Abstract
Background: Migraine is a common neurological disorder, and it is the second leading cause of disability worldwide. Manual techniques based on physical therapy have been proposed to improve migraine aspects; however, further research is needed on their effectiveness. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of a craniosacral therapy protocol on different features in migraine patients. Methods: Fifty individuals with migraine were randomly divided into two groups (n = 25 per group): (i) craniosacral therapy group (CTG), following a craniosacral therapy protocol, and (ii) sham control group (SCG), with a sham treatment. The analyzed variables were pain, migraine severity and frequency of episodes, functional, emotional, and overall disability, medication intake, and self-reported perceived changes, at baseline, after a 4 week intervention, and at 8 week follow-up. Results: After the intervention, the CTG significantly reduced pain (p = 0.01), frequency of episodes (p = 0.001), functional (p = 0.001) and overall disability (p = 0.02), and medication intake (p = 0.01), as well as led to a significantly higher self-reported perception of change (p = 0.01), when compared to SCG. In addition, the results were maintained at follow-up evaluation in all variables. Conclusions: A protocol based on craniosacral therapy is effective in improving pain, frequency of episodes, functional and overall disability, and medication intake in migraineurs. This protocol may be considered as a therapeutic approach in migraine patients.
1. Introduction
A migraine is a primary headache, and it is one of the major leading causes of disability in people under the age of 50 [1,2]. Migraine constitutes a complex brain network disorder with a strong genetic basis that involves multiple subcortical, cortical, and brainstem regions [3]. Moreover, patients with migraine may present musculoskeletal dysfunctions [4], which in turn facilitate the development of migraine [5]. Furthermore, there are other types of alterations that can mediate the generation of migraines, such as certain emotional disorders [6,7]. Indeed, emotional stress and negative emotional events have been shown to play an important role in precipitating or exacerbating migraine attacks [7].
The most common preventive and symptomatic treatment for migraine is pharmacological. However, this type of treatment involves some side-effects, such as gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, and central nervous system complications [8]; hence, other treatments may be an alternative, such as psychological treatment, patient education, acupuncture, supervised physical activity, and manual techniques (i.e., chiropractic treatment and physiotherapy) [9,10,11,12].
Regarding physiotherapy, some studies have suggested the effectiveness of manual techniques in individuals with migraine, specifically on pain intensity, number of days, duration of the episodes, disability, and medication intake [11,13,14]. Craniosacral therapy has also been used to treat headaches and migraines [15,16]. This therapy is characterized by being a set of noninvasive fascial techniques performed between the skull and the sacrum [17], whose objective is to relax myofascial structures and normalize sympathetic nerve activation, often increased in patients with chronic pain [18,19], thus improving body function [20]. Some studies have suggested positive effects of craniosacral therapy on pain intensity and frequency [15,21,22], disability [15,21,22,23], quality of life [15,21], medication intake [22], treatment credibility, and satisfaction [24] in migraine patients. However, the quality of previous studies hampers the possibility to determine the magnitude of this effect [25]. In addition, some studies have reported controversial results on the impact of migraine [25].
Furthermore, to date, no study has analyzed the effectiveness of this type of intervention on emotional disability in migraine patients. In this regard, it has been reported that migraine patients, unlike patients with other types of headaches or pain disorders, exhibit hypersensitivity to somatosensory stimuli, which may be due to an altered perception and cerebral processing of somatosensory stimuli [26]. Altered sensory processing has in turn been related to neurobiological differences [27] and can lead to disruptions in other cognitive domains, such as emotional processing [28]. In this context, the study of the effectiveness of these nonpharmacologic interventions on emotional-related variables in migraine sufferers becomes particularly important, in order to avoid their negative consequences.
Thus, the objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of a craniosacral therapy protocol on pain intensity, migraine severity and frequency, emotional, functional, and overall disability, self-reported perceived change, and medication intake after treatment in people with migraine, compared to a placebo treatment. Furthermore, the medium-term effects of the treatments on the assessed variables were assessed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recruitment and Participants
Fifty people diagnosed with migraine participated in the study. They were recruited from primary care centers in Valencia (Spain) in July 2018. Inclusion criteria were as follows: (i) individuals aged 18–50 years; (ii) diagnosed according the International Headache Society (IHS) criteria [29]; (iii) four or more episodes per month; (iv) more than 1 year history of migraine; (v) current acute and prophylactic migraine medication regimens being stabilized for 4 weeks prior to enrolment. Patients were excluded in case of concomitant tension-type headaches or other headaches, signs of vertebral artery or internal carotid artery commitment, temporomandibular disorders, spinal radiculopathy, decompensated blood pressure, vertigo, depression, or pregnancy (or pregnancy intention). Lastly, patients were to not have received any previous manual therapy treatment for migraine.
2.2. Study Design
This was a CONSORT-compliant randomized single-blind controlled trial (within a broader project, registration number NCT03555214). The sample was randomly divided into two groups: (a) craniosacral therapy group (CTG) (n = 25), and (b) sham control group (SCG) (n = 25). Both treatments lasted 4 weeks and included four sessions (one per week). Patients were assessed pre-intervention (T1), post-intervention (T2), and at a 1 month post-intervention follow-up (T3).
Signed written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to participation in the study. All procedures were conducted in agreement with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki principles. Lastly, all protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Valencia (H1509655117217).
2.3. Randomization, Blinding, and Masking
Patients and statisticians were blinded to treatment allocations. Blinding was maintained and ensured until the completion of the entire study by avoiding any information regarding study hypothesis, details of interventions, random assignment, outcome measures, and outcome analysis. The randomization method consisted of a computer-generated random sequence table with a non-balanced three-block design (GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
2.4. Interventions
All interventions were applied at the same time of day and in the same room, trying to standardize the treatment, and we tried to mimic the environment of a typical physiotherapy intervention (i.e., clinical tests, durations, and resources). The interventions were carried out with the patient in supine decubitus. The CTG received a manual therapy treatment focused on the craniosacral region including five techniques (Appendix A), and the SCG received a hands-on placebo intervention. After the intervention, individuals remained in supine with a neutral neck and head position for 10 min, to relax and diminish tension after treatment [30]. The techniques were executed by the same experienced physiotherapist in both groups. Participants were asked to report any side-effects during or after the intervention.
2.4.1. Craniosacral Therapy Group
Techniques were applied in each session according to the following predefined sequence:
Suboccipital inhibition technique. Both hands were placed under the occiput, with the fingers in contact with the atlas (posterior arch). Deep, sliding, and progressive pressure was applied for 10 min [31]. The objective of this technique was to relax the suboccipital muscles [32].
Frontal technique. The therapists’ ring and little fingers were placed along the outside of the frontal bone (zygomatic processes), while the middle and index fingers were positioned next to the frontal bone (midline). A slight pressure in a posterior direction was performed with the index fingers on the midline of the frontal bone, and, at the same time, the ring fingers were moved in an anterior and caudal direction for 5 min [33]. The aim of this technique was to relax the tissue around cranial structures [33], since extracranial tissues such as pericranial muscles and periosteum are innervated by some meningeal afferents, and such tissues may be related to migraine onset [34].
Sphenoid technique. The index finger was put over the sphenoid (greater wing), the middle finger on the pterion, the ring finger behind the ear over the asterion, and the little finger over the occiput (lateral angle). Both thumbs were applied together on the midline of the head. A gentle distraction force was performed for 5 min [35]. The objective of this technique was to relax the tissue around the cranial structures [35].
Fourth ventricle technique. Both hands with palms up were applied under the patient’s occiput, with the thumb tips together. The therapist made a slight approximation of the thenar eminence and a cephalic traction for 10 min [36]. This cranial technique may be helpful in cases of imbalance in the autonomic nervous system [37] and may accordingly provide analgesia and reduce pain sensitivity [38].
Lumbosacral technique. One flat and palm-up hand was located under the sacrum and the lumbar vertebrae L4–L5, whereas the other hand was placed flat and palm down on the pelvic upper surface, with both hands vertically aligned. The therapist performed a slight compression with both hands for 5 min [23]. The objective of this technique was to relax the muscles and other structures around the lumbosacral area to improve their movement and to improve the sagittal balance of the spine, since there are significant correlations between occipitocervical and spinopelvic alignment [39].
2.4.2. Sham Control Group
Placebo intervention. A hands-on placebo superficial contact was performed by placing both hand palms under the occiput for 10 min, without touching the suboccipital muscles. No force, pressure, or movement was performed [36,38].
2.5. Assessments
Pain, migraine severity, frequency of the episodes, and functional, emotional, and overall disability were assessed at baseline (T1), at 4 weeks (T2), and at 8 weeks (T3) after the intervention. Medication intake reduction and self-reported perceived changes after treatment were recorded only at T2 and T3.
Pain. Pain intensity was assessed using the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) [40], whereby patients rated their perceived pain intensity level on a horizontal 10 cm line, where 0 = “absence of pain” and 10 = “worst pain imaginable”. It is considered a valid and reliable instrument, with an ICC = 0.97 (95% CI = 0.86–0.98) [40].
Migraine severity and frequency of the episodes. The migraine severity (i.e., mild, moderate, and severe) and frequency of the episodes (i.e., once a month, 2–4 times a month, and once a week) were assessed responding to the relevant questions of the Headache Disability Index (HDI) [41]. HDI is a valid and reliable tool [41] that is widely accepted for assessing the effectiveness of nonpharmacological interventions in frequent episodic or chronic migraine [42], which covers the endpoints recommended by the IHS.
Functional emotional and overall disability. They were assessed using the HDI [41], which evaluates the migraine-induced disability in daily life. It includes 25 items that can be divided into a 12-item functional subscale (i.e., functional disability) and a 13-item emotional subscale (i.e., emotional disability). Each item has three possible answers (no = 0 points, sometimes = 2 points, yes = 4 points). The total score (i.e., overall disability) ranges from 0 = “no disability” to 100 = “maximum disability”. The Cronbach alpha reliability is α = 0.76 for the functional subscale, α = 0.82 for the emotional subscale, and 0.83 for the total score [41].
Medication intake. Symptomatic medication intake was registered in a standardized migraine diary, which also included information about migraine days, intensity (VAS scale), and severity (severe, moderate, or mild), so that the patients would remember these data for post-treatment evaluation. This variable was registered as the number of pills per day. The percentage of medication intake reduction was calculated as previously described [43].
Self-reported perceived change after treatment. This was evaluated by means of the Patients’ Global Impression of Change (PGIC) scale, consisting of a verbal scale, with seven points: “very much improved”, “much improved”, “minimally improved”, “no change”, “minimally worse”, “much worse”, and “very much worse” [44]. This scale has been previously used in chronic pain individuals [44] and has shown an excellent retest reliability (ICC = 0.90) [45].
2.6. Sample Size Calculation
Sample size was computed taking into consideration that our study included two groups (i.e., control and experimental groups), and that three measurements were conducted. We set a power of 80% and an effect size of d = 0.88 according to a previous study conducted by Espí-López et al. [31]. With this consideration, a minimum sample size of 24 participants (i.e., 12 participants per group) was required. However, the recruitment was doubled (i.e., 50 participants) taking into consideration possible dropouts.
2.7. Data Collection and Statistical Analyses
All statistical analyses were performed with SPSS v24 (IBM SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Standard statistical methods were used to obtain the mean and standard deviation (SD).
For the analysis of continuous variables measured three times (i.e., pain, emotional disability, functional disability, and overall disability), a two-factor mixed multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) was conducted with a between-subject factor “treatment group” having two categories (i.e., SCG and CTG) and a within-subject factor “time measurements” having three categories (i.e., T1, T2, and T3). Post hoc multiple comparisons were conducted using a single-step procedure, i.e., the Bonferroni method, which adjusts type I error based on the t-distribution (α/number of comparisons). We evaluated the assumption of homoscedasticity using Levene’s test and of sphericity using Mauchly’s test. For the categorical variables measured three times (i.e., Migraine severity and frequency of the episodes), the relationship between the categories of each variable and the time measurement (T1, T2, and T3), for each group, was explored using the chi-square test. Furthermore, the relationship between the categories of the variables and the groups were also explored using the chi-square test for each time measurement.
To analyze the effect of the treatment on the medication intake, a two-factor mixed MANOVA with the between-subject variable “group” and the within-subject variable “time” (i.e., T2 and T3) was used. A chi-square test was used for the analysis of the self-reported perceived change after treatment to evaluate the statistical differences between groups and between time measurements. Furthermore, to explore the similarity between groups at baseline, the chi-square test was used for the categorical variables and one-way ANOVA was used for the continuous variables. The α level was set below 0.05 for all tests. The effect size of all continuous variables was computed by Cohen’s d, thus rating the effect size as follows: large (>0.80), medium (0.50–0.80), or small (0.20–0.50), [46]. For categorical variables, the effect size was reported by the contingency coefficient (CC).
3. Results
3.1. Participants
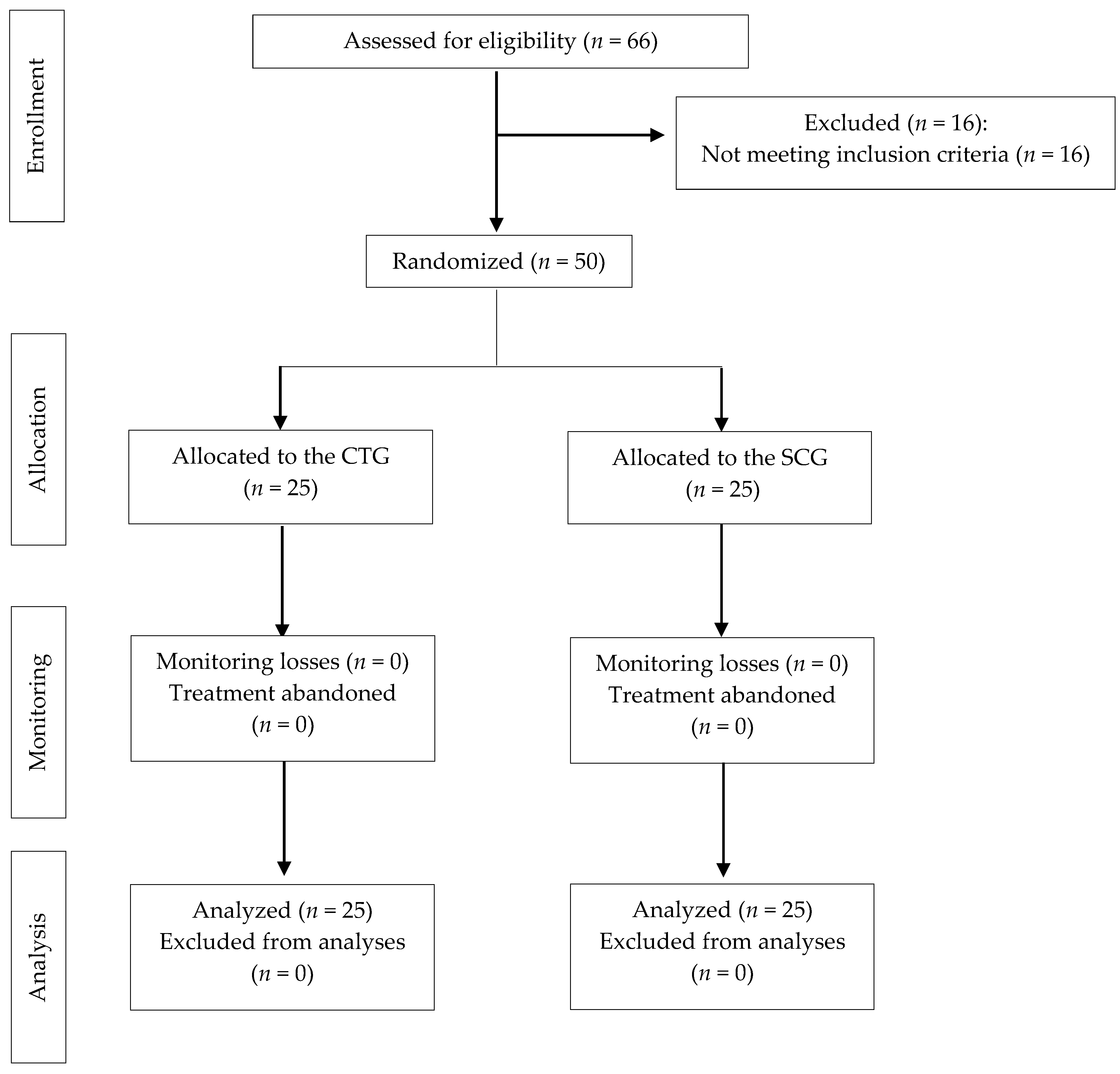
Sixty-six individuals were assessed for eligibility, but 16 failed to meet the inclusion criteria; thus, 50 people (40 women and 10 men) were randomized, and all of them completed the study (25 in CTG and 25 in SCG). Following the CONSORT guidelines, Figure 1 presents a flow diagram for this trial [47]. So that there were no dropouts, the sample was selected well, requesting adherence commitment, unless an adverse event arose due to the treatment or for other reasons; in addition, a rigorous follow-up of the subjects was carried out, which is why all subjects were able to comply with the treatment without dropouts.
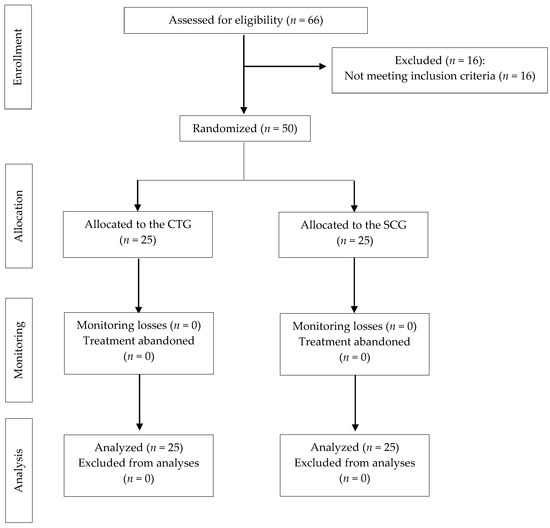
Figure 1.
Flowchart according to CONSORT Statement for the Reporting of randomized trials. CTG: craniosacral therapy group; SCG: sham control group.
The mean (SD) age of the participants was 40.1 (9.9) years. Table 1 shows the baseline demographic and migraine characteristics. There were no significant baseline differences between groups in any variable (p ≥ 0.05). Regarding intervention-related side-effects, some participants (n = 5) reported a slight dizziness lasting seconds to a few minutes when getting up from the stretcher, but no serious side-effect was reported.

Table 1.
Baseline demographic and migraine characteristics.
3.2. Effect of the Treatment on Pain and Disability
A significant interaction between factors “groups” and “intervention measurements” in total HDI F (2, 96) = 3.23, p < 0.05, η2 = 0.06, and in functional HDI F (2, 96) = 6.15, p < 0.05, η2 = 0.11, but not in pain and emotional HDI (p ≥ 0.05), was found.
The results of pairwise comparisons are shown in Table 2. When analyzing the effect of the treatment in each group and between groups, pain intensity was significantly reduced in T2 and T3 in the CTG compared to SCG. With regard to migraine-induced disability, there was a significant reduction in the values both on the functional subscale and in the global assessment after treatment, and such reduced scores were maintained at T3, as can be seen when comparing groups in T2 and T3.

Table 2.
Effect of the treatment on pain, functional, emotional, and overall disability and decrease in medication intake between measurement times and between groups.
3.3. Effect of the Treatment on Migraine Severity and Frequency of the Episodes
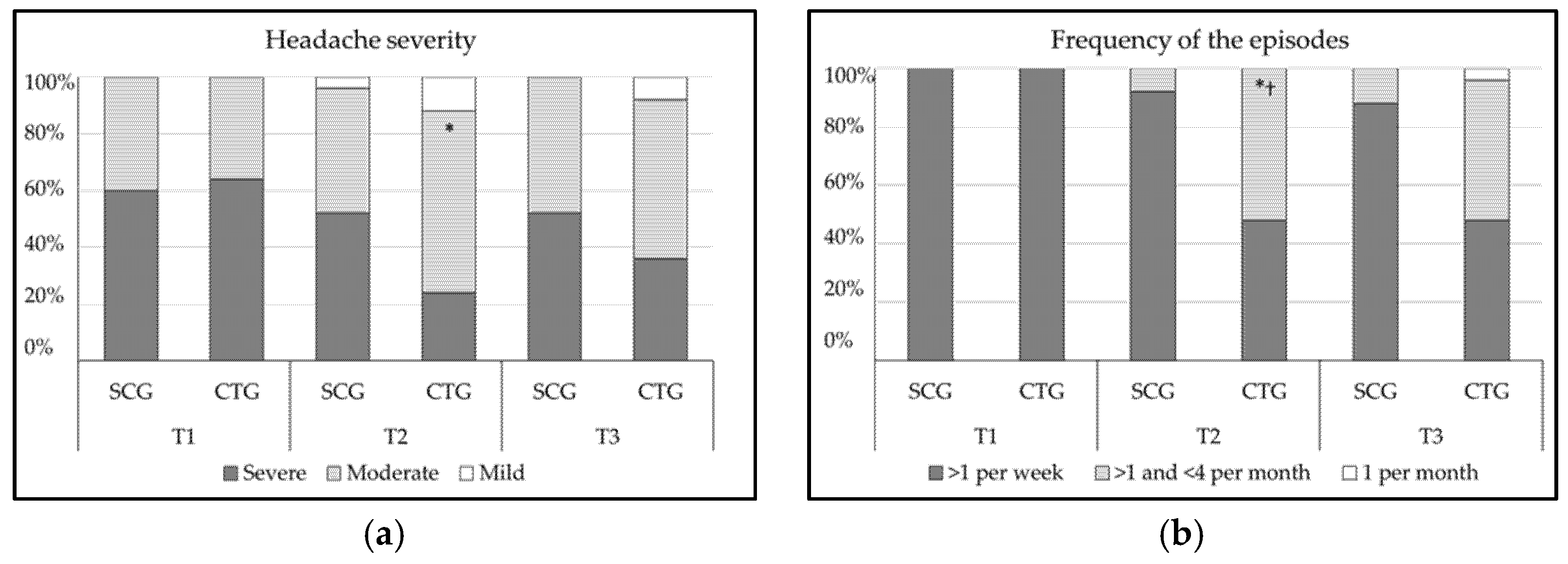
As a result of the chi-square tests, the SCG showed no significant relationship between migraine severity and the measurements conducted (p ≥ 0.05; data not shown). Nevertheless, the CTG presented a significant moderate improvement at T2 (χ2 (2) = 9.51, p = 0.009, CC = 0.40) as can be observed in Figure 2a. There were no significant differences between scale categories and groups at T2 or at T3 (p ≥ 0.05, respectively).
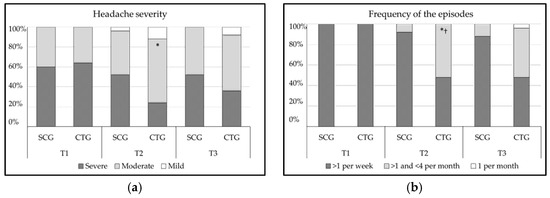
Figure 2.
(a) Percentage of participants who rated each category of the migraine severity of the Headache Disability Index (HDI; (b) percentage of participants who rated each category of the frequency of episodes of the Headache Disability Index (HDI). CTG: craniosacral therapy group; SCG: sham control group; T1: pre-treatment; T2: post-treatment; T3: follow-up; * p < 0.05 vs. T1; † p < 0.05 vs. SCG.
Similarly, there was no relationship between categories and measurement times in migraine frequency in the SCG (p ≥ 0.05; data not shown). However, when the CTG was analyzed, the results presented a significant moderate improvement at T2 (χ2 (1) = 17.57, p < 0.001, CC = 0.51) and at T3 (χ2 (2) = 17.57, p < 0.001, CC = 0.51), as noted in Figure 2b. In addition, in migraine frequency, there were significant differences between scale categories and groups at T2 (χ2 (1) =11.52, p < 0.001, CC = 0.43), and at T3 (χ2 (2) = 9.34, p < 0.01, CC = 0.40).
3.4. Effect of the Treatment on Medication Intake
Of the 50 individuals participating in the study, one participant did not take preventive or symptomatic medication at any time during the study; accordingly, this assessment was performed on 49 individuals. Table 2 shows that the drop in medication intake was significantly greater in CTG than in SCG at T2 t(47) = 2.62, p < 0.05, r = 0.35) and at T3 t(47) = 2.47, p < 0.05, r = 0.33).
3.5. Self-Reported Perceived Change after Treatment
Table 3 shows the results of the PGIC scale for the SCG and the CTG at T2 and T3 and the statistical results from the analysis of the association between scale categories and time measurements in each group.

Table 3.
Self-reported perceived change after treatment between measurement times.
A significant moderate association between scale categories and groups was found, both at T2 (χ2 (5) =13.23, p < 0.01, CC = 0.46) and at T3 (χ2 (4) = 20.14, p < 0.001, CC = 0.54), showing a higher proportion of participants in positive categories (i.e., much improved and very much improved) in the CTG compared to the SCG. Furthermore, only CTG showed a significant association between time measurements and categories, with the number of people in positive categories decreasing at T3 compared to T2.
4. Discussion
The results of the present study show that a craniosacral therapy protocol reduces pain, migraine severity, frequency of attacks, functional disability, emotional disability, overall disability, and medication intake in migraine patients. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to evaluate the therapeutic effects achieved following this manual therapy protocol on emotional disability in patients with migraine by applying different techniques on the cranial sphere and sacral region, techniques previously used independently in other studies.
Craniocervical and lumbosacral soft-tissue manual techniques, applied separately, both in patients with migraine and in those with tension or cervicogenic headaches, have previously shown good results in terms of pain, migraine severity, frequency of migraine episodes, overall disability, and medication intake [21,22,23,31,32,36]. However, in addition to such variables, our approach includes the emotional disability variable, an essential aspect in patients with primary headaches [48,49] and chronic pain [50].
The most studied pain-related variables in migraines are pain intensity/severity and the frequency of attacks [51]. Our results showed that CTG experienced an improvement in pain severity evaluated according to HDI. Thus, the percentage of patients experiencing severe pain at T1 dropped from 64% to 24% at T2. At T3, 56% of the patients still reported moderate pain. These results are in line with the reduction in pain intensity (VAS), which exhibited a difference with respect to the baseline measurement of 1.14 points at T2 and 1.20 points at T3 in the CTG, exceeding the minimal clinical important difference at both times [52]. Other authors reported a decrease of 1.67 points after manual therapy treatment in the orofacial and cervical region, reaching 2.25 points after 6 weeks and 3.50 points after 12 weeks [53]. Nevertheless, the results of the current study cannot be comparable with these studies, since their sample included chronic migraine patients with temporomandibular disorders, while our study excluded patients with such disorders. In terms of migraine frequency using the HDI, 52% of the CTG subjects who reported more than four migraine attacks per month at baseline experienced a reduction in frequency to less than four attacks at T2 and 48% maintained this improvement at T3; this supports the effectiveness for this variable. These results are consistent with those published by Cerritelli et al. [22], who observed that the average frequency dropped from 22.5 to 1.2 days per month after 6 months of manual therapy. However, the treatment period in their study was much longer and a protocol was not specified.
Pain, whether episodic or chronic, interferes with the patient’s life, affecting their physical and emotional condition [54,55]. On the one hand, the functional and overall disability improved at T2 by 23.21% and 23.02%, respectively, and at T3 by 21.12% and 21.12%, respectively. Likewise, previous results reported by our group showed an improvement in the overall disability collected by the MIDAS questionnaire in migraine patients treated with myofascial trigger point therapy and stretching exercises combined with the suboccipital inhibition technique [31]. However, in that case, an evaluation was only performed immediately after the intervention; thus, a longer follow-up could have determined the long-term effects of therapy. Other authors [23] reported improvements in overall disability according to the HIT-6 questionnaire, reducing the score from 62 to 58 points after an intervention using craniosacral therapy in subjects with migraine. However, a placebo group was not included in this study; hence, so improvements could not be attributed to the intervention itself, since the placebo effect of light massage was not studied. Our research shows that the improvement in both variables (i.e., functional and overall disability) was only evidenced in the manual therapy group, not in the placebo group. On the other hand, the emotional burden associated with migraine becomes especially important since it can influence prevalence, prognosis, treatment, and clinical results [56]. In fact, depression is a possible risk factor for migraine chronification [57,58] and, conversely, its approach could revert chronic migraine lasting less than 2 years back to episodic migraine [59]. In the present study, emotional disability improved significantly in the CTG only at T3, which could be due to the fact that the effect of the proposed treatment is not immediate and takes time to yield positive results for this variable [14]. However, the CTG showed a trend toward improvement at T2, with a similar magnitude of improvement (6 points) to that of T3 (5.36 points), where a significant reduction was indeed observed. In this aspect, our results cannot be compared with previous studies, since this is the first to address emotional disability in migraine patients treated with cranial, cervical, and lumbosacral soft-tissue manual therapy. D’Ippolito et al. [60] performed a retrospective review of the medical records of migraine patients treated from 2011 to 2015, and they observed a significant improvement in the level of anxiety; however, the nonrandomized selection of participants, the small sample size (n = 11), and the lack of a control group prevent extrapolation of the results and establishing whether the changes obtained were due to the intervention alone.
Interestingly, we observed a decrease in medication intake by 36.04% at T2 and 31% at T3 in CTG. In line with these results, other authors have observed that the overall use of analgesics, NSAIDs, and triptans was significantly lower after applying manual treatment compared to when TENS was used [61] or compared to the placebo treatment [22]. This can be explained given that the efficacy of symptomatic medication and a lower need for its use are associated with improved migraine parameters (such as the frequency of attacks) and lower emotional load [62].
The perception of change variable after a therapeutic intervention is important, since it provides clinically relevant information on the perceived effect of treatment [63]. In this regard, 52% of CTG participants at T2 and 12% at T3 felt that they had improved a fair amount or a great deal, i.e., they achieved a clinically significant improvement in this variable [64,65], consistent with the improvement of the variables previously analyzed. Other authors obtained positive results on the PGIC scale in patients with migraine [66]; however, the participants received a combined treatment of physical therapy and specific prescribed medication, while our study used only manual therapy techniques without pharmacological prescription. This implies that the changes obtained were only due to the protocol applied. Moreover, both of our study groups continued with their usual prescribed medication [51], and changes in symptomatic medication intake were likewise evaluated.
Given the possible side-effects of taking migraine drugs [8] and that migraine also tends to become chronic [57], our results showing a decrease in medication intake after the proposed treatment are especially relevant.
This study had some limitations, mainly related to the study participants’ characteristics. Firstly, we included only people suffering more than four episodes per month. Secondly, they were mostly women, which could bias the results; thus, the results are not entirely generalizable to all migraine patients. However, preventive treatments are now being considered in patients suffering from migraines ≥4 days per month, whereas people suffering one to four episodes are less prone to medication [67]. Furthermore, migraine is twice as prevalent in women as in men. In addition, the duration of treatment sessions was different between groups, but the aim of the study was to analyze the placebo effect previously described by the mere hands-on or massage factor [68]. Nevertheless, future studies including a control group without touch or other manual techniques which have been proven to be effective in other types of headaches (i.e., articulatory techniques [30]) may be of interest. Another possible limitation was the short duration of treatment or the lack of long-term follow-up; thus, we could not ascertain whether the observed beneficial the effects would remain after 2 months. Nevertheless, it is interesting to evaluate the effectiveness of short-term treatments, such as the one proposed in this article, since it facilitates adherence to treatment. Future studies addressing these issues are needed. Lastly, participants were recruited from primary care centers of one city, which may jeopardize generalizability. Thus, more studies applying this protocol in other populations and other migraine features (i.e., fewer than four episodes per month) are needed to generalize the results.
In general, all manual therapy techniques described here may be applied by different care providers, as long as they are well trained in manual therapy and craniosacral therapy. However, we recommend that these techniques are carried out by the same therapist throughout the entire treatment, in order to keep variations low (i.e., pressure, speed), to monitor the progress and to reinforce the therapeutic alliance. Furthermore, it is important to consider any possible contraindications to these techniques, such as vertebral artery or internal carotid artery commitment, spinal radiculopathy, vertigo, or decompensated blood pressure.
5. Conclusions
A treatment protocol based on craniosacral therapy is effective in reducing pain intensity, migraine severity, frequency of attacks, functional and emotional disability, and symptomatic medication intake, as well as improving the post-treatment perception of change in patients suffering from migraine ≥4 days per month, maintaining such changes 1 month after the intervention. This reproducible manual therapy protocol may be considered as a valid therapeutic approach in individuals with migraine.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.I., P.S.-A. and G.V.E.-L.; data curation, E.M.-G. and P.S.-A.; formal analysis, P.S.-A.; investigation, E.M.-G., M.A.-R., S.M.-C. and N.S.-R.; methodology, E.M.-G., M.A.-R., S.M.-C. and N.S.-R.; project administration, M.I., P.S.-A. and G.V.E.-L.; supervision, M.I. and G.V.E.-L.; writing—original draft, E.M.-G. and M.I.; writing—review and editing, E.M.-G., M.I., M.A.-R., S.M.-C., N.S.-R., P.S.-A. and G.V.E.-L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Valencia (H1509655117217).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Appendix A
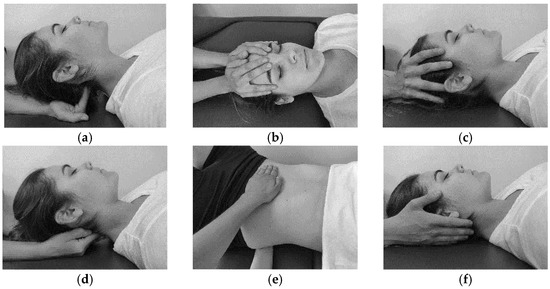
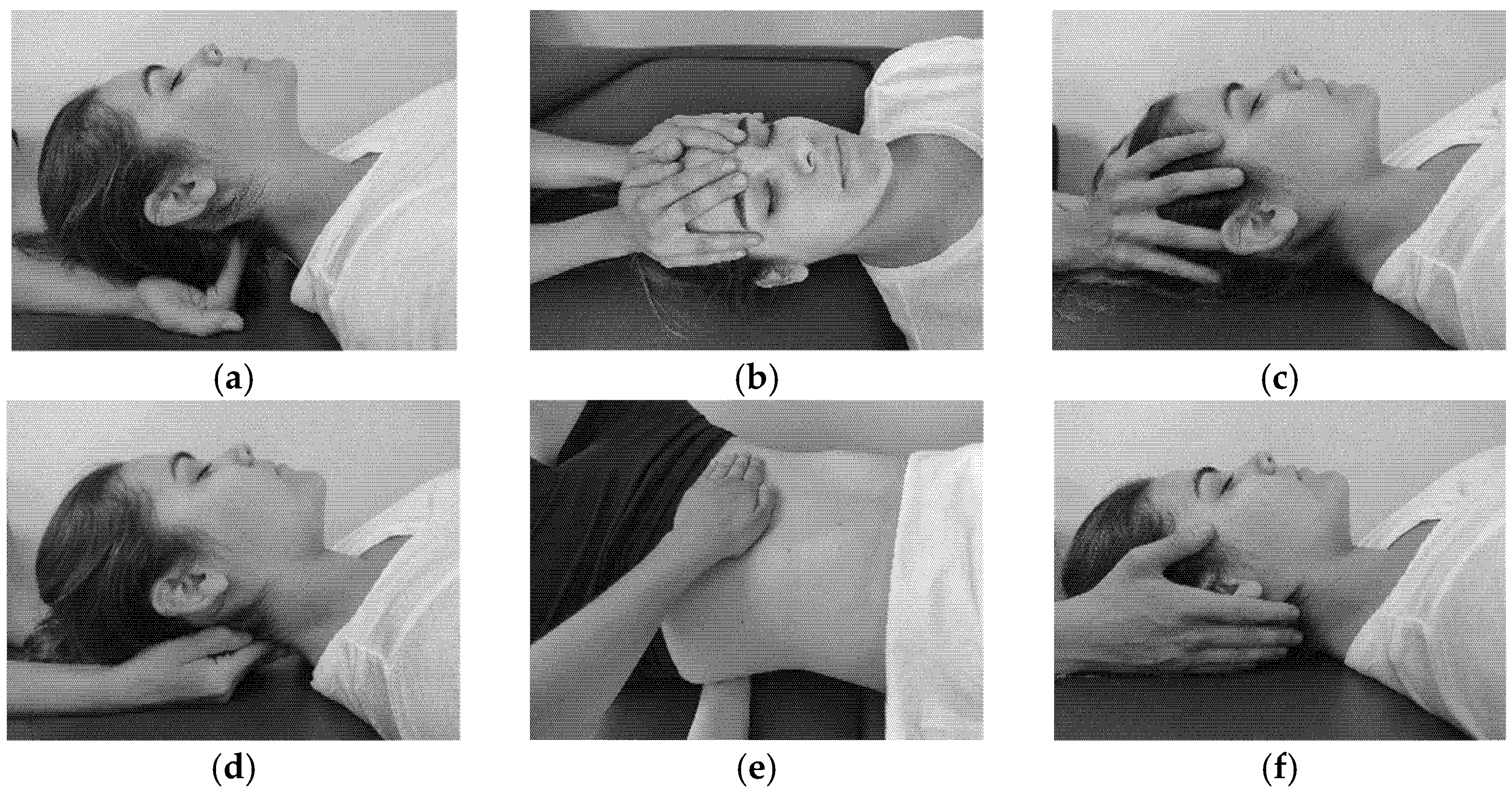
Figure A1.
Description of manual therapy interventions: (a) suboccipital inhibition technique; (b) frontal technique; (c) sphenoid technique; (d) fourth ventricle technique; (e) lumbosacral technique; (f) placebo technique.
Figure A1.
Description of manual therapy interventions: (a) suboccipital inhibition technique; (b) frontal technique; (c) sphenoid technique; (d) fourth ventricle technique; (e) lumbosacral technique; (f) placebo technique.
References
- Woldeamanuel, Y.W.; Cowan, R.P. Migraine affects 1 in 10 people worldwide featuring recent rise: A systematic review and meta-analysis of community-based studies involving 6 million participants. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 372, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, T.; Stovner, L.; Vos, T. Global Burden Disease 2015: Migraine is the third cause of disability in under 50s. J. Headache Pain 2016, 17, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puledda, F.; Messina, R.; Goadsby, P.J. An update on migraine: Current understanding and future directions. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luedtke, K.; Starke, W.; May, A. Musculoskeletal dysfunction in migraine patients. Cephalalgia 2017, 38, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferracini, G.N.; Florencio, L.L.; Dach, F.; Chaves, T.C.; Palacios-Ceña, M.; Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C. Myofascial Trigger Points and Migraine-related Disability in Women with Episodic and Chronic Migraine. Clin. J. Pain 2017, 33, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seng, E.K.; Seng, C.D. Understanding migraine and psychiatric comorbidity. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2016, 29, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelman, L. The triggers or precipitants of the acute migraine attack. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capi, M.; Gentile, G.; Lionetto, L.; Salerno, G.; Cipolla, F.; Curto, M.; Borro, M.; Martelletti, P. Pharmacogenetic considerations for migraine therapies. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedtke, K.; Allers, A.; Schulte, L.H.; May, A. Efficacy of interventions used by physiotherapists for patients with headache and migraine-systematic review and meta-analysis. Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 474–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maistrello, L.F.; Geri, T.; Gianola, S.; Zaninetti, M.; Testa, M. Effectiveness of Trigger Point Manual Treatment on the Frequency, Intensity, and Duration of Attacks in Primary Headaches: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front Neurol. 2018, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, D.; Callesen, H.E.; Carlsen, L.N.; Birkefoss, K.; Tómasdóttir, H.; Wűrtzen, H. Manual joint mobilisation techniques, supervised physical activity, psychological treatment, acupuncture and patient education in migraine treatment. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cephalalgia 2021, 42, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryans, R.; Decina, P.; Descarreaux, M.; Duranleau, M.; Marcoux, H.; Potter, B. Evidence-based guidelines for the chiropractic treatment of adults with neck pain. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2014, 37, 42–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaibi, A.; Tuchin, P.J.; Russell, M.B. Manual therapies for migraine: A systematic review. J. Headache Pain 2011, 12, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maistrello, L.F.; Rafanelli, M.; Turolla, A. Manual Therapy and Quality of Life in People with Headache: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2019, 23, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, H.; Lauche, R.; Sundberg, T.; Dobos, G.; Cramer, H. Craniosacral therapy for chronic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.E.; Page, J.S. Multipractitioner Upledger CranioSacral Therapy: Descriptive outcome study 2007-2008. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2011, 17, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.; Martin, C.; Bassett, K.; Kazanjian, A. A systematic review of craniosacral therapy: Biological plausibility, assessment reliability and clinical effectiveness. Complement. Ther. Med. 1999, 7, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, M.J.; Holland, B.S.; Stupski, B.A.; Gamber, R.G.; Smith, M.L. Cranial manipulation can alter sleep latency and sympathetic nerve activity in humans: A pilot study. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2005, 11, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miana, L.; Bastos, V.H.D.V.; Machado, S.; Arias-Carrión, O.; Nardi, A.E.; Almeida, L.; Ribeiro, P.; Machado, D.; King, H.; Silva, J.G. Changes in alpha band activity associated with application of the compression of fourth ventricular (CV-4) osteopathic procedure: A qEEG pilot study. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2013, 17, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäkel, A.; von Hauenschild, P. A systematic review to evaluate the clinical benefits of craniosacral therapy. Complement. Ther. Med. 2012, 20, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, K.; Liebnitzky, J.; Burmeister, U.; Sihvonen-Riemenschneider, H.; Beck, M.; Voigt, R.; Bergmann, A. Efficacy of osteopathic manipulative treatment of female patients with migraine: Results of a randomized controlled trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2011, 17, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerritelli, F.; Ginevri, L.; Messi, G.; Caprari, E.; Di Vincenzo, M.; Renzetti, C.; Cozzolino, V.; Barlafante, G.; Foschi, N.; Provinciali, L. Clinical effectiveness of osteopathic treatment in chronic migraine: 3-Armed randomized controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2015, 23, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rnadottir, T.S.; Sigurdardottir, A.K. Is craniosacral therapy effective for migraine? Tested with HIT-6 Questionnaire. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2013, 19, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, P.; Gaylord, S.A.; Park, J.; Faurot, K.R.; Coble, R.; Suchindran, C.; Coeytaux, R.R.; Wilkinson, L.; Mann, J.D. Credibility of low-strength static magnet therapy as an attention control intervention for a randomized controlled study of CranioSacral therapy for migraine headaches. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2011, 17, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamonseki, D.H.; Lopes, E.P.; Van Der Meer, H.A.; Calixtre, L.B. Effectiveness of manual therapy in patients with tension-type headache. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harriott, A.M.; Schwedt, T.J. Migraine is associated with altered processing of sensory stimuli. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2014, 18, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, J.P.; Marco, E.J.; Desai, S.; Fourie, E.; Harris, J.; Hill, S.; Arnett, A.; Mukherjee, P. Abnormal white matter microstructure in children with sensory processing disorders. NeuroImage Clin. 2013, 2, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.A.; Kats, A.; Williams, M.E.; Aziz-Zadeh, L. The importance of sensory processing in mental health: A proposed addition to the Research Domain Criteria (RDoC) and suggestions for RDoC 2.0. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar]
- Monzani, L.; Espí-López, G.V.; Zurriaga, R.; Andersen, L.L. Manual therapy for tension-type headache related to quality of work life and work presenteeism: Secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2016, 25, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espí-López, G.-V.; Ruescas-Nicolau, M.-A.; Nova-Redondo, C.; Benítez-Martínez, J.C.; Dugailly, P.-M.; Falla, D. Effect of Soft Tissue Techniques on Headache Impact, Disability, and Quality of Life in Migraine Sufferers: A Pilot Study. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2018, 24, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro-Velasco, C.; Arroyo-Morales, M.; Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C.; Cleland, J.A.; Hernández, F.J.B. Short-term effects of manual therapy on heart rate variability, mood state, and pressure pain sensitivity in patients with chronic tension-type headache: A pilot study. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2009, 32, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upledger, J.E. Craniosacral Therapy. In Complementary and Alternative Medicine; Novey, D.W., Ed.; Mosby: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 2000; pp. 381–392. [Google Scholar]
- Schueler, M.; Neuhuber, W.L.; De Col, R.; Messlinger, K. Innervation of rat and human dura mater and pericranial tissues in the parieto-temporal region by meningeal afferents. Headache: J. Head Face Pain 2014, 54, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Martos, I.; Valenza, M.C.; Valenza-Demet, G.; Benítez-Feliponi, A.; Robles-Vizcaíno, C.; Ruiz-Extremera, A. Effects of manual therapy on treatment duration and motor development in infants with severe nonsynostotic plagiocephaly: A randomised controlled pilot study. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2016, 32, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanten, W.P.; Olson, S.L.; Hodson, J.L.; Imler, V.L.; Knab, V.M.; Magee, J.L. The Effectiveness of CV-4 and Resting Position Techniques on Subjects with Tension-Type Headaches. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 1999, 7, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurowska, A.; Malak, R.; Kołcz-Trzęsicka, A.; Samborski, W.; Paprocka-Borowicz, M. Compression of the fourth ventricle using a craniosacral osteopathic technique: A systematic review of the clinical evidence. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 2974962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-De-Mello-E-Mello-Ribeiro, A.P.; Blanco, C.R.; Riquelme, I.; Heredia-Rizo, A.M.; Ricard, F.; Oliva-Pascual-Vaca, Á. Effects of the Fourth Ventricle Compression in the Regulation of the Autonomic Nervous System: A Randomized Control Trial. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 148285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Pereira, S.; Hitzl, W.; Bullmann, V.; Meier, O.; Koller, H. Sagittal balance of the cervical spine: An analysis of occipitocervical and spinopelvic interdependence, with C-7 slope as a marker of cervical and spinopelvic alignment. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2015, 23, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijur, P.E.; Silver, W.; Gallagher, E.J. Reliability of the Visual Analog Scale for Measurement of Acute Pain. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2001, 8, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, G.P.; Ramadan, N.M.; Aggarwal, S.K.; Newman, C.W. The Henry Ford Hospital Headache Disability Inventory (HDI). Neurology 1994, 44, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedtke, K.; Basener, A.; Bedei, S.; Castien, R.; Chaibi, A.; Falla, D.; Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C.; Gustafsson, M.; Hall, T.; Jull, G.; et al. Outcome measures for assessing the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions in frequent episodic or chronic migraine: A Delphi study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e029855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Gómez, E.; Inglés, M.; Serra-Añó, P.; Espí-López, G.V. Effectiveness of a manual therapy protocol based on articulatory techniques in migraine patients. A randomized controlled trial. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2021, 54, 102386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, L.; Scheman, J. Patient global impression of change scores within the context of a chronic pain rehabilitation program. J. Pain 2009, 10, S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamper, S.J.; Maher, C.G.; Mackay, G. Global Rating of Change Scales: A Review of Strengths and Weaknesses and Considerations for Design. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2009, 17, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalheimer, W.; Cook, S. How to calculate effect sizes from published research: A simplified methodology. Work-Learn. Res. 2002, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, K.F.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D. the CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 Statement: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMC Med. 2010, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuensalida-Novo, S.; Parás-Bravo, P.; Jiménez-Antona, C.; Castaldo, M.; Wang, K.; Benito-González, E.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C. Gender differences in clinical and psychological variables associated with the burden of headache in tension-type headache. Women Health 2020, 60, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, A.B.W.; Davis-Martin, R.E.; Houle, T.; Turner, D.P.; Smitherman, T. Perceived triggers of primary headache disorders: A meta-analysis. Cephalalgia 2017, 38, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnell, M.C.; Ceko, M.; Low, L. Cognitive and emotional control of pain and its disruption in chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, H.-C.; Tassorelli, C.; Dodick, D.W.; Silberstein, S.D.; Lipton, R.B.; Ashina, M.; Becker, W.J.; Ferrari, M.D.; Goadsby, P.J.; Pozo-Rosich, P.; et al. Guidelines of the International Headache Society for controlled trials of acute treatment of migraine attacks in adults: Fourth edition. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 687–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emshoff, R.; Bertram, S.; Emshoff, I. Clinically important difference thresholds of the visual analog scale: A conceptual model for identifying meaningful intraindividual changes for pain intensity. Pain 2011, 152, 2277–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrigós-Pedrón, M.; La Touche, R.; Navarro-Desentre, P.; Gracia-Naya, M.; Segura-Ortí, E. Effects of a Physical Therapy Protocol in Patients with Chronic Migraine and Temporomandibular Disorders: A Randomized, Single-Blinded, Clinical Trial. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2018, 32, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassorelli, C.; Tramontano, M.; Berlangieri, M.; Schweiger, V.; D’ippolito, M.; Palmerini, V.; Bonazza, S.; Rosa, R.; Cerbo, R.; Buzzi, M.G. Assessing and treating primary headaches and cranio-facial pain in patients undergoing rehabilitation for neurological diseases. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusson, J.E.; Becker, W.J. Migraine Frequency and Intensity: Relationship with Disability and Psychological Factors—PubMed. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2003, 43, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louter, M.; Pijpers, J.; Wardenaar, K.; van Zwet, E.; van Hemert, A.; Zitman, F.; Ferrari, M.; Penninx, B.; Terwindt, G. Symptom dimensions of affective disorders in migraine patients. J. Psychosom. Res. 2015, 79, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Kong, F.; Buse, D.C. Predictors of episodic migraine transformation to chronic migraine: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational cohort studies. Cephalalgia 2019, 40, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.C.; Greisman, J.D.; Baigi, K.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine Progression: A Systematic Review. Headache 2019, 59, 306–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, A.; Schulte, L.H. Chronic migraine: Risk factors, mechanisms and treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’ippolito, M.; Tramontano, M.; Buzzi, M.G. Effects of Osteopathic Manipulative Therapy on Pain and Mood Disorders in Patients with High-Frequency Migraine. J. Osteopat. Med. 2017, 117, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gandolfi, M.; Geroin, C.; Valè, N.; Marchioretto, F.; Turrina, A.; Dimitrova, E. Does myofascial and trigger point treatment reduce pain and analgesic intake in patients undergoing onabotulinumtoxin A injection due to chronic intractable migraine? Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 54, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-De-Las-Peñas, C.; Ceña, M.P.; Castaldo, M.; Wang, K.; Guerrero-Peral, Á.; Catena, A.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Variables associated with use of symptomatic medication during a headache attack in individuals with tension-type headache: A European study. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, H.; Bolton, J. Assessing the clinical significance of change scores recorded on subjective outcome measures. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2004, 27, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrot, S.; Lanteri-Minet, M. Patients’ Global Impression of Change in the management of peripheral neuropathic pain: Clinical relevance and correlations in daily practice. Eur. J. Pain 2019, 23, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, R.H.; Turk, D.C.; Wyrwich, K.W.; Beaton, D.; Cleeland, C.S.; Farrar, J.T.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Jensen, M.P.; Kerns, R.D.; Ader, D.N.; et al. Interpreting the Clinical Importance of Treatment Outcomes in Chronic Pain Clinical Trials: IMMPACT Recommendations. J. Pain 2008, 9, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilaqua-Grossi, D.; Gonçalves, M.C.; Carvalho, G.; Florencio, L.L.; Dach, F.; Speciali, J.G.; Bigal, M.E.; Chaves, T. Additional Effects of a Physical Therapy Protocol on Headache Frequency, Pressure Pain Threshold, and Improvement Perception in Patients with Migraine and Associated Neck Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S.L.U 2022 Viguera Editores. 1st Post-European Headache Federation Meeting: A Review of the Latest Developments Presented at the 2020 European Headache Federation Congress: Neurología.com. Available online: http://www.neurologia.com/articulo/2021155/eng (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- Geri, T.; Viceconti, A.; Minacci, M.; Testa, M.; Rossettini, G. Manual therapy: Exploiting the role of human touch. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2019, 44, 102044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).