A Four-Stepwise Electrocardiographic Algorithm for Differentiation of Ventricular Arrhythmias Originated from Left Ventricular Outflow Tract
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Populations
2.3. Electrophysiological Study
2.4. Mapping and Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation
2.5. ECG Analysis
2.6. Procedure Success and Follow-Up
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Mapping and Ablation
3.3. ECG Analysis
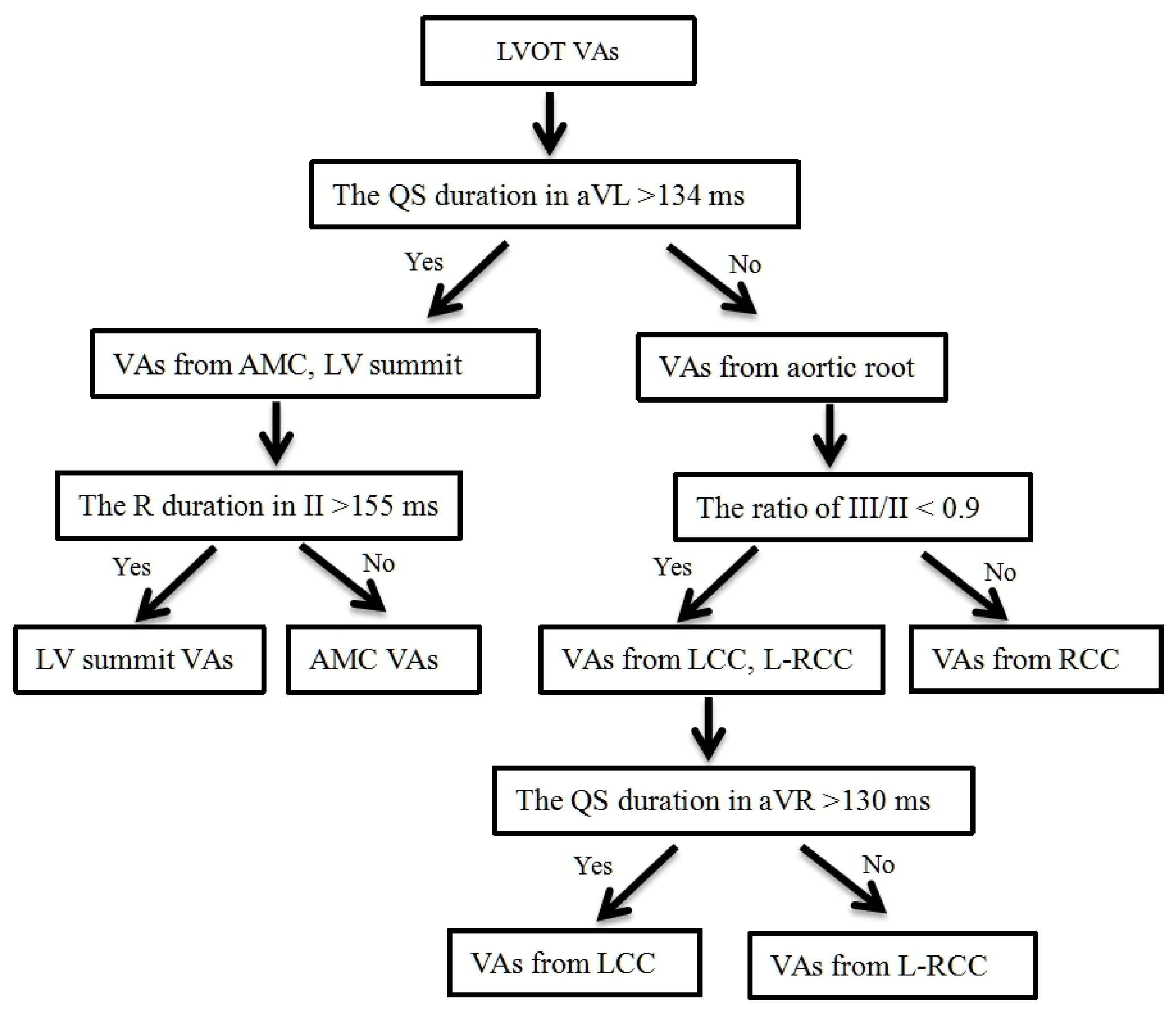
3.4. Develop a Stepwise ECG Algorithm to Differentiate LVOT VAs
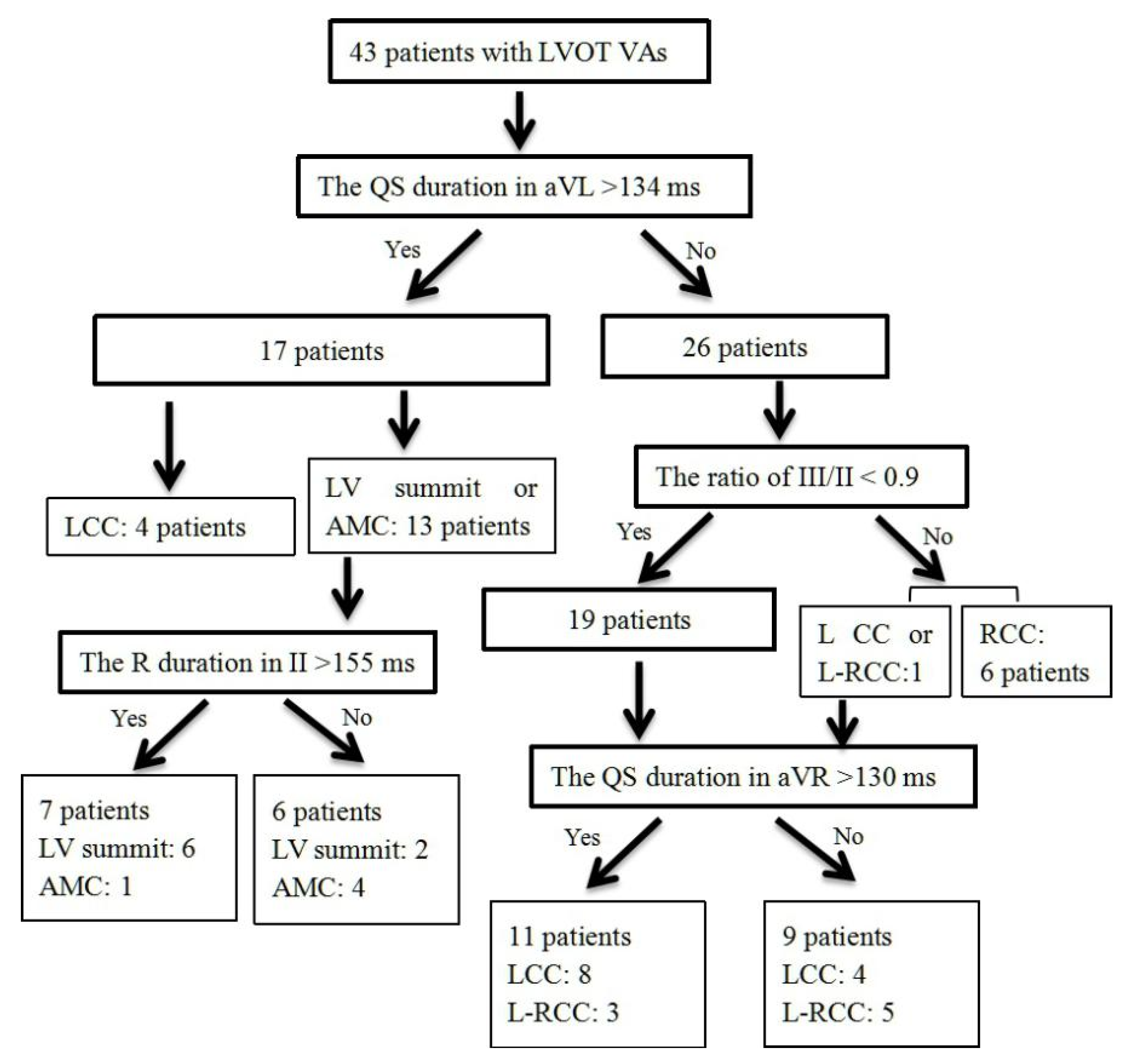
3.5. Validation of Four-Stepwise ECG Algorithm in the Prospective Study
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prystowsky, E.N.; Padanilam, B.J.; Joshi, S.; Fogel, R.I. Ventricular arrhythmias in the absence of structural heart disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 1733–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, K.R.; Satomi, K.; Kuck, K.H.; Ouyang, F.; Antz, M. Left ventricular outflow tract tachycardia including ventricular tachycardia from the aortic cusps and epicardial ventricular tachycardia. Herz 2007, 32, 226–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.D.; Kumar, S.; Parameswaran, R.; Wong, G.; Voskoboinik, A.; Sugumar, H.; Watts, T.; Sparks, P.B.; Morton, J.B.; McLellan, A.; et al. Differentiating Right- and Left-Sided Outflow Tract Ventricular Arrhythmias: Classical ECG Signatures and Prediction Algorithms. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2019, 12, e007392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reithmann, C.; Fiek, M. Left ventricular outflow tract arrhythmias with divergent QRS morphology: Mapping of different exits and ablation strategy. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2018, 51, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.W.; Anderson, R.H.; Markowitz, S.M.; Lerman, B.B. Catheter Ablation of Arrhythmias Originating From the Left Ventricular Outflow Tract. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Kubala, M.; Liang, J.J.; Hayashi, T.; Park, J.; Padros, I.L.; Garcia, F.C.; Santangeli, P.; Supple, G.E.; Frankel, D.S.; et al. Lead I R-wave amplitude to differentiate idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias with left bundle branch block right inferior axis originating from the left versus right ventricular outflow tract. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2018, 29, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Ju, W.; Zhu, L.; Chen, K.; Zhang, F.; Chen, H.; Yang, G.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Gu, K.; et al. V3R/V7 Index: A Novel Electrocardiographic Criterion for Differentiating Left From Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Arrhythmias Origins. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2018, 11, e006243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; Yamada, T.; McElderry, H.T.; Inden, Y.; Shimano, M.; Murohara, T.; Kumar, V.; Doppalapudi, H.; Plumb, V.J.; Kay, G.N. A novel electrocardiographic criterion for differentiating a left from right ventricular outflow tract tachycardia origin: The V2S/V3R index. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2014, 25, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, C.; Wan, Z.; Tse, G.; Letsas, K.P.; Liu, T.; Efremidis, M.; Li, J.; Lin, W. The V1-V3 transition index as a novel electrocardiographic criterion for differentiating left from right ventricular outflow tract ventricular arrhythmias. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2019, 56, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, M.; Nogami, A.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Kuroki, K.; Yamasaki, H.; Machino, T.; Yui, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Talib, A.K.; Murakoshi, N.; et al. The QRS morphology pattern in V5R is a novel and simple parameter for differentiating the origin of idiopathic outflow tract ventricular arrhythmias. Europace 2015, 17, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriquez, A.; Baranchuk, A.; Briceno, D.; Saenz, L.; Garcia, F. How to use the 12-lead ECG to predict the site of origin of idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias. Heart Rhythm. 2019, 16, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, F.; Mathew, S.; Wu, S.; Kamioka, M.; Metzner, A.; Xue, Y.; Ju, W.; Yang, B.; Zhan, X.; Rillig, A.; et al. Ventricular arrhythmias arising from the left ventricular outflow tract below the aortic sinus cusps: Mapping and catheter ablation via transseptal approach and electrocardiographic characteristics. Circ Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2014, 7, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; McElderry, H.T.; Doppalapudi, H.; Murakami, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Okada, T.; Tsuboi, N.; Inden, Y.; Murohara, T.; et al. Idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias originating from the aortic root: Prevalence, electrocardiographic and electrophysiologic characteristics, and results of radiofrequency catheter ablation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Lau, Y.R.; Litovsky, S.H.; Thomas McElderry, H.; Doppalapud, I.H.; Osorio, J.; Plumb, V.J.; Neal Kay, G. Prevalence and clinical, electrocardiographic, and electrophysiologic characteristics of ventricular arrhythmias originating from the noncoronary sinus of Valsalva. Heart Rhythm. 2013, 10, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anter, E.; Frankel, D.S.; Marchlinski, F.E.; Dixit, S. Effect of electrocardiographic lead placement on localization of outflow tract tachycardias. Heart Rhythm. 2012, 9, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betensky, B.P.; Park, R.E.; Marchlinski, F.E.; Hutchinson, M.D.; Garcia, F.C.; Dixit, S.; Callans, D.J.; Cooper, J.M.; Bala, R.; Lin, D.; et al. The V(2) transition ratio: A new electrocardiographic criterion for distinguishing left from right ventricular outflow tract tachycardia origin. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasdemir, C.; Aktas, S.; Govsa, F.; Aktas, E.O.; Kocak, A.; Bozkaya, Y.T.; Demirbas, M.I.; Ulucan, C.; Ozdogan, O.; Kayikcioglu, M.; et al. Demonstration of ventricular myocardial extensions into the pulmonary artery and aorta beyond the ventriculo-arterial junction. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2007, 30, 534–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hoff, P.I.; Rossvoll, O.; De Bortoli, A.; Solheim, E.; Sun, L.; Schuster, P.; Larsen, T.; Ohm, O.J. Ventricular arrhythmias originating from the aortomitral continuity: An uncommon variant of left ventricular outflow tract tachycardia. Europace 2012, 14, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, D.; Roberts-Thomson, K.C.; Seiler, J.; Inada, K.; Tedrow, U.B.; Mitchell, R.N.; Sobieszczyk, P.S.; Eisenhauer, A.C.; Couper, G.S.; Stevenson, W.G. Ventricular tachycardia arising from the aortomitral continuity in structural heart disease: Characteristics and therapeutic considerations for an anatomically challenging area of origin. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2009, 2, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, F.P.; Lin, C.Y.; Shirai, Y.; Futyma, P.; Santangeli, P.; Lin, Y.J.; Chang, S.L.; Lo, L.W.; Hu, Y.F.; Chang, H.Y.; et al. Outcomes of catheter ablation of ventricular arrhythmia originating from the left ventricular summit: A multicenter study. Heart Rhythm. 2020, 17, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szili-Torok, T.; van Malderen, S.; de Groot, N. ‘Born’ with a ‘dead’-end-tract resulting in arrhythmias in the aorto-mitral continuity: Coincidence, causation, and ‘commensuration’. Europace 2012, 14, 308–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, F.; Fotuhi, P.; Ho, S.Y.; Hebe, J.; Volkmer, M.; Goya, M.; Burns, M.; Antz, M.; Ernst, S.; Cappato, R.; et al. Repetitive monomorphic ventricular tachycardia originating from the aortic sinus cusp: Electrocardiographic characterization for guiding catheter ablation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Ilkhanoff, L.; Gerstenfeld, E.; Dixit, S.; Beldner, S.; Bala, R.; Garcia, F.; Callans, D.; Marchlinski, F.E. Twelve-lead electrocardiographic characteristics of the aortic cusp region guided by intracardiac echocardiography and electroanatomic mapping. Heart Rhythm. 2008, 5, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, Y.; Nogami, A.; Shinoda, Y.; Masuda, K.; Machino, T.; Kuroki, K.; Yamasaki, H.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Aonuma, K. Idiopathic Ventricular Arrhythmias Originating From the Vicinity of the Communicating Vein of Cardiac Venous Systems at the Left Ventricular Summit. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2018, 11, e005386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
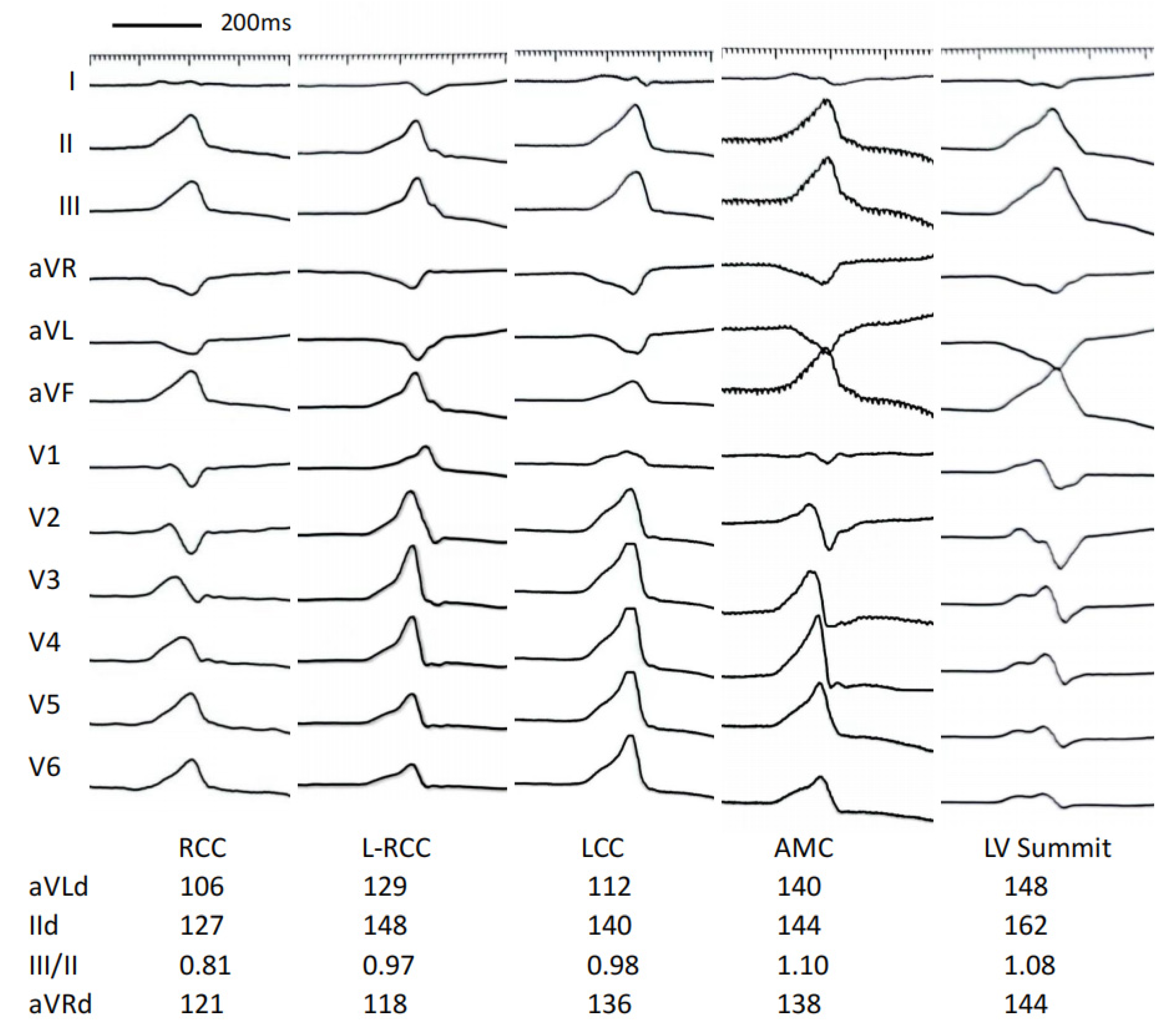

| Characteristic | RCC Group (n = 8) | L-RCC Group (n = 21) | LCC Group (n = 24) | AMC Group (n = 9) | LV Summit Group (n = 6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 45 ± 19 | 50 ± 16 | 56 ± 16 | 66 ± 15 | 54 ± 20 |
| Gender (male) | 1 (13%) | 7 (33%) | 11 (46%) | 5 (56%) | 4 (67%) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.9 ± 4.8 | 26.3 ± 6.2 | 25.2 ± 5.3 | 27.0 ± 7.1 | 25.3 ± 4.8 |
| Hypertension (n,%) | 3 (37%) | 7 (33%) | 9 (37%) | 4 (44%) | 2 (33%) |
| Diabetes | 1 (14%) | 2 (9%) | 3 (14%) | 1 (11%) | 0 |
| LVd (mm) | 45 ± 5 | 48 ± 4 | 50 ± 5 | 51 ± 3 | 49 ± 3 |
| LVEF (%) | 59 ± 3 | 65 ± 6 | 61 ± 5 | 61 ± 6 | 61 ± 7 |
| History (month) | 17 ± 13 | 21 ± 28 | 30 ± 31 | 30 ± 26 | 65 ± 58 *# |
| PVC burden (n/24 h) | 20,653 ± 13,707 | 23,279 ± 12,299 | 22,302 ± 8208 | 23,751 ± 11,356 | 34,843 ± 13,899 |
| VT (%) | 1 (13%) | 2 (9%) | 2 (8%) | 0 | 2 (33%) |
| Antiarrhythmics (n) | 2.1 ± 1.1 | 1.9 ± 1.3 | 2.0 ± 1.2 | 2.2 ± 1.2 | 1.8 ± 1.3 |
| Characteristic | RCC Group (n = 8) | L-RCC Group (n = 21) | LCC Group (n = 24) | AMC Group (n = 9) | LV Summit Group (n = 6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total QRS duration (ms) | 150 ± 28 | 142 ± 15 | 147 ± 13 | 158 ± 13 # | 178 ± 26 *#&$ |
| R wave duration (ms) | |||||
| Lead I | 100 ± 35 | 88 ± 33 | 83 ± 35 | 73 ± 26 | 103 ± 41 |
| Lead II | 132 ± 13 | 134 ± 16 | 142 ± 14 | 152 ± 11 *# | 171 ± 30 *#&$ |
| Lead III | 131 ± 11 | 129 ± 19 | 139 ± 16 | 152 ± 11 *# | 169 ± 34 *#& |
| Lead aVF | 130 ± 10 | 133 ± 17 | 141 ± 16 | 151 ± 11 *# | 168 ± 30 *#& |
| QS wave duration (ms) | |||||
| Lead I (S wave) | 35 ± 7 | 59 ± 23 | 64 ± 27 | 81 ± 29 | 71 ± 46 |
| Lead aVL | 113 ± 19 | 124 ± 18 | 130 ± 17 * | 147 ± 13 *#& | 153 ± 24 *#& |
| Lead aVR | 125 ± 14 | 128 ± 14 | 139 ± 15 *# | 146 ± 14 *# | 155 ± 15 *#& |
| R wave amplitude (mV) | |||||
| Lead I | 0.46 ± 0.27 | 0.43 ± 0.30 | 0.32 ± 0.22 | 0,20 ± 0.11 | 0.29 ± 0.21 |
| Lead II | 1.75 ± 0.33 | 2.07 ± 0.81 | 2.11 ± 0.57 | 1.71 ± 0.28 | 1.84 ± 0.53 |
| Lead III | 1.40 ± 0.45 | 1.95 ± 0.86 | 2.18 ± 0.69 * | 1.89 ± 0.39 | 1.93 ± 0.55 |
| Lead aVF | 1.60 ± 0.42 | 2.05 ± 0.89 | 2.14 ± 0.59 * | 1.79 ± 0.34 | 1.86 ± 0.53 |
| The ratio of III/II | 0.78 ± 0.15 | 0.94 ± 0.16* | 1.03 ± 0.13 * | 1.10 ± 0.16 *# | 1.06 ± 0.10 * |
| QS wave amplitude (mV) | |||||
| Lead I (S wave) | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.22 ± 0.13 | 0.31 ± 0.17 | 0.39 ± 0.11 | 0.24 ± 0.16 |
| Lead aVL | 0.58 ± 0.29 | 1.14 ± 0.53 * | 1.24 ± 0.35 * | 1.12 ± 0.21 * | 1.12 ± 0.30 * |
| Lead aVR | 1.02 ± 0.18 | 1.09 ± 0.42 | 1.09 ± 0.21 | 0.79 ± 0.15 #& | 0.96 ± 0.25 |
| The ratio of aVL/aVR | 0.58 ± 0.28 | 1.12 ± 0.36 * | 1.20 ± 0.36 * | 1.45 ± 0.38 *# | 1.18 ± 0.18 * |
| Characteristic | RCC Group (n = 8) | L-RCC Group (n = 21) | LCC Group (n = 24) | AMC Group (n = 9) | LV Summit Group (n = 6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R wave duration (ms) | |||||
| Lead V1 | 46 ± 10 | 52 ± 24 | 72 ± 32 * | 101 ± 52 *#& | 134 ± 17 *#& |
| Lead V2 | 54 ± 14 | 72 ± 33 | 88 ± 27 | 113 ± 35 *#& | 127 ± 12 *#& |
| Lead V3 | 92 ± 25 | 108 ± 24 | 112 ± 23 * | 124 ± 31 * | 132 ± 18 * |
| Lead V4 | 129 ± 15 | 127 ± 16 | 131 ± 14 | 137 ± 23 | 148 ± 22 *#& |
| Lead V5 | 134 ± 14 | 130 ± 14 | 135 ± 14 | 139 ± 22 | 150 ± 23 |
| Lead V6 | 113 ± 41 | 130 ± 13 | 134 ± 12 * | 142 ± 16 * | 147 ± 28 * |
| S wave duration (ms) | |||||
| Lead V1 | 79 ± 23 | 69 ± 23 | 60 ± 23 | 30 ± 1 *#& | 44 ± 7 * |
| Lead V2 | 73 ± 18 | 62 ± 29 | 56 ± 23 | 44 ± 13 * | 43 ± 6 * |
| Lead V3 | 45 ± 15 | 47 ± 21 | 40 ± 21 | 37 ± 12 | 42 ± 15 |
| R wave amplitude (mV) | |||||
| Lead V1 | 0.22 ± 0.07 | 0.34 ± 0.24 | 0.53 ± 0.42 * | 0.68 ± 0.57 *# | 0.83 ± 0.26 *# |
| Lead V2 | 0.45 ± 0.17 | 0.98 ± 0.65 | 1.07 ± 0.58 | 1.22 ± 0.76 | 1.47 ± 0.58 |
| Lead V3 | 0.93 ± 0.32 | 1.57 ± 0.97 | 1.85 ± 0.83 * | 1.77 ± 0.71 * | 2.42 ± 0.94 *# |
| Lead V4 | 1.79 ± 0.53 | 2.06 ± 1.11 | 2.25 ± 0.68 | 1.84 ± 0.52 | 2.68 ± 0.88 |
| Lead V5 | 1.92 ± 0.30 | 2.10 ± 0.88 | 2.18 ± 0.68 | 1.33 ± 0.43 #& | 2.28 ± 0.89 $ |
| Lead V6 | 1.75 ± 0.33 | 1.84 ± 0.67 | 1.77 ± 0.56 | 0.91 ± 0.34 *#& | 1.22 ± 0.37 #& |
| S wave amplitude (mV) | |||||
| Lead V1 | 1.28 ± 0.67 | 1.00 ± 0.58 | 0.61 ± 0.48 *# | 0.16 ± 0.11 *# | 0.37 ± 0.28 * |
| Lead V2 | 1.36 ± 0.61 | 1.25 ± 0.86 | 1.12 ± 0.66 | 0.48 ± 0.35 *#& | 0.50 ± 0.16 * |
| Lead V3 | 0.55 ± 0.43 | 0.69 ± 0.49 | 0.81 ± 0.52 | 0.58 ± 0.51 | 0.45 ± 0.17 |
| Sensitivity, % | Specificity, % | PPV, % | NPV, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The QS duration in aVL > 134 ms for differentiating VAs from AMC, LV summit and VAs from aortic root | 100.0 | 86.7 | 76.5 | 100.0 |
| The R duration in II > 155 ms for differentiating VAs from AMC and VAs from LV summit | 75.0 | 80.0 | 85.7 | 66.7 |
| The ratio of III/II < 0.9 for differentiating VAs from RCC and VAs from L-RCC, LCC | 100.0 | 95.0 | 85.7 | 100.0 |
| The QS duration in aVR > 130 ms for differentiating VAs from LCC and VAs from L-RCC | 66.7 | 62.5 | 72.7 | 55.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, H.-W.; Gao, W.-D.; Wang, X.-H.; Chen, Z.-S.; Liu, X.-B. A Four-Stepwise Electrocardiographic Algorithm for Differentiation of Ventricular Arrhythmias Originated from Left Ventricular Outflow Tract. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216398
Tan H-W, Gao W-D, Wang X-H, Chen Z-S, Liu X-B. A Four-Stepwise Electrocardiographic Algorithm for Differentiation of Ventricular Arrhythmias Originated from Left Ventricular Outflow Tract. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(21):6398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216398
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Hong-Wei, Wei-Dong Gao, Xin-Hua Wang, Zhi-Song Chen, and Xue-Bo Liu. 2022. "A Four-Stepwise Electrocardiographic Algorithm for Differentiation of Ventricular Arrhythmias Originated from Left Ventricular Outflow Tract" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 21: 6398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216398
APA StyleTan, H.-W., Gao, W.-D., Wang, X.-H., Chen, Z.-S., & Liu, X.-B. (2022). A Four-Stepwise Electrocardiographic Algorithm for Differentiation of Ventricular Arrhythmias Originated from Left Ventricular Outflow Tract. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(21), 6398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216398





