; Zavattero, E.; Dediol, E.; Uglešić, V.; Kovačič, Ž.; Vesnaver, A.; Konstantinovic, V.; Petrović, M.; Stephens, J.; et al. European Maxillofacial Trauma (EURMAT) project: A multicentre and prospective study. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfeld, M.; Manson, P.N.; Prein, J. Principles of Internal Fixation of the Craniomaxillofacial Skeleton: Trauma and Orthognathic Surgery; Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnel, T.S.; Reichert, T.E. Trauma of the midface. GMS Curr. Top. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 14, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, J.E.; Iezzi, Z.; Licata, J.J.; Othman, S.; Zwillenberg, S. An Update on Maxillary Fractures: A Heterogenous Group. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2020, 31, 1920–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Top, H.; Aygit, C.; Sarikaya, A.; Karaman, D.; Firat, M.F. Evaluation of maxillary sinus after treatment of midfacial fractures. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 62, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenkeit, C.P.; Lofgren, D.H.; Shermetaro, C. Maxillary sinus fracture. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mattos, J.L.; Rudmik, L.; Schlosser, R.J.; Smith, T.L.; Mace, J.C.; Alt, J.; Soler, Z.M. Symptom importance, patient expectations, and satisfaction in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, E.S.; Musselman, D.L.; Chyou, D.; Shukri, G.; Levine, C.G.; Sanghvi, S.; Zhang, H.; Casiano, R.R. Somatization, Depression, and Anxiety Disorders in a Rhinology Practice. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy. 2019, 33, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, A.; West, E.; Rahman, S.; Kim, S.; Sima, A.; Schuman, T.A. Pain Catastrophizing and Quality of Life in Adults with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, D.; Yadav, L.K.; Thapa, P. Chronic maxillary sinusitis: Clinical and microbiological evaluation. J. Coll. Med. Sci. 2011, 7, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FFokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58 (Suppl. S29), 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cengiz, M.; Celikbilek, G.; Andic, C.; Dosemeci, L.; Yilmaz, M.; Karaali, K.; Ramazanoglu, A. Maxillary sinusitis in patients ventilated for a severe head injury and with nostrils free of any foreign body. Injury 2011, 42, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballon, A.; Landes, C.A.; Zeilhofer, H.F.; Herzog, M.; Klein, C.; Sader, R. The importance of the primary reconstruction of the traumatized anterior maxillary sinus wall. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2008, 19, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira-Filho, V.A.; Gabrielli, M.F.; Gabrielli, M.A.; Pinto, F.A.; Rodrigues-Junior, A.L.; Klüppel, L.E.; Passeri, L.A. Incidence of maxillary sinusitis following Le Fort I osteotomy: Clinical, radiographic, and endoscopic study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, K.; Yoshizawa, K.; Moroi, A.; Tsutsui, T.; Fukaya, K.; Hiraide, R.; Takayama, A.; Tsunoda, T.; Saito, Y.; Iguchi , R.; et al. Evaluation of maxillary sinus after Le Fort I osteotomy using various fixation materials. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Watanabe, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Narita, M.; Kamio, T.; Takaki, T.; Shibahara, T.; Katakura, A. Prognostic factors for maxillary sinus mucosal thickening following Le Fort I osteotomy: A retrospective analysis. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 41, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhamruni, L.M.M.; Marzook, H.A.M.; Ahmed, W.M.S.; Abdul-Rahman, M. Experimental study on penetration of dental implants into the maxillary sinus at different depths. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 20, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouby, J.J.; Laurent, P.; Gosnach, M.; Cambau, E.; Lamas, G.; Zouaoui, A.; Leguillou, J.L.; Bodin, L.; Khac, T.D.; Marsault, C. Risk factors and clinical relevance of nosocomial maxillary sinusitis in the critically ill. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliklich, R.E.; Metson, R. Techniques for outcomes research in chronic sinusitis. Laryngoscope 1995, 105 Pt 1, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra-Pereira, I.; Vaz, P.; Faria-Almeida, R.; Braga, A.C.; Felino, A. CT maxillary sinus evaluation—A retrospective cohort study. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2015, 20, e419–e426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, E.; Kendall, M. Multivariate Analysis. Charles Griffin b Co. LTD. London, High Wycombe 1975. 210 s., 9 Abb., 27 Tab., 1 Anhang, £ 6,80. Biom. J. 1977, 19, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moons, K.G.; de Groot, J.A.; Bouwmeester, W.; Vergouwe, Y.; Mallett, S.; Altman, D.G.; Reitsma, J.B.; Collins, G.S. Critical appraisal and data extraction for systematic reviews of prediction modelling studies: The CHARMS checklist. PLoS Med. 2014, 11, e1001744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Perez, A.; Boracchia, A.C.; Lopez-Jornet, P.; Boix-Garcia, P. Characterization of the Maxillary Sinus Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography. A Retrospective Radiographic Study. Implant Dent. 2016, 25, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomeli, S.R.; Branstetter, B.T.; Ferguson, B.J. Frequency of a dental source for acute maxillary sinusitis. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, E.R.; Kittidumkerng, W. Analysis of treatment for isolated zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1996, 54, 386–400, discussion 400-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Tian, M.; Qin, S.; Li, X. Relationship Between Preoperative Hypoalbuminemia and Postoperative Pneumonia Following Geriatric Hip Fracture Surgery: A Propensity-Score Matched and Conditional Logistic Regression Analysis. Clin. Interv. Aging 2022, 17, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manji, A.; Faucher, J.; Resnik, R.R.; Suzuki, J.B. Prevalence of maxillary sinus pathology in patients considered for sinus augmentation procedures for dental implants. Implant Dent. 2013, 22, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, Y.J.; Yang, J.; Resnik, R.R.; Suzuki, J.B. Prevalence of Maxillary Sinus Pathology Based on Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of Multiethnicity Dental School Population. Implant Dent. 2019, 28, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manor, Y.; Mardinger, O.; Bietlitum, I.; Nashef, A.; Nissan, J.; Chaushu, G. Late signs and symptoms of maxillary sinusitis after sinus augmentation. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2010, 110, e1–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, U.; Orhan, K. Association between odontogenic conditions and maxillary sinus mucosal thickening: A retrospective CBCT study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penarrocha-Oltra, S.; Soto-Penaloza, D.; Bagan-Debon, L.; Bagan, J.V.; Penarrocha-Oltra, D. Association between maxillary sinus pathology and odontogenic lesions in patients evaluated by cone beam computed tomography. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2020, 25, e34–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-H.; Choi, B.-H.; Jeong, S.-M.; Li, J.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, H.-J. A retrospective study of the effects on sinus complications of exposing dental implants to the maxillary sinus cavity. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2007, 103, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hierl, T.; Doerfler, H.M.; Huempfner-Hierl, H.; Kruber, D. Evaluation of the Midface by Statistical Shape Modeling. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 202.e1–202.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, B.J.; Turco, L.M. Le Fort Fractures: A Collective Review. Bull. Emerg. Trauma 2017, 5, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetto, U.; Head, S.J.; Angelini, G.D.; Blackstone, E.H. Statistical primer: Propensity score matching and its alternatives. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2018, 53, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
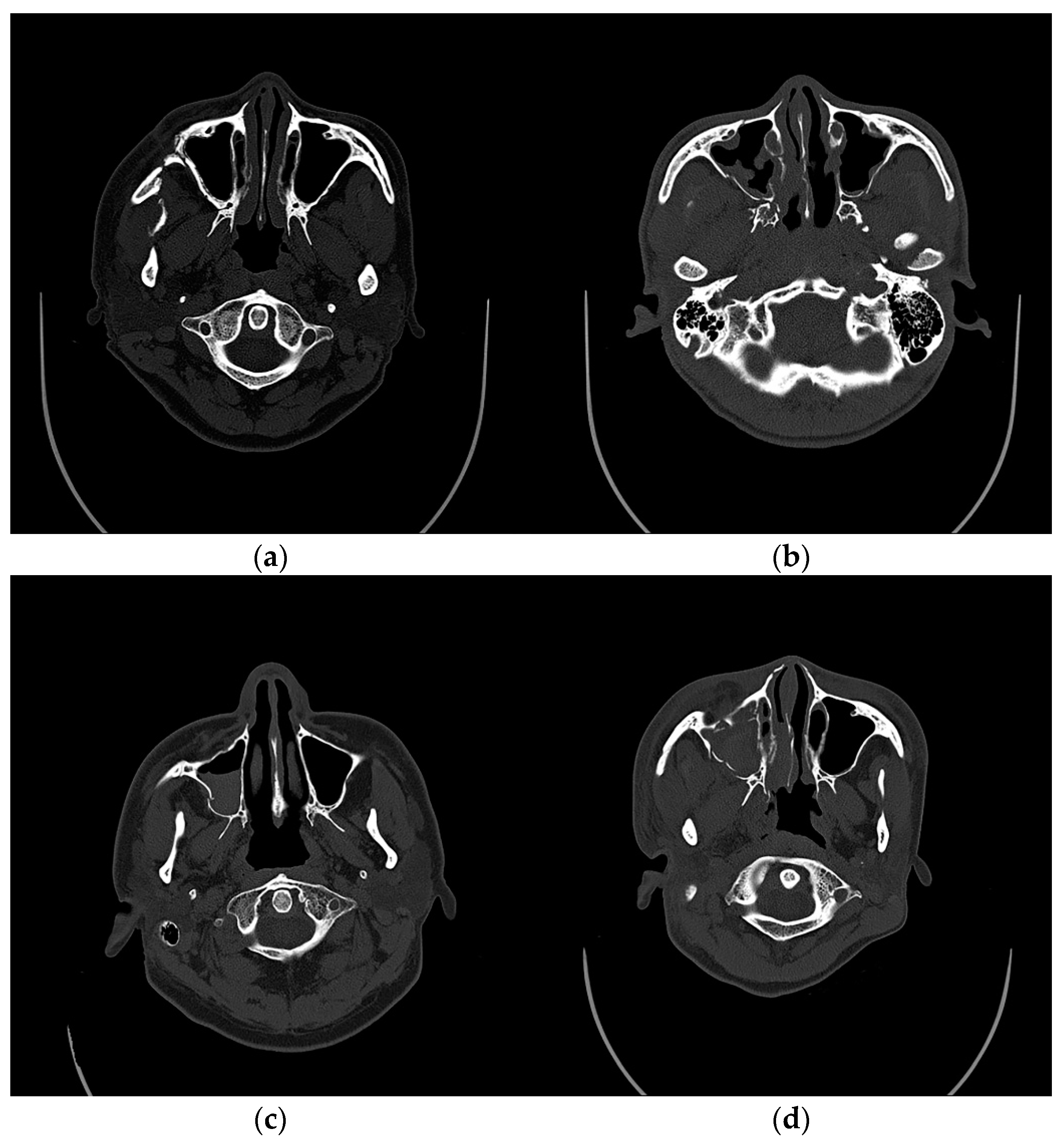
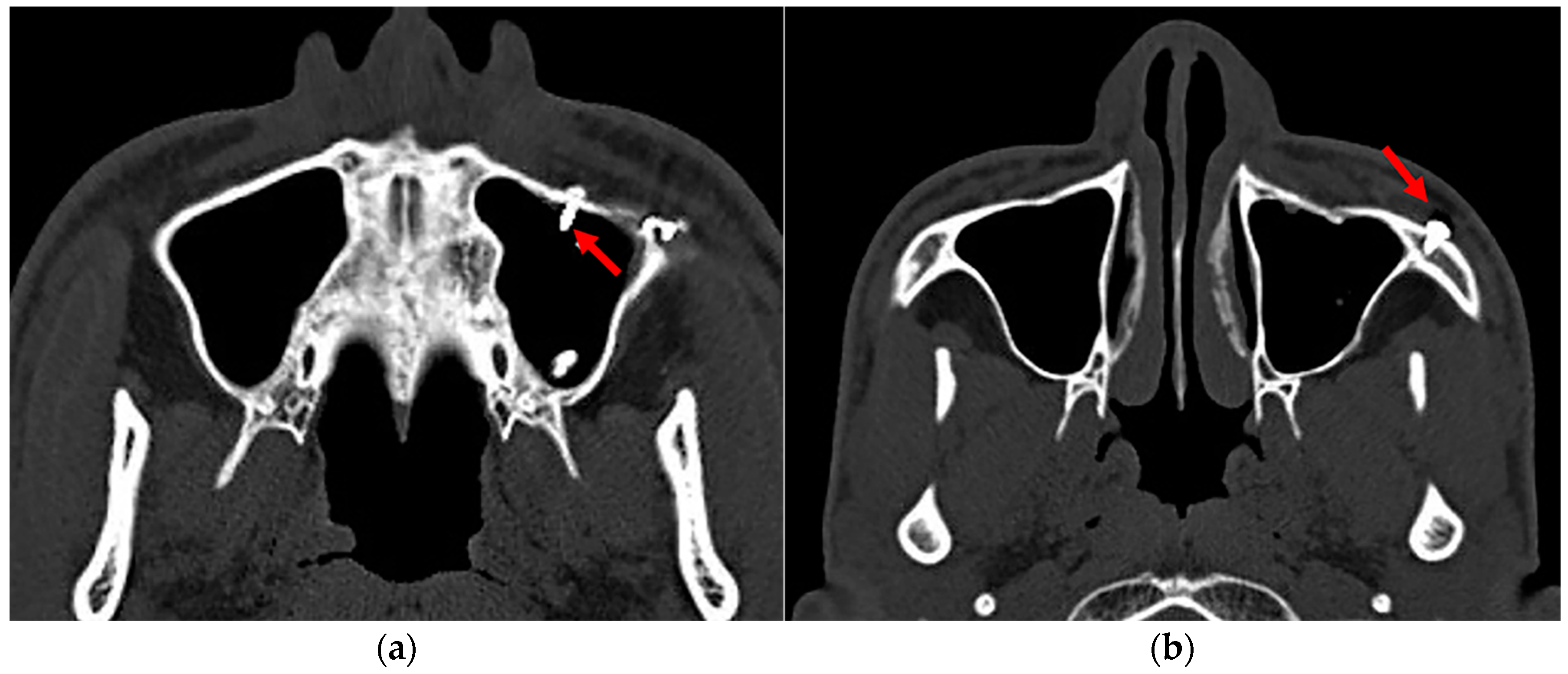
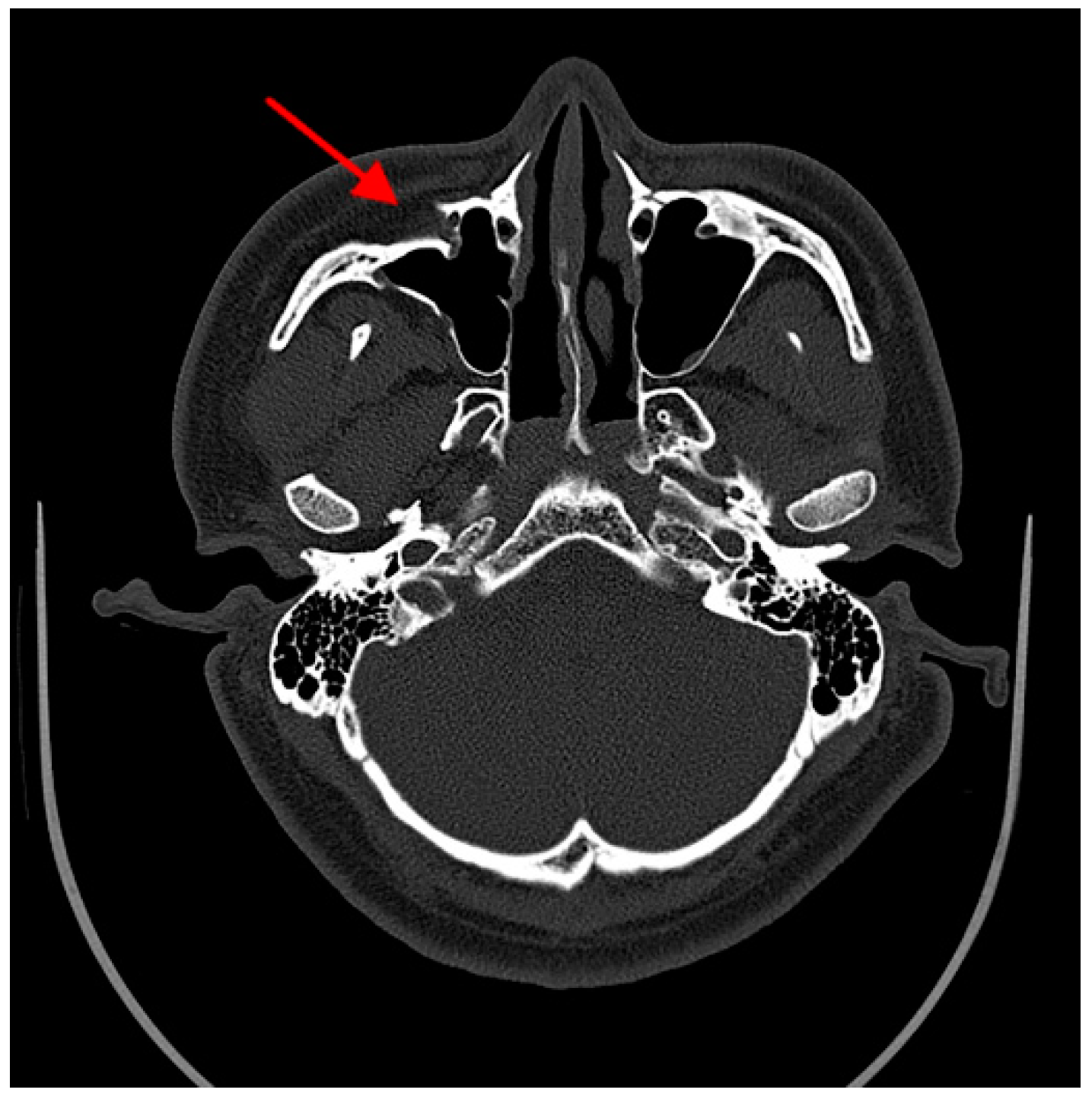
| Variables | Value |
|---|---|
| Maxillary sinus pathology (Y): | |
| No | 0 |
| Yes | 1 |
| Age group (X1): | |
| 0–17 | 0 |
| 18–59 | 1 |
| >60 | 2 |
| Gender (X2): | |
| Male | 0 |
| Female | 1 |
| History of diabetes (X3): | |
| No | 0 |
| Yes | 1 |
| Number of sinus walls involved (X4): | |
| Preoperative CT evaluation of maxillary sinus (X5): | |
| Normal | 0 |
| Mucosal thickening | 1 |
| Air–fluid level | 2 |
| Total opacification | 3 |
| The presence or absence of endotracheal intubation (X6) | |
| Endotracheal intubation | 0 |
| Tracheostomy tube | 1 |
| Number of screws implanted in the maxillary sinus (X7) | |
| Number of screws penetrating the maxillary sinus (X8) | |
| Fracture reduction of maxillary sinus wall (X9) | |
| Perfect | 0 |
| Imperfect | 1 |
| Variables | Post-Traumatic Maxillary Sinus Pathology | |
|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | |
| Age (patients): | ||
| 0–17 | 5 | 17 |
| 18–59 | 104 | 123 |
| >60 | 4 | 9 |
| Gender (patients): | ||
| Male | 83 | 115 |
| Female | 30 | 34 |
| History of diabetes (patients): | ||
| No | 108 | 145 |
| Yes | 5 | 4 |
| Number of sinus walls involved (sinus) | 3.30 ± 1.07 | 3.76 ± 0.98 |
| Preoperative CT evaluation of maxillary sinus (sinus): | ||
| Normal | 13 | 6 |
| Mucosal thickening | 61 | 89 |
| Air–fluid level | 24 | 25 |
| Total opacification | 56 | 98 |
| The presence or absence of endotracheal intubation (sinus): | ||
| Endotracheal intubation | 148 | 204 |
| Tracheostomy tube | 6 | 14 |
| Number of screws implanted in the maxillary sinus (sinus) | 11.94 ± 5.37 | 13.30 ± 5.38 |
| Number of screws penetrating the maxillary sinus (sinus) | 4.52 ± 2.83 | 5.56 ± 3.07 |
| Fracture reduction of maxillary sinus wall (sinus): | ||
| Perfect | 147 | 188 |
| Imperfect | 7 | 30 |
| Factors | Variables | p-Value | OR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | X1 | 0.062 | ||
| 18–59 | 0.023 | 0.325 | 0.123 to 0.856 | |
| >60 | 0.295 | 0.475 | 0.118 to 1.915 | |
| Gender (1) | X2 | 0.786 | 0.928 | 0.541 to 1.591 |
| History of diabetes | X3 | 0.390 | 0.613 | 0.201 to 1.869 |
| Number of sinus walls involved | X4 | 0.011 | 1.383 | 1.077 to 1.776 |
| Preoperative CT evaluation of maxillary sinus | X5 | 0.486 | ||
| Mucosal thickening (1) | 0.187 | 2.132 | 0.693 to 6.558 | |
| Air–fluid level (2) | 0.538 | 1.463 | 0.436 to 4.909 | |
| Total opacification (3) | 0.301 | 1.854 | 0.575 to 5.978 | |
| The presence or absence of endotracheal intubation | X6 | 0.320 | 1.707 | 0.595 to 4.894 |
| Number of screws implanted in the maxillary sinus | X7 | 0.966 | 0.999 | 0.952 to 1.048 |
| Number of screws penetrating the maxillary sinus | X8 | 0.007 | 1.124 | 1.033 to 1.222 |
| Fracture reduction of maxillary sinus wall (1) | X9 | 0.021 | 2.901 | 1.176 to 7.160 |
| Number of Sinus Walls Involved | Number of Screws Penetrating the Maxillary Sinus | Fracture Reduction of Maxillary Sinus Wall | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | OR | p-Value | Variables | OR | p-Value | Variables | OR | p-Value |
| Age | - | 0.907 | Age | - | 0.936 | Age | - | 0.592 |
| Gender | 1.207 | 0.604 | Gender | 1.099 | 0.755 | Gender | 0.575 | 0.483 |
| History of diabetes | 0.930 | 0.946 | History of diabetes | 1.077 | 0.959 | History of diabetes | 1.276 | 0.875 |
| Preoperative CT evaluation of maxillary sinus | - | 0.964 | Number of sinus walls involved | 0.957 | 0.887 | Number of sinus walls involved | 0.908 | 0.891 |
| The presence or absence of endotracheal intubation | 1.311 | 0.661 | Preoperative CT evaluation of maxillary sinus | - | 0.999 | Preoperative CT evaluation of maxillary sinus | - | 0.932 |
| Number of screws implanted in the maxillary sinus | 1.131 | 0.701 | The presence or absence of endotracheal intubation | 1.470 | 0.632 | The presence or absence of endotracheal intubation | 2.062 | 0.617 |
| Number of screws penetrating the maxillary sinus | 0.995 | 0.990 | Number of screws implanted in the maxillary sinus | 1.136 | 0.694 | Number of screws implanted in the maxillary sinus | 0.727 | 0.589 |
| Fracture reduction of the maxillary sinus wall | 0.471 | 0.322 | Fracture reduction of the maxillary sinus wall | 0.622 | 0.332 | Number of screws penetrating the maxillary sinus | 0.474 | 0.187 |
| Factors | Pre-Matching | Propensity Score Matching | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | p-Value | Chi-Square Value | p-Value | |
| Number of sinus walls involved | 1.383 (1.077 to 1.776) | 0.011 | 4.473 (64.04% vs. 48.31) | 0.034 |
| Number of screws penetrating the maxillary sinus | 1.124 (1.033 to 1.222) | 0.007 | 4.802 (64.23% vs. 50.41%) | 0.028 |
| Fracture reduction of maxillary sinus wall (1) | 2.901 (1.176 to 7.160) | 0.021 | 6.341 (80% vs. 51.43%) | 0.012 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, L.; Wu, M.; Li, H.; Liang, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, L. Risk Factors for Maxillary Sinus Pathology after Surgery for Midfacial Fracture: A Multivariate Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6299. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216299
Jiang L, Wu M, Li H, Liang J, Chen J, Liu L. Risk Factors for Maxillary Sinus Pathology after Surgery for Midfacial Fracture: A Multivariate Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(21):6299. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216299
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Linli, Mengsong Wu, Hui Li, Jiayu Liang, Jinlong Chen, and Lei Liu. 2022. "Risk Factors for Maxillary Sinus Pathology after Surgery for Midfacial Fracture: A Multivariate Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 21: 6299. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216299
APA StyleJiang, L., Wu, M., Li, H., Liang, J., Chen, J., & Liu, L. (2022). Risk Factors for Maxillary Sinus Pathology after Surgery for Midfacial Fracture: A Multivariate Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(21), 6299. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216299







