Role of Bronchial Artery Embolization as Early Treatment Option in Stable Cystic Fibrosis Patients with Sub-Massive Hemoptysis: Personal Experience and Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Procedural Planning
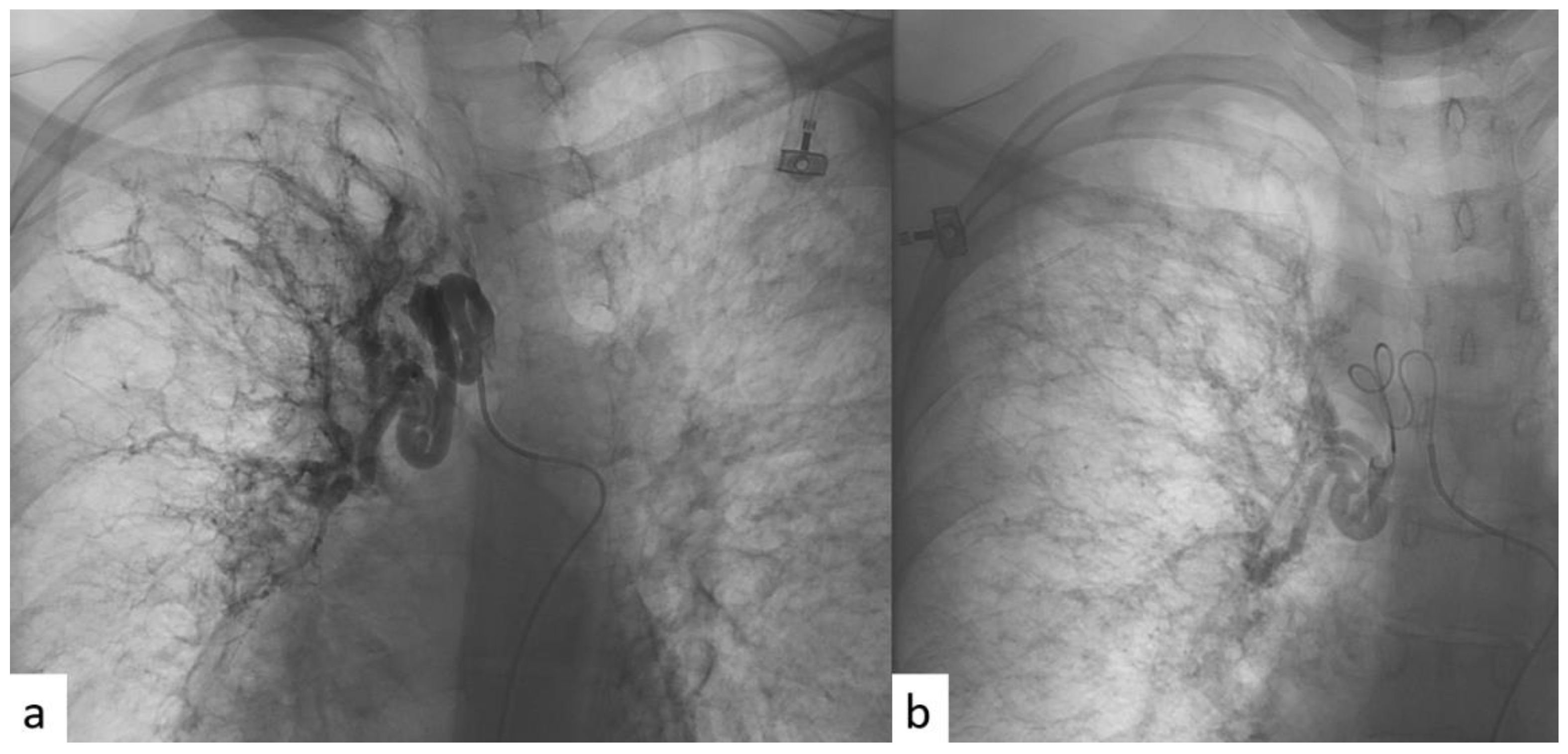
2.3. BAE Procedure
2.4. Endpoints
- (a)
- The safety of the procedure—that is, the rate of peri- and post-procedural complications and the mortality related to the procedure; CIRSE classification [24].
- (b)
- Technical success, defined as the percentage of procedures in which effective exclusion of the vessel to be treated was achieved with immediate post-procedure hemoptysis control; both the inability to catheterize the bronchial artery and all cases in which the final angiographic study is considered unsatisfactory were considered technical failure.
- (c)
- Primary clinical success, defined as the absence of recurrence of hemoptysis and hemoptysis-related mortality 1 month after the procedure.
- (d)
- Secondary clinical success, defined as the absence of recurrence of hemoptysis and hemoptysis-related mortality 6 month after the procedure.
- (e)
- Relative clinical success, defined as a reduction in blood quantitative at the first hemoptysis episode after BAE compared with blood quantitative at the hemoptysis episode before BAE.
- (f)
- Secondary outcomes were considered: the influence of the embolic agent and Pseudomonas infection rate in relapsing episodes and pre/post-procedural FEV1.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brinson, G.M.; Noone, P.G.; Mauro, M.A.; Knowles, M.R.; Yankaskas, J.R.; Sandhu, J.S.; Jaques, P.F. Bronchial Artery Embolization for the Treatment of Hemoptysis in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 1951–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barben, J.; Robertson, D.; Olinsky, A.; Ditchfield, M. Bronchial Artery Embolization for Hemoptysis in Young Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Radiology 2002, 224, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, M.; Midulla, F.; Tancredi, G.; Salvatori, F.M.; Bonci, E.; Cimino, G.; Flaishman, I. Bronchial Artery Embolization for the Management of Nonmassive Hemoptysis in Cystic Fibrosis. Chest 2002, 121, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweezey, N.B.; Fellows, K.E. Bronchial Artery Embolization for Severe Hemoptysis in Cystic Fibrosis. Chest 1990, 97, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vidal, V.; Therasse, E.; Berthiaume, Y.; Bommart, S.; Giroux, M.-F.; Oliva, V.L.; Abrahamowicz, M.; du Berger, R.; Jeanneret, A.; Soulez, G. Bronchial Artery Embolization in Adults with Cystic Fibrosis: Impact on the Clinical Course and Survival. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2006, 17, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.M.; Doershuk, C.F.; Stern, R.C. Bronchial artery embolization to control hemoptysis in cystic fibrosis. Radiology 1990, 175, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flume, P.A.; Yankaskas, J.R.; Ebeling, M.; Hulsey, T.; Clark, L.L. Massive Hemoptysis in Cystic Fibrosis. Chest 2005, 128, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barben, J.U.; Ditchfield, M.; Carlin, J.B.; Robertson, C.F.; Robinson, P.J.; Olinsky, A. Major haemoptysis in children with cystic fibrosis: A 20-year retrospective study. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2003, 2, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konstan, M.W.; Ms, D.J.P.; Van Devanter, D.R.; Wagener, J.S.; Morgan, W.J. Scientific Advisory Group and the Investigators and Coordinators of ESCF Epidemiologic Study of Cystic Fibrosis: 25 years of observational research. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2021, 56, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flight, W.G.; Barry, P.J.; Bright-Thomas, R.J.; Butterfield, S.; Ashleigh, R.; Jones, A.M. Outcomes Following Bronchial Artery Embolisation for Haemoptysis in Cystic Fibrosis. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 40, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohna, M.; Renz, D.M.; Stehling, F.; Dohna-Schwake, C.; Sutharsan, S.; Neurohr, C.; Wirtz, H.; Eickmeier, O.; Grosse-Onnebrink, J.; Sauerbrey, A.; et al. Coil embolisation for massive haemoptysis in cystic fibrosis. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2021, 8, e000985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira, M.A.P.; da Silveira, P.A.P.; Beltrami, F.G.; Scaffaro, L.A.; Dalcin, P.D.T.R. Clinical outcomes of cystic fibrosis patients with hemoptysis treated with bronchial artery embolization. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2021, 47, e20200557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolli, M.; Perini, S.; Valletta, E.A.; Mastella, G. Bronchial Artery Embolization in the Management of Hemoptysis in Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1995, 19, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.N.; Higgins, L.; Mohabir, P.; Sze, D.Y.; Hofmann, L.V. Bronchial Artery Embolization for Hemoptysis in Cystic Fibrosis Patients: A 17-Year Review. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin, I.L.D.; Hanissian, A.S.; Boulden, T.F.; Baum, S.L.; Gavant, M.L.; Gold, R.E.; George, P.; Green, W.J. Bronchial arteriography and embolotherapy for hemoptysis in patients with cystic fibrosis. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 1991, 14, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Bhalla, A.S.; Goyal, A. Bronchial artery embolization in hemoptysis: A systematic review. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 23, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, H.C.; Stein, M.; Benfield, J.R.; Link, D.P. Role of Bronchial Artery Embolization in the Management of Hemoptysis. Arch. Surg. 1998, 133, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knott-Craig, C.J.; Oostuizen, J.G.; Rossouw, G.; Joubert, J.R.; Barnard, P.M. Management and prognosis of massive hemoptysis Recent experience with 120 patients. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1993, 105, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Kudo, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Fukahori, T.; Shimizu, T.; Uchino, A.; Hayashi, S. Bronchial artery embolization for hemoptysis due to benign diseases: Immediate and long-term results. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2000, 23, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.L.; Johnson, C.M.; Prakash, U.B.S.; McKusick, M.A.; Andrews, J.C.; Stanson, A.W. Bronchial Artery Embolizationn: Experience with 54 patients. Chest 2002, 121, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.K.; Lee, H.-Y. Bronchial Artery Embolization for Treatment of Life-Threatening Hemoptysis. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2006, 23, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, W.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Chung, T.W.; Kang, H.K. Bronchial and Nonbronchial Systemic Artery Embolization for Life-threatening Hemoptysis: A Comprehensive Review. RadioGraphics 2002, 22, 1395–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, E.J.; Pierce, D.B.; Ingraham, C.R.; Johnson, G.E.; Shivaram, G.M.; Valji, K. An Interventionalist’s Guide to Hemoptysis in Cystic Fibrosis. RadioGraphics 2018, 38, 624–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kettenbach, J.; Ittrich, H.; Gaubert, J.Y.; Gebauer, B.; Vos, J.A. CIRSE Standards of Practice on Bronchial Artery Embolisation. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2022, 45, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Hara, M.; Ryuge, M.; Takafuji, J.; Youmoto, M.; Akira, M.; Nagasaka, Y.; Kabata, D.; Yamamoto, K.; Shintani, A. Efficacy and safety of super selective bronchial artery coil embolisation for haemoptysis: A single-centre retrospective observational study. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e014805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holsclaw, D.S.; Grand, R.J.; Shwachman, H. Massive hemoptysis in cystic fibrosis. J. Pediatr. 1970, 76, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.C.; Wood, R.E.; Boat, T.F.; Matthews, L.W.; Tucker, A.S.; Doershuk, C.F. Treatment and prognosis of massive hemoptysis in cystic fibrosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1978, 117, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapnadak, S.G.; Dimango, E.; Hadjiliadis, D.; Hempstead, S.E.; Tallarico, E.; Pilewski, J.M.; Faro, A.; Albright, J.; Benden, C.; Blair, S.; et al. Cystic Fibrosis Foundation consensus guidelines for the care of individuals with advanced cystic fibrosis lung disease. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2020, 19, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schidlow, D.V.; Taussig, L.M.; Knowles, M.R. Cystic fibrosis foundation consensus conference report on pulmonary complications of cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1993, 15, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Patient Characteristics | Patients | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 7 | 53.8% |
| Female | 6 | 46.2% |
| Age, Years | 30 | ±9.5 |
| Age at Diagnosis | 3 | (14) |
| Ethnicity | ||
| White | 13 | 100% |
| Respiratory Infection * | ||
| Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia | 2 | 15.4% |
| MRSA | 3 | 23.1% |
| Alcaligenes xylosoxidans | 1 | 7.7% |
| Mycobacterium Tuberculosis | 1 | 7.7% |
| Acinetobacter Baumannii | 1 | 7.7% |
| Pseudomonas Aeruginosa | 8 | 53.8% |
| Pulmonary function | ||
| FEV1% predicted pre procedure | 52.7 | ±14.9 |
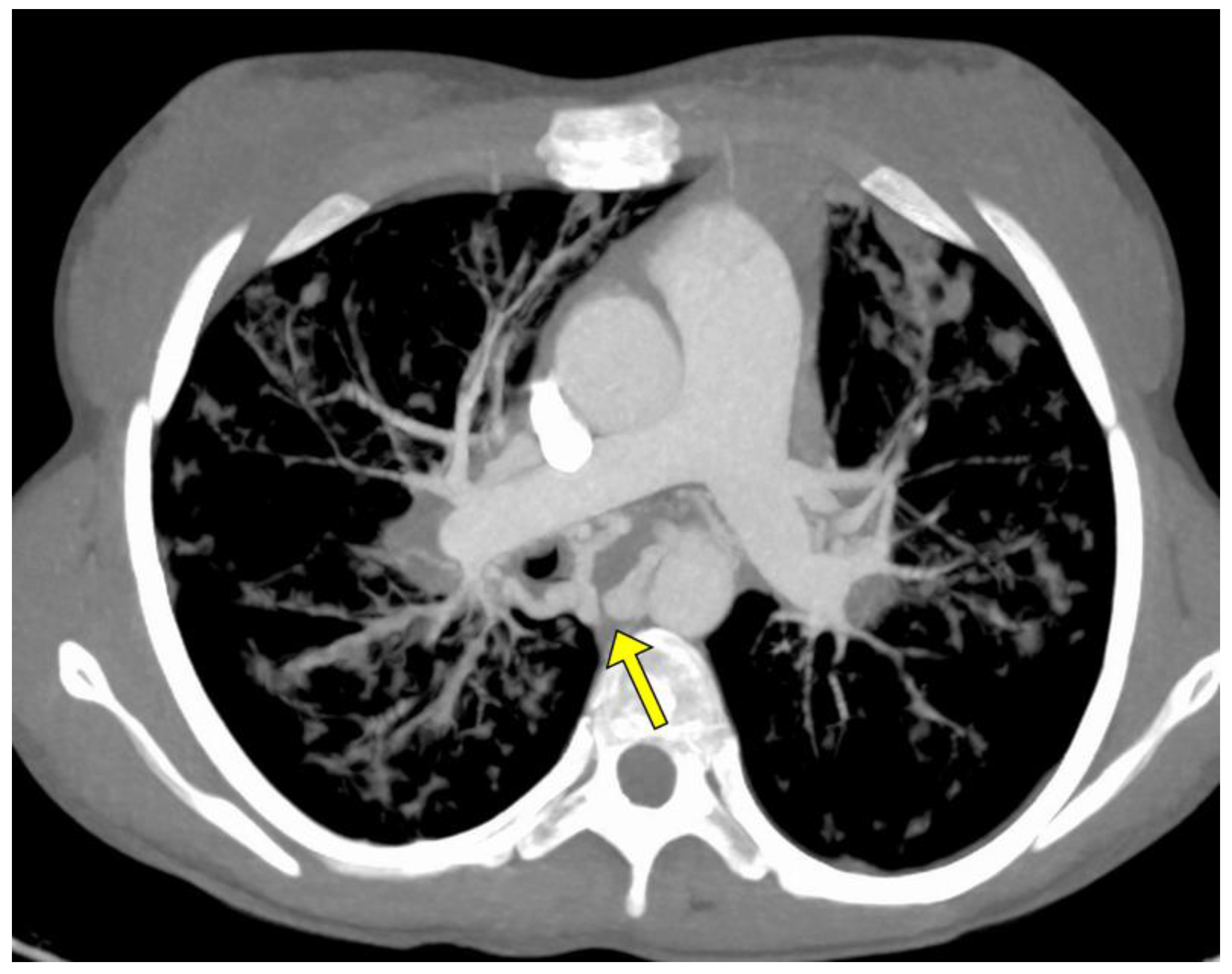
| Procedures | ID Pz. | Vessel Type Treated with BAE | Caliber of Treated Vessel (mm) Pre-Procedure CT | Untreated Vessel Size (mm) Pre-Procedure CT | ∆ Significant Caliber between Left and Right? | Arterial Vessel Studied in Diagnostic Angiography |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | Left | 5 | 2 | Yes | Bronchial left |
| 2 | 1 | Left | 5 | 3 | Yes | Bronchial left |
| 3 | 2 | Right | 6 | 2 | Yes | Bronchial right |
| 4 | 2 | Left + Right | 7.5 | 3.5 | Yes | Bronchial right and left * |
| 5 | 3 | Right | 6 | 3.5 | Yes | Bronchial right |
| 6 | 4 | Right | 7 | 6 | No | Bronchial right and left |
| 7 | 5 | Right | 3.5 | 3.5 | No | Bronchial right and left |
| 8 | 6 | Right | 8 | 5 | Yes | Bronchial right |
| 9 | 7 | Right | 5 | 2 | Yes | Bronchial right |
| 10 | 7 | Right | 5 | 2 | Yes | Bronchial right and left |
| 11 | 7 | Right | 5 | 2 | Yes | Bronchial right |
| 12 | 8 | Right | 3 | 2 | No | Bronchial right and left |
| 13 | 8 | Right | 4 | 2 | No | Bronchial right and left * |
| 14 | 9 | Left | 8 | 7 | No | Bronchial left * |
| 15 | 10 | Right | 7 | 1 | Yes | Bronchial right |
| 16 | 10 | Right | 7 | 1 | Yes | Bronchial right |
| 17 | 11 | Right | 5 | 3 | No | Bronchial right and left |
| 18 | 12 | Left | 7 | 4.5 | Yes | Mammary left |
| 19 | 13 | Right | 3.5 | 0.5 | Yes | Bronchial right |
| Study | n° Pz | n° Proc. | Follow-Up (Months) | Embolizing Materials | Complications | Technical Success | Recurrences | Death | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohen 1990 [6] | 20 | 36 | 37 | Coils, Gelfoam, PVA | Coil migration, chest pain, dysphagia, fever | 19 (100%) | 8 | 4 | Safe and Effective |
| Sweezey 1990 [4] | 25 | 38 | / | Gelfoam, Coils | Mild fever, chest pain | 21 (84%) | 13 | 6 | Safe and Effective |
| Tonkin 1991 [15] | 11 | 20 | 9 to 108 | Coils, Gelfoam, PVA | Dysphagia, chest pain, pseudoaneurysm femoral artery | 11 (100%) | 5 | 3 | Safe and Effective |
| Cipolli 1995 [13] | 14 | 17 | 10.5 | PVA | Chest pain, fever, dysphagia | 10 (71.4%) | 3 | 3 | Safe and Effective |
| Brinson 1998 [1] | 18 | 36 | 22 | Coils, Gelfoam, PVA | Chest pain, dysphagia | 18 (100%) | 3 | 2 | Safe and Effective |
| Antonelli 2002 * [3] | 8 | / | 36 | PVA | Chest pain, fever | 8 (100%) | / | 1 | Safe and Effective |
| Barben 2002 [2] | 20 | 38 | 61 | Coils, Gelfoam, PVA | / | 36 (95%) | 11 | 3 | Safe and Effective |
| Vidal 2006 [5] | 30 | 42 | 60 | Microspheres, PVA | Chest pain | 29 (96.6%) | 8 | 1 | Safe and Effective |
| Flight 2017 [10] | 27 | 51 | 26 | PVA | Chest pain, paresthesia, limb weakness | 27 (100%) | 10 | 9 | Safe and Effective |
| Martin 2020 [14] | 28 | 38 | 58 | TAG Microspheres, PVA | Chest pain, odynophagia, femoral artery thrombosis | 25 (89%) | 7 | / | Safe and Effective |
| Dohna 2021 [11] | 34 | 70 | 89.9 | Coils | Mild cough, chest pain | 34 (100%) | 20 | 12 | Safe and Effective |
| Silveira 2021 [12] | 17 | 39 | 130 | / | Chest pain, fever, dyspnea | 17 (100%) | 8 | 3 | Safe and Effective |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Floridi, C.; Boscarato, P.; Ventura, C.; Bruno, A.; Rossini, N.; Baldassari, M.; Lanza, C.; Fabrizzi, B.; Candelari, R.; Giovagnoni, A. Role of Bronchial Artery Embolization as Early Treatment Option in Stable Cystic Fibrosis Patients with Sub-Massive Hemoptysis: Personal Experience and Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216432
Floridi C, Boscarato P, Ventura C, Bruno A, Rossini N, Baldassari M, Lanza C, Fabrizzi B, Candelari R, Giovagnoni A. Role of Bronchial Artery Embolization as Early Treatment Option in Stable Cystic Fibrosis Patients with Sub-Massive Hemoptysis: Personal Experience and Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(21):6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216432
Chicago/Turabian StyleFloridi, Chiara, Pietro Boscarato, Claudio Ventura, Alessandra Bruno, Nicolo’ Rossini, Michela Baldassari, Cecilia Lanza, Benedetta Fabrizzi, Roberto Candelari, and Andrea Giovagnoni. 2022. "Role of Bronchial Artery Embolization as Early Treatment Option in Stable Cystic Fibrosis Patients with Sub-Massive Hemoptysis: Personal Experience and Literature Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 21: 6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216432
APA StyleFloridi, C., Boscarato, P., Ventura, C., Bruno, A., Rossini, N., Baldassari, M., Lanza, C., Fabrizzi, B., Candelari, R., & Giovagnoni, A. (2022). Role of Bronchial Artery Embolization as Early Treatment Option in Stable Cystic Fibrosis Patients with Sub-Massive Hemoptysis: Personal Experience and Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(21), 6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216432





