Long-Term Follow-Up of Biological Reconstruction with Free Fibular Graft after Resection of Extremity Diaphyseal Bone Tumors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Surgical Technique
2.3. Follow-Up
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
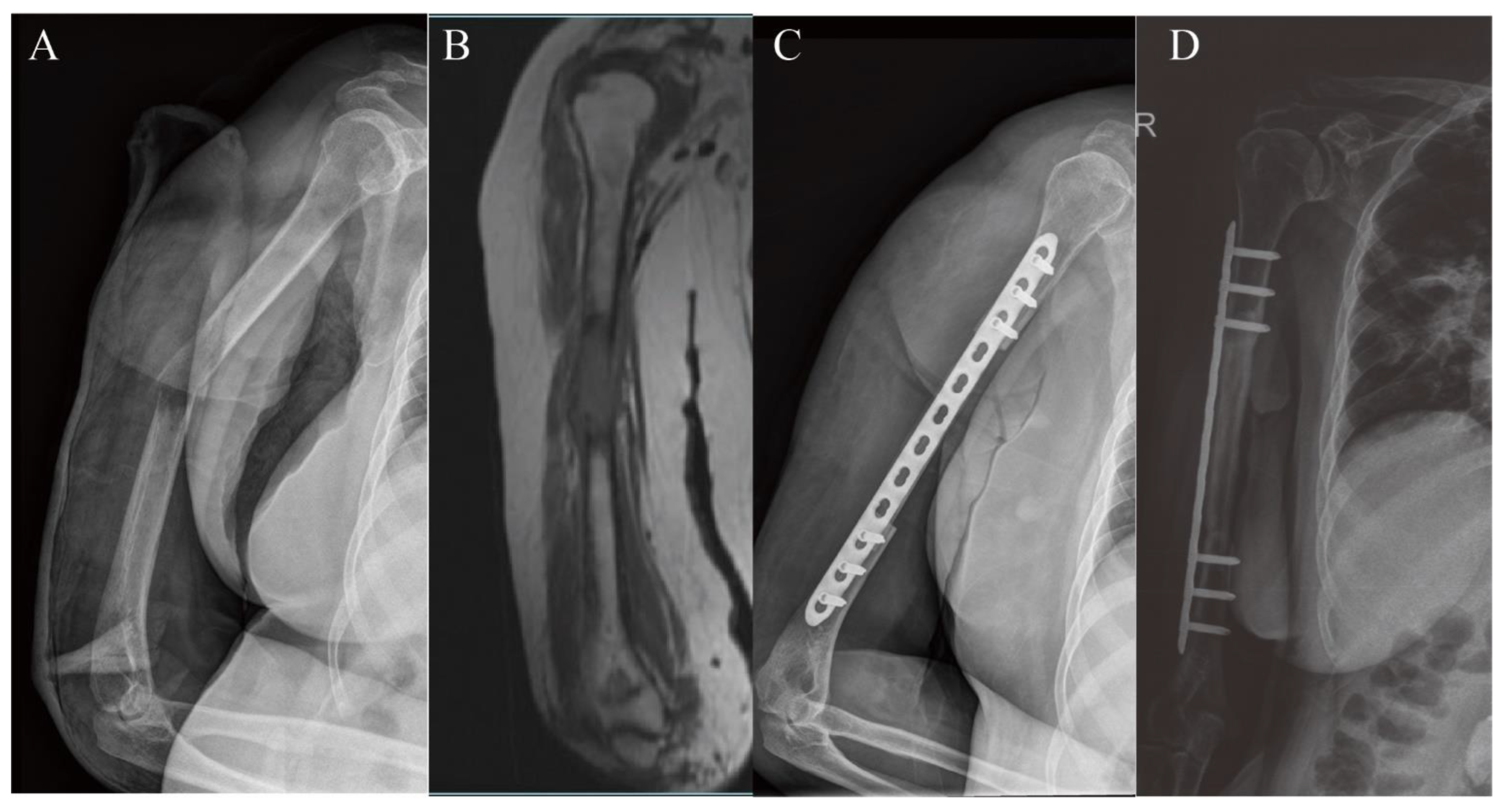
3.1. Upper Extremity Reconstruction Results
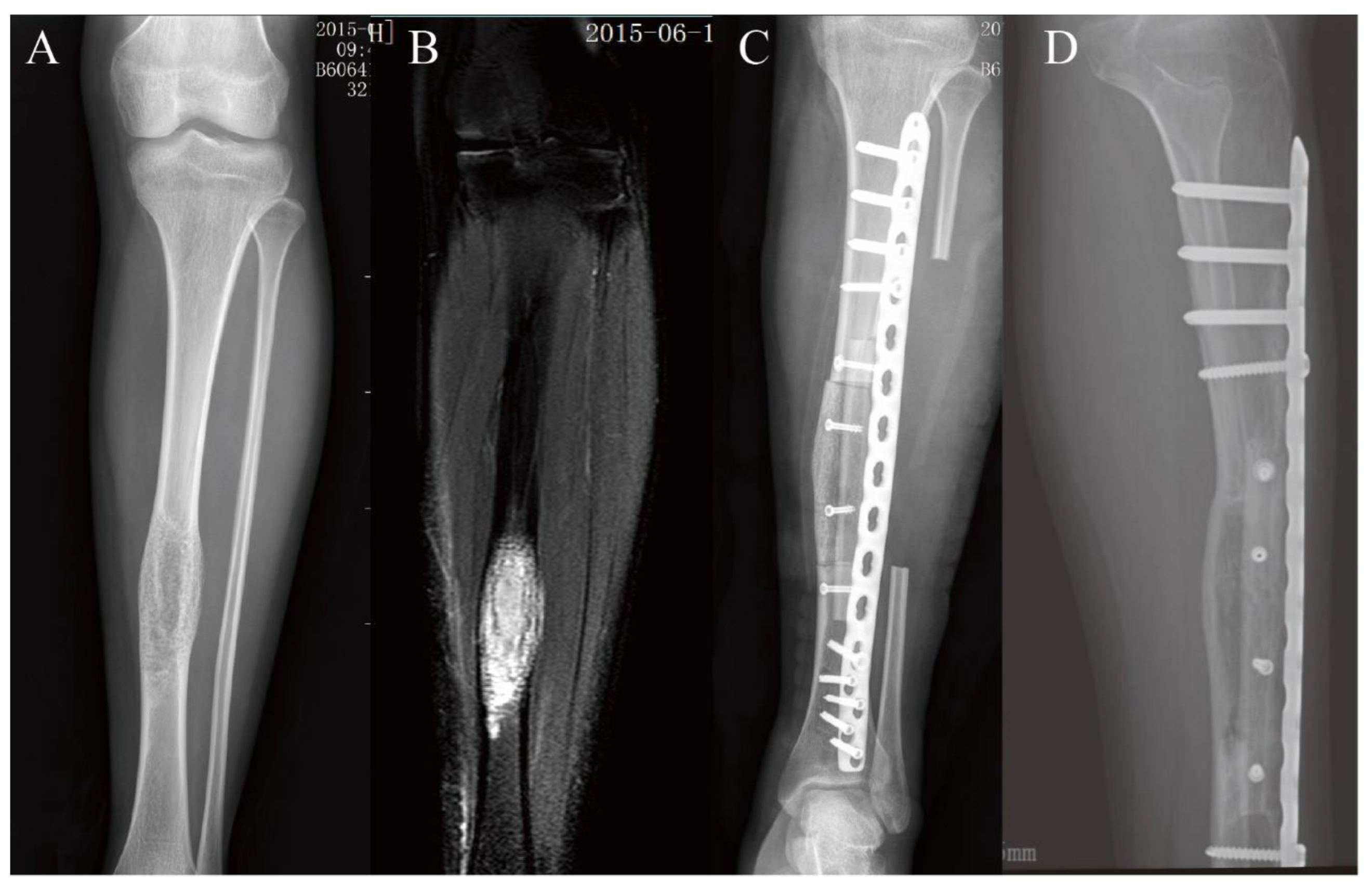
3.2. Lower Extremity Reconstruction Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perisano, C.; Scaramuzzo, L.; De Santis, V.; Piccioli, A.; Ziranu, A.; Barone, C.; Maccauro, G. Quality of Life Following Surgical Treatment of Lower Limb Metastases in Long Bone. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2015, 29, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, S.; Li, H.; Li, D.; Xia, J.; Yuan, Z.; Ren, M.; Yu, S.; Li, S.; et al. A comparative study between limb-salvage and amputation for treating osteosarcoma. J. Bone Oncol. 2016, 5, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauregui, J.J.; Nadarajah, V.; Munn, J.; Pivec, R.; Kapadia, B.H.; Lerman, D.M.; Maheshwari, A.V. Limb Salvage Versus Amputation in Conventional Appendicular Osteosarcoma: A Systematic Review. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 9, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emori, M.; Kaya, M.; Irifune, H.; Takahashi, N.; Shimizu, J.; Mizushima, E.; Murahashi, Y.; Yamashita, T. Vascularised fibular grafts for reconstruction of extremity bone defects after resection of bone and soft-tissue tumours: A single institutional study of 49 patients. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 99-B, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiland, A.J.; Daniel, R.K.; Riley, L.H. Application of the free vascularized bone graft in the treatment of malignant or aggressive bone tumors. Johns Hopkins Med. J. 1977, 140, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zekry, K.M.; Yamamoto, N.; Hayashi, K.; Takeuchi, A.; Alkhooly, A.Z.A.; Abd-Elfattah, A.S.; Elsaid, A.N.S.; Ahmed, A.R.; Tsuchiya, H. Reconstruction of intercalary bone defect after resection of malignant bone tumor. J. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, G.N.; Mavrogenis, A.F.; Mauffrey, C.; Lesenský, J.; Angelini, A.; Megaloikonomos, P.D.; Igoumenou, V.G.; Papanastassiou, J.; Savvidou, O.; Ruggieri, P.; et al. Intercalary reconstructions after bone tumor resections: A review of treatments. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2017, 27, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, M.W.; Chang, E.I.; Selber, J.C.; Lewis, V.O.; Oates, S.D.; Chang, D.W. Composite Extremity and Trunk Reconstruction with Vascularized Fibula Flap in Postoncologic Bone Defects: A 10-year experience. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eward, W.C.; Kontogeorgakos, V.; Levin, L.S.; Brigman, B.E. Free Vascularized Fibular Graft Reconstruction of Large Skeletal Defects after Tumor Resection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 468, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tao, S.; Tan, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, H.; Li, Z. Long-term follow-up of fibular graft for the reconstruction of bone defects. Medicine 2018, 97, e12605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, K.; Miyamoto, S.; Sakuraba, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Chuman, H.; Kawai, A. Intercalary Reconstruction after Wide Resection of Malignant Bone Tumors of the Lower Extremity Using a Composite Graft with a Devitalized Autograft and a Vascularized Fibula. Sarcoma 2015, 2015, 861575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landau, M.J.; Badash, I.; Yin, C.; Alluri, R.K.; Patel, K.M. Free vascularized fibula grafting in the operative treatment of malignant bone tumors of the upper extremity: A systematic review of outcomes and complications. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 117, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errani, C.; Ceruso, M.; Donati, D.M.; Manfrini, M. Microsurgical reconstruction with vascularized fibula and massive bone allograft for bone tumors. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2018, 29, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitiello, R.; Bocchi, M.B.; Gessi, M.; Greco, T.; Cianni, L.; de Maio, F.; Pesce, V.; Maccauro, G.; Perisano, C. Induced membrane by silver-coated knee megaprosthesis: Keep or toss? J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34 (Suppl. S1), 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna, S.A.; Sewell, M.D.; Aston, W.J.S.; Pollock, R.C.; Skinner, J.A.; Cannon, S.R.; Briggs, T.W.R. Femoral diaphyseal endoprosthetic reconstruction after segmental resection of primary bone tumours. J. Bone Jt. Surgery. Br. Vol. 2010, 92, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehadeh, A.; Noveau, J.; Malawer, M.; Henshaw, R. Late Complications and Survival of Endoprosthetic Reconstruction after Resection of Bone Tumors. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 2885–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekry, K.M.; Yamamoto, N.; Hayashi, K.; Takeuchi, A.; Higuchi, T.; Abe, K.; Taniguchi, Y.; Alkhooly, A.Z.A.A.; Abd-Elfattah, A.S.; Fouly, E.H.; et al. Intercalary frozen autograft for reconstruction of malignant bone and soft tissue tumours. Int. Orthop. 2017, 41, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanacci, D.A.; Totti, F.; Puccini, S.; Beltrami, G.; Scoccianti, G.; Delcroix, L.; Innocenti, M.; Capanna, R. Intercalary reconstruction of femur after tumour resection: Is a vascularized fibular autograft plus allograft a long-lasting solution? Bone Jt. J. 2018, 100-B, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceruso, M.; Falcone, C.; Innocenti, M.; Delcroix, L.; Capanna, R.; Manfrini, M. Skeletal Reconstruction with a Free Vascularized Fibula Graft Associated to Bone Allograft After Resection of Malignant Bone Tumor of Limbs. Handchir. Mikrochir. Plast. Chir. 2001, 33, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wen, L.; Qiao, J.; Zhu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Xiong, J.; Mao, H.; Wang, S. Clinical Outcome of Free Vascularized Fibula Graft in the Surgical Treatment of Extremity Osteosarcoma. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 12, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommarhem, A.; Roine, R.P.; Sintonen, H.; Halonen, T.; Tukiainen, E.; Repo, J.P. Free Vascularized Fibular Graft is Reliable in Upper Extremity Long-Bone Reconstruction with Good Long-Term Outcomes. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2016, 32, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Huang, M.; Zhang, C.; Chen, G.; Ji, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Is frozen tumour-bearing autograft with concurrent vascularized fibula an alternative to the Capanna technique for the intercalary reconstruction after resection of osteosarcoma in the lower limb? Bone Jt. J. 2020, 102-B, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aponte-Tinao, L.A.; Ayerza, M.A.; Muscolo, D.L.; Farfalli, G.L. Allograft Reconstruction for the Treatment of Musculoskeletal Tumors of the Upper Extremity. Sarcoma 2013, 2013, 925413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, L.D.; Ayerza, M.A.; Farfalli, G.; Aponte-Tinao, L.A. Proximal Tibia Osteoarticular Allografts in Tumor Limb Salvage Surgery. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, A.H.K.; Yamamoto, N.; Hayashi, K.; Takeuchi, A.; Miwa, S.; Tsuchiya, H. Epiphyseal Sparing and Reconstruction by Frozen Bone Autograft after Malignant Bone Tumor Resection in Children. Sarcoma 2015, 2015, 892141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, W.; Feng, R.; Li, D. Intercalary frozen autografts for reconstruction of bone defects following meta-/diaphyseal tumor resection at the extremities. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errani, C.; Alfaro, P.A.; Ponz, V.; Colangeli, M.; Donati, D.M.; Manfrini, M. Does the Addition of a Vascularized Fibula Improve the Results of a Massive Bone Allograft Alone for Intercalary Femur Reconstruction of Malignant Bone Tumors in Children? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2021, 479, 1296–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errani, C.; Tsukamoto, S.; Almunhaisen, N.; Mavrogenis, A.; Donati, D. Intercalary reconstruction following resection of diaphyseal bone tumors: A systematic review. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2021, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Chen, G.-J.; Fu, J.; Pei, G.-X. The use of allograft shell with intramedullary vascularized fibula graft for intercalary reconstruction after diaphyseal resection for lower extremity bony malignancy. J. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 102, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfrini, M.; Bindiganavile, S.; Say, F.; Colangeli, M.; Campanacci, L.; Depaolis, M.; Ceruso, M.; Donati, D. Is There Benefit to Free Over Pedicled Vascularized Grafts in Augmenting Tibial Intercalary Allograft Constructs? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2016, 475, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenze, U.; Pohlig, F.; Knebel, C.; Lenze, F.; Harrasser, N.; Mühlhofer, H.; Toepfer, A.; Rechl, H.; von Eisenhart-Rothe, R. Die autologe Fibulatransplantation zur Rekonstruktion knöcherner Defekte. Der Orthopäde 2017, 46, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenze, U.; Kasal, S.; Hefti, F.; Krieg, A.H. Non-vascularised fibula grafts for reconstruction of segmental and hemicortical bone defects following meta- /diaphyseal tumour resection at the extremities. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muramatsu, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Tominaga, Y.; Taguchi, T. Vascularized bone graft for oncological reconstruction of the extremities: Review of the biological advantages. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 2701–2707. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schuh, R.; Panotopoulos, J.; Puchner, S.E.; Willegger, M.; Hobusch, G.M.; Windhager, R.; Funovics, P.T. Vascularised or non-vascularised autologous fibular grafting for the reconstruction of a diaphyseal bone defect after resection of a musculoskeletal tumour. Bone Jt. J. 2014, 96-B, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdek, M.T.; Rose, P.S.; Milbrandt, T.A.; Stans, A.A.; Moran, S.L.; Sim, F.H. Comparison of Pediatric Intercalary Allograft Reconstructions with and without a Free Vascularized Fibula. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaghi, A.; Jackson, T.J.; Stans, A.A.; Shaughnessy, W.J.; Rose, P.S.; Moran, S.L.; Houdek, M.T. Intercalary Allograft Reconstruction of the Proximal Tibia with and Without a Free Fibula Flap in Pediatric Patients. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2020, 40, e833–e838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Yang, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Ji, C. Extracorporeally frozen tumour-bearing bone combined with free vascularised fibula for the intercalary reconstruction of femoral defect after resection of bony sarcoma. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2016, 69, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte-Tinao, L.; Farfalli, G.L.; Ritacco, L.E.; Ayerza, M.A.; Muscolo, L.D. Intercalary Femur Allografts Are an Acceptable Alternative After Tumor Resection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2012, 470, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.S.; Shin, A.Y.; Bishop, A.T.; Moran, S.L.; Sim, F.H. Vascularized Free Fibula Transfer for Oncologic Reconstruction of the Humerus. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2005, 438, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebert, C.; Hillmann, A.; Schwappach, A.; Hoffmann, C.; Hardes, J.; Kleinheinz, J.; Gosheger, G. Free vascularized fibular grafting for reconstruction after tumor resection in the upper extremity. J. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 94, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
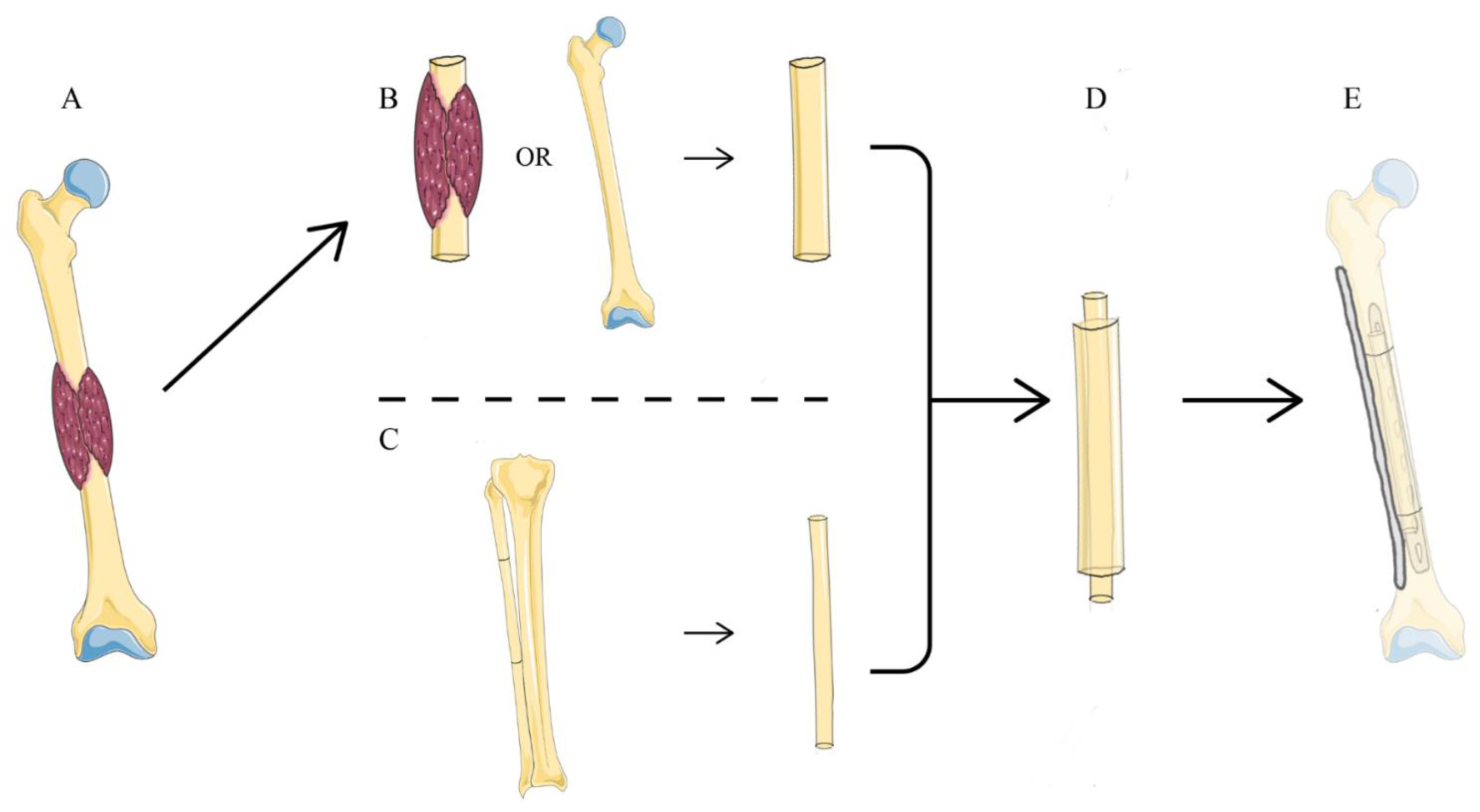


| Case | Gender | Age | Tumor Location | Side | Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Female | 27 | Humerus | Right | BMTC |
| 2 | Female | 61 | Humerus | Right | BMTC |
| 3 | Female | 17 | Humerus | Right | OS |
| 4 | Male | 56 | Humerus | Right | BMRCC |
| 5 | Male | 62 | Humerus | Left | BMRCC |
| 6 | Male | 46 | Humerus | Right | CS |
| 7 | Female | 37 | Humerus | Left | BMTC |
| 8 | Male | 42 | Humerus | Left | BMRCC |
| 9 | Male | 37 | Tibia | Left | OS |
| 10 | Male | 64 | Tibia | Right | BMBC |
| 11 | Female | 48 | Tibia | Right | AD |
| 12 | Female | 19 | Tibia | Left | AD |
| 13 | Female | 63 | Tibia | Right | HB |
| 14 | Female | 51 | Tibia | Right | OD |
| 15 | Female | 39 | Tibia | Left | OS |
| 16 | Female | 28 | Tibia | Left | AD |
| 17 | Male | 61 | Tibia | Right | BMRCC |
| 18 | Female | 51 | Tibia | Right | OD |
| 19 | Female | 45 | Tibia | Right | OS |
| 20 | Male | 58 | Tibia | Left | BMBC |
| 21 | Male | 43 | Femur | Left | OD |
| 22 | Female | 56 | Femur | Left | PO |
| 23 | Male | 18 | Femur | Right | OS |
| 24 | Male | 8 | Femur | Left | ES |
| 25 | Female | 40 | Femur | Left | ES |
| 26 | Male | 16 | Femur | Left | OS |
| Case | Resection Length (mm) | Fibula Length (mm) | Vascularized Fibula (Yes/No) | Type of Reconstruction | Operation Duration (min) | Blood Loss (mL) | Follow-Up (Month) | Time to Union (Month) | MSTS Score | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 120 | 140 | No | devitalized autograft, single plate | 150 | 600 | 51 | 3 | 30 | / |
| 2 | 85 | 110 | No | allograft, single plate | 150 | 500 | 62 | 5 | 29 | / |
| 3 | 70 | 100 | No | allograft, single plate | 150 | 400 | 96 | 3 | 30 | / |
| 4 | 90 | 120 | Yes | devitalized autograft, single plate | 105 | 500 | 37 | / | 21 | Infection, Nonunion |
| 5 | 100 | 130 | No | allograft, single plate | 180 | 500 | 57 | 7 | 28 | / |
| 6 | 90 | 120 | No | devitalized autograft, single plate | 280 | 850 | 83 | 6 | 30 | / |
| 7 | 75 | 110 | No | devitalized autograft, single plate | 120 | 500 | 74 | 3 | 30 | / |
| 8 | 85 | 110 | No | devitalized autograft, single plate | 150 | 500 | 66 | 5 | 27 | / |
| 9 | 115 | 150 | Yes | devitalized autograft, single plate | 247 | 1000 | 42 | 6 | 29 | / |
| 10 | 120 | 150 | Yes | devitalized autograft, single plate | 180 | 600 | 69 | 8 | 27 | / |
| 11 | 110 | 150 | Yes | devitalized autograft, single plate | 180 | 300 | 59 | 6 | 30 | / |
| 12 | 95 | 130 | No | devitalized autograft, single plate | 90 | 500 | 72 | 5 | 30 | / |
| 13 | 155 | 180 | Yes | devitalized autograft, single plate | 300 | 850 | 94 | / | 23 | Nonunion |
| 14 | 110 | 147 | Yes | devitalized autograft, single plate | 240 | 300 | 89 | 6 | 28 | / |
| 15 | 115 | 150 | Yes | devitalized autograft, single plate | 240 | 300 | 123 | 5 | 22 | / |
| 16 | 70 | 130 | Yes | devitalized autograft, single plate | 240 | 300 | 73 | 3 | 30 | / |
| 17 | 90 | 130 | No | devitalized autograft, single plate | 158 | 500 | 82 | 8 | 24 | / |
| 18 | 90 | 130 | No | devitalized autograft, single plate | 180 | 300 | 79 | 6 | 28 | / |
| 19 | 120 | 150 | Yes | devitalized autograft, single plate | 240 | 500 | 74 | 6 | 28 | / |
| 20 | 90 | 130 | No | devitalized autograft, single plate | 235 | 300 | 38 | 7 | 27 | / |
| 21 | 140 | 170 | No | allograft, double plate | 150 | 1000 | 124 | 9 | 29 | / |
| 22 | 110 | 130 | Yes | devitalized autograft, double plate | 495 | 1000 | 110 | 11 | 28 | / |
| 23 | 170 | 226 | Yes | devitalized autograft, double plate | 480 | 1450 | 38 | 10 | 19 | / |
| 24 | 130 | 150 | Yes | devitalized autograft, single plate | 420 | 1500 | 58 | 8 | 27 | Plate fracture |
| 25 | 150 | 170 | Yes | allograft, double plate | 330 | 1450 | 104 | / | 22 | Nonunion |
| 26 | 130 | 165 | Yes | devitalized autograft, double plate | 390 | 1450 | 64 | 6 | 30 | / |
| Follow-Up (Month) | Resection Length (mm) | Fibula Length (mm) | Overlap Length (mm) | Operation Duration (min) | Blood Loss (mL) | Time to Union (Month) | MSTS Score | Bony Union Rate | Incidence of Complication | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper extremity | 65.8 ± 18.6 | 89.4 ± 15.5 | 117.5 ± 12.8 | 28.1 ± 4.6 | 160.6 ± 53.2 | 543.8 ± 134.8 | 4.6 ± 1.6 | 28.1 ± 3.1 | 87.5% | 12.5% |
| Lower extremity | 77.3 ± 26.4 | 117.2 ± 25.7 | 152.1 ± 24.3 | 34.9 ± 10.9 | 266.4 ± 115 | 755.6 ± 463.6 | 6.9 ± 2 | 26.7 ± 3.3 | 91.7% | 16.7% |
| Total | 73.8 ± 24.5 | 108.7 ± 26.3 | 141.5 ± 26.7 | 32.8 ± 9.8 | 233.8 ± 110.8 | 690.4 ± 401.5 | 6.2 ± 2.2 | 27.2 ± 3.2 | 88.5% | 15.4% |
| Vascularized graft | 73.9 ± 27.1 | 121.1 ± 25.7 | 154.9 ± 25.8 | 33.8 ± 12.2 | 291.9 ± 116.7 | 821.4 ± 484.7 | 6.8 ± 2.3 | 26.0 ± 3.8 | 82.1% | 28.6% |
| Non-vascularized graft | 73.7 ± 22.3 | 94.2 ± 19.0 | 125.8 ± 18.3 | 31.7 ± 6.5 | 166.1 ± 49.9 | 537.5 ± 203.5 | 5.6 ± 2.0 | 28.5 ± 1.8 | 100% | 0 |
| Metaphyseal junctions | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 100% | / |
| Diaphyseal junctions | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | 85.7% | / |
| Upper Extremity | Lower Extremity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vascularized Graft | Non-Vascularized Graft | Vascularized Graft | Non-Vascularized Graft | p-Value | |
| Operation duration (min) | 105 * | 168.6 ± 52.1 | 306.3 ± 107.7 | 162.6 ± 52.4 | 0.012 |
| Bleeding volume (ml) | 500 * | 550 ± 144.3 | 846.2 ± 495.2 | 520 ± 286.4 | 0.189 |
| Time to union (month) | / | 4.6 ± 1.6 | 6.8 ± 2.3 | 7 ± 1.6 | 0.875 |
| MSTS Score | 21 * | 29.1 ± 1.2 | 26.4 ± 3.6 | 27.6 ± 2.3 | 0.501 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Pan, Z.; Guo, H.; Fei, X.; Cheng, D.; Yang, Q. Long-Term Follow-Up of Biological Reconstruction with Free Fibular Graft after Resection of Extremity Diaphyseal Bone Tumors. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237225
Li Z, Pan Z, Guo H, Fei X, Cheng D, Yang Q. Long-Term Follow-Up of Biological Reconstruction with Free Fibular Graft after Resection of Extremity Diaphyseal Bone Tumors. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(23):7225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237225
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhaohui, Zhen Pan, Hua Guo, Xiang Fei, Dongdong Cheng, and Qingcheng Yang. 2022. "Long-Term Follow-Up of Biological Reconstruction with Free Fibular Graft after Resection of Extremity Diaphyseal Bone Tumors" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 23: 7225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237225
APA StyleLi, Z., Pan, Z., Guo, H., Fei, X., Cheng, D., & Yang, Q. (2022). Long-Term Follow-Up of Biological Reconstruction with Free Fibular Graft after Resection of Extremity Diaphyseal Bone Tumors. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(23), 7225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11237225






